Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Energy Balance Analysis
- Ei = Energy input (kJ/gVS)
- P = Power required for pretreatment (W)
- t = Microwave pretreatment time (s)
- V = Volume of biomass (L)
- TS = Total solid in biomass (g TS/L)
- Eo = Energy output (kJ/gVS)
- ΔP = Hydrogen yield (ml H2/gVS)
- ε = Calorific value of hydrogen (120,000 kJ/m3)
2.4. Mathematical Kinetic Models
- B = Cumulative biogas volume at digestion time t (mL)
- BP = Biogas production potential (mL)
- MBPR = Maximum biogas production rate (mL/h)
- BPDT = Biogas production delay time (h)
- t = Total digestion time (h)
- N = Number of points
- RSS = Residual sum of square
- K = Number of model parameters
- ΔAIC = The relative difference between the two AIC values
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biogas and Hydrogen Production
3.2. Energy Assessment
3.3. Mathematical Kinetic Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ei | Energy input (kJ/gVS) |
| P | Power required for pretreatment (W) |
| t | Microwave pretreatment time (s) |
| V | Volume of biomass (L) |
| TS | Total solid in biomass (g TS/L) |
| Eo | Energy output (kJ/gVS) |
| ΔP | Hydrogen yield (mL H2/gVS) |
| ε | Calorific value of hydrogen (120,000 kJ/m3) |
| B | Cumulative biogas volume at digestion time t (mL) |
| BP | Biogas production potential (mL) |
| MBPR | Maximum biogas production rate (mL/h) |
| BPDT | Biogas production delay time (h) |
| t | Total digestion time (h) |
| N | Number of points |
| RSS | Residual sum of square |
| K | Number of model parameters |
| ΔAIC | The relative difference between the two AIC values |
| MW | Microwave |
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| H2 | Hydrogen |
| H2S | Hydrogen Sulfide |
| CH4 | Methane |
| VFAs | Volatile Fatty Acids |
| HRAP | High Rate Algal Ponds |
| CM | Cattle Manure |
| HRT | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| TSS | Total Suspension Solids |
| VSS | Volatile Suspension Solids |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| (L-M) | Levenberg-Marquardt |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| SCOD | Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| DTG | Difference Thermo Gravimetry |
References
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Lee, D.J. Biogas from anaerobic digestion processes: Research updates. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, A.; Antonio, G.; Esposito, G.; Frunzo, L.; Iodice, P.; Pirozzi, F. The Effect of Substrate-Bulk Interaction on Hydrolysis Modeling in Anaerobic Digestion Process. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8348–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzoury, M.A.; Allam, N.K. Impact of nanotechnology on biogas production: A mini-review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Salvadó, H.; Passos, F.; Garfí, M.; Ferrer, I. Strategies to Optimize Microalgae Conversion to Biogas: Co-Digestion, Pretreatment and Hydraulic Retention Time. Molecules 2018, 23, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathiraja, B.; Chakravarthy, M.; Ranjith Kumar, R.; Yogendran, D.; Yuvaraj, D.; Jayamuthunagai, J.; Praveen Kumar, R.; Palani, S. Aquatic biomass (algae) as a future feed stock for bio-refineries: A review on cultivation, processing and products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 634–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Sialve, B.; Bernet, N.; Steyer, J.P. Comparison of ultrasound and thermal pretreatment of Scenedesmus biomass on methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, A.; Kumar, G.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Shobana, S.; Saratale, G.D.; Kim, H.W.; Luongo, V.; Esposito, G.; Munoz, R. Bio-hythane production from microalgae biomass: Key challenges and potential opportunities for algal bio-refineries. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.G.; Mariano, A.B.; Vargas, J.V.C. A review on microalgae, a versatile source for sustainable energy and materials. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, O.; Santis, J.; Ruiz-Fillipi, G.; Zuñiga, M.E.; Fermoso, F.G.; Chamy, R. Microalgae digestive pretreatment for increasing biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, O.; Passos, F.; Chamy, R. Physical Pretreatment Methods for Improving Microalgae Anaerobic Biodegradability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Houtmeyers, S.; Degrève, J.; Van Impe, J.; Dewil, R. Influence of microwave pre-treatment on sludge solubilization and pilot scale semi-continuous anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, F.; Solé, M.; García, J.; Ferrer, I. Biogas production from microalgae grown in wastewater: Effect of microwave pretreatment. Appl. Energy 2013, 108, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.; Ferrer, I.; del Mar Baeza, M.; Artola, A.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Effects of thermal and mechanical pretreatments of secondary sludge on biogas production under thermophilic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Kennedy, K.J.; Eskicioglu, C. Effect of low temperature microwave pretreatment on characteristics and mesophilic digestion of primary sludge. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sólyom, K.; Mato, R.B.; Pérez-Elvira, S.I.; Cocero, M.J. The influence of the energy absorbed from microwave pretreatment on biogas production from secondary wastewater sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10849–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, C.; Kennedy, K.J.; Droste, R.L. Characterization of soluble organic matter of waste activated sludge before and after thermal pretreatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.-J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Hwang, S.; Lee, C.-K. Effect of output power, target temperature, and solid concentration on the solubilization of waste activated sludge using microwave irradiation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S13–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, C.; Kennedy, K.J.; Droste, R.L. Enhanced disinfection and methane production from sewage sludge by microwave irradiation. Desalination 2009, 248, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zaidi, A.A.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y. Optimisation of Microwave Pretreatment for Biogas Enhancement through Anaerobic Digestion of Microalgal Biomass. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2018, 63, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, F.; Antunes, F.; Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.P. Nanotechnology for Bioenergy and Biofuel Production. In Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–18. ISBN 978-3-319-45458-0. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Ren, G. Anaerobic co-digestion of animal manure and wheat straw for optimized biogas production by the addition of magnetite and zeolite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 97, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, H.; Niu, Q.; Chi, Y.; Li, Y. Trace metals requirements for continuous thermophilic methane fermentation of high-solid food waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-delRisco, M.; Orupõld, K.; Dubourguier, H.C. Particle-size effect of CuO and ZnO on biogas and methane production during anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.; Wang, J.; Giannis, A. Optimization of micronutrient supplement for enhancing biogas production from food waste in two-phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, E.; Barrena, R.; Garcia, A.; Gonzalez, E.; Delgado, L.; Busquets-Fite, M.; Font, X.; Arbiol, J.; Glatzel, P.; Kvashnina, K.; et al. Programmed iron oxide nanoparticles disintegration in anaerobic digesters boosts biogas production. Small 2014, 10, 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanon, F.; Sun, Q.; Mama, D.; Li, J.; Dimon, B.; Yu, C.P. Effect of nanoscale zero-valent iron and magnetite (Fe3O4) on the fate of metals during anaerobic digestion of sludge. Water Res. 2016, 88, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Attia, Y.A.; Abdel-Hadi, M.A.; Hassan, H.E.; Badr, Y. Influence of zero valent iron nanoparticles and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of manure. Energy 2017, 120, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; RuiZhe, F.; Shi, Y.; Khan, S.Z.; Mushtaq, K. Nanoparticles augmentation on biogas yield from microalgal biomass anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 14202–14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Attia, Y.A.; Abdel-Hadi, M.A.; Hassan, H.E.; Badr, Y. Effects of Co and Ni nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 141, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Attia, Y.A.; Abdel-hadi, M.A.; Hassan, H.E.; Badr, Y. Comparison of nanoparticles effects on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of cattle dung slurry. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.Z.; Yuan, Y.; Abdolvand, A.; Schmidt, M.; Crouse, P.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Sharp, M.; Watkins, K.G. Generation and characterization of NiO nanoparticles by continuous wave fiber laser ablation in liquid. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Jacob, A.; Tabassum, M.R.; Herrmann, C.; Murphy, J.D. Production of hydrogen, ethanol and volatile fatty acids through co-fermentation of macro- and micro-algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syaichurrozi, I.; Budiyono; Sumardiono, S. Predicting kinetic model of biogas production and biodegradability organic materials: Biogas production from vinasse at variation of COD/N ratio. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepanraj, B.; Sivasubramanian, V.; Jayaraj, S. Effect of substrate pretreatment on biogas production through anaerobic digestion of food waste. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26522–26528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, J.O.; Pantula, S.G.; Dickey, D.A. Applied Regression Analysis: A Research Tool, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.S.; Li, W.K. A note on the corrected Akaike information criterion for threshold autoregressive models. J. Time Ser. Anal. 1998, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuez, M.; Mahdy, A.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; González-Fernández, C.; Ballesteros, M. Enzymatic cell disruption of microalgae biomass in biorefinery processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdy, A.; Mendez, L.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernández, C. Enhanced methane production of Chlorella vulgaris and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by hydrolytic enzymes addition. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, S.; Yukesh Kannah, R.; Yeom, I.T.; Do, K.-U.; Banu, J.R. Combined thermo-chemo-sonic disintegration of waste activated sludge for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Li, X.; Xu, X.D.; Wang, S.; Bai, J.W.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.B.; Sciences, M. Effect of alkali treated walnut shell (Juglansregia) on high performance thermosets, study of curing behavior, thermal and thermomechanical properties. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2018, 13, 857–873. [Google Scholar]
- Ehimen, E.A.; Holm-Nielsen, J.-B.; Poulsen, M.; Boelsmand, J.E. Influence of different pre-treatment routes on the anaerobic digestion of a filamentous algae. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanon, F.; Sun, Q.; Li, M.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, C.P. Application of nanoscale zero valent iron and iron powder during sludge anaerobic digestion: Impact on methane yield and pharmaceutical and personal care products degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Conductive Fe3O4 nanoparticles accelerate syntrophic methane production from butyrate oxidation in two different lake sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

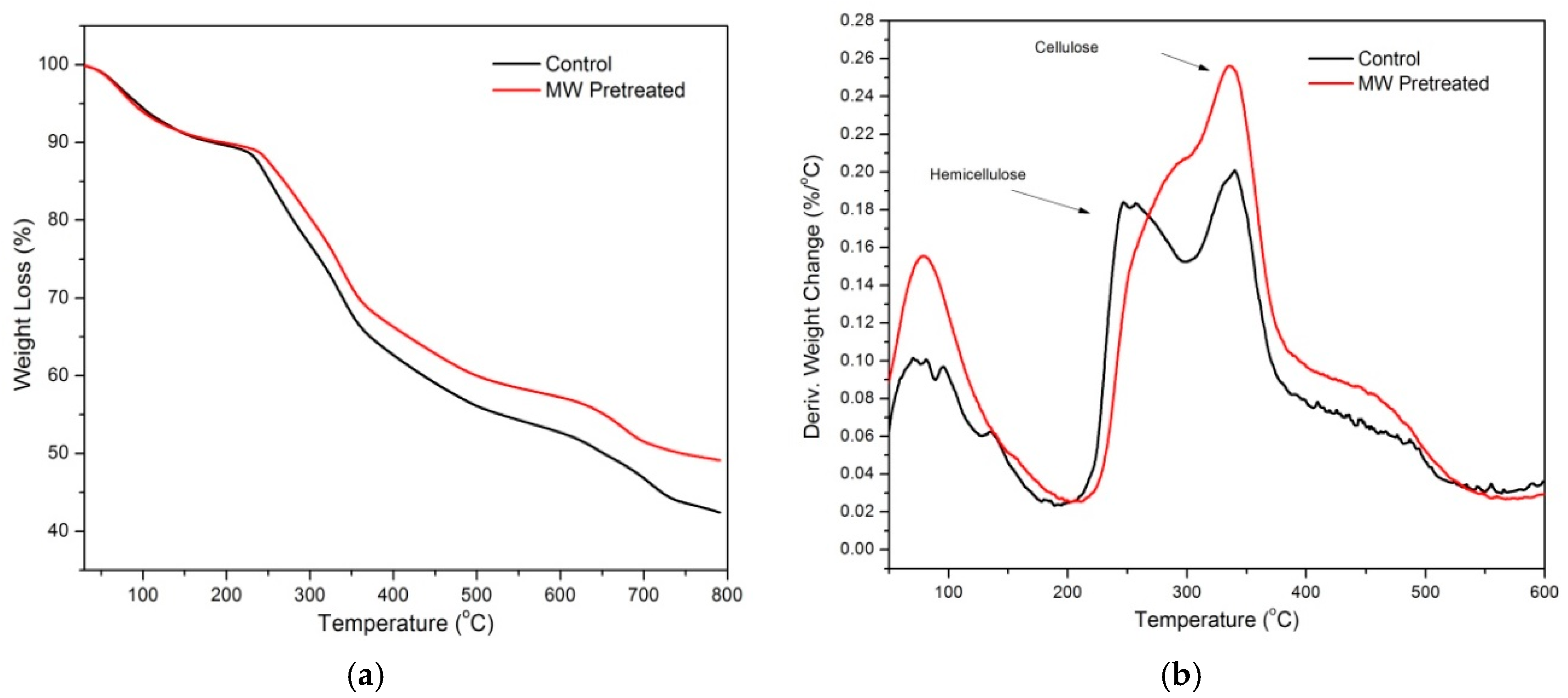
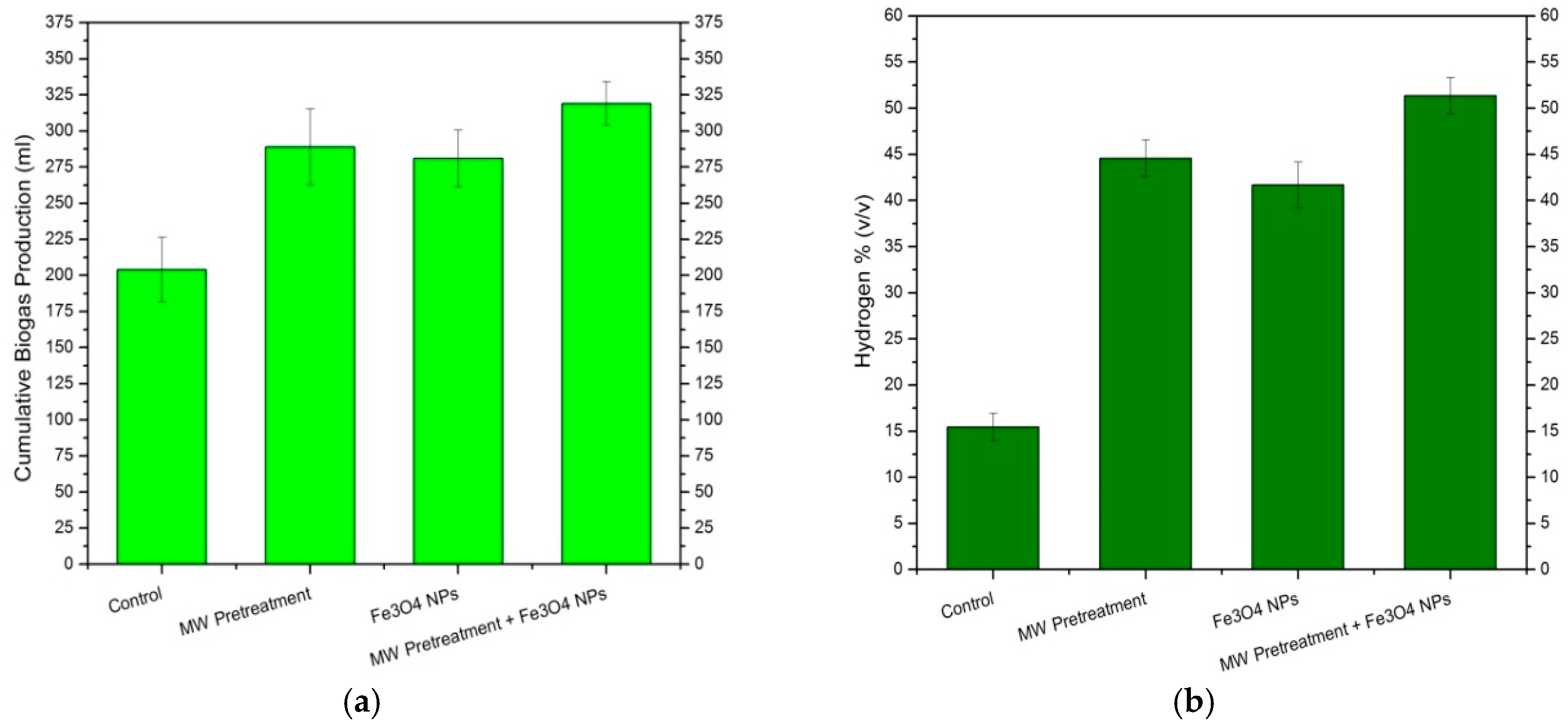
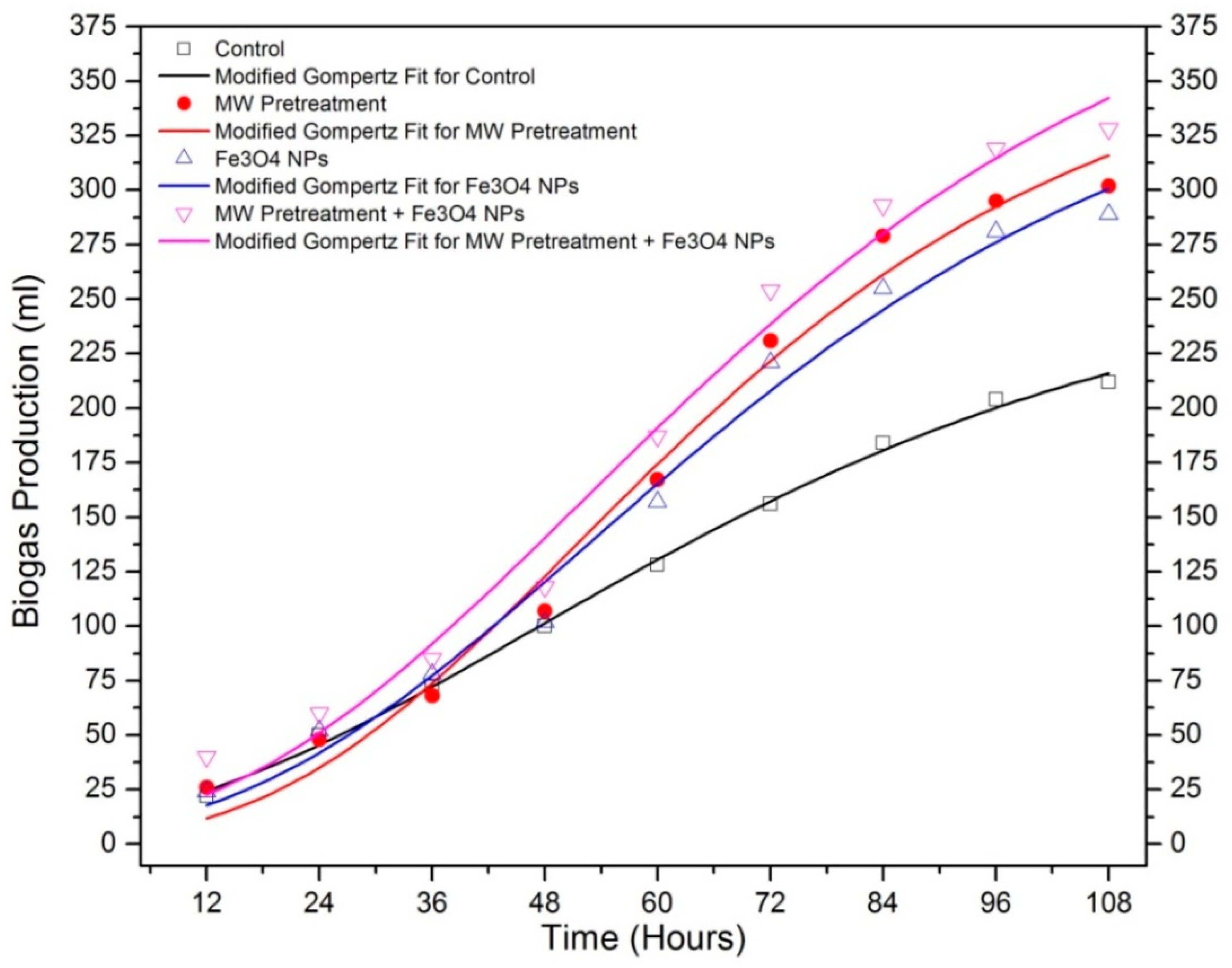
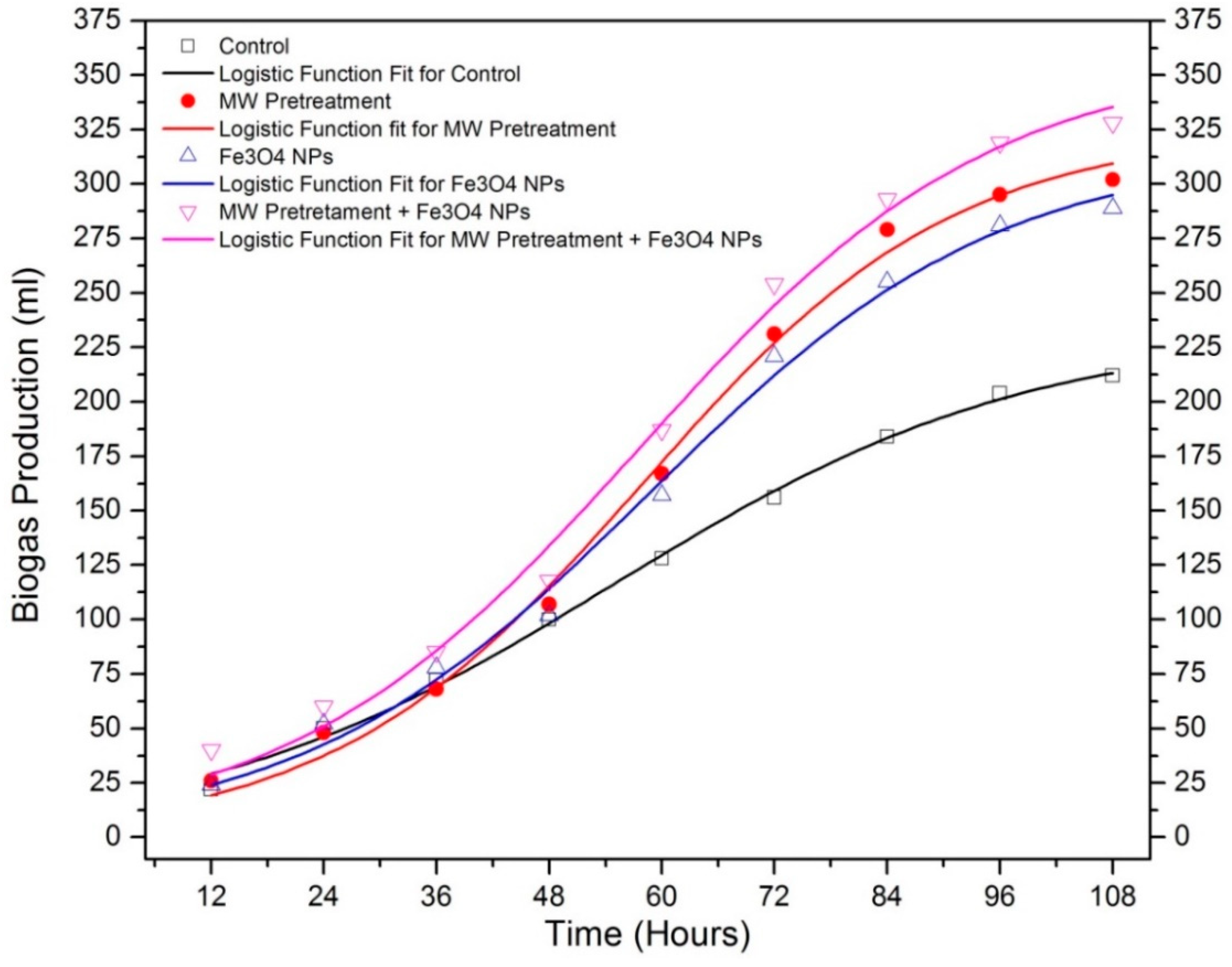
| Sample | T5% (°C) | T10% (°C) | Yc (%) at 600 °C | Cellulose DTG Peak (°C) | Hemicellulose DTG Peak (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 94 | 183 | 42 | 341 | 251 |
| MW Pretreated | 88 | 196 | 49 | 336 | 297 |
| Ein (kJ/gVS) | Eout (kJ/gVS) | Energy Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 3.93 | - |
| MW Pretreatment | 10.80 | 16.15 | 1.49 |
| Fe3O4 NPs | - | 14.45 | - |
| MW Pretreatment + Fe3O4 NPs | 10.80 | 20.28 | 1.87 |
| Parameter | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MW Pretreatment | Fe3O4 NPs | MW Pretreatment + Fe3O4 NPs | |
| Bp (mL) | 268.11 | 374.09 | 374.528 | 426.354 |
| MBPR (mL/h) | 2.468 | 4.326 | 3.773 | 4.236 |
| BPDT (h) | 0.287 | 0.816 | 0.672 | 0.618 |
| R2 | 0.99728 | 0.98227 | 0.98457 | 0.98017 |
| Predicted Biogas Yield (mL) | 215.891 | 315.977 | 300.682 | 342.302 |
| Measured Biogas Yield (mL) | 212 | 302 | 289 | 328 |
| Difference between measured and predicted biogas yield (%) | 1.83 | 4.62 | 4.04 | 4.36 |
| Parameter | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MW Pretreatment | Fe3O4 NPs | MW Pretreatment + Fe3O4 NPs | |
| Bp (mL) | 232.56 | 324.72 | 316.10 | 358.53 |
| MBPR (mL/h) | 2.628 | 4.870 | 4.230 | 4.771 |
| BPDT (h) | 0.443 | 1.023 | 0.887 | 0.839 |
| R2 | 0.99651 | 0.99414 | 0.99298 | 0.99184 |
| Predicted Biogas Yield (mL) | 213.244 | 309.394 | 295.084 | 335.453 |
| Measured Biogas Yield (mL) | 212 | 302 | 289 | 328 |
| Difference between measured and predicted biogas yield (%) | 0.58 | 2.44 | 2.10 | 2.27 |
| Model | RSS | N | AIC | Akaike Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Gompertz Model | 77.44757 | 9 | 37.37139 | 0.75284 |
| Logistic Function Model | 99.19747 | 9 | 39.59899 | 0.24716 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaidi, A.A.; Feng, R.; Malik, A.; Khan, S.Z.; Shi, Y.; Bhutta, A.J.; Shah, A.H. Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae. Processes 2019, 7, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010024
Zaidi AA, Feng R, Malik A, Khan SZ, Shi Y, Bhutta AJ, Shah AH. Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae. Processes. 2019; 7(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaidi, Asad A., Ruizhe Feng, Adil Malik, Sohaib Z. Khan, Yue Shi, Asad J. Bhutta, and Ahmer H. Shah. 2019. "Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae" Processes 7, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010024
APA StyleZaidi, A. A., Feng, R., Malik, A., Khan, S. Z., Shi, Y., Bhutta, A. J., & Shah, A. H. (2019). Combining Microwave Pretreatment with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enhanced Biogas and Hydrogen Yield from Green Algae. Processes, 7(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010024






