Abstract
Towards the bioremediation of toxic compounds from aquatic environments using living microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris has emerged as a promising candidate for the removal of heavy metals. The present study advances the scale-up of the microalga’s culture and investigates its efficiency in multi-metal removal (Cu, Cd, Ni, Pb, and Zn at 1 ppm each). Two aeration conditions were investigated: standard/conventional aeration (SA), and an innovative, custom-built micro-bubble aeration (MBA), which optimizes CO2 residence time to enhance photosynthesis. Conducted in a pilot-scale 30 L photobioreactor (PBR) over a cultivation period of 7 days, control and multi-metal treated cultures were monitored for pH, cell population growth, and pigment content. Heavy metal removal efficiency was evaluated by means of atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) on Days 3 and 7 of cultivation. The comparative results reveal that MBA significantly enhances both the population and the photosynthetic pigment content of the cultures. Furthermore, the heavy metal removal efficiency under MBA reached up to 95% even by Day 3 of cultivation, remarkably higher than the 67% of the SA treated culture. These findings not only demonstrate Chlorella vulgaris’s effectiveness in multi-metal treated systems but also highlight the potential of advanced aeration systems to enhance bioremediation efficiency in larger-scale aquatic environments.
1. Introduction
Water pollution is a critical issue in environmental research and related scientific studies. Pollutants such as chemicals, plastics and microplastics, heavy metals, nutrients, microbial contaminants, and even thermal pollution affect aquatic ecosystems globally [1]. Water contamination with heavy metals has emerged as a significant environmental and public health issue, due to their toxicity and bioaccumulation [2,3,4]. Despite the natural occurrence of heavy metals in the Earth’s crust, and consequently in aquatic systems, their concentration can be significantly amplified by several human activities, such as industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and mining procedures.
The remediation of heavy metals in wastewater is performed with several methods, including adsorption, electrochemical treatment, membrane filtration, and bioremediation, the latter employing microorganisms to absorb metals [5]. To this direction, the use of microalgae for wastewater bioremediation is considered as a promising and green solution, due to their low cost, the CO2 consumption achieved through photosynthesis, and the possibility of reusing both the microalgae biomass and the recovered heavy metals after treatment [6,7,8,9,10].
Until now, heavy metal bioremediation using microalgae cultures has been proven promising for various strains, including Chlorella vulgaris (C. vulgaris) and Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis, mainly under single metal treatment (mono metal-treated, mono-MT) systems [11,12,13,14]. However, there is still a significant gap in the literature surrounding the use of microalgae in multi metal-treated (multi-MT) systems [8,15,16,17,18].
Despite the microalgae potential in heavy metal bioremediation, such studies are mostly focused on laboratory-scale experiments, with typical cultivation volumes ranging from 120 mL to 1 L [15,19,20,21,22,23]. The problems and challenges associated with scaling up experiments should also be taken into consideration. As their study—and consequently their implementation—is demanding [5,10], pilot-scale and industrial-scale experiments and applications are scarce [24], with the main drawbacks being the high cost and difficulties in monitoring [25]. Nevertheless, scaling up is crucial to be examined, as the aforementioned downsides can be handled with the fast growth rate of microalgae [26] and the reuse of the treated biomass and/or recovered metals, together with recent and still evolving progress in monitoring, such as machine learning and big data analysis [27].
Scaling up in photobioreactors (PBRs) encounters challenges that influence microalgae growth and health, due to phenomena such as sedimentation, cell membrane disruption, and nutrient distribution, while slow movement leads to light depletion [28]. Apart from the conventional aeration of cultures using bubbles—with plain air, or enriched in CO2 air [29]—advanced aeration systems have also been proposed, such as conventional aeration coupled with stirring [30], and the use of micro- and nano-bubbles [29]. The latter, apart from enhanced aeration due to higher CO2 dissolving rate, longer retention time, and lower buoyancy [29], also enhances flow mixing, thus improving light and nutrient uptake from the microalgae [28,31].
Based on the above, this preliminary study aims to assess whether micro-bubble aeration improves scaled-up cultivation of C. vulgaris, to evaluate the multi-metal removal efficiency at pilot scale, and to examine the potential of cultivation and removal efficiency due to advanced aeration. A previous laboratory scale study under standard aeration, using both mono- and multi-MT, showed that the presence of multiple heavy metals can lead to synergistic or antagonistic effects on the microalga’s growth and heavy metal removal efficiency [18]. The present study focuses specifically on multi-MT systems, as a realistic model to evaluate the impact of aeration on biomass growth and bioremediation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalga Cultivation Conditions
C. vulgaris (strain NIVA-CHL 108), purchased from NORCCA (Oslo, Norway), was cultivated in a 30 L PBR in Bold’s Basal Medium (BBM) (pH = 6.8) [18,32], under a 12 h light:12 h dark illumination cycle, using a full spectrum LED array light source (LUMATEK, London, UK, ATTIS 200 W, ~160 μmol photons m−2·s−1) at 28 ± 0.5 °C.
Two aeration conditions were applied. The first one, referred to as standard aeration (SA), involved a continuous aeration using a gas mixture consisting of 30% CO2 in air, at a flow rate of 1.67 L/min, using two pumps of 50 L/h each. The second, micro-bubble aeration (MBA), operated at the same flow rate using the same gas mixture. In this case, aeration was applied for 10 min every hour. The setup and the specifications of the MBA system are described in Appendix A.
Multi-MT cultures were subjected to both aeration conditions, while untreated cultures (Control) were also cultivated under the same conditions for comparison. For the multi-MT cultures, Cu, Cd, Ni, Pb, and Zn were added at 1 ppm each (a concentration typically found in moderately contaminated industrial wastewater [33]), in the form of nitrate salt solutions, and the cultivation period was 7 days.
2.2. Analytical and Imaging Methods for Biomass Growth, Pigment Content and Heavy Metal Removal
Cell population and morphological characteristics were determined daily by optical microscopy (CX43RF microscope equipped with an EP50 camera, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) using an improved Neubauer hemocytometer. The pigment content of the cultures was estimated on Days 0, 3, and 7 of cultivation by means of UV-Vis spectrophotometry (Lambda 25, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA), using methanol for the extraction [34]:
where Chl.a, Chl.b, Chl.tot, and Chl.x are the concentrations of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophylls, and total carotenoids, respectively, while A is the absorbance measured at different wavelengths, after the subtraction of A750, for turbidity correction [35]. The heavy metal residual concentration was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) (AAnalyst 800, Perkin–Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) and the total % removal was calculated on Days 3 and 7 of cultivation compared to the initial concentration at Day 0 (also determined with AAS and found to range between 0.98 to 1.03 ppm). All measurements were performed in duplicate; the results are expressed as the mean of the two values with their standard deviation (SD).
3. Results
The effect of the aeration conditions on the growth, pigment content and heavy metal removal efficiency of C. vulgaris is described below.
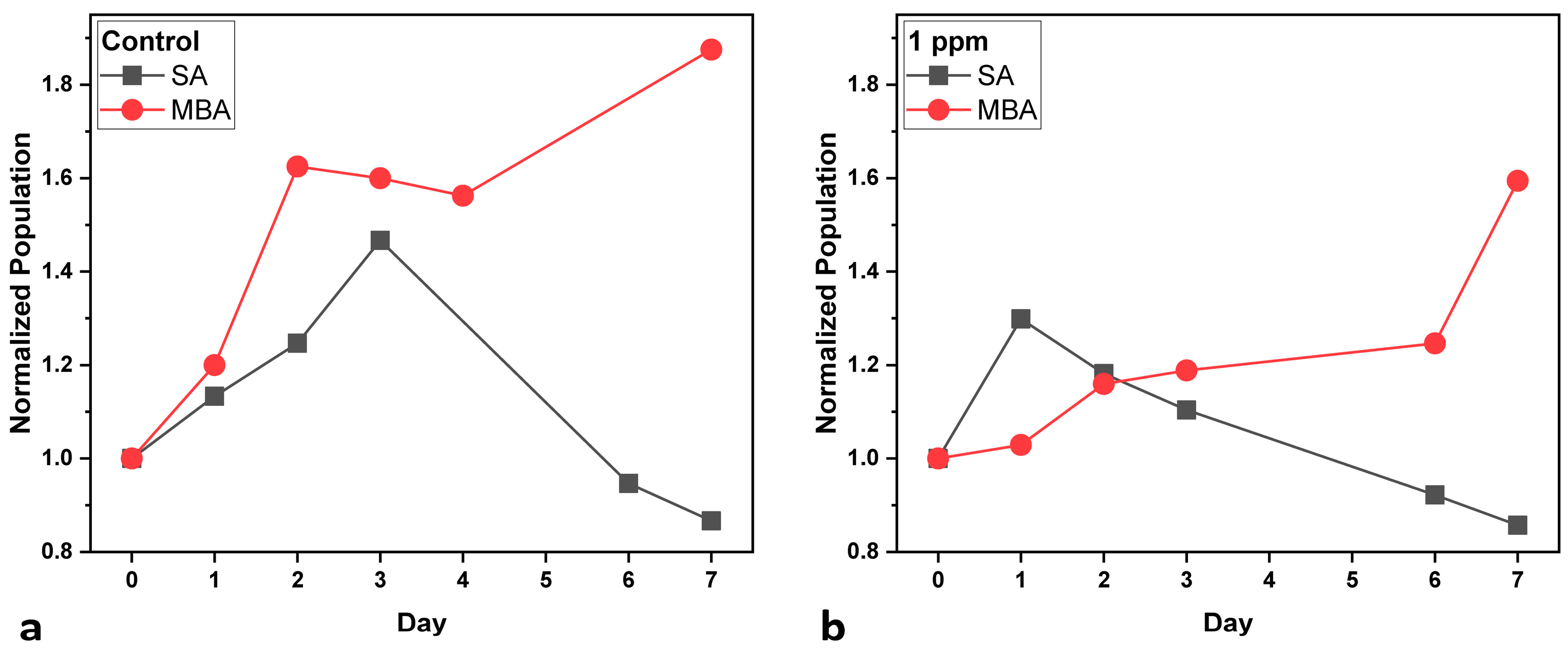
Figure 1 shows the normalized cell population of all cultures, as well as under both aeration conditions. In the Control cultures (Figure 1a), under SA, cell population increases up to Day 3, after which the decline phase follows until Day 7. On the other hand, when MBA is applied, the population increases rapidly up to Day 2, presents a stationary phase until Day 4, and then increases again until Day 7. With the addition of 1 ppm of heavy metals, the pattern of cell growth shifts (Figure 1b): under SA, population starts to increase slightly on Day 1 and then firmly declines until the end of the experiment. Under MBA, a stationary phase is observed during the first day, probably due to cell adjustment to metal exposure and at the same time to enhanced aeration. After that, there is a gradual but steady increase until Day 6, and on the final day, there is a sharp increase, indicating that cell division prevails. In both cases, the beneficial effects of MBA can probably be attributed to the enhanced CO2 availability and nutrient transport that may enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis and detoxification processes. Furthermore, the findings suggest that while heavy metals exert a toxic effect on the growth of C. vulgaris [36], MBA can enhance cellular tolerance and adaptation to the toxic environment [37].
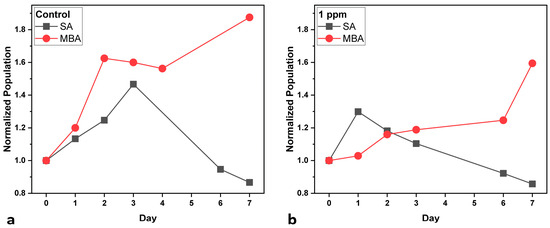
Figure 1.
Normalized cell population curves of C. vulgaris (compared to initial population at Day 0) under standard aeration (SA) and micro-bubble aeration (MBA): (a) Control cultures, and (b) multi metal-treated (multi-MT) cultures. Standard deviation (SD) did not exceed ±2.5%.
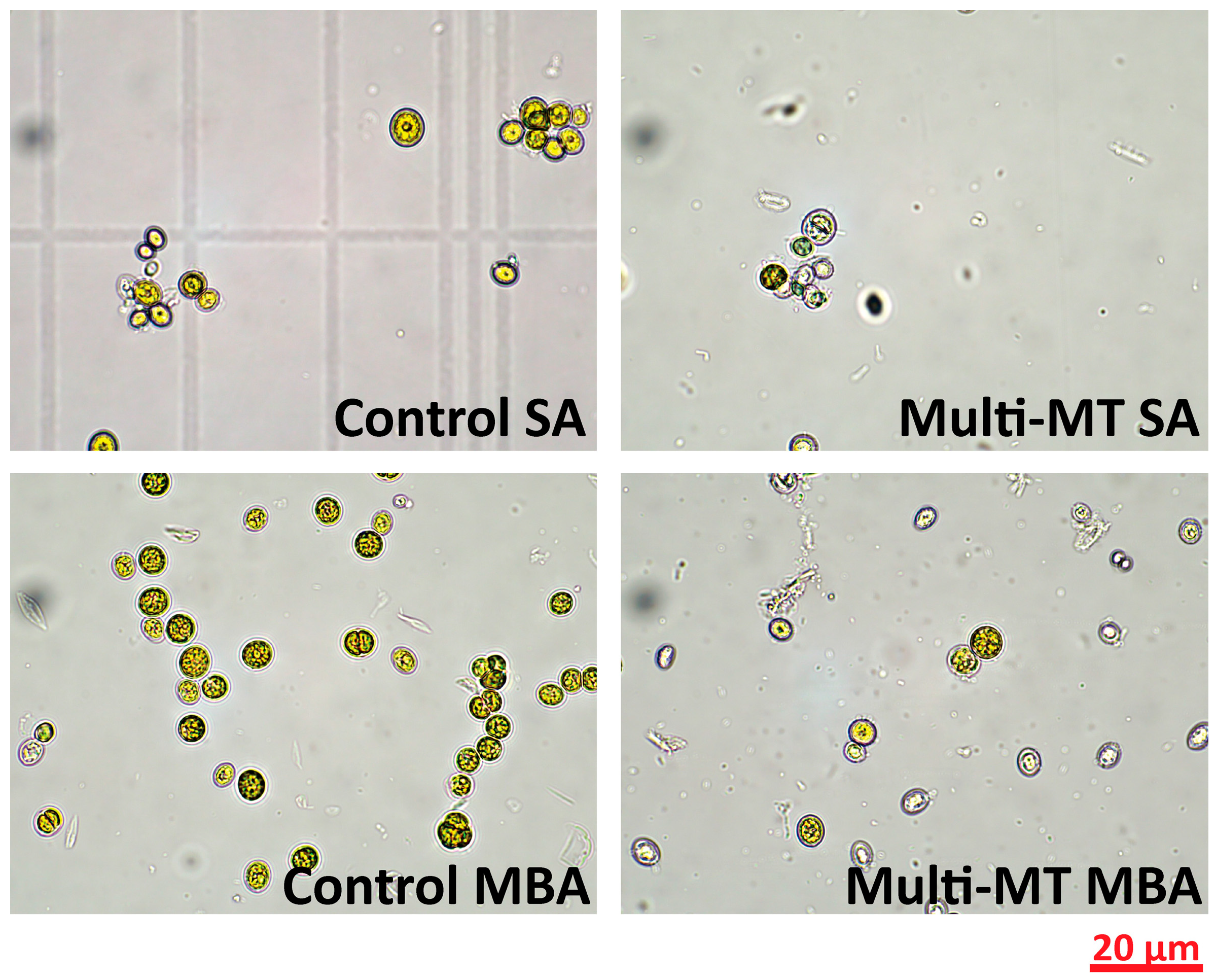
As presented in Figure 2, microscopic observation of C. vulgaris cells on Day 7 of cultivation reveals distinct morphological differences depending on the aeration condition and heavy metal exposure. Under SA, control cells exhibit healthy morphology, whereas cells exposed to 1 ppm of heavy metals show reduced density and signs of structural deformation [18]. Under MBA, the control cells appear denser and uniform, while metal-treated cells preserve their structural integrity. These findings suggest that MBA enhances cellular resistance to the stress induced by the heavy metal effect. The aeration mode significantly influences C. vulgaris morphological features, heavy metal tolerance, and removal capacity.
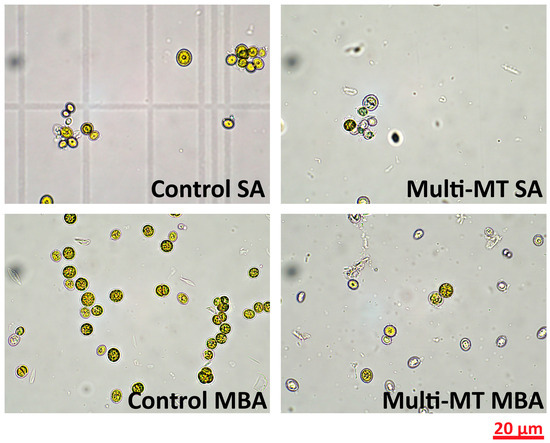
Figure 2.
Optical microscopy images of control and multi-MT cultures under both aeration conditions, as collected on day 7 of cultivation using a 60× objective lens.
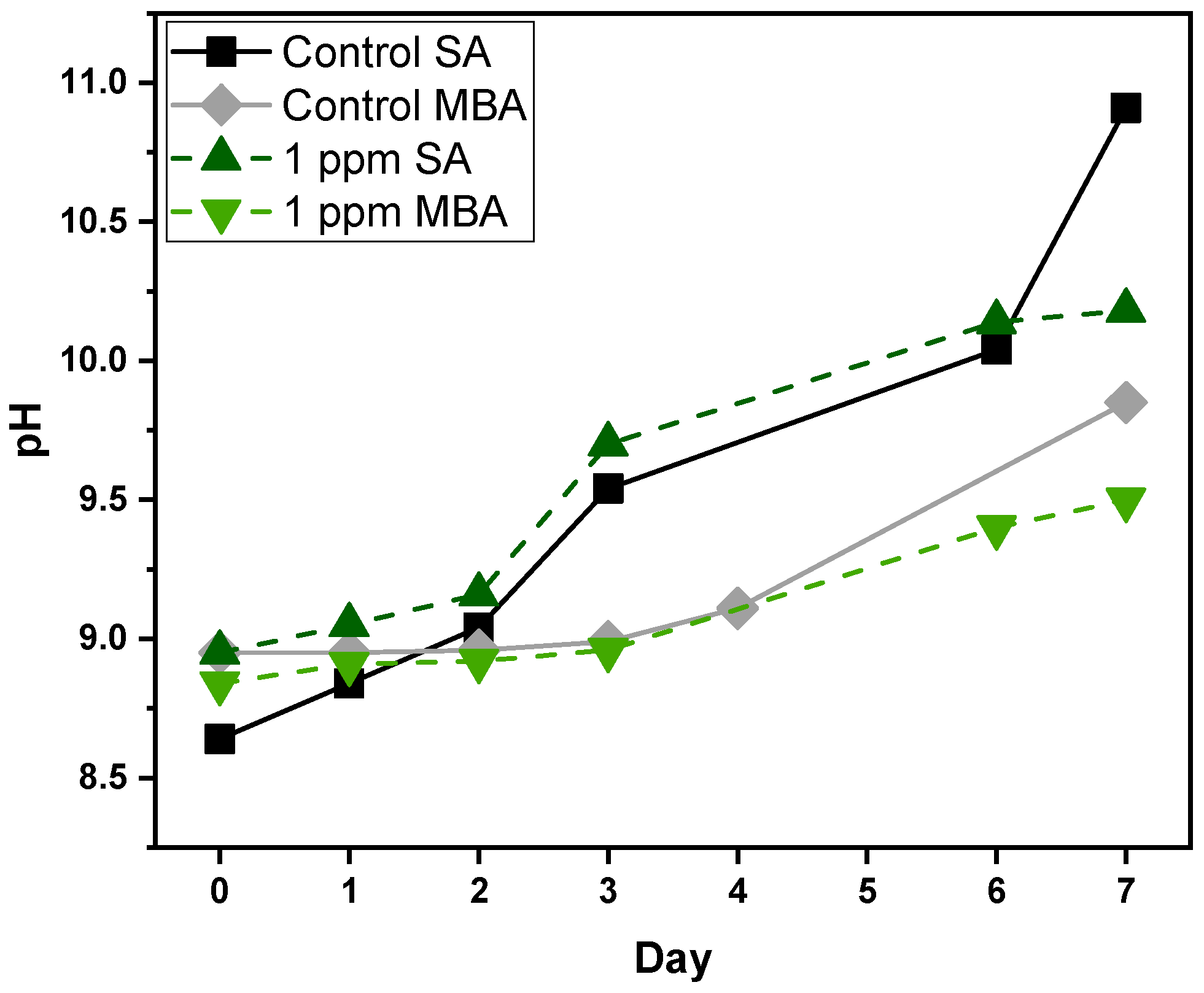
During the cultivation period, as presented in Figure 3, pH increases both for Control and 1 ppm multi-MT cultures, with variations between the two aeration conditions. In the case of the Control cultures, SA triggers a continuous rise in pH from 8.64 on Day 1, to 10.91 on Day 7, indicating significant alkalinization, apparently as a result of high-level photosynthetic CO2 uptake and minimal replenishment. The Control culture under MBA exhibits a less pronounced rise, from 8.95 to 9.85, pointing to increased CO2 availability and buffering capacity, due to enhanced gas–liquid exchange. In multi-MT cultures, pH also increases with time but follows a different pattern. Under SA, pH grows from 8.9 to 10.18, and under MBA from 8.84 to 9.50. The presence of heavy metals most probably suppresses photosynthesis, or changes nutrient assimilation, thereby moderating the pH change [38]. The overall trend suggests the coupling of photosynthetic CO2 fixation with nitrate assimilation, both of which are responsible for medium alkalinization. MBA seems to have a stabilizing effect to the carbonate system balance, potentially mitigating metal-induced stress by improving gas exchange and buffering capacity [39].
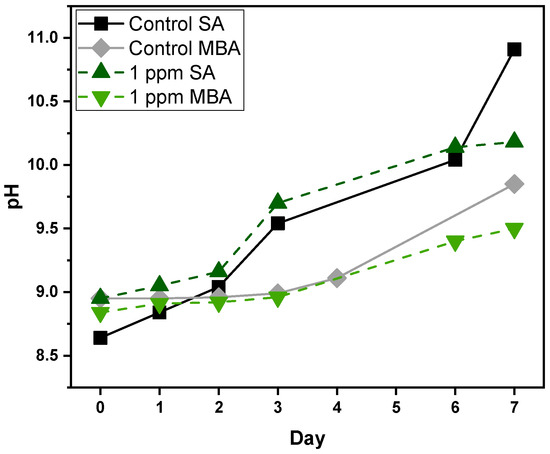
Figure 3.
pH measurements of Control and multi-MT cultures for both aeration conditions. SD did not exceed ±1%.
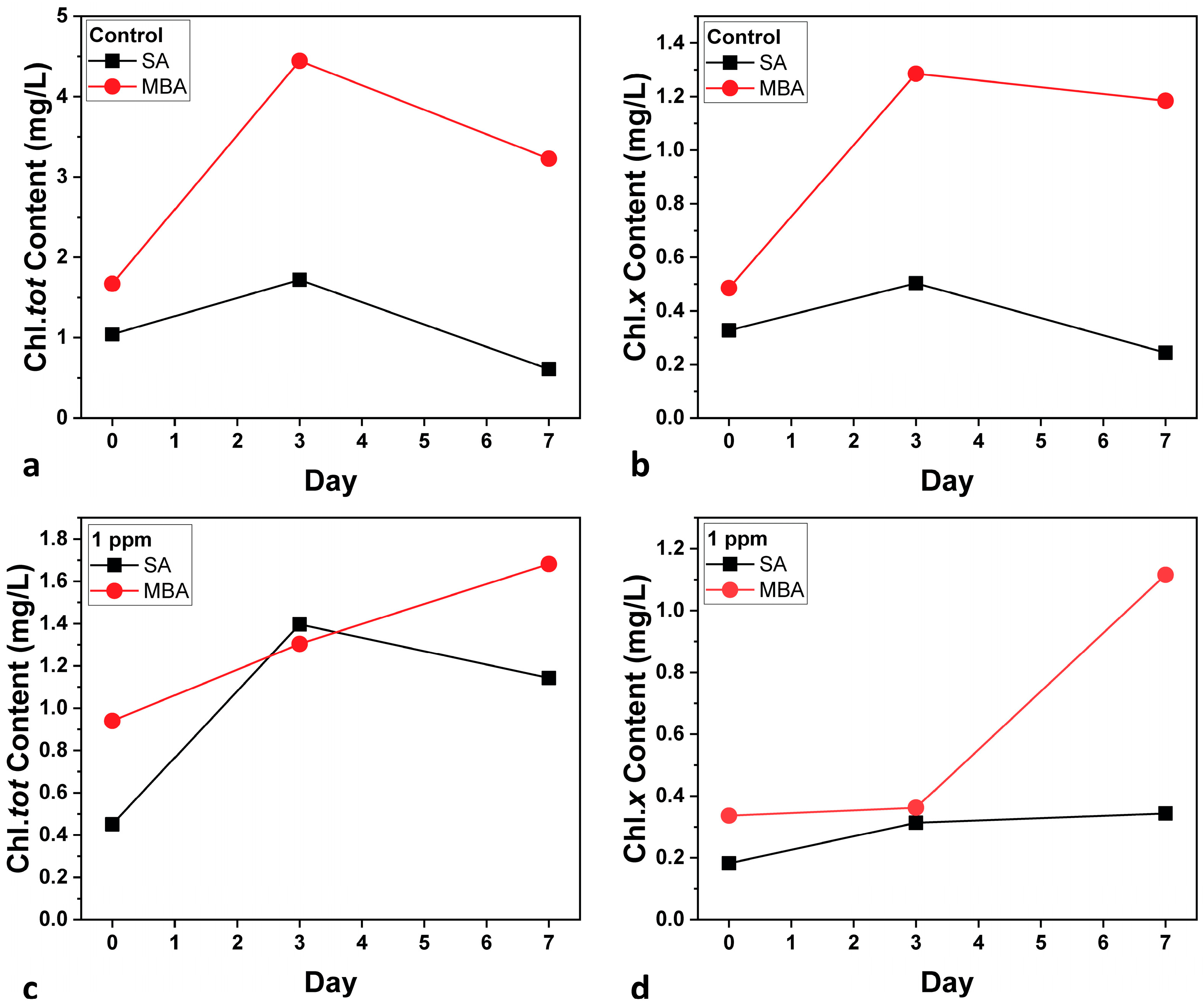
The pigment content of the microalga was estimated as a health indicator of the cultures [40]. Figure 4 shows the Chl.tot and Chl.x content for both aeration conditions. In general, the pigment content follows the population results. Regarding the Control cultures (Figure 4a,b), considerable differentiations between the two conditions are observed; Chl.tot and Chl.x are both significantly higher under MBA than SA. This enhancement indicates increased photosynthetic activity and, consequently, higher biomass accumulation under MBA [41]. The improvement can be explained by the increased CO2 solubility and enhanced nutrient transport provided by microbubbles, which allows better photosynthesis capacity in C. vulgaris cells. In the case of the multi-MT cultures (Figure 4c,d), Chl.tot is decreased for both aeration conditions, in comparison to the Control cultures because of the metal exposure [42]. Nevertheless, the elevated carotenoid content under MBA is noted. Increased carotenoid levels are a stress indicator, due to a number of factors, such as high light intensity [43]. Other factors such as nutrient depletion, oxidative stress due to heavy metal exposure, salinity stress, and temperature fluctuations cannot be taken into consideration, as the same conditions were applied to the SA one.
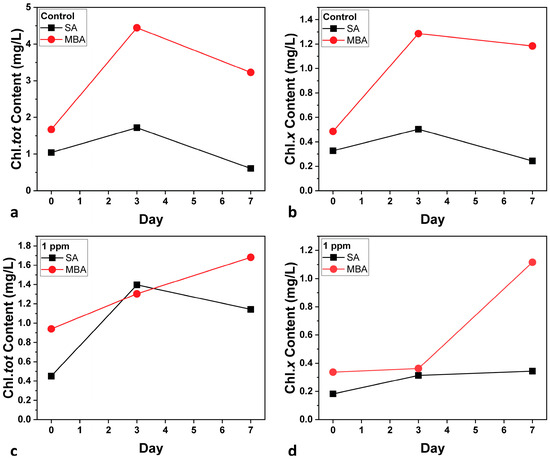
Figure 4.
Total chlorophyll content (Chl.tot) (a,c) and carotenoid content (Chl.x) (b,d) for both aeration conditions. SD did not exceed ±2%.
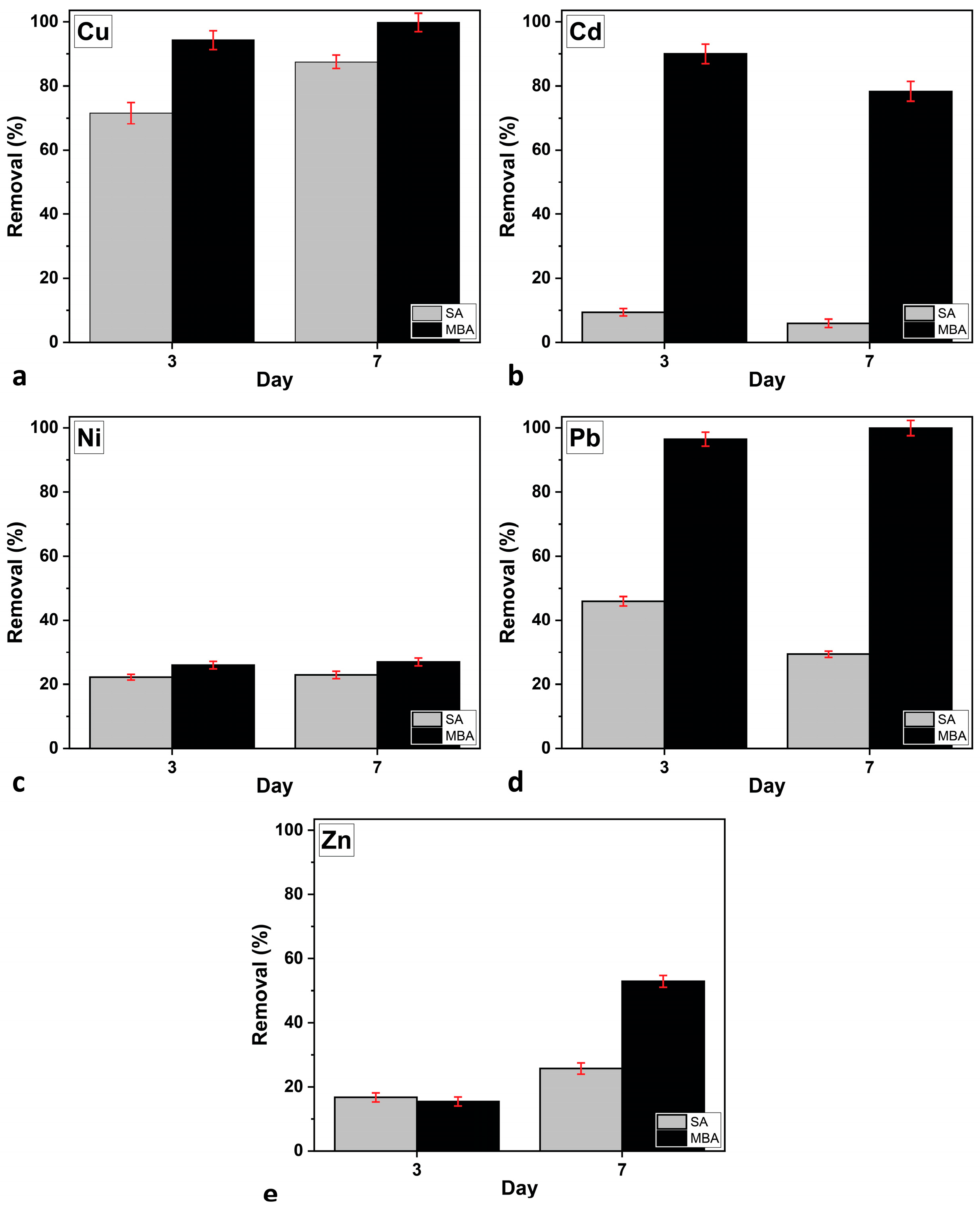
Figure 5 presents the metal-removal efficiency of C. vulgaris under the two aeration conditions, as measured on Days 3 and 7 of cultivation. The results indicate that the removal efficiency was significantly higher in the MBA culture condition compared to SA. By Day 3, the MBA culture achieved nearly 95% removal of Cu and Pb, while Cd, Ni, and Zn showed removal rates of 90% ± 3.0%, 26% ± 1.2%, and 15.4% ± 1.4%, respectively. In contrast, the SA culture exhibited much lower efficiency, with only Cu reaching 87.5% ± 2.1% by Day 7, while the other metals remained below 30%. Over time, metal removal further improved, with the MBA culture maintaining 100% removal for Cu and Pb, while Cd, Zn, and Ni increased to 78.3% ± 3.1%, 52.9% ± 1.8%, and 27% ± 1.2%, respectively. SA culture also showed some improvement, particularly for Cu (87.5% ± 2.1% removal), but still lagged significantly behind the MBA culture [44]. Overall, the presence of MBA culture played a crucial role in enhancing heavy metal removal, especially for Pb and Cd, which showed a significant improvement compared to SA culture.
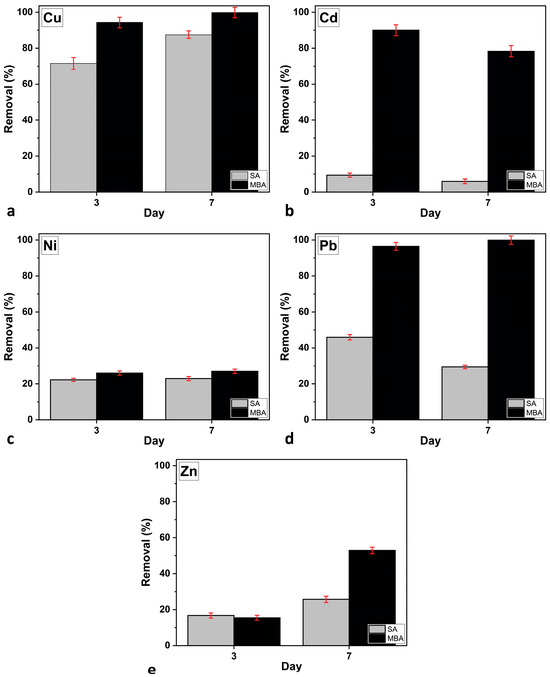
Figure 5.
Heavy metal removal efficiency of C. vulgaris in multi-MT cultures on Days 3 and 7 of cultivation under the two aeration conditions for: (a) Cu, (b) Cd, (c) Ni, (d) Pb, and (e) Zn. Error bars indicate SD.
4. Discussion
This preliminary study evaluates the effect of micro-bubble aeration on scaled-up cultivation of C. vulgaris for heavy metal bioremediation. MBA led to better cell morphological features, higher biomass production and photosynthetic pigment content of the microalga in both Control and multi-MT cultures, in agreement with previous findings [28]. In the 30 L pilot-scale cultivation that was used for the present study, an exponential growth phase was achieved until Day 7 when MBA was applied, while SA resulted in a prolonged decline. In comparison with a previous laboratory scale study (500 mL) using the same cultivation conditions but using SA only [18], scaling up to 30 L in the present study resulted in reduced biomass growth under SA. On the other hand, the introduction of MBA in the present pilot scale Control culture improved growth, thus confirming the positive effect of enhanced aeration in metal-free conditions during scaling up. Nurrusyda et al., who studied the effect of various environmental conditions on C. vulgaris biomass growth under laboratory-scale cultivation, found that aeration, and in particular constant SA, significantly affects the microalga’s growth [45]. In contrast, the present study demonstrates that when scaling up to pilot-scale, SA leads to reduced growth, while MBA significantly enhances biomass growth.
The evaluation of the heavy metal removal efficiency of C. vulgaris during the scale-up of cultivation was performed by comparing the present results with that of a previous study at laboratory (small) scale [18]. Under conventional aeration, the small-scale (500 mL) multi-MT cultures at 1 ppm exhibited a Pb removal efficiency of ~50%, while the other metals (Cu, Cd, Ni, and Zn) showed removal efficiencies above 90%. In the present pilot-scale (30 L) study under SA, Cu exhibited removal efficiency values comparable to those observed at small-scale, whereas the other metals showed values below 45%. This comparison reveals a consistent increase in removal efficiency when C. vulgaris is cultivated under MBA. In both cultivation scales, Cu and Cd exhibited the highest removal efficiencies due to their strong affinity for algal surface functional groups and stable chelation or intracellular sequestration. However, in the present 30 L MBA system, removal rates of Cu and Pb reached nearly 95% by Day 3, and 100% by Day 7, higher than in the previously studied 500 mL cultures, particularly under multi-MT conditions, where competition is expected to reduce efficiency. Cd also showed enhanced removal under MBA (90% on Day 3 and 80% on Day 7), consistent with its proven capacity for stable biosorption and bioaccumulation. Conversely, the more sensitive metals, i.e., Ni and Zn, were removed less efficiently but still significantly more under MBA (27% ± 1.2% and 52.9% ± 1.9%, respectively) than under SA, where their removal remained below 30%. Thus, the large-scale MBA setup not only replicated trends observed in small-scale systems, but also amplified the removal potential across all metals, emphasizing the scalability and robustness of MBA for optimizing heavy metal bioremediation.
It should be noted that the enhanced heavy metal removal efficiency that was observed under MBA may be related to physiological and biochemical defense mechanisms that are activated by the microalga in response to the induced stress conditions. One of the main pathways evolves enhancing its antioxidant defenses, which help protect the cells from damage caused by excess reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are produced under stress. Significant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) are activated to neutralize harmful ROS and protect cellular components from oxidative damage [8,46]. Furthermore, C. vulgaris accumulates proline, an amino acid that functions both as an osmoprotectant and as an antioxidant, which helps to neutralize harmful ROS and maintains water balance, and protects cellular proteins and membranes [47,48,49]. Furthermore, C. vulgaris produces metal-binding peptides such as phytochelatins and metallothioneins, which capture and isolate toxic metal ions, reducing their concentration in the cytoplasm and minimizing key metabolic processes from disruption [50]. In response to metal stress, cells adjust their membrane permeability and activate transporters that remove toxic ions from the cytoplasm, maintaining intracellular metal homeostasis and protecting vital metabolic processes [46]. Ultrastructural analyses have shown that exposure to heavy metals can lead to significant alterations in the cellular architecture of microalgae, notably affecting chloroplast integrity and cytoplasmic organization. Despite these structural disruptions, C. vulgaris demonstrates resilience by maintaining essential metabolic functions through adaptive mechanisms. These adaptations include the activation of antioxidant defenses and the modulation of metal ion transport systems, which collectively mitigate the detrimental effects of metal-induced stress [46,51]. Another important adaptive response is the alteration of lipid metabolism. Under stress conditions, C. vulgaris increases the accumulation of neutral lipids, as part of its survival strategy. This shift not only serves as a reservoir of carbon and energy, but also stabilizes cellular membranes against oxidative and metal-induced damage. Changes in membrane lipid composition help maintain membrane integrity and functionality during stress exposure [52,53].
Finally, it should be noted that C. vulgaris not only has the ability to be cultivated under extreme CO2 concentrations [54], but also presents enhanced bioremediation performance, as supported by the present study. MBA aeration led to improved cell health, population, and removal efficiency in comparison to SA.
The scale-up of the experiment, from laboratory (500 mL) to pilot-scale, presented results that are promising even for large-scale applications. Apart from cultivation experiments at large-scale for feasibility evaluation, future work should exploit various microalgae strains, for application under various water and environmental factors (i.e., salinity and temperature fluctuations). Moreover, microalgae removal efficiency of various combinations of heavy metals should be also studied, together with the potential for biomass reuse after metal treatment. Preliminary studies have shown that lipid, protein, and saccharide content is retained after bioremediation, supporting potential applications in energy production [18,55,56,57]. Regarding the feasibility of this approach, studies on the use of real wastewater at pilot and large scales, and the potential of recycling the used biomass and recovery of biosorbed metals, are in progress. Future work should also include a detailed energy and cost analysis comparisons between SA and MBA, to further evaluate the economic viability of scale-up.
5. Conclusions
This preliminary study introduces the use of advanced aeration in pilot-scale C. vulgaris cultivation using a 30 L PBR. In comparison to SA conditions, MBA significantly improved the microalga cell morphology, health, and biomass growth, as indicated by pigment content and cell population measurements. MBA also led to the complete removal of Cu and Pb by Day 7 of cultivation, and improved Cd, Zn, and Ni removal in multi-MT systems. In comparison to previous results contacted at the laboratory-scale (500 mL), MBA showed the same or improved removal efficiencies despite the scaling up challenges. These results demonstrate the successful role of advanced aeration in scaling up C. vulgaris cultivation for bioremediation purposes. Towards the feasibility of wastewater bioremediation using C. vulgaris cultures, ongoing work includes the application of MBA to real wastewater and further upscaling the PBR volume.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.K.; methodology, E.K., N.K., L.M., E.N., N.C.T. and N.A.K.; software, N.A.K.; validation, E.K., N.K., L.M. and N.A.K.; formal analysis, E.K., N.K. and L.M.; investigation, E.K., N.K., L.M., E.N., N.C.T. and N.A.K.; resources, N.A.K.; data curation, E.K. and N.K. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K., N.K. and L.M.; writing—review and editing, E.K., N.K., L.M. and N.A.K.; visualization, L.M.; supervision, N.A.K.; project administration, N.A.K.; funding acquisition, N.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The implementation of this research was financially supported under the Research Project “ALGEBRA—Innovative waste bioremediation practice for the removal of toxic compounds with the use of microalgae in the context of a circular economy”, which is funded by the program “NATURAL ENVIRONMENT & INNOVATIVE ACTIONS 2022”, PRIORITY AXIS 3: RESEARCH & IMPLEMENTATION, total budget: 199,501.23 €, Green Fund, Athena—Research & Innovation Center in Information Communication & Knowledge Technologies.
Data Availability Statement
The original data used for this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank T.D. Karapantsios (Department of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki) for kindly providing the custom-made software for the detection and size estimation of spherical bubbles in the digital images used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| A | Absorbance |
| AAS | Atomic absorption spectroscopy |
| ATR | Attenuated total reflectance |
| BBM | Bold’s Basal Medium |
| CAT | Catalase |
| C. vulgaris | Chlorella vulgaris |
| Chl.a | Chlorophyll a |
| Chl.b | Chlorophyll b |
| Chl.tot | Total chlorophyll (a and b) |
| Chl.x | Total carotenoid |
| GPX | Glutathione peroxidase |
| MBA | Micro-bubble aeration |
| mono-MT | Single (mono) metal-treated |
| multi-MT | Multi metal-treated |
| PBR | Photobioreactor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SA | Standard aeration |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
Appendix A. Custom-Built Aeration Setup
The dynamic mixing of a liquid and a gaseous phase results in the creation of a solution containing numerous bubbles with a wide range of diameters. The generation of micro- (or even nano-) bubbles can be achieved through various techniques. Some of these include electrolysis, the introduction of a gas phase into the liquid under high shear rates, the use of ceramic or glass porous spargers, a Venturi tube, acoustic cavitation, sequential cycles of gas compression/decompression in the liquid, or combinations of the above. For the present study, the generation of micro-bubbles (Ø < 50 μm) was accomplished using a custom-made aeration system (Figure A1). Its purpose was to enhance and extend gas–liquid mixing and bubble residence time. This was accomplished in two stages that took place in the following main parts:
- A Venturi pipe, which is a section of piping/tubing with a sudden reduction in diameter. As a first step, gas suction takes place at the Venturi pipe due to the liquid pressure reduction (Bernoulli effect) and is introduced into the liquid phase, resulting in the creation of initial bubbles.
- A centrifugal pump with a power of 150 watts. The two-phase mixture, as produced from the first step, passes through the pump and the initially created bubbles are further shared into smaller ones.
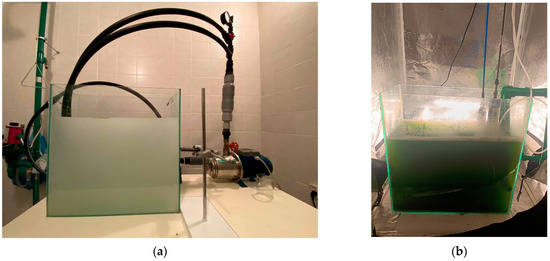
Figure A1.
Micro-bubble production in a 30 L PBR: (a) Distilled water, (b) Microalga culture.
Figure A1.
Micro-bubble production in a 30 L PBR: (a) Distilled water, (b) Microalga culture.

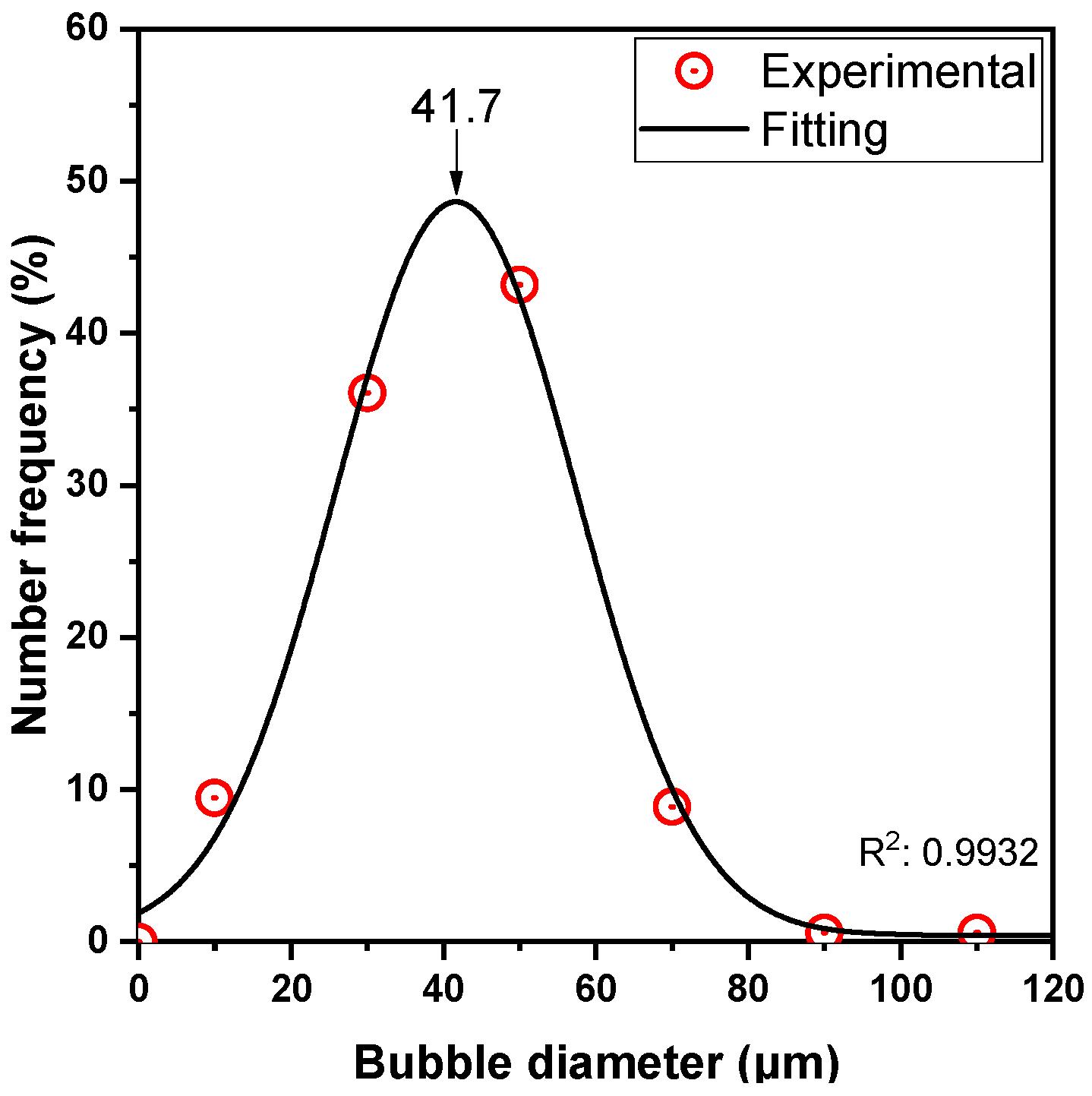
Bubble size distribution was estimated with the photographic technique, using a Nikon D90 camera (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), equipped with a 70 mm F2.8 DG MACRO lens (SIGMA GLOBAL, Kawasaki, Japan). The collected images were imported to a custom-made software [58,59] to automatically estimate the bubble size distribution. The average size of the bubbles was found to be ~40 μm (μ = 42.2 μm and σ = 15.1 μm) (Figure A2).
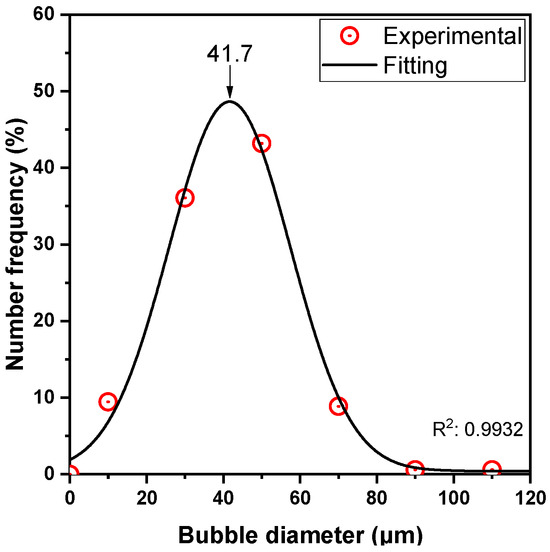
Figure A2.
Bubble size distribution.
Figure A2.
Bubble size distribution.
However, it must be noted that bubbles of size less than 5 μm could not be observed, limited by the resolution of the photographic technique (size of a single pixel). The existence of submicron bubbles was investigated using a visual method based on light scattering (Figure A3).
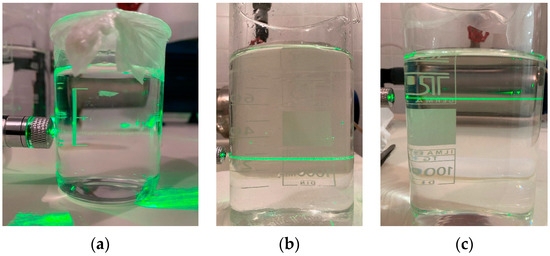
Figure A3.
Visual examination of submicron bubbles. (a) Plain water, without any aeration application, (b) under MBA, after a period of 4 days, and (c) under MBA, after a period of 36 days.
Figure A3.
Visual examination of submicron bubbles. (a) Plain water, without any aeration application, (b) under MBA, after a period of 4 days, and (c) under MBA, after a period of 36 days.
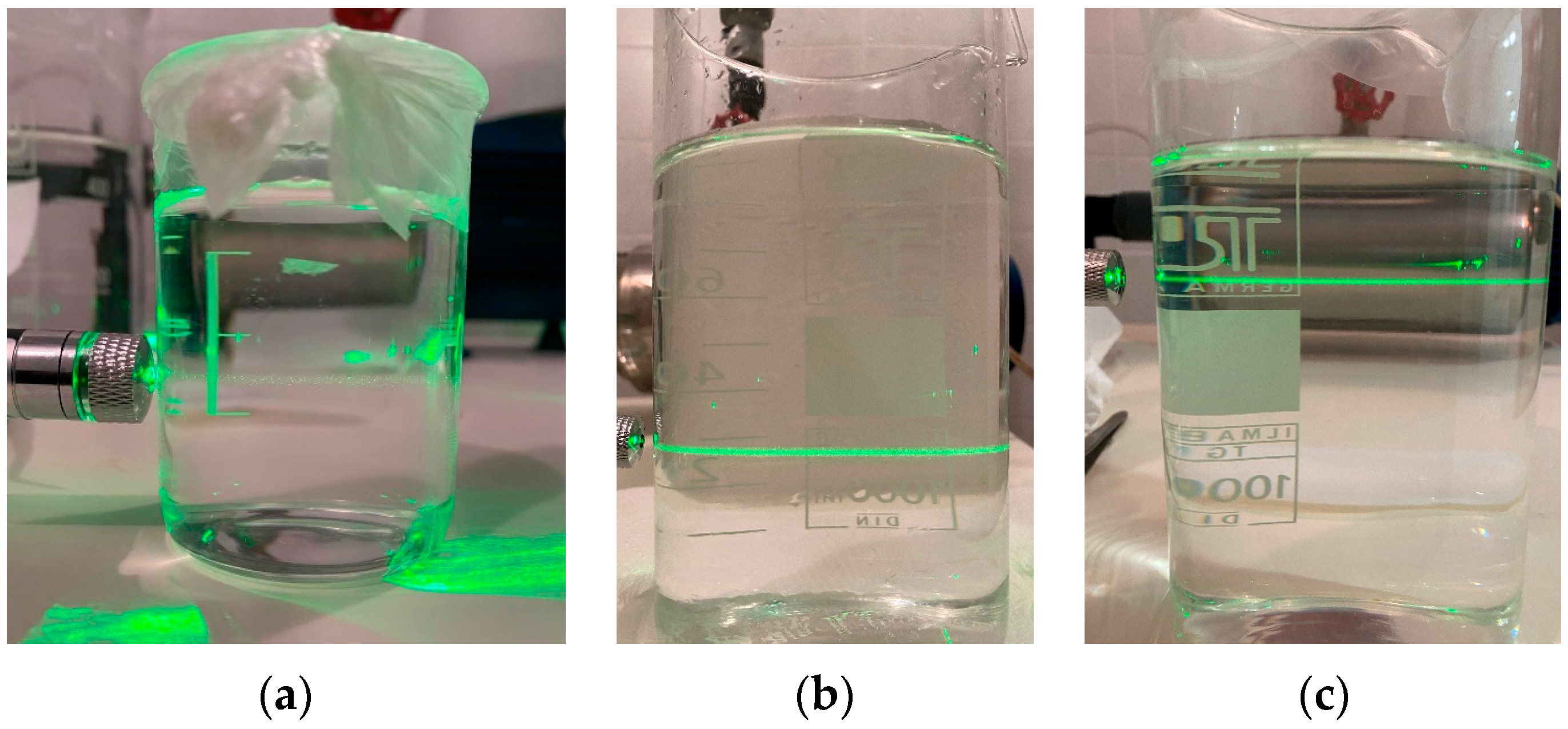
For this purpose, bubbles were produced in a 30 L tank filled with distilled water for a few minutes and then the pump was turned off. The two-phase mixture was allowed to reach a steady state and was meticulously transferred from the tank to beakers after various time periods. A green laser beam was then passed through the beakers. The beam can hardly be seen through the liquid phase in the reference sample (distilled water without any bubbles, Figure A3a) due to the absence of any bubbles. On the other hand, the beam is significantly more intense in the samples with the two-phase mixture, even 36 days later (residence time of bubbles in the tank), which means that bubbles smaller than 1 μm are also produced as derived from Stokes’ law.
References
- Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Heavy metal detoxification mechanisms by microalgae: Insights from transcriptomics analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, F.; Karbassi, A.; Golzary, A. Removal of Heavy Metal Contaminants from Wastewater by Using Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck: A Review. Curr. Environ. Manag. 2019, 6, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.K.; Agrawal, K.; Shah, M.P.; Verma, P. Bioremediation of heavy metals from wastewater: A current perspective on microalgae-based future. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.A. Green approaches to heavy metal removal from wastewater: Microalgae solutions in a circular economy framework. Soc. Impacts 2025, 5, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.; Baruah, P.P. Cyanobacteria as a potent platform for heavy metals biosorption: Uptake, responses and removal mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Gaur, J.P. Use of algae for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: Progress and prospects. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, W.; Jin, M.; Zhang, L.; Qin, L.; Geng, W. Responses and tolerance mechanisms of microalgae to heavy metal stress: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 183, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar, K.; Dahms, H.U.; Won, E.J.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, K.H. Microalgae—A promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaamoush, M.; El-Agawany, N.; Salhin, H.E.; El-Zeiny, A. Monitoring effect of nickel, copper, and zinc on growth and photosynthetic pigments of Spirulina platensis with suitability investigation in Idku Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 78942–78959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Ana Culicov, O.; Frontasyeva, M.; Pavlov, S.; Kirkesali, E.; Akshintsev, A.; Rodlovskaya, E. Spirulina platensis as biosorbent of chromium and nickel from industrial effluents. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11103–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.S.; Rodrigues, M.S.; de Carvalho, J.C.M.; Lodi, A.; Finocchio, E.; Perego, P.; Converti, A. Adsorption of Ni2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+ onto dry biomass of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis and Chlorella vulgaris. I. Single metal systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, M.; Soreanu, G.; Balan, C.D.; Buciscanu, I.I.; Maier, V.; Cretescu, I. Study of Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira) Development under the Heavy Metals Influence, as a Potential Promoter of Wastewater Remediation. Water 2023, 15, 3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, R.; Muñoz, R.; Taboada, M.E.; Vega, M.; Bolado, S. Comparative uptake study of arsenic, boron, copper, manganese and zinc from water by different green microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Ferreira, L.S.; de Carvalho, J.C.M.; Lodi, A.; Finocchio, E.; Converti, A. Metal biosorption onto dry biomass of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis and Chlorella vulgaris: Multi-metal systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malletzidou, L.; Kyratzopoulou, E.; Kyzaki, N.; Nerantzis, E.; Kazakis, N.A. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Growth Estimation of Spirulina platensis Cultures. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyratzopoulou, E.; Kyzaki, N.; Malletzidou, L.; Nerantzis, E.; Kazakis, N.A. The Efficiency of Chlorella vulgaris in Heavy Metal Removal: A Comparative Study of Mono- and Multi-Component Metal Systems. Clean Technol. 2025, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Long, D.; Jian, Y.; Tan, Q.; Wang, H. Effects of Cu (II) on the Growth of Chlorella vulgaris and Its Removal Efficiency of Pollutants in Synthetic Piggery Digestate. Toxics 2024, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Ramírez, R.; Lobos, M.-G.G.; Córdova, O.; Poirrier, P.; Chamy, R. Effect of growth conditions on cell wall composition and cadmium adsorption in Chlorella vulgaris: A new approach to biosorption research. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.M.; Mazur, L.P.; Mayer, D.A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Pires, J.C.M. Inhibition effect of zinc, cadmium, and nickel ions in microalgal growth and nutrient uptake from water: An experimental approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Ni, W.; Li, N.; Li, Y. Response and tolerance ability of Chlorella vulgaris to cadmium pollution stress. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 4391–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytryk, A.; Saeid, A.; Chojnacka, K. Biosorption of microelements by spirulina: Towards technology of mineral feed supplements. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 356328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkina, A.; Ginnever, N.E.; Fernandes, F.; Fuentes-Grünewald, C. Large-Scale Waste Bio-Remediation Using Microalgae Cultivation as a Platform. Energies 2019, 12, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.S.; Roh, H.S.; Dev, S.; Khan, M.A.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.H. Algae as a green technology for heavy metals removal from various wastewater. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B.; Singh, S.; Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B. Microalgae: Gizmo to Heavy Metals Removal. In The Role of Microalgae in Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviyanathan, V.A.; Ker, P.J.; Hoon Tang, S.G.; Amin, E.P.; Yee, W.; Hannan, M.A.; Jamaludin, Z.; Nghiem, L.D.; Indra Mahlia, T.M. Microalgae biomass and biomolecule quantification: Optical techniques, challenges and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Feng, A.; Liu, C. Dynamic Modelling of Microalgae Growth under Micro-Aeration Conditions. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 88, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Yang, L.; Chu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Micro-nano-bubbles and their application in microalgae production: Wastewater treatment, carbon capture and microalgae separation. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Pei, H. Enhanced Production of Microalgal Metabolites Through Aeration Coupled with Stirring. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Lai, X.; Ye, Q.; Guo, W.; Xu, J.; Ren, W.; Zhou, J. A novel jet-aerated tangential swirling-flow plate photobioreactor generates microbubbles that enhance mass transfer and improve microalgal growth. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBM Medium. CCCryo Culture Collection of Cryophilic Algae 2020, 06/2020. Available online: https://cccryo.fraunhofer.de/sources/files/medien/BBM.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Kumar, S.; Mondal, P.; Purkait, M.K. Hazardous Effects of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters and Their Remediation Through Green Technology. In Green Technologies for Industrial Waste Remediation. Environmental Science and Engineering; Mathuriya, A.S., Pandit, S., Singh, N.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-3-031-46858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Strickland, J.D. Discussion of spectrophotometric determination of marine-plant pigments, with revised equations for ascertaining chlorophylls and carotenoids. J. Mar. Res. 1963, 21, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Expósito, N.; Carafa, R.; Kumar, V.; Sierra, J.; Schuhmacher, M.; Papiol, G.G. Performance of Chlorella vulgaris Exposed to Heavy Metal Mixtures: Linking Measured Endpoints and Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Ohde, D.; Matthes, S.; Engelmann, C.; Bubenheim, P.; Terasaka, K.; Schlüter, M.; Liese, A. Comparative investigation of fine bubble and macrobubble aeration on gas utility and biotransformation productivity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Ying, R.; Yin, A.; Ji, W. Heavy Metals Can Affect Plant Morphology and Limit Plant Growth and Photosynthesis Processes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizzul, A.M.; Hellier, P.; Purton, S.; Baganz, F.; Ladommatos, N.; Campos, L. Combined remediation and lipid production using Chlorella sorokiniana grown on wastewater and exhaust gases. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Truong, V.K.; Elbourne, A.; Gangadoo, S.; Cheeseman, S.; Rajapaksha, P.; Latham, K.; Crawford, R.J.; Cozzolino, D. Combining Chemometrics and Sensors: Toward New Applications in Monitoring and Environmental Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 6048–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnezhad, M.; Shamsaie Mehrgan, M.; Kamali, A.; Javaheri Baboli, M. Effects of microelements (Fe, Cu, Zn) on growth and pigment contents of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2020, 19, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondzior, P.; Butarewicz, A. Effect of heavy metals (Cu and Zn) on the content of photosynthetic pigments in the cells of algae Chlorella vulgaris. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isar, M.; Cirik, S.; Turan, G. Production of Natural and Functional Pigments in Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis cultivated in Laboratory Conditions. Bull. Biotechnol. 2022, 3, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, G.; Alhamed, Y.; Alzahrani, A. Biosorption of Cadmium and Lead from Aqueous Solutions by Chlorella vulgaris Biomass: Equilibrium and Kinetic Study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurrusyda, F.S.; Subroto, T.; Hardianto, A.; Sumeru, H.A.; Ishmayana, S.; Pratomo, U.; Oktavia, D.N.; Latifah, R.G.; Dewi, D.A.S.L.A.; Rachmadona, N. Analyzing the Impact of Physicochemical Factors on Chlorella vulgaris Growth Through Design of Experiment (DoE) for Carbon Capture System. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.M.; Castro, P.M.L.; Malcata, F.X. Metal uptake by microalgae: Underlying mechanisms and practical applications. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.H.; Komor, E. Mechanism of proline uptake by Chlorella vulgaris. BBA—Biomembr. 1983, 735, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, O.; Plöhn, M.; Funk, C. The cell wall of green microalgae and its role in heavy metal removal. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.K.; Gaur, J.P. Heavy metal-induced proline accumulation and its role in ameliorating metal toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris. New Phytol. 1999, 143, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Wen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liu, H. Toxicity of Cu (II) to the green alga Chlorella vulgaris: A perspective of photosynthesis and oxidant stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17910–17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sommerfeld, M.; Jarvis, E.; Ghirardi, M.; Posewitz, M.; Seibert, M.; Darzins, A. Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: Perspectives and advances. Plant J. 2008, 54, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Schuhmann, H.; Schenk, P.M. High lipid induction in microalgae for biodiesel production. Energies 2012, 5, 1532–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, Y.K.; Lam, M.K.; Yusup, S.; Lim, J.W.; Show, P.L.; Tan, I.S.; Lee, K.T. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using sequential-flow bubble column photobioreactor: A stress-inducing strategy for lipid accumulation and carbon dioxide fixation. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 41, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malletzidou, L.; Kyratzopoulou, E.; Kyzaki, N.; Nerantzis, E.; Kazakis, N.A. Towards the Sustainable Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater Using Arthrospira platensis: A Laboratory-Scale Approach in the Context of a Green Circular Economy. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y.; Ali, S.S. Microalgae-based bioremediation of refractory pollutants: An approach towards environmental sustainability. Microb. Cell Factories 2025, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, H.S.; Illiyanasafa, N.; Jaya, D.E.C.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Putra, N.R. Utilization of the microalga Chlorella vulgaris for mercury bioremediation from wastewater and biomass production. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 37, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabulis, X.; Papara, M.; Chatziargyriou, A.; Karapantsios, T.D. Detection of densely dispersed spherical bubbles in digital images based on a template matching technique: Application to wet foams. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 309, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenidis, S.P.; Kazakis, N.A.; Karapantsios, T.D. Bubbly flow characteristics during decompression sickness: Effect of surfactant and electrolyte on bubble size distribution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 365, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).