Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H-SiC Using Multi-Catalyst Synergistic Activation of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Approach
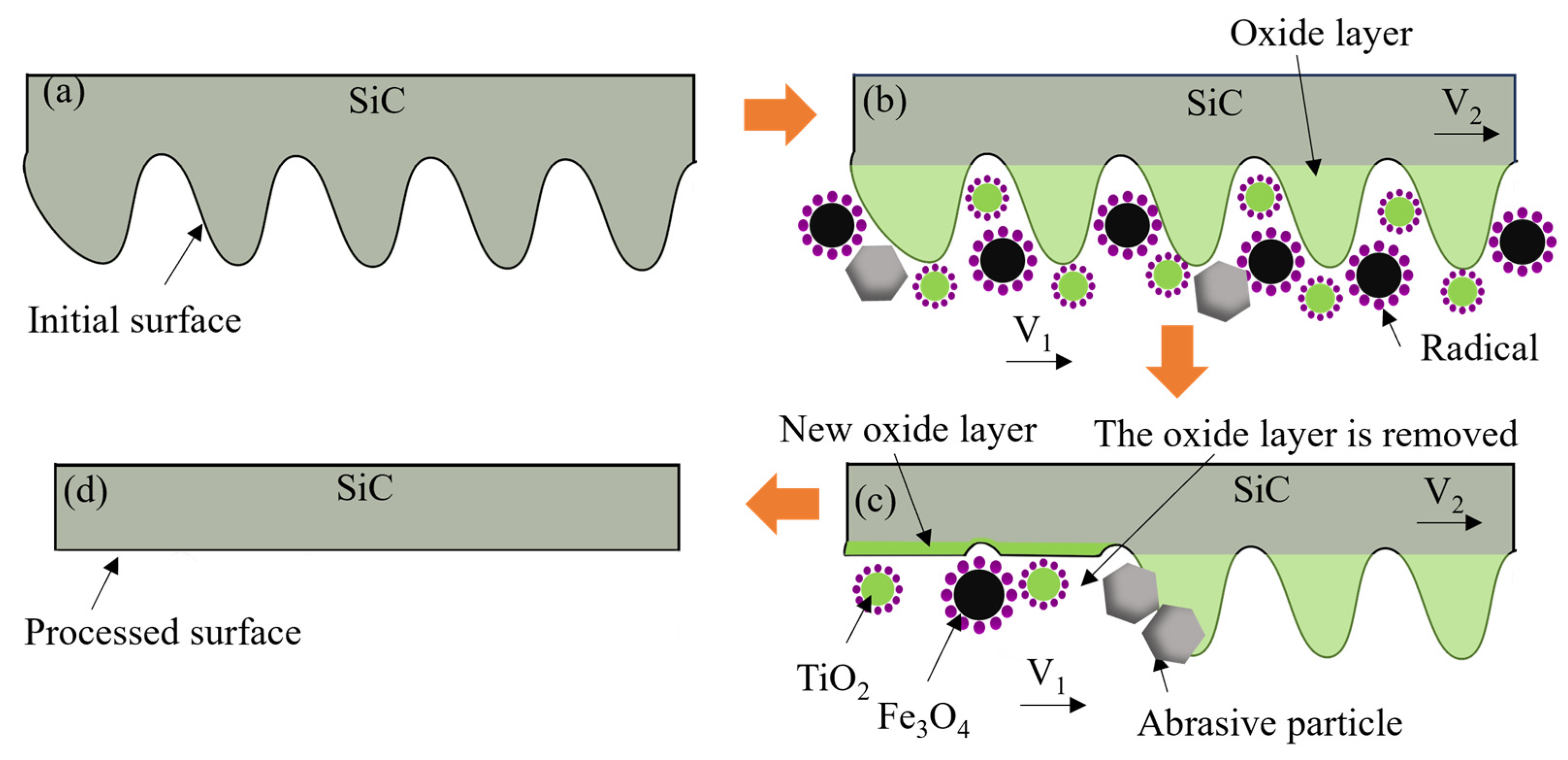
2.1. Activation of Oxone and Removal Mechanism of 4H-SiC
2.2. Preparation of Polishing Slurry
2.3. Polishing Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
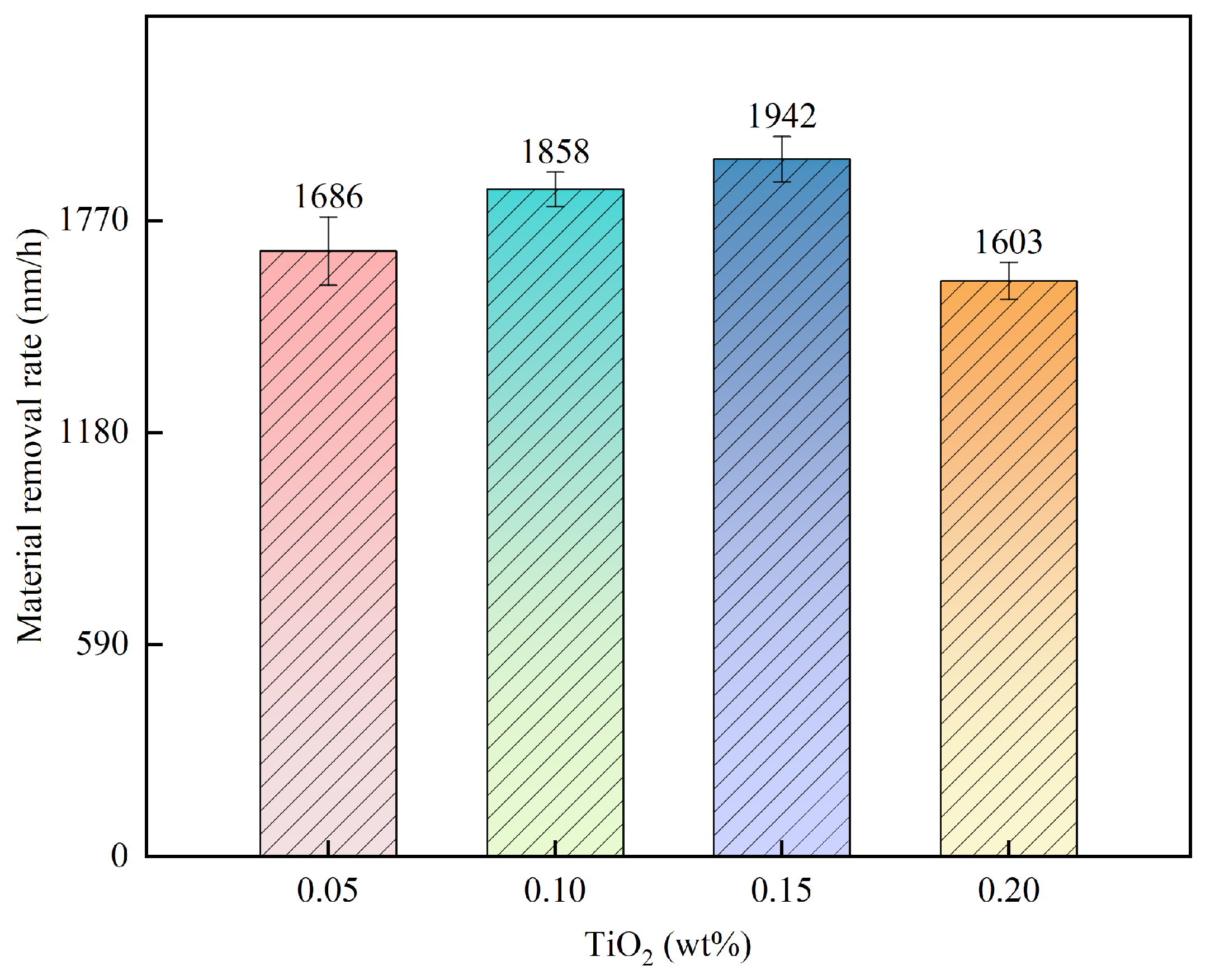
3.1. Effect of TiO2 Concentration on 4H-SiC MRR
3.2. Effect of Fe3O4 Concentration on 4H-SiC MRR
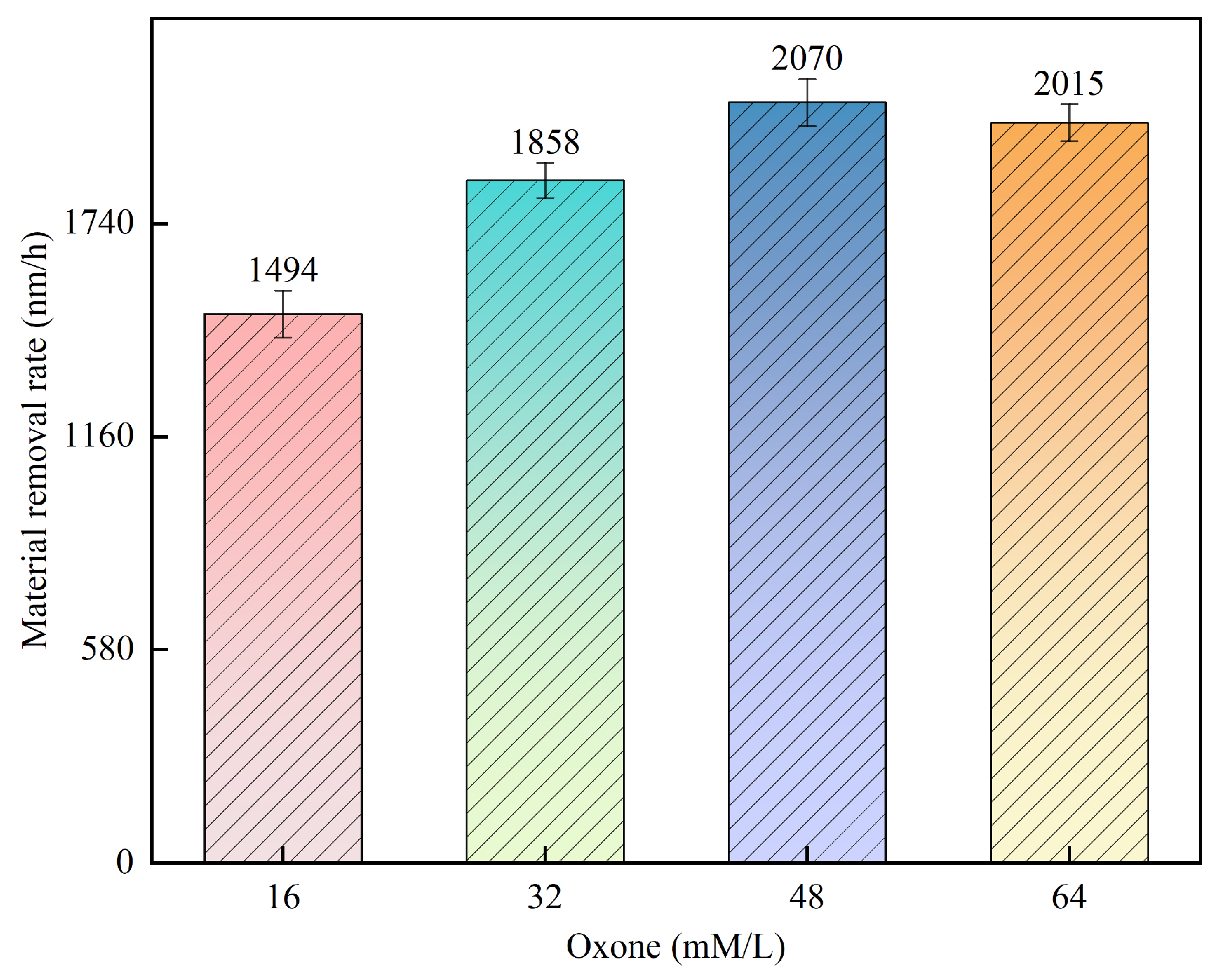
3.3. Effect of Oxone Concentration on 4H-SiC MRR
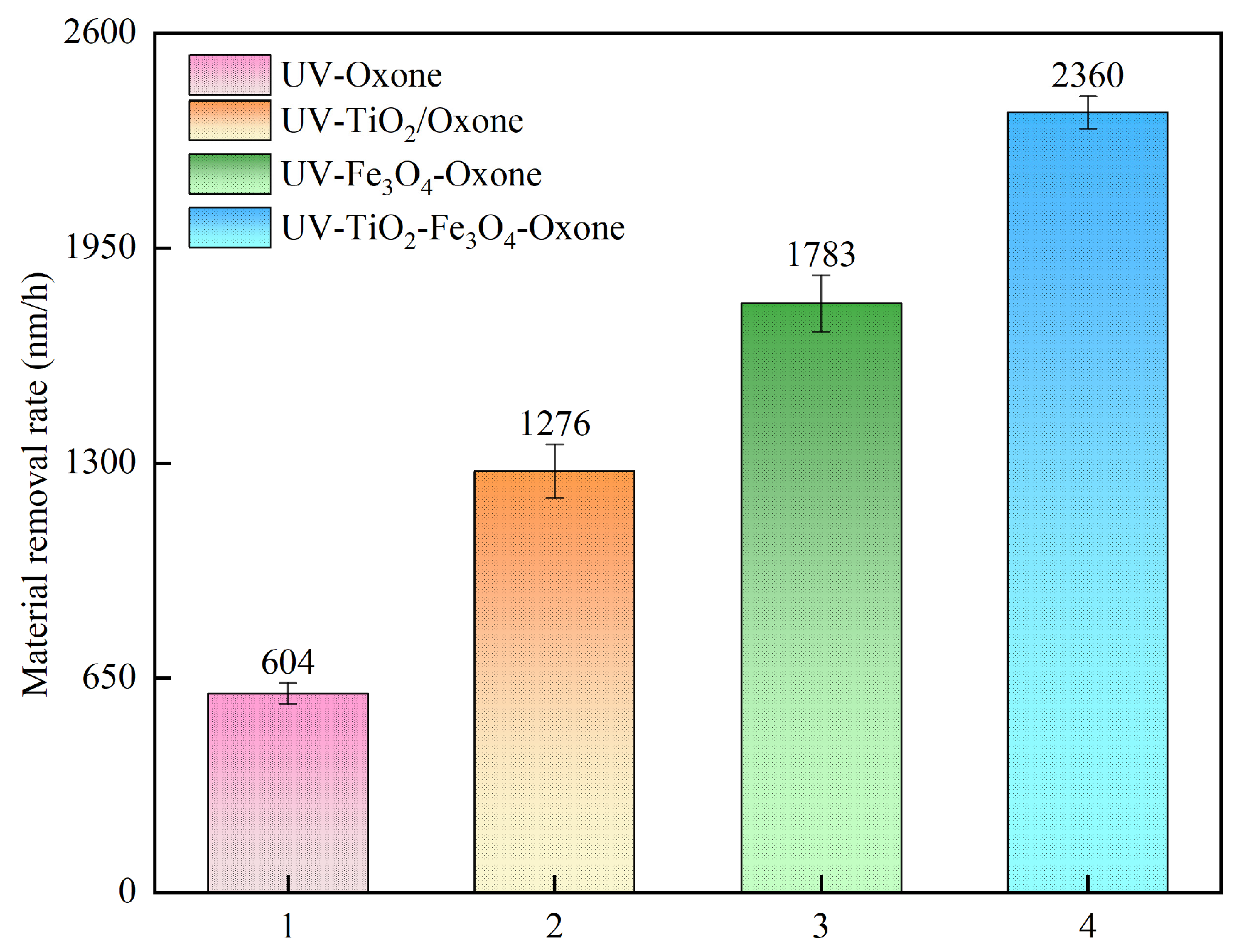
3.4. Comparison of Different Catalytic Methods
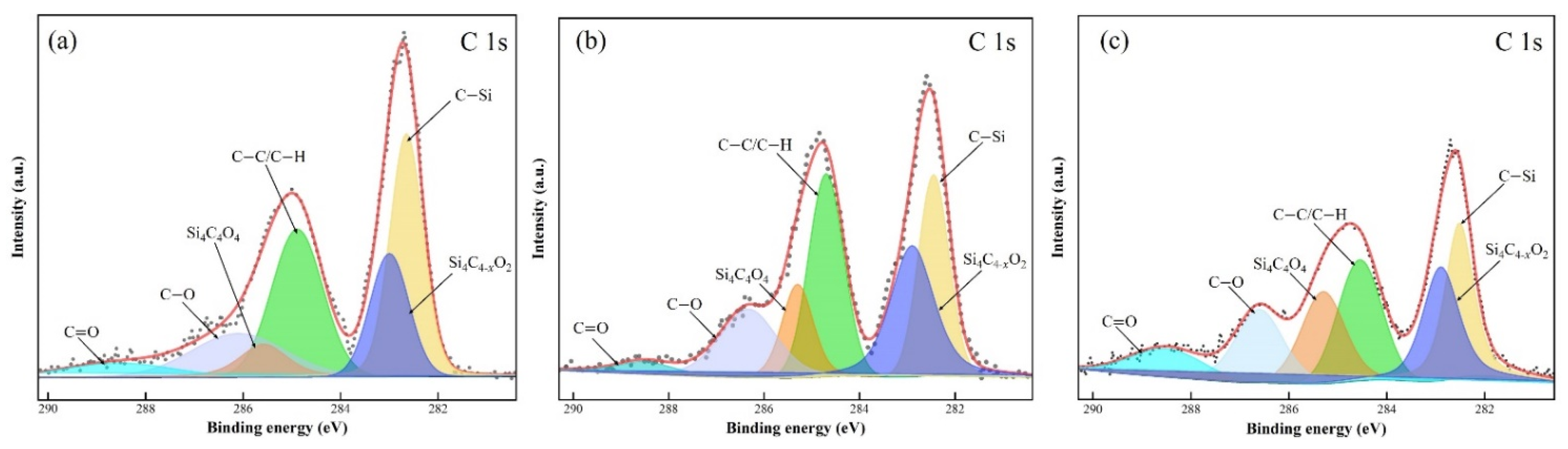
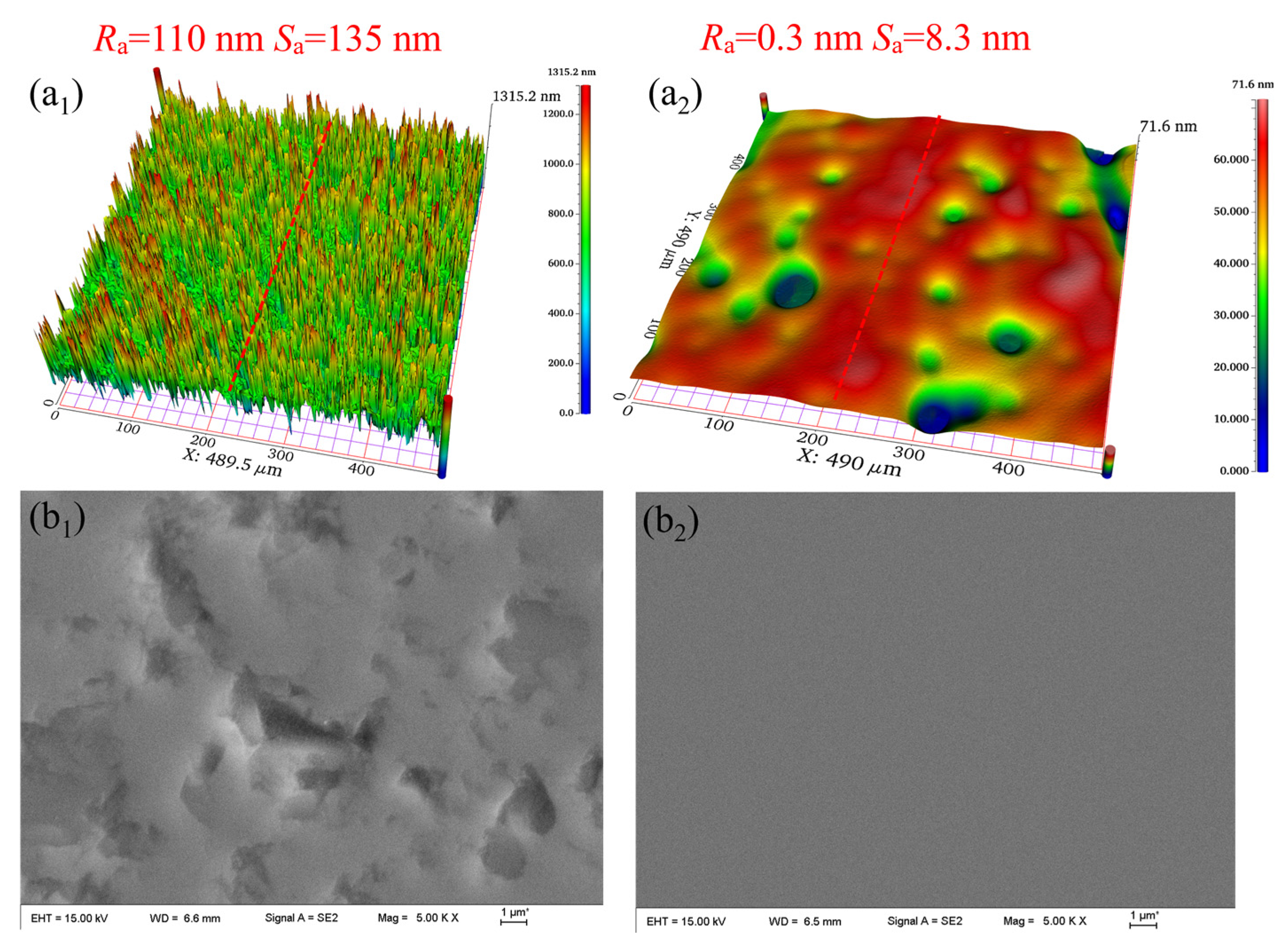
3.5. Surface Analyses
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The principle underlying the multi-catalyst activation of Oxone was briefly discussed relative to its application as a novel approach for polishing 4H-SiC. Multiple sets of single-factor experiments were conducted to investigate the impact of the Oxone, TiO2, and Fe3O4 concentrations on the SiC MRR accordingly. The results indicated that the highest MRR of 2360 nm/h was achieved when using 0.75 wt% Fe3O4, 0.15 wt% TiO2, and 48 mM Oxone.
- (2)
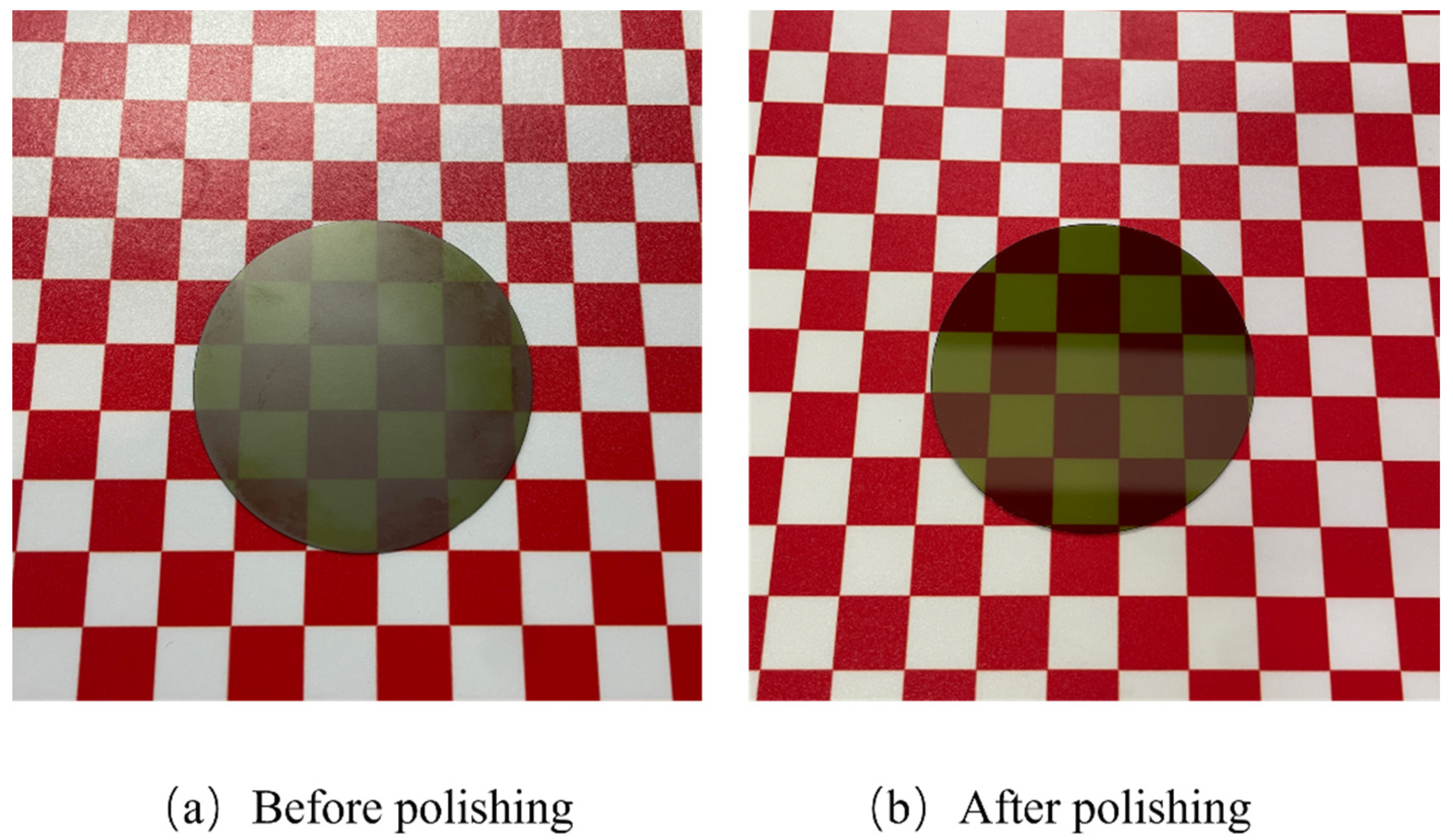
- Comparative experiments and XPS analyses were undertaken to confirm that the synergistic effect of UV irradiation, TiO2, and Fe3O4 significantly enhanced the oxidizing properties of the polishing slurry, thereby improving the MRR and surface quality of the polished 4H-SiC. Furthermore, observations conducted using WLI and SEM indicated a supersmooth surface with a surface roughness Ra of 0.304 nm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, M.; Wu, L.; Wei, M.; Chen, H.; Yuan, J.; Lyu, B.; Deng, H.; To, S.; Beri, T.H.; Hang, W. High-efficiency free-damage electrochemical shear-thickening polishing of single-crystal silicon carbide. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 132, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Hosoya, K.; Imanishi, Y.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. Electro-chemical mechanical polishing of single-crystal SiC using CeO2 slurry. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 52, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yamamura, K. Smoothing of reaction sintered silicon carbide using plasma assisted polishing. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, S24–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, M.L. The Fenton Reaction. Dependence of the Rate on pH. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Yagi, K.; Murata, J.; Yasui, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Hara, H.; Sano, Y.; Yamauchi, K. A Study on a Surface Preparation Method for Single-Crystal SiC Using an Fe Catalyst. J. Elec Mater. 2009, 38, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Q.; Lu, J. The mechanism of Fenton reaction of hydrogen peroxide with single crystal 6H-SiC substrate. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by Sulfate Radical-based Advanced Oxidation Processes (SR-AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Zeng, N. Improvement in chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC wafer by activating persulfate through the synergistic effect of UV and TiO2. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 295, 117150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Green, I.R.; Ahmed, I. Journey Describing Applications of Oxone in Synthetic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3329–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.L.; Chu, W.; Wang, Y.H. Naphthalene degradation by Fe2+/Oxone/UV—Applying an unconventional kinetics model and studying the reaction mechanism. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Pignatello, J.J. Role of Quinone Intermediates as Electron Shuttles in Fenton and Photoassisted Fenton Oxidations of Aromatic Compounds. Env. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Xue, D.; Pan, H.; Feng, J.; Li, Y. Degradation of ibuprofen by a synergistic UV/Fe(III)/Oxone process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.L.; Chu, W.; Xu, W. Photocatalysis of naphthalene by Fe3O4/Oxone/UV: Simultaneous radical and non-radical pathways. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, B. Metalloporphyrins as versatile catalysts for oxidation reactions and oxidative DNA cleavage. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1411–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Abdelhaleem, A.; Chu, W.; Pu, S.; Qi, F.; Zou, J. S-doped TiO2 photocatalyst for visible LED mediated oxone activation: Kinetics and mechanism study for the photocatalytic degradation of pyrimethanil fungicide. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Photocatalysis assisted by peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for benzotriazole degradation: Effect of pH on sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Altaee, A. Visible and UV photocatalysis of aqueous perfluorooctanoic acid by TiO2 and peroxymonosulfate: Process kinetics and mechanistic insights. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Metal-free activation of Oxone using one-step prepared sulfur-doped carbon nitride under visible light irradiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Quiles, R.; de Andrés, J.M.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Study of the Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 and Fe2+ in the Activation of Peroxymonosulfate. Water 2021, 13, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Chu, W.; Lam, S.H.; Lin, A.Y.-C. Ibuprofen degradation and toxicity evolution during Fe2+/Oxone/UV process. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, C.; van Eldik, R. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Oxidation of Sulfur (IV) Oxides. Atmos. Relev. Process. Mech. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 119–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, R.; Tlili, S.; Chiron, S.; Barbati, S. Removal of carbamazepine from urban wastewater by sulfate radical oxidation. Env. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wei, M.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Hong, B.; Lyu, B.; Chen, H.; Hang, W. Dominant parameters and mechanisms influencing the electrochemical shear-thickening polishing of 4H-SiC. Ceram. Int. 2024, 51, 10351–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, K.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wei, J.; Qi, Y.; Tu, Z.; Qu, R.; Yan, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, F. Degradation of pentachlorophenol in peroxymonosulfate/heat system: Kinetics, mechanism, and theoretical calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal Using Combined Metal Ions and Heat Activated Peroxymonosulfate/H2O2 Solutions. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Ohta, A.; Znad, H.T.; Kawase, Y. UV light assisted decolorization of dark brown colored coffee effluent by photo-Fenton reaction. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wei, M.; Wu, L.; Hong, B.; Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Yuan, J.; Lyu, B.; Wang, C.; Deng, H.; et al. Microwave plasma modification-assisted shear-thickening polishing of single-crystal silicon carbide. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2025, 94, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Lei, H.; Zhang, J. Preparation of SiO2@MnO2 composite abrasives and their performance in chemical-mechanical polishing of SiC substrates. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 34796–34805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, R.; Radtke, C.; Boudinov, H.; Da Silva, E.F. Improvement of SiO2/4H-SiC interface properties by oxidation using hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Rusli, E.; Xia, J.H.; Tan, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Tin, C.C.; Yoon, S.; Zhu, W.; Ahn, J. Study of Carbon in Thermal Oxide Formed on 4H-SiC by XPS. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 483–485, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Guo, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Pan, G. Picosecond Laser-Assisted Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP): Aiming at the Si-Face of Single-Crystal 6H-SiC Wafer. ECS J. Solid. State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, G.; Shi, X.; Xu, L.; Zou, C.; Gong, H.; Luo, G. XPS, UV–vis spectroscopy and AFM studies on removal mechanisms of Si-face SiC wafer chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 50 ± 2 |
| Thickness (um) | 350 ± 25 |
| Surface roughness (nm) | 110.844 |
| Range of resistivity (Ω·cm) | 0.015–0.028 |
| Doping element | Nitrogen |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Polishing pad | Polyurethane |
| Abrasive | 100 nm diamond |
| Rotational speed of the polishing head (rpm) | 30 |
| Rotational speed of the polishing pad (rpm) | 60 |
| Polishing slurry flow rate (mL/min) | 80 |
| Load (kg) | 12 |
| pH | 3 |
| Experiment Group | TiO2 Concentration (wt%) | Fe3O4 Concentration (wt%) | Oxone Concentration (mM/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2 | 0.5 | 32 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1 | 32 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 16, 32, 48, 64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Shen, M.; Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lyu, B.; Yuan, J. Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H-SiC Using Multi-Catalyst Synergistic Activation of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate. Processes 2025, 13, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041094
Li C, Shen M, Li X, Fu Y, Dong Y, Lyu B, Yuan J. Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H-SiC Using Multi-Catalyst Synergistic Activation of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Congzheng, Mengmeng Shen, Xuelai Li, Yuhan Fu, Yanfang Dong, Binghai Lyu, and Julong Yuan. 2025. "Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H-SiC Using Multi-Catalyst Synergistic Activation of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate" Processes 13, no. 4: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041094
APA StyleLi, C., Shen, M., Li, X., Fu, Y., Dong, Y., Lyu, B., & Yuan, J. (2025). Chemical–Mechanical Polishing of 4H-SiC Using Multi-Catalyst Synergistic Activation of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate. Processes, 13(4), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041094






