Multi-Scale Graph Learning with Seasonal and Trend Awareness Electricity Load Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multi-scale graph neural network (GNN) module is proposed to capture trend and seasonal dependencies across different temporal scales, addressing the limitations of existing approaches in modeling cross-scale relationships.
- A Hawkes attention mechanism is introduced to efficiently aggregate sequential features, enabling the model to capture the dynamic and time-varying characteristics of electricity demand.
- A trend–seasonal spatio-temporal fusion method is developed, which integrates trend and seasonal spatio-temporal features through an attention-driven strategy to further enhance prediction accuracy.
- Experimental results on multiple datasets indicate that the proposed model achieves superior predictive performance compared with both non-graph-based and graph-based electricity load forecasting methods.
2. Related Works
2.1. Non-Graph-Based Models
2.2. Graph-Based Models
3. Methodology
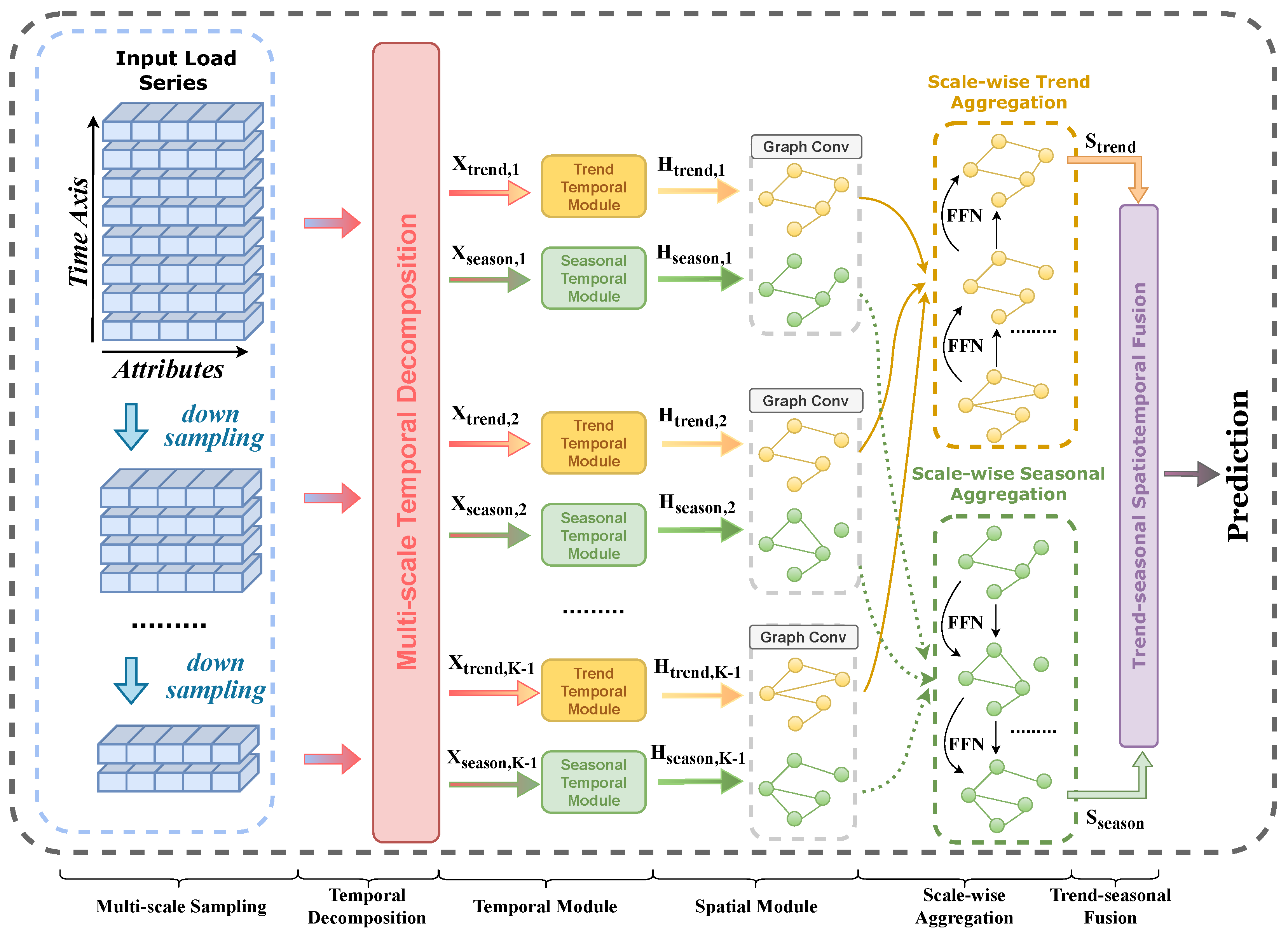
3.1. Overall Framework
3.2. Multi-Scale Sampling Module
3.3. Multi-Scale Temporal Decomposition
| Algorithm 1: Multi-scale Temporal Decomposition (PyTorch-like) |
 |
3.4. Multi-Scale Temporal Module
3.5. Multi-Scale Spatial Module
3.5.1. Multi-Scale Graph Construction
3.5.2. Multi-Scale Graph Aggregation
3.6. Scale-Wise Trend and Seasonal Aggregation
3.6.1. Trend Aggregation
3.6.2. Seasonal Aggregation
3.7. Trend–Seasonal Spatio-Temporal Fusion
3.8. Prediction and Optimization
4. Experiment
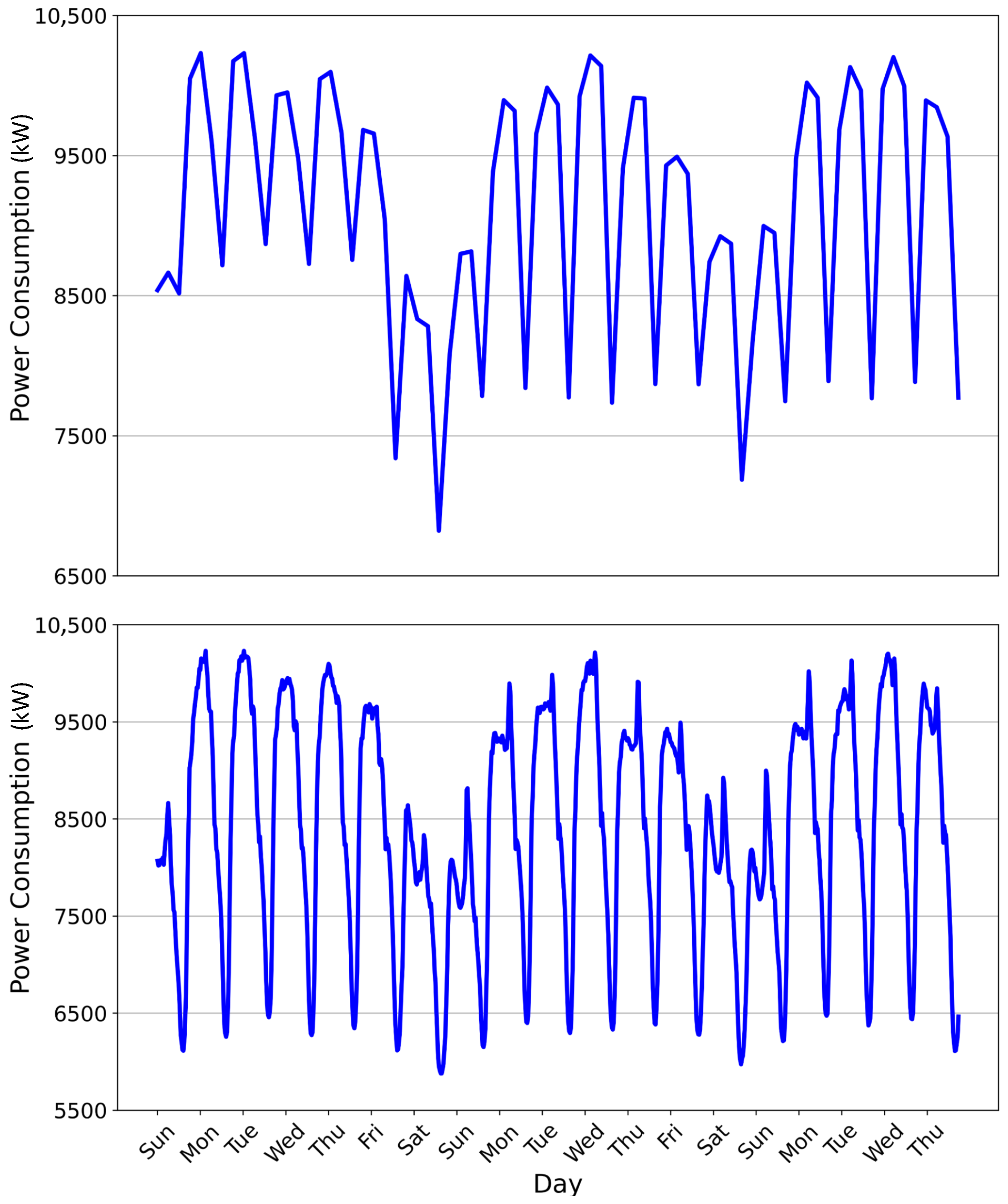
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Baseline Methods
4.2.1. Non-Graph-Based Methods
4.2.2. Graph-Based Methods
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Result Analysis
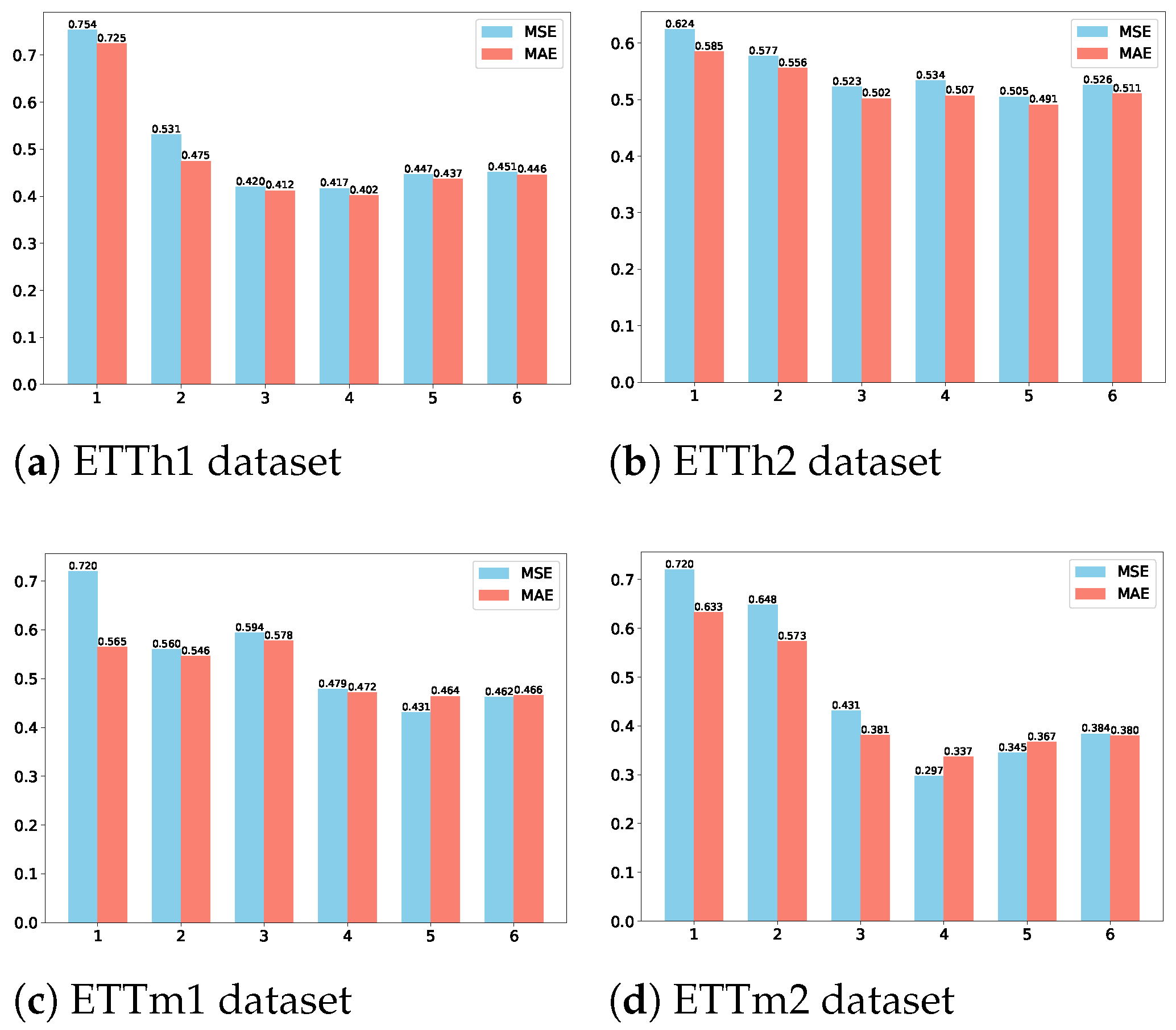
4.5. Ablation Study
4.6. Hyperparameter Analysis
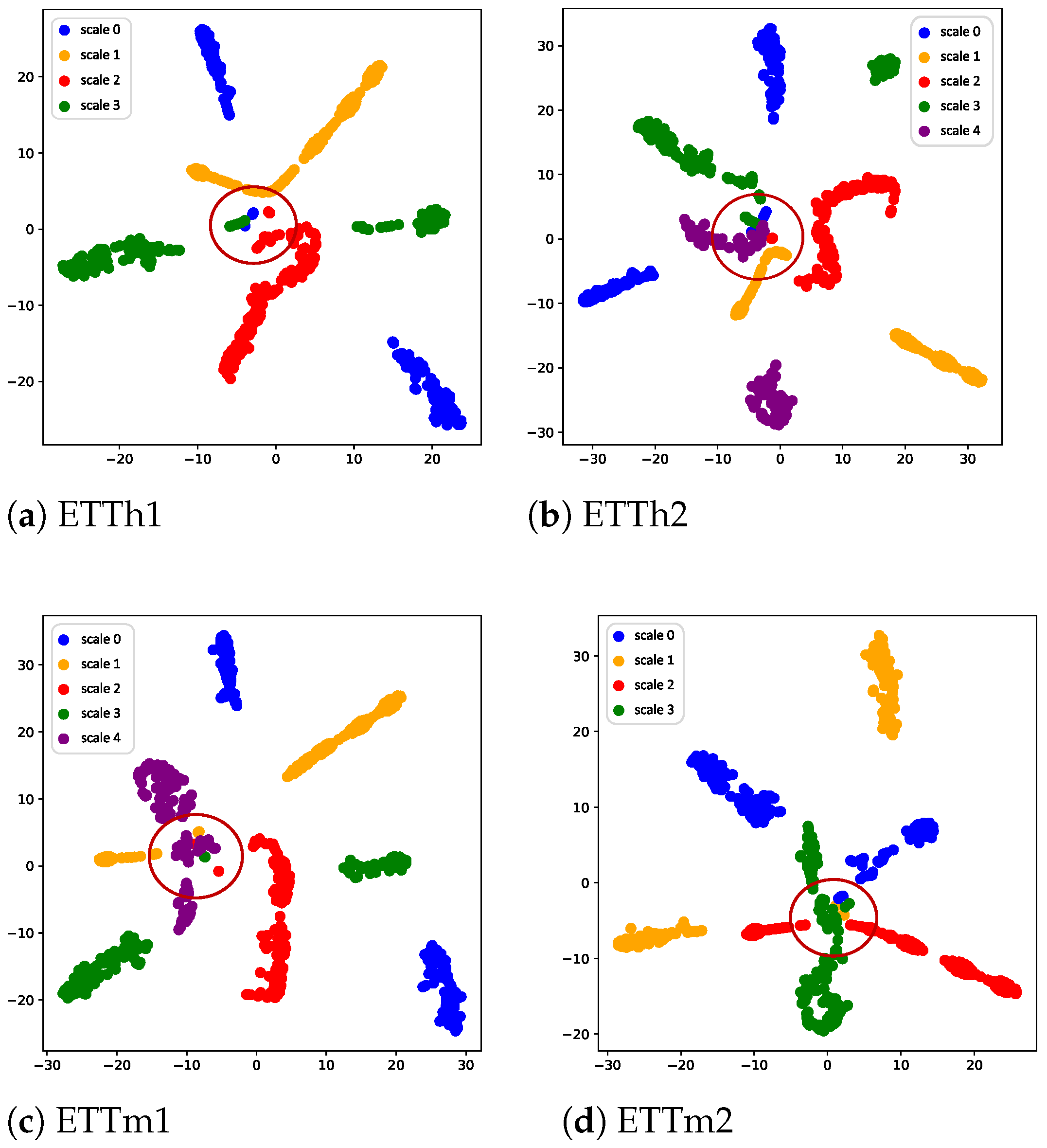
4.7. Visualization Analysis
4.7.1. Trend Spatio-Temporal Embedding Visualization
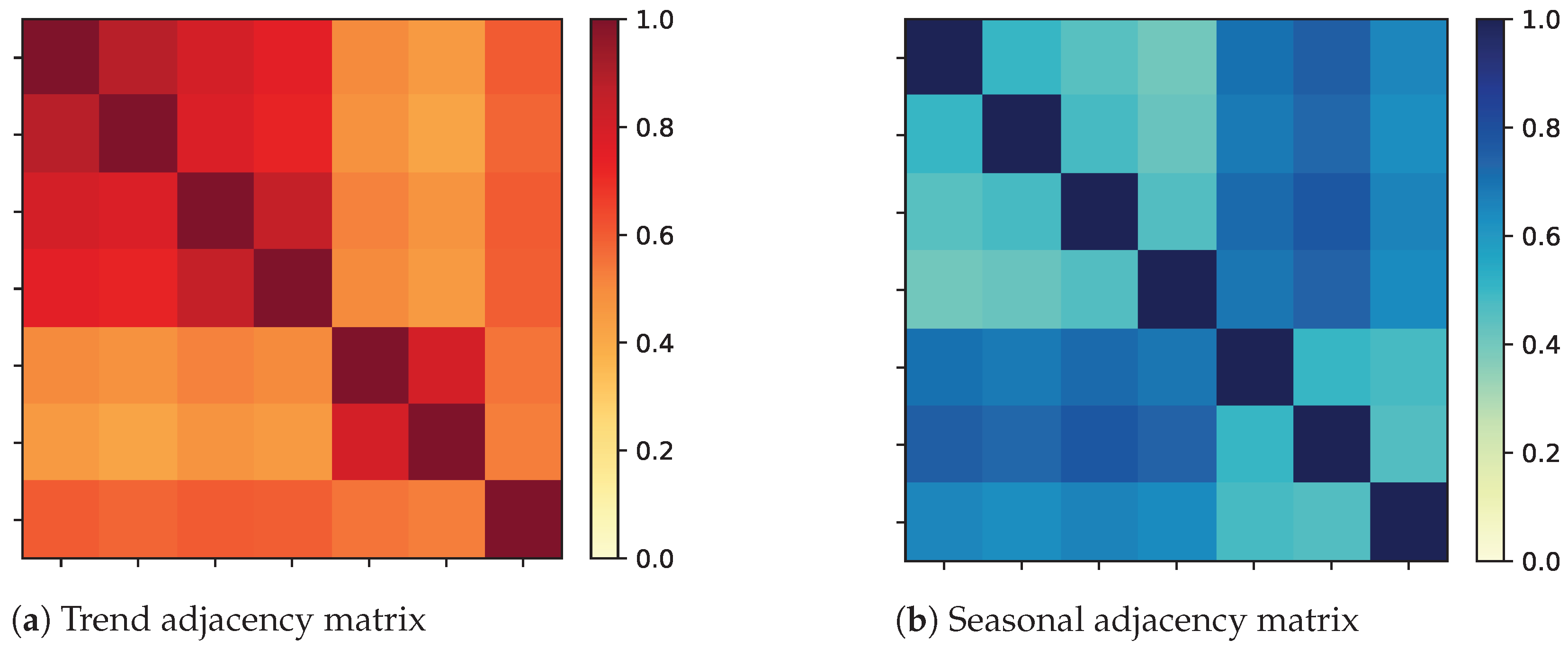
4.7.2. Adjacency Matrix Visualization
4.8. Complexity Analysis
4.9. Training and Inference Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhuang, W.; Pan, G.; Gu, W.; Zhou, S.; Hu, Q.; Gu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, S.; Qiu, H. Hydrogen economy driven by offshore wind in regional comprehensive economic partnership members. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2014–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, S.; Gu, W.; Zhuang, W.; Gao, M.; Chan, C.; Zhang, X. Coordinated planning model for multi-regional ammonia industries leveraging hydrogen supply chain and power grid integration: A case study of Shandong. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Meng, F.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, H.; Gu, W.; Yang, Y. Multi-dimensional assessment of decarbonization technologies and pathways in China’s iron and steel industry: An energy-process chain perspective. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 61, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfares, H.K.; Nazeeruddin, M. Electric load forecasting: Literature survey and classification of methods. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2002, 33, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, C.; Rezgui, Y.; Mourshed, M. Electrical load forecasting models: A critical systematic review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, A.; Grolinger, K.; Capretz, M.A. Transformer-based model for electrical load forecasting. Energies 2022, 15, 4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinoz, T.; Eminoglu, U. Short term and medium term power distribution load forecasting by neural networks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Rahman, S. Short-term electrical load forecasting through heuristic configuration of regularized deep neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, K.; Seljom, P.; Madsen, H.; Fischer, D.; Korpås, M. Long-term electricity load forecasting: Current and future trends. Util. Policy 2019, 58, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Ko, C.N. Short-term load forecasting using lifting scheme and ARIMA models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 5902–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Deng, S.; Wang, D. A short-term power load forecasting method based on k-means and SVM. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 5253–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Kong, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T. Short-term load forecasting of industrial customers based on SVMD and XGBoost. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Fu, X.; Zong, C. Short-term load forecasting method based on feature preference strategy and LightGBM-XGboost. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 75257–75268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Qin, H.; Przystupa, K.; Majka, M.; Kochan, O. Individualized short-term electric load forecasting using data-driven meta-heuristic method based on LSTM network. Sensors 2022, 22, 7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, G.; Miao, S.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, S. A short-term electric load forecast method based on improved sequence-to-sequence GRU with adaptive temporal dependence. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 137, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xia, C.; Chi, L.; Chang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, T.; Zomaya, A.Y. Short-term load forecasting based on the transformer model. Information 2021, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.; Fan, J.; Xia, M.; Zhu, K. A multi-scale spatial–temporal graph neural network-based method of multienergy load forecasting in integrated energy system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 15, 2652–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, C.; Zhu, H. Graph neural networks for learning real-time prices in electricity market. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Pi, D.; Ping, M.; Zhang, H. Short-term load forecasting using spatial-temporal embedding graph neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 225, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 22419–22430. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Shi, X.; Hu, T.; Luo, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, J. Timemixer: Decomposable multiscale mixing for time series forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, F.; Rehman, A.; Shah, H.A.; Diyan, M.; Chen, J.; Kang, J.M. SmartFormer: Graph-based transformer model for energy load forecasting. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2025, 73, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Wang, B.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pang, X. Stacking integration algorithm based on CNN-BiLSTM-Attention with XGBoost for short-term electricity load forecasting. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.M.; Tentzeris, M.M. Short-term power load forecasting using grey correlation contest modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediger, V.Ş.; Akar, S.; Uğurlu, B. Forecasting production of fossil fuel sources in Turkey using a comparative regression and ARIMA model. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 3836–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W. Short-term electricity demand forecasting using double seasonal exponential smoothing. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2003, 54, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W. Triple seasonal methods for short-term electricity demand forecasting. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 204, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, S.; Gu, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, A.; Wang, X. MMGPT4LF: Leveraging an optimized pre-trained GPT-2 model with multi-modal cross-attention for load forecasting. Appl. Energy 2025, 392, 125965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; He, M.; Di, F.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Lv, F. Research on power load forecasting method based on LSTM model. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1657–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Pang, S.; Shi, M.; Goh, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. General short-term load forecasting based on multi-task temporal convolutional network in COVID-19. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 147, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Ensemble power load forecasting based on competitive-inhibition selection strategy and deep learning. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 51, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, M.; Li, R. Deep learning for household load forecasting—A novel pooling deep RNN. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 5271–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhuang, W.; Xia, M.; Fang, W.; Liu, J. Optimizing attention in a Transformer for multihorizon, multienergy load forecasting in integrated energy systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 10238–10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lin, W. Efficient residential electric load forecasting via transfer learning and graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 14, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rui, L.; Ma, J. A short-term residential load forecasting scheme based on the multiple correlation-temporal graph neural networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 146, 110629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, H.; Gull, M.S.; Rauf, H.; Khalid, M.; Arshad, N. Graph Convolutional Networks based short-term load forecasting: Leveraging spatial information for improved accuracy. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 230, 110263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J. Hierarchical Adaptive Temporal-Relational Modeling for Stock Trend Prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 3691–3698. [Google Scholar]
- Marmolin, H. Subjective MSE measures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. 1986, 16, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Shu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Q.; Yang, B.; Guo, C. Pathformer: Multi-scale transformers with adaptive pathways for time series forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.05956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Long, G.; Jiang, J.; Chang, X.; Zhang, C. Connecting the dots: Multivariate time series forecasting with graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 August 2020; pp. 753–763. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset | # Train | # Val | # Test | Length | # Variable | Sampling Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETTh1 | 12,194 | 1742 | 3484 | 120 | 7 | Hourly |
| ETTh2 | 12,194 | 1742 | 3484 | 120 | 7 | Hourly |
| ETTm1 | 48,776 | 6968 | 13,936 | 120 | 7 | 15 min |
| ETTm2 | 48,776 | 6968 | 13,936 | 120 | 7 | 15 min |
| AEL | 61,353 | 8765 | 17,530 | 120 | 6 | 30 min |
| Electricity | 18,412 | 2630 | 5262 | 168 | 321 | Hourly |
| Methods | Metrics | ETTh1 | ETTh2 | ETTm1 | ETTm2 | AEL | Electricity | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | |||
| Non-graph -based | ARIMA | MSE | 1.043 | 0.906 | 0.961 | 0.808 | 0.726 | 0.912 | ||||||
| MAE | 0.815 | 0.687 | 0.793 | 0.671 | 0.665 | 0.702 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.325 | 0.298 | 0.316 | 0.289 | 0.274 | 0.296 | ||||||||
| Holt-Winters | MSE | 0.985 | 0.812 | 0.901 | 0.790 | 0.701 | 0.845 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.802 | 0.676 | 0.781 | 0.663 | 0.652 | 0.689 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.317 | 0.285 | 0.308 | 0.276 | 0.263 | 0.287 | ||||||||
| LSTM | MSE | 0.928 | 0.595 | 0.778 | 0.739 | 0.613 | 0.682 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.791 | 0.571 | 0.595 | 0.602 | 0.617 | 0.645 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.284 | 0.236 | 0.228 | 0.241 | 0.235 | 0.229 | ||||||||
| GRU | MSE | 0.958 | 0.608 | 0.786 | 0.776 | 0.635 | 0.695 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.798 | 0.583 | 0.604 | 0.579 | 0.650 | 0.658 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.278 | 0.241 | 0.235 | 0.222 | 0.239 | 0.230 | ||||||||
| CNN-BiLSTM -Attention | MSE | 0.876 | 0.675 | 0.507 | 0.762 | 0.526 | 0.491 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.759 | 0.585 | 0.505 | 0.576 | 0.537 | 0.490 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.254 | 0.217 | 0.196 | 0.208 | 0.183 | 0.179 | ||||||||
| Graph -based | GAT | MSE | 0.629 | 0.598 | 0.569 | 0.651 | 0.602 | 0.442 | ||||||
| MAE | 0.585 | 0.577 | 0.538 | 0.558 | 0.614 | 0.420 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.209 | 0.212 | 0.200 | 0.196 | 0.208 | 0.159 | ||||||||
| MTGNN | MSE | 0.561 | 0.537 | 0.474 | 0.599 | 0.421 | 0.387 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.533 | 0.529 | 0.472 | 0.510 | 0.442 | 0.355 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.195 | 0.192 | 0.184 | 0.179 | 0.162 | 0.138 | ||||||||
| STEGNN | MSE | 0.446 | 0.536 | 0.510 | 0.327 | 0.396 | 0.301 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.438 | 0.533 | 0.490 | 0.356 | 0.411 | 0.384 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.167 | 0.193 | 0.176 | 0.141 | 0.158 | 0.129 | ||||||||
| SmartFormer | MSE | 0.434 | 0.530 | 0.455 | 0.334 | 0.392 | 0.195 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.430 | 0.528 | 0.484 | 0.370 | 0.403 | 0.280 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.159 | 0.190 | 0.172 | 0.147 | 0.154 | 0.101 | ||||||||
| PathFormer | MSE | 0.431 | 0.525 | 0.446 | 0.334 | 0.388 | 0.192 | |||||||
| MAE | 0.427 | 0.519 | 0.474 | 0.370 | 0.399 | 0.262 | ||||||||
| MAPE | 0.157 | 0.187 | 0.168 | 0.145 | 0.151 | 0.096 | ||||||||
| MTSGNN | Value | Std | Value | Std | Value | Std | Value | Std | Value | Std | Value | Std | ||
| MSE | 0.417 | 0.003 | 0.505 | 0.005 | 0.431 | 0.004 | 0.297 | 0.004 | 0.377 | 0.005 | 0.168 | 0.004 | ||
| MAE | 0.402 | 0.003 | 0.491 | 0.004 | 0.464 | 0.005 | 0.337 | 0.005 | 0.387 | 0.005 | 0.253 | 0.004 | ||
| MAPE | 0.148 | 0.002 | 0.173 | 0.003 | 0.160 | 0.004 | 0.131 | 0.003 | 0.144 | 0.004 | 0.089 | 0.003 | ||
| Methods | Metrics | ETTh1 | ETTh2 | ETTm1 | ETTm2 | AEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o MTD | MSE | 0.584 | 0.671 | 0.529 | 0.568 | 0.574 |
| MAE | 0.527 | 0.658 | 0.542 | 0.462 | 0.569 | |
| w/o MTM | MSE | 0.556 | 0.576 | 0.614 | 0.462 | 0.421 |
| MAE | 0.512 | 0.552 | 0.569 | 0.416 | 0.450 | |
| w/o MSM | MSE | 0.739 | 0.630 | 0.671 | 0.758 | 0.516 |
| MAE | 0.683 | 0.545 | 0.653 | 0.622 | 0.553 | |
| w/o TSF | MSE | 0.434 | 0.558 | 0.473 | 0.365 | 0.392 |
| MAE | 0.413 | 0.510 | 0.485 | 0.360 | 0.396 | |
| MTSGNN | MSE | 0.417 | 0.505 | 0.431 | 0.297 | 0.377 |
| MAE | 0.402 | 0.491 | 0.464 | 0.337 | 0.387 |
| Methods | Complexity | Training Time (s) | Inference Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PathFormer | 1034.23 | 3.09 | |
| MTSGNN (Ours) | 503.15 | 3.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, H.; Wei, L. Multi-Scale Graph Learning with Seasonal and Trend Awareness Electricity Load Forecasting. Processes 2025, 13, 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123865
Hu Z, Ji Y, Xu H, Zhu H, Wei L. Multi-Scale Graph Learning with Seasonal and Trend Awareness Electricity Load Forecasting. Processes. 2025; 13(12):3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123865
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zijian, Ye Ji, Honghua Xu, Hong Zhu, and Lei Wei. 2025. "Multi-Scale Graph Learning with Seasonal and Trend Awareness Electricity Load Forecasting" Processes 13, no. 12: 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123865
APA StyleHu, Z., Ji, Y., Xu, H., Zhu, H., & Wei, L. (2025). Multi-Scale Graph Learning with Seasonal and Trend Awareness Electricity Load Forecasting. Processes, 13(12), 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123865






