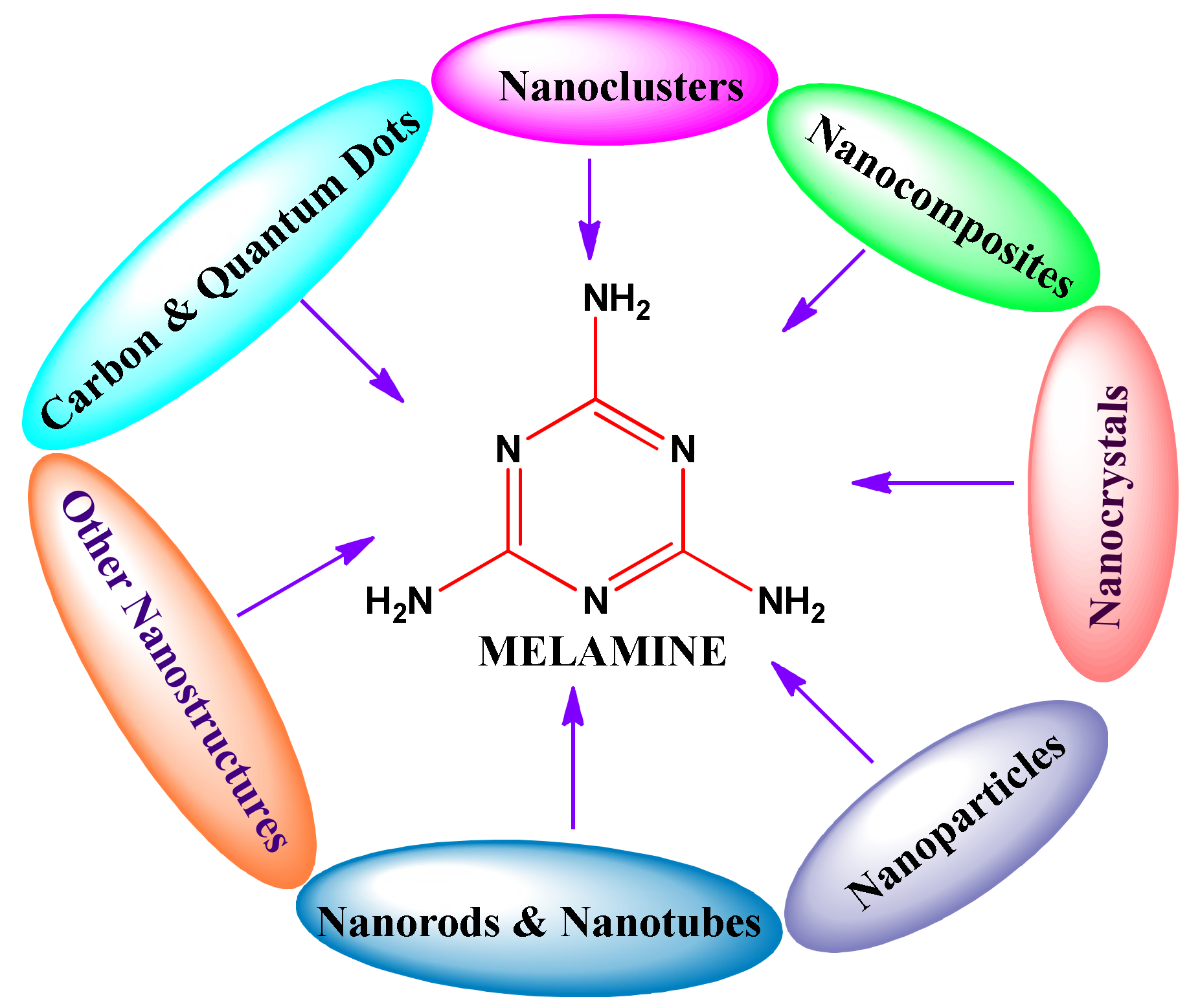
Review on Nanomaterial-Based Melamine Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
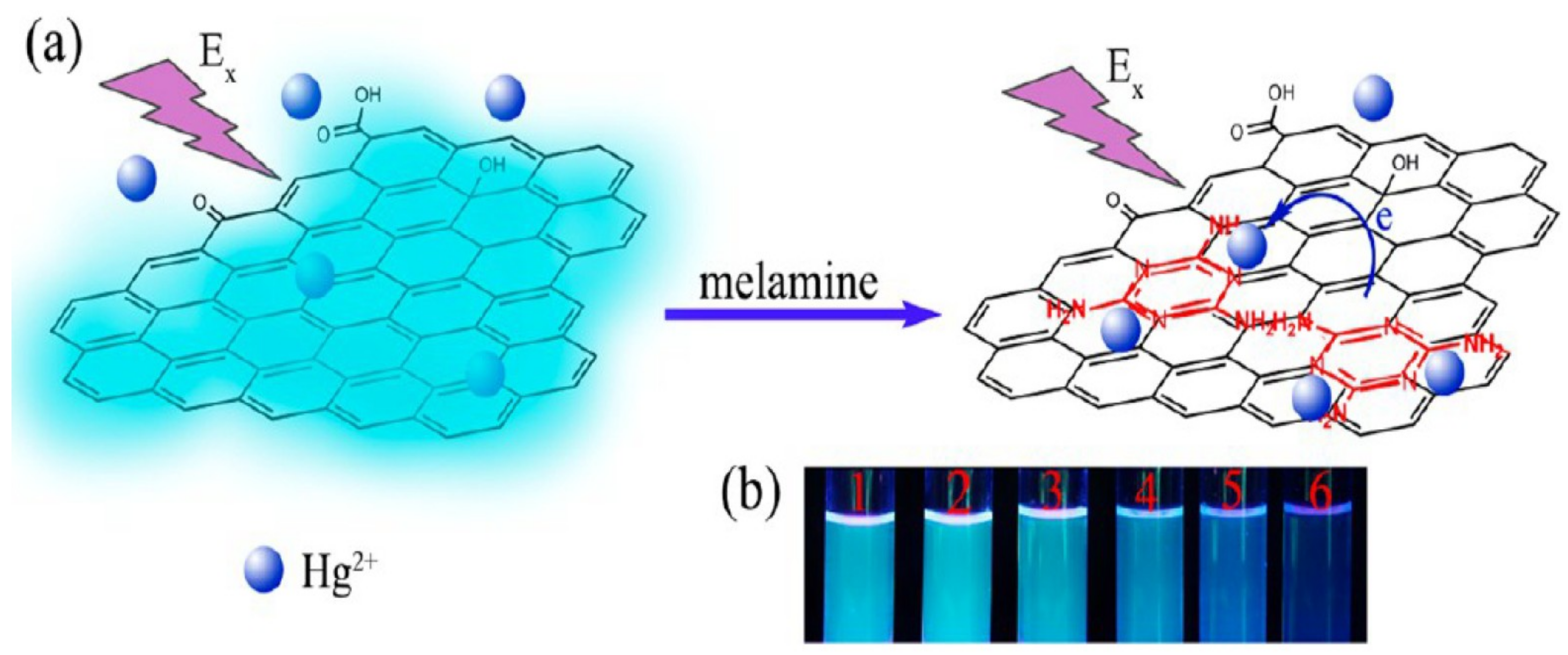
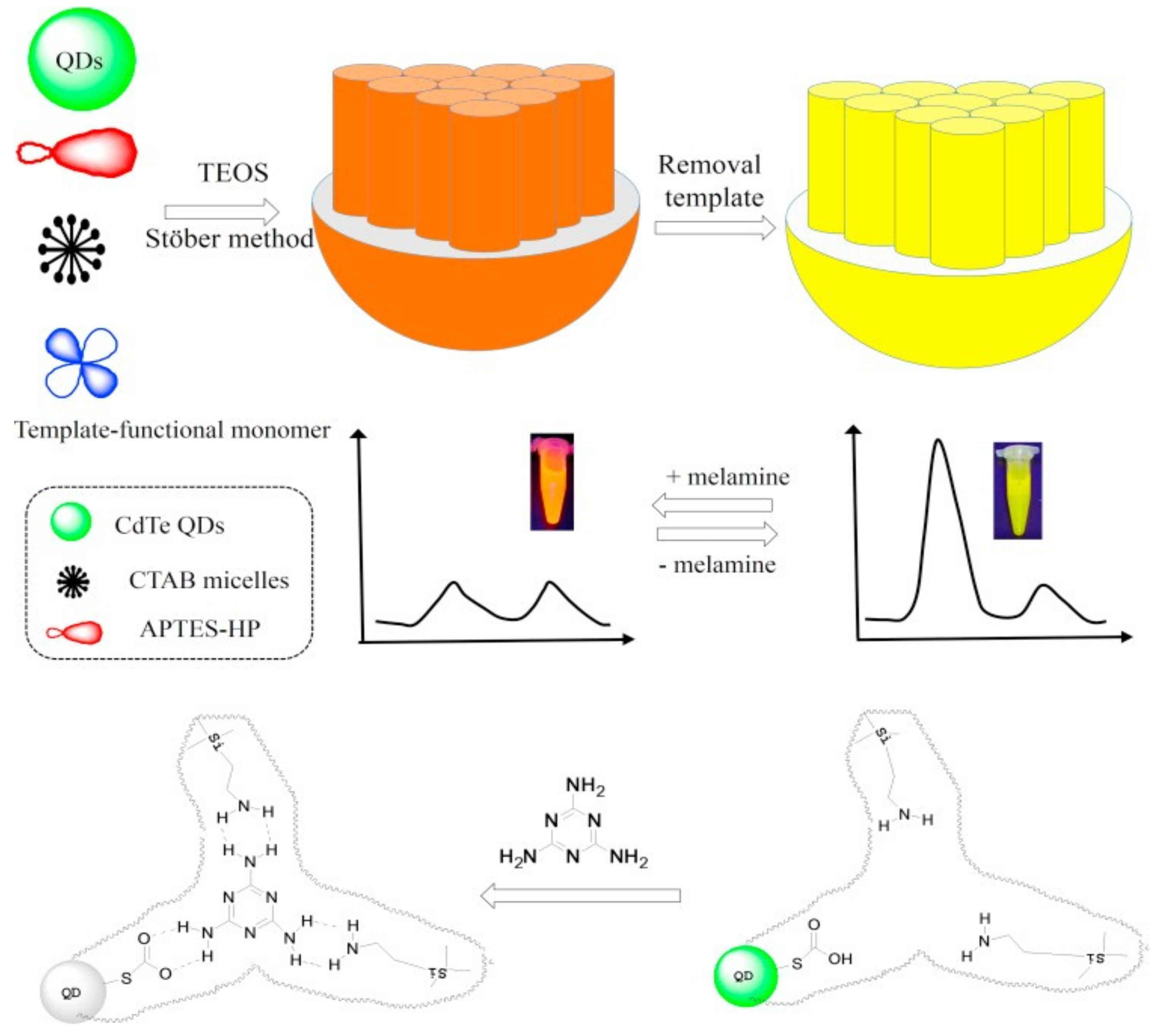
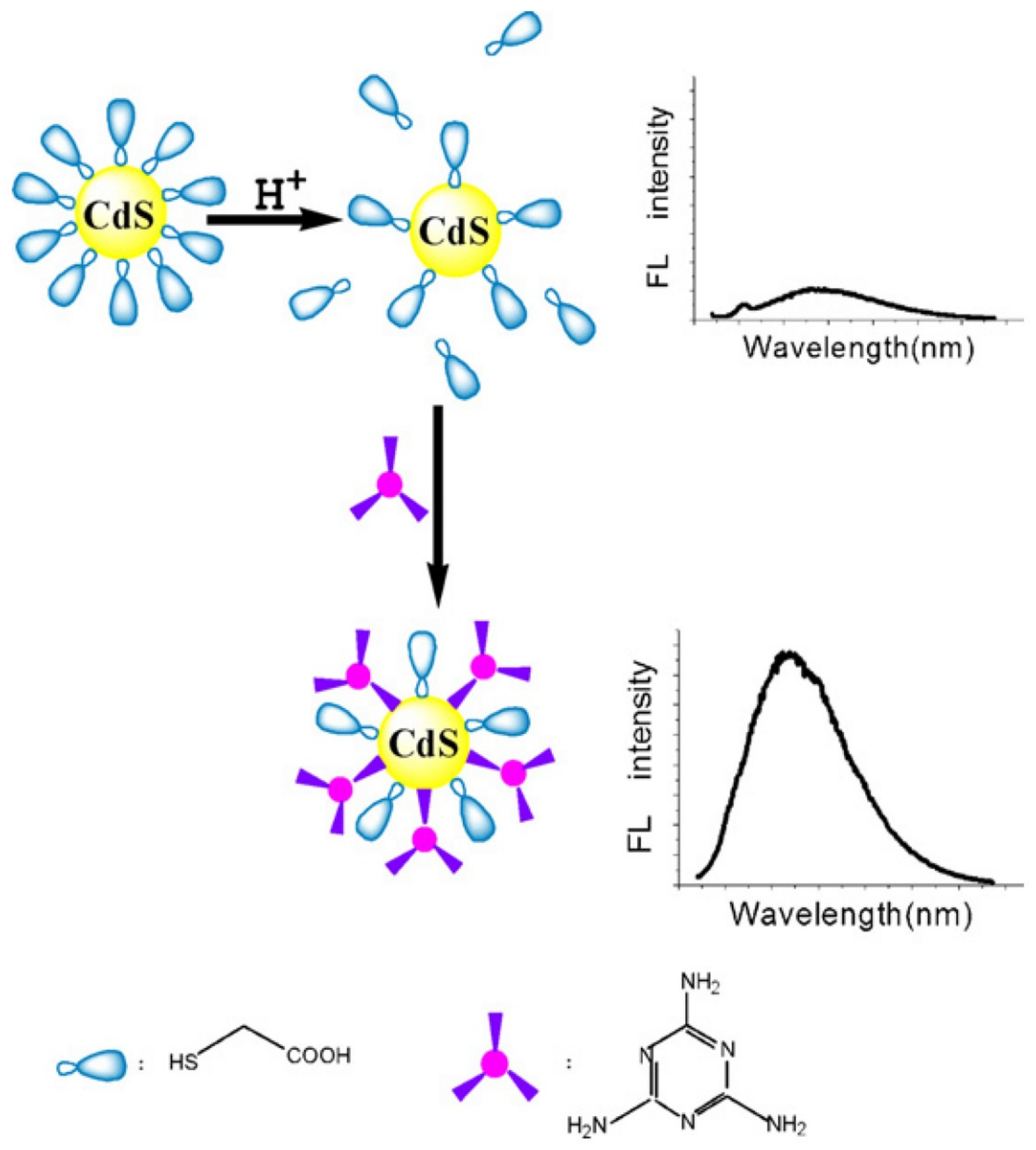
2. Carbon and Quantum Dots for Melamine Detection
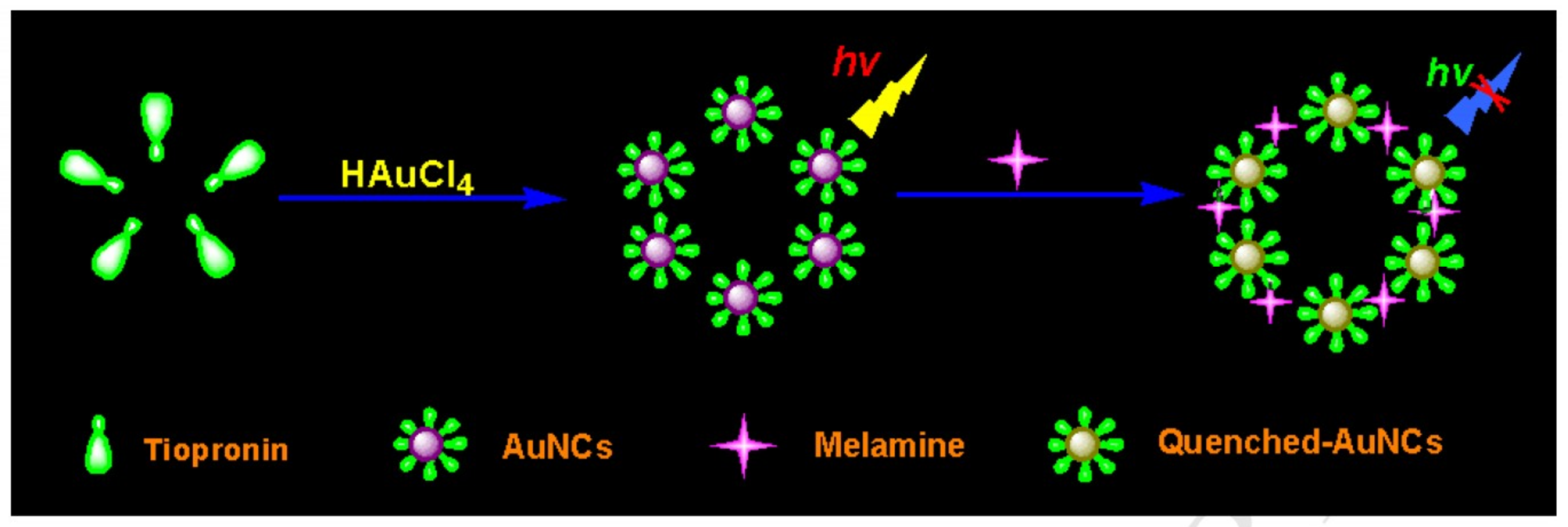
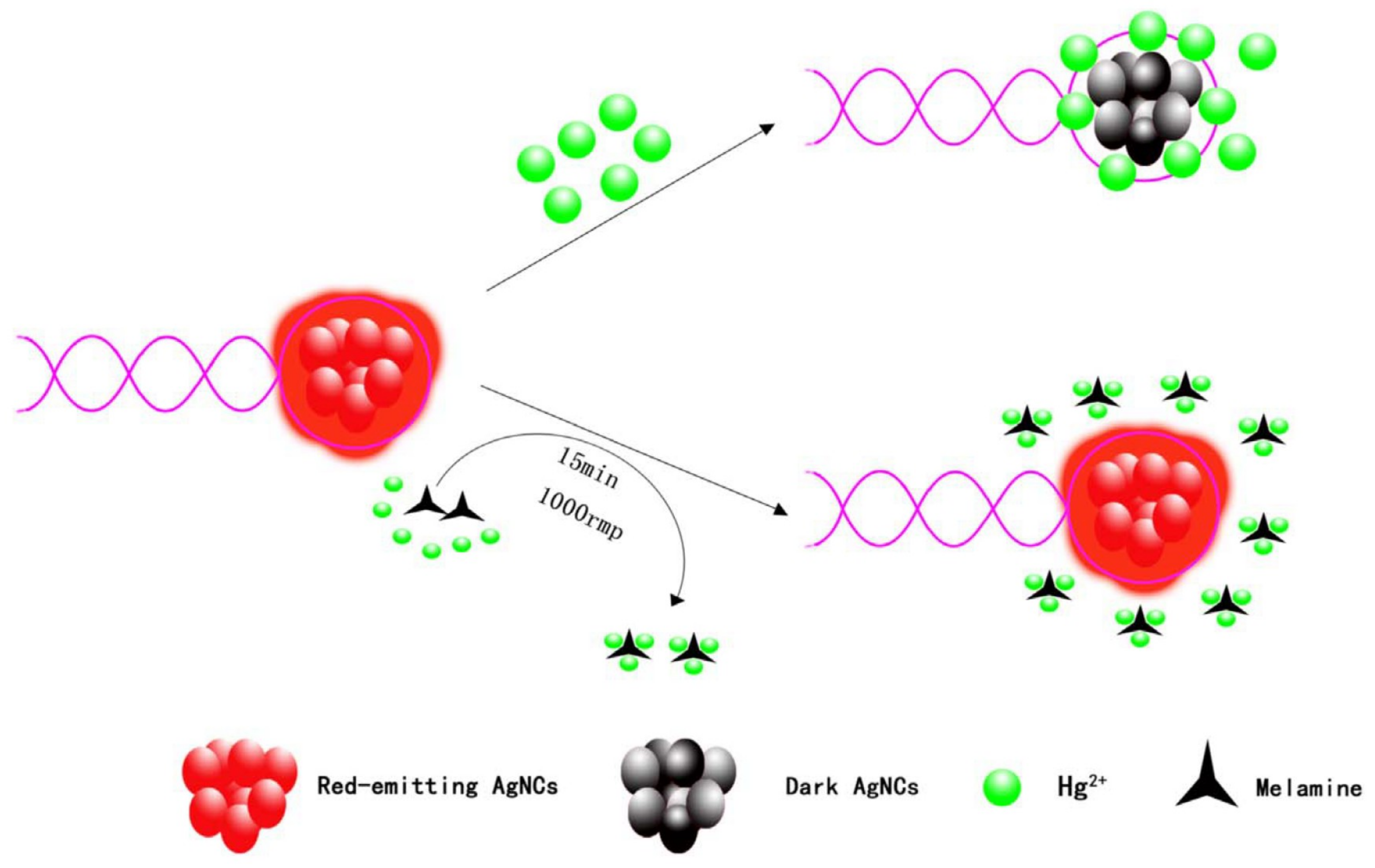
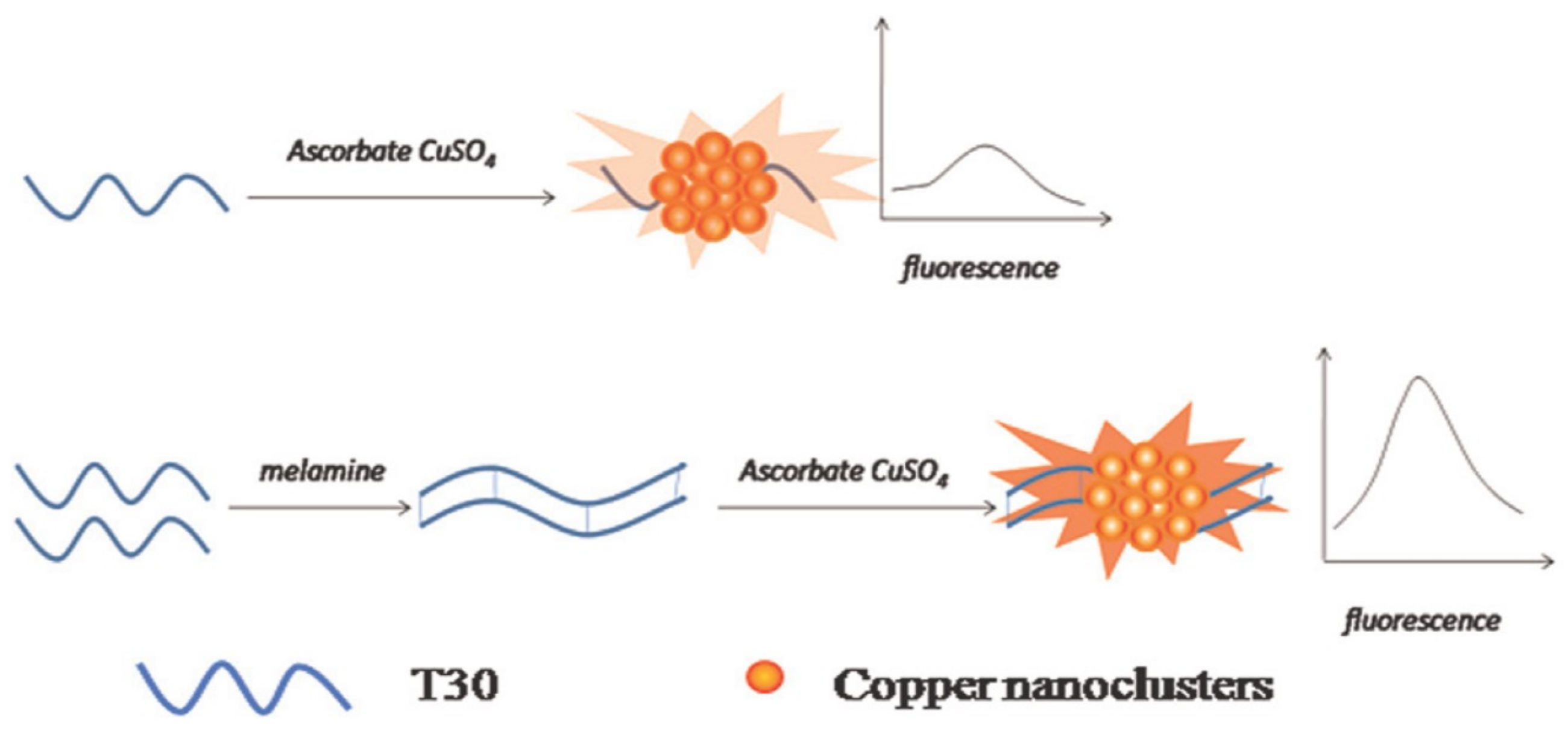
3. Metal Nanoclusters Towards Melamine Determination
4. Melamine Assay by Nanocomposites
5. Nanocrystals in Melamine Recognition
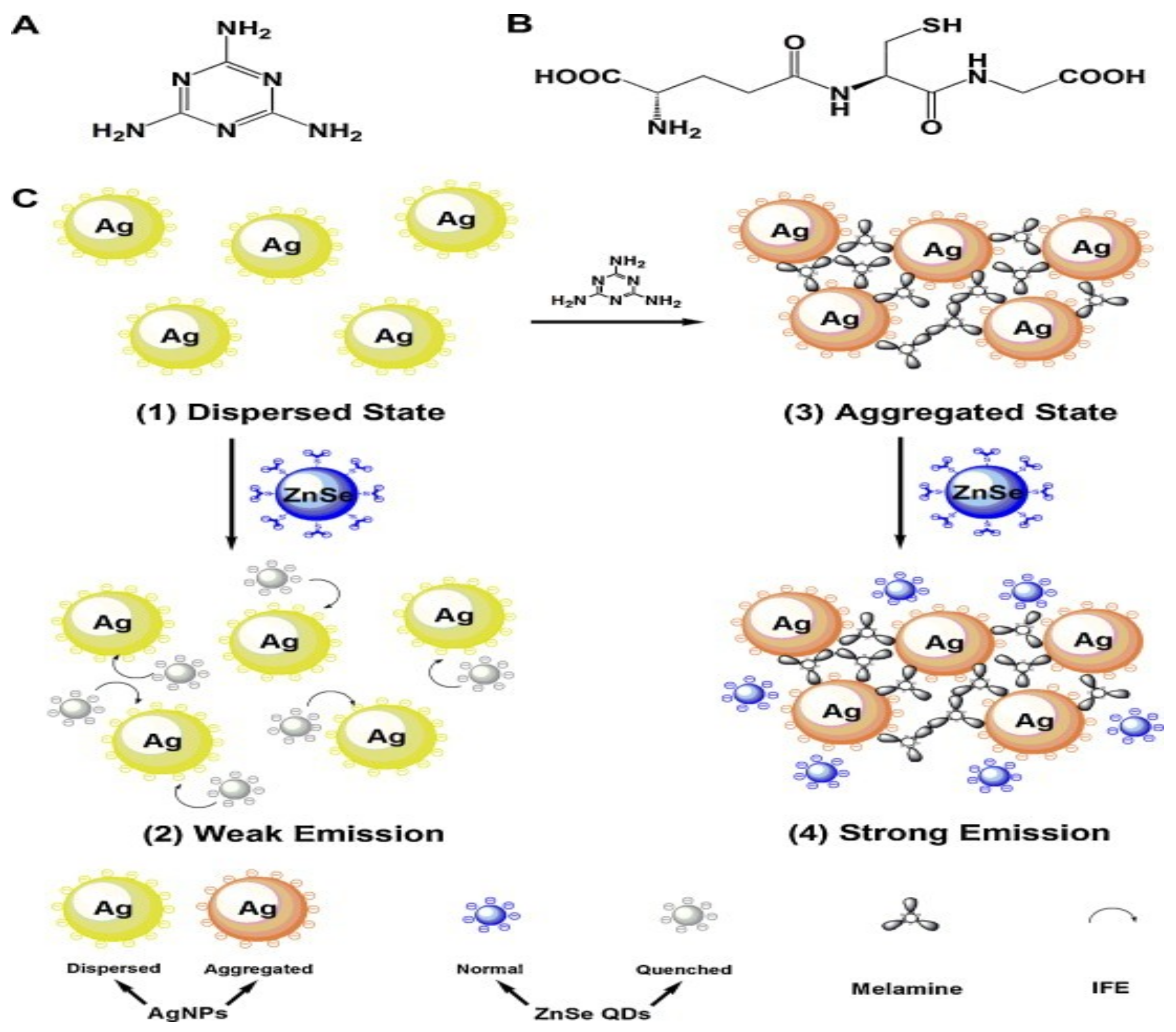
6. Nanoparticles in Melamine Quantification
7. Nanorods and Nanotubes in Melamine Assay
8. Other Nanostructures in Melamine Discrimination
9. Advantages and Limitations
10. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Tan, H. Foodborne illness outbreaks in China, 2000–2014. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, M.B.; Raats, M.M.; Grubb, S.M.; Eves, A.; Lumbers, M.L.; Dean, M.S.; Adams, M.R. A review of food safety and food hygiene training studies in the commercial sector. Food Control 2007, 18, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, F.H.; Chik, C.T.; Muhammad, R.; Yusoff, N.M. Food safety knowledge and personal hygiene practices amongst mobile food handlers in Shah Alam, Selangor. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 222, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Miguel, E.; Meza-Márquez, O.G.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Téllez-Medina, D.I.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Cornejo-Mazón, M.; Hernández-Martínez, D.M.; Gallardo-Velazquez, T. Detection of cyanuric acid and melamine in infant formula powders by Mid-FTIR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 7926768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelfinger, J.R. Melamine and the global implications of food contamination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2745–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, P.F.; Bergana, M.M.; Yakes, B.J.; Xie, Z.; Zbylut, S.; Downey, G.; Mossoba, M.; Jablonski, J.; Magaletta, R.; Holroyd, S.E.; et al. Effects of the adulteration technique on the Near-Infrared detection of melamine in milk powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5799–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Christa, J.; Deepa, J.R. Extraction of melamine from milk using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, T.; Shellaiah, M.; Steffi, P.; Sun, K.W.; Ko, F.-H. Development of extremely stable dual functionalized gold nanoparticles for effective colorimetric detection of clenbuterol and ractopamine in human urine samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1023, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellaiah, M.; Simon, T.; Venkatesan, P.; Sun, K.W.; Ko, F.-H.; Wu, S.-P. Nanodiamonds conjugated to gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of clenbuterol and chromium(III) in urine. Microchim. Acta 2017, 185, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Miao, L.; Wu, A. A rapid colorimetric sensor of clenbuterol based on cysteamine-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, M.G.; Fassbender, B.; Spiess, H.W.; Thomas, A.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Catalyst-free preparation of melamine-based microporous polymer networks through schiff base chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7216–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboorani, A.; Riedl, B. Improving performance of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) as a binder for wood by combination with melamine based adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2011, 31, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviello, G.; Ricciotti, L.; Ferone, C.; Colangelo, F.; Tarallo, O. Fire resistant melamine based organic-geopolymer hybrid composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 59, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Kurogi, T.; Murata, H. Effect of melamine foam cleaning on the surface condition of composite resin artificial teeth. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovina, K.; Siddiquee, S. A review of recent advances in melamine detection techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 43, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Analytical methods and recent developments in the detection of melamine. Trac Trend. Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, C. Chemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of melamine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1125–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of melamine and analogs in complex matrices: Advances and trends. J. Separat. Sci. 2016, 40, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.A.; Jeong, K.-S.; Poppenga, R.H.; Puschner, B.; Miller, D.M.; Ellis, A.E.; Kang, K.-I.; Sum, S.; Cistola, A.M.; Brown, S.A. Outbreaks of renal failure associated with melamine and cyanuric acid in dogs and cats in 2004 and 2007. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2007, 19, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, G.; Lambert, M.; Smith, P.; Wiesner, L.; Hiss, D. Melamine contamination in nutritional supplements—Is it an alarm bell for the general consumer, athletes, and ‘Weekend Warriors’? Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analytical chemistry, toxicology, epidemiology and health impact assessment of melamine in infant formula: Recent progress and developments. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, F.; Busato, M.; Piletska, E.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Karim, K.; Guerreiro, A.; del Valle, M.; Giorgetti, A.; Piletsky, S. Computational design of molecularly imprinted polymer for direct detection of melamine in milk. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, L.J.; Chernyshova, A.A.; Hiatt, A.; Deering, A.; Davis, R. Melamine detection in infant formula powder using Near- and Mid-Infrared spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, G.; Pan, M.; Li, M.; Lee, N.A.; Wang, S. A Review of Methods for Detecting Melamine in Food Samples. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittlemier, S.A. Methods for the analysis of melamine and related compounds in foods: A review. Food Addit. Contamin. A 2010, 27, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; He, L.; Awika, J.; Yang, L.; Ledoux, D.R.; Li, H.; Mustapha, A. Detection of melamine in gluten, chicken feed, and processed foods using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and HPLC. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, T129–T134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Todd, E.E.D.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J.-R.; Liu, X.-J. Recent developments in the detection of melamine. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M. A review of traditional and novel detection techniques for melamine and its analogues in foods and animal feed. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2009, 3, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Zhu, W.; Yao, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. SERS-based sensing technique for trace melamine detection—A new method exploring. Talanta 2016, 153, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 30 Tsai, T.-H.; Thiagarajan, S.; Chen, S.-M. Detection of melamine in milk powder and human urine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4537–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Pan, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Development of a surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for detecting melamine in milk products and Pet Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12471–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filigenzi, M.S.; Tor, E.R.; Poppenga, R.H.; Aston, L.A.; Puschner, B. The determination of melamine in muscle tissue by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 4027–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Ding, J.; Zheng, J.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Qiao, X. Detection of melamine in milk products by surface desorption atmospheric pressure cemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaleel, J.A.; Pramod, K. Artful and multifaceted applications of carbon dot in biomedicine. J. Cont. Release 2018, 269, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.H.; Zhao, X.E.; Jiao, S.L.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.Y.; You, J.M. A turn-on fluorescent sensor for the detection of melamine based on the anti-quenching ability of Hg2+ to carbon nanodots. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4438–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, G.; Hong, T.; Yin, Z.; Sun, D.; Abdel-Halim, E.S.; Zhu, J.-J. Graphene quantum dots as fluorescence probes for turn-off sensing of melamine in the presence of Hg2+. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ping, H.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Guan, F.; Sun, C.; Liu, J. Rapid determination of melamine in milk using water-soluble CdTe quantum dots as fluorescence probes. Food Addit. Contamin. A 2012, 29, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Kuang, H.; Feng, L.; Yi, S.; Xia, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; Zeng, Y. An ultrasensitive method for the determination of melamine using cadmium telluride quantum dots as fluorescence probes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 802, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Huy, B.; Seo, M.-H.; Zhang, X.; Lee, Y.-I. Selective optosensing of clenbuterol and melamine using molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H. One-pot synthesis of mesoporous structured ratiometric fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for highly sensitive detection of melamine from milk samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Visual detection of melamine by using a ratiometric fluorescent probe consisting of a red emitting CdTe core and a green emitting CdTe shell coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-L.; Jiao, H.-J.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Dong, Y.-M.; Li, Z.-J. Enhanced fluorescence sensing of melamine based on thioglycolic acid-capped CdS quantum dots. Talanta 2012, 93, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, J. Efficient inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on the fluorescence of CdS quantum dots for sensitive detection of melamine in raw milk. Food Control 2013, 34, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, H.; Fan, Z. Water-soluble Eu(iii)-doped ZnS quantum dots for the room-temperature phosphorescence detection of melamine in milk products. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6114–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirhan, B.E.; Demirhan, B.; Kara, H.E.S. Room-temperature phosphorescence determination of melamine in dairy products using l-cysteine-capped Mn-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS) quantum dots. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2992–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Su, X. CuInS2 quantum dots-based fluorescence turn off/on probe for detection of melamine. Talanta 2012, 101, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapiella-Alfonso, L.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Pereiro, R.; Sanz-Medel, A. Synthesis and characterization of hapten-quantum dots bioconjugates: Application to development of a melamine fluorescent immunoassay. Talanta 2013, 106, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Ding, S. Rapid and sensitive fluoroimmunoassay based on quantum dots for detection of melamine in milk. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Li, Z. Label-free turn-on fluorescent detection of melamine based on the anti-quenching ability of Hg2+ to gold nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Jia, Z.; Tan, Z.; Xu, H.; Luo, N.; Liao, X. Determination of melamine in infant formulas by fluorescence quenching based on the functionalized Au nanoclusters. Food Control 2016, 70, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.-X.; Wu, X.-M.; Dong, Y.-M.; Li, Z.-J.; Wang, G.-L. Colorimetric determination of melamine based on the reversal of the mercury(II) induced inhibition of the light-triggered oxidase-like activity of gold nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Hsu, N.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W. Microwave-assisted synthesis of BSA-stabilised gold nanoclusters for the sensitive and selective detection of lead(ii) and melamine in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79020–79027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiyarasan, G.; Anusuya, K.; Joseph, J. Melamine dependent fluorescence of glutathione protected gold nanoclusters and ratiometric quantification of melamine in commercial cow milk and infant formula. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, T.; Lin, Y.-W. Fluorescence sensing of mercury(ii) and melamine in aqueous solutions through microwave-assisted synthesis of egg-white-protected gold nanoclusters. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Z.; Hu, L.; Parveen, S.; Xu, G. Oligonucleotide-stabilized fluorescent silver nanoclusters for turn-on detection of melamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Qu, F.; Mao, B.; Zhu, S.; You, J. Turn-on fluorescent detection of melamine based on Ag nanoclusters–Hg2+ system. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8459–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Jin, L. Silver nanoclusters functionalized by chromotropic acid and layered double hydroxides for the turn-on detection of melamine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 6104–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, M.; Guo, L.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G.; Cai, Z. The detection of melamine base on a turn-on fluorescence of DNA-Ag nanoclusters. J. Lumin. 2017, 186, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.H.; Liu, S.G.; Ling, Y.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Fluorescence detection of melamine based on inhibiting Cu2+-induced disaggregation of red-emitting silver nanoclusters. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 201, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Wang, Q.; Mao, G.; Liu, H.; Yu, R.; Ren, X. Periodic silver nanocluster arrays over large-area silica nanosphere template as highly sensitive SERS substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 437, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-W.; Dai, W.-X.; Yu, X.-D.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Poly thymine stabilized copper nanoclusters as a fluorescence probe for melamine sensing. Talanta 2015, 144, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-M.; Liu, Y.-N. Surface-enhanced Raman detection of melamine on silver-nanoparticle-decorated silver/carbon nanospheres: Effect of metal ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, M.; Sun, C. Rapid and highly-sensitive melamine sensing based on the efficient inner filter effect of Ag nanoparticles on the fluorescence of eco-friendly ZnSe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 202, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Dutta, S.; Pal, T. Tailored “Sandwich” strategy in surface enhanced Raman scattering: Case study with para-phenylenediamine and application in femtomolar detection of melamine. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 28152–28161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Dai, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, C.; Roy, V.A.L. Low-cost, disposable, flexible and highly reproducible screen printed SERS substrates for the detection of various chemicals. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, X.; Liao, X.; Cheng, L. A microfluidic chip based on an ITO support modified with Ag-Au nanocomposites for SERS based determination of melamine. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, B.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z. In situ loading of Ag nanocontacts onto silica nanospheres: A SERS platform for ultrasensitive detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2776–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Ma, W.-F.; Wei, C.; You, L.-J.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.-C. Detecting trace melamine in solution by SERS using Ag nanoparticle coated poly(styrene-co-acrylic acid) nanospheres as novel active substrates. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14539–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, A.-I.; Sharma, B.; Cardinal, M.F.; Kurouski, D.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy biosensing: In vivo diagnostics and multimodal imaging. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6638–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-F.; Qiang, Y.; Meng, X.-H.; Yang, J.-L.; Shi, Y.-P. Ultrasensitive colorimetric assay melamine based on in situ reduction to formation of CQDs-silver nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 260, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Mo, S.; Liu, S.G.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. A Sensitive “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for melamine based on FRET effect between polydopamine-glutathione nanoparticles and Ag nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2174–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoori, J.L.; Amjadi, M.; Hassanzadeh, J. Enhancement of the chemiluminescence of permanganate-formaldehyde system by gold/silver nanoalloys and its application to trace determination of melamine. Microchim. Acta 2011, 175, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Guan, F.; Guo, J.; Shen, F.; Luo, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L. Sensitive fluorescent detection of melamine in raw milk based on the inner filter effect of Au nanoparticles on the fluorescence of CdTe quantum dots. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; Jiang, X.; Kaneti, Y.V.; Yu, A. Deposition of gold nanoparticles on β-FeOOH nanorods for detecting melamine in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, K.; Xian, Y. Determination of melamine in food contact materials using an electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S. Functionalized Au-Fe3O4 nanocomposites as a magnetic and colorimetric bimodal sensor for melamine. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 226, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Feng, Y.; Han, X.-X.; Gao, Z.-N. Sensitive electrochemical detection of melamine based on gold nanoparticles deposited on a graphene doped carbon paste electrode. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2526–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neng, J.; Tan, J.; Jia, K.; Sun, P. A fast and cost-effective detection of melamine by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy using a novel hydrogen bonding-assisted supramolecular matrix and gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Chen, M.; Ge, H.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zou, P.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y. A novel electrochemical sensor based on Au@PANI composites film modified glassy carbon electrode binding molecular imprinting technique for the determination of melamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Liu, Q.; Shang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ouyang, J. Dual-emission fluorescent sensor based on AIE organic nanoparticles and Au nanoclusters for the detection of mercury and melamine. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8457–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.K.; Reddy, A.V.R.; Satpati, A.K. Determination of melamine by a reduced graphene oxide–gold nanoparticle composite carbon paste electrode. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2703–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Li, J.; Fang, W.; Shen, A.; Hu, J. A tip–gap mesh-like bilayer SERS substrate for highly sensitive detection. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Ni, P.; Li, Z. A carbon dot based biosensor for melamine detection by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 202, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Xu, X.; You, J. A new dual-emission fluorescence sensor based on carbon nanodots and gold nanoclusters for the detection of melamine. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9438–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovina, K.; Siddiquee, S. Electrochemical sensor based rapid determination of melamine using ionic liquid/zinc oxide nanoparticles/chitosan/gold electrode. Food Control 2016, 59, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ye, Q.; Cui, P.; Zhang, L. Efficient fluorescence energy transfer system between CdTe-doped silica nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles for turn-on fluorescence detection of melamine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4550–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Du, L.; Su, X. Detection of melamine based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe QDs and Rhodamine B. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4060–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, S. Label-free fluorescence turn-on sensing for melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe/CdS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61667–61672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chang, H.; Li, J.-J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.-W. Dual-mode melamine detection based on gold nanoparticles aggregation-induced fluorescence “turn-on” and “turn-off” of CdTe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 239, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Liao, J.; Chen, S. A solid-state electrochemiluminescent sensor based on C60/graphite-like carbon nitride nanosheet hybrids for detecting melamine. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 13217–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Huang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Chen, X.; Oyama, M.; Chen, X. A highly selective melamine sensor relying on intensified electrochemiluminescence of the silica nanoparticles doped with [Ru(bpy)3]2+/molecularly imprinted polymer modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 236, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, G.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Novel MOFs@XC-72-nafion nanohybrid modified glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive determination of melamine. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 211, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yin, W.; Ni, G.; Peng, J. Hydrogen-bonding-induced colorimetric detection of melamine based on the peroxidase activity of gelatin-coated cerium oxide nanospheres. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarvar, Z.; Hadian, Z.; Mashayekh, M. Nanocomposites in food packaging applications and their risk assessment for health. Electron. Physician 2016, 8, 2531–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Q.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, L. Inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on the fluorescence of rare-earth phosphate nanocrystals and its application for determination of biological aminothiols. J. Lumin. 2013, 141, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, C.; Adusumalli, V.N.K.B.; Mahalingam, V. 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid-capped upconverting nanocrystals for the selective detection of melamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7833–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, D.; González, M.C.; Escarpa, A. Sensing colorimetric approaches based on gold and silver nanoparticles aggregation: Chemical creativity behind the assay. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 751, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, N.; Qie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, B.; Gao, Z. Development of gold nanoparticle-based rapid detection kit for melamine in milk products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12006–12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, Z. Visual detection of melamine based on the peroxidase-like activity enhancement of bare gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Deng, H.-H.; Hong, L.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, A.-L.; Lin, X.-H.; Xia, X.-H. Bare gold nanoparticles as facile and sensitive colorimetric probe for melamine detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 5382–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhong, J.; Wu, J.; Fu, F.; Chen, G.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S. Visual detection of melamine in milk products by label-free gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2010, 82, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Liu, B.; Guan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.-Y. A simple, reliable and sensitive colorimetric visualization of melamine in milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2010, 135, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Cheng, D.; Mao, L. Visual detection of melamine in raw milk using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Zeng, G.; Zhai, K.; Li, L.; He, Z. Determination of melamine in milk powder based on the fluorescence enhancement of Au nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Cai, M.; Liang, H.; Hao, J. Size-dependent colorimetric visual detection of melamine in milk at 10 ppb level by citrate-stabilized Au nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Seth, R.; Kumar, H. Colorimetric detection of melamine in milk by citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 456, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Huang, Y.; Yun, W.; Tang, D.; Zhang, H.; Du, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W. Simple pretreatment and portable UV-Vis spectrum instrument for the rapid detection of melamine in milk products. J. Food Qual. 2015, 38, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, I.E.; Rajeshwari, A.; Prathna, T.C.; Raichur, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Colorimetric detection of melamine based on the size effect of AuNPs. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Xiong, Q. A coordination and ligand replacement based three-input colorimetric logic gate sensing platform for melamine, mercury ions, and cysteine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 59106–59113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Lam, R.; Cheng, S.; Lu, S.; Ho, D.; Li, N. Rapid detection of melamine in whole milk mediated by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 133702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.-Y.; Dong, C.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Comparative studies on the quick recognition of melamine using unmodified gold nanoparticles and p-nitrobenzenesulfonic grafted silver nanoparticles. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2011, 58, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.-B.; Wu, Y.-G.; Zhan, S.-S.; Zhou, P. A Rapid colorimetric detection of melamine in raw milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, P.; Manhas, S.; Navani, N.K. A simple method for detection of anionic detergents in milk using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 233, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xue, S.; Yin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for ultrasensitive detection of melamine based on a new fluorescence probe and AuNPs. Analyst 2015, 140, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, I.E.; Rajeshwari, A.; Satija, J.; Raichur, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Fluorescence based study for melamine detection using gold colloidal solutions. J. Fluoresc. 2016, 26, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, G.; Tinnefeld, P.; He, Z. Visual detection of melamine in milk samples based on label-free and labeled gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2011, 85, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, K.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L. Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced color change of gold nanoparticles for visual detection of melamine in raw milk and infant formula. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9496–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, L.; Ding, N.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, G. Hydrogen-bonding-induced colorimetric detection of melamine by nonaggregation-based Au-NPs as a probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Chu, S.-P.; Tseng, W.-L. Selective extraction of melamine using 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid–capped gold nanoparticles followed by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7800–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.J.; Wu, D.; Ling, J.; Huang, C.Z. Visual and light scattering spectrometric detections of melamine with polythymine-stabilized gold nanoparticles through specific triple hydrogen-bonding recognition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4893–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Chen, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chu, H.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Kotov, N.A.; et al. Crown ether assembly of gold nanoparticles: Melamine sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wei, H.; Cui, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Z.; You, X.; Zhang, X.-E. Colorimetric detection of melamine in complex matrices based on cysteamine-modified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhong, J.; Wu, J.; Fu, F.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S. Sensitive turn-on fluorescent detection of melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Analyst 2011, 136, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Fan, H.; Ai, S.; Wu, N.; Fan, H.; Bian, P.; Liu, J. Selective determination of melamine in milk samples using 3-mercapto-1-propanesulfonate-modified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Talanta 2011, 85, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Peng, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Rapid detection of melamine with 4-mercaptopyridine-modified gold nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xue, Y.; Cao, Q.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z. Colorimetric detection of melamine during the formation of gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2574–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Saha, A.; Nandi, A.K. Melamine sensing through riboflavin stabilized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, A.; Zhou, L.; Qin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, Z. A Highly sensitive aptamer-nanogold catalytic resonance scattering spectral assay for melamine. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.F.; Zhao, H.W.; Xu, D.; Wu, L.P.; Huang, C.Z. Colorimetric assay of melamine based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, R.K.; Raj, C.R. Naked eye sensing of melamine using rationally tailored gold nanoparticles: Hydrogen-bonding and charge-transfer recognition. Analyst 2011, 136, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Kuang, H. Rapid on-site determination of melamine in raw milk by an immunochromatographic strip. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xue, Y.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z. Colorimetric Determination of Melamine by Pyridine-3-Boronic Acid Modified Gold Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 2412–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazgan, N.N.; Boyacı, İ.H.; Topcu, A.; Tamer, U. Detection of melamine in milk by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with magnetic and Raman-labeled nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasimalai, N.; Abraham John, S. Picomolar melamine enhanced the fluorescence of gold nanoparticles: Spectrofluorimetric determination of melamine in milk and infant formulas using functionalized triazole capped goldnanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Zhan, S.; Wu, Y.; He, L.; Zhou, P. Sensitive colorimetric detection of melamine in milk with an aptamer-modified nanogold probe. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17424–17430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mei, Y.; Song, R.; Tian, D.; Huang, H. Colorimetric sensing strategy for mercury(ii) and melamine utilizing cysteamine-modified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2013, 138, 5338–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z. Colorimetric detection of melamine based on the interruption of the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, W.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Tu, D.; Xie, W.; Huang, Y. Aptamer-based rapid visual biosensing of melamine in whole milk. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Gold nanoparticles-based chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer for ultrasensitive detection of melamine. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 149, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, K.; Lu, Z.; Li, T.; Shao, K.; Shao, F.; Han, H. Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles for the determination of the migration of melamine monomers using dynamic light scattering. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 845, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Fu, S.; Yang, T.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H. Raman probing trace melamine in milk by a functionalized test paper. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 193, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.-H.; Yu, X.; Dong, H.; Cai, J.; Yang, P.-H. Visual and absorption spectroscopic detections of melamine with 3-mercaptopriopionic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles: A synergistic strategy induced nanoparticle aggregates. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Highly sensitive detection of melamine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between rhodamine B and gold nanoparticles. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 111, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.-P.; Dinh, Q.-K.; Hoang, T.-L.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Tran, T.-H.; Nguyen, T.-D. Water-soluble acetylated chitosan-stabilized gold nanosphere bioprobes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 149–150, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, A.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, Z. Sensitive colorimetric detection of melamine with 1,4-dithiothreitol modified gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.-X.; Chen, D.-D.; Lin, K.; Fan, H.-C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, C.-G. Colorimetric detection of melamine based on methanobactin-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Wang, Z.; Peng, X.; Fan, J. In situ colorimetric recognition of melamine based on thymine derivative-functionalized gold nanoparticle. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 12011–12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Q.; Li, H. Rapid colorimetric detection of melamine by H2O2–Au nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32897–32901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Long, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. An upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer nanosensor for one step detection of melamine in raw milk. Talanta 2015, 136, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pauli, J.; Niessner, R.; Resch-Genger, U.; Knopp, D. Gold nanoparticle-catalyzed uranine reduction for signal amplification in fluorescent assays for melamine and aflatoxin B1. Analyst 2015, 140, 7305–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Hu, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, J. Development of aptamer-modified SERS nanosensor and oligonucleotide chip to quantitatively detect melamine in milk with high sensitivity. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 228, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, P.; Wu, F. Colorimetric detection of melamine based on p-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid-modified AuNPs. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Ye, Y.; Chen, W. Gold nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay with largely amplified sensitivity for rapid melamine screening. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Q.; Hu, X.; Lin, Z.; Sun, H.; Jiang, M.; Hu, J. Colorimetric detection of melamine in milk by using gold nanoparticles-based LSPR via optical fibers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Bie, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Shen, F.; Sun, C.; Yu, Y. Highly sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric detection of melamine in raw milk with cysteamine-stabilized gold nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.; Singh, T.; Madhumitha, G.; Phulukdaree, A.; Gengan, R.M.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Biosynthesis and computational analysis of amine-ended dual thiol ligand functionalized gold nanoparticles for conventional spectroscopy detection of melamine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 169, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Chen, X.; Liou, P.; Lin, M. Development of nanofibrillated cellulose coated with gold nanoparticles for measurement of melamine by SERS. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2801–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Huang, P.; Wu, F. Colorimetric detection of melamine in milk based on Triton X-100 modified gold nanoparticles and its paper-based application. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 192, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhen, S.; Huang, C. Visual and light scattering spectrometric method for the detection of melamine using uracil 5′-triphosphate sodium modified gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 173, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecker, L.C.; Tyner, K.M.; Kauffman, J.F.; Arzhantsev, S.; Mans, D.J.; Gryniewicz-Ruzicka, C.M. Selective melamine detection in multiple sample matrices with a portable Raman instrument using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy-active gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 733, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Huang, Y.-F.; Chattopadhyay, S. In Detection of melamine on fractals of unmodified gold nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannozzi, A.M.; Rolle, F.; Sega, M.; Abete, M.C.; Marchis, D.; Rossi, A.M. Rapid and sensitive detection of melamine in milk with gold nanoparticles by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Pang, S.; He, L. Integration of colorimetric and SERS detection for rapid screening and validation of melamine in milk. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6426–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-T.; Tomalová, I.; Preisler, J.; Chang, H.-T. Detection of melamine in infant formula and grain powder by surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun.Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Feng, S.; Shi, Y.; Lyu, J.; Lv, J. Sensitive and simple sonoluminescence detection of melamine via aggregation of Au nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5162–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, G.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, M. Determination of melamine in milk using surface plasma effect of aggregated Au@SiO2 nanoparticles by SERS technique. Food Control 2016, 68, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabela, M.; Balme, S.; Bechelany, M.; Janot, J.-M.; Bisetty, K. A Review of gold and silver nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensing assays. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhang, T. Visual detection of melamine in raw milk by label-free silver nanoparticles. Food Control 2012, 23, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Yu, L.; Chang, M.; Ci, L. One-step, room temperature, colorimetric melamine sensing using an in-situ formation of silver nanoparticles through modified Tollens process. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 137, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, H.; Mann, B.; Seth, R. Colorimetric determination of melamine in milk using unmodified silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 2016, 156, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittar, D.B.; Catelani, T.A.; Nigoghossian, K.; Barud, H. d. S.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R. Optimized synthesis of silver nanoparticles by factorial design with application for the determination of melamine in milk. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, H. Visual detection of melamine in infant formula at 0.1 ppm level based on silver nanoparticles. Analyst 2010, 135, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y. One-step synthesis of silver/dopamine nanoparticles and visual detection of melamine in raw milk. Analyst 2011, 136, 4192–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, A.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, Z. A Simple and sensitive resonance scattering spectral assay for detection of melamine using aptamer-modified nanosilver probe. Plasmonics 2011, 6, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Xu, S.; Li, M.; Kong, F.; Luo, Y.; Li, G. Self-assembly of noble metallic spherical aggregates from monodisperse nanoparticles: Their synthesis and pronounced SERS and catalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3362–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Xavier, S.S.; Karthikeyan, C.; Gnana kumar, G.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Colorimetric detection of melamine using β-cyclodextrin-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8165–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wu, F.; Wan, Y.; Ma, L.-H. Visual test for melamine using silver nanoparticles modified with chromotropic acid. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wu, F.; Wan, Y.; Ma, L. Colorimetric detection of melamine in pretreated milk using silver nanoparticles functionalized with sulfanilic acid. Food Control 2015, 50, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ma, P.; Yu, A.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Determination of melamine and malachite green by surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy using starch-coated silver nanoparticles as substrates. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8116–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, H.P.; Patil, C.D.; Salunkhe, R.B.; Suryawanshi, R.K.; Salunke, B.K.; Patil, S.V. Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles as a novel colorimetric probe for melamine detection in raw milk. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2014, 62, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleeswaran, P.; Nandhini, T.; Pitchumani, K. Naked eye sensing of melamine: Aggregation induced recognition by sodium d-gluconate stabilised silver nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3869–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Qin, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, K. A ratiometric nanosensor based on conjugated polyelectrolyte-stabilized AgNPs for ultrasensitive fluorescent and colorimetric sensing of melamine. Talanta 2016, 151, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, K.; Devasena, T.; Senthil, B.; Kalpana, R.; Jayavel, R. Silver nanoparticles for melamine detection in milk based on transmitted light intensity. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2017, 11, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, M. Quantitative determination of melamine in milk using Ag nanoparticle monolayer film as SERS substrate. Phys. E 2017, 88, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.F.; Laskar, A.A.; Ahmed, S.; Shaida, M.A.; Younus, H. Colorimetric method for the detection of melamine using in-situ formed silver nanoparticles via tannic acid. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 183, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.C.G.K.; Nirupa Julius, L.A.; Gorthi, S.S. Instantaneous detection of melamine by interference biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, S.; Kiruba Daniel, S.C.G.; Gorthi, S.S. Rapid sensing of melamine in milk by interference green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, P.; Xie, X.; Wei, H.; Li, Z.; Mack, N.H.; Han, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.-L. Acid-directed synthesis of SERS-active hierarchical assemblies of silver nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lv, D.Y.; Zhu, Q.X.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.M.; Chai, Y.F.; Lu, F. Chromatographic separation and detection of contaminants from whole milk powder using a chitosan-modified silver nanoparticles surface-enhanced Raman scattering device. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Shen, A.; Hu, J. Simultaneous enzymatic and SERS properties of bifunctional chitosan-modified popcorn-like Au-Ag nanoparticles for high sensitive detection of melamine in milk powder. Talanta 2015, 140, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.Q.; Zou, H.Y.; Lan, J.; Huang, C.Z. Aggregation-induced superior peroxidase-like activity of Cu2−xSe nanoparticles for melamine detection. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7516–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhi, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Che, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles suitable for melamine detection using test strips. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2015, 7, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S. Detection of melamine by a magnetic relaxation switch assay with functionalized Fe/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 203, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.G.; Lin, S.M.; Fan, Y.Z.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Visible and fluorescent detection of melamine in raw milk with one-step synthesized silver nanoparticles using carbon dots as the reductant and stabilizer. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 248, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Han, K.; Sun, H.; Yin, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; Tang, Y. Melamine functionalized silvern as the probe for electrochemical sensing of clenbuterol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8667–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Z.; Yu, R.; Wei, X.-W. Template-based in situ fabrication and melamine sensing of bis(8-quinolinolato)zinc(II) complex nanorod arrays. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zapien, J.A.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, S.T. ZnO/Au composite nanoarrays as aubstrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-M.; Liu, Y.-N. Ag-nanoparticle-modified single Ag nanowire for detection of melamine by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.; Li, Z. Silver nanoparticles coated zinc oxide nanorods array as superhydrophobic substrate for the amplified SERS effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9977–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kuang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M. A novel electrochemical method for sensitive detection of melamine in infant formula and milk using ascorbic acid as recognition element. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Dang, A.; Li, T. Electrochemical determination of melamine with a glassy carbon electrode coated with a multi-wall carbon nanotube/chitosan composite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, K141–K145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Dodson, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Demir, H.V.; Ling, X.Y.; Xiong, Q. Vertically aligned gold nanorod monolayer on arbitrary substrates: Self-assembly and femtomolar detection of food contaminants. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5993–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chabu, J.M.; Jin, R.; Xiao, J. Single gold-nanoparticles-decorated silver/carbon nanowires as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 26102–26109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Liao, J.-D.; Liu, B.H.; Yao, C.-K. Focused-ion-beam-fabricated Au nanorods coupled with Ag nanoparticles used as surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active substrate for analyzing trace melamine constituents in solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 800, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.-E.; Li, L.; Yang, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, J. A disordered silver nanowires membrane for extraction and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 2525–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Mei, F.; Xiao, X.; Liao, L.; Fu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; et al. “Rings of saturn-like” nanoarrays with high number density of hot spots for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 033515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.; Qiu, G. ZnGa2O4 nanorod arrays decorated with Ag nanoparticles as surface-enhanced Raman-scattering substrates for melamine detection. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Liao, J.-D.; Liu, B.H.; Yu, L.C. AuGa2 on focused Ga ion beam fabricated Au nanorod array for trace detection of melamine cyanurate in milk solution. Appl. Phys. Exp. 2015, 8, 017001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lian, S.; Ma, Y.; Peng, A.; Tian, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X. Electrochemiluminescence sensor for melamine based on a [Ru(bpy)3]2+-doped silica nanoparticles/carboxylic acid functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion composite film modified electrode. Talanta 2016, 146, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Su, X.-O.; Yao, Y.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. Highly sensitive detection of melamine using a one-step sample treatment combined with a portable Ag nanostructure array SERS sensor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.A.; Keffous, A.; Giovannozzi, A.M.; Rossi, A.M.; Cara, E.; D’Ortenzi, L.; Sparnacci, K.; Boarino, L.; Gabouze, N.; Soukane, S. Fabrication of flexible silicon nanowires by self-assembled metal assisted chemical etching for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 93649–93659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yola, M.L.; Eren, T.; Atar, N. A Molecular imprinted voltammetric sensor based on carbon nitride nanotubes: Application to determination of melamine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, B588–B593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, X.-J.; You, T.-T.; Wang, G.-S.; Yin, P.-G.; Guo, L. Controlled assembly of one-dimensional MoO3@Au hybrid nanostructures as SERS substrates for sensitive melamine detection. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7805–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.L.; Carson, C.S.; Marvinney, C.E.; Giorgio, T.D.; Mu, R.R. Sensing trace levels of molecular species in solution via zinc oxide nanoprobe Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2017, 48, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sahoo, R.; Chowdhury, J.; Bhattacharya, T.S.; Agarwal, R.; Pal, T. Directional growth of Ag nanorod from polymeric silver cyanide: A potential substrate for concentration dependent SERS signal enhancement leading to melamine detection. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 183, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, N.; You, T.; Zhang, C.; Yin, P. Superhydrophobic “wash free” 3D nanoneedle array for rapid, recyclable and sensitive SERS sensing in real environment. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 267, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Ma, D.; Xu, K.; Zhao, Y. 3D silver nanoparticles decorated zinc oxide/silicon heterostructured nanomace arrays as high performance surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5725–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, K.; Jayram, N.D.; Mangalaraj, D.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T. One step ‘dip’ and ‘use’ Ag nanostructured thin films for ultrahigh sensitive SERS Detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, S.; Zhang, L.; Tang, A.; Wang, Z. Quantitative surface enhanced Raman scattering detection based on the “sandwich” structure substrate. Spectrochim. Acta A 2011, 79, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahmed, J. Cd-doped Sb2O4 nanostructures modified glassy carbon electrode for efficient detection of melamine by electrochemical approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, R.A.; Hallam, K.R.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Tahira, A.; Jawaid, S.; Hussain Sherazi, S.T.; Sirajjuddin; Willander, M. A highly selective and sensitive electrochemical determination of melamine based on succinic acid functionalized copper oxide nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105090–105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, L.; Lv, H.; Zhao, B.; Choo, J. One-step detection of melamine in milk by hollow gold chip based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Talanta 2014, 122, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, R.-D.; Chiu, K.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Liu, D.-M. Functionalized silica nanoparticles by nanometallic Ag decoration for optical sensing of organic molecule. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15633–15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, W.; Kanda, P.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Huan, S. Silver deposited polystyrene (PS) microspheres for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic-encoding and rapid label-free detection of melamine in milk powder. Talanta 2013, 113, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, M.L.; Su, W.-N.; Chen, C.-H.; Hwang, B.-J. Ag@SiO2 nanocube loaded miniaturized filter paper as a hybrid flexible plasmonic SERS substrate for trace melamine detection. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6823–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Yang, Y.; Qin, D. Hollow nanocubes made of Ag–Au alloys for SERS detection with sensitivity of 10−8 M for melamine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9934–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, M.; Xiao, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, G. Urchin-like LaVO4/Au composite microspheres for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 443, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Xing, T.T.; Ge, L.; Yang, T.; Chen, B.; Huang, C.Z. A portable multi-channel sensing device using Au nano-urchins as probes for melamine detection in milk. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7806–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Ly, N.H.; Kwak, C.H.; Huh, Y.S.; Joo, S.-W. On-site detection of sub-mg/kg melamine mixed in powdered infant formula and chocolate using sharp-edged gold nanostar substrates. Food Addit. Contam. A 2018, 35, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shi, J.; Sun, X.; Lin, M.; Yu, P.; Li, H. Gold coated zinc oxide nanonecklaces as a SERS substrate. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3509–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Martin, J.W.; Oosterbeek, R.N.; Novikova, N.I.; Wang, X.; Malmström, J.; Williams, D.E.; Simpson, M.C. Gold-sputtered Blu-ray discs: Simple and inexpensive SERS substrates for sensitive detection of melamine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Yuan, K.; Yu, J.; Delaunay, J.-J.; Che, R. Ultrafast self-assembly of silver nanostructures on carbon-coated copper grids for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of trace melamine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Bairi, P.; Nandi, A.K. Supramolecular assembly of melamine and its derivatives: Nanostructures to functional materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1708–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ou, C.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z. Visualized detection of melamine in milk by supramolecular hydrogelations. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12873–12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, R.S.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Bhosale, S.V.; Bhargava, S.; Bhosale, S.V. Flower-like supramolecular self-assembly of phosphonic acid appended naphthalene diimide and melamine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Banerjee, S.S.; Bhowmick, A.K.; Das, P. DNA–melamine hybrid molecules: From self-assembly to nanostructures. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Acha, N.; Elosua, C.; Matias, I.; Arregui, F. Luminescence-based optical sensors fabricated by means of the layer-by-layer nano-assembly technique. Sensors 2017, 17, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, N.; Ding, Q.; Cao, X. Melamine tunable effect in a lenalidomide-based supramolecular self-assembly system via hydrogen bonding. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7924–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, R.S.; La, D.D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Bhosale, S.V.; Bhosale, S.V. Melamine and spermine mediated supramolecular self–assembly of octaphosphonate tetraphenyl porphyrin. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellaiah, M.; Sun, K. Luminescent metal nanoclusters for potential chemosensor applications. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

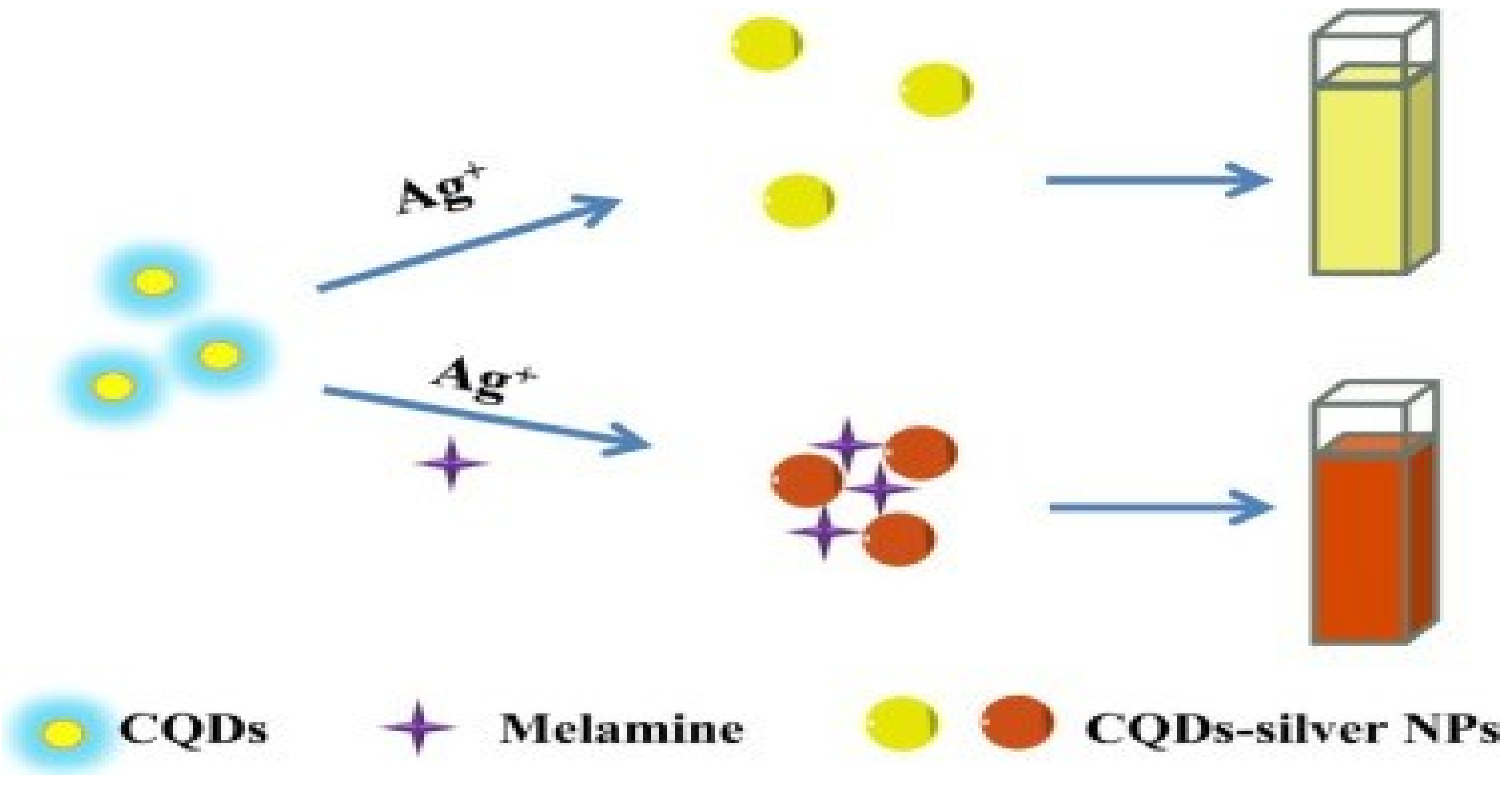
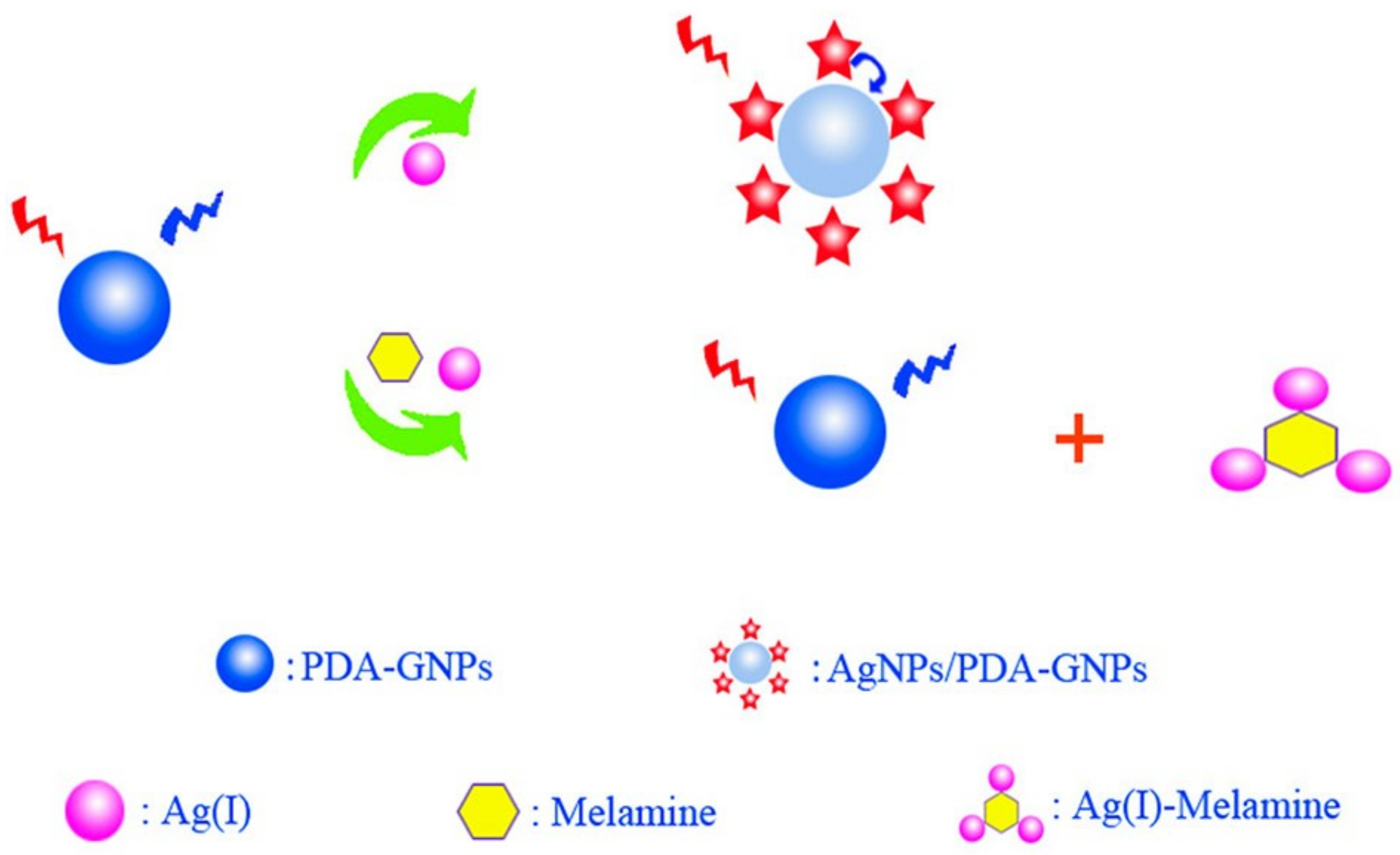

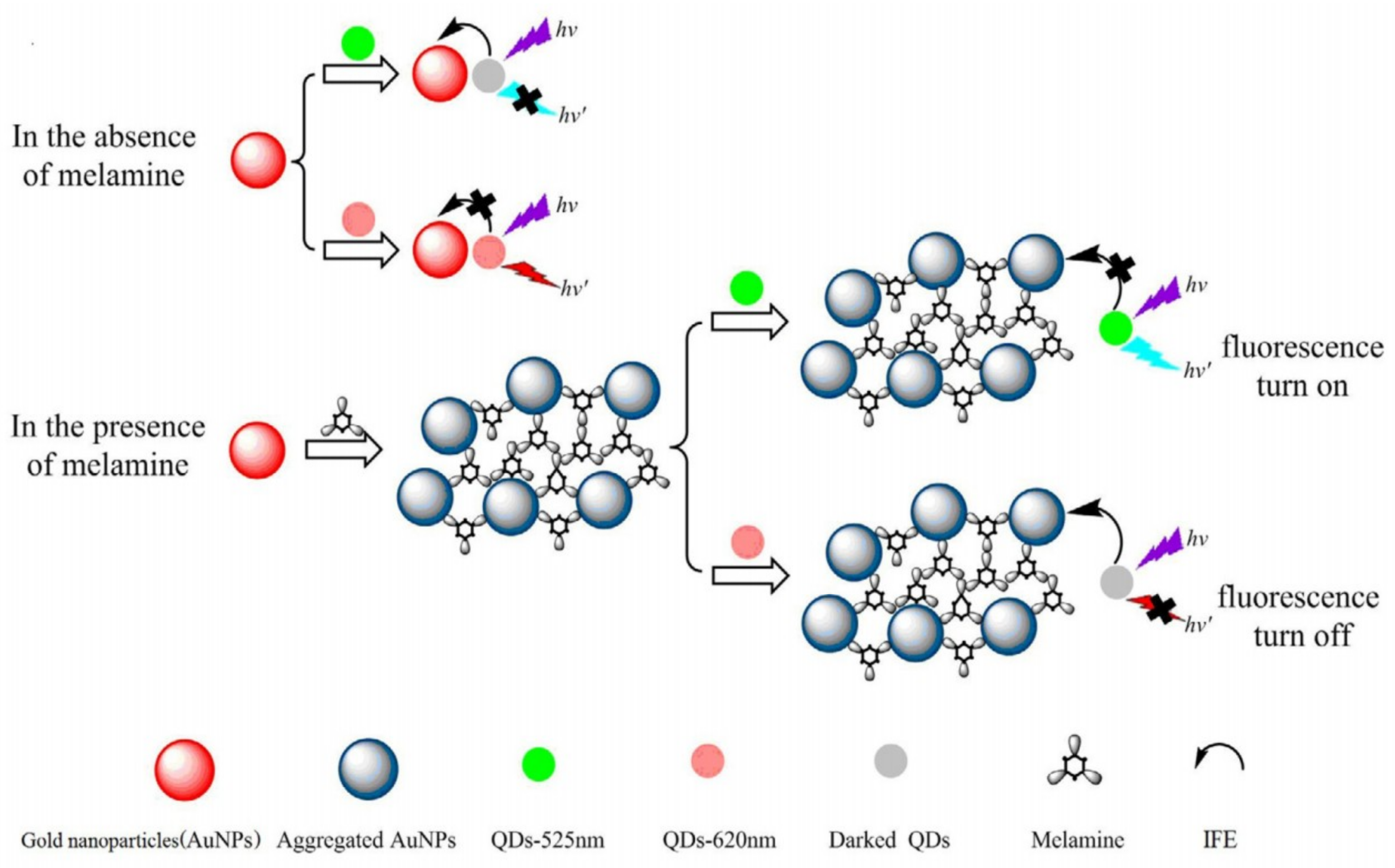
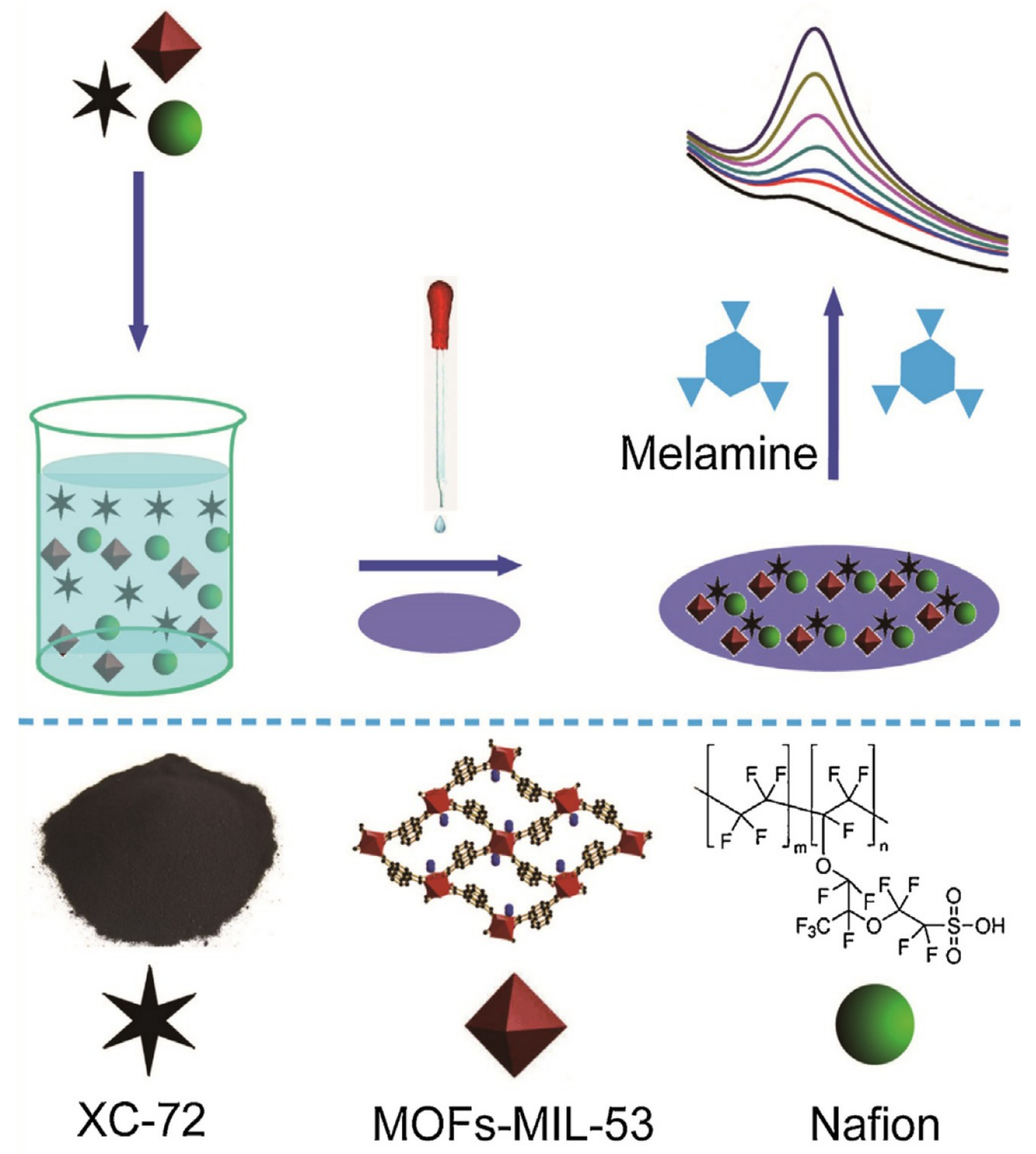

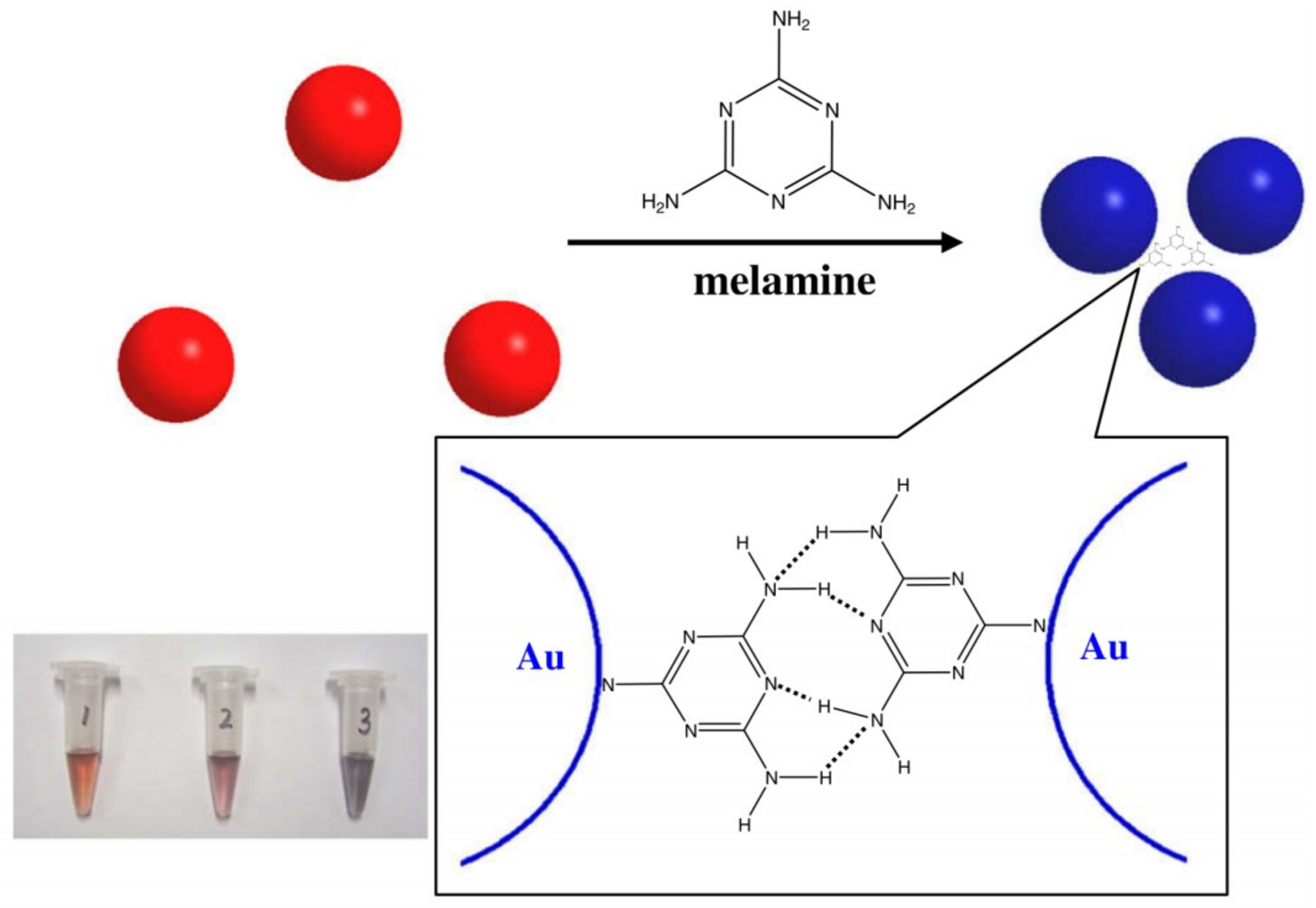
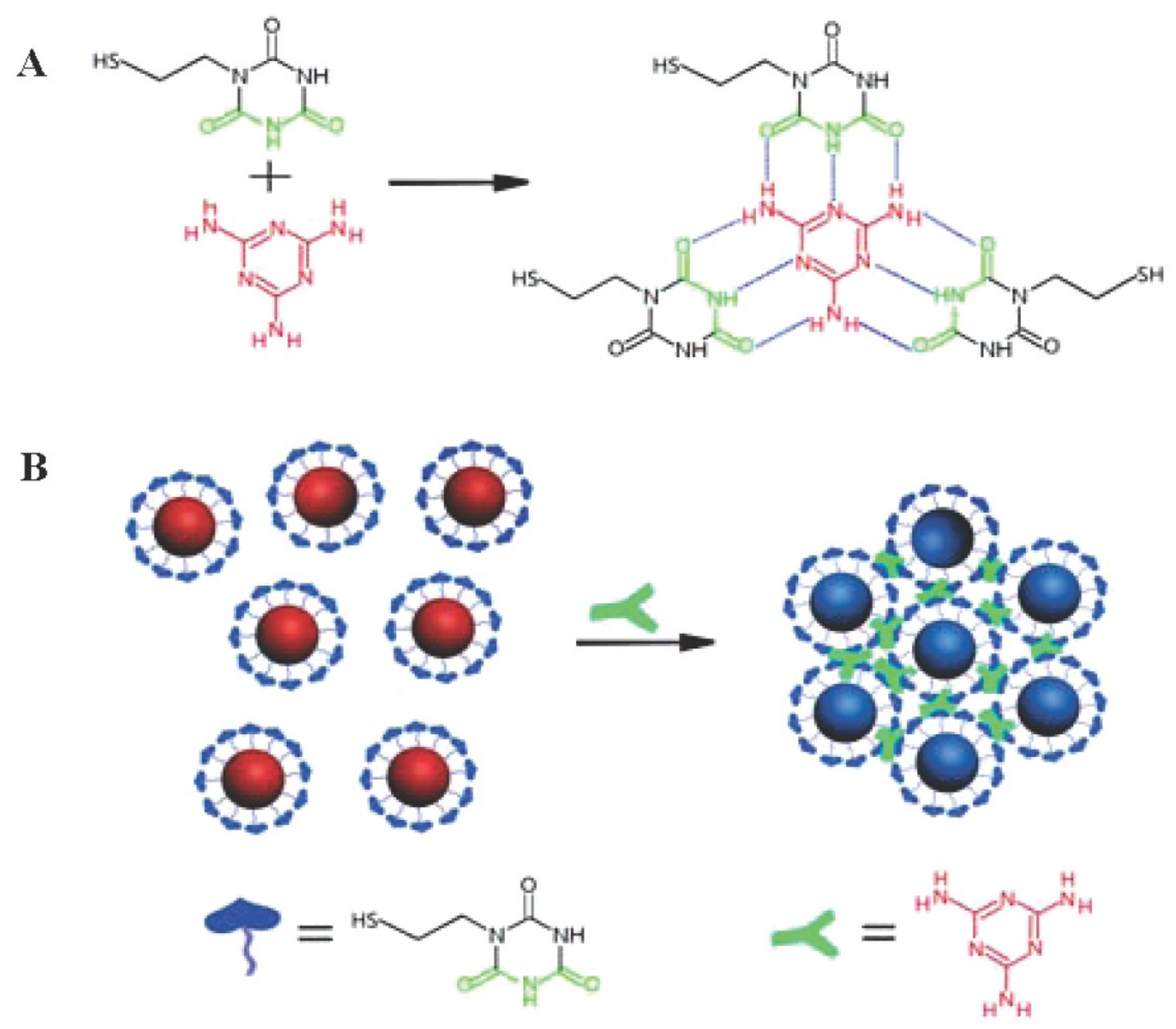
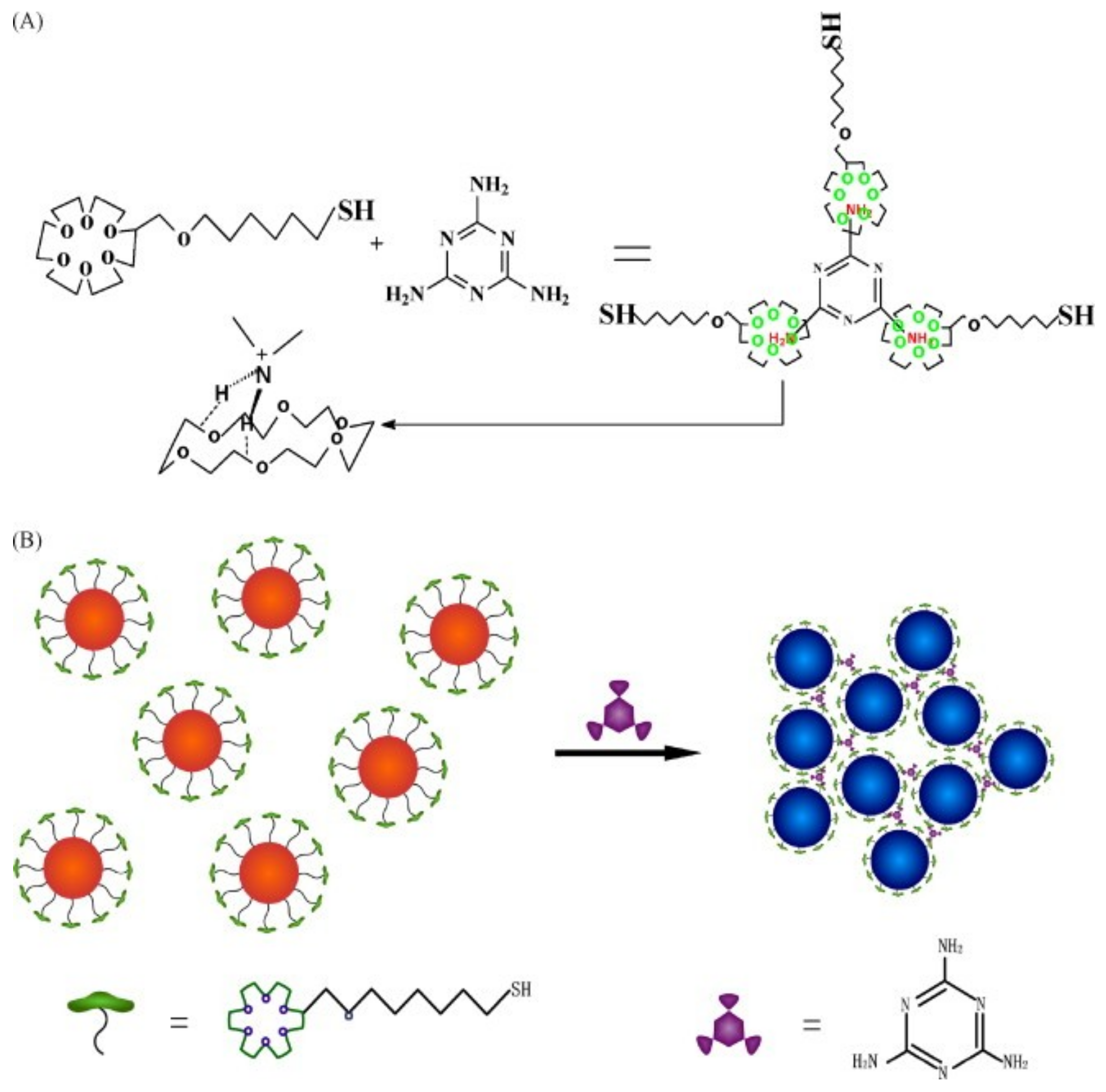
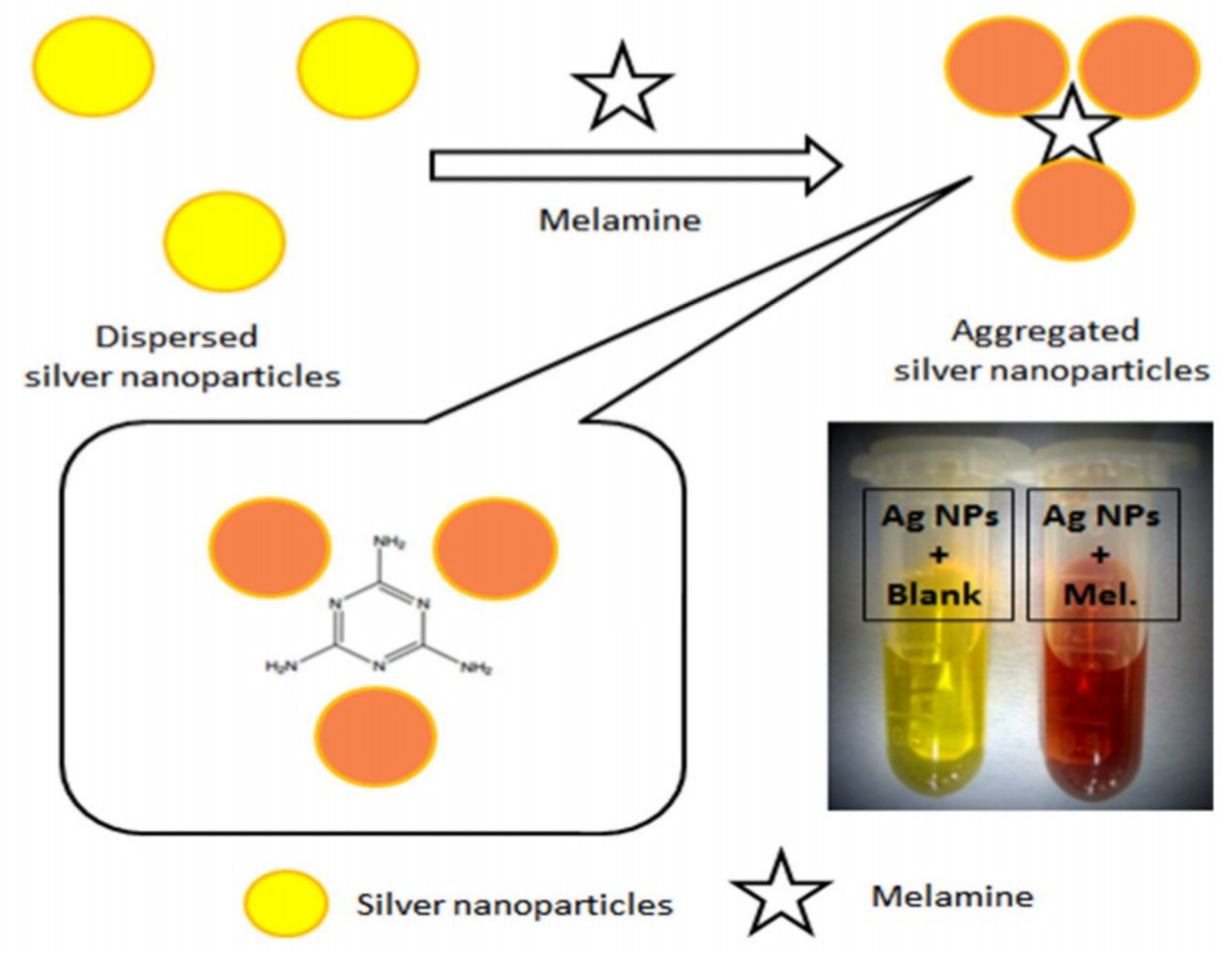
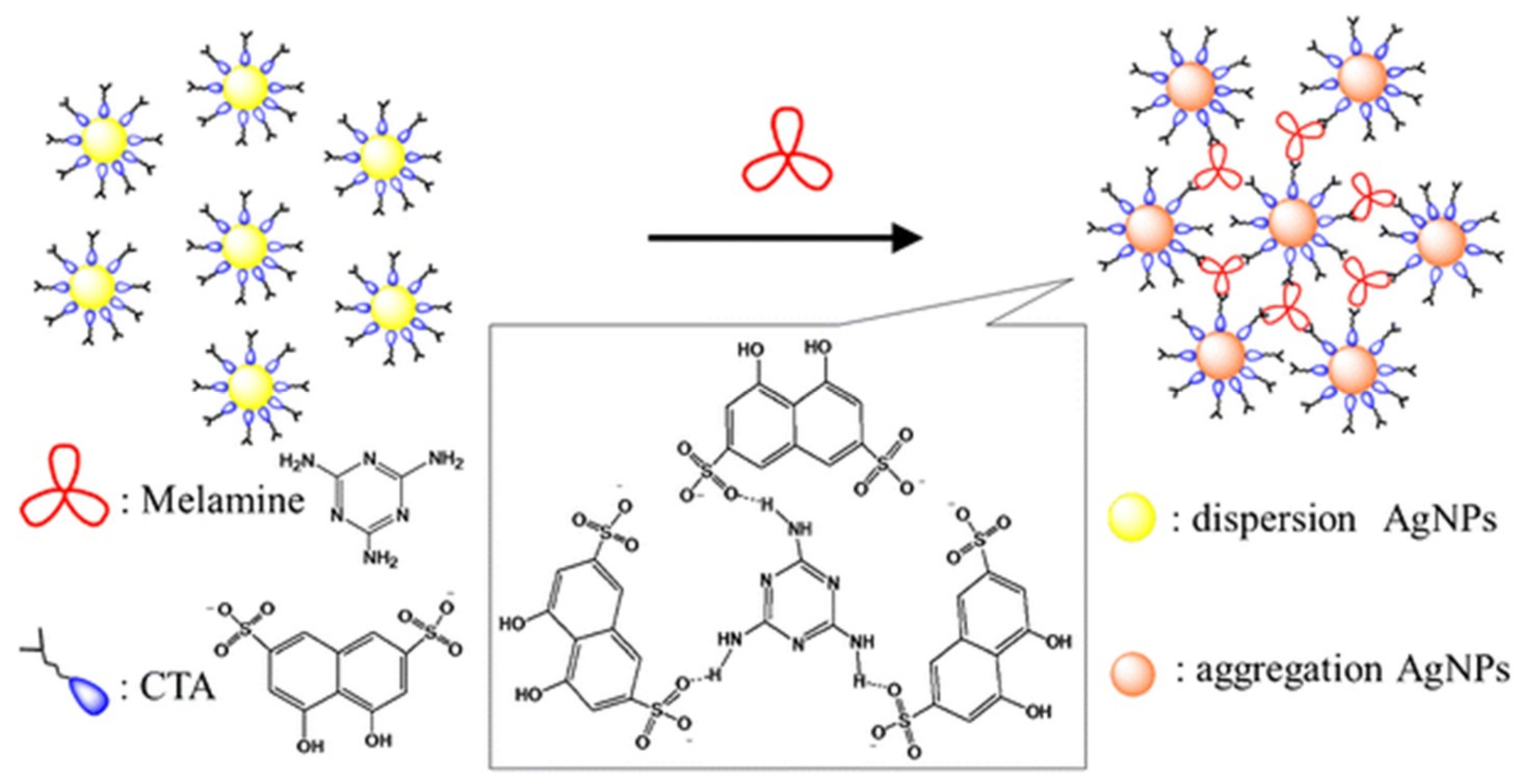
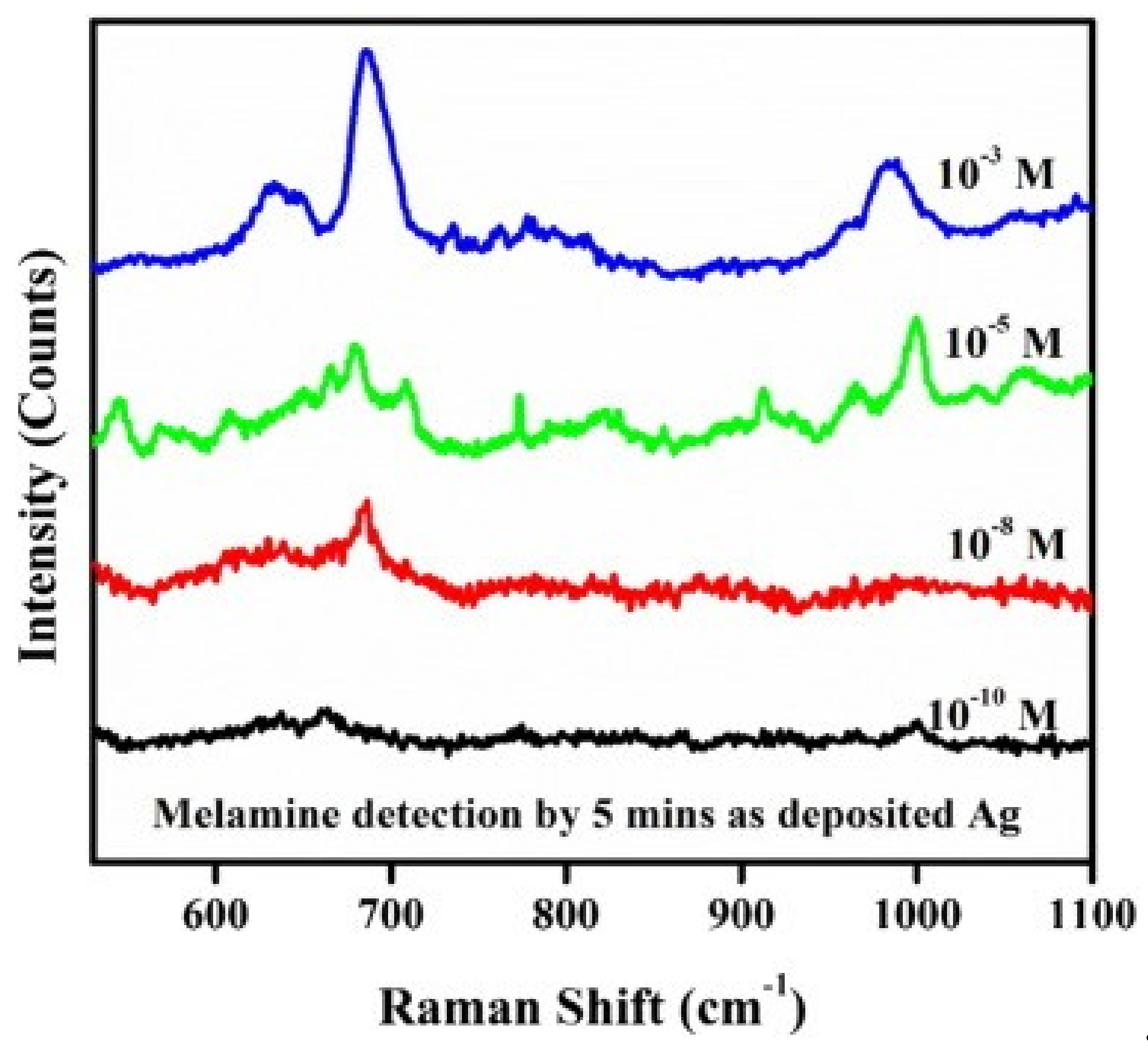

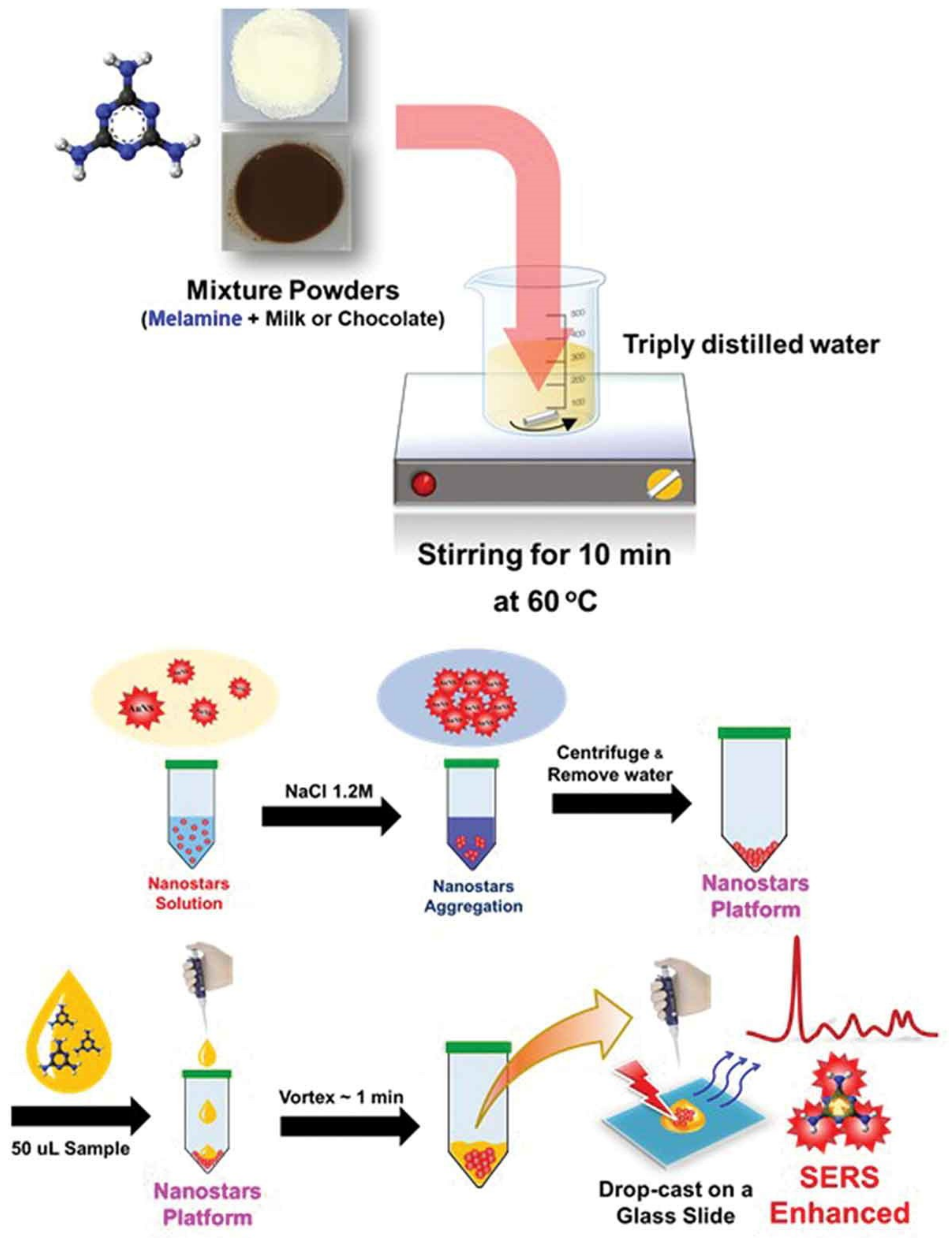
| Au NPs-Based Probe | Method of Detection | Instruments Employed | Optimization Status and Time Required | Linear Range | LOD | Recoveries of Spiked Samples | RSDs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Complicated and 10 min | 7.93 µM–0.95 mM | 7.93 µM | NA | NA | [98] |
| Bare Au NPs | Colorimetric (peroxidase-like activity) | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Complicated and 30 min | 1–800 nM | 0.2 nM | 94.55–120.50% | 0.07–0.99% | [99] |
| Bare Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 7 min | 39.64 nM–1.59 µM | 1.59 nM | 97.6–107% | 0.8–2.4% | [100] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 20 min | 0–634 µM | 19.8 µM | NA | NA | [101] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 2 min | 0–1.9 µM | 198 nM | NA | NA | [102] |
| Label free Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 12 min | 1.59–79.3 µM | 3.2 µM | 97–105% | 0–2% | [103] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Fluorescent | UV-Vis and PL spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.8–80 nM | 0.61 nM | 97.92–98.54% | NA | [104] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 1 min | NA | 39.64 nM | NA | NA | [105] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 10 min | 0.79–15.9 µM | 0.4 µM | 95–105% | 1.28–10.53% | [106] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 15 min | 1.6–159 µM | 15.86 µM | 105–116% | NA | [107] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes, DLS and UV-Vis spectrometer | Complicated and NA | 1–100 µM | 33 nM, 23.7 nM and 89 nM | 91–104% | 0.23–4.43% | [108] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >15 min | 0.95–3.9 µM | 317 nM | NA | NA | [110] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.79–79 µM | >3.2 µM | NA | NA | [111] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 20 min | 0–2 µM | 555 nM | 90–120 % | NA | [112] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.198–2.4 µM & 0.792–7.13 µM | 182 nM and 729 nM | 97.5–101.1% | NA | [113] |
| Citrate-stabilizedAu NPs | Fluorescent | PL spectrometer | Moderate and >30 min | 10 nM–4 µM | 3 nM | 92–108% | 0.80–4.21% | [114] |
| Citrate-stabilized-Au NPs | Fluorescent | DLS and PL spectrometer | Complicated and 5 min | 40–700 nM | 0.35 nM | 97–100% | 2.1–4.28% | [115] |
| Citrate and DNA-Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 5 min | NA | 41.7 nM amd 46.5 nM | 82.9–102.6% | 0.80–2.06% | [116] |
| 1-(2-mercaptoethyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione (MTT)-stabilizedAu NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Mild and 5 min | 7.93–39.64 µM | 19.82 nM | NA | NA | [117] |
| Hexadecy ltrimethyl ammonium chloride (CTAC)-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 50 min | 1 nM–10 µM | 0.8 nM | NA | NA | [118] |
| 11-Mercapto-undecanoic acid (MUA)-stabilized Au NPs | Capillary electrophoresis-UV | Naked eyes and UV absorbance detector | Complicated and 90 min | 1–1000 nM | 77 pM | 97–101% and 95–99% | NA | [119] |
| Polythymine (Poly Tn)-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes, DLS and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 80–1000 nM | 20 nM | NA | NA | [120] |
| 18-crown-6Ether-functionalized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >1 min | 79.3 nM–3.96 µM | 47.57 nM | 98.4–105.6 % | 1.7–5.8% | [121] |
| Cysteamine-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >30 min | 7.92 µM–1.59 mM | 7.92 µM | NA | NA | [122] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs with Fluorescein | FRET | PL spectrometer | Moderate and >12 min | 0.1 µM–4 µM | 1 nM | NA | NA | [123] |
| 3-mercapto-1-propane-sulfonate-modifiedAu NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 10–150 nM & 150–600 nM | 8 nM | 98.0–104.5% 93.6–101.6% | 1.6–3.7% and 3.9–5.9% | [124] |
| 4-mercaptopyridine-modified Au NPs | SERS | UV-Vis and Raman spectrometer | Moderate and >0.5 min | 3.96–793 nM | 793 pM | 88.5–119.2% | NA | [125] |
| pyrocatechol-3,5-disodiumsulfonate-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 80 min | 4.8 nM–1.6 µM | 0.64 nM | 93–107 % | NA | [126] |
| ssDNA-stabilized Au NPs | Resonance Rayleigh Scattering (RRS) and Cat RRS | Eclipse fluorescence spectro-photometer | Moderate and >30 min | 15–650 nM and 5–38 pM | 7.8 and 3 pM | 99.2–100% | 0.8–1.7% | [128] |
| Thioglycolic-Acid-Modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >15 min | 0–19.66 µM | NA | 101.1–102% | 1.6–2.3% | [129] |
| 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-sulfonic acid (TNBS) tailored Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >10 min | 0–634 nM | 39.64 nM | NA | NA | [130] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Strip method | immuno-chromatographic strip analyzer | Complicated and NA | 23.8–99 nM | 35.4 nM | NA | NA | [131] |
| Pyridine-3-Boronic Acid-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >20 min | 60 nM–1.6 µM | 30 nM | 95–102% | NA | [132] |
| Bare Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >15 min | 1.6–159 µM | 3.1 µM | 95–109% | 0.77–4.21% | [133] |
| 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole-capped Au NPs | Colorimetric & Fluorimetry | Naked eyes, UV-Vis and PL spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.1–1 nM | 10 fM | NA | NA | [134] |
| ssDNA-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 40 min | 0.1–1.0 µM | 34 nM | 94–120% | NA | [135] |
| Cysteamine-modified Au NPsdified | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 45 min | 0.08–1.6 µM | 80 nM | 98–102% | 1.7–2.6% | [136] |
| Au NPs synthesized by ellagic acid (EA) | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Mild and 30 min | 16 nM–160 µM | 1.6 nM | 93–106% | NA | [137] |
| Aptamer-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 1.2–2.4 µM and 2.4–20.62 µM | 793 nM | 95–105 % | 3.9% | [138] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (CRET) | Chemiluminescence analyzer, PL and UV-Vis spectrometer | Mild and 45 min | 3.2 pM–0.32 µM | 0.3 pM | 94.1–104.2% | 1.5–4.5% | [139] |
| p-DNA-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) | Naked eyes, DLS and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and >3 min | 39.64 nM–2.54 µM | 15.9 nM | NA | NA | [140] |
| Citrate and dodecasodium salt of phytic acid functionalized Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate & 90 min | 10–100 µM | 5 µM | 93.6% | NA | [141] |
| 3-Mercapto-propionic acid functionalized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate & 10 min | 4.8–333 nM | 3.2 nM | 96–105% | NA | [142] |
| Citrate stabilized Au NPs with Rhodamine B | FRET | PL and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate & >40 min | 39.64 nM–7.93 µM | 1.43 nM | 95.9–102.2% | 0.8–3.0% | [143] |
| Acetylated chitosan-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes, CV and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate & NA | 396 nM –7.93 µM | 389 nM | 94–111% | NA | [144] |
| 1,4-dithiothreitol-modified (DTT) Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 5 min | 80 nM–1.5 µM | 24 nM | 96–103% | NA | [145] |
| Au NPs synthesized by Methanobactin (Mb) | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 50 min | 0.39–3.97 µM | 0.238 µM | 97.5–103.1% | 0.8% | [146] |
| Thymine derivative-functionalized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 10 min | 0.75–5.00 μM | 3.5 nM | 96.5–102.0% | 4.0–11.8% | [147] |
| H2O2–Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 35 min | 0.4–160 µM | 0.078 µM | 90–113.7% | NA | [148] |
| Up-conversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and Au NPs | FRET | PL spectrometer | Moderate and 12 min | 32–500 nM | 18 nM | 98.8–102% | 2.32–4.44% | [149] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | Fluorescent and UV-Vis | UV-Vis and PL spectrometer | Complicated and 60 min | 0.4–2 μM | 0.88 µM | NA | NA | [150] |
| Polythymine (T) aptamer -modified Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and NA | 0–31.7 fM | 7.9 fM | 97.3–109.53% | NA | [151] |
| p-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 15 min | 0.6–1.5 µM | 2.3 nM | 97.9–103% | 0.1–6.5% | [152] |
| BSA conjugated Au NPs | Colorimetric | Signal amplified lateral flow strip | Complicated and NA | 7.93 nM–1.59 µM | 11.1 nM | NA | NA | [153] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 0–0.9 μM | 33 nM | 99.2–111% | 0.56–1.91% | [154] |
| Cysteamine-stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 6 min | 1–24 nM | 0.389 nM | 92.8–112.2% | NA | [155] |
| amine-ended dual thiol ligand functionalized Au NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Complicated and NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | [156] |
| Cellulose-coated Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate and 15 min | 0–79.3 µM | 7.93 µM | 87.6–92.3% | NA | [157] |
| Triton X-100-modifiedAu NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.75–1.75 µM | 5.1 nM | 99–111% | 0.73–2.91% | [158] |
| uracil 5’-triphosphate sodium-modified Au NPs | Colorimetric and light scattering | Naked eyes, DLS and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 300–900 nM and 200–950 nM | NA | 98.5–104% | 3.6–4.6% | [159] |
| Citrate-stabilized Au NPs | SERS | UV-Vis and Raman spectrometer | Moderate and 10 min | 0–1.59 µM | 793 nM | NA | NA | [160] |
| Unmodified Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | NA | 0–79.3 µM | 793 nM | NA | NA | [161] |
| Citrate stabilized Au NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate and >30 min | 2.5–39.64 µM | 1.35 µM | 96.3–99.9% | 3.8–9.6% | [162] |
| Citrate stabilized Au NPs | Colorimetric & SERS | Naked eyes and Raman spectrometer | Moderate and 20 min | 0–1.98 µM | NA | NA | NA | [163] |
| Citrate stabilized Au NPs | Mass Analysis | surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometer | Complicated and >0.5 min | NA | NA | NA | NA | [164] |
| Citrate stabilized Au NPs | Sonoluminescence | Sonoluminescence analyzer | Moderate and >12 min | 10–240 nM | 3 nM | 95% | NA | [165] |
| SiO2 shell-isolated Au NPs | SERS | UV-Vis and Raman spectrometer | Moderate and >6 min | 3.96–39.64 µM | 7.93 µM | 94.6–102.5% | 5.4–9.5% | [166] |
| Ag NPs-Based Probe | Method of Detection | Instruments Employed | Optimization Status and Time Required | Linear Range | LOD | Recoveries of Spiked Samples | RSDs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label-free Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 50 min | 2–250 µM | 2.32 µM | 88.83–114. 29% | 2.04–3.10% | [168] |
| Bare Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 40–880 nM | 10 nM | 97.5–105% | 2.98–4.83% | [169] |
| Unmodified Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 20 min | 0–15.86 µM | 0.32 pM | 92.5–99.4% | 5.26–8.18% | [170] |
| Bare Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 0.26 pM–11.89 µM | 71.4 nM | 61.9–96.3% | NA | [171] |
| p-nitroaniline-modified Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 10 min | 0.79 µM–79.3 mM | 0.79 µM | NA | NA | [172] |
| Dopamine-stabilized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 60 min | 0.08–10.0 µM | 79.3 nM | 92–105% | NA | [173] |
| ssDNA-stabilizedAg NPs | Resonance scattering | PL and CD spectrometers etc… | Complicated and 90 min | 0.05–3 μM | 23.8 nM | 98.7–100.9% | 0.8–3.6% | [174] |
| Oleylamine capped Ag NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >0.5 min | 0.1–100 µM | 100 nM | NA | NA | [175] |
| β-cyclodextrin-functionalized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 30 min | 1 mM–50 µM | 4.98 µM | 80.5–109.02% | 2.27–3.03% | [176] |
| Chromotropic acid (CTA)-modified Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 6 min | 0.10–1.5 μM | 36 nM | 91–105 % | NA | [177] |
| Sulfanilic acid-modified Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 5 min | 0.1–3.1 µM | 10.6 nM | 97–109% | 0.9–1.9% | [178] |
| Starch-coated Ag NPs | SERS | UV-Vis and Raman spectrometers | Complicated and NA | 15.9 µM–0.4 mM | 4.8 nM | 94–104% | 2.39–4.53% | [179] |
| Bio-functionalized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Complicated and 20 min | 0.015–1 mM | 2 µM | 96–122% | 0.44–2.22% | [180] |
| Sodium D-gluconate-stabilized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.5–500 µM | 476 nM | 90–98% | NA | [181] |
| Polyelectrolyte-stabilized Ag NPs | Colorimetric and Fluorescence | Naked eyes, UV-Vis and PL spectrometers | Complicated and 20 min | 1 nM–1.5 µM and 1.5 nM–150 µM | 0.1 and 0.45 nM | 99–114% | 1.66–4.37% | [182] |
| Citrate and Borohydride stabilized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | [183] |
| Ag NPs monolayer film | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >15 min | 0.79 pM–39.6 µM | 0.32 pM | 90–95.4% | 3.7–6.9% | [184] |
| Tannic acid-stabilized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and 20 min | 0.05–1.4 µM | 0.01 µM | 98.5–106.5% | 1.04–3.19% | [185] |
| Bio-functionalized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | UV-Vis and Raman spectrometers | Moderate and >1 min | 0.79–40 µM | 0.79 and 3.96 µM | 96% | NA | [186] |
| Green synthesized Ag NPs | Colorimetric | Naked eyes and UV-Vis spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 0.79–79.3 µM | 793 nM | NA | NA | [187] |
| Acid-directed synthesis of Ag NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and NA | 0–0.396 mM | 39.64 µM | NA | NA | [188] |
| Chitosan-modified Ag NPs | SERS | Chromatography and Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >1 min | 0–79.3 µM | 7.93 µM | NA | NA | [189] |
| Nanotube/Nanorod/Nanowire Arrays | Method of Detection | Instruments Employed | Optimization Status and Time Required | Linear Range | LOD | Recoveries of Spiked Samples | RSDs | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bis(8-quinolinolato) zinc (II) complex nanorod arrays | Fluorescence | PL spectrometer | Moderate and NA | 39.6 nM–238 n M | NA | NA | NA | [196] |
| ZnO/Au composite nano arrays | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >0.5 min | 100 μM–10 nM | 10 nM | NA | NA | [197] |
| Ag-nanoparticle-modified single Ag nanowire | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and 60 min | 10 nM–22 μM | 10 nM | NA | NA | [198] |
| hydroxyapatite/carbon nanotubes | Electrochemical | Cyclic voltammeter | Complicated and 9 min | 10–350 nM | 1.5 nM | 98.5–102.5% | 1.32–2.58% | [200] |
| glassy carbon electrode coated with a multi-wall carbon nanotube/chitosan | Electrochemical | Cyclic voltammeter | Complicated and 20 min | 9.9–190 nM | 3 nM | 104.8% | NA | [201] |
| Vertically aligned monolayer of Aunanorods | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and 90 min | NA | ~0.9 fM | NA | NA | [202] |
| Single gold nanoparticles decorated silver/carbon nanowires | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and 60 min | 0.1–220 μM | 0.1 μM | NA | NA | [203] |
| Au nanorods coupled with Ag nanoparticles | SERS | Focus ion beam and Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >0.5 min | 1 mM–1 pM | 1 pM | NA | NA | [204] |
| disordered silver nanowires membrane | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate and >0.5 min | 7.93 µM–0.79 mM | NA | NA | NA | [205] |
| Ag nanoparticles surrounding triangular nanoarrays | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and NA | 0.5–500 μM | 10 μM | NA | NA | [206] |
| ZnGa2O4 Nanorod Arrays Decorated with Ag Nanoparticles | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicated and >1 min | 0.1–100 μM | 0.1 μM | NA | NA | [207] |
| Au nanorod arrays fabrication using a focused gallium (Ga) ion beam | SERS | Focus ion beam and Raman spectrometer | Complicate & >1 min | 100 μM–1 pM | 1 pM | NA | NA | [208] |
| [Ru (bpy)3]2+-doped Si NPs/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion composite electrode | Electro-chemiluminescence | Multifunction chemiluminescence detector | Complicate & NA | 0.1 μM –0.5 pM | 0.1 pM | 99.7–102% | 1.1–3.1% | [209] |
| Ag nanorod (Ag NR) array | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate & >0.5 min | 15.86 µM – 1.59 mM | 7.1 µM | 89.7–93.3% | 1.08–2.02% | [210] |
| Flexible silicon nanowires | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate & >0.5 min | 79 pM – 0.79 mM | 2.5 nM | NA | NA | [211] |
| CarbonNitride Nanotubes | Molecular Imprinted Voltammetry | Cyclic voltammeter | Moderate & 30 min | 0.1–5 nM | 10 pM | 98.68–102.94% | NA | [212] |
| Molybdenum Oxide-nanowires @ Au | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicate & >24 h | 0.79 nM–0.79 mM | 0.792 nM | NA | NA | [213] |
| Zinc oxide Nanowires decorated with Ag NPs | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate & 60 min | 12 μM–76 μM | NA | NA | NA | [214] |
| Ag nanorod from polymeric silver cyanide | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Moderate & NA | 1 mM–1 pM | NA | NA | NA | [215] |
| Ag nanoparticles decorated Cu(OH)2 nanoneedle | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicate & NA | NA | 0.792 nM | NA | NA | [216] |
| Ag NPs decorated Zinc Oxide/Siliconhetrostructured nanomace Arrays | SERS | Raman spectrometer | Complicate & >0.5 min | 10 μM–0.1 nM | 10 fM | NA | NA | [217] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shellaiah, M.; Sun, K.W. Review on Nanomaterial-Based Melamine Detection. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010009
Shellaiah M, Sun KW. Review on Nanomaterial-Based Melamine Detection. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleShellaiah, Muthaiah, and Kien Wen Sun. 2019. "Review on Nanomaterial-Based Melamine Detection" Chemosensors 7, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010009
APA StyleShellaiah, M., & Sun, K. W. (2019). Review on Nanomaterial-Based Melamine Detection. Chemosensors, 7(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010009






