Enzyme-Based Single Solid-State Nanochannel Biosensors
Abstract
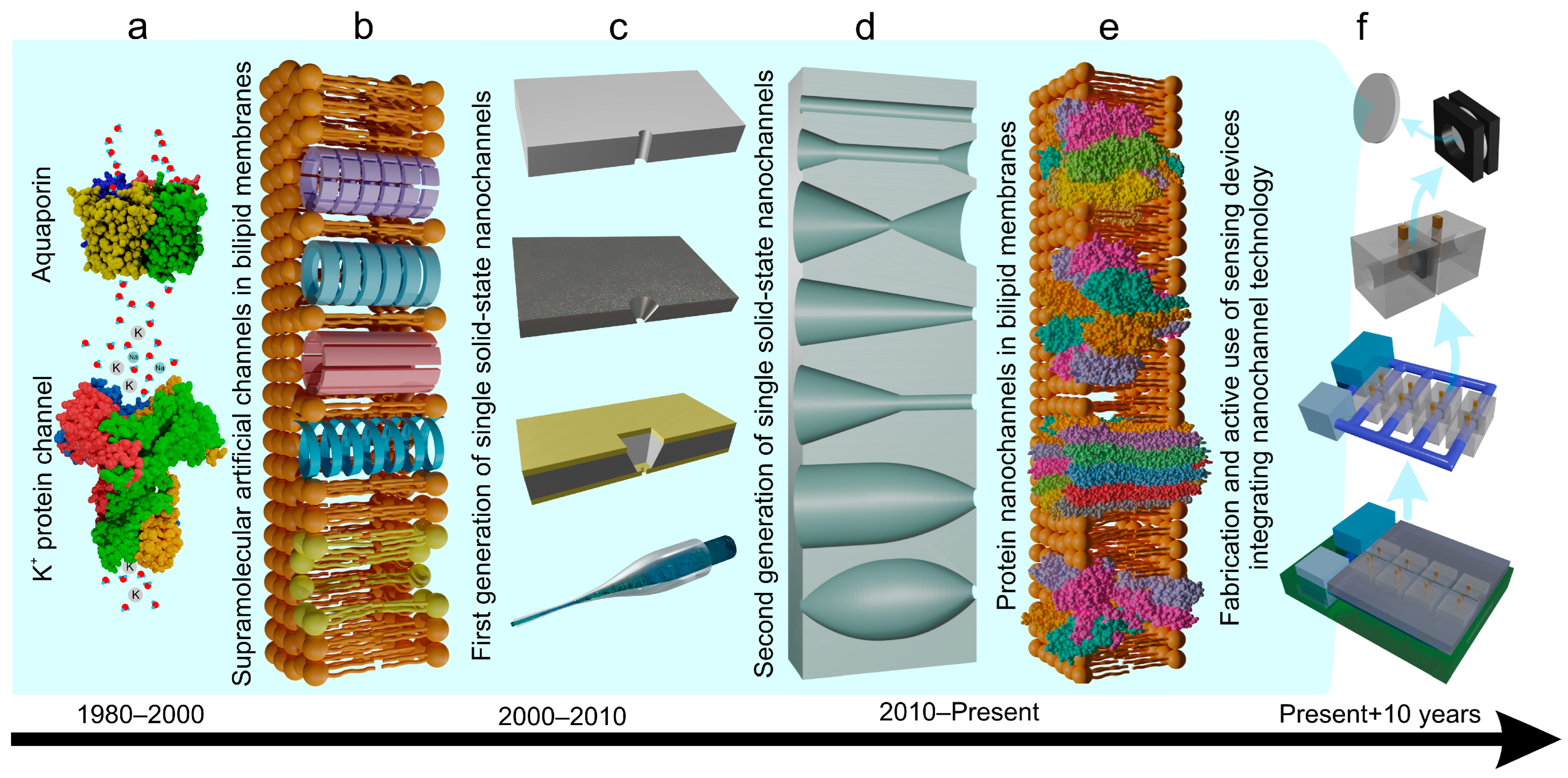
1. Introduction
2. Physicochemical Aspects of Single Nanochannel System
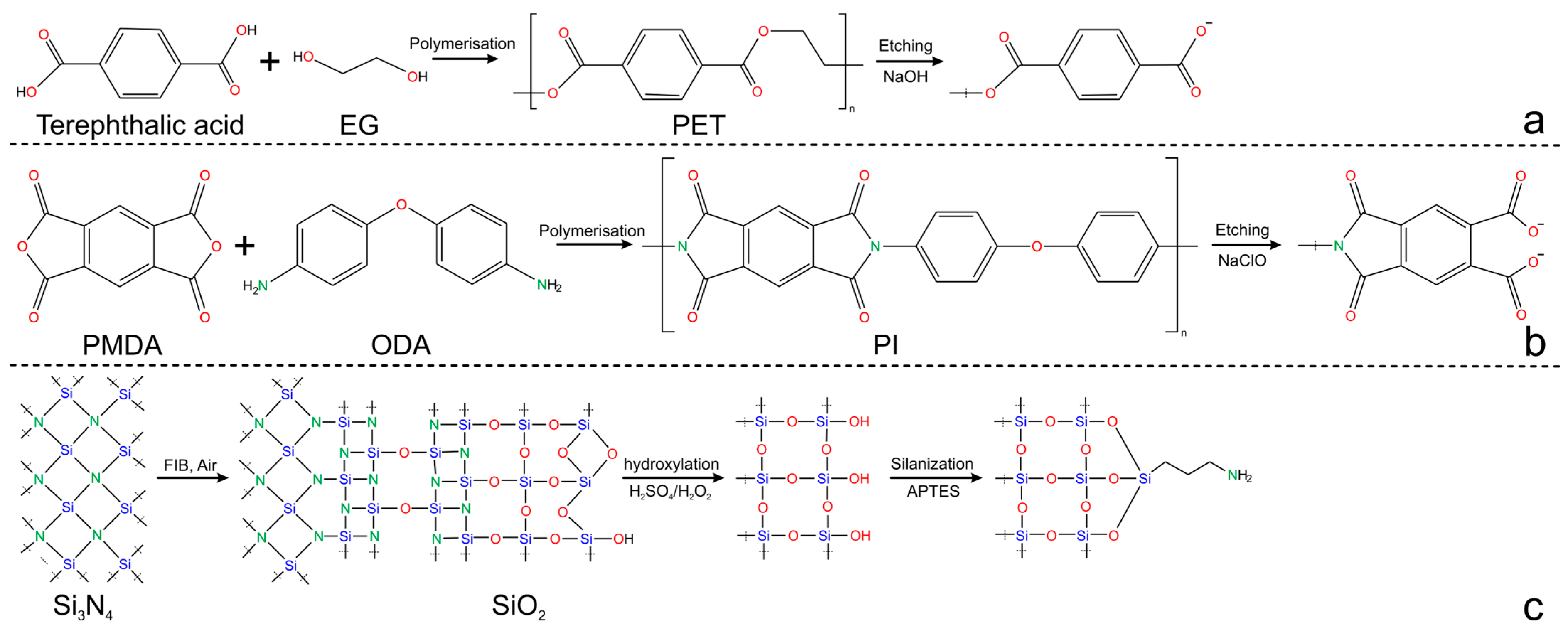
2.1. Single Nanochannel Fabrication: Materials and Methods
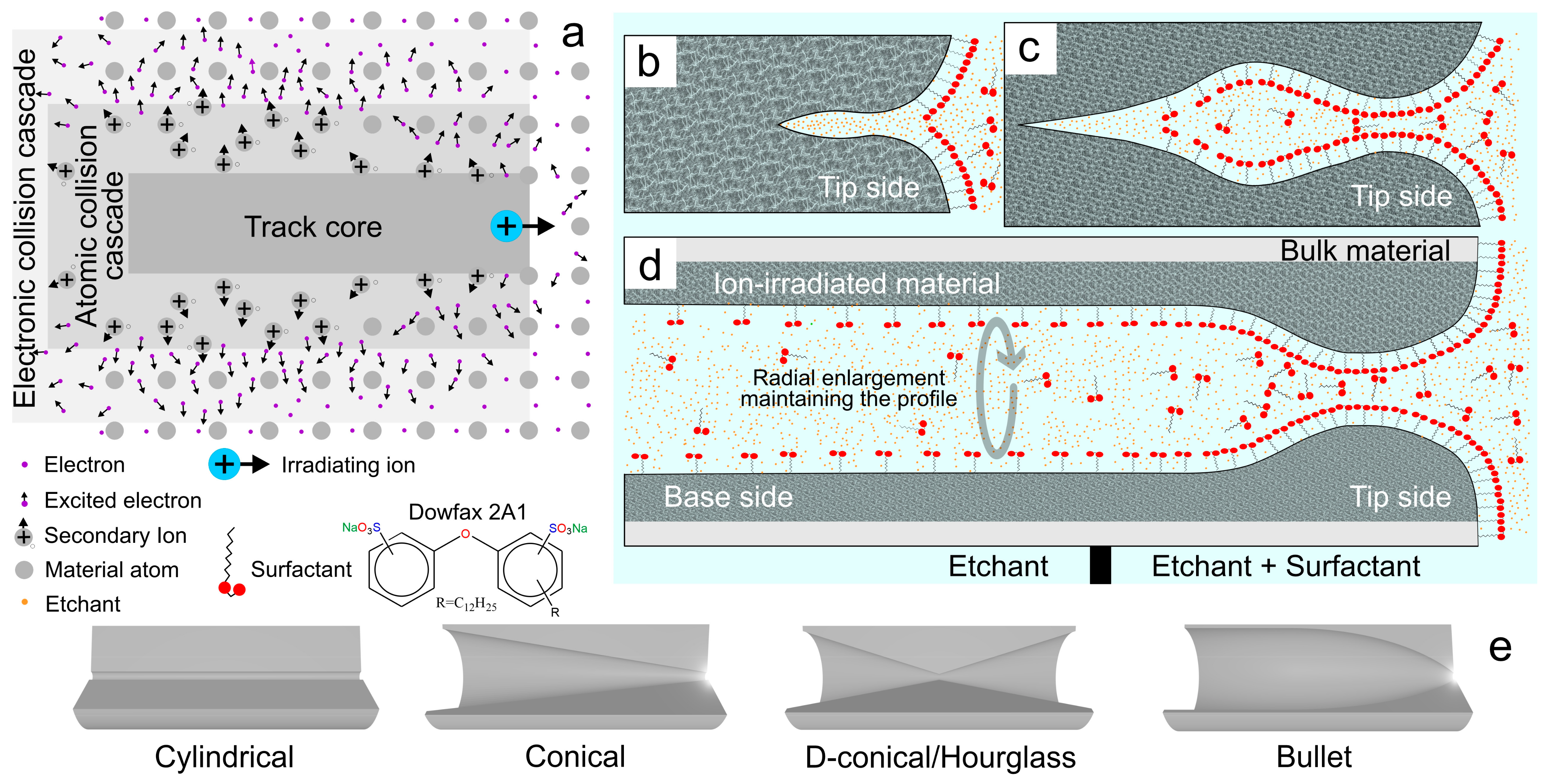
2.1.1. Ion-Track Chemical Etching
| Support | Fabrication Specifications (Tip Side|Base Side) 1 | Shape | Etching Time (Minutes) | Etching T (°C) | Size (nm) 2 (Tip/Base/Length) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Ion-track asymmetrical chemical etching (6 M NaOH + 0.05% w/w Dowfax 2A1|6 M NaOH) 6 min, 60 °C | Bullet | 6 | 60 | (90/600/12,000) | [103] |
| (76/560/12,000) | [104] | |||||
| (55/500/12,000) | [92] | |||||
| (60/600/12,000) | [91] | |||||
| (No specified) | [90] | |||||
| (85/600/12,000) | [89] | |||||
| (55/900/12,000) | [88] | |||||
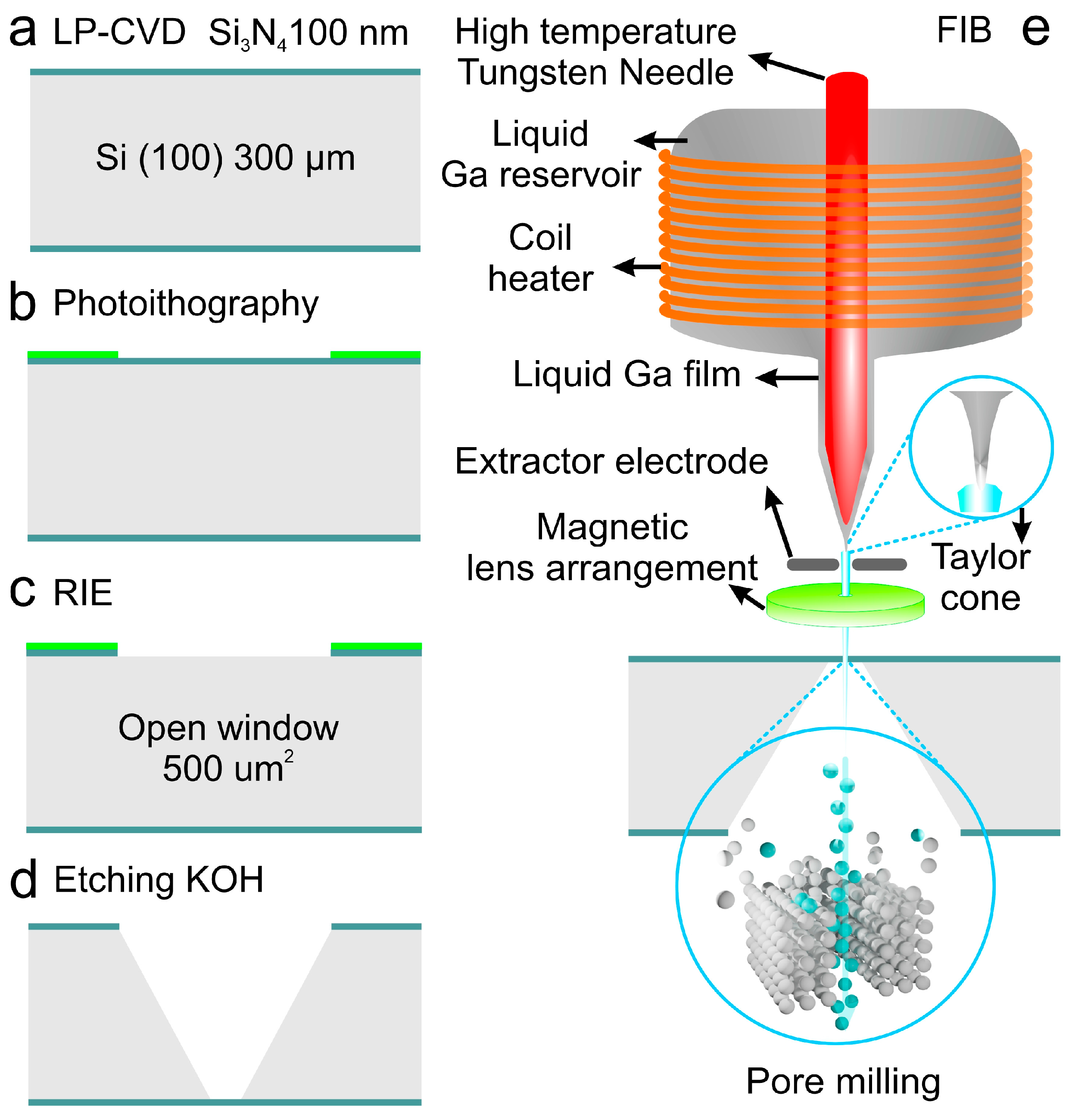
| Si3N4 | Photolithography-RIE-FIB Ga+ 30 kV 1pA | Cylindrical | 0.025 | Ion beam | (50/50/100,000) | [105] |
| PI | Ion-track chemical etching (NaClO4|NaClO4), etching stop with addition of 1 M KI | Double conical | Electrochemically controlled etching stop time | 25 | (25/1300/12,000) | [96] |
| PET | Ion-track UV-sensitized asymmetrical etching (1 M KCl + 1 M HCOOH|9 M NaOH), etching stop with addition of 1 M KCl + 1 M HCOOH | Conical | 30 | (30/860/12,000) | [99] | |
| PET | Conical | 25 | (8/210/12,000) | [106] | ||
| PET | Ion-track UV-sensitized etching 35 h (4 M NaOH + 0.02% v/v Dowfax 2A1|6 M NaOH), etching stop with addition of 1 M HCl | Conical | 60 | (20/2500/12,000) | [107] |
2.1.2. Photolithography-Reactive Ion Etching FIB
2.2. Single Nanochannel Physical and Chemical Properties
2.2.1. Morphology and Surface Chemistry
2.2.2. Wettability
2.3. Transport in Single Nanochannels
2.3.1. The Nanoconfinement Effects
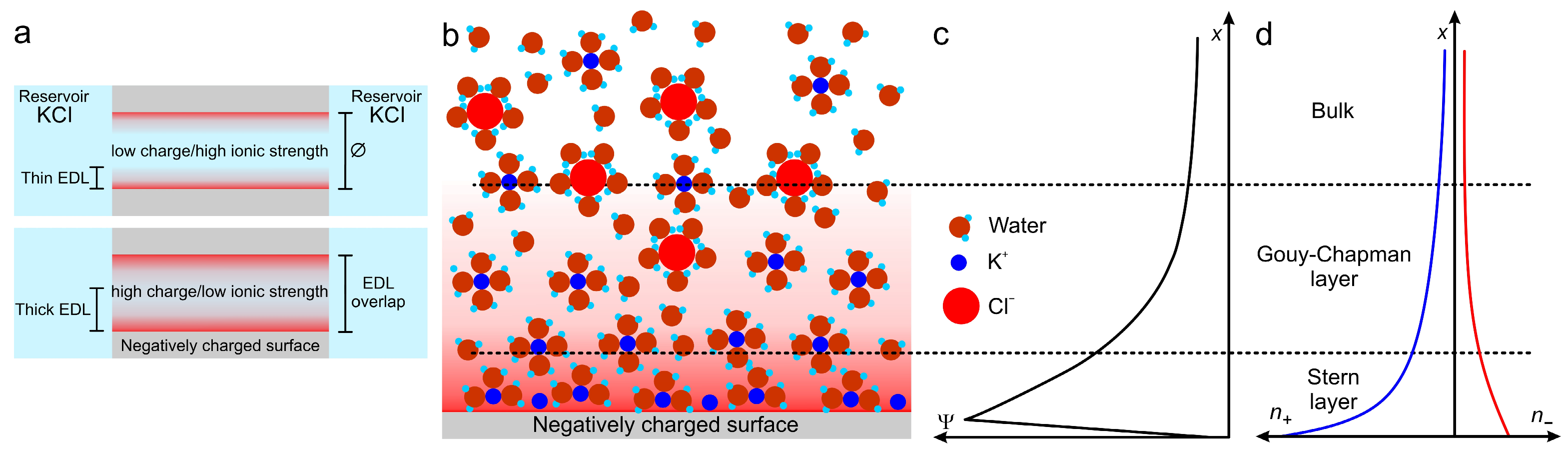
2.3.2. Forces Regulating Ion Behavior
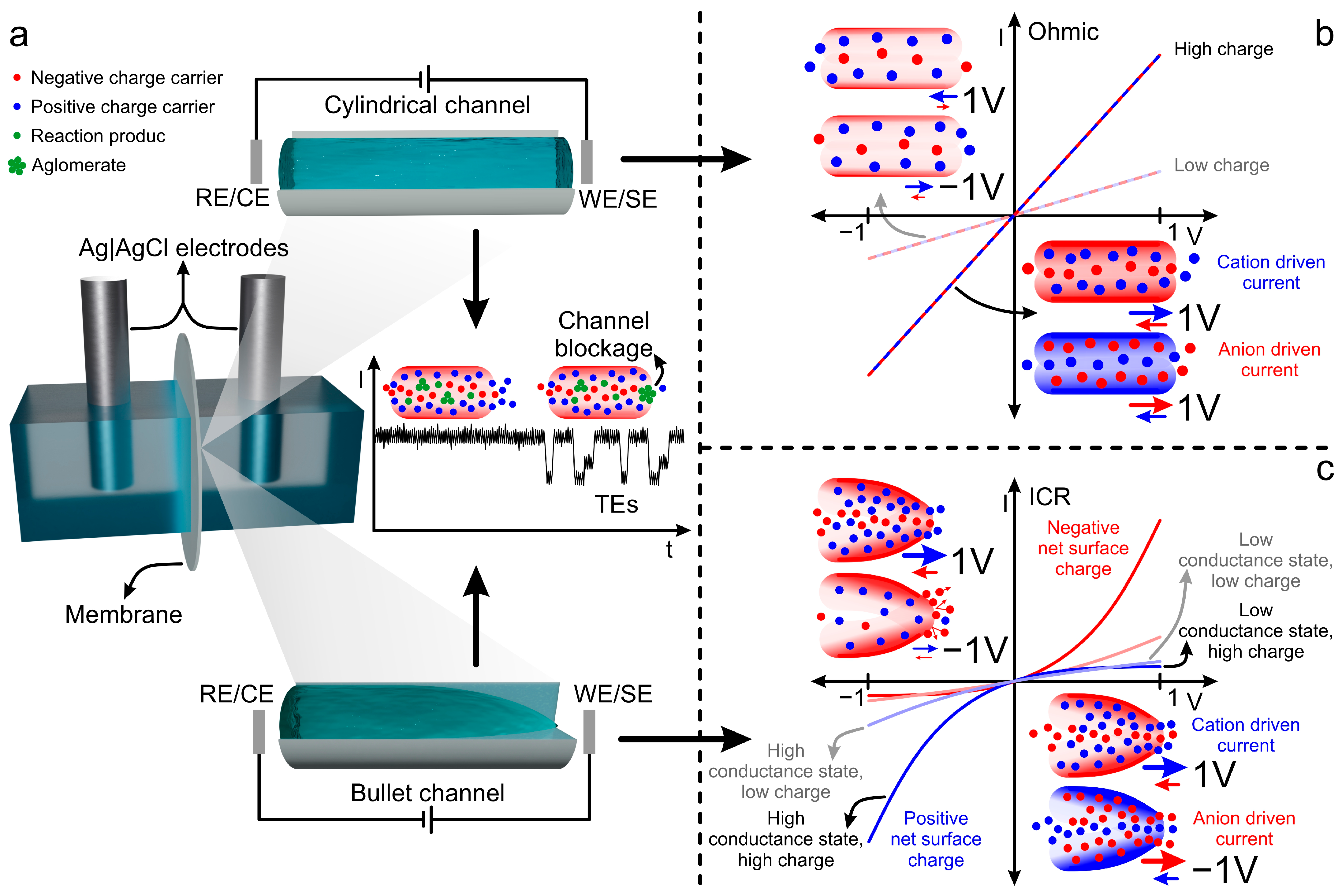
2.3.3. Signal Sources in Nanochannels: Iontronic Current, ICR, and TEs
3. Sensing Platform Nanoarchitecture
3.1. Functional Blocks Integration
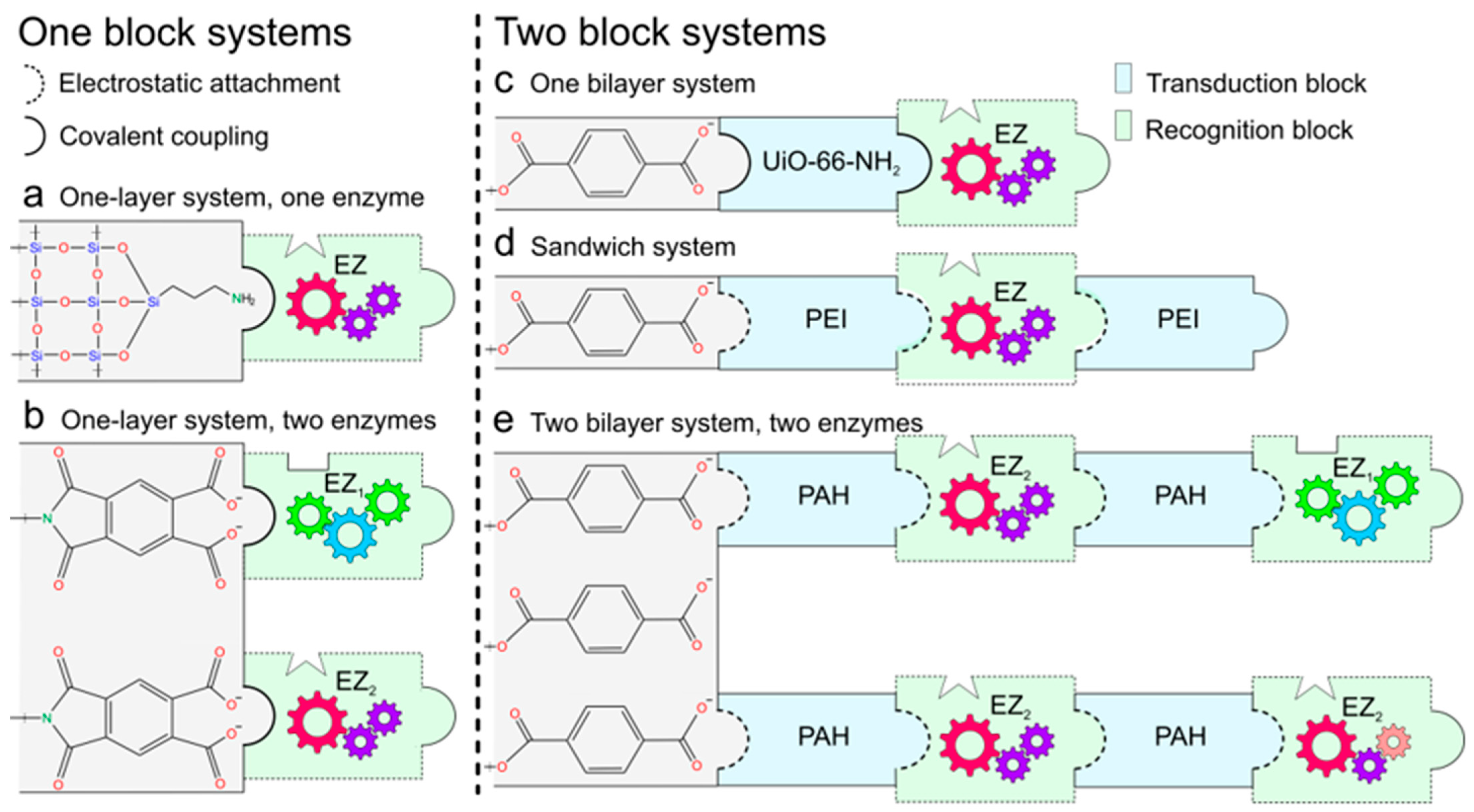
3.1.1. One-Block Systems
3.1.2. Two-Block Systems
| Building Block Layers | Blocks Integration | Transduction Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-NH2-Urease | One-pot MOF synthesis, DVS-mediated crosslinking by drop-coating | pH change effect over frec, single reaction | [103] |
| PAH/ADA/PAH | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating and drop-coating | pH change effect over frec, single reaction | [104] |
| PAH/Urease/PAH/Urease: Arginase | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating | pH change effect over frec, cascade concerted functions | [92] |
| PEI/CD/PEI | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating and drop-coating | pH change effect over frec, single reaction | [91] |
| PAH/Urease | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating | pH change effect over frec, steric obstruction | [90] |
| PEI/AchE | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating and drop-coating | pH change effect over frec, single reaction | [89] |
| PAH/Urease | Layer-by-layer self-assembly by dip-coating | pH change effect over frec, single reaction | [88] |
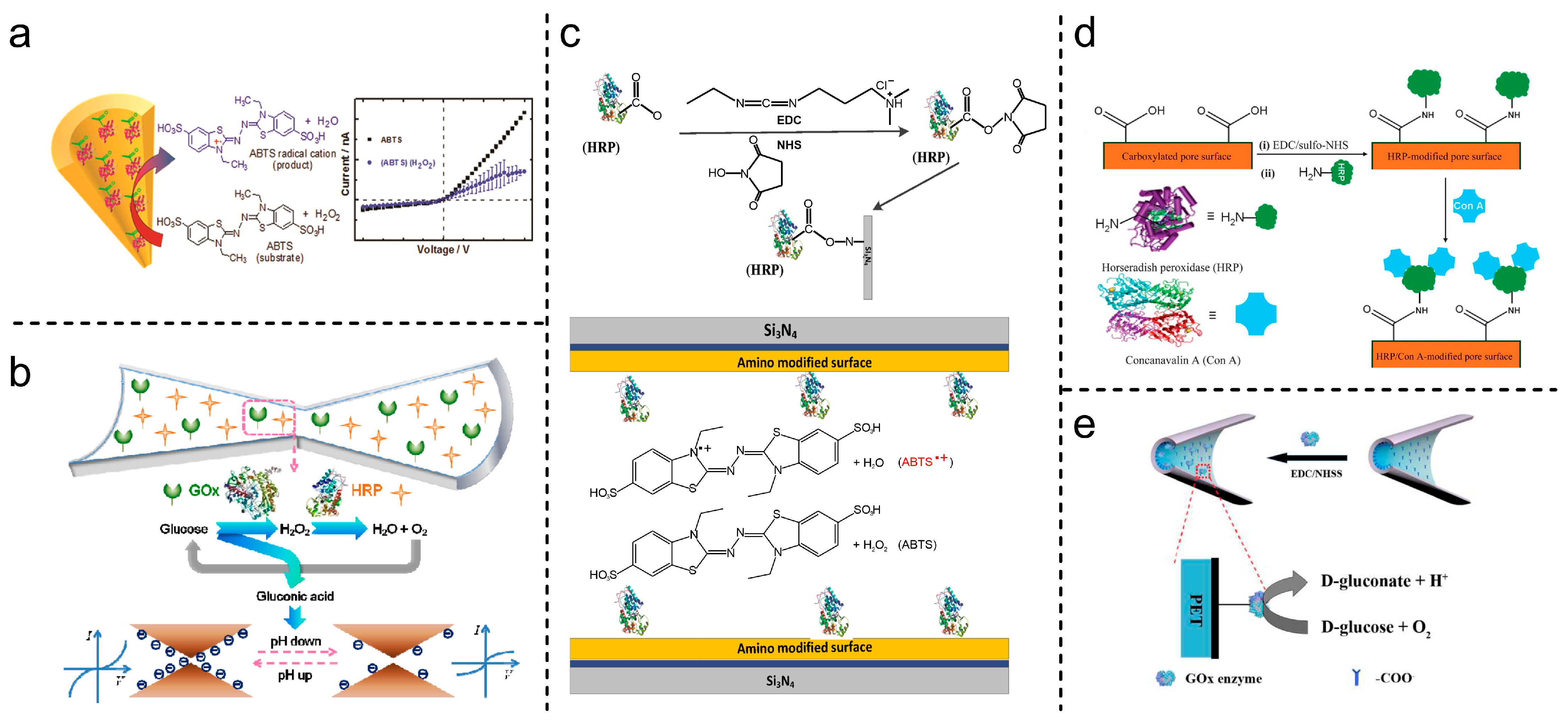
| HRP | EDC-NHS covalent coupling | Translocation events (ABTS●+ aggregates) | [105] |
| GOx/HRP | pH change influence over transmembrane current cascade concerted functions | [96] | |
| GOx | pH-sensitive, single reaction | [99] | |
| HRP | Steric obstruction, specific interaction | [106] | |
| HRP | ABTS●+-sensitive, electrostatic interaction, and steric obstruction | [107] |
3.2. Recognition and Transduction Mechanism
4. Enzyme-Based SSN Platforms
| Year | Target | LOD (µM) | Dynamic Ranges (µM) | Response Time (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Urea | 10 | 10–10,000 | ≈1 | [103] |
| 2025 | Adenosine | 0.01 | 0.01–500 | 4 | [104] |
| 2025 | Arginine | 3 | 30–3000 | 5 | [92] |
| 2025 | Creatinine | 0.005 | 0.005–100 | 2.5 | [91] |
| 2024 | Urea | 0.0001 | 0.0001–0.01 and 0.001–1 | ≈3 | [90] |
| 2022 | Acetylcholine | 0.016 | 0.001–22.5 and 25–100 | ≈3 | [89] |
| 2018 | Urea | 0.001 | 0.001–1 | 1.5 | [88] |
| 2017 | H2O2 | 500 | 500 Qualitative analysis | 0.01–1.4 | [105] |
| 2014 | Glucose | 15 | 15–100 | ≈10 | [96] |
| 2014 | Glucose | 0.001 | 0.001–1000 | N/F | [99] |
| 2011 | Concanavalin A 1 | 10 | 10 Qualitative analysis | 180 | [106] |
| 2011 | H2O2 | 0.01 | 0.01–1 | 0.8–1.6 | [107] |
5. Challenges: Toward Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| CR39 | Poly (allyl diglycol carbonate) |
| frec | Rectification factor |
| TEs | Translocation events |
| PNP | Poisson–Nernst–Planck |
| ICR | Ion current rectification |
| PI | Polyimide |
| PBD | Protein data bank |
| SSNs | Solid-state nanochannels |
| EBL | Electron beam lithography |
| RIE | Reactive ion etching |
| FIB | Focused ion beam |
| IBS | Ion beam sculping |
| EE-PEO | Embedding electrospun polyethylene oxide |
| EB | Electron beam |
| LMIS | Liquid metal ion source |
| PFA | Perfluoroalkyl passivation |
| EDC | 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide |
| NHS | N-Hydroxy succinimide |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| DVS | Divinyl sulfone |
| PAH | Poly (allylamine hydrochloride) |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| EZ | Enzyme |
| GOx | Glucose oxidase |
| ADA | Adenosine deaminase |
| CD | Creatinine deaminase |
| AchE | Acetyl cholinesterase |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| PLL | Poly-L-Lysine |
| Con A | Concanavalin A |
| CV | Cyclic voltammetry |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| LP-CVD | Low-pressure chemical vapor deposition |
| EDL | Electrical double layer |
| Surface charge density | |
| Faraday constant | |
| Gas constant | |
| Surface density | |
| Net charge | |
| Valence of ion | |
| Electron charge | |
| Electric potential | |
| Vacuum permittivity | |
| Relative permittivity | |
| Boltzmann constant | |
| Spatial coordinate | |
| Absolute temperature | |
| Bulk volume density | |
| Volume density | |
| Debye length | |
| Debye–Hückel parameter | |
| Ionic strength | |
| Conductance | |
| Mobility | |
| Fluid velocity | |
| Length | |
| Radial coordinate | |
| Current | |
| Potential | |
| Diffusion coefficient | |
| Flux per area | |
| Electric potential | |
| Concentration | |
| Density | |
| Viscosity | |
| Pressure |
References
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints: Preferred Definitions and Conceptual Framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci-Çekiç, S.; Özkan, G.; Avan, A.N.; Uzunboy, S.; Çapanoğlu, E.; Apak, R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucker, N.; do Nascimento, S.N.; Bernardini, L.; Charão, M.F.; Garcia, S.C. Biomarkers of Exposure, Effect, and Susceptibility in Occupational Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhadi, V.K.; Armengol, G. Molecular Biomarkers in Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaboğa, M.N.S.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Biosensor Approaches on the Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Sensing the Past to the Future. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Ai, J.; Wang, N.; Pu, Q. Recent Progress of Smartphone-Assisted Microfluidic Sensors for Point of Care Testing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Artificial Intelligence Enhanced Sensors-Enabling Technologies to next-Generation Healthcare and Biomedical Platform. Bioelectron. Med. 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Seo, B.; Jeong, Y.; Park, I. A Review of Recent Advancements in Sensor-Integrated Medical Tools. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, M.; Du, Y.; Liu, Q.; Emran, M.Y.; Kotb, A.; Sun, M.; Ma, C.-B.; Zhou, M. Artificial Enzyme Innovations in Electrochemical Devices: Advancing Wearable and Portable Sensing Technologies. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Rohilla, R.; Rana, S.; Rani, S.; Prabhakar, N. Recent Advances in Protein Biomarkers Based Enzymatic Biosensors for Non-Communicable Diseases. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 174, 117683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ulstrup, J. Towards Continuous Potentiometric Enzymatic Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2024, 46, 101549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, C.; Barrias, S.; Chaves, R.; Adega, F.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Fernandes, J.R. Biosensors as Diagnostic Tools in Clinical Applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.; Aguilar, M.R.; Pattiya Arachchillage, K.G.G.; Chandra, S.; Rangan, S.; Ghosal Gupta, S.; Artes Vivancos, J.M. Biosensors for Public Health and Environmental Monitoring: The Case for Sustainable Biosensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 10296–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chung, K.; Yu, S.; Lee, L.P. Nanoplasmonic Biosensors for Environmental Sustainability and Human Health. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10491–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckmann, C.M.; Paradisi, F. Looking Back: A Short History of the Discovery of Enzymes and How They Became Powerful Chemical Tools. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 6082–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanoi, F. History of The Enzymes: 1950–2023. In The Enzymes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 54, pp. 3–11. ISBN 9780443136917. [Google Scholar]
- Suckling, C.J. Enzyme Chemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; ISBN 978-94-010-7317-2. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode Systems for Continuous Monitoring in Cardiovascular Surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Updike, S.J.; Hicks, G.P. The Enzyme Electrode. Nature 1967, 214, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, F.T.T.; de A. Falcão, I.R.; da S. Souza, J.E.; Rocha, T.G.; de Sousa, I.G.; Cavalcante, A.L.G.; de Oliveira, A.L.B.; de Sousa, M.C.M.; dos Santos, J.C.S. Designing of Nanomaterials-Based Enzymatic Biosensors: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Electrochem 2021, 2, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghraby, Y.R.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Azzazy, H.M.E.-S. Enzyme Immobilization Technologies and Industrial Applications. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5184–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, R. Potassium Channels and the Atomic Basis of Selective Ion Conduction (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agre, P. Aquaporin Water Channels. Biosci. Rep. 2004, 24, 127–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrimin, P.; Tecilla, P. Model Membranes: Developments in Functional Micelles and Vesicles. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matile, S.; Som, A.; Sordé, N. Recent Synthetic Ion Channels and Pores. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 6405–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokel, G.W.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Synthetic Models of Cation-Conducting Channels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001, 30, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, Z.; Apel, P.; Baur, D.; Dobrev, D.D.; Korchev, Y.E.; Neumann, R.; Spohr, R.; Trautmann, C.; Voss, K.O. Preparation of Synthetic Nanopores with Transport Properties Analogous to Biological Channels. Surf. Sci. 2003, 532–535, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Janot, J.; Balme, S. Track-Etched Nanopore/Membrane: From Fundamental to Applications. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Keçeci, K. Review—Track-Etched Nanoporous Polymer Membranes as Sensors: A Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Schmitz, F.; Isaksson, S.; Glas, J.; Arbab, O.; Andersson, M.; Sundell, K.; Eriksson, L.A.; Swaminathan, K.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; et al. High-Resolution Structure of a Fish Aquaporin Reveals a Novel Extracellular Fold. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202201491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuniga, D.; Zoumpoulakis, A.; Veloso, R.F.; Peverini, L.; Shi, S.; Pozza, A.; Kugler, V.; Bonneté, F.; Bouceba, T.; Wagner, R.; et al. Biochemical, Biophysical, and Structural Investigations of Two Mutants (C154Y and R312H) of the Human Kir2.1 Channel Involved in the Andersen-Tawil Syndrome. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoikov, I.I.; Antipin, I.S.; Konovalov, A.I. Artificial Ion Channels. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2003, 72, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Wu, C.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Biomimetic Nanochannels: From Fabrication Principles to Theoretical Insights. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbacher, S.; Bass, R.; Strop, P.; Rees, D.C. Structures of the Prokaryotic Mechanosensitive Channels MscL and MscS. Curr. Top. Membr. 2007, 58, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Hirano, N.; Kaneko, J.; Kamio, Y.; Yao, M.; Tanaka, I. 2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol Induces Spontaneous Assembly of Staphylococcal A-hemolysin into Heptameric Pore Structure. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Caaveiro, J.M.M.; Morante, K.; González-Manãs, J.M.; Tsumoto, K. Structural Basis for Self-Assembly of a Cytolytic Pore Lined by Protein and Lipid. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Haque, F.; Guo, P. Engineering of Protein Nanopores for Sequencing, Chemical or Protein Sensing and Disease Diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 51, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; de Souza Santos, M.; Li, Y.; Tomchick, D.R.; Orth, K. High-Resolution Cryo-EM Structures of the E. Coli Hemolysin ClyA Oligomers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grahame, D.A.S.; Bryksa, B.C.; Yada, R.Y. Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity. In Improving and Tailoring Enzymes for Food Quality and Functionality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 11–55. ISBN 9781782422976. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, D.; Su, Z.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Recent Advances in Enzyme Immobilization Based on Novel Porous Framework Materials and Its Applications in Biosensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 459, 214414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Woodley, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Is Enzyme Immobilization a Mature Discipline? Some Critical Considerations to Capitalize on the Benefits of Immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 6251–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, C.; Liu, W.; Lou, X.; Jiang, L.; Xia, F. Solid-State Nanochannels for Bio-Marker Analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 6270–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucirica, G.; Toum Terrones, Y.; Cayón, V.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Marmisollé, W.; Azzaroni, O. Biomimetic Solid-State Nanochannels for Chemical and Biological Sensing Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Y.; Kong, X.-Y.; Wen, L. Bioinspired Solid-State Nanochannels for Molecular Analysis. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Liu, J. Bioinspired Artificial Nanochannels: Construction and Application. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 1610–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Gao, P.; Ma, Q.; Wang, D.; Xia, F. Biomolecule-Functionalized Solid-State Ion Nanochannels/Nanopores: Features and Techniques. Small 2019, 15, 1804878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Si, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Gao, P.; Xia, F. Functional Solid-State Nanochannels for Biochemical Sensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuanaeva, R.M.; Vaneev, A.N.; Gorelkin, P.V.; Erofeev, A.S. Nanopipettes as a Potential Diagnostic Tool for Selective Nanopore Detection of Biomolecules. Biosensors 2024, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yu, R.-J.; Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Electrochemically Confined Effects on Single Enzyme Detection with Nanopipettes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 908, 116086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, G.; Chaves, G.; Olivier, J.; Ozel, R.E.; Pourmand, N. Nanopipettes as Monitoring Probes for the Single Living Cell: State of the Art and Future Directions in Molecular Biology. Cells 2018, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tang, H.; Qiu, X.; Li, Y. Solid-State Glass Nanopipettes: Functionalization and Applications. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202400281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Qian, R. Nanopipettes for Chemical Analysis in Life Sciences. ChemBioChem 2025, 26, e202400879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, J.; Pourmand, N. Nanopipettes—The Past and the Present. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Reisner, W. Fabrication and Characterization of Nanopore-Interfaced Nanochannel Devices. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 455301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Stein, D.; McMullan, C.; Branton, D.; Aziz, M.J.; Golovchenko, J.A. Ion-Beam Sculpting at Nanometre Length Scales. Nature 2001, 412, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.J.; Aref, T.; Bezryadin, A. Fabrication of Symmetric Sub-5 Nm Nanopores Using Focused Ion and Electron Beams. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3264–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürjes, P. Controlled Focused Ion Beam Milling of Composite Solid State Nanopore Arrays for Molecule Sensing. Micromachines 2019, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J. A Simple Cost-Effective Method to Fabricate Single Nanochannels by Embedding Electrospun Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibers. ChemistryOpen 2024, 13, e202400008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Galusha, J.; Shiozawa, P.G.; Wang, G.; Bergren, A.J.; Jones, R.M.; White, R.J.; Ervin, E.N.; Cauley, C.C.; White, H.S. Bench-Top Method for Fabricating Glass-Sealed Nanodisk Electrodes, Glass Nanopore Electrodes, and Glass Nanopore Membranes of Controlled Size. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4778–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Lei, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hou, X. Current Progress in Glass-Based Nanochannels. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2024, 15, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Ni, Z.; Liu, L.; Yi, H.; Chen, Y. A Novel Method of Fabricating a Nanopore Based on a Glass Tube for Single-Molecule Detection. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 175304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamai, H.; Xu, Y. Fabrication of Ultranarrow Nanochannels with Ultrasmall Nanocomponents in Glass Substrates. Micromachines 2021, 12, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yu, S.; Harrell, C.C.; Martin, C.R. Conical Nanopore Membranes. Preparation and Transport Properties. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Shen, W.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y. Fabrication and Application of Nanoporous Polymer Ion-Track Membranes. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Dmitriev, S.N.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Presz, A.; Sartowska, B.A. Fabrication of Nanopores in Polymer Foils with Surfactant-Controlled Longitudinal Profiles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 305302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, T.W.; Apel, P.Y.; Schiedt, B.; Trautmann, C.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Karim, S.; Neumann, R. Investigation of Nanopore Evolution in Ion Track-Etched Polycarbonate Membranes. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2007, 265, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.; Hnatowicz, V. Transport Processes in Low-Energy Ion-Irradiated Polymers. In Transport Processes in Ion-Irradiated Polymers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 47–91. ISBN 978-3-662-10608-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Laskin, J. Ion Beams in Nanoscience and Technology; Hellborg, R., Whitlow, H.J., Zhang, Y., Eds.; Particle Acceleration and Detection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-00622-7. [Google Scholar]
- Apel, P. Track Etching Technique in Membrane Technology. Radiat. Meas. 2001, 34, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Lizunov, N.E.; Olejniczak, K.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Sartowska, B.A.; Dmitriev, S.N. Asymmetrical Nanopores in Track Membranes: Fabrication, the Effect of Nanopore Shape and Electric Charge of Pore Walls, Promising Applications. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2017, 53, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Didyk, A.Y.; Dmitriev, S.N.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Root, D.; Samoilova, L.I.; Vutsadakis, V.A. Surfactant-Enhanced Control of Track-Etch Pore Morphology. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2001, 179, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautmann, C.; Brüchle, W.; Spohr, R.; Vetter, J.; Angert, N. Pore Geometry of Etched Ion Tracks in Polyimide. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1996, 111, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Apel, P.Y.; Dmitriev, S.N.; Healy, K.; Siwy, Z.S. Versatile Ultrathin Nanoporous Silicon Nitride Membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21039–21044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toum Terrones, Y.; Laucirica, G.; Cayón, V.M.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Ionic Nanoarchitectonics for Nanochannel-Based Biosensing Devices. In Materials Nanoarchitectonics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 429–452. ISBN 9780323994729. [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky, D. Nuclear Energy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-387-20778-0. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, D.; Miroshnik, V.W. The Political Economy of Nuclear Energy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-27028-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fleisher, R.L.; Price, P.B.; Walker, R.M. Nuclear Tracks in Solids: Principles and Applications; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer, R.L. Etching Nuclear Tracks. In Tracks to Innovation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–25. ISBN 978-1-4612-4452-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saifulin, M.M.; O’Connell, J.H.; Janse van Vuuren, A.; Skuratov, V.A.; Kirilkin, N.S.; Zdorovets, M.V. Latent Tracks in Bulk Yttrium-Iron Garnet Crystals Irradiated with Low and High Velocity Krypton and Xenon Ions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2019, 460, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D. Transport Processes in Ion-Irradiated Polymers; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 65, ISBN 978-3-642-05894-3. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D.A. Etching of Radiation Damage in Lithium Fluoride. Nature 1958, 182, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, P.B.; Walker, R.M. Chemical Etching of Charged-Particle Tracks in Solids. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J.; Shen, J.; Lin, M.; Xia, F. Solid-State Nanopore/Nanochannel Sensors with Enhanced Selectivity through Pore-in Modification. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.-Y.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Nanochannels. Materials 2015, 8, 6277–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L. Building Bio-Inspired Artificial Functional Nanochannels: From Symmetric to Asymmetric Modification. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5296–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Smart Asymmetric Nanochannel Membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 322–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
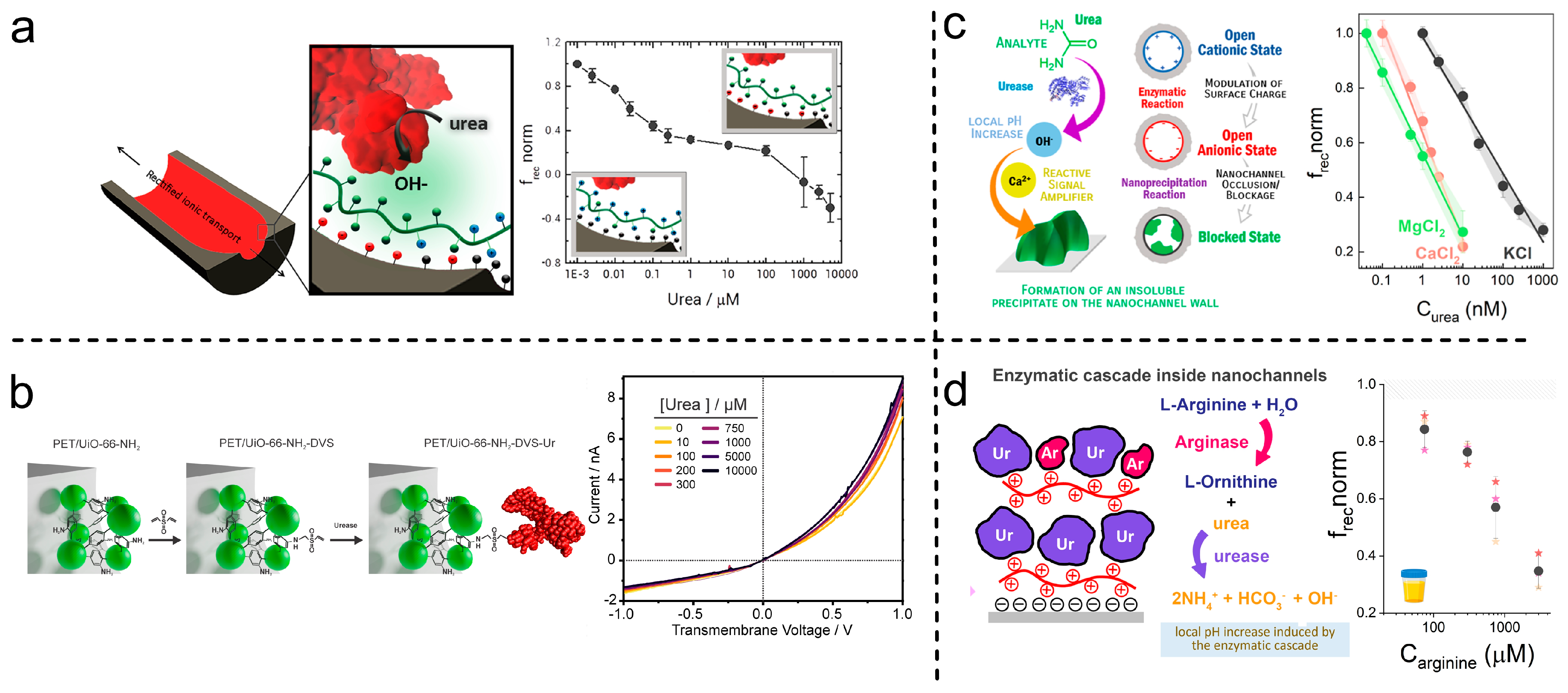
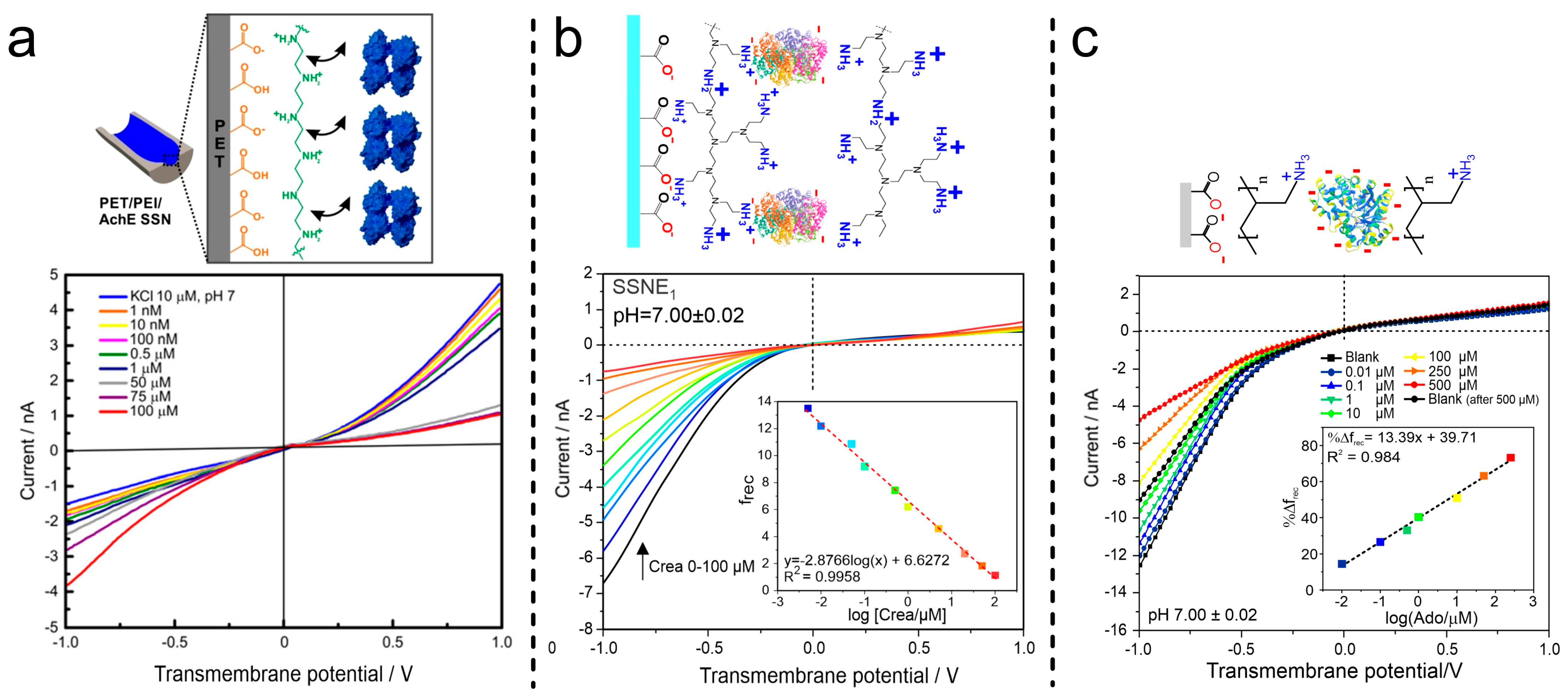
- Pérez-Mitta, G.; Peinetti, A.S.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Azzaroni, O. Highly Sensitive Biosensing with Solid-State Nanopores Displaying Enzymatically Reconfigurable Rectification Properties. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toum Terrones, Y.; Laucirica, G.; Cayón, V.M.; Fenoy, G.E.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Mamisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Highly Sensitive Acetylcholine Biosensing via Chemical Amplification of Enzymatic Processes in Nanochannels. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10166–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinetti, A.S.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Azzaroni, O. Nanoprecipitation-Enhanced Sensitivity in Enzymatic Nanofluidic Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 5282–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, L.M.H.; Laucirica, G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Marmisollé, W.; Azzaroni, O. Sensing Creatinine in Urine via the Iontronic Response of Enzymatic Single Solid-State Nanochannels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 268, 116893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramajo, M.E.; Otero Maffoni, L.; Hernández Parra, L.M.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Peinetti, A.S.; Azzaroni, O. Harnessing Concerted Functions in Confined Environments: Cascading Enzymatic Reactions in Nanofluidic Biosensors for Sensitive Detection of Arginine. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Root, D.; Vutsadakis, V.; Dmitriev, S.N. Effect of Nanosized Surfactant Molecules on the Etching of Ion Tracks: New Degrees of Freedom in Design of Pore Shape. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2003, 209, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Dmitriev, S.N.; Mamonova, T.I.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Sartowska, B.; Yamauchi, Y. Surfactant-Controlled Etching of Ion Track Nanopores and Its Practical Applications in Membrane Technology. Radiat. Meas. 2008, 43, S552–S559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Ensinger, W.; Mujahid, S.A.; Maaz, K.; Khan, E.U. Effect of Etching Conditions on Pore Shape in Etched Ion-Track Polycarbonate Membranes. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yan, J.; Li, J. Small-Molecule Triggered Cascade Enzymatic Catalysis in Hour-Glass Shaped Nanochannel Reactor for Glucose Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10546–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, D.; Boda, D.; He, Y.; Apel, P.; Siwy, Z.S. Synthetic Nanopores as a Test Case for Ion Channel Theories: The Anomalous Mole Fraction Effect without Single Filing. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.S. Ion-Current Rectification in Nanopores and Nanotubes with Broken Symmetry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhang, H.; Xie, G.; Xiao, K.; Wen, L.; Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Ultratrace Detection of Glucose with Enzyme-Functionalized Single Nanochannels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19131–19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mitta, G.; Marmisolle, W.A.; Burr, L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Azzaroni, O. Proton-Gated Rectification Regimes in Nanofluidic Diodes Switched by Chemical Effectors. Small 2018, 14, 1703144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Dmitriev, S.N. Diode-like Ion-Track Asymmetric Nanopores: Some Alternative Methods of Fabrication. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2009, 267, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, K.; Scheuerlein, M.C.; Ali, M.; Nasir, S.; Ensinger, W. Enhancement of Heavy Ion Track-Etching in Polyimide Membranes with Organic Solvents. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huamani, A.L.; Laucirica, G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Marmisollé, W.; Azzaroni, O.; Rafti, M. Expanding the Synergy between MOFs and Solid-State-Nanochannels: Post-Synthetic Modification for the Covalent Anchoring of Urease in Urea Detection. to be submitted.
- Miguel Hernandez Parra, L.; Gramajo, M.E.; Maffoni, L.O.; Gregorio, L.; Peinetti, A.S.; Cortez, M.L.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Waldemar, A.M.; Azzaroni, O. Single Nanochannel-Based Iontronic Detection of Adenosine at Nanomolar Concentrations. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Gu, D.; Liu, Q. Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing Based on Inner Surfaces Modification of Solid-State Nanopore. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Ramirez, P.; Tahir, M.N.; Mafe, S.; Siwy, Z.; Neumann, R.; Tremel, W.; Ensinger, W. Biomolecular Conjugation inside Synthetic Polymer Nanopores via Glycoprotein–Lectin Interactions. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Tahir, M.N.; Siwy, Z.; Neumann, R.; Tremel, W.; Ensinger, W. Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing with Horseradish Peroxidase-Modified Polymer Single Conical Nanochannels. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, K.; Fardoost, A.; Mhatre, N.; Rajan, J.; Boisvert, D.; Javanmard, M. A Thorough Review of Emerging Technologies in Micro- and Nanochannel Fabrication: Limitations, Applications, and Comparison. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Dai, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, W.; Shan, W.; Duan, H. Recent Advances in Focused Ion Beam Nanofabrication for Nanostructures and Devices: Fundamentals and Applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 1529–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melngailis, J. Focused Ion Beam Technology and Applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 1987, 5, 469–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, K.; Losic, D. FIB Nanostructures; Wang, Z.M., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Nanoscale Science and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 20, ISBN 978-3-319-02873-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Review in Manufacturing Methods of Nanochannels of Bio-Nanofluidic Chips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, A.A. Recent Developments in Nanofabrication Using Focused Ion Beams. Small 2005, 1, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedev, D.; Malyshev, G.; Ryzhkov, I.; Mozharov, A.; Shugurov, K.; Sharov, V.; Panov, M.; Tumkin, I.; Afonicheva, P.; Evstrapov, A.; et al. Focused Ion Beam Milling Based Formation of Nanochannels in Silicon-Glass Microfluidic Chips for the Study of Ion Transport. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnković, A.; Srnko, M.; Anderluh, G. Biological Nanopores: Engineering on Demand. Life 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Nothling, M.D.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Q.; Qiao, G.G. Thin Film Composite Membranes for Postcombustion Carbon Capture: Polymers and Beyond. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 126, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, R.B. Silicon Nitride Ceramics: Structure, Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Greener Routes for Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, J.V. Pet Waste Management by Chemical Recycling: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephans, L.E.; Myles, A.; Thomas, R.R. Kinetics of Alkaline Hydrolysis of a Polyimide Surface. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4706–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sypabekova, M.; Hagemann, A.; Rho, D.; Kim, S. Review: 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) Deposition Methods on Oxide Surfaces in Solution and Vapor Phases for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors 2022, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.I.; Rao, S.; Sansom, M.S.P. Water in Nanopores and Biological Channels: A Molecular Simulation Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10298–10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Kong, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, K.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Light- and Electric-Field-Controlled Wetting Behavior in Nanochannels for Regulating Nanoconfined Mass Transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4552–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkner, J.P.; Poolman, B.; Koçer, A. Hydrophobic Gating of Mechanosensitive Channel of Large Conductance Evidenced by Single-Subunit Resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12944–12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckstein, O.; Sansom, M.S.P. Liquid–Vapor Oscillations of Water in Hydrophobic Nanopores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7063–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, M.R.; Cleary, L.; Davenport, M.; Shea, K.J.; Siwy, Z.S. Electric-Field-Induced Wetting and Dewetting in Single Hydrophobic Nanopores. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, X.-Y.; Xie, G.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Electrostatic-Charge- and Electric-Field-Induced Smart Gating for Water Transportation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9703–9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junk, A.; Riess, F. From an Idea to a Vision: There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom. Am. J. Phys. 2006, 74, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouaux, E.; MacKinnon, R. Principles of Selective Ion Transport in Channels and Pumps. Science 2005, 310, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, B. Nanoconfined Fluids: What Can We Expect from Them? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 4678–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plecis, A.; Schoch, R.B.; Renaud, P. Ionic Transport Phenomena in Nanofluidics: Experimental and Theoretical Study of the Exclusion-Enrichment Effect on a Chip. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silies, L.; Andrieu-Brunsen, A. Programming Ionic Pore Accessibility in Zwitterionic Polymer Modified Nanopores. Langmuir 2018, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Saidi, M.H.; Moosavi, A.; Kröger, M. Tuning Electrokinetic Flow, Ionic Conductance, and Selectivity in a Solid-State Nanopore Modified with a PH-Responsive Polyelectrolyte Brush: A Molecular Theory Approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 18513–18531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, F.M.; Tagliazucchi, M.; Azzaroni, O.; Szleifer, I. Ionic Conductance of Polyelectrolyte-Modified Nanochannels: Nanoconfinement Effects on the Coupled Protonation Equilibria of Polyprotic Brushes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4789–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliazucchi, M.; Azzaroni, O.; Szleifer, I. Responsive Polymers End-Tethered in Solid-State Nanochannels: When Nanoconfinement Really Matters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12404–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliazucchi, M.; Szleifer, I. Stimuli-Responsive Polymers Grafted to Nanopores and Other Nano-Curved Surfaces: Structure, Chemical Equilibrium and Transport. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7292–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucirica, G.; Hernández Parra, L.M.; Huamani, A.L.; Wagner, M.F.; Albesa, A.G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Marmisollé, W.; Azzaroni, O. Insight into the Transport of Ions from Salts of Moderated Solubility through Nanochannels: Negative Incremental Resistance Assisted by Geometry. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 12599–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurupath, V.P.; Coasne, B. Mixture Adsorption in Nanoporous Zeolite and at Its External Surface: In-Pore and Surface Selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 9596–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Pan, S.; Qian, J.; Pan, B. Metastable Zirconium Phosphate under Nanoconfinement with Superior Adsorption Capability for Water Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. Enzyme Catalysis Induced Polymer Growth in Nanochannels: A New Approach to Regulate Ion Transport and to Study Enzyme Kinetics in Nanospace. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ye, D.-K.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lu, T.; Xia, X.-H. Insights into the “Free State” Enzyme Reaction Kinetics in Nanoconfinement. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiguji, H. Ion Transport in Nanofluidic Channels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmerich, T.; Ronceray, N.; Agrawal, K.V.; Garaj, S.; Kumar, M.; Noy, A.; Radenovic, A. Nanofluidics. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2024, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliazucchi, M.; Szleifer, I. Transport Mechanisms in Nanopores and Nanochannels: Can We Mimic Nature? Mater. Today 2015, 18, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, R.B.; Han, J.; Renaud, P. Transport Phenomena in Nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Davoodabadi, A.; Huang, D.; Luo, T.; Ghasemi, H. Transport Phenomena in Nano/Molecular Confinements. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16348–16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Han, Y.; Jin, W. Artificial Channels for Confined Mass Transport at the Sub-Nanometre Scale. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayannidis, G.P.; Chatziavgoustis, A.P.; Achilias, D.S. Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Recycling and Recovery of Pure Terephthalic Acid by Alkaline Hydrolysis. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2002, 21, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, R.; Fan, R.; Yue, M.; Li, D.; Yang, P.; Majumdar, A. Electrostatic Control of Ions and Molecules in Nanofluidic Transistors. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Revil, A. Electrochemical Charge of Silica Surfaces at High Ionic Strength in Narrow Channels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, D.; Kruithof, M.; Dekker, C. Surface-Charge-Governed Ion Transport in Nanofluidic Channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 035901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Abbas, Z.; Kleibert, A.; Green, R.G.; Goel, A.; May, S.; Squires, T.M. Determination of Surface Potential and Electrical Double-Layer Structure at the Aqueous Electrolyte-Nanoparticle Interface. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblhoff-Dier, K.; Koper, M.T.M. Modeling the Gouy–Chapman Diffuse Capacitance with Attractive Ion–Surface Interaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 16664–16673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, Ø.G.; Heiskanen, A. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 9780128191071. [Google Scholar]
- Stojek, Z. The Electrical Double Layer and Its Structure. In Electroanalytical Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–9. ISBN 978-3-642-02915-8. [Google Scholar]
- Saboorian-Jooybari, H.; Chen, Z. Calculation of Re-Defined Electrical Double Layer Thickness in Symmetrical Electrolyte Solutions. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Ottewill, R.H., Rowell, R.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; 399p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Perry, J.M.; Jacobson, S.C. Transport and Sensing in Nanofluidic Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 4, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Alibakhshi, M.A.; Xie, Q.; Riordon, J.; Xu, Y.; Duan, C.; Sinton, D. Exploring Anomalous Fluid Behavior at the Nanoscale: Direct Visualization and Quantification via Nanofluidic Devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparreboom, W.; van den Berg, A.; Eijkel, J.C.T. Principles and Applications of Nanofluidic Transport. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, D.G.; Harms, Z.D.; Jacobson, S.C. Electroosmotic Flow in Nanofluidic Channels. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11174–11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, W.; Li, C. Ion Current Rectification in Asymmetric Nanochannels: Effects of Nanochannel Shape and Surface Charge. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 208, 124038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucirica, G.; Albesa, A.G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Shape Matters: Enhanced Osmotic Energy Harvesting in Bullet-Shaped Nanochannels. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Seifollahi, Z.; Khatibi, M.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Impacts of the Shape of Soft Nanochannels on Their Ion Selectivity and Current Rectification. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 399, 139376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Sherwood, J.D.; Chang, H.-C. Solid-State Nanopore Hydrodynamics and Transport. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Guo, W.; Jiang, L. Biomimetic Smart Nanopores and Nanochannels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2385–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubeil, C.; Bund, A. The Role of Nanopore Geometry for the Rectification of Ionic Currents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7866–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, J.; Schiedt, B.; Neumann, R.; Mafé, S.; Ramírez, P. Ionic Conduction, Rectification, and Selectivity in Single Conical Nanopores. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, P.; Apel, P.Y.; Cervera, J.; Mafé, S. Pore Structure and Function of Synthetic Nanopores with Fixed Charges: Tip Shape and Rectification Properties. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 315707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Asymmetric Ion Transport through Ion-Channel-Mimetic Solid-State Nanopores. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, P.Y.; Hsu, J.P. Influence of Shape and Charged Conditions of Nanopores on Their Ionic Current Rectification, Electroosmotic Flow, and Selectivity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 658, 130696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Biomimetic Solid-State Nanochannels: From Fundamental Research to Practical Applications. Small 2016, 12, 2810–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, H.S.; Bund, A. Ion Current Rectification at Nanopores in Glass Membranes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Smirnov, S.; Siwy, Z. Ionic Selectivity of Single Nanochannels. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yameen, B.; Ali, M.; Neumann, R.; Ensinger, W.; Knoll, W.; Azzaroni, O. Ionic Transport Through Single Solid-State Nanopores Controlled with Thermally Nanoactuated Macromolecular Gates. Small 2009, 5, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punekar, N.S. ENZYMES: Catalysis, Kinetics and Mechanisms; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; ISBN 978-981-97-8178-2. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.M.; Gatto, G.J.; Hines, J.K.; Tymoczko, J.L. Biochemistry; Macmillan Learning: New York, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 1319417469. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Kyratzis, I. Covalent Immobilization of Proteins on Carbon Nanotubes Using the Cross-Linker 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)Carbodiimide—A Critical Assessment. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, A.; Giesbers, M.; Rosso, M.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; Schroën, K.; White, R.G.; Yang, L.; Linford, M.R.; Zuilhof, H. Covalent Biofunctionalization of Silicon Nitride Surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6233–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Rocha-Martin, J.; Moreno-Gamero, D. Enzyme Immobilization Strategies for the Design of Robust and Efficient Biocatalysts. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 35, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Russell, T.P.; Shi, S. Layer-by-Layer Engineered All-Liquid Microfluidic Chips for Enzyme Immobilization. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariga, K.; Ji, Q.; Hill, J.P. Enzyme-Encapsulated Layer-by-Layer Assemblies: Current Status and Challenges Toward Ultimate Nanodevices. In Modern Techniques for Nano- and Microreactors/-Reactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 51–87. ISBN 978-3-642-12873-8. [Google Scholar]
- Argaman, O.; Ben-Barak Zelas, Z.; Fishman, A.; Rytwo, G.; Radian, A. Immobilization of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase on Montmorillonite Using Polyethyleneimine as a Stabilization and Bridging Agent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 212, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, D.; del Agua, I.; Schaafsma, W.; ElMahmoudy, M.; Uguz, I.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Sardon, H.; Castro, B.; Malliaras, G.G.; Mecerreyes, D. Low-Temperature Cross-Linking of PEDOT:PSS Films Using Divinylsulfone. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18254–18262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.; Elremaily, M.; Hernández-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Rajora, P. Optimization of the Activity in Porous Media of Proton-generating Immobilized Enzymatic Reactions by Weak Acid Facilitation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1985, 27, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; An, P.; Qin, C.; Sun, C.-L.; Sun, M.; Ji, Z.; Wang, C.; Du, G.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y. Bioinspired Dual-Responsive Nanofluidic Diodes by Poly-L-Lysine Modification. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4501–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Hou, L.; Duan, X.; Shi, T.; Li, W.; Shi, A.-C. Translocation of Micelles through a Nanochannel. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 6487–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Ion/Molecule Transportation in Nanopores and Nanochannels: From Critical Principles to Diverse Functions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8658–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Sirkin, Y.A.; Vigil De Maio, M.; Tagliazucchi, M. Mechanisms of Enzymatic Transduction in Nanochannel Biosensors. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilozny, B.; Actis, P.; Seger, R.A.; Pourmand, N. Dynamic Control of Nanoprecipitation in a Nanopipette. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Jimenez, M.; Lugli-Arroyo, J.; Fenoy, G.E.; Piccinini, E.; Knoll, W.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Transduction of Amine–Phosphate Supramolecular Interactions and Biosensing of Acetylcholine through PEDOT-Polyamine Organic Electrochemical Transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 61419–61427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucirica, G.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Dangerous Liaisons: Anion-Induced Protonation in Phosphate–Polyamine Interactions and Their Implications for the Charge States of Biologically Relevant Surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 8612–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucirica, G.; Pérez-Mitta, G.; Toimil-Molares, M.E.; Trautmann, C.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Amine-Phosphate Specific Interactions within Nanochannels: Binding Behavior and Nanoconfinement Effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 28997–29007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technology | Materials | Diameter (nm) | Shape | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBL + RIE | Si3N4 | Around 20 | Rectangular | [55] |
| RIE/FIB + IBS | Si3N4 | 1.8–100 | Cylindrical-bowl-shaped cavity | [56] |
| FIB + IBS | Si3N4/Si | >1 | Cylindrical-bowl-shaped cavity | [57] |
| FIB | Au/Si3N4/Au; PFA/Si3N4/PFA | 20–140 | Conically narrowing | [58] |
| EE-PEO | PDMS | >100 | Cylindrical | [59] |
| Bench-top | Glass based | >86 | Conical | [60] |
| Bench-top/laser pulling | Glass based | >40 | Hourglass | [61] |
| Thermal pulling | Glass based borosilicate | Around 30 | Surficial (rectangular and conical) | [62] |
| EB + dry etching + FIB | Silica glass substrate | 58–655 | Conical-trumpet-shaped | [63] |
| Ion-track + dry plasma etching | PC | 10–1000 variable | Etching-dependent | [64] |
| Ion-track + UV exposure + chemical etching | PET, PC, PP, PVDF, PI | 5–300 variable | [65] | |
| PET | 50–600 variable | [66] | ||
| Ion-track + UV exposure + chemical/electrochemical etching | PC | >2 nm variable | [67] | |
| Ion-track + chemical/electrochemical etching | PET, PC, PI, PVDF | [30] | ||
| Ion-track + chemical etching | PET, PC, PI, PVDF, PP | [68] | ||
| PET, PC, PI, PVDF, SiO2, Mica | [69] | |||
| PET, PC, PI, PVDF, PP, CR39 | [70] | |||
| PET | [71] | |||
| PET, PC | >100 variable | [72] | ||
| PI | 10–1000 variable | [73] | ||
| SiN | >100 | [74] |
| KCl (M) | (nm) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 0.3 |
| 10−1 | 1.0 |
| 10−2 | 3.1 |
| 10−3 | 9.6 |
| 10−4 | 30.5 |
| 10−5 | 96.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández Parra, L.M.; Azzaroni, O.; Marmisollé, W.A. Enzyme-Based Single Solid-State Nanochannel Biosensors. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080275
Hernández Parra LM, Azzaroni O, Marmisollé WA. Enzyme-Based Single Solid-State Nanochannel Biosensors. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(8):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080275
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández Parra, L. Miguel, Omar Azzaroni, and Waldemar A. Marmisollé. 2025. "Enzyme-Based Single Solid-State Nanochannel Biosensors" Chemosensors 13, no. 8: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080275
APA StyleHernández Parra, L. M., Azzaroni, O., & Marmisollé, W. A. (2025). Enzyme-Based Single Solid-State Nanochannel Biosensors. Chemosensors, 13(8), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080275






