A Carbazole-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission “Turn-On” Sensor for Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
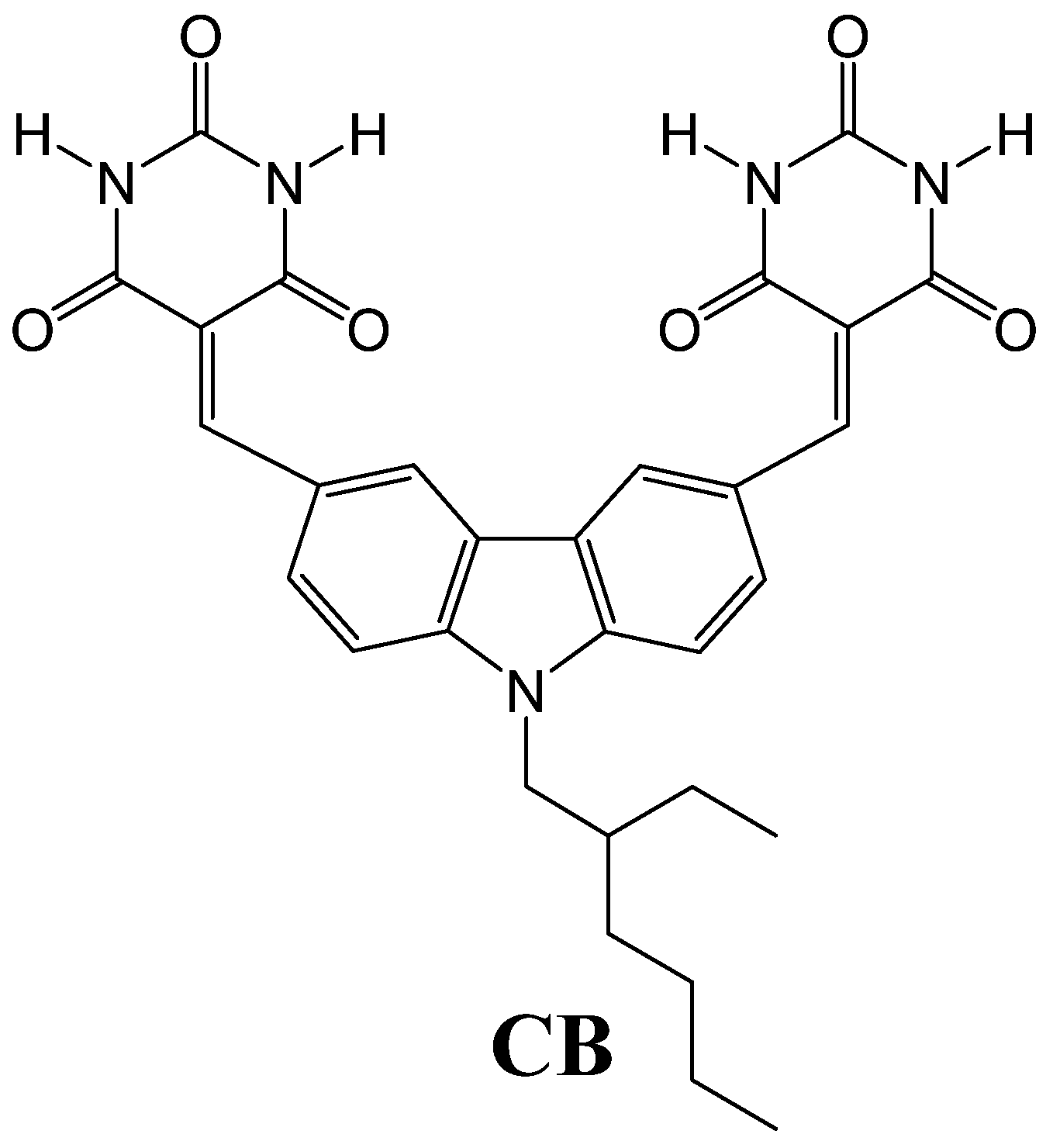
2.2. Preparation of CB Aggregates
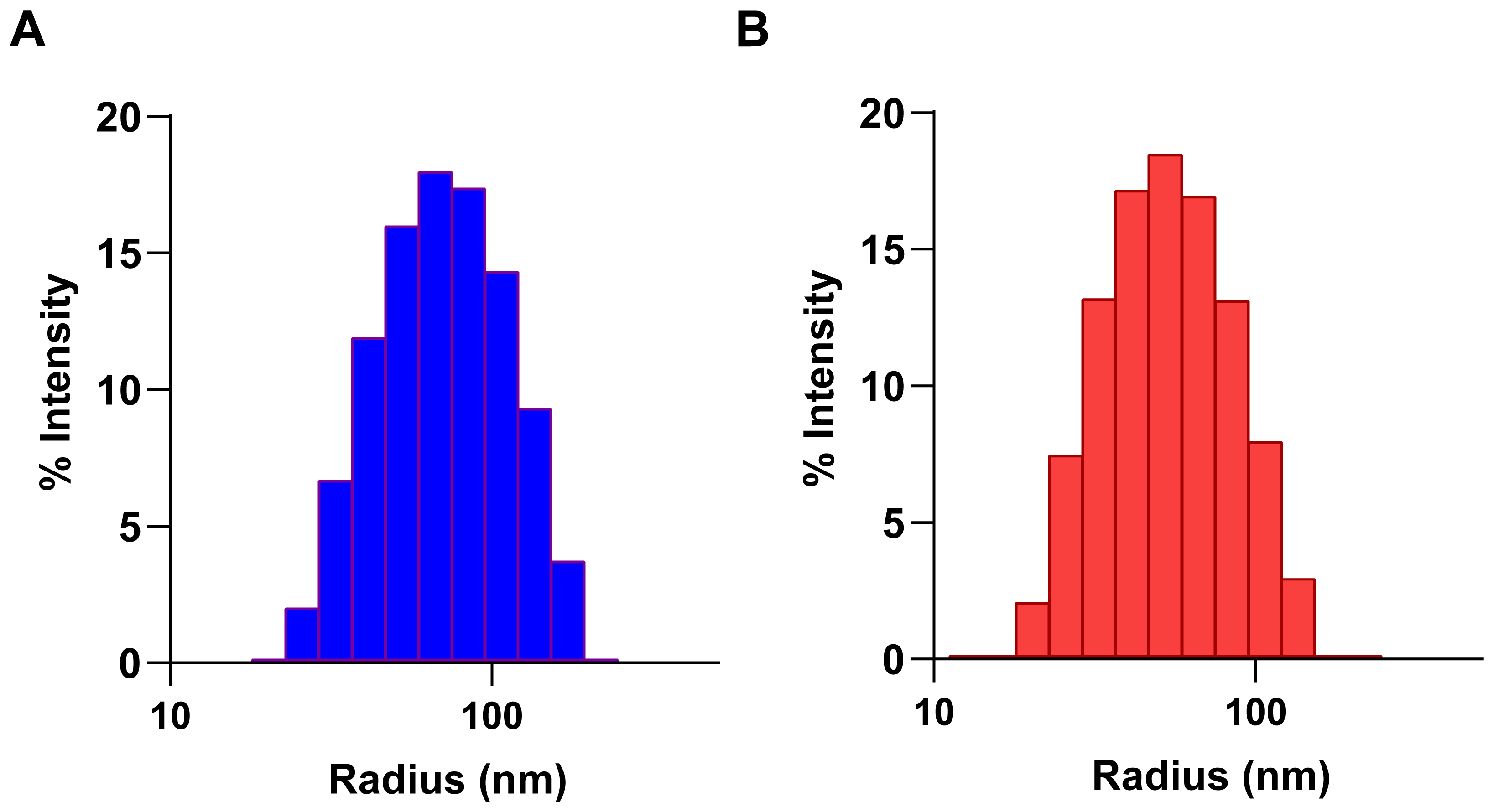
2.3. Particle Size Distribution Analysis on Nanoaggregates
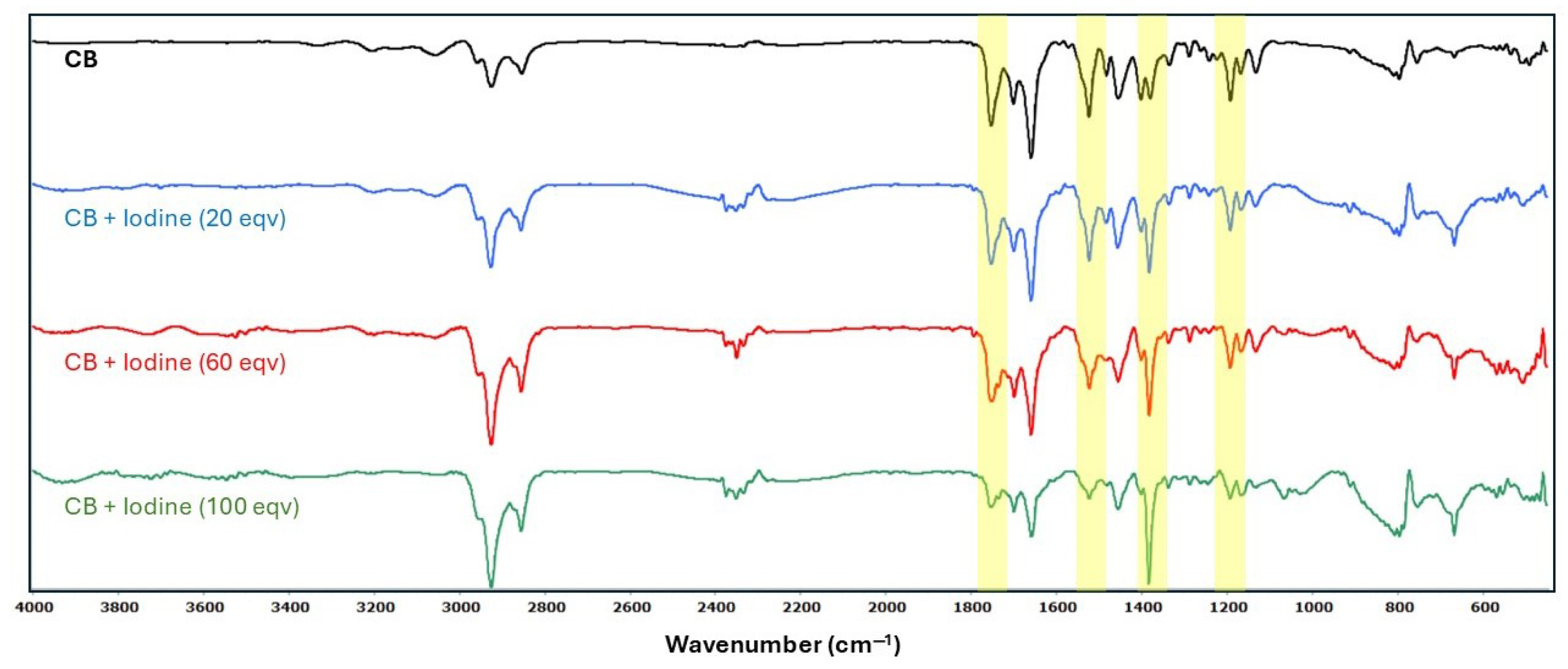
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry (FTIR)
2.5. Fluorescence Detection of Iodine and Hg2+
2.6. Study on Fluorescence Response of CB Towards Different Cationic Metal Ions
3. Results and Discussion
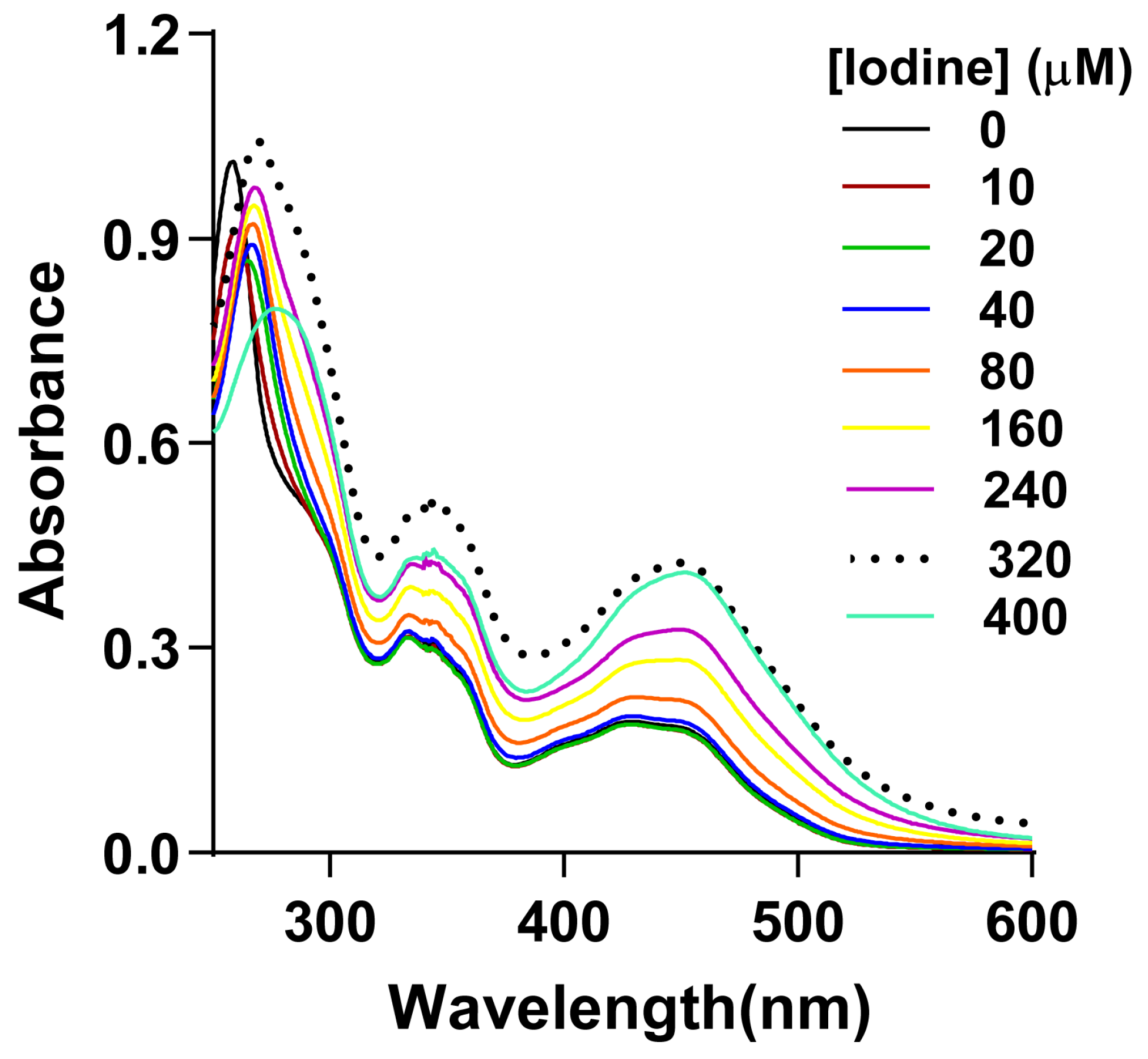
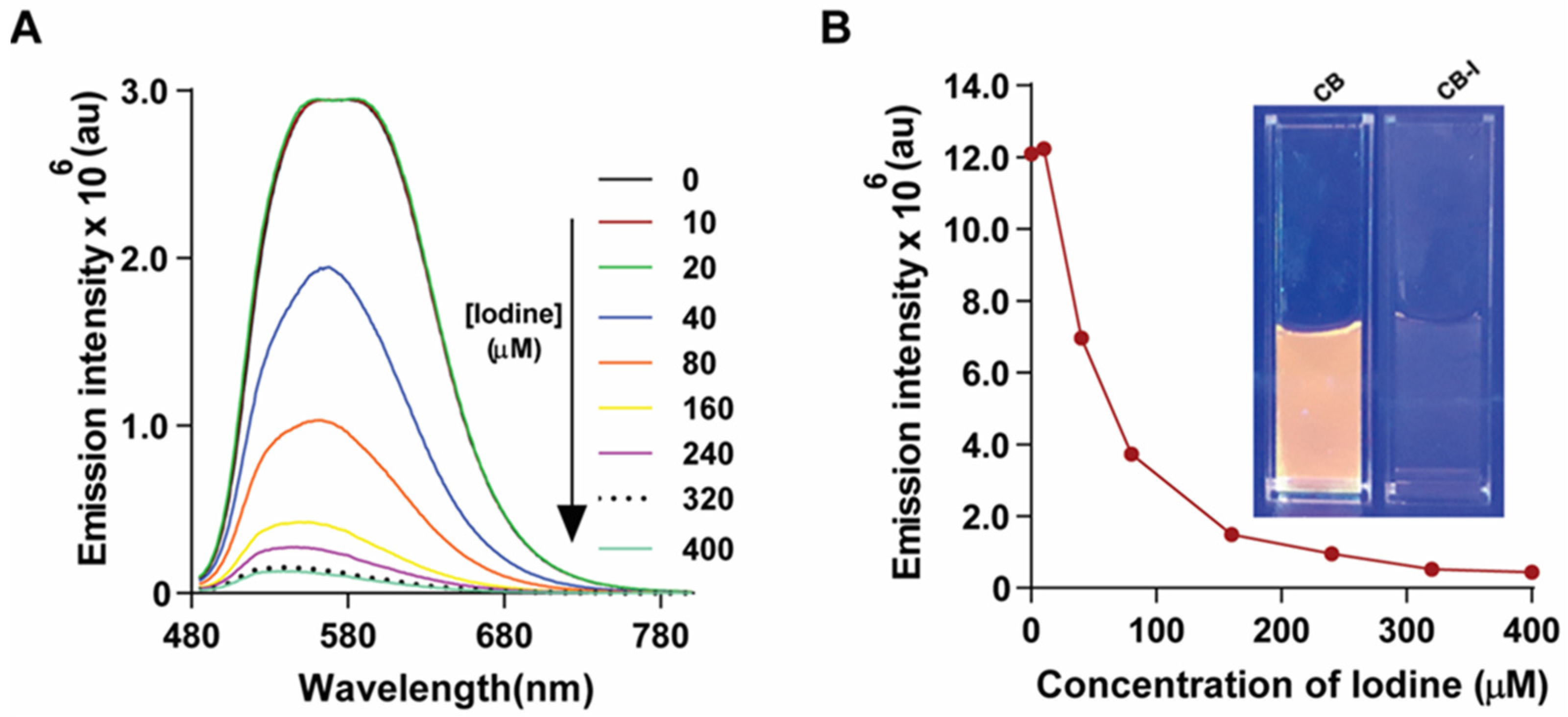
3.1. Effect of Elemental Iodine on CB
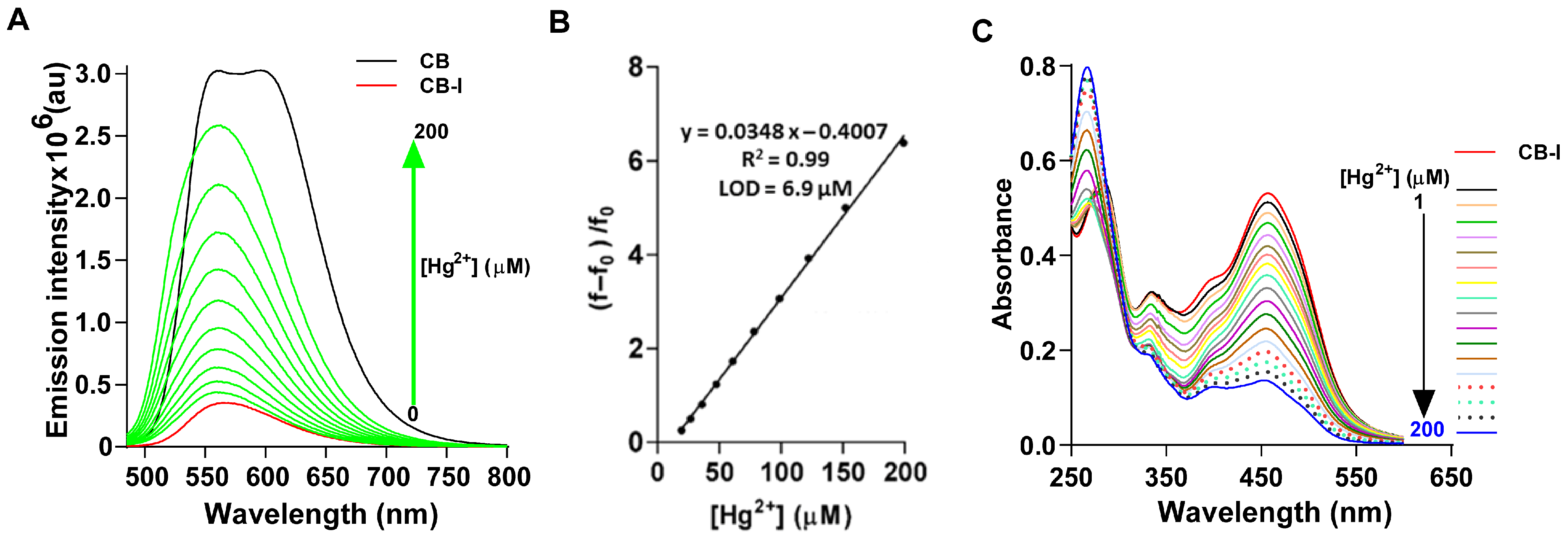
3.2. Effect of Hg2+ on Emission of CB-I
3.3. Effect of Metal Cations on the Fluorescent Detection of Hg2+ Ions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keremane, K.S.; Acharya, M.G.; Naik, P.; Malakar, C.C.; Wang, K.; Poudel, B. Recent Advances in Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Fluorescent Sensors for Biomolecule Detection. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Gao, G.; Luo, G.; Tang, B.Z. Biomedical Application of Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen-Based Fluorescent Sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.; Zhang, L. Near-infrared Aggregation-induced Emission Materials: Bibliometric Analysis and Their Application in Biomedical Field. Aggregate 2024, 5, e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaelpourfarkhani, M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Aggregation-Induced Emission-Based Aptasensors for the Detection of Various Targets: Recent Progress. Talanta 2025, 292, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J.; Guo, J.; Li, D. Aggregation-Induced Emission(AIE)for next-Generation Biosensing and Imaging: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 271, 117067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Ke, C.; Tang, B.Z. Journey of Aggregation-Induced Emission Research. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3267–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, R.; Vitor, R.F.; Al-Sayah, M.H. A Fluorescence-Based Chemical Sensor for Detection of Melamine in Aqueous Solutions. Chemosensors 2021, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, R.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Development of Liposome-Based Immunoassay for the Detection of Cardiac Troponin I. Molecules 2021, 26, 6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, R.; Shahzadi, S.K.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Fluorescent Immunoassays for Detection and Quantification of Cardiac Troponin I: A Short Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, B.; Li, H.; Ren, S.; Wu, J.-R.; Wang, H. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Probes in Fluorescent Sensing: Progress and Applications for Pesticide Detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xiong, L.-H.; He, X. Applications of Aggregation-Induced Emission Materials in Immunology: From Diagnostics to Immunotherapy. Chem. Biomed. Imaging 2025, cbmi.5c00016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, S.; Mouli, M.S.S.V.; Tamrakar, A.; Wani, M.A.; Mishra, A.K.; Pandey, R.; Pandey, M.D. Recent Advances in AIEgen-Based Chemosensors for Small Molecule Detection, with a Focus on Ion Sensing. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 4431–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, R. AIE Polymers for Biosensing Applications. Polym. Chem. 2025, 16, 1897–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Miao, R.; Chen, H. Inorganic-Based Aggregation-Induced Luminescent Materials: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xing, J.; Gong, Q.; Chen, L.-C.; Liu, G.; Yao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.-L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q. Reducing Aggregation Caused Quenching Effect through Co-Assembly of PAH Chromophores and Molecular Barriers. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: A Trailblazing Journey to the Field of Biomedicine. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1768–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B. Zinc (II) and AIEgens: The “Clip Approach” for a Novel Fluorophore Family. A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Caruso, U.; Gentile, F.S.; Di Costanzo, L.; Panunzi, B. A Novel L-Shaped Fluorescent Probe for AIE Sensing of Zinc (II) Ion by a DR/NIR Response. Molecules 2021, 26, 7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Nurchi, V.M.; Sahoo, S.K. Mercury Toxicity and Detection Using Chromo-Fluorogenic Chemosensors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadhane, K.S.; Bhosale, S.R.; Gunjal, D.B.; Nille, O.S.; Kolekar, G.B.; Kolekar, S.S.; Dongale, T.D.; Anbhule, P.V. Tetraphenylethene-Based Fluorescent Chemosensor with Mechanochromic and Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Properties for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Hg2+ and Ag+ Ions in Aqueous Media: Application to Environmental Analysis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 34888–34900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, T.; Möslein, A.F.; Mollick, S.; Kachwal, V.; Babal, A.S.; Amin, N.; Tan, J.-C. Nanoconfinement of Tetraphenylethylene in Zeolitic Metal-Organic Framework for Turn-on Mechanofluorochromic Stress Sensing. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Li, P.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, N.; Zhao, N. A Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Sensor with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for the Detection of Iodide and Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10479–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqadas; Shabbir, A.; Khan, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Khan, A.M.; Shahzad, S.A. Synthesis and Construction of AIE Based Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Solid Phase Sensing of 4-Nitroaniline: Solvatochromism, Acidochromism, Mechanochromism and Applications in Latent Fingerprints and Invisible Ink. Microchem. J. 2025, 214, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Enhanced AIE and Different Stimuli-Responses in Red Fluorescent (1,3-Dimethyl)Barbituric Acid-Functionalized Anthracenes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-S.; Osman, A.I.; Hosny, M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Rooney, D.W.; Chen, Z.; Rahim, N.S.; Sekar, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; et al. The Toxicity of Mercury and Its Chemical Compounds: Molecular Mechanisms and Environmental and Human Health Implications: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5100–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Umesh, M.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Duhan, L.; Gummadi, S.N.; Pasrija, R.; Jayaraj, I.; Dasarahally Huligowda, L.K. A Retrospection on Mercury Contamination, Bioaccumulation, and Toxicity in Diverse Environments: Current Insights and Future Prospects. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, H.; Melles, S.J.; Laursen, A.E. Does Selenium Offset Methylmercury Toxicity across Trophic Levels in a Primary Producer, Auxenochlorella Pyrenoidosa, and a Detritovore, Aeolosoma Variegatum? FACETS 2025, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Mercury Exposure and Health Effects: What Do We Really Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, E.; Silva, I.; Nyland, J. Mercury and Autoimmunity: Implications for Occupational and Environmental Health. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 207, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Yang, L. Mercury-Induced Toxicity: Mechanisms, Molecular Pathways, and Gene Regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 943, 173577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M. Estimating Detection Limits in Chromatography from Calibration Data: Ordinary Least Squares Regression vs. Weighted Least Squares. Separations 2018, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Huang, W.; Lin, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, H. Adsorptive Separation of Aromatic Compounds from Alkanes by π–π Interactions in a Carbazole-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56385–56392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refat, M.S.; El-Didamony, A.M.; Grabchev, I. UV–Vis, IR Spectra and Thermal Studies of Charge Transfer Complex Formed between Poly(Amidoamine) Dendrimers and Iodine. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 67, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, S.; Walker, L.A.; Sension, R.J. Femtosecond Studies of the Iodine–Mesitylene Charge-Transfer Complex. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 7877–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Guo, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Feng, S.; Lin, Y. Robust Fluorescent Detection of Iodine Vapor by a Film Sensor Based on a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Wang, Z.; Tan, L.; Shang, L. Tailoring Electron-Rich Fluorescent Supramolecular Organic Frameworks for Efficient Capture and Visual Monitoring of Iodine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2413694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciureanu, M. Infrared Studies of Iodine Complexes with Several Aromatic Amines. Adv. Mol. Relax. Interact. Process. 1979, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.T.; Khan, A. Polyiodine and Polyiodide Species in an Aqueous Solution of Iodine + KI: Theoretical and Experimental Studies. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, A.M.; Chappa, S.; Ojha, S.; Pandey, A.K. Functionalized Glass Fiber Membrane for Extraction of Iodine Species. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashukha, H.L.; Sitanurak, J.; Sulistyarti, H.; Nacapricha, D.; Uraisin, K. Simple and Equipment-Free Paper-Based Device for Determination of Mercury in Contaminated Soil. Molecules 2021, 26, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.; Li, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Redshaw, C.; Feng, X.; Lam, J.W.Y.; et al. Pyrene-Based Blue Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens: The Synergistic Effect of Through-Space Conjugation for High Exciton Utilization Efficiency and Narrow-Band and Blue OLEDs. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2025, 13, 2402567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Perebikovsky, A.; Benice, O.; Holmberg, S.; Madou, M.; Ghazinejad, M. Rapid Iodine Sensing on Mechanically Treated Carbon Nanofibers. Sensors 2018, 18, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, F.; Wei, P.; Lei, Y. Mechanism of Mercury-Iodine Species Binding on Carbonaceous Surface: Insight from Density Functional Theory Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayindir, S.; Hussein, A.S.; Lafzi, F.; Toprak, M. The Switchable Fluorescent Detection of Mercury, Copper, and Iodine in Real Water Samples Using Bola-Amphiphilic-Tetraphenylethene. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 382, 121939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Su, M. Enhanced Turn-On Fluorescence Detection of Aqueous Lead Ions with Size-Shrinkable Hydrogels. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11897–11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radha, R.; Valliyengal, M.S.; Al-Sayah, M.H. A Carbazole-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission “Turn-On” Sensor for Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080276
Radha R, Valliyengal MS, Al-Sayah MH. A Carbazole-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission “Turn-On” Sensor for Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(8):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080276
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadha, Remya, Mohammed S. Valliyengal, and Mohammad H. Al-Sayah. 2025. "A Carbazole-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission “Turn-On” Sensor for Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution" Chemosensors 13, no. 8: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080276
APA StyleRadha, R., Valliyengal, M. S., & Al-Sayah, M. H. (2025). A Carbazole-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission “Turn-On” Sensor for Mercury Ions in Aqueous Solution. Chemosensors, 13(8), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080276





