Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to infer a dynamic graph as a global (collective) model of time-varying measurements at a set of network nodes. This model captures both pairwise as well as higher order interactions (i.e., more than two nodes) among the nodes. The motivation of this work lies in the search for a connectome model which properly captures brain functionality across all regions of the brain, and possibly at individual neurons. We formulate it as an optimization problem, a quadratic objective functional and tensor information of observed node signals over short time intervals. The proper regularization constraints reflect the graph smoothness and other dynamics involving the underlying graph’s Laplacian, as well as the time evolution smoothness of the underlying graph. The resulting joint optimization is solved by a continuous relaxation of the weight parameters and an introduced novel gradient-projection scheme. While the work may be applicable to any time-evolving data set (e.g., fMRI), we apply our algorithm to a real-world dataset comprising recorded activities of individual brain cells. The resulting model is shown to be not only viable but also efficiently computable.
1. Introduction
The increased and ubiquitous emergence of graphs provides a great approach for quantifying interaction between different elements in a great variety of network-based applications. Analyzing and discovering the underlying structure of a graph for a given dataset has become central to various signal processing research problems with such a potential interpretation. For example, in social media [1] (e.g., Facebook and LinkedIn), the basic interaction/relation between two individuals being represented by a link, yields the notion of a graph known as the social network, which is used for inferring further characteristics among all involved individuals [2]. The power of the graph representation paradigm is in fact so fundamental that it captures the very structure of life [3,4], namely the interactions among atoms/molecules to reflect the behavior of different materials or bacteria. The rather recent connectome paradigm [5] in neuroscience is based on the hypothesis that the brain is a massively connected network due to its activity and connectivity. The network connectivity, hence behavioral variation, is in response to an external stimulus, may be used to investigate a brain’s structure and its functionality [6,7]. In our validation of this framework, we consider sparse images of the brain’s visual cortex where non-zero components vary in time. Our proposed approach is just as applicable to dense images as well as medium-dense images such as Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging data. Our ready access to and experience in the data at hand thus influenced the choice.
Establishing connectivity among neurons, currently follows two main approaches, (i) Noise correlation analysis [8,9], often used in neuroscience to uncover the connectivity among neurons, (ii) Static graph learning [10,11] used to extract a fixed graph over time. When noise correlation is significant, it is commonly used in neuroscience as a short-time connectivity metric between every pair of neurons. Requiring abundant observations, this method cannot, however, yield an acceptable and reliable connectivity estimate over an observation interval. Additionally, the acquired connectivity does not yield simple rationalization following an experiment with a specific stimulus. To that end, and for additional interpretational potential, graph structures that are learned from data have been of great research interest. Research in this direction has pervasively been based on graphs’ topology and signals’ smoothness, as well as the application of the graph Laplacian. Other recent work includes deep neural network modeling, for which training/testing was performed on graph datasets to generate a graph, representing patterns under given signals ultimately. These studies have primarily focused on static graphs with non-sparse signals, as well as on the consistency assumption of the graphs over time. These models require sufficiently adequate samples for training and testing, once again making it difficult to use neuronal signals whose sample size is typically small for adequately assessing variations over rather short time intervals. Graphs’ dynamics with a potential impact on temporal data characterization have also been of much interest to [12,13]. In this theme, the models are used to predict the links given previous graphs and associated signals. All these approaches require much prior information on known structures and sufficient data for training and predicting future graphs. Moreover, game-theoretic techniques, which have been proposed to address multi-objective optimization problems [14], may be seen as potentially useful in our use case by interpreting our interacting neurons as a multi-player game. It is, however, difficult to achieve a single comprehensive model with a capacity to capture the neurons’ large variability and time-varying characteristics.
To analyze the characteristics and representation of a graph, topological data analysis has been shown to measure the shape or connectome of a graph [15]. In addition to investigating pairwise connections between every pair of nodes, higher-order information, using simplices and homology, was proposed to determine the prevailing homology, thus affording an interpretation of a topological hole/cycle as the inefficiency of (or slow down) information diffusion [16]. While this approach is practical when analyzing a given graph, it is more challenging to account for differential constraints to optimize the construction of a graph associated with distributed data.
In this work, we build on the wealth of prior research work in neuroscience as well as in graph learning [11], to propose a new model, with a target dynamic structure to track neurons’ temporal connectivity, as well as higher-order connectivity (three neurons connected sets), referred to as 2-simplex information. To that end, our proposed dynamic graph learning will include vertices/nodes with their connectivity reflected by graph edges. An edge attribute is defined as the probability of connection between a pair of neurons, and that of a 2-simplex to reflect the connectivity degree of pairwise connection for all three neurons in a 2-simplex.
To proceed, the outline of our paper follows, in order, our contributions in the sequel. Firstly, exploiting the insight from prior research on graph learning with graph Laplacian [11,17], we propose a formulation to estimate an optimal graph short time intervals, which in turn reflects the evolving transformation of the connectivity. Secondly, we modify our model to fit sparse signals to verify our optimized solution on a neuronal signal dataset. Thirdly, we call on a tensor to model connectivity tracking among three neurons to account for higher-order information. Fourthly, we propose three alternative methods to simplify the optimization procedures so that the optimization problems’ solution procedures are simplified and help reach the optimal points. We finally proceed to test our proposed model using a neuronal dataset, to improve our understanding of the neuronal interaction and their process of signal/information propagation.
2. Problem Setup and Background
Throughout the paper, we will adopt an upper and lower case bold letter to respectively denote a matrix and a vector, and the superscripts to respectively denote a matrix transpose and inverse. The operator denotes a matrix trace. The identity, zero and “1” matrices are respectively denoted by , and , while represents the i-th row, j-th column element of a matrix .
2.1. Definition of Graph and Graph Laplacian
Our neuronal-activity dataset will be N-dimensional, and will be characterized by a connectivity graph , where V denotes the vertex set , E is the edge set with attributes reflecting the connectivity between each pair of vertices quantified by as a connectivity strength. A time series of observations with , is associated with each node . For simplicity, we will aggregate the nodes’ finite-length time series into a matrix , where . Our problem formulation will seek for each observed , either a static graph G or a time dependent graph series of graphs .
The well-known graph Laplacian of an undirected graph can help describe its topology, and can serve as the second derivative operator of the underlying graph. The corresponding Laplacian matrix is commonly defined as [18], with , for i, j adjacent nodes, and otherwise, and , where denotes the degree of node i. Its simple matrix expression is , where is a diagonal matrix of degrees.
The Laplacian matrix may also usefully adopt, in some context, a second derivative interpretation of graphs: Given an assignment of real numbers to the nodes, the Laplacian matrix may be found as the second derivative of as , where denotes a N-dimensional vector whose elements are all 0s, except the i-th element being respectively 1 and j-th element . As may be seen, represents the first derivative of the edge between the i-th and j-th node. The notion of a Laplacian will be exploited in this sequel for a given data set as a structural regularizer when an optimal graph is sought.
2.2. Topological Basics
Euler characteristic originally proposed for polyhedron is also invoked in the homology theory, with a motivation of comparing two shapes by taking into account any dimensional holes proper to their topology. For instance, the difference between a disk and a circle in homology is that a one-dimensional hole exists in a circle. In this sense, homology theory provides an alternative definition of shapes in topological spaces by decomposing a shape S into a family of abelian groups [19].
In geometry, a simplex is a general concept of a fully connected shape in any dimensions, where a k-simplex is a k-dimensional polyhedron of vertices. As an example, a disk can be simplified and assimilated to a 0-simplex, while a circle is distinguished as a chain complex with a one-dimensional hole. Two different strategies are used to construct simplex-based structures for computational purposes in homological data analysis. In a so-called Vietoris-Rips complex, two nodes are said to be connected to each other if their neighborhoods (balls around the node) overlap, thus making the polytope a simplex. In a Cech complex, a simplex is, on the other hand, defined if and only if any given node is connected to any other nodes with overlapping of all neighbors. Therefore, a simplex in a Cech complex is a stricter connection in any dimension. These simplices are illustrated in Figure 1.
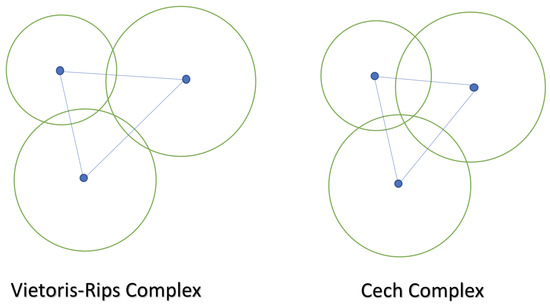
Figure 1.
Vietoris-Rips Complex and Cech Complex.
In our neuronal-activity dataset, we translate the connectivity among three neurons into 2-simplex with the criteria in Cech complex with a mathematical equation, and the result gives higher order connection information beyond pairwise connectivity.
3. Dynamic Graph Learning
3.1. Static Graph Learning
Prior to proposing the dynamic structure learning of a graph, we briefly revisit the basic notions of static graph learning [11]. Using the Laplacian quadratic form as a smoothness regularizer of the data , and the degree of connectivity K as a tuning parameter, ref. [11] discovers a K-sparse graph from noisy signals . This is the result of solving the following,
where and K are tuning parameters, is the noiseless signals, and its noisy observation. is the adjacency weight matrix for the undirected graph, with the additional relaxation of the individual weights to the interval .
3.2. Dynamic Graph Learning
Please note that in [11], a single connectivity graph is inferred over the entire observation time interval, thus overlooking the practically varying connections between every pair of nodes over time. To account for these events evolving over short term intervals and hence capture the true underlying structure of the graph, we propose to learn the graph’s dynamics. Learning these dynamics is consistent with our goal of modeling the brain signals to elicit timely information. These would particularly aim to pick up the responses to corresponding stimuli in that time interval and account for their dependence on previous graph instances and time intervals. This also introduces a practical constraint which needs to be accounted for by way of the similarity of temporally adjacent graphs in the overall functionality of the sequence of graphs in congruence with the observed data by selecting a 1-norm distance of connectivity weight matrices between consecutive time intervals, we can proceed with the graph sequence discovery, and hence the dynamics by seeking the solution to the following,
where is a penalty coefficient, , is the observed data in the t-th time interval, is the corresponding noise-free data, is the weight matrix in the t-th time interval, and K is a tuning parameter.
3.3. Dynamic Graph Learning from Sparse Signals
The solution given by [11] provides the static graph learning, but the observed signals may often be sparse, which poses a problem: noting that is the Laplacian quadratic form, we use to reflect the distance between two signals, whose minimization will unveil some problematic nodes with very similar signals over a small time interval.
Technical and Practical Constraints
While the above formulation (2) captures the principles of the dynamics of interest, additional practical difficulties arise in the case when and are close to 0, making their distance close to 0. This, as a result, introduces unexpected false edges when sparse signals are present. Such an instance may arise for, say, given sparse signals written as , where the dimension of is , is an matrix and is . Given that 2-norm is non-negative and the Laplacian matrix is positive semi-definite, we can find a trivial optimal solution of , where is sparse, such that , and the weight matrix can be represented by some block matrix, .
Given that our given graph learning problem is a convex and non-negative problem, one can show that the optimal loss value is 0 by inserting the solution and . This indicates that the presence of sparse signals (which happens to be the case for brain firing patterns) results in a solution of the formulated optimization that may not be unique. Additionally, this leads to optimal points that establish connectivity between zeros-signal nodes (i.e., erroneous and perhaps meaningless connections).
Proposition 1.
where η is a penalty coefficient,is the i-th node’s signal in the t-th time interval, and.
Proving this proposition is tantamount to lifting the fore-noted difficulty of sparse signals. To that end, we introduce a constraint term to help focus on the nodes with significant values, specifically we constrain edge nodes energy to be of relevance.
Since the weight matrix for an undirected graph is symmetric, therefore this additional part of the new optimization can be simplified as follows:
where is a diagonal matrix defined above from weight matrix . Combining the two expressions from Equations (3) and (4) will yield the simpler form. With a little more attention, one could note that this procedure naturally prefers nodes of higher energy by associating a higher weight.
3.4. Dynamic Graph Learning with Higher-Order Information
The quadratic form of over in optimization model (3) accounts for pairwise connections between nodes. To exploit higher order than pairwise interaction among nodes requires a topology-driven information structure across nodes in a graph. To that end, and to bypass the computational complexity of homology assessment of the topological complex resulting from a set of nodes, we propose a practically computable alternative in the optimization model which quantifiably reflects the connectivity among three neurons, thus capturing the inherent information within a 2-simplex.
Proposition 2.
In the basic Vietoris-Rips complex, if three given neurons are connected to each other, we will consider these three neurons as a 2-simplex. We hence propose the following strategy for considering all connections among three neurons in the t-th time interval: . The formulation is in fact a direct result of the simplex definition in a VR-complex, making the proximity between every pair of signals in a triplet of nodes, a 2-simplex is generated. In other words, we regard this 2-simplex information as a tight connection among these three neurons.
As with the development for pair-wise node interaction, we proceed to tackle the 3-way node interaction by introducing a weight attribute tensor , when recalling the non-negative characteristic of . Our inclusion of a constraint to force to construct the tightest higher order connections may hence be achieved. As with the afore-discussed issue about sparse signals yielding non-realistic connections among three weak/zero node signals, we proceed to constrain such a solution out by adding a energy penalty term at each node: . By accounting for all these factors, we obtain Proposition 2 which considers both the pairwise connection and a 2-simplex connection/information.
4. Algorithm Numerical Solution
Solving Propositions 1 and 2 by the conventional Lagrangian duality is computationally complex, and an alternative is in order. To that end, we propose a coupled pair of computational steps to solve Equation’s optimization (5). The first facilitates solving the optimization by the periodic updates of the proximal operator as detailed, and the other seeks to relax graph adjacency weight terms to be continuous on below.
4.1. Proximal Operator
are updated with gradient descent method. On account of the non-smoothness of the norm in Equation (5), we call on the proximal operator to first rewrite model (3) and proceed to solve it [20,21]. Firstly, the term in optimization (3) may be affected by the order of updating s. To reduce the impact of the order of updating variables, we introduce an auxiliary variable , with the constraint that of the order of updating variables, we introduce to replace the this term, and add a new constraint that . This substitution allows an update of with no influence by the others weight matrices, and provides the relaxation between each pair of adjacency weight matrices. This results in an equivalence to the previous optimization problem, with the advantage a reduced impact on the optimization caused by the variables updating order. We introduce as the Lagrange multiplier of the equality constraints .
Claim: As a result, the Lagrangian duality form of the optimization can hence be re-expressed as,
We now have a function of , denoted as , which is a convex and non-smooth function over . to alleviate the numerical difficulty of the non-differentiable contribution to Equation (6), we adopt the proximal operator approach to search for an optimal . The function is defined as where is a tuning parameter, which can be interpreted as the gradient step in the proximal algorithm. It is clear that we achieve the optimal point , if and only if we have , therefore for the k-th iteration, we update the variable as .
4.2. Projection Method
To address this issue, we associate a subspace structure W to the set of constraints, where is the whole weight space for graphs, with , and , such that . We next construct a projection procedure of onto W to ensure a subspace membership of the next iterate. Considering an updated weight matrix as a point in a high dimensional space, we minimize its distance to the subspace within the whole space by enforcing , and . A similar membership-set projection can equally be applied to by vectorizing the associated tensor. Applying the Lagrangian Duality on this minimization problem yields,
4.3. Algorithm
With the update in hand, we proceed to unfold the various steps of the algorithmic solution of model (5). The functional dependent on being convex smooth allows the calculation of the differential of the optimization formulation over and and yielding the following iteration.
Since the functional depending on s are smooth, we use gradient descent to update each . The whole algorithm is presented in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: algorithm for dynamic graph learning |
 |
5. Experiments and Results
The following experiments on neural activity data also provide, as a result, a new analysis and a potential new exploratory tool in neuroscience and machine learning. The neuronal activity data was provided by Dr. S. L. Smith’s Laboratory at UCSB.
5.1. Computational Complexity
The computational complexity is defined as the execution time of our program which is, in turn, dependent on the number of nodes N as well as on the number of time intervals T. We fix all other parameters and vary the choice of N and T, respectively, to discuss our model’s complexity. The results are shown in Figure 2.
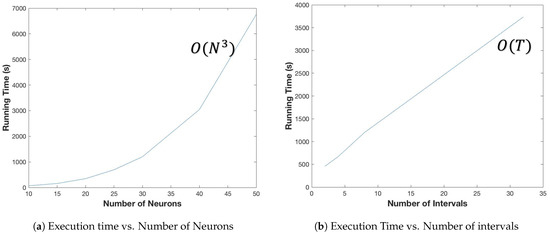
Figure 2.
Computational Complexity Test.
5.2. Synthetic Data Generation
Modeling and analyzing experimental/real data of neural activity with inference objectives were the primary motivation of this work. Our goal of thoroughly evaluating our model of neural activity is unfortunately met with limited amounts of real data available for validation, as noted, which led us to generate a set of synthetic signals from pre-defined connections based on biological criteria. This affords us a characterization and retrieval of all associated structural features to compare our modeled-based results with graph representations obtained using Pearson correlation-based edge connection. This is widely used in neuroscience to evaluate neuronal connectivity of observed signals.
5.2.1. Synthetic Data Model
Following computational neuroscience guidelines [22], we postulate the following model to generate signals mirroring the relevant dynamics,
where is the measured spiking signal of i-th neuron at time t, represents the number of supposed arrival spikes generated from Poisson Distribution, is an indicator function, which indicates the i-th neuron firing/not, p function is a probabilistic process for determining each spike firing/not, and represents a measurement noise.
The number of arrival spikes is described by a probabilistic model, where the probability of a firing spike in an interval is in direct proportion to [22],
is the firing rate for generating the number of arriving spikes, hence, parameterizing a Poisson distribution .
The indicator function supports the non-uniform firing of neurons due to the same stimulus. The fact that only a subset of the neurons in a given region are active at each trial, indicates that the proportion of event-related neurons should be a tuning parameter.
p function imitates the idea of the perceptron model in the visual cortex, making the output the result of a weighted summation of neurons’ contributions in the previous layer, i.e., , with describing the degree of influence of each neuron, as some bias, and representing an activation function. In the proposed model, the probability of each neuron i firing/not is dependent on its neighborhood’s neurons signals/contributions and computed as follows: , where denotes neuron spike, its neighborhood. The combined model accounts for the probability of spike firing and the Poisson nature of the generated spikes, together with the Bernoulli process of a turn on, yields under a connectivity schedule, some generated information.
The measurement noise , assumed white and Gaussian , was experimentally determined to best fit the generative process.
5.2.2. Synthetic Data
To first evaluate the viability of the proposed model, we qualitatively show the behavior of the model’s respective densities and of the real data in Figure 3. We also show the degree of correlation between the neuronal data for various trials and the degree of the correlation between different neurons in the same trial. The original intensities, X-axis, are all normalized between 0 and 1 using , Y-axis presents the number of times that the values occurred within the intervals set by the X-axis. The results are shown in Figure 3.
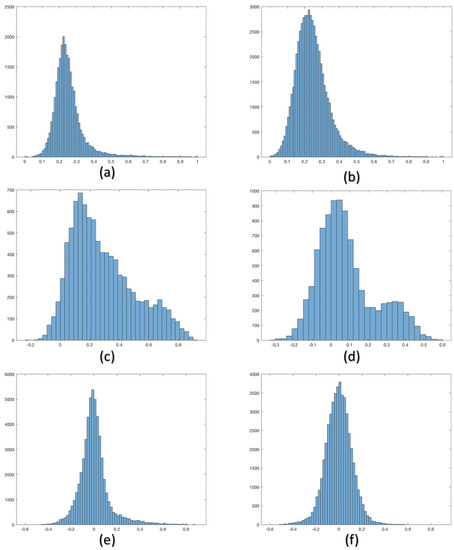
Figure 3.
Distribution comparison: (a) The distribution of data intensity of neuronal activity data. (b) The distribution of data intensity of synthetic data. (c) Distribution of trial-to-trial variability of neuronal data. (d) Distribution of trial-to-trial variability of synthetic data. (e) Distribution of correlations between neurons of neuronal data. (f) Distribution of correlations between neurons of synthetic data.
5.2.3. Simulated Connectivity Graph
To evaluate the effectiveness of generating neuronal networks by merely using the Pearson correlation, we manually subdivide the signals into 3 intervals. We use the same constraint parameter K, where for our model. At the same time, we select K largest correlation values after calculating the Pearson correlation between every two nodes’ signals. Upon applying the same process on N synthetic sets of signals, we obtain the graph representation sets for our model, and using Pearson correlation, t representing t-th time interval, and i denoting i-th trial. By calculating and , we determine the consistency of edge connectivity over trials by defining a threshold to count those edges repeating more than times.
To get an additional assessment of our activity network generation model against that obtained by Pearson correlation, we use the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and further illustrate the two methods’ capabilities. We use 100 synthetic trials and record connections in each trial over each time interval. By choosing different threshold , we select N consistent edges and then count the number of correct edges n based on the ground truth, which is set to 30 in our synthetic data experiment. The total number of edges of an undirected graph among 50 nodes is 1225. Therefore, the ROC curve is true positive rate, , vs. false negative rate, .
From Figure 4, the ROC curve for graphs using the Pearson correlation shows that it is close to a random-select model. In other words, the Pearson correlation can hardly recover the correct connectivity among all nodes. Compared with the Pearson correlation method, our model shows a significantly better performance in every state. Even with limited synthetic data trials, our model can also restore the essential connectivity (ground truth) accurately. Our model recovers the essential graphs for each state with 10 generated trials, by choosing those edges repeating more than 5 times. As shown in Table 1, the correct number of edges number in each state is 30, the number of selected edges from our model for each state is shown in the third column, and the number of correct edges for each state is shown in the last column. Those edges with a high repetition rate infer the essential structure of the underlying connectivity.
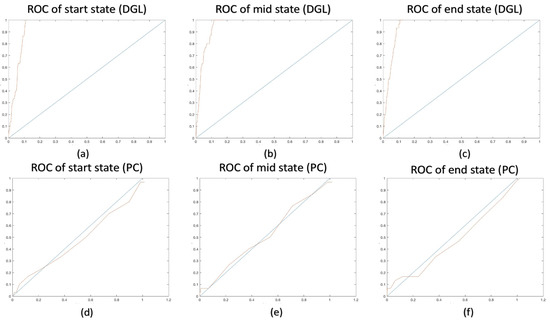
Figure 4.
ROC curve: (a–c): ROC curve for our model (DGL) in different states. (d–f): ROC curve for using the Pearson correlation (PC) in different states.

Table 1.
Synthetic data results.
5.3. Neuronal-Activity Data
Neurons, as the brain’s basic active elements, receive and transmit information to a center and one another (typically the pre-frontal cortex in the primates). Information collected by sensory organs, such as visual information, olfactory, etc., is encoded into neural signals, which are membrane potentials, which are, in turn, propagated in the brain for decision making. The widely accepted model distinguishes the brain’s visual sensorial part as the visual cortex. The visual cortex [23,24], a widely studied part of the brain for its importance and relevance here, is often used to explore the cause-effect of visual stimuli. The visual cortex study may comprise several layers, the first being the so-called V1 area, known for its directional sensitivity. The two cardinal features of neurons in the V1 area are driven by 2 types, orientation selectivity and direction selectivity [25], where orientation stands for the stimulus angle outline, and direction stands for the motion tendency. Most neurons in the V1 area are orientation-selective, which means that they are highly active under a specific angle of the stimulus for both directions. Some neurons are direction-selective, where they are sensitive to a specific angle and moving direction of a stimulus. As a result, models are constructed to explain motion detection in the primary visual cortex [26,27], which suggest that a few simple cells with quadrature phases and directions jointly define and transfer the information of motion direction to the higher-level visual cortex.
5.3.1. Real Experimental Data
The data were collected in S. L. Smith’s Laboratory at UCSB [8]. A two-photon electro-microscope [28] was used to collect fluorescent signals. The whole experiment consists of 3 specific scenarios with a 20 trial measurement, with the same stimuli in each trial. The stimuli for each of the scenarios are shown in Figure 5, consisting of a “gray” movie, an artificial movie, and natural movie 1 and movie 2 (which we will not discuss here and defer to future work). The dataset includes 590 neurons in the V1 area, and the sample rate is approximately 13.3 Hz. In the artificial movie data we have used in our experiments, each stimulus is characterized by an orientation and pattern motion direction. This is adapted to be detectable and trackable in the brain V1 area. We qualify two stimuli as similar if they share both orientation and direction of pattern motion. The stimuli are deemed related if they share the same orientation but differ in the pattern motion direction.
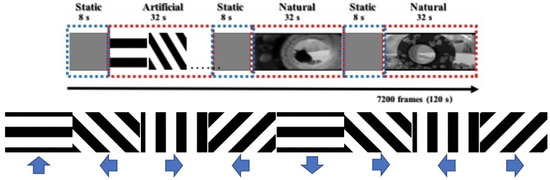
Figure 5.
Visual Stimuli: The visual stimuli for the mouse in a single trial.
5.3.2. Pre-Processing
The presumed and accepted neuronal redundancy in the brain is equivalent to observing a diverse neuronal activity pattern for the exact same stimulus. As is also known, additive noise causes unexpected firings of neurons. Moreover, much noise, such as unexpected firing, is contained in signals. To better cope with such variability and improve our analysis quality, we select the 50 most active and consistent neurons from the 590 neurons in the V1 area. Specifically, the selection is based on the highest correlation of each neuron activity across trials. We consider these neurons as the most consistently functioning neurons due to the same stimulus over trials. Neuronal signals stimulated by the artificial movie in two different trials are presented in Figure 6a, where X-axis reflects time, Y-axis indexes the 50 neurons, while the brightness reflects the normalized data intensities. Figure 6b depicts the 50 selected neurons’ relative positions, where numbering reflects the consistency (i.e., #1 is the most consistently active neuron).
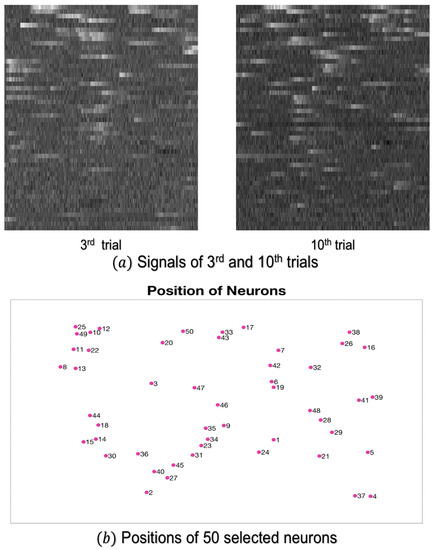
Figure 6.
Neurons’ Signals and Associated Positions.
5.3.3. Interval Partitioning of Data
The brain’s reaction time for stimuli is approximately 100 ms, and the delay of the device is around 50 to 100 ms; the time difference between 2-time points is 75 ms; therefore, we choose in the optimization model to capture the change within 150 ms, and we have 25 to 26 graphs for each stimulus. We choose (5 percent of the total edge number of a complete graph) to enforce a sparse graph. Uniformly adopting these parameters on the data across 20 trials, we obtain as a result, 213 graphs for each trial , where . Great variations can be observed between graphs across the different trials. We obtain a neuronal connectivity graph/adjacency matrix, by setting the weights (probabilities) less than 0.5, to zero. The sum of the adjacency matrices from different trials in the same time interval , are also used to determine the connectivity consistency. All consistencies greater than 5 are preserved.
A graph correlation is obtained by way of cross-correlating the duly vectorized weight matrices, e.g., the element value of i-th row and j-th column of the matrix stands for the correlation between i-th and j-th graphs’ weight vectors, and the matrix is symmetric. The red dash lines divide the plot of Figure 7 into small blocks, representing the exact time interval corresponding to each specific stimulus shown on the left of the plot, and Figure 7 provides an intuitive view of the memories (time delay) between consecutive stimuli and similarities of graphs activated by similar stimuli.
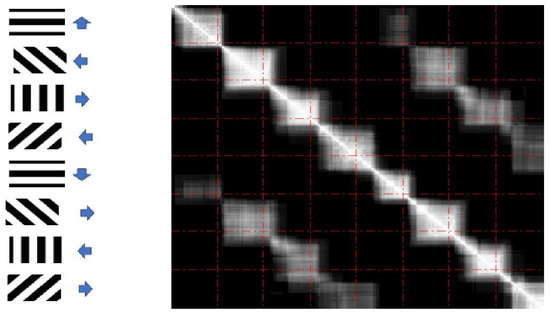
Figure 7.
Correlation matrix between graphs.
5.3.4. Improvement with 2-Simplex Information
To reduce the computational complexity and explore information gain by considering 3-way interaction relative to pairwise connection, we repartition the artificial movie into 8- time intervals corresponding to 8 different stimuli. These are also grouped into 4 groups of related stimuli based on the orientation information. According to the result we have in Figure 7, we can observe that the fifth stimulus’s neuronal response is highly correlated with that of the fourth stimulus, so two related stimuli, first and fifth stimuli, are not analyzed in this subsection. Further analysis focuses on the comparison of graph representations under other related stimuli (2nd–4th, 6th–8th stimuli).
We run the optimization model in Equations (3) and (5), respectively, with the same hyper-parameter settings on our neuronal-activity dataset. We apply the same post-processing after optimizing the model as in the previous subsection. From Equation (3), we reach the optimal solution and for 20 trials, where . Then, we transform each weight matrix into an adjacency matrix and each simplex tensor into a binary tensor by setting the weights to 1 if they are greater than 0.5 and 0 otherwise. Afterward, we aggregate the adjacency matrices and the binary tensor, respectively, within the same time intervals from different trials and set the threshold of valid weight matrices to 8 and the simplex tensor threshold to 4. In other words, we only plot the graphs with edges repeating more than 8 times and 2-simplex connections repeating more than 4 times in the same time interval across the 20 trials, thereby capturing response consistency of neurons over trials. The results we get from Equation (3) are called graph representation without simplex information, and those we get from Equation (5) are called graph representation with simplex information. We use a red triangle to fill the space to represent the tight (simplex) connection among three neurons. As shown in Figure 6, plot (a) shows the graph representation calculated from Equation (5) under the second stimulus with red simplex information, while plot (c) shows the graph representation calculated from Equation (3) under the same stimulus without simplex information.
From the graph representations in Figure 8, we can observe that the pairwise connection representations with and without 2-simplex connections are similar to each other under the same or related stimuli. In contrast, the 2-simplex connections under related stimuli are intuitively different. Therefore, we vectorize the weight matrices and calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between weight vectors under related stimuli. The result is shown in Table 2, and Graph i stands for the graph representation under i-th stimulus.
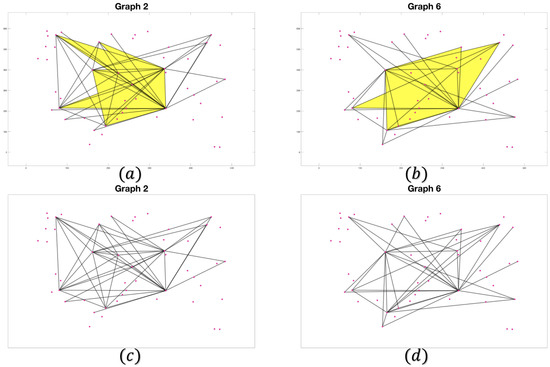
Figure 8.
Comparison between related stimuli with and without simplex information: Second and sixth stimuli are related stimuli. The yellow triangle stands for 2-simplex connections. (a) The graph representation for the second stimulus with simplex information. (b) The graph representation for the sixth stimulus with simplex information. (c) The graph representation for the second stimulus without simplex information. (d) The graph representation for the sixth stimulus without simplex information.

Table 2.
Comparison between related stimuli with and without simplex information.
Based on the result, , shown in Table 2, and the intuitive observation of the difference between 2-simplex connections under different stimuli, we come up with a hypothesis that the pairwise connection space neglecting higher-order information (), can be decomposed into a new pairwise connection space () and a 2-simplex connection space (). The new pairwise connection space primarily includes orientation information, and the 2-simplex connection space contains more direction information. The hypothesis can be concluded per the following formula:
To verify the hypothesis that 2-simplex connections may contain more directional information, and due to the limited neuronal-activity dataset for comparative test for the same stimulus, we randomly divide 20 trials into 2 groups each of 10 trials. By setting the thresholds for pairwise connection and 2-simplex connection matrix to 5 and 2, respectively, we apply the same post-process to both results with or without simplex information. In a similar way described earlier, we calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between pairwise connectivity results with or without 2-simplex connections under the same and related stimuli. Our analysis is based on the results under related stimuli in 2 groups.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 show all the correlations calculated in the experiments for pairwise connectivity and 2-simplex connectivity. In Figure 9, the 2 subplots in the first row are graph representations with and without 2-simplex connections for one stimulus in the first group; the 2 subplots in the second row are graph representations with and without 2-simplex connections for the same stimulus in the second group; the 2 subplots in the third row are graph representations with and without 2-simplex connections for the related stimulus in the first group, and the 2 subplots in the fourth row are graph representations with and without 2-simplex connections for the related stimulus in the second group. The marked numbers in Figure 9 represent 6 correlations for pairwise connectivity, which are: (1, 5): correlations between pairwise connection under related stimuli in the same group; (2, 6): correlations between pairwise connection under the same stimulus in different groups; (3, 4): correlations between pairwise connection under related stimuli in different groups. The marked numbers in Figure 10 represent 6 correlations for 2-simplex connectivity, which are: (1’, 2’): correlations between 2-simplex connection under the same stimulus in different groups; (3’, 4’, 5’, 6’): correlations between 2-simplex connection under related stimuli within each group or in the different groups. Table 3 shows all the correlations between graph representations without simplex information. Table 4 shows all the correlations between graph representations with simplex information, and Table 5 shows all the correlations between 2-simplex connections. We run the program 20 times and calculate the mean value of correlations.
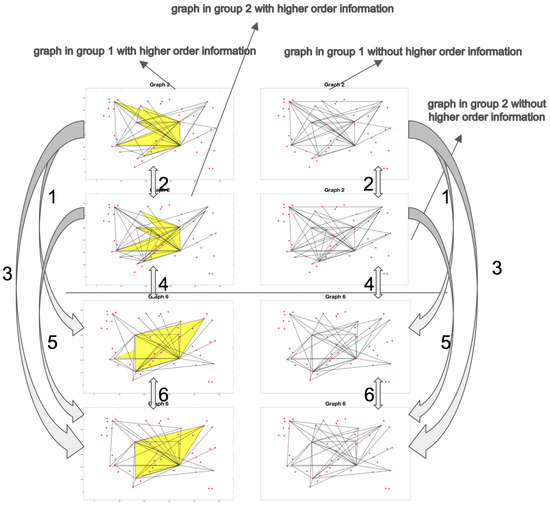
Figure 9.
Pairwise connectivity comparison.
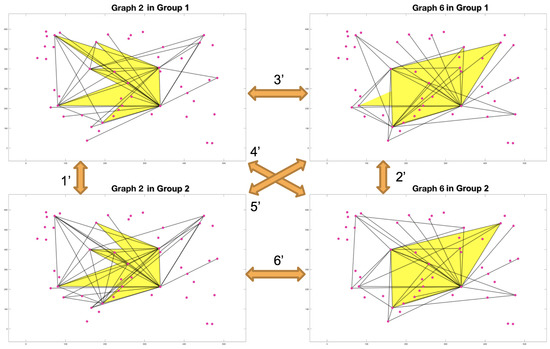
Figure 10.
2-Simplex connectivity comparison.

Table 3.
Correlation between pairwise connections without 2-simplex connectivity.

Table 4.
Correlation between pairwise connections with 2-simplex connectivity.

Table 5.
Correlation between 2-Simplex connectivity.
We observe that by decomposing the original pairwise connectivity information into new pairwise connectivity information and 2-simplex connectivity information, the correlations of pairwise connectivity representations between related stimuli or same stimulus in different groups (in Table 3) mostly increases by 10 percent compared with those between the original pairwise connectivity representations (in Table 2). Moreover, the first and second columns of Table 4 show the correlations of 2-simplex connectivity representations between the same stimulus in different groups, which is around 15 percent higher than those between related stimuli in the third to the sixth columns.
6. Discussion
Learning and analyzing structures from signals, as captured by a graph, is an interesting topic in not only neural-science but also in the computer science realm. Graph structures are instrumental in conveying the potentially complex interacting structure of signals and efficiently preserving all associated information.
Model: The challenge of this neuronal dataset is the low sample size as tens of data points can hardly support learning an adequate graph model, thus making static graph embedding unattainable by partitioning the data into smaller batches. With no prior knowledge about data and no interpolation, our proposed model acquires the data’s dynamics and inherent structure. We have also introduced a functional and practical means of tracking the homology of the underlying complex with the advantage of gleaning motion information as explained.
Dataset: From this neuron signal dataset, by way of the mathematical model, we observe variations of neuron connectivity over trials, while preserving similar patterns for similar stimuli in the V1 area, and by looking at different time scales, we also see hysteresis from one stimulus to another. These observations can be seen as an essential step for studying a brain’s functional connectivity in response to specific stimuli.
Results: Based on the results of the given neuronal-activity dataset, we were able to conclude that orientation information in the V1 area is adequately reflected by pairwise connectivity. In contrast, direction information may be gleaned from a structure obtained by the connections among neurons beyond pairwise connections. This is an empirical finding based on the model awaiting experimental biological validation.
7. Future Work
Natural movie: While our model was tested on artificial movie data, much work remains in investigating natural movie stimuli. While we expect higher-order information structures will have a stronger presence, variability will also be a great challenge.
8. Conclusions
This paper introduces an optimization driven approach to learning the dynamics of graphs. Three alternative perspectives were presented to capturing the evolution of a graph in time while accounting for the dynamics generated by the nodal activities. In particular, we addressed the difficulty of the low sample rate for detecting graphs and discovered the functional connectivity due to specific stimuli instead of revealing the physical connections of neurons. Future work will include the collaborative activity of neurons and graph transformation to characterize the evolution better.
Author Contributions
Methodology, B.J., Y.H., A.P. and H.K.; software, B.J.; validation, B.J.; formal analysis, B.J.; investigation, B.J.; resources, Y.Y. and S.L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.J.; writing—review and editing, H.K. and Y.H.; visualization, B.J.; supervision, H.K.; project administration, H.K.; funding acquisition, H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is in large part funded by the generous support of ARO grant W911NF1910202.
Data Availability Statement
The neuronal activity data was collected by one of the collaborating co-authors, S.L. Smith’s lab at UCSB, who cannot make the data publically available due to IRB restrictions. We have full control of the synthetic data generator developed. Please contact bjiang8@ncsu.edu.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jagadish, S.; Parikh, J. Discovery of Friends Using Social Network Graph Properties. U.S. Patent 8,744,976, 3 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Krim, H.; Panahi, A.; Dai, L. Community detection and improved detectability in multiplex networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, G.; Wapstra, A.; Thibault, C. The AME2003 atomic mass evaluation: (II). Tables, graphs and references. Nucl. Phys. A 2003, 729, 337–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canutescu, A.A.; Shelenkov, A.A.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr. A graph-theory algorithm for rapid protein side-chain prediction. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. Discovering the Human Connectome; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Polanía, R.; Paulus, W.; Antal, A.; Nitsche, M.A. Introducing graph theory to track for neuroplastic alterations in the resting human brain: A transcranial direct current stimulation study. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocker, G.K.; Hu, Y.; Buice, M.A.; Doiron, B.; Josić, K.; Rosenbaum, R.; Shea-Brown, E. From the statistics of connectivity to the statistics of spike times in neuronal networks. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 46, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Stirman, J.N.; Dorsett, C.R.; Smith, S.L. Mesoscale correlation structure with single cell resolution during visual coding. bioRxiv 2018, 469114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sompolinsky, H.; Yoon, H.; Kang, K.; Shamir, M. Population coding in neuronal systems with correlated noise. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 051904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretic, H.P.; Thanou, D.; Frossard, P. Graph learning under sparsity priors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 6523–6527. [Google Scholar]
- Chepuri, S.P.; Liu, S.; Leus, G.; Hero, A.O. Learning sparse graphs under smoothness prior. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 6508–6512. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Chhetri, S.R.; Canedo, A. dyngraph2vec: Capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 187, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Kamra, N.; He, X.; Liu, Y. Dyngem: Deep embedding method for dynamic graphs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.11273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guizani, M. Game Theory for Wireless Communications and Networking; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Baloch, S.; Krim, H.; Kogan, I.; Zenkov, D. Rotation invariant topology coding of 2D and 3D objects using Morse theory. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2005, Genova, Italy, 14 September 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 3, p. III-796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chung, M.K.; Kang, H.; Lee, D.S. Hole detection in metabolic connectivity of Alzheimer’s disease using k- Laplacian. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Boston, MA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Thanou, D.; Frossard, P.; Vandergheynst, P. Learning Laplacian matrix in smooth graph signal representations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 6160–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.R.; Graham, F.C. Spectral Graph Theory; Number 92; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- MacLane, S. Homology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, N.; Boyd, S. Proximal algorithms. Found. Trends Optim. 2014, 1, 127–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combettes, P.L.; Pesquet, J.C. A proximal decomposition method for solving convex variational inverse problem. Inverse Probl. 2008, 24, 065014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Amari, S.I.; Arai, K.; Brown, E.N.; Diekman, C.O.; Diesmann, M.; Doiron, B.; Eden, U.T.; Fairhall, A.L.; Fiddyment, G.M.; et al. Computational neuroscience: Mathematical and statistical perspectives. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2018, 5, 183–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F.; Koch, C. Are we aware of neural activity in primary visual cortex? Nature 1995, 375, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niell, C.M.; Stryker, M.P. Modulation of visual responses by behavioral state in mouse visual cortex. Neuron 2010, 65, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelson, E.H.; Bergen, J.R. Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. JOSA A 1985, 2, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.C.; Goyal, M.S. Velocity computation in the primate visual system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Freeman, J.; Smith, S.L. Technologies for imaging neural activity in large volumes. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).