- Article
An Integrated Numerical Model for a BBDB OWC Wave Energy Converter
- Fengru Yang,
- Rongxiang Fu and
- Ying Cui
- + 3 authors
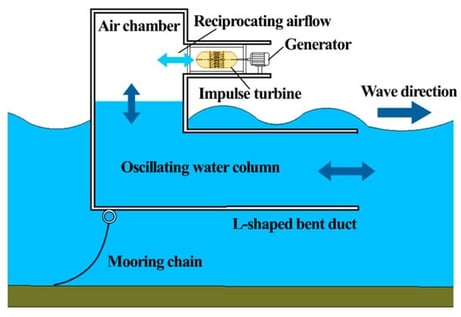
Examining the mechanism of two-way interaction between the air turbine and generator is essential for accurately predicting the performance of oscillating water column (OWC) devices. This study developed a fully integrated model for a back-bent duct buoy device, which incorporated the chamber, impulse turbine, permanent magnet synchronous generator, PI controller, and speed control strategies. The models of chamber–turbine and turbine-control systems were validated separately against wave-flume experimental results under regular and irregular wave conditions. In addition, a comparative study of two control strategies based on Best Efficiency Point Tracking was conducted by analysing key performance parameters at each energy conversion. The mechanism of two-way interaction between the turbine and the generator was elucidated. The integrated model demonstrated a great potential in predicting the conversion performance of wave energy to electrical energy under real sea conditions, as well as testing control strategies and algorithms before physical deployment.
12 March 2026