A First-Order Autoregressive Process with Size-Biased Lindley Marginals: Applications and Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SBL-AR(1): Model Construction and Innovation Distribution
3. Structural Properties Associated with the SBL-AR(1) Model
3.1. Some Statistical Conditional Measures
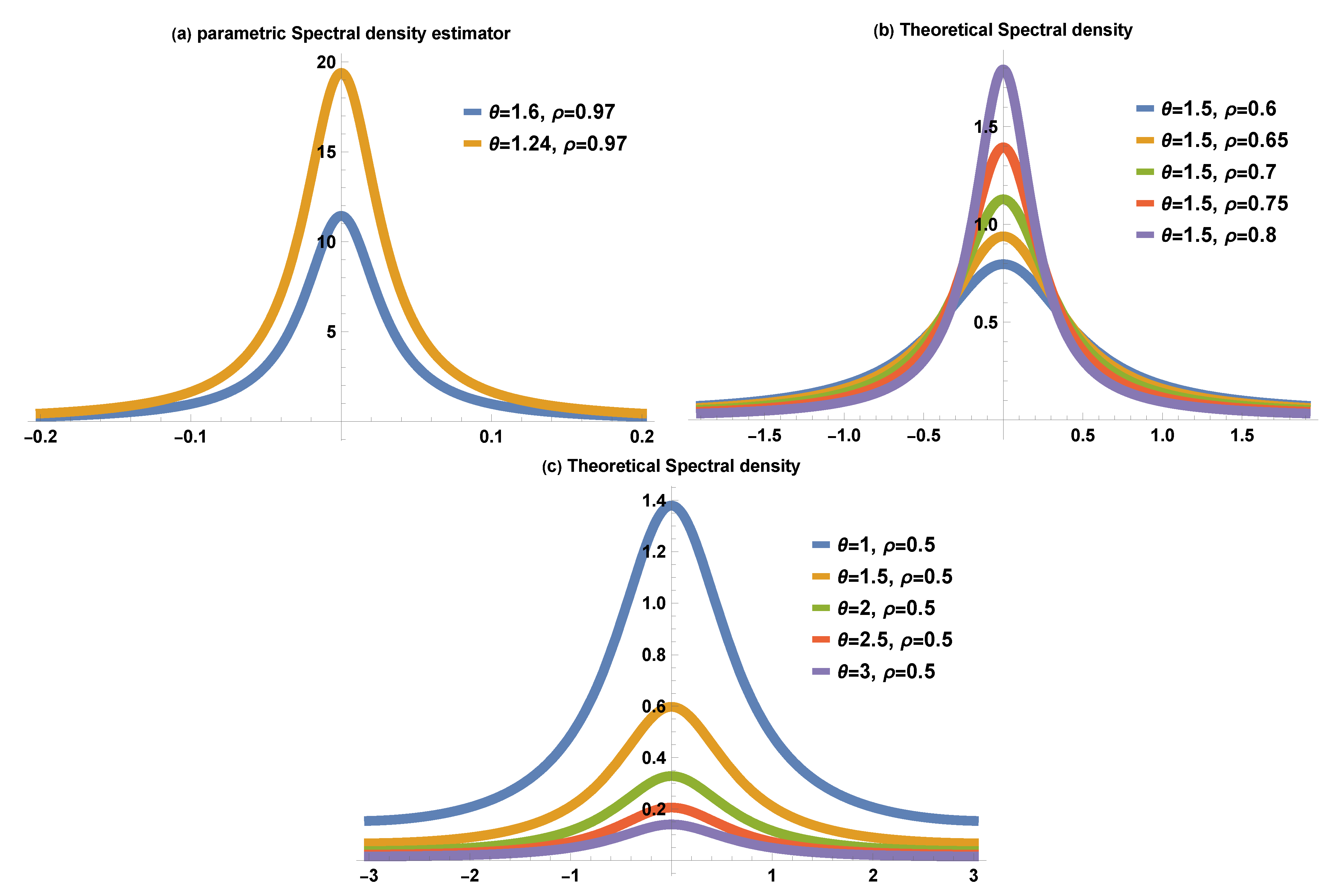
3.2. Joint Distribution, Autocorrelation, and Spectral Density Function
4. Parameter Estimation and Simulation Studies
4.1. Estimation via Conditional Least Squares Procedure
4.2. Gaussian Estimation Approach
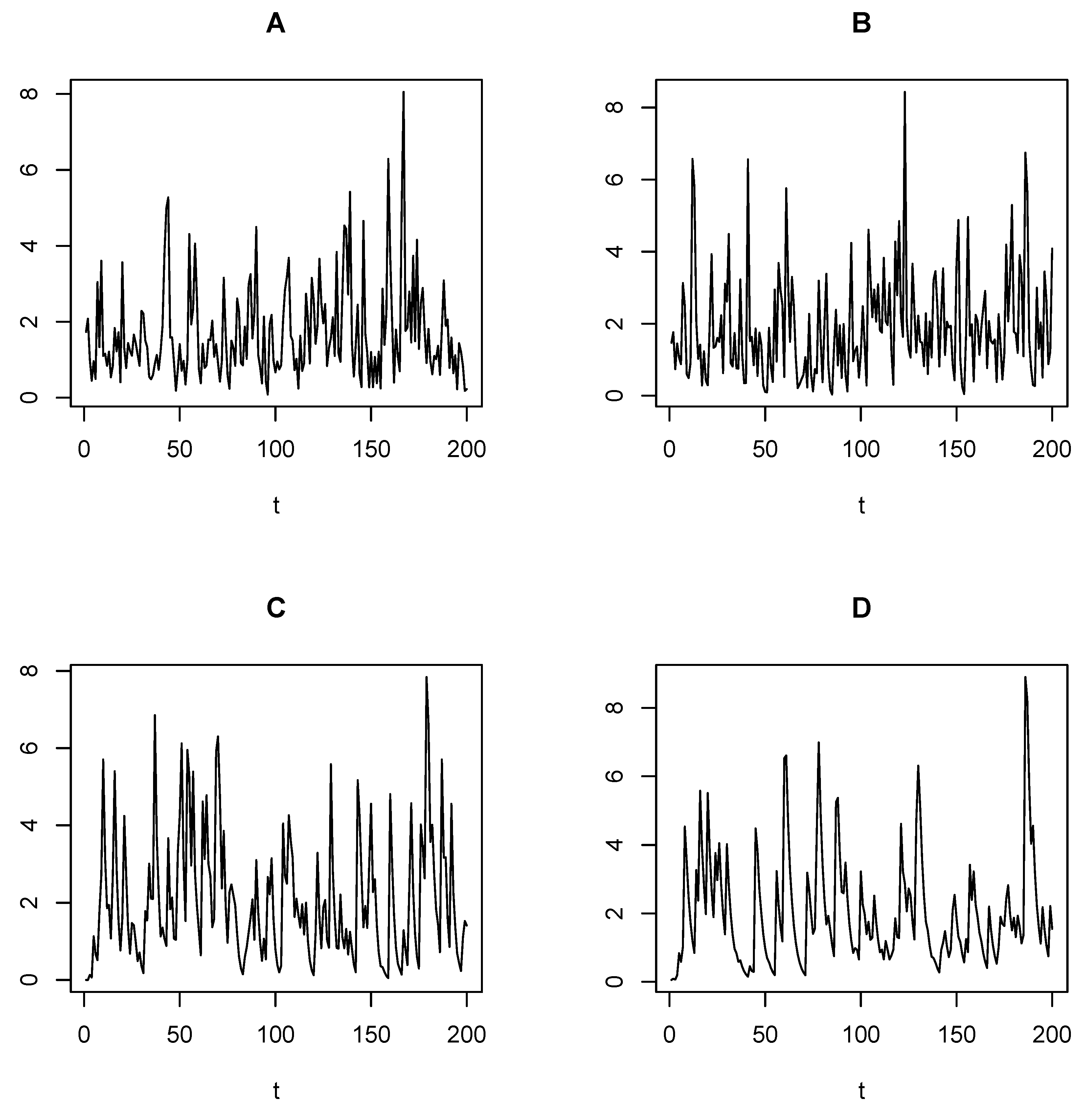
4.3. Monte Carlo Simulation and Experimental Analysis
- (a) (b)
- (c) (d)
- (e) (f)
| Algorithm 1: Simulation algorithm for the SBL-AR(1) process |
|
5. Real-Life Data Analysis and Model Selection
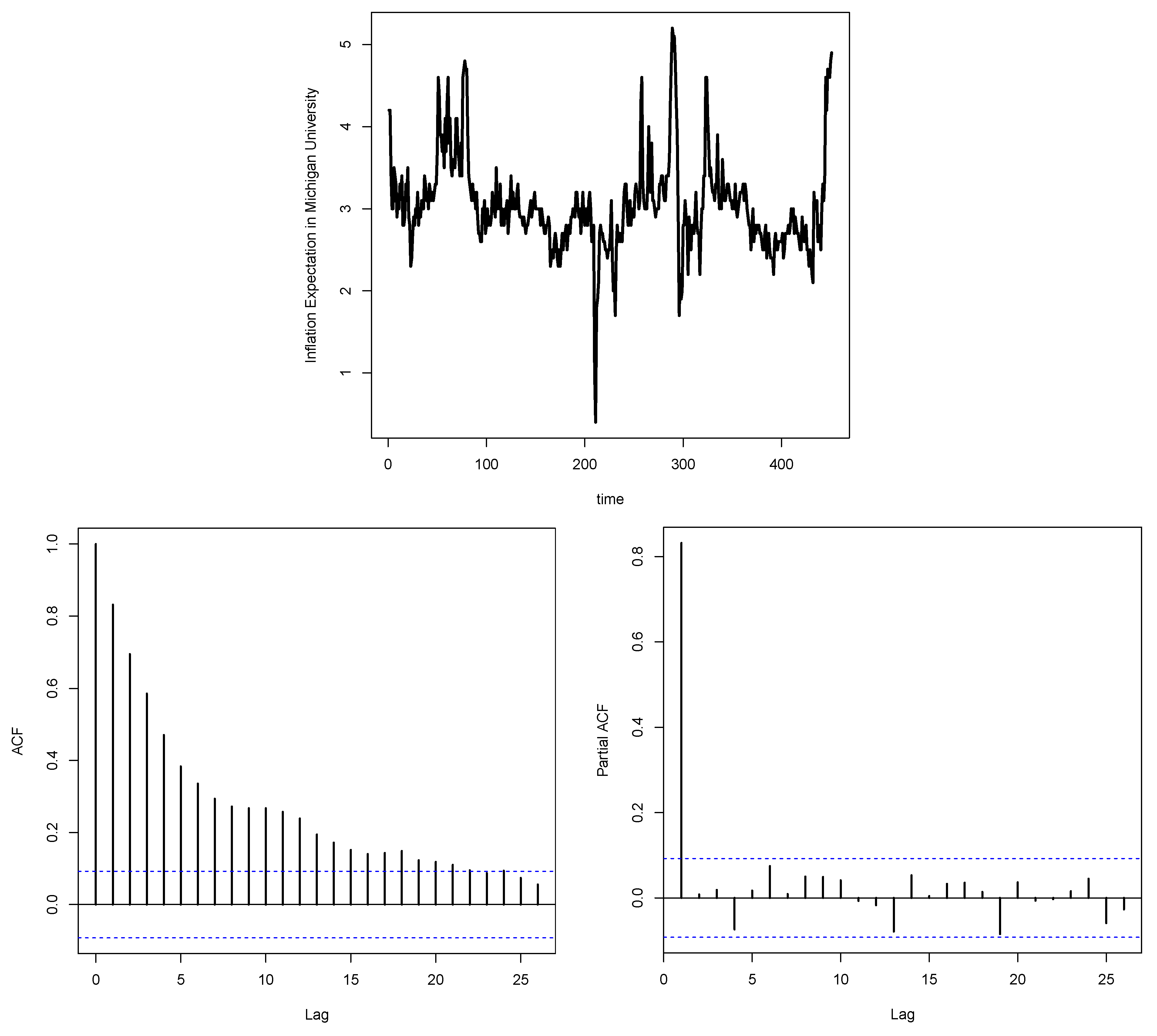
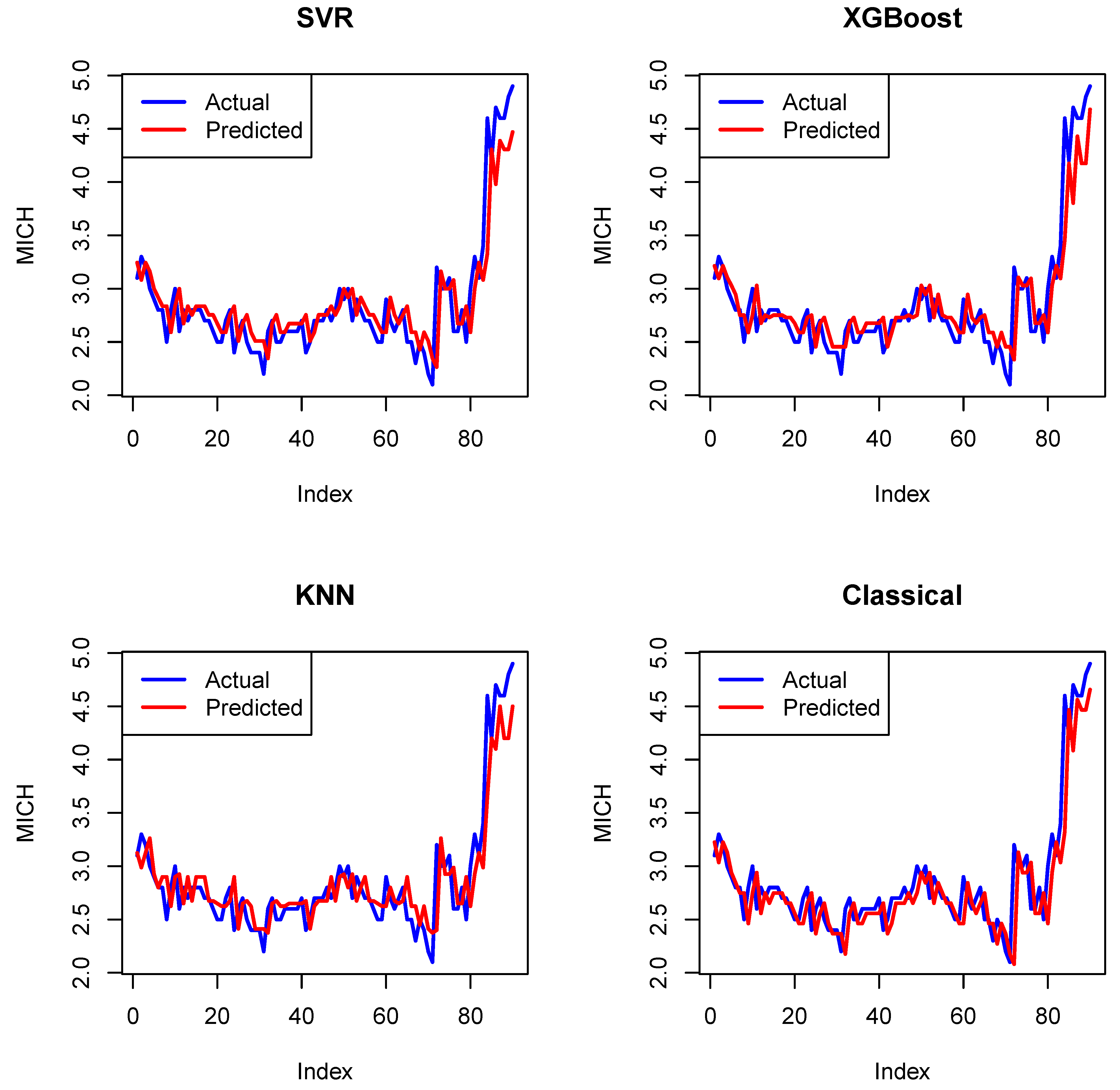
- The first dataset consists of 451 observations, representing the monthly University of Michigan Inflation Expectation (MICH) from 5 January 1984 to 1 November 2021. These data can be found at https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/MICH (accessed on 12 June 2024).
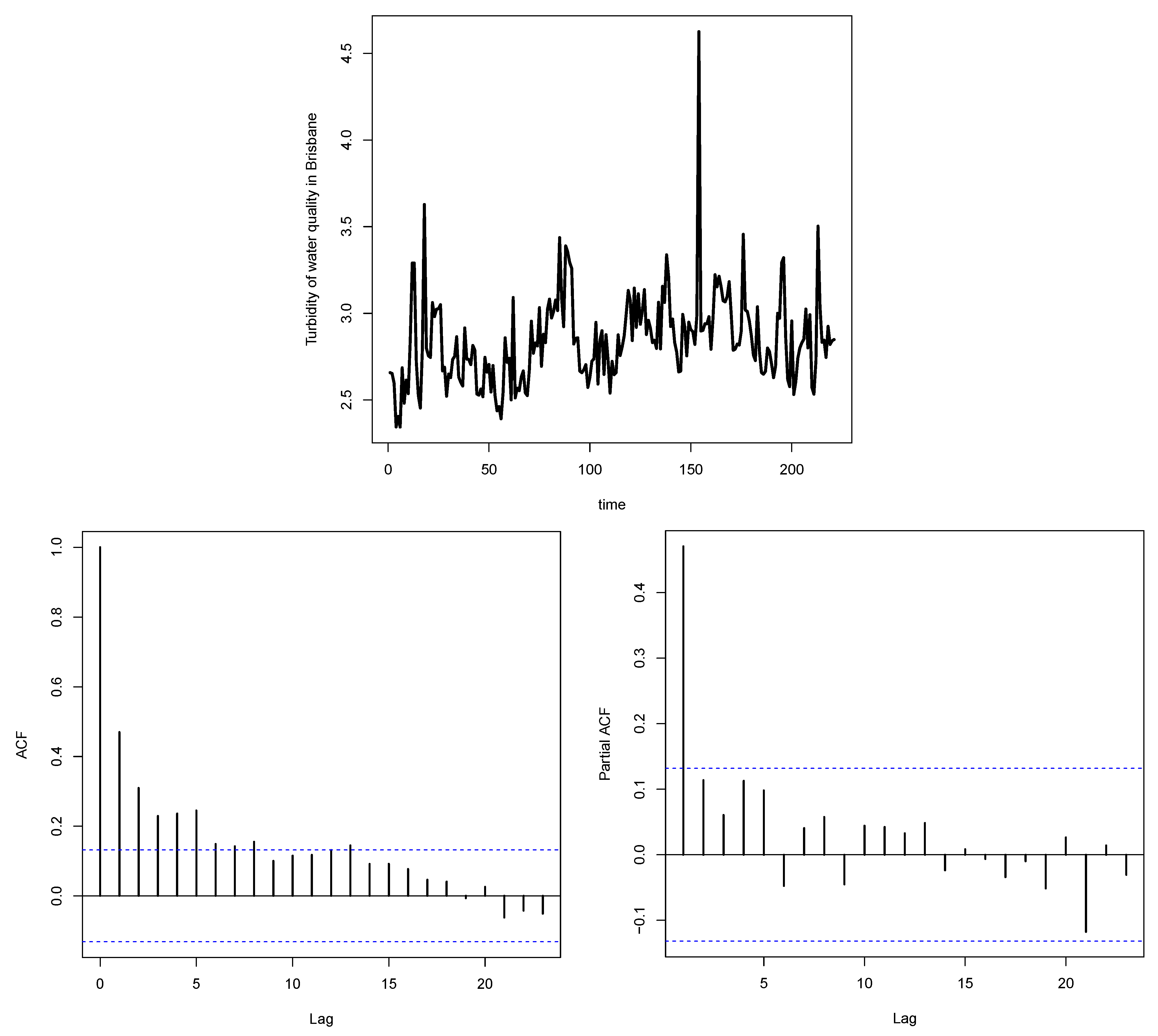
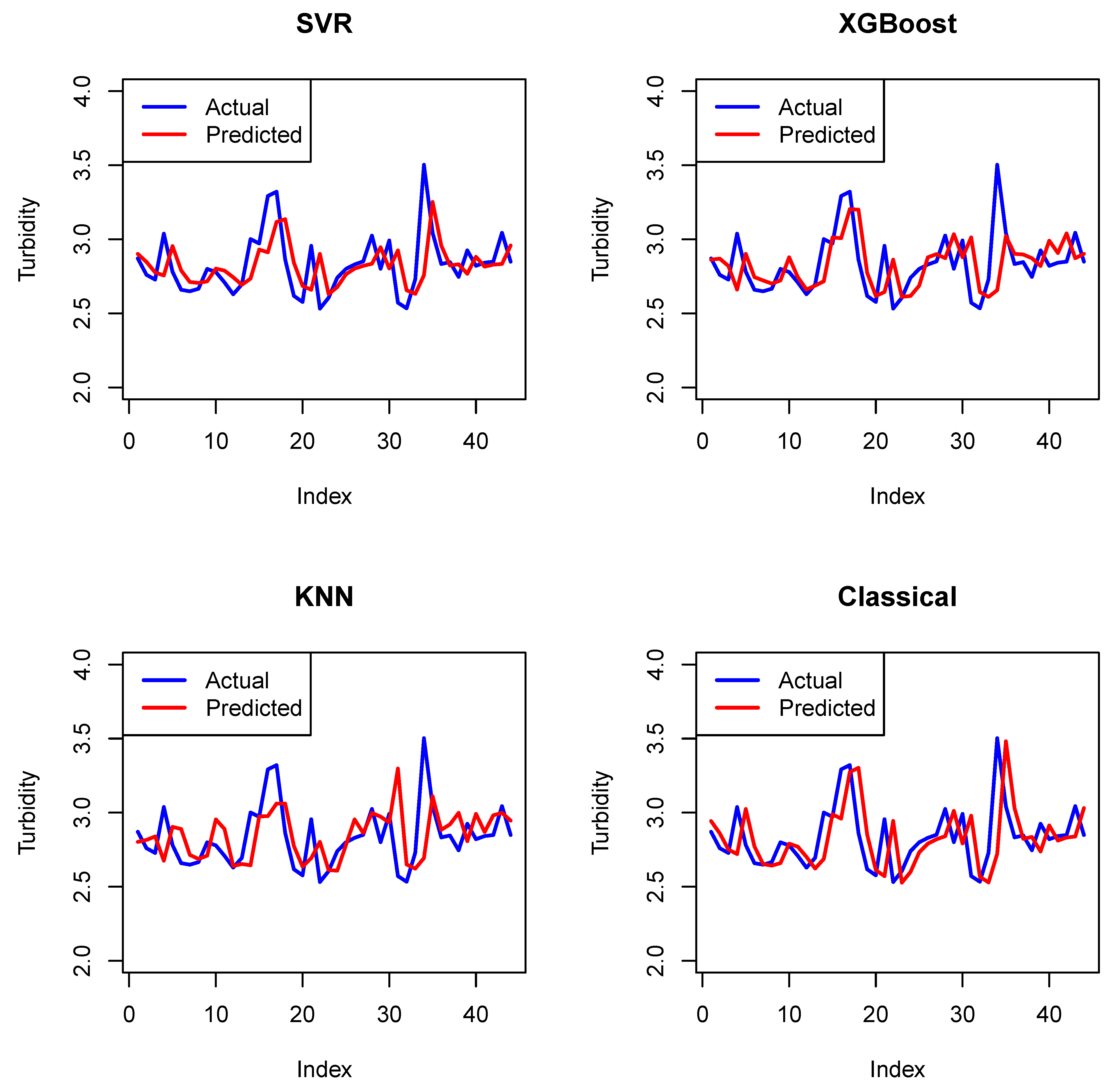
- The second dataset comprises 221 observations that represent the turbidity of water quality in Brisbane, measured every 10 min during the period from 23 June 2024, at 07:10, to 24 June 2024, at 19:30. These data can be obtained from https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/downshift/water-quality-monitoring-dataset (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- E-AR(1) with exponential marginals (Gaver and Lewis [1]):
- G-AR(1) with gamma marginals (Gaver and Lewis [1]):
- INGAR(1)-I with inverse Gaussian marginals (Abraham and Balakrishna [4]):
- INGAR(1)-II with inverse Gaussian marginals (Abraham and Balakrishna [4]):
- L-AR(1) with Lindley marginals (Bakouch and Popovíc [7]):
- GaL-AR(1) with gamma Lindley marginals (Mello et al. [9]):
- AR-L(1) with Lindley innovations (Nitha and Krishnarani [21]):
6. Forecasting
6.1. Classical Conditional Expectation Method
6.2. Machine Learning Forecasting Methods
6.2.1. Support Vector Regression
6.2.2. Extreme Gradient Boosting
6.2.3. K-Nearest Neighbors
6.3. Forecasting Evaluation
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)It is the square root of MSE; in the same units as the target variable:
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE)It measures the average absolute difference between predicted and actual values:
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE)It measures error as a percentage of actual values:
- For the considered machine learning methods, hyperparameter tuning was performed via grid search to determine the optimal values for the key parameters that achieve the lowest RMSE of each method.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SBL | Size-biased Lindley |
| SBL-AR(1) | Size-biased Lindley autoregressive of order 1 |
| ACF | Autocorrelation function |
| PACF | Partial autocorrelation function |
| ADF | Augmented Dickey–Fuller |
| CLS | Conditional least squares |
| GE | Gaussian estimation |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| E-AR | Exponential autoregressive |
| G-AR | Gamma autoregressive |
| INGAR | Inverse Gaussian autoregressive |
| L-AR | Lindley autoregressive |
| GaL-AR | Gamma Lindley autoregressive |
| AR-L | Autoregressive with Lindley innovations |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian information criterion |
| HQIC | Hannan–Quinn information criterion |
| SE | Standard error |
| ML | Machine learning |
| SVR | Support vector regression |
| XGBoost | Extreme gradient boosting |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| RMSE | Root mean squared error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
References
- Gaver, D.P.; Lewis, P.A. First-order autoregressive gamma sequences and point processes. Adv. Appl. Probab. 1980, 12, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.H. Simulation of Weibull and gamma autoregressive stationary process. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 1986, 15, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mališić, J.D. Mathematical Statistics and Probability Theory: Volume B; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, B.; Balakrishna, N. Inverse Gaussian autoregressive models. J. Time Ser. Anal. 1999, 20, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, K.K.; Tomy, L.; Sreekumar, J. Autoregressive processes with normal-Laplace marginals. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2008, 78, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, B.V. AR (1) time series with approximated beta marginal. Publ. Inst. Math. 2010, 88, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakouch, H.S.; Popović, B.V. Lindley first-order autoregressive model with applications. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2016, 45, 4988–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitha, K.U.; Krishnarani, S.D. On a class of time series model with double Lindley distribution as marginals. Statistica 2021, 81, 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, A.B.; Lima, M.C.; Nascimento, A.D. The title of the cited article. Environmetrics 2022, 33, e2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilesh, V.; Jayakumar, K. On first order autoregressive asymmetric logistic process. J. Indian Soc. Probab. Stat. 2023, 24, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitha, K.U.; Krishnarani, S.D. Exponential-Gaussian distribution and associated time series models. Revstat Stat. J. 2023, 21, 557–572. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, G.P.; Rao, C.R. Weighted distributions and size-biased sampling with applications to wildlife populations and human families. Biometrics 1978, 34, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheaffer, R. Size-biased sampling. Technometrics 1972, 14, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Maddala, G.S. Modeling Income Distributions and Lorenz Curves; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Drummer, T.D.; McDonald, L.L. Size bias in line transect sampling. Biometrics 1987, 43, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, A. Size biased Lindley distribution and its properties a special case of weighted distribution. J. Appl. Math. 2017, 8, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, P. Gaussian estimation in stationary time series. Bull. Int. Stat. Inst. 1961, 39, 105–129. [Google Scholar]
- Crowder, M. Gaussian estimation for correlated binomial data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 1985, 47, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nachawati, H.; Alwasel, I.; Alzaid, A.A. Estimating the parameters of the generalized Poisson AR (1) process. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1997, 56, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwasel, I.; Alzaid, A.; Al-Nachawati, H. Estimating the parameters of the binomial autoregressive process of order one. Appl. Math. Comput. 1998, 95, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitha, K.U.; Krishnarani, S.D. On autoregressive processes with Lindley-distributed innovations: Modeling and simulation. Stat. Transit. New Ser. 2024, 25, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, O. Dimensionality reduction by unsupervised k-nearest neighbor regression. In Proceedings of the 2011 10th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications and Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 December 2011; pp. 275–278. [Google Scholar]

| Scenarios | n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) () = (0.97, 1.24) | |||||
| 50 | 0.905966 | 1.467342 | 0.976374 | 1.251286 | |
| (−0.064034, 0.008183) | (0.227342, 0.344839) | (0.007344, 0.000575) | (0.012526, 0.021865) | ||
| 100 | 0.93888 | 1.446866 | 0.975805 | 1.262123 | |
| (−0.03112, 0.002239) | (0.206866, 0.248877) | (0.006775, 0.000366) | (0.023363, 0.019913) | ||
| 500 | 0.963309 | 1.401944 | 0.977312 | 1.2481 | |
| (−0.006691, 0.000184) | (0.161944, 0.062201) | (0.008282, 0.000164) | (0.00934, 0.004442) | ||
| 1000 | 0.966316 | 1.287918 | 0.977207 | 1.249197 | |
| (−0.003684, 0.000082) | (0.047918, 0.010303) | (0.008177, 0.00012) | (0.010437, 0.002362) | ||
| (b) () = (0.97, 1.6) | |||||
| 50 | 0.904868 | 1.743993 | 0.973699 | 1.589438 | |
| (−0.065132, 0.009001) | (0.143993, 0.465764) | (0.004669, 0.000633) | (−0.008962, 0.030876) | ||
| 100 | 0.939137 | 1.731105 | 0.975531 | 1.601991 | |
| (−0.030863, 0.002211) | (0.131105, 0.31464) | (0.006501, 0.000409) | (0.003591, 0.027661) | ||
| 500 | 0.962916 | 1.695561 | 0.974227 | 1.596723 | |
| (−0.007084, 0.000178) | (0.095561, 0.062953) | (0.005197, 0.000148) | (−0.001677, 0.00524) | ||
| 1000 | 0.966588 | 1.626271 | 0.974214 | 1.597994 | |
| (−0.003412, 0.00008) | (0.026271, 0.01708) | (0.005184, 0.000096) | (−0.000406, 0.001813) | ||
| (c) () = (0.5, 1.4) | |||||
| 50 | 0.468009 | 1.607588 | 0.465563 | 1.565282 | |
| (−0.031991, 0.015481) | (0.207588, 0.128041) | (−0.033937, 0.013012) | (0.166682, 0.110757) | ||
| 100 | 0.480446 | 1.594822 | 0.468969 | 1.513646 | |
| (−0.019554, 0.007864) | (0.194822, 0.073287) | (−0.030531, 0.006731) | (0.115046, 0.052598) | ||
| 500 | 0.493206 | 1.569898 | 0.479231 | 1.477341 | |
| (−0.006794, 0.001392) | (0.169898, 0.035519) | (−0.020269, 0.001619) | (0.078741, 0.013248) | ||
| 1000 | 0.498065 | 1.569096 | 0.478064 | 1.474208 | |
| (−0.001935, 0.000822) | (0.169096, 0.031902) | (−0.021436, 0.001079) | (0.075608, 0.009266) |
| Scenarios | n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (d) () = (0.7, 1.4) | |||||
| 50 | 0.654573 | 1.661771 | 0.667823 | 1.606182 | |
| (−0.045427, 0.011906) | (0.261771, 0.225731) | (−0.031477, 0.008301) | (0.207582, 0.184589) | ||
| 100 | 0.67598 | 1.596147 | 0.673644 | 1.549443 | |
| (−0.02402, 0.005558) | (0.196147, 0.107849) | (−0.025656, 0.004115) | (0.150843, 0.088059) | ||
| 500 | 0.69441 | 1.569192 | 0.68007 | 1.483746 | |
| (−0.00559, 0.001021) | (0.169192, 0.041562) | (−0.01923, 0.001081) | (0.085146, 0.019932) | ||
| 1000 | 0.697751 | 1.56935 | 0.682625 | 1.474496 | |
| (−0.002249, 0.000516) | (0.16935, 0.034756) | (−0.016675, 0.000684) | (0.075896, 0.012019) | ||
| (e) () = (0.1, 1.5) | |||||
| 50 | 0.094844 | 1.661526 | 0.114486 | 1.541434 | |
| (−0.005156, 0.019144) | (0.161526, 0.061588) | (0.014486, 0.011496) | (0.041434, 0.046460) | ||
| 100 | 0.095026 | 1.650353 | 0.104383 | 1.520137 | |
| (−0.004974, 0.009954) | (0.150353, 0.040085) | (0.004383, 0.006490) | (0.020137, 0.022047) | ||
| 500 | 0.100031 | 1.642151 | 0.099709 | 1.502587 | |
| (0.000031, 0.002009) | (0.142151, 0.023514) | (−0.000291, 0.001577) | (0.002587, 0.004227) | ||
| 1000 | 0.099556 | 1.640809 | 0.099946 | 1.499580 | |
| (−0.000444, 0.000976) | (0.140809, 0.021493) | (−0.000054, 0.000787) | (−0.00042, 0.002101) | ||
| (f) () = (0.5, 1.5) | |||||
| 50 | 0.470984 | 1.571149 | 0.465673 | 1.509039 | |
| (−0.029016, 0.012418) | (0.071149, 0.065098) | (−0.034327, 0.012710) | (0.009039, 0.075593) | ||
| 100 | 0.483163 | 1.550975 | 0.472834 | 1.471724 | |
| (−0.016837, 0.007294) | (0.050975, 0.036887) | (−0.027166, 0.006639) | (−0.028276, 0.037763) | ||
| 500 | 0.496301 | 1.532860 | 0.476945 | 1.437758 | |
| (−0.003699, 0.001462) | (0.032860, 0.007463) | (−0.023055, 0.001755) | (−0.062242, 0.010739) | ||
| 1000 | 0.498410 | 1.532106 | 0.477350 | 1.434703 | |
| (−0.001590, 0.000741) | (0.032106, 0.004187) | (−0.022650, 0.001148) | (−0.065297, 0.007641) |
| Dataset | n | Min. | Mean | Max. | Var | p-Value (ADF) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCIH | 451 | 0.400 | 2.700 | 3.000 | 3.044 | 3.200 | 5.200 | 0.3385 | 0.03571 |
| Turbidity | 221 | 2.344 | 2.667 | 2.821 | 2.843 | 2.981 | 4.625 | 0.0665 | 0.01031 |
| Model | GE Estimates (SE) | AIC | BIC | HQIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBL-AR | = 0.9722689 (0.006470897) = 1.2350076 (0.137368908) | 253.3235 | 261.5464 | 256.5642 |
| L-AR | = 0.9615126 (0.00501119) = 1.1524668 (0.06931619) | 268.7283 | 276.9512 | 271.9689 |
| GaL-AR | = 0.9695075 (0.005533153) = 1.0218001 (0.108046443) = 0.9895284 (0.293700792) | 262.2251 | 274.5595 | 267.0861 |
| E-AR | = 0.9597630 (0.00505366) = 0.8991799 (0.05621214) | 274.4090 | 282.6319 | 277.6497 |
| G-AR | = 0.9736072 (0.007168259) = 0.5314403 (0.203203788) = 0.5480252 (0.297268206) | 265.7606 | 278.0950 | 270.6216 |
| INGAR-I | = 0.9582729 (0.003857915) = 1.1860471 (0.096928851) | 274.3043 | 282.5272 | 277.5449 |
| INGAR-II | = 0.9932729 (0.00163749) = 1.9887342 (0.44900524) = 1.0075656 (0.58975847) | 260.5591 | 272.8935 | 265.4201 |
| AR-L | = 0.9353976 (0.006316815) = 8.6482145 (0.540094410) | 270.5227 | 278.7457 | 273.7634 |
| Model | GE Estimates (SE) | AIC | BIC | HQIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBL-AR | = 0.9677021 (0.00751236) = 1.6010980 (0.17560826) | 46.89545 | 53.69178 | 49.63968 |
| L-AR | = 0.9717271 (0.006628198) = 1.1756744 (0.127043976) | 49.18248 | 55.97881 | 51.92672 |
| GaL-AR | = 0.9718353 (0.006936761) = 1.1164845 (0.175881692) = 0.7821798 (0.246680549) | 51.60417 | 61.79866 | 55.72052 |
| E-AR | = 0.9633879 (0.006277054) = 1.0429649 (0.090100243) | 56.95756 | 63.75388 | 59.70179 |
| G-AR | = 0.9524641 (0.008869184) = 1.5172295 (0.395848932) = 1.4776463 (0.495027829) | 71.70304 | 81.89753 | 75.81939 |
| INGAR-I | = 0.9622654 (0.004742255) = 0.8843855 (0.098468366) | 59.35630 | 66.15262 | 62.10053 |
| INGAR-II | = 0.9970946 (0.0002890516) = 1.5959593 (0.2560154481) = 0.3071916 (0.1316577834) | 50.63486 | 60.82935 | 54.75122 |
| AR-L | = 0.9049345 (0.00977161) = 7.0817431 (0.56402558) | 96.52965 | 103.32598 | 99.27389 |
| Dataset | p-Value of Ljung-Box Test | p-Value of Box-Pierce Test |
|---|---|---|
| MCIH | 0.6371 | 0.6382 |
| Turbidity | 0.3715 | 0.3747 |
| Measure | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 0.2695047 | 0.1890921 | 6.447078% |
| XGBoost | 0.2621252 | 0.1792437 | 6.073617% |
| KNN | 0.2508839 | 0.1831944 | 6.270608% |
| Classical | 0.2679958 | 0.1809712 | 6.098343% |
| Measure | RMSE | MAE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 0.1993664 | 0.1448703 | 4.984548% |
| XGBoost | 0.2093979 | 0.1462492 | 5.040056% |
| KNN | 0.2249225 | 0.1538455 | 5.342222% |
| Classical | 0.2300879 | 0.1660202 | 5.728669% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakouch, H.S.; Gabr, M.M.; Aljeddani, S.M.A.; El-Taweel, H.M. A First-Order Autoregressive Process with Size-Biased Lindley Marginals: Applications and Forecasting. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111787
Bakouch HS, Gabr MM, Aljeddani SMA, El-Taweel HM. A First-Order Autoregressive Process with Size-Biased Lindley Marginals: Applications and Forecasting. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111787
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakouch, Hassan S., M. M. Gabr, Sadiah M. A. Aljeddani, and Hadeer M. El-Taweel. 2025. "A First-Order Autoregressive Process with Size-Biased Lindley Marginals: Applications and Forecasting" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111787
APA StyleBakouch, H. S., Gabr, M. M., Aljeddani, S. M. A., & El-Taweel, H. M. (2025). A First-Order Autoregressive Process with Size-Biased Lindley Marginals: Applications and Forecasting. Mathematics, 13(11), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111787





