Inference with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for US Election Law
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. A Motivating Example
1.2. Utility of Pólya-Gamma Augmentation in Bayesian Methods
2. The Pólya-Gamma Distribution for Binomial VRA Datasets
2.1. The 2021 VRA Model
2.2. The Pólya-Gamma (PG) Distribution
2.3. A Simplified Application of Pólya-Gamma Augmentation
3. New MLN Model with PG Augmentation
3.1. Basic Setup
3.2. Model Likelihood and Priors
3.3. Conditional Posterior Distributions for Regression Coefficients and PG Variables
- vs. (- vs. )conditional on being drawn from for each j.
- − vs. (− vs. )conditional on being drawn from for each j.
- − vs. ( vs. )conditional on being drawn from for each j.
3.4. Conditional Posterior Distribution for the Variable Selection Parameters
3.5. Conditional Posterior Distribution for Random Effects Covariance
3.6. Conditional Posterior Distribution for Random Effects Variables
3.7. Gibbs Sampling Algorithm
- (see Section 3.3): Draw PG random values for each jurisdiction and outcome category as follows:where is as defined in Section 3.3.
- (see Section 3.3): Draw coefficients for as follows:where and are defined as in Section 3.3, and the prior covariance matrix B for is defined as in Section 3.4.
- (see Section 3.4): For each covariate , drawwhere the matrices and R, as well as the proportions for each i, are as defined in Section 3.4.
- (see Section 3.5): Drawwhere is defined as in Section 3.5, is set to be the identity matrix , and is set to 3, due to the three disjoint outcome categories.
4. 2021 VRA Data Analysis Results
4.1. Data Description
- Logit-transformed fraction of voting-age persons who are citizens;
- Logit-transformed fraction of citizens that are limited English-proficient;
- Proportion of voting-age persons who are non-Hispanic White in each geography;
- Proportion of voting-age persons with no college education in each geography;
- Average number of voting-age people per housing unit in each geography;
- Average age among voting-age persons in any AIAN LMG in each geography;
- Proportion of voting-age persons in poverty in each geography;
- Proportion of voting-age persons speaking a language other than English at home in each jurisdiction;
- Proportion of foreign-born voting-age persons in each jurisdiction;
- Average years in US (as of 2019) of voting-age foreign-born persons in each jurisdiction.
4.2. Model Comparison
4.2.1. Bangladeshi LMG Results
4.2.2. Sri Lankan LMG Results
4.2.3. Overall Results
4.2.4. Improvement Rates
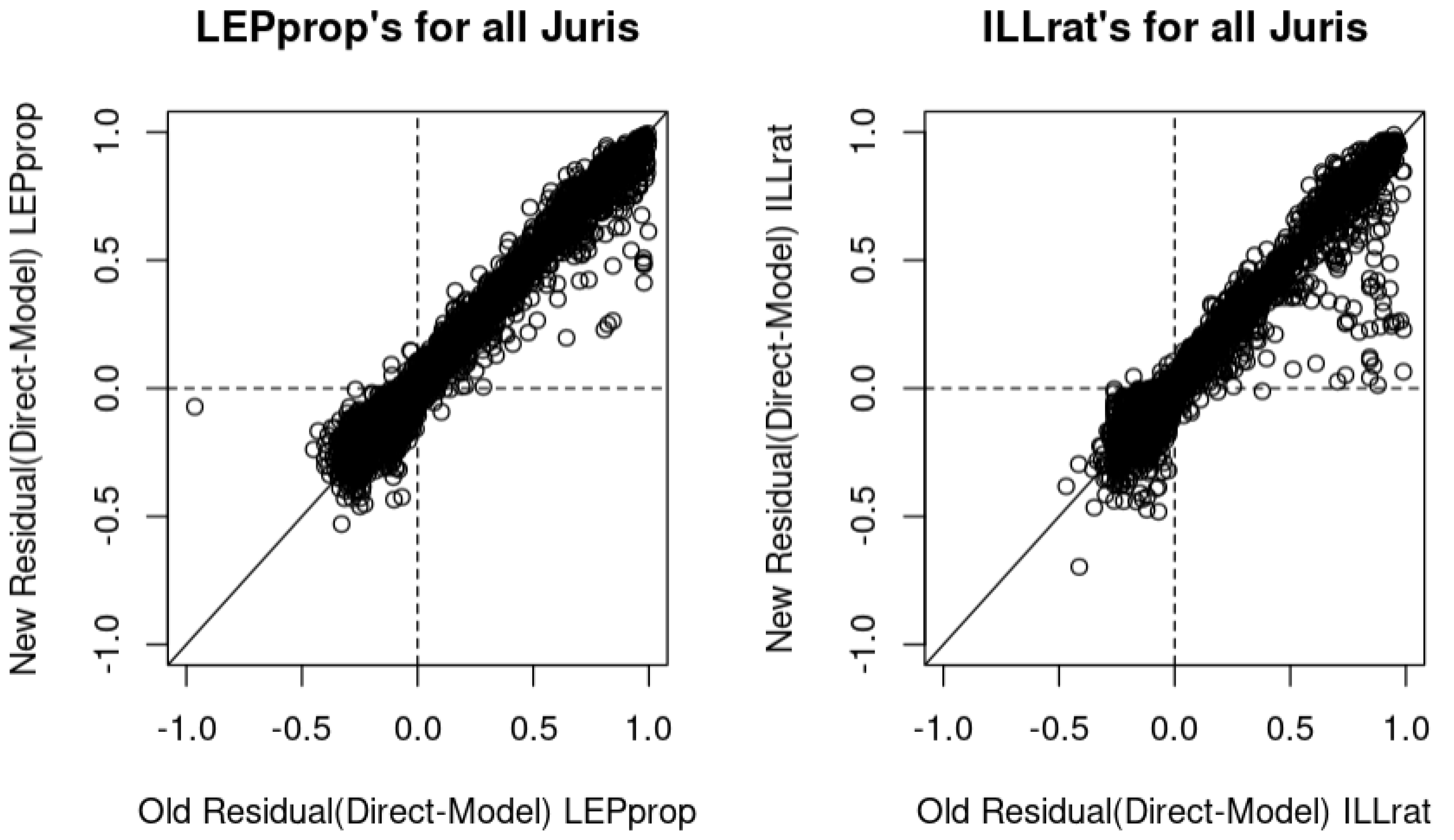
4.2.5. Residual Plots
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of the Posterior [6]
Appendix B. Derivation of the Posterior for the VRA Model
Appendix C. Derivation of
Appendix D. Derivation of
Appendix E. Algebraic Basics: Sum of Quadratic Matrices
Appendix E.1. Sum of Two Quadratic Matrices
Appendix E.2. Sum of N Quadratic Matrices
References
- Slud, E.V.; Franco, C.; Hall, A.; Kang, J. Statistical Methodology (2021) for Voting Rights Act, Section 203 Determinations. 2022. Available online: https://www.census.gov/library/working-papers/2022/adrm/RRS2022-06.html (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Joyce, P.M.; Malec, D.; Little, R.J.; Gilary, A.; Navarro, A.; Asiala, M.E. Statistical Modeling Methodology for the Voting Rights Act Section 203 Language Assistance Determinations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2014, 109, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slud, E.V.; Ashmead, R.; Joyce, P.; Wright, T. Statistical Methodology (2016) for Voting Rights Act, Section 203 Determinations. 2018. Available online: https://www.census.gov/library/working-papers/2018/adrm/RRS2018-12.html (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Bates, D.M. Approximations to the Log-Likelihood Function in the Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Model. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1995, 4, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A probabilistic programming language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polson, N.G.; Scott, J.G.; Windle, J. Bayesian Inference for Logistic Models Using Polya Gamma Latent Variables. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2013, 108, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, N.G.; Scott, J.G.; Windle, J. Package: BayesLogit 2.1. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/BayesLogit/index.html (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- George, E.I.; McCulloch, R.E. Variable Selection via Gibbs Sampling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Casella, G. The Bayesian Lasso. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 103, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Jurisdiction | # of Voting-Aged Persons | CITprop | LEPprop | ILLprop | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jurisdiction 1 | 1000 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.01 | |
| Jurisdiction 2 | 10 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.19 | 0.07 | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Jurisdiction N | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.93 | 0.10 | 0.01 |
| Binomial Prob. | Ratio | Equivalent Prob. | Log-Likelihood Contribution for a Jurisdiction |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIT/VOT | |||
| LEP/CIT | |||
| ILL/LEP |
| [1, 4] | [5, 12] | [13, 25] | [26, 50] | [51, 200] | [201, ] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta (Old) | 611.9 | 9.7 | −143.0 | −47.5 | −319.9 | −64.3 |
| PctRel (Old) | 47.2 | 0.4 | −6.2 | −1.9 | −3.1 | −0.4 |
| Stdiz (Old) | 3.2 | 0.0 | −0.5 | −0.2 | −0.6 | −0.1 |
| Delta (New) | 223.6 | −117.3 | −126.1 | −62.4 | 42.4 | 8.5 |
| PctRel (New) | 17.3 | −5.3 | −5.5 | −2.5 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Stdiz (New) | 1.2 | −0.4 | −0.5 | −0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| [1, 4] | [5, 12] | [13, 25] | [26, 50] | [51, 200] | [201, ] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta (Old) | 228.5 | −143.3 | −55.9 | −8.3 | −49.6 | −11.4 |
| PctRel (Old) | 54.3 | −18.4 | −6.7 | −1.9 | −3.6 | −1.4 |
| Stdiz (Old) | 2.5 | −1.0 | −0.3 | −0.1 | −0.2 | −0.1 |
| Delta (New) | 87.2 | −174.3 | 11.5 | 62.9 | −2.5 | −9.7 |
| PctRel (New) | 20.7 | −22.4 | 1.4 | 14.4 | −0.2 | −1.2 |
| Stdiz (New) | 0.9 | −1.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | −0.1 |
| [1, 4] | [5, 12] | [13, 25] | [26, 50] | [51, 200] | [201, ] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | 104.9 | 50.1 | 43 | 28.7 | 21.7 | 12.9 |
| New | 79.7 | 44.0 | 39 | 22.0 | 17.0 | 8.5 |
| (0, 4] | (4, 12] | (12, 25] | (25, 50] | (50, 200] | (200, ] | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # LMGs with |Stdiz|>1.96 (Old) | 15 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 24 |
| # LMGs with |Stdiz|>1.96 (New) | 7 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 16 |
| # LMGs with |Stdiz|>1.96 (Old and New) | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| # LMGs with |Stdiz|>1.96 (Old or New) | 15 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 26 |
| # LMGs with |Stdiz|>1.96 (Improved) | 14 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 22 |
| % LMGs with |Stidz|>1.96 (Improved) | 93% | 57% | 100% | 100% | 100% | NA | 85% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hall, A.C.; Kang, J. Inference with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for US Election Law. Mathematics 2025, 13, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060945
Hall AC, Kang J. Inference with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for US Election Law. Mathematics. 2025; 13(6):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060945
Chicago/Turabian StyleHall, Adam C., and Joseph Kang. 2025. "Inference with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for US Election Law" Mathematics 13, no. 6: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060945
APA StyleHall, A. C., & Kang, J. (2025). Inference with Pólya-Gamma Augmentation for US Election Law. Mathematics, 13(6), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060945





