Towards Dynamic Learner State: Orchestrating AI Agents and Workplace Performance via the Model Context Protocol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Learner State
2.1. Competencies and CBL/CBT
2.2. Multi-Dimensional Learner State
3. Theoretical Foundations
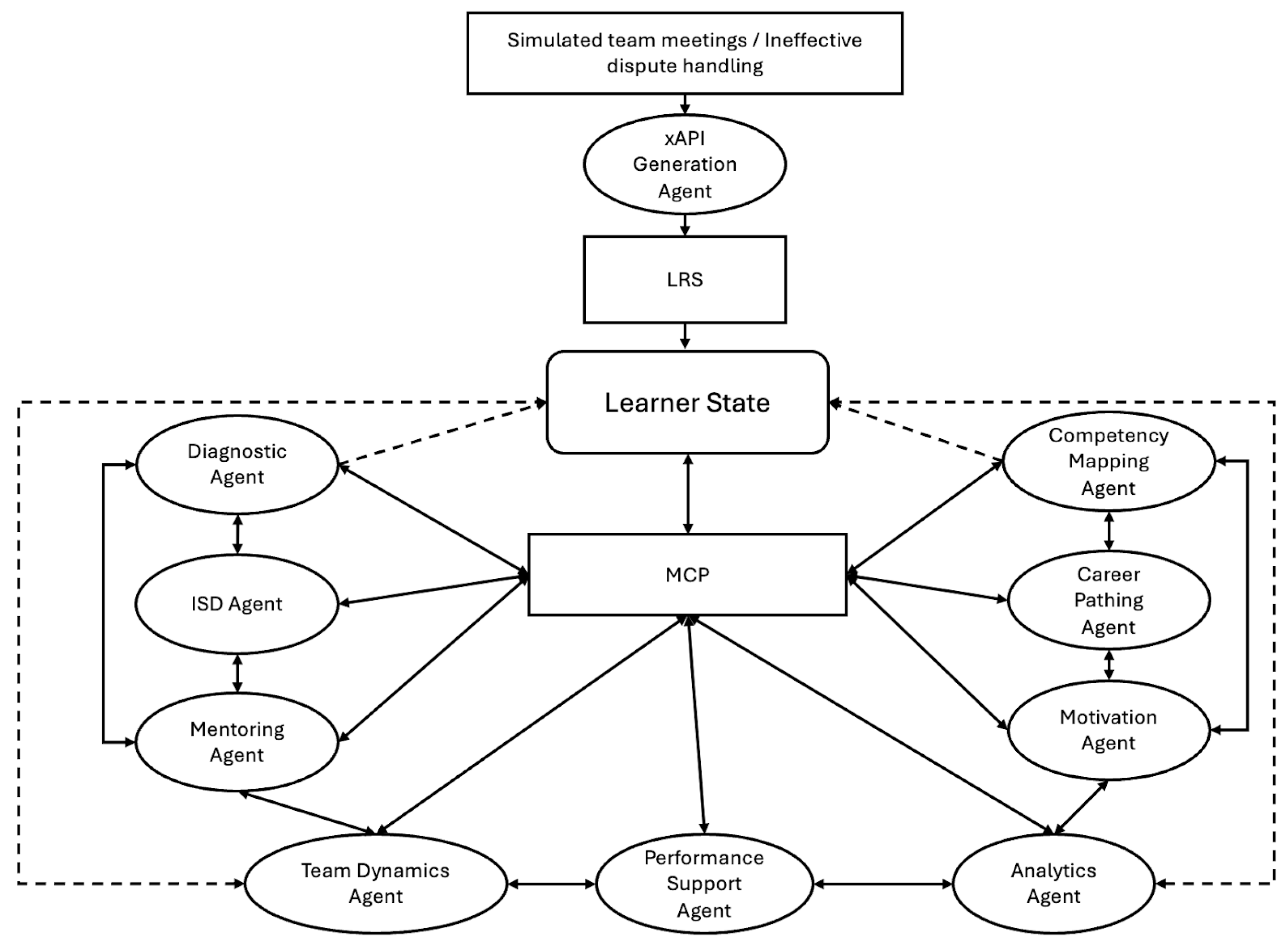
4. The Orchestration Layer: Model Context Protocol (MCP) and AI Agents
4.1. Model Context Protocol (MCP)
4.2. The Proposed AI Agents Suite
5. Integrating Workplace Performance
5.1. The Need for Integrating In-Workflow Performance
5.2. Infrastructure for In-Workflow Data
5.3. Adoption Challenges
6. Roadmap to Building a Learner-State Ecosystem
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| MCP | Model Context Protocol |
| LRS | Learning Record Stores |
| LMS | Learning management systems |
| xAPI | Experience API |
| L&D | Learning and development |
| CBL | Competency-based learning |
| CBT | Competency-based training |
| HR | Human Resource |
| HRD | Human resource development |
| ISD | Instructional Systems Design |
| ROI | Return on investment |
| OCB | Organizational Citizenship Behavior |
| SRL | Self-regulated learning |
| CRM | Customer relationship management |
| EPSS | Electronic Performance Support System |
References
- Alainati, S., Alshawi, S., & Al-Karaghouli, W. (2010, April 12–13). The effect of education and training on competency. European and Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. [Google Scholar]
- Anthropic. (2024, November 25). Introducing the model context protocol. Model Context Protocol. Available online: https://modelcontextprotocol.io/introduction (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Arditi, D., Gluch, P., & Holmdahl, M. (2013). Managerial competencies of female and male managers in the Swedish construction industry. Construction Management and Economics, 31(9), 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghode, V., Heminger, S., & McLean, G. N. (2021). Career self-efficacy and education abroad: Implications for future global workforce. European Journal of Training and Development, 45(1), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokiasamy, L., Mansouri, N., Balaraman, R. A., & Kassim, N. M. (2017). A literature review of competence development on academic career advancement: A human resource development perspective. Global Business and Management Research, 9(1s), 403. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhurst, D. (2009). Reflections on activity theory. Educational Review, 61(2), 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, T. T., & Ford, J. K. (1988). Transfer of training: A review and directions for future research. Personnel Psychology, 41(1), 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. (2023). Cultivate self-efficacy for personal and organizational effectiveness. In Principles of organizational behavior: The handbook of evidence-based management (3rd ed., pp. 113–135). John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Basit, A. A. (2019). Examining how respectful engagement affects task performance and affective organizational commitment: The role of job engagement. Personnel Review, 48(3), 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, T. S., & Organ, D. W. (1983). Job satisfaction and the good soldier: The relationship between affect and employee “citizenship”. Academy of Management Journal, 26(4), 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B. S. (1968). Learning for mastery. Instruction and curriculum. Regional education laboratory for the carolinas and virginia, topical papers and reprints, number 1. Evaluation comment, 1(2), n2. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, B. S. (1984). The 2 sigma problem: The search for methods of group instruction as effective as one-to-one tutoring. Educational Researcher, 13(6), 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, W. C., & Motowidlo, S. J. (1997). Task performance and contextual performance: The meaning for personnel selection research. Human Performance, 10(2), 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boud, D., & Garrick, J. (2001). Understandings of workplace learning. In D. Boud, & J. Garrick (Eds.), Understanding learning at work (pp. 1–11). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Boyatzis, R. E. (1991). The competent manager: A model for effective performance. John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Boyatzis, R. E. (2008). Competencies in the 21st century. Journal of Management Development, 27(1), 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, B. A. (2022). The impact of self-efficacy based prebriefing on nursing student clinical competency and self-efficacy in simulation: An experimental study. Nurse Education Today, 109, 105260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brightwell, A., & Grant, J. (2013). Competency-based training: Who benefits? Postgraduate Medical Journal, 89(1048), 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. (2005). Ecological systems theory (1992). In U. Bronfenbrenner (Ed.), Making human beings human: Bioecological perspectives on human development (pp. 106–173). Sage Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R. B. (1993). Meta-competence: A recipe for reframing the competence debate. Personnel Review, 22(6), 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaleta, X., Alsina, M., De Torres, E., & Fonseca, D. (2024). Automated monitoring of human–Computer interaction for assessing teachers’ digital competence based on LMS data extraction. Sensors, 24, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, G., Iandoli, L., & Zollo, G. (2006). A situationalist perspective to competency management. Human Resource Management, 45(3), 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W. R., Nesbit, P. L., Badham, R. J., Parker, S. K., & Sung, L. K. (2018). The effects of employee engagement and self-efficacy on job performance: A longitudinal field study. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(17), 2483–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasoli, C. P., Alliger, G. M., Donsbach, J. S., & Mathieu, J. E. (2018). Antecedents and outcomes of informal learning behaviors: A meta-analysis. Journal of Business and Psychology, 33(2), 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C. C. (2004). The relationship between the performance and the perceived benefits of using an electronic performance support system (EPSS). Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 41(3), 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D., Lin, M., Hajian, S., & Wang, Q. (2023). Educational design principles of using AI chatbot that supports self-regulated learning in education: Goal setting, feedback, and personalization. Sustainability, 15, 12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, N. I., Jariko, M. A., Mushtaque, T., Mahesar, H. A., & Ghani, Z. (2017). Impact of working environment and training & development on organization performance through mediating role of employee engagement and job satisfaction. European Journal of Training and Development Studies, 4(2), 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. L. (2015). The relationship of leader psychological capital and follower psychological capital, job engagement and job performance: A multilevel mediating perspective. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 26(18), 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. (2024). A classification tool to foster self-regulated learning with generative artificial intelligence by applying self-determination theory: A case of ChatGPT. Educational Technology Research and Development, 72(4), 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K., Ahmad, Z., Ismailov, M., & Sanusi, I. T. (2024). What are artificial intelligence literacy and competency? A comprehensive framework to support them. Computers and Education Open, 6, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, M. S., Garza, A. S., & Slaughter, J. E. (2011). Work engagement: A quantitative review and test of its relations with task and contextual performance. Personnel Psychology, 64(1), 89–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S. (2021). An empirical study of displaceable job skills in the age of robots. European Journal of Training and Development, 45(6/7), 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clanton, J., Gardner, A., Cheung, M., Mellert, L., Evancho-Chapman, M., & George, R. L. (2014). The relationship between confidence and competence in the development of surgical skills. Journal of Surgical Education, 71(3), 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G. M., & Luthans, F. (2007). Diversity training: Analysis of the impact of self-efficacy. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 18(1), 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D. A., Brydges, R., Zendejas, B., Hamstra, S. J., & Hatala, R. (2013). Mastery learning for health professionals using technology-enhanced simulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Academic Medicine, 88(8), 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeanu, A., & Iliescu, D. (2023). The link between work engagement and job performance. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 22(3), 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M. (2020). Ecological Systems theory: Exploring the development of the theoretical framework as con-ceived by Bronfenbrenner. Journal of Public Health Issues and Practices, 4(2), 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, N. (2007). Ecological systems theory: The person in the center of the circles. Research in Human Development, 4(3–4), 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J. D. (2022). The modern learning ecosystem: A new L&D mindset for the ever-changing workplace. Association for Talent Development. [Google Scholar]
- Draganidis, F., & Mentzas, G. (2006). Competency based management: A review of systems and approaches. Information Management & Computer Security, 14(1), 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus, H. L., & Dreyfus, S. E. (1984). Putting computers in their proper place: Analysis versus intuition in the classroom. Teachers College Record, 85(4), 578–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, L. C., & Berge, Z. L. (2018). Microlearning: Knowledge management applications and competency-based training in the workplace. Knowledge Management & E-Learning, 10(2), 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Engeström, R. (2009). Who is acting in an activity system. In A. L. Sannino, A. Sannino, H. Daniels, & K. D. Gutiérrez (Eds.), Learning and expanding with activity theory (pp. 257–273). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Engeström, Y. (2000). Activity theory as a framework for analyzing and redesigning work. Ergonomics, 43(7), 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eraut, M. (2005). Initial teacher training and the NVQ model. In J. Burke (Ed.), Competency based education and training (pp. 161–172). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Farashah, A. D., Thomas, J., & Blomquist, T. (2019). Exploring the value of project management certification in selection and recruiting. International Journal of Project Management, 37(1), 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqe, F., Watkins, R., & Medsker, L. (2021). Competency model approach to AI literacy: Research-based path from initial framework to model. arXiv, arXiv:2108.05809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K. W. (1980). A theory of cognitive development: The control and construction of hierarchies of skills. Psychological Review, 87, 477–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K. W., & Bidell, T. R. (2006). Dynamic development of action and thought. In R. M. Lerner, W. Damon, R. M. Lerner, & W. Damon (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Theoretical models of human development (pp. 313–399). John Wiley &Sons Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, L. (2016). Training perceptions, engagement, and performance: Comparing work engagement and personal role engagement. Human Resource Development International, 19(1), 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A. (2017). The viability of online competency based education: An organizational analysis of the impending paradigm shift. The Journal of Competency-Based Education, 2(4), e01055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, S., McIlroy, J., Oulanova, O., Eva, K., & Regehr, G. (2010). Toward authentic clinical evaluation: Pitfalls in the pursuit of competency. Academic Medicine, 85(5), 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gist, M. E., Stevens, C. K., & Bavetta, A. G. (1991). Effects of self-efficacy and post-training intervention on the acquisition and maintenance of complex interpersonal skills. Personnel Psychology, 44(4), 837–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, M., Chan, T. M., Zaver, F., & Ellaway, R. (2022). Confidence-competence alignment and the role of self-confidence in medical education: A conceptual review. Medical Education, 56(1), 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., Du, H., Xie, B., & Mo, L. (2017). Work engagement and job performance: The moderating role of perceived organizational support. Anales de Psicología/Annals of Psychology, 33(3), 708–713. [Google Scholar]
- Guskey, T. R. (2022). Implementing mastery learning. Corwin Press. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, H. (2009). Competence and competency-based training: What the literature says. National Centre for Vocational Education Research Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Haruna, A. Y., & Marthandan, G. (2017). Foundational competencies for enhancing work engagement in SMEs Malaysia. Journal of Workplace Learning, 29(3), 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härkönen, U. (2007). The Bronfenbrenner ecological systems theory of human development. In Scientific articles of V international conference. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/67678654/The_Bronfenbrenner_ecological_systems_theory_of_human_development (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Henri, M., Johnson, M. D., & Nepal, B. (2017). A review of competency-based learning: Tools, assessments, and recommendations. Journal of Engineering Education, 106(4), 607–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, E. F., III, Bates, R. A., & Ruona, W. E. (2000). Development of a generalized learning transfer system inventory. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 11(4), 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J. (2019). Artificial intelligence: Implications for the future of work. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 62(11), 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y., & Klein, J. D. (2023). Mobile performance support systems: Characteristics, benefits, and conditions. TechTrends, 67(1), 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., & Klein, J. D. (2025). Benefits and challenges in adopting mobile performance support systems. TechTrends, 69(3), 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M., Maseleno, A., Teh, K. S. M., Don, A. G., Basiron, B., Jasmi, K. A., Mustari, M., Nasir, B. M., & Ahmad, R. (2018). Understanding Modern Learning Environment (MLE) in big data era. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (Online), 13(5), 71. [Google Scholar]
- Ilić, M., Mikić, V., Kopanja, L., & Vesin, B. (2023). Intelligent techniques in e-learning: A literature review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 56, 14907–14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S., Im, K., Yoo, M., Roll, I., & Seo, K. (2023). Supporting students’ self-regulated learning in online learning using artificial intelligence applications. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, D. H., & Rohrer-Murphy, L. (1999). Activity theory as a framework for designing constructivist learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 47(1), 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, W. A. (1990). Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management Journal, 33(4), 692–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya-Ozyer, K., & Yildiz, Z. (2022). Design and evaluation of an electronic performance support system for quantitative data analysis. Education and Information Technologies, 27(2), 2407–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, K. A., O’Leary-Kelly, A. M., & Martocchio, J. J. (1993). The impact of feedback and self-efficacy on performance in training. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 14(4), 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoudis, K., & Magoulas, G. D. (2018). User model interoperability in education: Sharing learner data using the Experience API and distributed ledger technology. In B. H. Khan, J. R. Corbeil, & M. E. Corbeil (Eds.), Responsible analytics and data mining in education (pp. 156–178). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Karsten, R., & Roth, R. M. (1998). Computer self-efficacy: A practical indicator of student computer competency in introductory IS courses. Informing Science, 1(3), 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kert, S. B., & Kurt, A. A. (2012). The effect of electronic performance support systems on self-regulated learning skills. Interactive Learning Environments, 20(6), 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. (2017). Examining mediation effects of work engagement among job resources, job performance, and turnover intention. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 29(4), 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, J. D., & Kirkpatrick, W. K. (2016). Kirkpatrick’s four levels of training evaluation. Association for Talent Development. [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers, M. T., & Scheerens, J. (2006). Career competencies for the modern career. Journal of Career Development, 32(4), 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmin, K. L., Ley, T., & Normak, P. (2017, October 11–12). Towards a data driven competency management platform for Industry 4.0. Workshop Papers of i-Know (Vol. 2025, p. 1), Graz, Austria. [Google Scholar]
- Leiß, T. V., Rausch, A., & Seifried, J. (2022). Problem-solving and tool use in office work: The potential of electronic performance support systems to promote employee performance and learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 869428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liles, R. T., & Mustian, R. D. (2004). Core competencies: A systems approach for training and organizational development in extension. The Journal of Agricultural Education and Extension, 10(2), 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LinkedIn Learning. (2021). Workplace learning report. Available online: https://learning.linkedin.com/resources/workplace-learning-report-2021 (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Loia, V., De Maio, C., Fenza, G., Orciuoli, F., & Senatore, S. (2010, July 18–23). An enhanced approach to improve enterprise competency management. IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (pp. 1–8), Barcelona, Spain. [Google Scholar]
- Lustri, D., Miura, I., & Takahashi, S. (2007). Knowledge management model: Practical application for competency development. The Learning Organization, 14(2), 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, K., Dissanayake, P., Pathirana, C., Deegahawature, D., & Silva, R. (2023). A competency-based training guide model for labourers in construction. International Journal of Construction Management, 23(8), 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, M. F. (2020). Dynamic skill theory: An integrative model of psychological development. In M. F. Mascolo, & T. Bidell (Eds.), Handbook of integrative psychological development (pp. 91–135). Routledge/Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Mbarushimana, N., & Kuboja, J. M. (2016). A paradigm shift towards competence-based curriculum: The experience of Rwanda. Saudi Journal of Business and Management Studies, 1(1), 6–17. [Google Scholar]
- McBeath, G. (1990). Practical management development: Strategies for management resourcing and development in the 1990s. John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- McGaghie, W. C., Adler, M., & Salzman, D. H. (2020). Instructional design and delivery for mastery learning. In W. C. McGaghie, J. H. Barsuk, & D. B. Wayne (Eds.), Comprehensive healthcare simulation: Mastery learning in health professions education (pp. 71–88). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- McKinsey, & Company. (2025). AI in the workplace: Empowering people to unlock AI’s full potential at work. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- McMullan, M., Endacott, R., Gray, M. A., Jasper, M., Miller, C. M., Scholes, J., & Webb, C. (2003). Portfolios and assessment of competence: A review of the literature. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 41(3), 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M. A., Salleh, R., & Baharom, M. N. R. (2016). The link between training satisfaction, work engagement and turnover intention. European Journal of Training and Development, 40(6), 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motowidlo, S. J., & Van Scotter, J. R. (1994). Evidence that task performance should be distinguished from contextual performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79(4), 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T. S., Owen, E., & McGaw, B. (2005). Learning a living: First results of the adult literacy and life skills survey. Statistics Canada and the Organization for Cooperation and Development.
- National Center for Education Statistics. (n.d.). International adult literacy survey (IALS). U.S. Department of Education. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/surveys/ials/index.asp (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Neal, J. W., & Neal, Z. P. (2013). Nested or networked? Future directions for ecological systems theory. Social Development, 22(4), 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D., Tan, C., & Leung, J. (2024). Empowering student self-regulated learning and science education through ChatGPT: A pioneering pilot study. British Journal of Educational Technology, 55, 1328–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolajevaite, M., & Sabaityte, E. (2016). Relationship between employees’ competencies and job satisfaction: British and Lithuanian employees. Psychology Research, 6(11), 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noercahyo, U. S., Maarif, M. S., & Sumertajaya, I. M. (2021). The role of employee engagement on job satisfaction and its effect on organizational performance. Jurnal Aplikasi Manajemen, 19(2), 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberländer, M., Beinicke, A., & Bipp, T. (2020). Digital competencies: A review of the literature and applications in the workplace. Computers & Education, 146, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R., Kersten, H., Vinkka-Puhakka, H., Alpasan, G., Bearn, D., Cema, I., Delap, E., Dummer, P., Goulet, J. P., Gugushe, T., Jeniati, E., Jerolimov, V., Kotsanos, N., Krifka, S., Levy, G., Neway, M., Ogawa, T., Saag, M., Sidlauskas, A., … White, D. (2008). Curriculum structure: Principles and strategy. European Journal of Dental Education, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palan, R. (2007). Competency management—A practitioner’s guide. Specialist Management Resources Sdn Bhd. [Google Scholar]
- Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). Academic Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P. R., & De Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82(1), 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratisto, E., & Danoetirta, D. (2025). Design and user analysis of a learning management system: Student competency-based learning. Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence Journal, 5(1), 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott-Clements, L., Van Der Vleuten, C. P., Schuwirth, L. W., Hurst, Y., & Rennie, J. S. (2008). Evidence for validity within workplace assessment: The Longitudinal Evaluation of Performance (LEP). Medical Education, 42(5), 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyché, V., Tremblay, D. G., Miladi, F., & Yagoubi, A. (2023). A competency framework for training of AI projects managers in the digital and AI Era. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 11(5), 537–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasdi, R. M., Idris, F. H., Krauss, S. E., & Omar, M. K. (2024). Exploring artificial intelligence competencies for the future workforce: A systematic literature review using the PRISMA protocol. In Y. G. Ng, D. D. Daruis, & N. W. Abdul Wahat (Eds.), Human factors and ergonomics toward an inclusive and sustainable future. HFEM 2023 (Vol. 46). Springer Series in Design and Innovation. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, B. L., Lepine, J. A., & Crawford, E. R. (2010). Job engagement: Antecedents and effects on job performance. Academy of Management Journal, 53(3), 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesterer, T., & Shacklette, D. (2025, May 22). Precision skills intelligence: Moving beyond self-assessments in sales performance. Corporate Visions. Available online: https://corporatevisions.com/blog/precision-skills-intelligence/ (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Roberts, D. R., & Davenport, T. O. (2002). Job engagement: Why it’s important and how to improve it. Employment Relations Today, 29(3), 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Saks, A. M., Gruman, J. A., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Organization engagement: A review and comparison to job engagement. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, 9(1), 20–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M., Ganie, S. A., & Saleem, I. (2020). The concept of competence: A thematic review and discussion. European Journal of Training and Development, 44(6/7), 717–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaik, P. V., Pearson, R., & Barker, P. (2002). Designing electronic performance support systems to facilitate learning. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 39(4), 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W. B., Bakker, A. B., & Salanova, M. (2006). The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: A cross-national study. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66(4), 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W. B., Salanova, M., González-Romá, V., & Bakker, A. B. (2002). The measurement of engagement and burnout: A two sample confirmatory factor analytic approach. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B. (1982). Competency based learning: A literature review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 19(3), 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhar, C., Patwardhan, M., & Vyas, V. (2018). Linking work engagement to job performance through flexible human resource management. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 20(1), 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, B. (2021). Developing and investigating an electronic performance support system (EPSS) for academic performance. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 37(6), 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzmann, T., & Weinhardt, J. M. (2018). Training engagement theory: A multilevel perspective on the effectiveness of work-related training. Journal of Management, 44(2), 732–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, R. E. (1987). Mastery learning reconsidered. Review of Educational Research, 57(2), 175–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B., Hernandez, M., & Gordon, J. (2019). Competency-based learning in 2018. Advanced Distributed Learning Initiative (ADL). [Google Scholar]
- Snyman, M., & Van den Berg, G. (2018). The significance of the learner profile in recognition of prior learning. Adult Education Quarterly, 68(1), 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G. W. (2012). A critical review of the science and practice of competency modeling. Human Resource Development Review, 12(1), 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D. B., Norman, G. R., & Linn, R. L. (1995). Performance-based assessment: Lessons from the health professions. Educational Researcher, 24(5), 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrinjarić, B. (2022). Competence-based approaches in organizational and individual context. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 9(1), 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The SFIA Foundation. (2025). SFIA: The global skills and competency framework for a digital world. Available online: https://sfia-online.org/en (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Tuxworth, E. (2005). Competence based education and training: Background and origins. In J. Burke (Ed.), Competency based education and training (pp. 9–22). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Tyas, A. A. W. P., Tippe, S., & Sutanto, S. (2020). How employee competency and self efficacy affect employee work engagement in human resource development agency (BPSDM) ministry of law and human rights Republic of Indonesia. IJHCM (International Journal of Human Capital Management), 4(2), 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakola, M., Eric Soderquist, K., & Prastacos, G. P. (2007). Competency management in support of organisational change. International Journal of Manpower, 28(3/4), 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirani, N. (2010). Review paper: Competencies and competency model–A brief overview of its development and application. SIES Journal of Management, 7(1), 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R. W. (1959). Motivation reconsidered: The concept of competence. Psychological Review, 66(5), 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingreen, S. C., & Blanton, J. E. (2007). A social cognitive interpretation of person-organization fitting: The maintenance and development of professional technical competency. Human Resource Management, 46(4), 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., Lowell, V. L., Exter, M., Richardson, J., & Olenchak, F. R. (2025). Transfer of training and learner attitude: A mixed-methods study on learner experience in an authentic learning program. Human Resource Development International, 28(3), 346–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., Lowell, V. L., Talafha, A. M., & Harbor, J. (2020). Transfer of training, trainee attitudes and best practices in training design: A multiple-case study. TechTrends, 64(2), 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., & Watson, S. L. (2022). Attitudinal influences on transfer of training: A systematic literature review. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 34(4), 327–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R., Liu, L., & Feng, G. (2021). An Overview of Recent Advances in Distributed Coordination of Multi-Agent Systems. Unmanned Systems, 10, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarifian, P. (1999). Objectif compétence. Pour une nouvelle logique (p. 229). Editions Liaisons. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B. J. (1990). Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: An overview. Educational Psychologist, 25(1), 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41(2), 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Paradigm shift and data foundation | Infrastructure for initial agents and insights | Performance integration and holistic development | Predictive intelligence and continuous evolution |
| Objective | To initiate organizational L&D paradigm shift and build unified secure data foundation capturing diverse learning and performance events from across the organization | To enable precision skill mapping and build and integrate foundational MCP and AI infrastructure | To integrate in-workflow performance, enable a continuous and authentic understanding of individual performance and skill application, and develop a comprehensive multidimensional learner state | To leverage advanced AI to forecast future talent needs, proactively manage employee development, and continuously refine the entire learning experience |
| Key activities | Strategic alignment Data source identification LRS establishment and xAPI generation agent Initial MCP layer design Multi-dimensional learner state design Data security and ethical use framework | Develop and train initial set of AI agents (xAPI generation, competency mapping, diagnostic, ISD, mentoring, analytics) Core MCP layer development and agent integration | Instrument key operational software and hardware Advanced xAPI Generation Develop advanced MCP capabilities for complex data flows Other AI agents (performance support, team dynamic, career pathing) | Develop advanced AI models to personalize encouragement and engagement strategies (motivation agent) MCP optimization and scalability Implement advanced AI algorithms for ISD agent Human oversight and refinement |
| Example tools | PostgreSQL, Docker, Python, REST APIs, LRS, xAPI, MCP | TensorFlow, Hugging Face, Kubernetes, FastAPI, MCP | Existing enterprise systems, IoT sensors, MongoDB, Redis, MCP, Apache Kafka | Edge AI, Microservices, enterprise systems and platform, MCP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Lovett, N.; Li, B.; Hou, Z. Towards Dynamic Learner State: Orchestrating AI Agents and Workplace Performance via the Model Context Protocol. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081004
Yang M, Lovett N, Li B, Hou Z. Towards Dynamic Learner State: Orchestrating AI Agents and Workplace Performance via the Model Context Protocol. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(8):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081004
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mohan, Nolan Lovett, Belle Li, and Zhen Hou. 2025. "Towards Dynamic Learner State: Orchestrating AI Agents and Workplace Performance via the Model Context Protocol" Education Sciences 15, no. 8: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081004
APA StyleYang, M., Lovett, N., Li, B., & Hou, Z. (2025). Towards Dynamic Learner State: Orchestrating AI Agents and Workplace Performance via the Model Context Protocol. Education Sciences, 15(8), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081004






