Fluorine-Free Single-Component Polyelectrolyte of Poly(ethylene glycol) Bearing Lithium Methanesulfonylsulfonimide Terminal Groups: Effect of Structural Variance on Ionic Conductivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Instruments
2.2.2. Measurement of Ion Conductivity
2.3. Synthesis of Polymers
2.3.1. Synthesis of DEGMME-LiMSSI2
2.3.2. Synthesis of TMPE450-LiMSSI3
2.3.3. Synthesis of PEG200-LiMSSI2 (Typical Procedure)
2.3.4. Synthesis of Other Polymers Bearing LiMSSI Termini
3. Results and Discussion
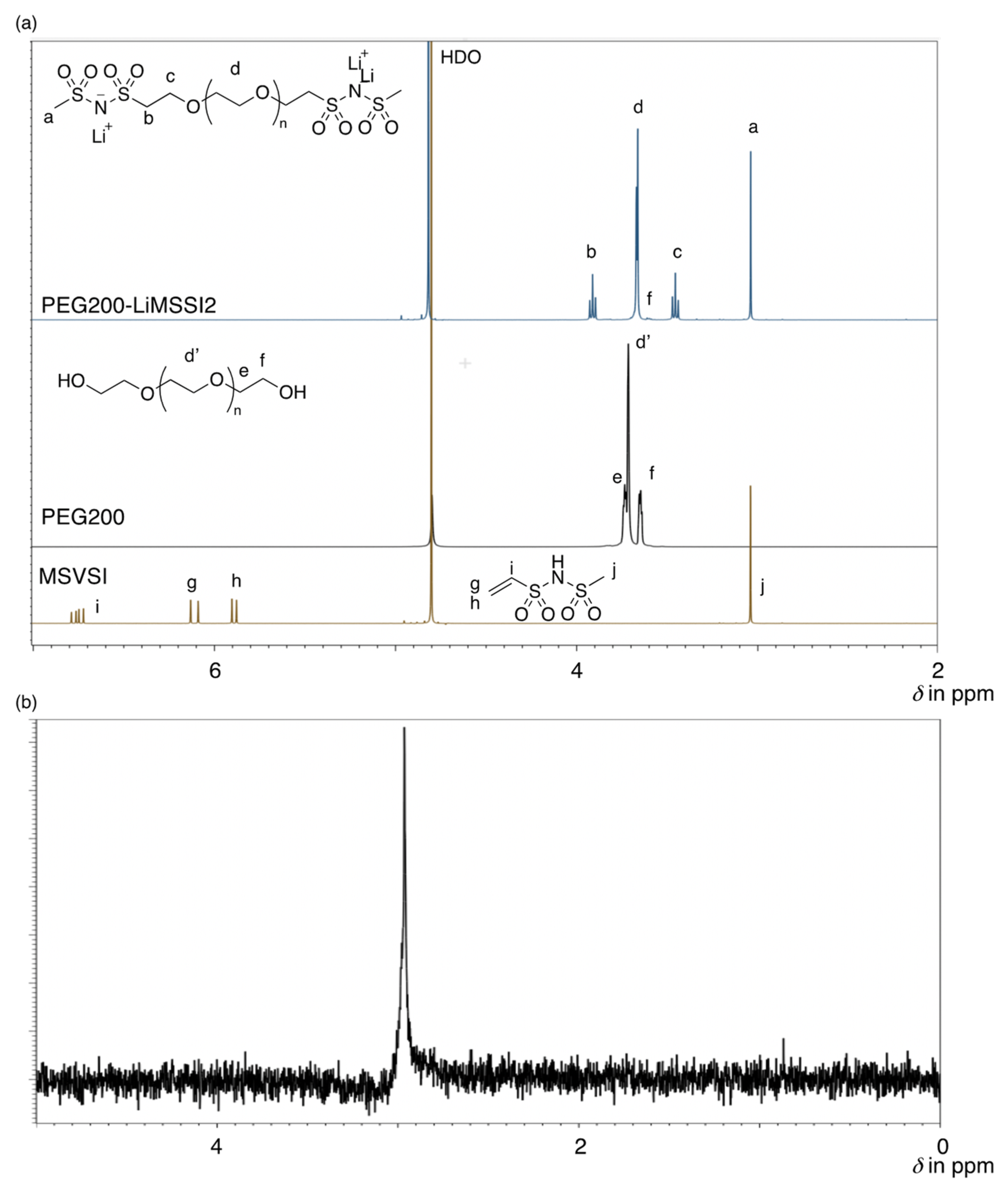
3.1. Synthesis of PEGs with LiMSSI Termini
3.2. Properties of PEGs with LiMSSI Termini
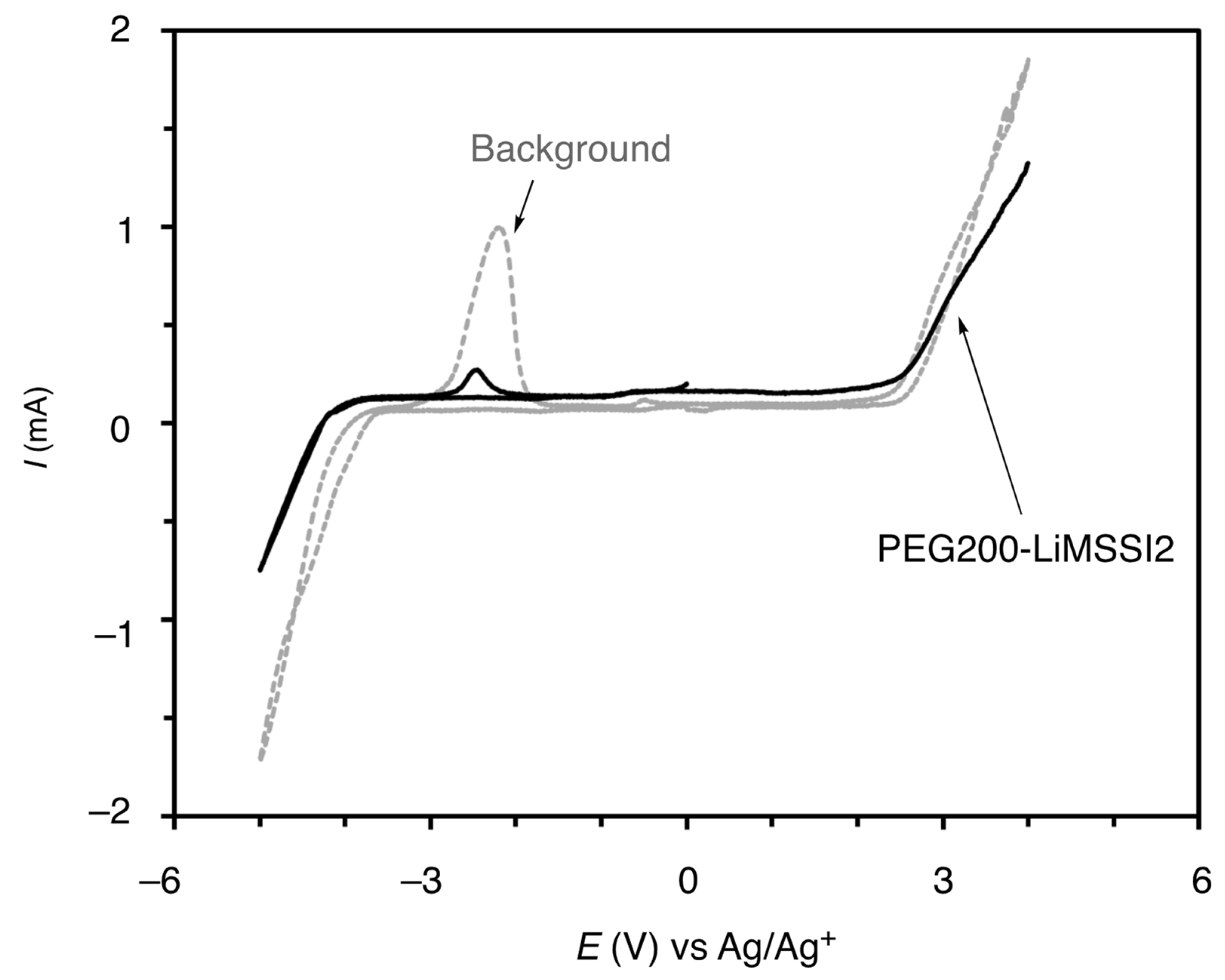
3.2.1. Electrochemical Stability
3.2.2. Thermal Behaviors
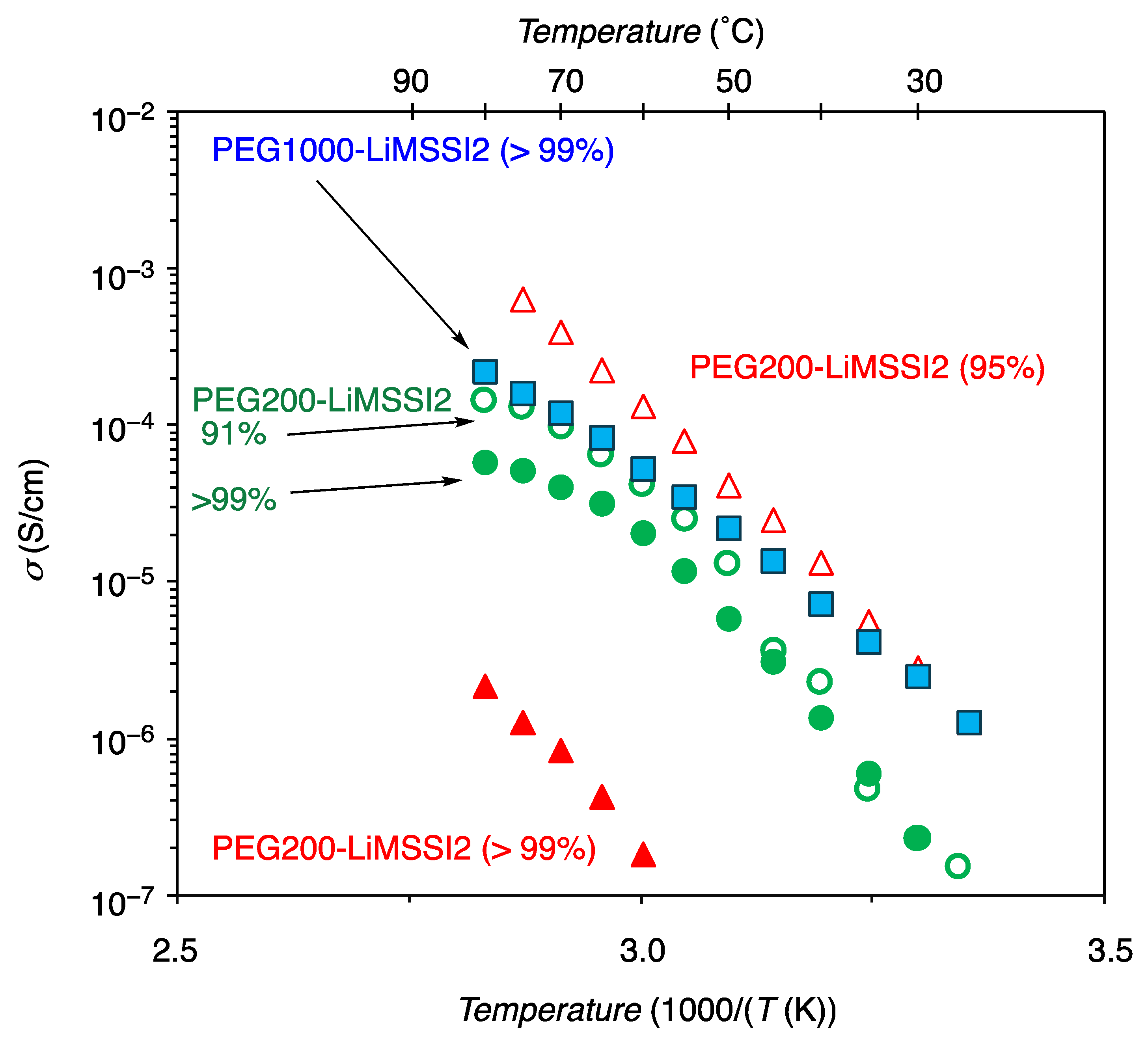
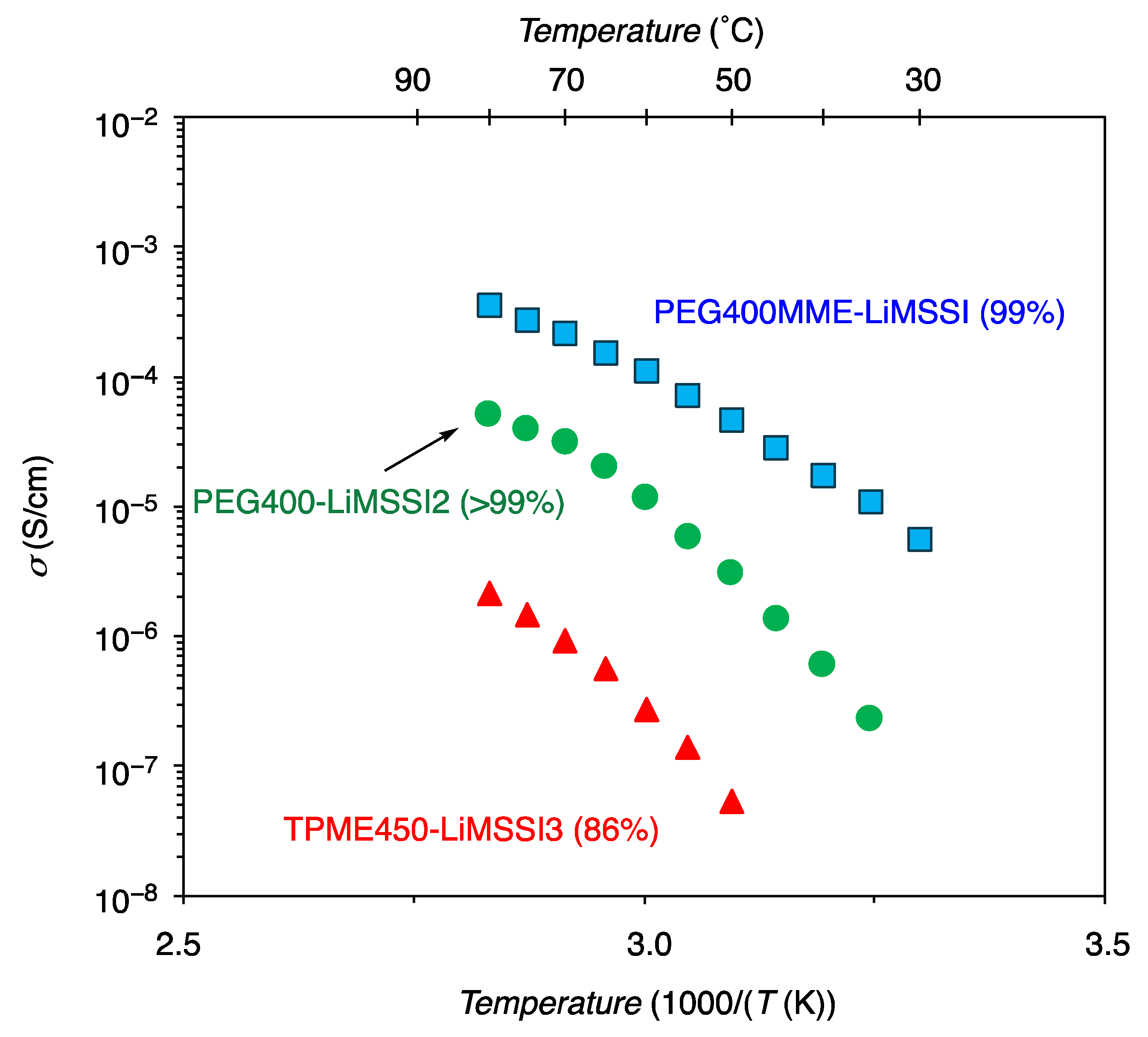
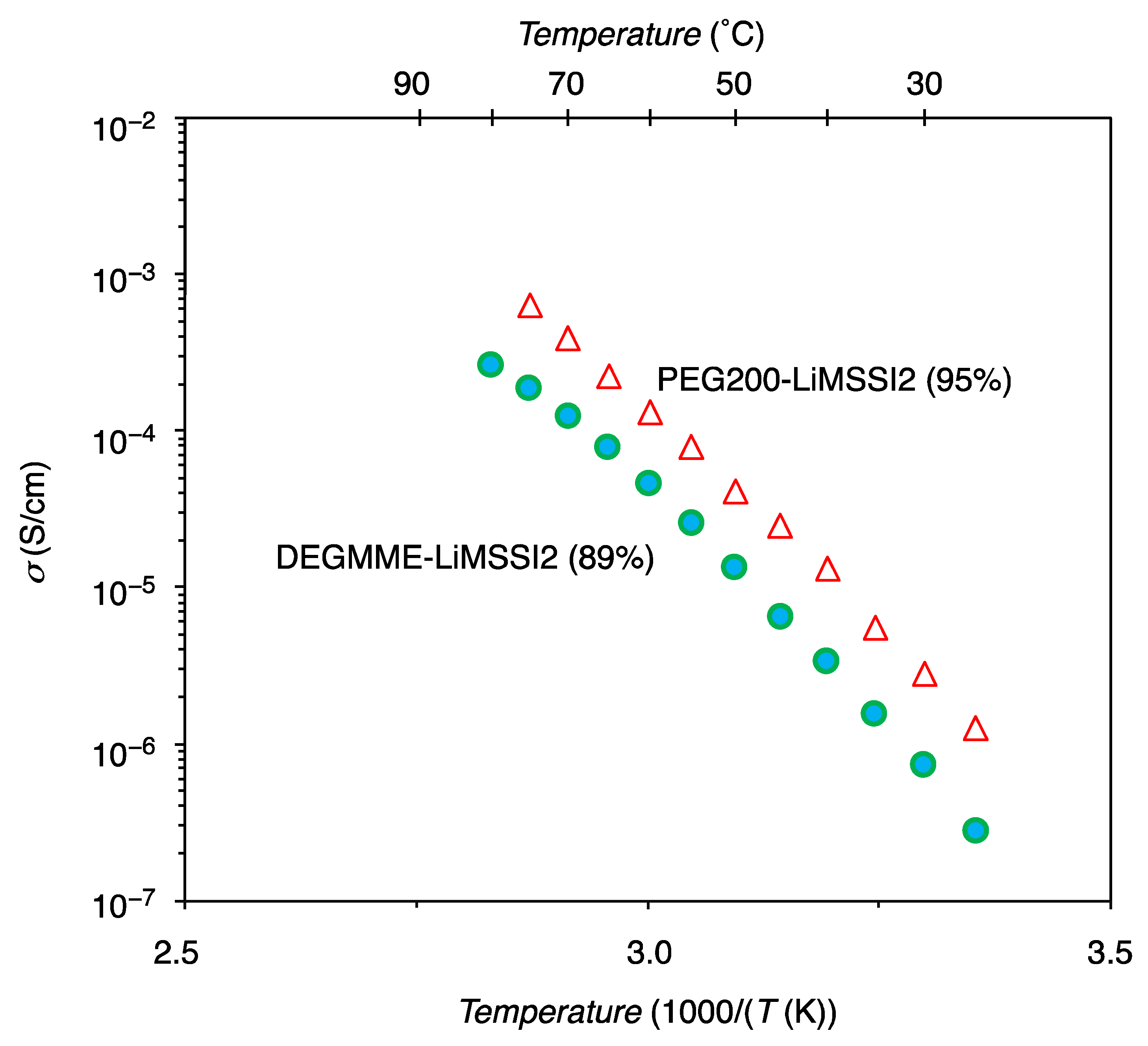
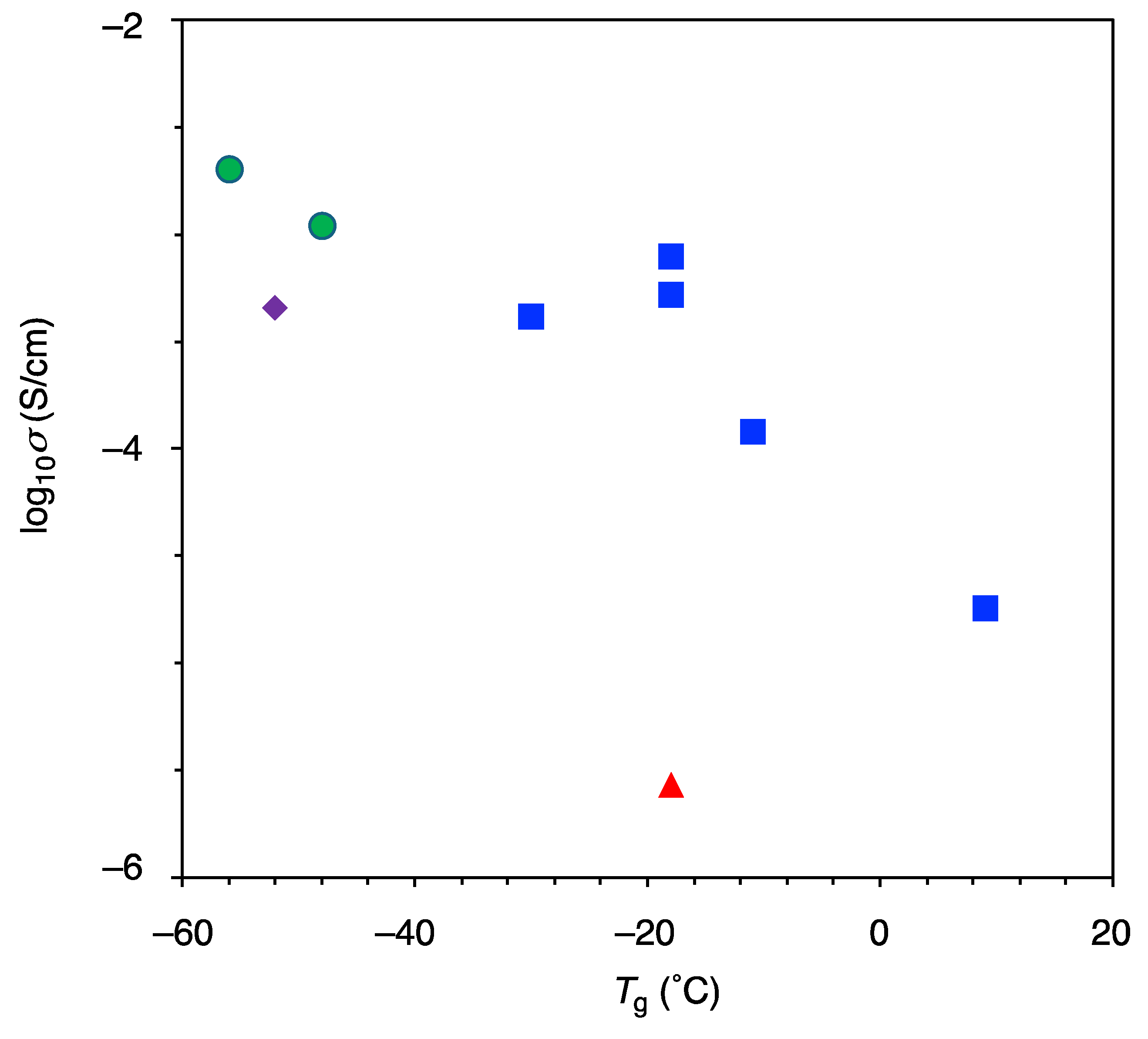
3.2.3. Ionic Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murata, K.; Izuchi, S.; Yoshihisa, Y. An overview of the research and development of solid polymer electrolyte batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Piszcz, M.; Coya, E.; Rojo, T.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M.; Armand, M.; Zhou, Z. Single lithium-ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes: Advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Song, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H. Ion transport and structural design of lithium-ion conductive solid polymer electrolytes: A perspective. Mater. Futures 2022, 1, 042103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Ito, K. Poly(ethylene oxide)s having carboxylate groups on the chain end. Polymer 1995, 36, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Tominaga, Y.; Ohno, H. Polyether/salt hybrid (IV). Effect of benzenesulfonate group(s) and PEO molecular weight on the bulk ionic conductivity. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Nishina, N.; Ohno, H. High lithium ionic conductivity of poly(ethylene oxide)s having sulfonate groups on their chain ends. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Ohno, H. High ionic conductivity of PEO/sulfonamide salt hybrids. Solid State Ion. 1999, 124, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Ohno, H. Lithium ion conduction in linear- and network-type polymers of PEO/sulfonamide salt hybrids. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 3081–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, T.; Buzoujima, Y. Novel lithium salts exhibiting high lithium ion transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2003, 119–121, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobukawa, H.; Tokuda, H.; Tabata, S.; Watanabe, M. Preparation and transport properties of novel lithium ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygadło-Monikowska, E.; Florjańczyk, Z.; Ostrowska, J.; Bołtromiuk, P.; Frydrych, J.; Sadurski, W.; Langwald, N. Synthesis and characterization of new trifluoroalkoxyborates lithium salts of ionic liquid properties. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 57, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygadło-Monikowska, E.; Florjańczyk, Z.; Służewska, K.; Ostrowska, J.; Langwald, N.; Tomaszewska, A. Lithium conducting ionic liquids based on lithium borate salts. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6055–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygadło-Monikowska, E.; Florjańczyk, Z.; Tomaszewska, A.; Pawlicka, M.; Langwald, N.; Kovarsky, R.; Mazor, H.; Golodnitsky, D.; Peled, E. New boron compounds as additives for lithium polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-González, G.; Alvarez-Tirado, M.; Olmedo-Martínez, J.L.; Picchio, M.L.; Casado, N.; Forsyth, M.; Mecerreyes, D. Lithium borate ionic liquids as single-component electrolytes for batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2202974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallac, B.B.; Geiculescu, O.E.; Rajagopal, R.V.; Creager, S.E.; DesMarteau, D.D. Lithium-conducting ionic melt electrolytes from polyether-functionalized fluorosulfonimide anions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5985–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, M.B.; Creager, S.E.; Rajagopal, R.V.; Geiculescu, O.E.; DesMarteau, D.D. Ionic conduction in polyether-based lithium arylfluorosulfonimide ionic melt electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5877–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachard, D.; Rolland, J.; Obadia, M.M.; Serghei, A.; Bouchet, R.; Drockenmuller, E. A 1,2,3-triazolate lithium salt with ionic liquid properties at room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9035–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.W.; Shi, D.Y.; Liu, F.; Zheng, L.P.; Nie, J.; Feng, W.F.; Huang, X.J.; Armand, M.; Zhou, Z.B. Single lithium-ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on poly[(4-styrenesulfonyl)(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide] anions Electrochim. Acta 2013, 93, 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchet, R.; Maria, S.; Meziane, R.; Aboulaich, A.; Lienafa, L.; Bonnet, J.-P.; Phan, T.N.T.; Bertin, D.; Gigmes, D.; Devaux, D.; et al. Single-ion BAB triblock copolymers as highly efficient electrolytes for lithium-metal batteries. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, P.; Nie, J.; Feng, W.; Hu, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Single lithium-ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on a super-delocalized polyanion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T. Design and synthesis of ionic-conductive epoxy-based networked polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankley, G.T.; Cureton, P.; Hoke, R.A.; Houde, M.; Kumar, A.; Kurias, J.; Lanno, R.; McCarthy, C.; Newsted, J.; Salice, C.J.; et al. Assessing the Ecological risks of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Current state-of-the science and a proposed path forward. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 564–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, H.; Arnold, G.; Körner, W.; Rippen, G.; Steinhäuser, K.G.; Valentin, I. PFAS: Forever chemicals—Persistent, bioaccumulative and mobile. Reviewing the status and the need for their phase out and remediation of contaminated sites. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Sooksimuang, T.; Griffin, B.; Padhi, A.; Filler, R. New lithium salts for rechargeable battery electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2004, 175, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheers, J.; Lim, D.-H.; Kim, J.-K.; Paillard, E.; Henderson, W.A.; Johansson, P.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jacobsson, P. All fluorine-free lithium battery electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Bab-Anari, E.; Boschin, A.; Mandai, T.; Masu, H.; Moth-Poulsen, K.; Johansson, P. Fluorine-free salts for aqueous lithium-ion and sodium-ion battery electrolytes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85194–85201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Bresser, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Cao, X.; Su, Y.; Jia, H.; et al. Fluorine-free water-in-ionomer electrolytes for sustainable lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ibañez, M.; Sanchez-Diez, E.; Qiao, L.; Meabe, L.; Santiago, A.; Zhu, H.; O’Dell, L.A.; Carrasco, J.; Forsyth, M.; Armand, M.; et al. Weakly coordinating fluorine-free polysalt for single lithium-ion conductive solid polymer electrolytes. Batter. Supercaps 2020, 3, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, G.; Mogensen, R.; Younesi, R.; Mindemark, J. Fluorine-free electrolytes for lithium and sodium batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2022, 5, e202100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Shiraiwa, T.; Hayasaka, T.; Yoshida, S.; Ochiai, B. Synthesis of fluorine-free highly ion conductive polymer electrolyte having lithium bissulfonimide unit. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B3119–B3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Okahara, M.; Dishong, D.M.; Gokel, G.W. Crown cation complex effects. 22. Enhancement of cation binding in lariat ethers bearing a methyl group at the quaternary, pivot carbon atom. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, J.; Spence, G. Novel single ion, comb-branched polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1999, 123, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polymer | PEG | Introduction Efficiency (%) a | [Li]/[O] b | Yield (%) | Tg (°C) c | Tm (°C) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG400MME-LiMSSI1 | PEG400MME | >99 | 0.10 | 45 d | −48 | n.o.h |
| PEG1000MME-LiMSSI1 | PEG1000MME | 95 | 0.045 | 50 d | −56 | 27 |
| PEG200-LiMSSI2 | PEG200 | 95 | 0.46 | ca. 40 d,e | −18 | n.o.h |
| >99 | 0.48 | 34 d | 9 | n.o.h | ||
| PEG400-LiMSSI2 | PEG400 | 91 | 0.19 | 70 d | −30 | n.o.h |
| >99 | 0.21 | ca. 15 d,e | −11 | n.o.h | ||
| PEG1000-LiMSSI2 | PEG1000 | >99 | 0.082 | 70 d | −18 | n.o.h |
| DEGMME-LiMSSI2 | DEGMME-diol | 89 | 0.36 | 12 f | −52 | n.o.h |
| TMPE450-LiMSSI3 | TPME450 | 86 | 0.30 | 25 g | −18 | n.o.h |
| Category | Polymer | IE (%) a | σtotal (S/cm) | Tg (°C) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-free | PEG400MME-LiMSSI1 | >99 | 5.5 × 10−6 @ 30 °C 1.1 × 10−4 @ 60 °C | −48 | This work |
| PEG1000MME-LiMSSI1 | 95 | 3.0 × 10−5 @ 30 °C 2.0 × 10−4 @ 60 °C | −56 | This work | |
| PEG200-LiMSSI2 | 95 | 1.3 × 10−6 @ 30 °C 7.8 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −18 | This work | |
| >99 | 1.8 × 10−7 @ 60 °C | 9 | This work | ||
| PEG400-LiMSSI2 | 91 | 2.3 × 10−7 @ 30 °C 4.1 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −30 | This work | |
| >99 | 8.1 × 10−8 @ 30 °C 1.2 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −11 | This work | ||
| PEG1000-LiMSSI2 | >99 | 2.5 × 10−6 @ 30 °C 5.2 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −18 | This work | |
| DEGMME-LiMSSI2 | 89 | 7.3 × 10−7 @ 30 °C 4.5 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −52 | This work | |
| TMPE450-LiMSSI3 | 86 | 2.7 × 10−7 @ 60 °C | −18 | This work | |
| PEG350-(SO3Li)1 | N/A | 4.45 × 10−6 @ 30 °C | −53 | [7] | |
| PEG600-(SO3Li)2 | N/A | 1.43 × 10−6 @ 30 °C | −31 | [7] | |
| PEG550-SO2N(Li)CH2CH2OCH3 | N/A | 2.5 × 10−5 @ 30 °C | not reported | [8] | |
| PEG1900-(SO2N(Li)Ph)2 | N/A | 1.08 × 10−6 @ 30 °C 3.23 × 10−6 @ 50 °C | Semi-crystalline (Tm = 27 °C) | [9] | |
| Networked PEG2000-SO2N(Li)Ph | N/A | 1.40 × 10−6 @ 30 °C 4.34 × 10−6 @ 50 °C | Rubbery (Tm = 34 °C) | [9] | |
| MeO(CH2CH2O)3CH2-1,2,3-triazolate | N/A | 8.0 × 10−7 @ 30 °C | −60 > | [18] | |
| Li{B[O(CH2CH2O)nCH3]3C4H9} | N/A | 2 × 10−5 @ 30 °C | −79 | [13] | |
| Poly(LiMSVSI-co-PEGMA) | N/A | 8.4 × 10−5 @ 25 °C 9.2 × 10−4 @ 70 °C | −62 | [31] | |
| F-containing | Li+{Al[(OCH2CH2)nOMe]2(SO2CF3)2]− (n = 11.8) | N/A | 4.9 × 10−5 @ 30 °C | −53 | [10] |
| Li+{B[(OCH2CH2)4OMe]2HFIP2}− | N/A | 4.6 × 10−6 @ 30 °C | −54 | [11] | |
| MeOPEG550OCF2CFHOCF2CF2SO2N(Li)SO2CF3 | N/A | 5.3 × 10−6 @ 30 °C | not reported | [16] | |
| MeO(CH2CH2O)12C6H4SO2N(Li)SO2CF3 | N/A | 7.1 × 10−6 @ 30 °C | −38 | [17] | |
| Li+{B[(OCH2CH2)3OMe]2-HFIP-But}− | N/A | 1.89 × 10−4 @ 25 °C | not reported (liquid) | [15] | |
| P(EOMA-co-FBSALi) | N/A | 4.0 × 10−4 @ 30 °C | −51 | [33] | |
| P(LiSTFSI-co-MPEGA) | N/A | 7.7 × 10−6 @ 25 °C 1.0 × 10−4 @ 60 °C | −47 | [19] | |
| LiPSTFSI-b-PEO-b-LiPSTFSI | N/A | 1.3 × 10−5 @ 60 °C | −25 | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochiai, B.; Hirabayashi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Matsumura, Y. Fluorine-Free Single-Component Polyelectrolyte of Poly(ethylene glycol) Bearing Lithium Methanesulfonylsulfonimide Terminal Groups: Effect of Structural Variance on Ionic Conductivity. Technologies 2024, 12, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12050065
Ochiai B, Hirabayashi K, Fujii Y, Matsumura Y. Fluorine-Free Single-Component Polyelectrolyte of Poly(ethylene glycol) Bearing Lithium Methanesulfonylsulfonimide Terminal Groups: Effect of Structural Variance on Ionic Conductivity. Technologies. 2024; 12(5):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12050065
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchiai, Bungo, Koki Hirabayashi, Yudai Fujii, and Yoshimasa Matsumura. 2024. "Fluorine-Free Single-Component Polyelectrolyte of Poly(ethylene glycol) Bearing Lithium Methanesulfonylsulfonimide Terminal Groups: Effect of Structural Variance on Ionic Conductivity" Technologies 12, no. 5: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12050065
APA StyleOchiai, B., Hirabayashi, K., Fujii, Y., & Matsumura, Y. (2024). Fluorine-Free Single-Component Polyelectrolyte of Poly(ethylene glycol) Bearing Lithium Methanesulfonylsulfonimide Terminal Groups: Effect of Structural Variance on Ionic Conductivity. Technologies, 12(5), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12050065







