1. Introduction
Probabilistic linguistics (see, e.g.,
Bod 2015) is a framework that places variation and linguistic usage at the forefront, understanding that grammatical variation and change are, by nature, gradual rather than categorical. It assumes that linguistic knowledge includes knowledge of the probabilities of occurrence and selection of a particular linguistic construction in a specific context. Probabilistic grammar adopts the assumptions of variationist linguistics and tends to focus its attention on alternative ways of expressing the same meaning. Recent work within this framework has focused on syntactic alternations, such as the English dative and genitive alternations (e.g.,
Szmrecsanyi et al. 2017) and the Chinese dative alternation (e.g.,
Zhang and Xu 2023). In these studies, probabilistic grammar serves as a framework for a study of language whose goal is to explain and predict the choices made by speakers between two or more linguistic variants based on factors of a varying nature (pragmatic, syntactic, conceptual, geographic, social, etc.). Typically, these models employ statistical tools such as logistic regression, which allow for modeling the relationship between a dependent variable and a set of independent variables expected to condition and therefore explain variation in the former.
Despite the popularity of this approach, the probabilistic grammar of Galician remains largely uncharted.
Brown and Rivas (
2019) and
Rivas and Brown (
2021) recently kicked off this line of work in Galician linguistics, focusing on inflected infinitives, a distinguishing feature of the language. Their results reveal that inflected infinitives are favored by subjects with a low degree of accessibility and clauses with a low degree of syntactic complexity, thus enriching the traditional conception of the phenomenon. The present paper aims to expand probabilistic approaches to Galician grammar by examining mood selection in uncertainty adverb constructions, a phenomenon that has only been studied in Spanish so far. Therefore, the main goal of this paper is to identify and characterize the factors conditioning the choice between the indicative and the subjunctive when an adverb of uncertainty precedes the finite verb.
Many languages feature a formal distinction in the verb known as (verbal) mood, which includes categories such as indicative (IND), subjunctive (SBJV), and imperative. Descriptive, historical, and variationist approaches have produced abundant contributions to the literature on the distribution of the indicative and the subjunctive in Romance, largely focusing on the behavior of mood in complement clauses and other contexts of subordination. Indeed, the subjunctive mood is usually restricted to these kinds of environments, but some exceptions exist. When an epistemic adverb precedes a finite verb, mood can alternate between the indicative and the subjunctive, as in the next Galician examples:
| (1) | a. | Probablemente esta será a última vez que visite esta cidade | |
| | ‘This will probably beind the last time I will visit this city.’ | (CORGA) |
| b. | Mañá probablemente sexan só tres os que estean traballando tralo mostrador | |
| | ‘Tomorrow there will probably besbjv only three people working behind the counter.’ | (CORGA) |
In both the above examples, the verb
ser ‘be’ follows the uncertainty adverb
probablemente ‘probably’ and refers to a state of affairs in the future. However, (1a) employs the future indicative, while (1b) uses the present subjunctive. Crucially, swapping both forms—while adjusting for number agreement—would be considered perfectly grammatical. This phenomenon of mood variability following adverbs of uncertainty has continuously attracted attention in Spanish linguistics since the pioneering work of
Woehr (
1972), and there have been recent experimental and quantitative approaches to the matter (
Deshors and Waltermire 2019;
Hirota 2021;
Waltermire 2017;
Yelin and Czerwionka 2017). Nonetheless, the phenomenon has been almost exclusively discussed in relation to Spanish, with focus primarily on the adverb
quizá(s) ‘maybe’ despite it being documented in other Ibero-Romance languages, such as Galician (
Álvarez and Xove 2002, p. 180), Brazilian Portuguese (
Carvalho et al. 2017), and Catalan (
López and Morant 2002, p. 1840). I will briefly summarize below the most important findings of previous studies, which amounts to discussing the Spanish data.
The relationship between mood choice and time reference is arguably the most well-established fact in the literature.
Woehr (
1972) noted that the subjunctive is favored when the verb refers to the present or, especially, the future, and disfavored when it refers to the past. Several studies have verified this fact in different experimental settings (
DeMello 1995;
De Sterck 1998;
Finanger 2011;
García 2011;
Yelin and Czerwionka 2017).
The rate of subjunctive selection also depends on which uncertainty adverb precedes the finite verb. A recurrent pattern found in many studies on Spanish is that adverbs like
quizá(s) and
tal vez ‘perhaps’ combine with the subjunctive more often than others like
seguramente ‘surely’,
probablemente ‘probably’, and
posiblemente ‘possibly’, which have a stronger tendency to occur with the indicative (
DeMello 1995;
Deshors and Waltermire 2019;
Hirota 2021;
Kratochvílová 2013).
Other syntagmatic elements have also been found to play a role in mood selection. This is the case for variables such as clause type, verb lemma, and the distance between the adverb and the verb. The factors that favor the subjunctive over the indicative are main clauses (vs. subordinate clauses), frequent verbs (such as the auxiliaries
ser ‘be’,
tener ‘have’, and
poder ‘can’ vs. less frequent verbs), and adjacent contexts (vs. contexts in which there is intervening material between the adverb and the verb) (
Deshors and Waltermire 2019;
Finanger 2011;
García 2011;
Hirota 2021).
Deshors and Waltermire (
2019) included verb type as a factor conditioning mood choice. This variable corresponds to the inherent lexical aspect of verbs, as described by
Vendler (
1957) and
Dowty (
1979, pp. 55–60), which distinguishes between states, activities, accomplishments, and achievements. According to
Deshors and Waltermire’s (
2019) results, when accomplishment and activity verbs are involved, speakers choose the indicative more frequently than the subjunctive.
Hirota (
2021) also examined a verb type factor, classifying verbs into categories such as copular, intransitive, transitive, reflexive, and auxiliary, but this classification did not yield statistically significant results.
Regarding non-linguistic context, the subjunctive has been associated with written language and formal registers, while other extra-linguistic sources of variation include geography and the gender of the speaker (
De Sterck 1998;
García 2011;
Hirota 2021). While geography is not pertinent to this study, gender does play a role, since, according to
Hirota (
2021), women are less likely to use the subjunctive in these constructions compared to men.
Regarding negative results, research has shown that neither the person nor the number of the verb, the age of the speaker (
Hirota 2021), or negation (
Finanger 2011;
García 2011) significantly affect mood selection. The lack of impact of negation might be surprising given the usual influence of polarity on mood, modality, and related categories. This is evident in the contrasting mood choices in complement clauses, such as the Galician
creo que ‘I think that’ + IND vs.
non creo que ‘I don’t think that’ + SBJV.
Some things we must bear in mind when dealing with the literature on mood selection after uncertainty adverbs (in Spanish) are differences in the methods and data used. Most studies are corpus-based, but few of them use advanced statistical tools, and only
Deshors and Waltermire (
2019) and
Hirota (
2021) use regression modeling, which has become the norm for syntactic alternation research in recent times (
Gries 2017). Nevertheless,
Deshors and Waltermire (
2019) do not restrict their survey to uncertainty adverbs but also consider other expressions, such as
ser imposible que and
poder ser que, which precludes the inclusion of the important variable time reference and makes the results of their study harder to compare.
This paper provides the first variationist account of mood variability with uncertainty adverbs in Galician, a phenomenon that has not been studied in depth so far in the language, having only been mentioned in descriptive grammars. This study uses data obtained from corpora of present-day language which were contextually annotated for syntactic, semantic, and extra-linguistic variables. The findings reveal the central role of temporal reference and adverbs in conditioning mood choice in uncertainty adverb constructions and recognize the interaction of register (fiction–nonfiction) in moderating the effects of verb semantics and the speaker/writer’s gender. The analysis underscores the non-significant influence of clause type and distance on mood choice, contrasting with the findings of previous Spanish studies. These findings enrich the understanding of Galician probabilistic grammar and contribute to the future development of research in this area.
2. Materials and Methods
The goal of this study was to identify the factors that significantly affect the choice between the indicative and the subjunctive in Galician. This section shows how data were obtained, explains what variables were taken into consideration and how they were annotated, and describes the statistical approach.
2.1. Corpus Data
This paper contrasts uses of the indicative and the subjunctive moods after adverbs of uncertainty. The data were extracted from two corpora of present-day Galician, namely CORGA
1 and CORILGA.
2 Both corpora are publicly available on the web. CORGA is the reference corpus of Galician and includes more than 43 million words from 1975 to 2020 that are balanced between fiction (dramatic and narrative prose), newspapers, and essays. The scarcity of spoken material in CORGA (less than half a million words) led to the inclusion of data from CORILGA, which specializes in speech and contains around 1.4 million words of recordings corresponding to different registers (formal and informal speech, urban and rural varieties, and standard and literary language), as well as conversations, interviews, discourses, and conferences.
All occurrences of five different uncertainty adverbs were extracted from CORGA and CORILGA. These five adverbs are those known to trigger the indicative/subjunctive alternation (
Álvarez and Xove 2002, p. 180):
quizais ‘maybe’,
talvez ‘perhaps’,
posiblemente ‘possibly’,
probablemente ‘probably’, and
seguramente ‘surely’. A total of 24,684 tokens were obtained, but only a portion of these were relevant to the study as many examples did not include the adverb followed by a finite verb—mood distinctions are only relevant for finite verb forms, and the alternation is possible only when the adverb precedes the verb. Given material limitations, the analysis was restricted to a random sample of 1702 observations of an adverb followed by a finite verb. These included 899 occurrences of the indicative and 803 occurrences of the subjunctive. The overall distribution of moods across adverbs is shown in
Table A1 (
Appendix A).
2.2. Annotation of Variables
In order to identify the factors that significantly affect mood selection in Galician, all observations were manually annotated at the syntactic and semantic levels, whereas information on extra-linguistic variables was obtained from CORGA and CORILGA. A total of eight variables were considered on account of their roles in previous studies. These include the response variable (MOOD) and several explanatory variables (ADVERB, DISTANCE, CLAUSE TYPE, VERB TYPE, TIME, GENDER, and REGISTER). The corresponding levels for each variable are presented in
Table 1.
The response variable MOOD has two levels, indicative and subjunctive, illustrated in (1) above. The annotation of this variable was mostly unproblematic as most Galician verb forms are not ambiguous between one mood category or the other. However, for some verb forms ending in -ra, it could not be determined whether they corresponded to the antepretérito (pluperfect), an indicative tense, or the past subjunctive. Therefore, observations with ambiguous -ra forms were left out.
VERB TYPE pertains to the inherent lexical aspect of verbal predicates as originally formulated by
Vendler (
1957). Thus, a verbal predicate may correspond to one of four event classes: state, activity, accomplishment, or achievement. A typical organization of these classes is provided by
Smith (
1991), who classifies them on the basis of three binary features, which are gathered in
Table 2.
Dynamicity has to do with the presence of some change or internal dynamism in the state of affairs—whether or not ‘something happens.’ Duration focuses on the temporal extent of an event, distinguishing verbs that describe momentary occurrences or protracted states of affairs. Telicity is concerned with whether a predicate possesses a natural endpoint or culmination. Telic predicates imply a sense of completion, indicating events with defined boundaries, while atelic predicates lack inherent endpoints, often representing ongoing or repetitive events without a specific conclusion. These three semantic properties can be identified through several tests (
Dowty 1979, pp. 55–60), and their combination leads to the four different classes in
Table 2. Each type of verb is illustrated in (2) in the order in which they are displayed in the table; the target finite verb is emphasized.
| (2) | a. | Ernesto probabelmente nunca amou a Sara como Sara si o quixo a el. | |
| | ‘Ernesto probably never loved Sara as much as Sara loved him.’ | (CORGA) |
| b. | Mais el quizais non procuraba poemas como os da autora italoarxentina … | |
| | ‘But perhaps he wasn’t looking for poems like those of the Italo-Argentinian author …’ | (CORGA) |
| c. | … tal vez escriba un conto. | |
| | ‘… perhaps I will write a story.’ | (CORGA) |
| d. | Como posiblemente non se decatou da entrada da neta, Anaiansi acércase a modo … | |
| | ‘As she possibly did not notice her granddaughter’s entrance, Anaiansi approaches slowly …’ | (CORGA) |
Crucially, verb types are not associated with particular verbs but must be determined at the predicate level (i.e., considering both the verb and its complements). For instance, a verb like vir ‘come’ usually conveys an achievement, as in (3a), but can also convey a state, as in (3b). Thus, context was extremely important when annotating this variable.
| (3) | a. | … quizais a enfermidade veu despois. | |
| | ‘… maybe the illness came later.’ | (CORGA) |
| b. | … talvez viría ben ir baixando o ton … | |
| | ‘… perhaps it would be a good thing to start to tone down …’ | (CORGA) |
The annotation of the rest of the variables was straightforward:
ADVERB corresponds to one of the five adverbs that precede a finite verb; different variants of the same adverb were considered under the same label (e.g., talvez in (3b) and tal vez in (2c)).
DISTANCE captures whether there is intervening linguistic material between the adverb and the finite verb; (3b) is an example of adjacency and (2a) is an example of distance.
CLAUSE TYPE corresponds to either a main clause (2a) or a subordinate clause (2d).
TIME corresponds to the time reference of the clause in which the adverb and finite verb occur. Three values were distinguished: past, present, and future. They are illustrated, respectively, in (2a), (3b), and (2c).
GENDER is divided into female and male, as provided by the electronic corpora used; cases of unknown gender or multiple authorship with mixed genders (e.g., a woman and a man who produced a document together) were excluded.
REGISTER corresponds to one of four different written text types (narrative, drama, essay, or press) or speech. Given the involvement of this variable in a great number of interactions, its structure was simplified to avoid data sparsity problems, thus conflating narrative and drama under ‘fiction’ and the rest of levels under ‘nonfiction’.
2.3. Statistical Approach
After data annotation, a fixed-effects logistic regression model was fitted to the data. All statistical procedures were conducted in the software environment
R (
R Core Team 2024). The analysis was performed using the
lrm function from the rms
R package (
Harrell 2024). The initial model is represented in (4). It includes all individual predictors (4a), plus the interactions of ADVERB with most of the other predictors (4b), the interactions of REGISTER with all other predictors (4d), and other theoretically relevant interactions (4c).
| (4) | MOOD ∼ 1 |
| a. + ADVERB + DISTANCE + CLAUSE TYPE + VERB TYPE + TIME + GENDER + REGISTER |
| b. + ADVERB:DISTANCE + ADVERB:CLAUSE TYPE + ADVERB:TIME + ADVERB:GENDER |
| c. + CLAUSE TYPE:VERB TYPE + VERB TYPE:TIME |
| d. + REGISTER:ADVERB + REGISTER:DISTANCE + REGISTER:CLAUSE TYPE + REGISTER:VERB TYPE + REGISTER:TIME + REGISTER:GENDER |
Then, the anova function from the lrm package was used to obtain the final model. This function takes the initial model as input and conducts likelihood ratio tests on all independent variables in the model, including interactions. The function checks whether a predictor makes a statistically significant contribution to the model based on its p-value and allows us to delete irrelevant predictors. The resulting final model is highly significant (p < 0.0001) and includes five significant terms—three individual predictors and two interactions—as summarized below:
| (5) | MOOD ∼ 1 + ADVERB + TIME + VERB TYPE + REGISTER:VERB TYPE + REGISTER:GENDER |
The index of concordance
C of the final model, which measures the ability of the model to discriminate between the two outcomes, is 0.797. This is just below the 0.8 level, which is considered excellent discrimination (
Hosmer et al. 2013, p. 177). The overall accuracy of the model is 72.80%, which is much higher than the baseline classification accuracy of 52.82%, corresponding to the predicted probability of the most frequent outcome (the indicative). The final model returned an
R2 value of 0.356.
3. Results
A summary of the significant factors in the regression model is shown in
Table 3. Model predictions correspond to the subjunctive. Note that the leftmost column contains the name of each level in lowercase preceded by the name of its variable in uppercase and that the reference levels are not shown in the table. The most important measures for interpreting the results are the estimates, expressed in log odds ratios, and the
p-values (i.e., the second and last columns of the table). The former tell us the size and direction of the effect and take values between
and ∞; positive values suggest a preference for the subjunctive, while negative values indicate a preference for the indicative. The
p-values inform us of the statistical significance of an effect at the 0.05 level—values above this threshold indicate an effect that is not statistically significant.
Regarding ADVERB, the results indicate that
probablemente and
seguramente significantly influence the speaker/writer’s choice of one mood over the other when compared with
quizais, which cannot be distinguished from
talvez and
posiblemente in this respect. The remaining pairwise comparisons were computed with the
R package emmeans (
Lenth 2024). These comparisons show that
talvez is not significantly different from
posiblemente (
punadjusted = 0.093) and that
talvez and
posiblemente significantly increase the chances of the subjunctive when they are compared with
probablemente and
seguramente (
punadjusted < 0.0001 for all relevant comparisons except for
posiblemente—
probablemente, where
punadjusted = 0.0006).
Probablemente and
seguramente are also significantly different from each other (
punadjusted < 0.0001), with
probablemente favoring the subjunctive when compared with
seguramente.
As for TIME, both the present and the future significantly increase the chances of the subjunctive when compared with the past, which favors the indicative. Pairwise comparisons show that the future also has a significant effect in favor of the subjunctive vis-à-vis the present (punadjusted < 0.0001).
The coefficients of VERB TYPE must be interpreted with caution given that this variable is involved in an interaction with REGISTER, that is, the effects of VERB TYPE are not constant across the levels of REGISTER. The summary of the model in
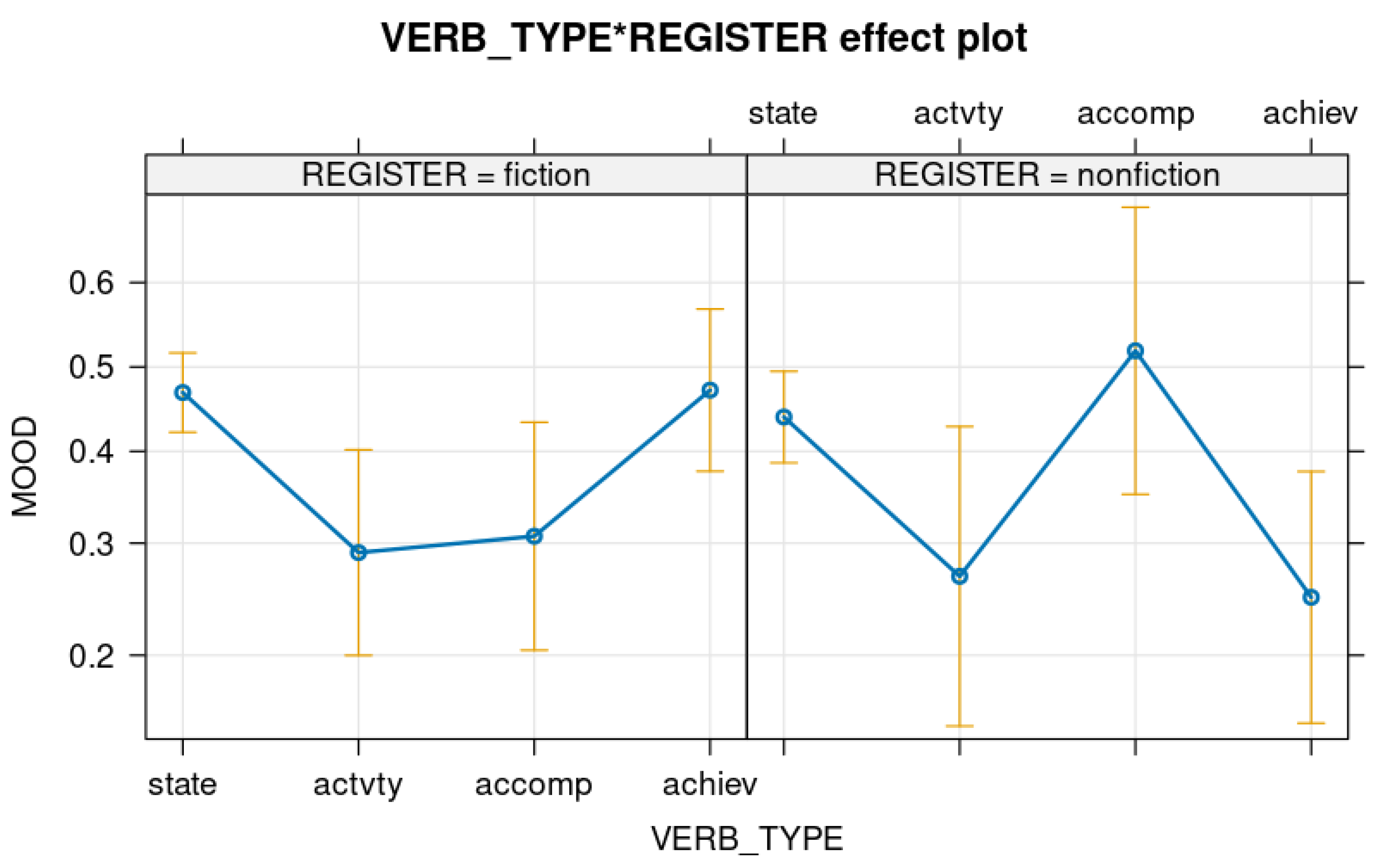
Table 3 tells us that states significantly increase the odds of the subjunctive when compared with activities and accomplishments and that states are not significantly different from achievements. However, this is only partly true. Let us explore the interaction between the two variables with the help of
Figure 1.
The effects of VERB TYPE gathered in
Table 3 are only valid when fictional texts are considered (the left panel of the figure), since in nonfictional ones (right panel), states are significantly different from achievements (
punadjusted = 0.0082) and not significantly different from accomplishments (
punadjusted = 0.3899). Similarly, activities are significantly different from achievements but only in fiction, since in nonfiction they cannot be distinguished (
punadjusted = 0.8309), whereas activities are not significantly different from accomplishments in fiction (
punadjusted = 0.8323) but are actually different in nonfiction (
punadjusted = 0.0325). States and activities are significantly different both in fiction (
punadjusted = 0.0038) and nonfiction (
punadjusted = 0.0428). In other words, accomplishments and achievements behave differently depending on the register.
The second interaction in the model is between GENDER and REGISTER. The value shown in the model summary (
Table 3) is not significant, but pairwise comparisons reveal a significant difference between male and female speakers/writers that only happens in fiction (
punadjusted = 0.0032): males favor the subjunctive and females the indicative.
4. Discussion
A comparison with previous studies reveals that the results of this paper corroborate the well-founded observations by
Woehr (
1972), who noted a predilection for the subjunctive when verbs refer to present or future events. This tendency has been validated several times in the subsequent literature and can now be extended to the Galician language. These results have implications for theoretical approaches to mood. The strong association between non-past (present and future) time references and the subjunctive mood highlights the interplay between time and grammatical mood, aligning with the claim that the subjunctive is inherently linked with an irrealis perspective on the event, which is traditionally associated with future or hypothetical scenarios (
Elliot 2000;
Palmer 2001). Thus, the role of time reference in mood selection remains a cornerstone of the indicative/subjunctive distinction in uncertainty adverb constructions.
As for the role of the adverb that precedes the finite verb, the results have separated adverbs into three significantly different groups according to their preference for the subjunctive:
quizais,
talvez,
posiblemente >
probablemente >
seguramente. A comparison with the previous literature on Spanish faces some shortcomings. On one hand,
Deshors and Waltermire (
2019) found that
quizás and
tal vez trigger the subjunctive more frequently than
posiblemente and
probablemente, which lean toward the indicative. However, a limitation of
Deshors and Waltermire’s (
2019) study, as pointed out by
Hirota (
2021), is the fact that they conflated the levels corresponding to
probablemente and
posiblemente, thus obscuring the potential differences between the two adverbs. On the other hand, in
Hirota’s (
2021) study, adverbs were grouped into two categories: those favoring the subjunctive (
posiblemente,
probablemente,
quizá,
quizás, and
tal vez) and those favoring the indicative (
acaso,
a lo mejor,
seguramente, and
igual). In the first group,
posiblemente showed the highest probability of co-occurring with the subjunctive, followed, in decreasing order of probability, by
tal vez,
quizás,
probablemente, and
quizá. This ranking corresponds to pairwise comparisons with
a lo mejor, so we do not know whether the differences between the adverbs of the first group are significant.
The results concerning adverbs may be interpreted in the light of the relation between mood and epistemic commitment. According to
Hoff (
2019), speakers may use verbal mood to express different degrees of certainty, with the subjunctive being preferred when conveying uncertain events. The different epistemic values of the adverbs considered in this study are relevant at this point:
Álvarez and Xove (
2002, pp. 627–28) point out that while
quizais and
talvez qualify an event as possible and far from sure,
posiblemente,
probablemente, and
seguramente express increasing degrees of probability. Thus, uncertainty adverbs in Galician form an epistemic scale that has
quizais and
talvez at the lowest rank and
seguramente at the highest, with
probablemente and
posiblemente in intermediary positions, as represented in (6).
| (6) | > seguramente [+ probable] |
| > probablemente |
| > posiblemente [− probable] |
| > quizais, talvez [possible] |
According to the present study, mood distribution forms a cline that corresponds to this epistemic scale: as one climbs up the scale, that is, as the degree of uncertainty conveyed by the adverb decreases, the use of the subjunctive decreases as well, with
seguramente conveying the highest degree of assurance and showing the weakest association with the subjunctive. The fact that
quizais and
talvez are not significantly different regarding mood selection is in accordance with this idea since both encode the same epistemic value. Consequently, one would expect
posiblemente to yield a significant difference given its probability meaning, but this is not the case. A plausible explanation for this lies in the fact that
posiblemente originally expressed a value of possibility (
Míguez 2024, pp. 107–8) and might still be close both semantically (in terms of epistemic commitment) and morphosyntactically (in terms of mood selection) to expressions of possibility. The present results suggest an association of the subjunctive mood with uncertain events —since stronger assertions of likelihood tend to sway mood choice toward the indicative—and support the notion of mood selection ‘as a gradient means of conveying pragmatic information about speaker epistemic commitment’ (
Hoff 2019).
The final model included two significant interactions, both involving REGISTER, that is, the difference between fictional and nonfictional texts. This difference moderates the effects that VERB TYPE and GENDER have on mood selection. Similarly to
Deshors and Waltermire’s (
2019) results, activity and accomplishment predicates were found to favor the indicative when compared with state and achievement predicates, but in our study, this was only true in fiction. In nonfiction, accomplishments and achievements change roles, whereas the contrast between states and activities remains relevant across registers. The precise nature of this complex interaction is a matter for future research, but the results of the current survey highlight the importance of considering the semantic characteristics of verb forms carrying mood categories when dealing with mood selection.
The influence of GENDER on mood selection presents a compelling aspect of linguistic variation. The present study supports the view that gender plays a role in mood selection since in fictional texts, female speakers/writers were found to be less likely to use the subjunctive mood vis-à-vis male speakers/writers, in line with
Hirota’s (
2021) finding. In Galician, the subjunctive has been linked with doubt and mitigation (
Freixeiro Mato 2006, pp. 354–58), whereas the idea that women make broader use of mitigating devices in conversation has been in circulation for a long time (
Lakoff 1975). According to this, one would expect women to favor the more mitigating alternative, the subjunctive, over the more neutral one, the indicative, but the opposite is true in constructions with uncertainty adverbs in fictional texts. Nevertheless, this expectation is unfounded since the relation between women’s language and mitigation has long been debunked (e.g.,
Holmes 1990). The present results contribute to underscoring the complex nature of sociolinguistic factors in language use, suggesting the need for a more profound understanding of the role gender plays in linguistic choices and encouraging further examination of sociocultural variables in shaping language use.
5. Conclusions
This study provided an initial variationist analysis of mood selection in Galician, representing a step toward a more comprehensive understanding of mood variability in the language and contributing to the nascent body of research on probabilistic grammar from a Galician perspective. A logistic regression model identified the effects of various factors that significantly influence the choice between the indicative and subjunctive moods.
The findings show that time reference plays a crucial role in mood selection, with present and future events significantly favoring the use of the subjunctive. This aligns with previous studies focused on Spanish and confirms the importance of temporal context in this example of syntactic alternation. The influence of adverbs on mood selection was also evident, as reflected in a clear distinction between those adverbs that encode stronger epistemic commitment and favor the indicative and other adverbs that convey weaker epistemic values and favor the subjunctive. This supports the notion that semantic contrasts between temporal references and adverbs play a role in shaping mood choice, implying that mood categories capture differences in epistemic commitment. Verb type and gender emerged as additional influential factors whose effects are moderated by the distinction between fictional and nonfictional registers.
As stated above, the present contribution represents a first step in the study of mood selection in Galician from a variationist perspective. A further development in this line of work would be the use of a mixed-effects approach to regression since it would make the results more accurate and reliable. This and other studies (
Deshors and Waltermire 2019;
Hirota 2021) have used binomial logistic regression to account for the choice between the indicative and the subjunctive on the basis of a number of fixed effects but have not incorporated the contribution of random effects. These effects arise in cases of non-independent observations, such as when a single speaker contributes multiple observations to a dataset. Previous research shows that mood choice is highly sensitive to individual preferences; the ratio of subjunctive selection after Spanish
quizá(s) may range from 100% in one speaker to 20% in another (
Kratochvílová 2018, p. 44). Similarly, the occurrence of the subjunctive is not even across verb lemmas, with frequent verbs favoring the use of the subjunctive (
Finanger 2011;
García 2011). The individual preferences of speakers and lexical items have an influence on mood choice and must be taken into account when explaining the phenomenon. Thus, the use of a mixed-effects model that includes both fixed and random effects would be a welcome development in future studies.
Future investigations might also benefit from integrating experimental approaches to corroborate the findings of corpus-based research. The incorporation of psychological experiments could elucidate the real-time processing involved in syntactic choices, offering a means to validate whether corpus-based inquiries accurately mirror the cognitive processes guiding the language behavior of native speakers. In this regard,
Klavan (
2017) showed the benefits of comparing the results of different modeling techniques and then evaluating their performance on the basis of experimental data.
Finally, the investigation of cross-linguistic parallels and contrasts in mood selection within uncertainty adverb constructions across different Ibero-Romance varieties, including Galician and Spanish but also potentially Catalan and Brazilian Portuguese, is an avenue yet to be explored through multifactorial methods.