Abstract
Variation in the ways by which an individual processes codeswitched language may reveal fundamental dynamics of the language system that are otherwise obscured under unilingual conditions. Despite this, an important aspect that has been largely neglected in the field is the role of the bilingual experience in language processing. Drawing on corpus-driven and experimental research, the corpus-to-cognition approach to codeswitching integrates field- and laboratory-based work to examine how the bilingual experience may influence language processing. In this review, we elaborate on the best practices for investigating codeswitching, with converging evidence from different methodologies across different bilingual populations.
1. Introduction
While psycholinguistics has traditionally focused on unilingual language processing, the past decade has observed a plethora of studies devoted to codeswitching, recognizing that this linguistic behavior is not a haphazard circumstance, but one that is characteristic of many bilingual communities throughout the world. Psycholinguists have come to see that variation in the ways individuals process codeswitched language may reveal fundamental dynamics of the language system that are otherwise obscured under unilingual conditions. Despite this, an important aspect that has been largely neglected in the field is the role of bilingual experience in language processing. Codeswitching1 by definition is a uniquely bilingual skill (Myers-Scotton and Jake 2015). Additionally, sociolinguistic research has shown that codeswitching is a pattern-governed communicative behavior that conforms to community-specific norms (e.g., Poplack 1980). Prioritizing the community over the individual in the study of codeswitching is important because not all bilinguals codeswitch and not all codeswitching bilinguals will adhere to the same usage patterns (Beatty-Martínez and Dussias 2017; Valdés Kroff et al. 2018). Given this, a better understanding of the role that the bilingual experience plays in language processing requires the use of a convergent approach between sociolinguistics and psycholinguistics. Fortunately, there is a growing trend toward interdisciplinary research that recognizes the need to more fully characterize those aspects of bilingual language experience that may impact language form and influence cognition more generally (e.g., Munarriz and Parafita Couto 2014). Experience-based approaches (Bybee 2010; Dell and Chang 2014; MacDonald 2013) are at the forefront of this paradigm shift. Such accounts maintain that distributional usage patterns that arise from linguistic variation serve as probabilistic constraints for language processing. In this way, language processing is linked to the probability of a linguistic event in an individual’s previous input experience. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to the psycholinguistic study of codeswitching that we have termed the corpus-to-cognition approach. It is our view that the heterogeneity in linguistic exposure experienced by bilinguals affords unique opportunities to observe the consequences of language experience by testing how the different interactional contexts in which bilinguals find themselves modulate language processes (Green and Abutalebi 2013). Our starting point is the observation that linguistic data found in naturalistic corpora are a valuable source of insights into distributional codeswitching patterns and can thus improve our appreciation of the experiences that speakers have with language. Because codeswitching emerges in some bilingual communities but not in others, it is possible to more readily link bilinguals’ processing of codeswitched speech in experimental settings to their expectations in processing a particular linguistic input in a naturalistic environment. In this review, we elaborate on the best practices for investigating codeswitching, with converging evidence from different methodologies across different bilingual populations.2 We start with an overview of the current limitations and methodological challenges in the study of bilingual language processing.
1.1. Current Limitations and Methodological Challenges in the Study of Codeswitching
Experimental evidence broadly suggests that switching between languages is cognitively costlier (i.e., leads to processing costs) as compared to staying in the same language (e.g., Altarriba et al. 1996; Litcofsky and van Hell 2017; Meuter and Allport 1999; cf. Blanco-Elorrieta and Pylkkännen 2017). Yet codeswitching is common within certain bilingual communities and does not appear to impede or disrupt comprehension. The apparent inconsistency between the experimental evidence and actual bilingual language use is likely in part due to a series of methodological challenges to the experimental study of codeswitching (see also Beatty-Martínez and Dussias 2017; González-Vilbazo et al. 2013; Gullberg et al. 2009; Johns et al. 2018; Munarriz and Parafita Couto 2014; Valdés Kroff and Fernández-Duque 2017; Valdés Kroff et al. 2018). Psycholinguistic methods are in a naturally tense relationship with the ecological study of codeswitching. In particular, the protocols for well-designed psycholinguistic experiments aim at minimizing variability in experimental stimuli, resulting in context-less and tightly controlled sentences in which codeswitches are typically represented as single-word switches (1).
| 1. | I went to the store to buy some | manzanas |
| apples |
Although the goal of experimental design is to minimize variables of no interest (e.g., lexical frequency, word length, grammatical class, etc.) while maximizing the critical manipulation of interest, some higher level cognitive acts may be too complex to capture in typical experimental paradigms (Gullberg et al. 2009; Hasson et al. 2004; Hasson et al. 2012; Munarriz and Parafita Couto 2014; Valdés Kroff and Fernández-Duque 2017). Codeswitching may be one such cognitive act. By its own definition, codeswitching occurs in interactive dialogue; thus, its use is primarily a socially driven phenomenon.
We have previously argued that there are three primary methodological issues that researchers must consider in the experimental study of codeswitching (Valdés Kroff et al. 2018). The first issue concerns the experimental techniques and tasks employed. Many experimental techniques interrupt or artificially constrain the unfolding speech stream. Techniques such as self-paced reading or rapid serial visual presentation (commonly known as RSVP) either serially present new material or place time constraints in how participants read or listen to stimuli. These constraints, which are advantageous from the perspective of tightly controlled experimental design, may force codeswitches to be processed as unexpected language switches (Moreno et al. 2002). Similarly, the experimental task that accompanies the main experiment (e.g., conducting a grammaticality judgment on critical trials or indicating whether a codeswitch sounds natural, etc.) likely draws from top-down (social and/or pragmatic) influences which ultimately may manifest themselves as switch costs. Second, prior research reveals that the syntactic junctures where codeswitches occur are varied and can differ across language pairs (Chang 2009; Poplack 1988). This variation is guided by within-community preferences (Poplack 1988; Torres Cacoullos and Travis 2015). However, this observation is not always reflected in psycholinguistic research where experimental stimuli commonly include single-word switches that overwhelmingly represent switches into nouns (e.g., Altarriba et al. 1996; Johns et al. 2018; Li 1996; Moreno et al. 2002). Finally, the bilingual sample must be an important consideration in codeswitching studies. Although bilingual speakers may share intuitions on broad restrictions on where codeswitches may occur (i.e., between subject pronouns and verbs; MacSwan 2009), bilingual codeswitchers further engage in more intricate switches, even demonstrating asymmetric preferences when involving codeswitches between the same grammatical categories (see Section 2.1 and Section 2.2). Thus, it is crucially important to assess participants’ background with respect to their use of and exposure to codeswitching (Beatty-Martínez and Dussias 2017; Valdés Kroff and Fernández-Duque 2017).
These methodological challenges potentially conspire to obscure the cognitive processes that guide successful comprehension of codeswitching as employed by bilingual codeswitchers. Hence, these challenges lead us to ask whether we are studying the processing of codeswitched language or whether we are more closely mirroring exogenously cued language switching phenomena (e.g., Meuter and Allport 1999). This difference is not trivial, as the cognitive and neural underpinnings supporting these phenomena may be the same, different, or only partially overlap. The current landscape in psycholinguistic approaches to codeswitching leads us to highlight the need for the integration of experimental- and corpus-based approaches to inform codeswitching research, as interest grows in the relationship between language form and language use; language variation and processing; and between language production and comprehension.
1.2. Roadmap
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. First, we describe examples of codeswitching sites based on naturally-occurring Spanish-English codeswitching data. We then present an overview of codeswitching assessment techniques using experimental elicitation tasks, and we discuss other methodological considerations regarding experimental design. Subsequently, we focus on the experimental contributions of eye-tracking and event-related potential (ERP) techniques to the understanding of codeswitching processes, and we present four illustrative studies based on prior work in our group. Guzzardo Tamargo et al. (2016) employ the eye-tracking technique to examine the processing of Spanish-English codeswitches in present progressive and present perfect structures during reading. Halberstadt (2017) examines the rates of codeswitching disfluencies and eye movements while reading aloud to discriminate frequently occurring codeswitches from those that are not part of the linguistic repertoire of habitual codeswitchers. Valdés Kroff et al. (2017) use the visual world paradigm to test how exposure to codeswitching can lead to modulations in predictive processes of grammatical gender agreement. Finally, Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017) use the ERP technique to examine the grammatical gender asymmetry of determiner-noun codeswitches in two groups of bilinguals who differed in codeswitching experience (codeswitchers and non-codeswitchers). Together, these studies are illustrative of the ways in which codeswitching research can provide insights into experience-based variation in language processing when accompanied by a representative bilingual sample and by experimental materials that reflect actual codeswitching practices.
2. Corpus-Based Analysis of Codeswitching
It has been argued quite extensively in linguistic and psycholinguistic studies of codeswitching that intra-sentential switches require greater simultaneous control of both languages, creating a unique opportunity to observe the interaction between two linguistic systems (e.g., Green and Wei 2014; Torres Cacoullos and Travis 2015). Languages across the world differ in their statistical regularities even when surface structure is similar (e.g., Dussias et al. 2010). This raises the question of how bilingual speakers successfully navigate between two languages within the same sentence. Do bilinguals follow the specific distributional statistics of one language or the other when engaged in codeswitching? Do they develop knowledge of when codeswitches are more likely to occur? If the interaction between linguistic systems and the constraints that guide their successful integration during codeswitching can be systematically characterized, it would provide a valuable means of investigating questions concerning the mechanisms that regulate the comprehension and production of codeswitched language.
One research strategy that has been employed to investigate these questions has been to capitalize on the syntactic asymmetries that are found in codeswitching corpora. Quantitative studies on intrasentential codeswitching have revealed that certain types of syntactic sites are more likely to serve as the loci of codeswitches than others. One question, then, is whether bilinguals are sensitive to the distributional patterns with which different types of switches occur and use this information when producing and processing codeswitched language.
“Codeswitching sites” refer to syntactic constituents at which bilingual speakers appear to systematically switch from one language to another. Codeswitching preferences conform to community-based norms, and are therefore not necessarily generalizable across bilingual populations, even within the same language pair (Blokzijl et al. 2017; Poplack 1988). Identification of distributional patterns is achieved by the quantification and extraction of codeswitching sites from recordings of naturalistic language (Poplack 1980; Torres Cacoullos and Travis 2015). The systematicity underlying codeswitching sites is generally described in reference to the syntactic site at which the codeswitch takes place. Below we describe two types of asymmetries to illustrate the logic of this approach. We broadly adopt the perspective discussed in Joshi (1985) which assumes an asymmetric relationship between the two languages within the clause.
2.1. Asymmetries in Verb Phrases
Several studies examining the production of Spanish-English intra-sentential codeswitches (e.g., Lipski 1978; Poplack 1980) have alluded to an asymmetry involving alternations within the auxiliary phrase. Specifically, codeswitches into an English participle preceded by the Spanish progressive auxiliary estar ‘be’ (2) occur as frequently in corpora as codeswitches in which both the auxiliary and the participle appear in English.
| 2. | los actores están | rehearsing their lines |
| the actors are |
However, codeswitches into an English participle preceded by the Spanish perfect auxiliary haber ‘have’ (3) are less frequent than codeswitches in which both the auxiliary and the participle appear in English (4).
| 3. | los actores han | rehearsed their lines |
| the actors have |
| 4. | los actors | have rehearsed their lines |
| the actors |
Guzzardo Tamargo et al. (2016), examined available oral and written Spanish-English codeswitching corpora to confirm the distributional patterns involving switches at these two syntactic sites. The oral corpus examined was the Bangor Miami Corpus (Deuchar et al. 2014), which consists of recordings of informal conversations between Spanish-English bilingual speakers living in Miami, Florida. Twenty-six transcriptions (approximately 390,000 words) were examined. The written corpus was derived from a weekly editorial column entitled “La Calentita: Gibraltar’s National Dish”, which is included in the online version of the Gibraltar newspaper, Panorama, in the opinions section (http://gibraltarpanorama.gi/14775/s/opinion). This column, which is written in informal language, roleplays dialogue between two middle-aged women who review the country’s current events. The conversations include numerous instances of Spanish-English codeswitching. Eighty-eight editorial column entries that appeared between 2004 and 2011 (approximately 25,300 words) were examined. Despite obvious differences between written and spoken language, the data extracted from the two types of corpora confirmed the claim made in past codeswitching literature: switches at the auxiliary and at the participle occur with similar frequency when the verb phrase includes the progressive structure, but when it involves the perfect structure, there is an asymmetry in that switches at the verbal boundary (i.e., at the auxiliary) are more frequent than switches at the participle verb.
2.2. Asymmetries in Mixed-Noun Phrases
Corpus analyses of Spanish-English codeswitching in the United States have reported two systematic tendencies in speakers’ spontaneous productions of mixed noun phrases (henceforth, mixed NPs; Clegg 2006; Herring et al. 2010; Jake et al. 2002; Pfaff 1979; Valdés Kroff 2016). The first asymmetric tendency concerns switches between determiners and nouns. When bilinguals codeswitch within the noun phrase, they prefer switching between a Spanish determiner and an English noun (e.g., el dog ‘the-SPAN dog-ENG’), rather than in the opposite direction (e.g., the perro ‘the-ENG dog-SPAN’).3 The second tendency is characterized in the widespread use of the masculine determiner el ‘the-MASC’ with English nouns whose Spanish translations equivalents are masculine such as el fork ‘the-MASC fork-MASC’ or feminine such as el spoon ‘the-MASC spoon-FEM’. Codeswitches involving the feminine article la ‘the-FEM’ have been observed to occur less frequently and are restricted to English nouns whose translation equivalents are feminine such as la spoon ‘the-FEM spoon-FEM’ and not masculine as in *la fork ‘la-FEM fork-MASC’. This second asymmetry differs from that in unilingual contexts, where masculine and feminine nouns are evenly distributed (Eddington 2002), suggesting a codeswitching strategy that results from the interaction between the two languages.
For example, Valdés Kroff (2016) extracted all instances of mixed NPs from the Bangor Miami corpus (Deuchar et al. 2014) in order to replicate and quantify these patterns of usage from a spontaneous spoken language corpus that includes a heterogeneous group of Spanish-English bilinguals from a range of ages and professions. This procedure resulted in 316 mixed NP tokens of which 304 tokens (96%) were composed of Spanish determiner-English noun phrases. Furthermore, the results robustly replicated prior findings: that is, these Spanish determiner mixed NPs where overwhelmingly marked by Spanish masculine determiners (e.g., el fork), which consisted of masculine (n = 185) and feminine (n = 103) translation equivalents. In contrast, of the remaining eight feminine marked tokens, seven unambiguously referred to Spanish feminine translation equivalents. As in the case of the verbal domain, these results strongly confirmed a production asymmetry whereby the use of Spanish masculine determiners are greatly preferred in mixed NPs.
2.3. Accounting for Codeswitching Distributions
What determines the direction and form of codeswitching preferences? There are several possible reasons for the asymmetric differences in the production of codeswitches. One approach posits that the distributional properties of codeswitches are influenced by the interaction of the grammatical features and participating role of each language.
Elaborating on Joshi’s (1985) original insight, Myers-Scotton (2002) argued that codeswitching asymmetries could be applied not only within clauses, as Joshi had observed, but also across a corpus of bilingual speech. For example, the Matrix Language framework (Myers-Scotton 2002) proposes an asymmetric relationship between the two constituent languages such that one language provides the morphosyntactic frame (i.e., the matrix language) and the other primarily contributes content elements. This account finds empirical support in the language selection of determiners in mixed NPs, which correspond to the matrix language of the clause (Blokzijl et al. 2017; Herring et al. 2010; Parafita Couto and Gullberg 2017). On the other hand, generative accounts suggest that Spanish determiners should be preferred due to the overt grammatical checking features necessary for Spanish gender assignment and agreement (e.g., Liceras et al. 2008, 2016). Alternative accounts argue that these asymmetries may be derived from language-internal properties (see Guzzardo Tamargo et al. 2016; Valdés Kroff et al. 2017).
Some researchers have instead proposed that such distributional asymmetries reflect the presence of social forces and community-based norms (Hebblethwaite 2010; Torres Cacoullos and Travis 2015) and that extralinguistic factors may influence speakers’ linguistic choices that give rise to codeswitching asymmetries. Consistent with this idea, Blokzijl et al. (2017) observed that codeswitches in two bilingual corpora were more likely to be towards the language associated with higher social prestige. From a probabilistic or experience-based perspective, the critical point is that an individual’s history with prior linguistic patterns of codeswitching will likely inform the difficulty that the individual will encounter in comprehending these very same patterns. In the sections that follow, we discuss a few measures that have allowed researchers to assess codeswitching experience and to characterize the processing demands linked to that experience.
3. Codeswitching Assessment Tasks
3.1. Speech Elicitation Tasks
The use of codeswitched language in experimental settings poses unique challenges largely because codeswitching is mostly found in informal in-group interactions and often carries social stigma (Parafita Couto et al. 2015; Poplack 1980). One advantage of using speech elicitation tasks to collect samples of codeswitched language is that when they are carefully designed, they can be ecologically valid and still allow researchers to maintain the level of experimental control typically needed in lab-based studies (Gullberg et al. 2009; Munarriz and Parafita Couto 2014; Valdés Kroff and Fernández-Duque 2017). One viable candidate for eliciting codeswitched speech is the film description task. Halberstadt (2017) used a film description task, which was embedded as a “distractor task” in an auditory memory-load sentence repetition task, to generate spontaneous bilingual speech (Figure 1) that was subsequently used to extract distributional properties of participants’ own codeswitched speech. Participants in this study were recruited from Albuquerque, New Mexico, U.S., an area where bilingual communities engage regularly in Spanish-English codeswitching (Travis and Torres Cacoullos 2013). First, they listened to a codeswitched sentence (see Figure 1, Panel 1) that was previously extracted from a Spanish-English codeswitching corpus (i.e., the New Mexico Spanish-English codeswitching corpus; Torres Cacoullos and Travis 2018). Sentences found in spontaneously produced bilingual corpora were employed to add ecological validity to the experimental context. To elicit the use of a variety of verbal phrases, participants watched a 20-s silent-film clip with intricate action sequences (Figure 1, Panel 2) and were subsequently asked to describe what they had seen in each film clip (Figure 1, Panel 3). Importantly, because the film clips lacked dialogue and sound, there was no inherent language bias associated with the films, encouraging the participants to use Spanish, English, or both when describing them. Immediately after the completion of the film description, participants repeated the original sentence (Figure 1, Panel 4):
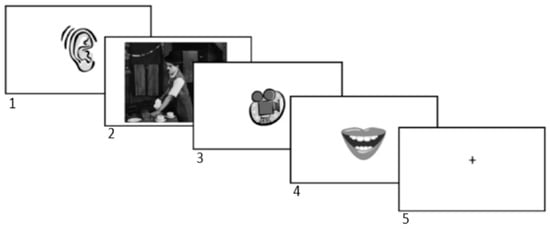
Figure 1.
Example experimental trial of the memory loaded sentence repetition task in Halberstadt (2017) (used with the author’s permission).
Using this method, Halberstadt (2017) generated a corpus consisting of approximately 10 h and 13 min of audio and 53,138 words, with a distribution of unilingual Spanish, unilingual English, and codeswitched stretches of language that resembled the ratios found in corpora of larger spontaneous bilingual speech recorded through the community-based method of sociolinguistic interviews. To illustrate, the Bangor Miami Corpus of Bilingual Speech (Deuchar et al. 2014), which is made up of approximately 390,000 words collected during 35 h, contains 26,801 utterances that are unilingual English, 13,999 that are unilingual Spanish, and 2527 that are codeswitched, where utterances are defined as complementizer phrases. In line with this, Halberstadt’s (2017) corpus contained 2702 codeswitched sentences, with the remaining utterances being more or less equally distributed into unilingual stretches of Spanish and English discourse.
The codeswitching map task (Beatty-Martínez and Dussias 2017, Experiment 3) is a guided production task designed to assess codeswitching behaviors in bilingual speakers. The goal of the task is for director/matcher pairs to verbally communicate to reproduce on the matcher’s map a set of images printed on the director’s map within a designated time limit.4 In this version of the task, conversational partners are free to use whichever language they choose, as no language restrictions are imposed. To prompt participants to engage in codeswitching, they are paired with a bilingual confederate from an established codeswitching community. While the dialogues are unscripted, the confederate intentionally codeswitches following the same conventions from her/his own speech community to induce a bilingual language mode. Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017) used the codeswitching map task to assess the codeswitching behaviors of two groups of Spanish-English bilinguals from two different interactional contexts. They specifically tested whether both groups showed the attested preference for masculine determiners before switching to an English noun, regardless of the gender of the translation equivalent. The first group (non-codeswitchers; n = 22) consisted of bilinguals immersed in a predominantly Spanish-speaking context and who reported little-to-no previous exposure to codeswitching. The second group (codeswitchers; n = 22) were bilingual speakers who had immigrated to the United States in early childhood and were raised in established Spanish-English codeswitching communities. The codeswitching map task generated a corpus consisting of approximately 8 h and 48 min of audio. A total of 10,144 noun phrases were transcribed, consisting of 7075 unilingual Spanish noun phrases, 2396 unilingual English noun phrases, and 673 mixed noun phrases. Participants’ mixed NPs were coded for gender of the noun (i.e., masculine or feminine) and gender agreement between the noun and its accompanying determiner (i.e., congruent or incongruent). The results showed quantitative and qualitative differences in the codeswitching tendencies of the two groups, reinforcing the assertion that not all communities of bilingual speakers exhibit the same patterns or rates of codeswitching, even within the same language pair (Figure 2).
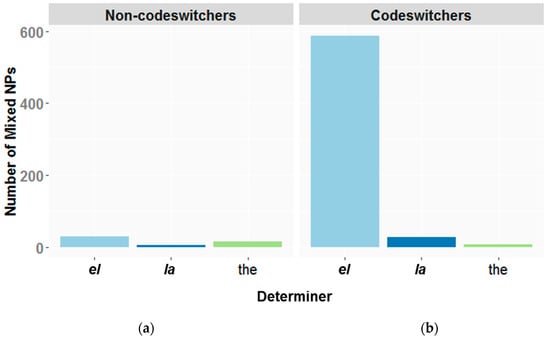
Figure 2.
Distribution of mixed noun phrases (NPs) produced by (a) non-codeswitchers and (b) codeswitchers in Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017) Codeswitching Map Task.
At the same time, the utterances produced by codeswitchers mirrored the proportional distribution of mixed NPs between codeswitchers’ map task data and the mixed NPs observed in Valdés Kroff’s (2016) analysis of the Bangor Miami Corpus (Figure 3). Because both studies yield converging evidence for the same codeswitching behavior, we believe that this validates the use of speech elicitation tasks as an important research tool in the experimental study of codeswitching.
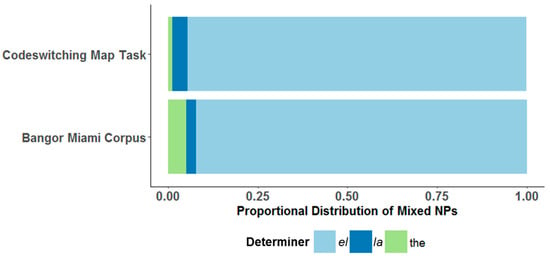
Figure 3.
Proportional distribution of mixed NPs produced by codeswitchers in the Codeswitching Map Task and by speakers in the Bangor Miami Corpus.
3.2. Other Methodological Considerations
Psycholinguistic studies that focus on sentence comprehension have shown that the way in which participants process sentences is heavily influenced by the particular task that they are asked to perform during the experimental session (Hahne and Friederici 2001; Macizo and Bajo 2006; Newman et al. 2009; Williams 2006). However, this topic is still understudied in lab-based work examining the processing of codeswitched language. Two tasks that are often employed in codeswitching processing studies are acceptability judgment tasks and sentence comprehension tasks. One important question, then, is to ask whether the type of task influences processing patterns when bilinguals listen to or read codeswitched sentences. Guzzardo Tamargo (2012) examined this question by asking whether participants’ eye movements were affected by the task that they were asked to perform while reading codeswitched stimuli. Participants were Spanish-English bilingual speakers who reported codeswitching regularly with other bilinguals. Two types of switches were compared: switches between the Spanish auxiliary estar ‘be’ and an English present participle (e.g., cooking), which are more frequent in naturalistic data, and switches between the Spanish auxiliary haber ‘have’ and the English past participle (e.g., cooked), which are less frequent in codeswitching corpora (Guzzardo Tamargo 2012; Pfaff 1979; Poplack 1980). During the experimental session, participants completed two experimental blocks. In one block, after reading each sentence, they were asked to answer a comprehension question about the content of the sentence. In the other block, they performed an acceptability judgment on the sentence. The results showed that the two tasks brought about different reading patterns. When reading for comprehension, participants displayed processing difficulties with haber + English participle switches compared to estar + English participle switches, suggesting that production frequency of the two types of switches was linked to the processing patterns in comprehension. When performing the acceptability judgment task, participants exhibited overall longer reading times and processing difficulties with both types of switches, consequently leading to reading patterns that no longer mirrored natural production patterns. These results suggest that the type of task that is employed in the experimental study of codeswitching can affect how bilinguals process codeswitched language, which may not reflect codeswitching usage patterns in their community.
Another important consideration in experimental studies of codeswitching is whether the way stimuli are presented during the experimental sessions affects how they are processed. Johns et al. (2018) examined this question in an eye-tracking-while-reading study that compared reading times on codeswitched and unilingual Spanish sentences across two modes of presentation: a blocked mode, where one block contained unilingual Spanish sentences and another one contained codeswitched sentences; and a mixed mode, where both unilingual and codeswitched sentences were mixed together in a randomized fashion.
The results indicated that codeswitches took significantly longer to process in the blocked mode than in the mixed mode—a finding that, at first glance, is counterintuitive but is in line with corpus data. Specifically, when bilinguals codeswitch, they do not solely codeswitch for long stretches of time, but instead intrasentential codeswitching is embedded within longer stretches of unilingual discourse (Meechan and Poplack 1995). While a few studies have hinted at the potential confounds related to the presentation of codeswitched or language-switching stimuli (i.e., Gullifer et al. 2013), this finding highlights that lab-based studies examining bilingual codeswitching, as well as the cost (or lack thereof) associated with processing codeswitched stimuli, should take direction from sociolinguistic and corpus-based research because the prior experience that participants bring into the lab can interact with the experimental design. In other words, experimental designs that do not attempt to incorporate sociolinguistic insights into how bilinguals engage with codeswitching may tap into parsing strategies that are not typically recruited in everyday bilingual interactions.
4. Experimental Contributions of Eye-Tracking and Event-Related Potential Methodologies to the Psycholinguistic Study of Codeswitching
One finding that emerges from the psycholinguistic work on codeswitching is that switching between codes incurs a processing cost: a slowdown in processing emerges when individuals move back and forth between their two languages (e.g., Altarriba et al. 1996; Litcofsky and van Hell 2017; Meuter and Allport 1999; Moreno et al. 2002; Van der Meij et al. 2011). Costs have been reported during the reading of codeswitched text (e.g., Dalrymple-Alford 1985; Kolers 1966) and during speech production (e.g., Fairchild and Van Hell 2017; Macnamara 1967; Macnamara et al. 1968; Macnamara and Kushnir 1971; Thomas and Allport 2000). However, it is also possible for bilinguals to mitigate the costs associated with codeswitching if they switch freely (Gollan and Ferreira 2009; Taylor 1971), if they have increased exposure to a given codeswitched structure within discourse (Dussias 2001), or if they have linguistic cues available to aid processing (Gullifer et al. 2013; Guzzardo Tamargo et al. 2016; Fricke et al. 2016).
It has been a common practice in studies examining the processing of codeswitched language to recruit bilingual speakers without examining their codeswitching background (e.g., Altarriba et al. 1996; Hernandez et al. 2001) and to employ experimental stimuli that contain switches that do not necessarily form part of the linguistic repertoire of the bilinguals being tested (for reviews, see Van Hell et al. 2015, 2018). To illustrate, in an eye-tracking study, Altarriba et al. (1996) reported that first fixation durations were longer for high frequency Spanish words in semantically constraining English sentences compared to their English counterparts (5).
| 5. | he wanted to deposit all of his | dinero | at the credit union |
| money |
It is unclear, however, whether the bilinguals tested were accustomed to producing the type of Spanish single word insertions found in the experimental materials. Another example comes from a seminal study by Proverbio et al. (2004). To examine the neural correlates of intrasentential codeswitching, the authors recruited Italian-English simultaneous interpreters—whose codeswitching experience most likely involved intersentential and not intrasentential codeswitches—and employed stimuli with language switches in both directions (from the first to the second language and vice versa), although corpus studies have shown that bilinguals typically favor only one direction of switching (Beatty-Martínez and Dussias 2017; Blokzijl et al. 2017; Pfaff 1979; Poplack 1988).
Sociolinguists have long underscored the importance of collecting data from a stratified random sample of community members to understand linguistic patterns (Poplack and Meechan 1998). The processing of codeswitched language is therefore better situated when studied in bilinguals who codeswitch and who belong to well-defined codeswitching community (Bills and Vigil 2008; Poplack 1989; Travis and Torres Cacoullos 2013). Stimuli derived from real speech samples are also necessary; corpus data as well as psycholinguistic experimental data are both “viable sources of evidence” in experience-based theory so long as the factors acting upon the linguistic behavior are understood (Bybee 2010, p. 9). Therefore, the next stage of research should consider the linguistic experiences of codeswitching bilinguals and the implications of those experiences for the processing of codeswitched language. The studies described below are a first attempt at this.
4.1. Eye-Tracking Contributions to Mixed Verb and Noun Alternations
The recording of eye movements has become a popular method among researchers interested in uncovering how structural processing proceeds when native and second language speakers comprehend language. Why are eye-movement records informative? Theories of sentence processing attempt to explain the on-line (or incremental) nature of comprehension processes. As soon as each word is processed, readers are assumed to make structural decisions about how to integrate each word within the on-going syntactic structure. Over three decades of eye-movement research has shown that when eye movements are recorded during reading, there are systematic relations between fixation durations and the characteristics of the fixated words (Ehrlich and Rayner 1981; Just and Carpenter 1980; Rayner 1978, 1983). For example, we know that readers spend more time fixating on harder words and on key words than on easier words. Longer words are also more likely to be fixated on than shorter words, and words that are likely to be skipped are short, such as function words. When text becomes more complex or contains uncommon or contextually-implausible words, eye fixation duration increases and saccade length (the small jumps made by the eye to move through text) decreases (Duchowski 2002). What is crucial is that researchers interested in language processing can employ eye movements as a window to understand the structural decisions that people make during reading and listening.
We mentioned earlier a study by Guzzardo Tamargo et al. (2016) in which eye-movement records of Spanish-English bilinguals were recorded while they read two types of verb-phrase codeswitches: present-progressive Spanish estar ‘be’ + English present participle switches (6) and present-perfect Spanish haber ‘have’ + English past participle switches (7).
| 6. | Los turistas están | enjoying their stay at the hotel |
| The tourists are |
| 7. | Los turistas han | enjoyed their stay at the hotel | |
| The tourists have | |||
Estar + participle switches, which are produced frequently by bilingual speakers, were read with ease, but haber + participle switches were consistently more difficult to process. Elsewhere we have speculated about what factors may be responsible for the production asymmetries of these two types of codeswitches, but these findings exemplify the sensitivity of bilingual speakers to their own linguistic experience.
In a recent study, Halberstadt (2017) investigated the comprehension of codeswitched language by recording the eye movements of Spanish-English bilinguals for whom codeswitching was an integral part of their discourse mode, while they read aloud short paragraphs that included estar + English participle switches. The paragraphs for the eye-tracking experiment were derived from the narratives generated by the same participants while they were engaged in a prior film description task (see Figure 4). This was done to examine how bilingual codeswitchers processed the very same types of switches that they produced in their daily interactions. Participants were asked to read aloud—instead of following the conventional practice of silent reading typical of eye-tracking studies—because numerous studies have demonstrated that during reading, language users are continuously forming expectations about which words will appear next (e.g., Altmann 2011; Fricke and Kootstra 2016; Kootstra and Muysken 2017), and processing becomes labored (e.g., in the form of a slowdown during silent reading or speech disfluencies during reading aloud) when readers’ expectations are not confirmed by the incoming input. By asking participants to read aloud while their eye movements were recorded (e.g., Gollan et al. 2014), it would, therefore, be possible to obtain converging measures of processing difficulty. A disfluent utterance was one in which a pause, a repetition, or filler was present.

Figure 4.
Codeswitched narrative produced by a Spanish-English bilingual during the film description task in Halberstadt (2017; used with author’s permission). Spanish is italicized; English is emboldened; estar + English participle codeswitches are underlined and other codeswitches are highlighted. Translation: The police were arresting a man that was in a straitjacket and they were near a window in a building. A woman peaked out from the window and then returned inside and came out with a frying pan. She hit the police with the frying pan and later accidentally hit the nice man. She was trying to hit the other man, but she hit the man that was trying to help and then all of them just started touching their heads and afterward they left walking.
One main finding was that processing estar + English participle switches took more time to read than the corresponding no-switch controls, suggesting that there was a cost associated with reading these switches. However, disfluency analyses carried out on the participants’ oral output revealed that estar + English participle switches did not cause any major disruptions. Importantly, if only the eye-tracking data had been examined, it would have been reasonable to conclude that reading codeswitches are costly to the comprehension system. It is only when converging methods to study codeswitching are used that it becomes clear that switching costs fall on a continuum, with some switches causing significant disruption and others producing negligible costs. This is an important distinction; measuring cost in a nuanced way can shed light on how bilinguals are harnessing their linguistic repertoire to support language processing.
Following a similar logic, Valdés Kroff et al. (2017) used a visual world task coupled with eye-tracking to investigate the processing patterns of mixed NPs in Spanish-English bilinguals. Having observed the gender asymmetry in Spanish determiner-English noun phrases in production (i.e., preference for Spanish masculine determiners in mixed NPs), the goal was to test whether this asymmetry would also be found in processing. The visual world eye-tracking technique was used because prior research had demonstrated that Spanish children and adults are able to utilize grammatical gender predictively to anticipate upcoming nouns in informative contexts, i.e., when pairs of objects are presented that differ in gender (Lew-Williams and Fernald 2007). Subsequently, the prediction was that Spanish-English codeswitchers should only show this anticipatory effect for feminine-marked mixed NPs because only feminine determiners reliably signal upcoming nouns that are feminine in Spanish (even when produced in English, e.g., la spoon ‘the-FEM spoon-FEM’). For masculine translation target items paired with feminine translation distractors, bilinguals would have to wait until the onset of the noun because the masculine determiner may lead to codeswitched nouns that are masculine or feminine in Spanish. These predictions were confirmed in the study, thus providing further evidence for the link between language use and language processing.
4.2. Electrophysiological Sensitivity to Codeswitching Patterns
Event-related potentials are signal-averaged epochs of variations in electrical brain activity that are time-locked to a particular event (e.g., the onset of a codeswitch; Luck 2014). The technique provides high temporal resolution indices at different stages of processing as reflected in modulations of distinguishable ERP components. In contrast to behavioral measures (e.g., self-paced reading) which reflect the cumulative outcome of several processes, ERPs provide a continuous measure of processing necessary to track the allocation of attentional resources over time, making it possible to determine the neural processes underlying the comprehension of a codeswitch. While the use of the ERP technique offers a unique contribution to the study of codeswitching, there are methodological issues to be considered (for more detailed discussion, see Swaab et al. 2012). Unlike eye-tracking studies, where readers may use parafoveal information to extract visual information about upcoming words (e.g., Bruni et al. 2017), ERP reading experiments typically use word-by-word rapid visual presentation of sentences to minimize motor artifacts from eye movements. Because differences in lexical features (e.g., word length and lexical frequency) and sentential position of words have been observed to influence ERP components, it is suggested that both surrounding and critical words be controlled for such factors, to the extent possible, and appear in the same structural position across conditions. These considerations are especially warranted for codeswitching as it necessarily involves the comparison of different lexical items (i.e., translation equivalents) which are liable to language effects (e.g., Midgley 2017). Despite this potential caveat, Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017, Experiment 2) recently revealed that translation equivalents elicited comparable ERPs.
A related, additional caveat in examining electrophysiological responses to codeswitches concerns the nature of the codeswitching site. To test speakers’ sensitivity to codeswitching regularities, experimental conditions should ideally be able to isolate the effects of asymmetric codeswitching alternations, where one structure is preferred over the other (i.e., switch vs. switch), from the effects of codeswitching itself (switch vs. no-switch). To illustrate the potential confounding effect, consider a hypothetical experimental manipulation of codeswitching at the complementizer (que vs. that). Previous research with Spanish-English bilinguals (Dussias 2002) has shown a preference for codeswitching between a complementizer and its sentential complement (8) rather than at the head of the complementizer phrase (9).
This experimental manipulation potentially confounds the distinction between processing a codeswitch and processing a switch site that is distributionally less likely to occur and therefore unexpected. Other codeswitching sites such as linguistically hybrid constructions (e.g., hacer + English infinitive; Balam and de Prada Pérez 2016; Wilson 2013) which have no unilingual equivalent in either language, may additionally present challenges in comparing the outcomes of codeswitching. Lastly, as the aforementioned studies have shown, a comprehensive description of the bilingual sample recruited is critical to the interpretation of ERP effects.
| 8. | La niña dijo que | the puppy wanted a treat | |
| The girl said that | |||
| 9. | La niña dijo | that the puppy wanted a treat | |
| The girl said | |||
Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017, Experiment 1) use ERPs to examine the grammatical gender asymmetry of mixed NPs in two groups of bilinguals who differed in codeswitching experience (codeswitchers and non-codeswitchers; see description in Section 3.1). Participants were asked to read short stories that contained different types of codeswitches while their electrophysiological data were recorded. The goal of the study was to test whether bilinguals’ electrophysiological responses to the mixed NP asymmetry differed as a function of codeswitching experience. In their design, Beatty-Martínez and Dussias (2017) compared the processing of different types of mixed NPs (congruent gender switch vs. incongruent gender switch) as well as the processing of mixed NPs relative to unilingual noun phrases (switch vs. no-switch) across the two groups of participants. As depicted in Figure 5, codeswitched conditions elicited a frontal positive deflection in the ERP waveform peaking between 200–300 ms for non-codeswitchers but not for codeswitchers. What this suggests is that for non-codeswitching bilinguals, reading codeswitched stimuli requires a greater allocation of cognitive resources. For switch vs. switch comparisons, codeswitchers demonstrated N400 sensitivity to congruency manipulations, suggesting that masculine targets in incongruent noun phrases (i.e., la fork) were more difficult to integrate relative to masculine targets in congruent noun phrases (i.e., el fork). Importantly, codeswitches that adhered to participants’ usage patterns found in the codeswitching map task did not result in switching costs in the ERP experiment. Overall, the study provides converging evidence that individuals are highly sensitive to the variation in their language experience, addressing the need for accounting for the linguistic repertoire of speakers in the interpretation of lab-based results. The findings demonstrate how switching costs largely depend not only on the type of codeswitch but also the bilingual’s language experience.
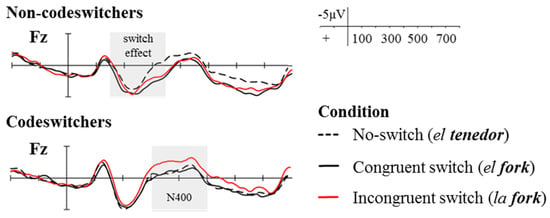
Figure 5.
Event-related potentials time-locked to the onset of masculine switched and non-switched nouns (emboldened) for non-codeswitchers (top) and codeswitchers (bottom) at the electrode site frontal zero (Fz)5 (adapted from Journal of Memory and Language, 95, Beatty-Martínez and Dussias, Bilingual experience shapes language processing: Evidence from codeswitching, 173–89, Copyright (2017), with permission from Elsevier).
5. Concluding Remarks
The main objective of this paper was to integrate field- and laboratory-based research in the study of codeswitching. As research on codeswitching continues to grow, we suggest that more interdisciplinary studies are needed that prioritize the role of experience in language processing. An exciting aspect of recent work is that we are beginning to see more theoretical and empirical developments that take into account the linguistic repertoire (e.g., Adamou and Shen 2017) and the interactional context (e.g., Green and Abutalebi 2013) of speakers. We capitalize on the importance of pairing linguistically informed stimuli with an appropriate bilingual sample and encourage future research to adopt the corpus-to-cognition approach we have described here. While this work has particularly focused on the importance of corpus data to explain experimental results, we note that the flow of benefits of this approach is not unidirectional. That is, experimental data may help determine the range of distributional information that speakers are sensitive to, providing information with respect to issues of language change. In sum, the study of codeswitching offers unique opportunities to examine the role of variation in language processing, but examining this relationship warrants further investigations through converging methodologies and special consideration for the type of stimuli presented and the bilingual sample recruited.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to this work.
Funding
This work was supported in part by NSF grants BCS-1535124, OISE-0968369, OISE-1545900; NIH grants HD082796, HD071758 to Paola E. Dussias.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rosa E. Guzzardo Tamargo, Lauren Halberstadt, and Michael A. Johns for allowing us to include their research in this paper. We are also thankful to the Editors and two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Adamou, Evangelia, and Xingjia Rachel Shen. 2017. There are no language switching costs when codeswitching is frequent. International Journal of Bilingualism, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarriba, Jeanette, Judith F. Kroll, Alexandra Sholl, and Keith Rayner. 1996. The influence of lexical and conceptual constraints on reading mixed-language sentences: Evidence from eye fixations and naming times. Memory & Cognition 24: 477–92. [Google Scholar]
- Altmann, Gerry T. M. 2011. The mediation of eye movements by spoken language. In The Oxford Handbook of Eye Movements. Edited by Simon P. Liversedge, Iain D. Gilchrist and Stefan Everling. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 979–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Balam, Osmer, and Ana de Prada Pérez. 2016. On the productive use of ‘Hacer+ V’ in Northern Belize bilingual/trilingual code-switching. In Spanish-English Codeswitching in the Caribbean and the US. Edited by Rosa E. Guzzardo Tamargo, Catherine M. Mazak and M. Carmen Parafita Couto. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 261–79. [Google Scholar]
- Beatty-Martínez, Anne L., and Paola E. Dussias. 2017. Bilingual experience shapes language processing: Evidence from codeswitching. Journal of Memory and Language 95: 173–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, Garland D., and Neddy A. Vigil. 2008. The Spanish Language of New Mexico and Southern Colorado: A Linguistic Atlas. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Elorrieta, Esti, and Liina Pylkkännen. 2017. Bilingual language switching in the laboratory versus in the wild: The spatiotemporal dynamics of adaptive language control. Journal of Neuroscience 37: 9022–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokzijl, Jeffrey, Margaret Deuchar, and M. Carmen Parafita Couto. 2017. Determiner asymmetry in mixed nominal constructions: The role of grammatical factors in data from Miami and Nicaragua. Languages 2: 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, Michelle, Megan Zirnstein, and Paola E. Dussias. 2017. Hidden in Plain Sight: How Bilinguals Use Parafoveal Preview to Anticipate Code-Switches. Poster presented at the 58th Annual Meeting of the Psychonomic Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, November 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bybee, Joan L. 2010. Language, Usage and Cognition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Franklin. 2009. Learning to order words: A connectionist model of heavy NP shift and accessibility effects in Japanese and English. Journal of Memory and Language 61: 374–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, Jens H. 2006. Lone English-Origin Nouns in the Spanish of New Mexico: A Variationist Analysis of Phonological and Morphological Adaptations. Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple-Alford, Ernest C. 1985. Language switching during bilingual reading. British Journal of Psychology 76: 111–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, Gary S., and Franklin Chang. 2014. The P-chain: Relating sentence production and its disorders to comprehension and acquisition. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 369: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuchar, Margaret, Peredur Davies, Jon Herring, M. Carmen Parafita Couto, and Diana Carter. 2014. Building bilingual corpora. In Advances in the Study of Bilingualism. Edited by Enlli M. Thomas and Ineke Mennen. Bristol: Multilingualism Matters, pp. 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Duchowski, Andrew. 2002. A breadth-first survey of eye-tracking applications. Behavior Methods, Research, Instruments, and Computers 34: 455–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussias, Paola. E. 2001. Psycholinguistic complexity in codeswitching. International Journal of Bilingualism 5: 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussias, Paola. E. 2002. On the relationship between comprehension and production data in codeswitching. In Romance Phonology and Variation: Selected Papers from the 30th Linguistic Symposium on Romance Languages. Edited by Caroline Wiltshire and Joaquim Camps. Gainesville and Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dussias, Paola E., Alejandra Marful, Chip Gerfen, and M. Teresa Bajo Molina. 2010. Usage frequencies of complement-taking verbs in Spanish and English: Data from Spanish monolinguals and Spanish-English bilinguals. Behavior Research Methods 42: 1004–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddington, David. 2002. Spanish gender assignment in an analogical framework. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics 9: 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, Susan F., and Keith Rayner. 1981. Contextual effects on word perception and eye movements during reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 20: 641–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, Sarah, and Janet G. Van Hell. 2017. Determiner-noun code-switching in Spanish heritage speakers. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 20: 150–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, Melinda, and Gerrit Jan Kootstra. 2016. Primed codeswitching in spontaneous bilingual dialogue. Journal of Memory and Language 91: 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, Melinda, Judith F. Kroll, and Paola E. Dussias. 2016. Phonetic variation in bilingual speech: A lens for studying the production–comprehension link. Journal of Memory and Language 89: 110–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollan, Tamar H., and Victor S. Ferreira. 2009. Should I stay or should I switch? A cost–benefit analysis of voluntary language switching in young and aging bilinguals. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 35: 640–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollan, Tamar H., Elizabeth R. Schotter, Joanne Gomez, Mayra Murillo, and Keith Rayner. 2014. Multiple levels of bilingual language control: Evidence from language intrusions in reading aloud. Psychological Science 25: 585–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Vilbazo, Kay, Laura Bartlett, Sarah Downey, Shane Ebert, Jeanne Heil, Bradely Hoot, Bryan Koronkiewicz, and Sergio Ramos. 2013. Methodological considerations in code-switching research. Studies in Hispanic and Lusophone Linguistics 6: 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, David W., and Jubin Abutalebi. 2013. Language control in bilinguals: The adaptive control hypothesis. Journal of Cognitive Psychology 25: 515–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, David. W., and Li Wei. 2014. A control process model of code-switching. Language, Cognition, and Neuroscience 29: 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, Marianne, Peter Indefrey, and Pieter Muysken. 2009. Research Techniques for the Study of Code-Switching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Gullifer, Jason W., Judith F. Kroll, and Paola E. Dussias. 2013. When language switching has no apparent cost: Lexical access in sentence context. Frontiers in Psychology 4: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzardo Tamargo, Rosa E. 2012. Linking Comprehension Costs to Production Patterns during the Processing of Mixed Language. Ph.D. dissertation, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzardo Tamargo, Rosa E., Jorge R. Valdés Kroff, and Paola E. Dussias. 2016. Examining the relationship between comprehension and production processes in code-switched language. Journal of Memory and Language 89: 138–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahne, Anja, and Angela D. Friederici. 2001. Processing a second language: Late learners’ comprehension mechanisms as revealed by event-related brain potentials. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 4: 123–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberstadt, Lauren P. 2017. Investigating Community Norms and Linguistic Mechanisms in Codeswitching: Bridging Linguistic Theory and Psycholinguistic Experimentation. Ph.D. dissertation, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Hasson, Uri, Yuval Nir, Ifat Levy, Galit Fuhrmann, and Rafael Malach. 2004. Intersubject synchronization of cortical activity during natural vision. Science 303: 1634–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasson, Uri, Asif A. Ghazanfar, Bruno Galantucci, Simon Garrod, and Christian Keysers. 2012. Brain-to-brain coupling: A mechanism for creating and sharing a social world. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 16: 114–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebblethwaite, Benjamin. 2010. Adverb code-switching among Miami’s Haitian Creole-English second generation. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 13: 409–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, Arturo E., Mirella Dapretto, John Mazziotta, and Susan Bookheimer. 2001. Language switching and language representation in Spanish–English bilinguals: An fMRI study. NeuroImage 14: 510–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, Jon Russell, Margaret Deuchar, M. Carmen Parafita Couto, and Mónica Moro Quintanilla. 2010. ‘I saw the madre’: Evaluating predictions about codeswitched determiner-noun sequences using Spanish–English and Welsh–English data. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism 13: 553–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jake, Janice L., Carol Myers-Scotton, and Steven Gross. 2002. Making a minimalist approach to codeswitching work: Adding the Matrix Language. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 5: 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, Michael A., Jorge R. Valdés Kroff, and Paola E. Dussias. 2018. Mixing Things Up: How blocking and mixing affect the processing of codemixed sentences. International Journal of Bilingualism. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Aravind K. 1985. Processing of sentences with intrasentential switching. In Natural Language Parsing. Edited by David R. Dowty, Lauri Karttunen and Arnold M. Zwicky. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 190–205. [Google Scholar]
- Just, Marcel. A., and Patricia A. Carpenter. 1980. A theory of reading: From eye fixations to comprehension. Psychological Review 87: 329–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolers, Paul. A. 1966. Reading and talking bilingually. The American Journal of Psychology 79: 357–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kootstra, Gerrit Jan, and Pieter Muysken. 2017. Cross-linguistic priming in bilinguals: Multidisciplinary perspectives on language processing, acquisition, and change. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 20: 215–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew-Williams, Casey, and Anne Fernald. 2007. Young children learning Spanish make rapid use of grammatical gender in spoken word recognition. Psychological Science 18: 193–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Ping. 1996. Spoken word recognition of code-switched words by Chinese–English bilinguals. Journal of Memory and Language 35: 757–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liceras, Juana M., Raquel Fernández Fuertes, Susana Perales, Rocío Pérez-Tattam, and Kenton Todd Spradlin. 2008. Gender and gender agreement in bilingual native and non-native grammars: A view from child and adult functional-lexical mixings. Lingua 118: 827–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liceras, Juana M., Raquel Fernández Fuertes, and Rachel Klassen. 2016. Language dominance and language nativeness: The view from English-Spanish code-switching. In Spanish-English Codeswitching in the Caribbean and the US. Edited by Rosa E. Guzzardo Tamargo, Catherine M. Mazack and M. Carmen Parafita Couto. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 107–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lipski, John M. 1978. Code-switching and the problem of bilingual competence. In Aspects of Bilingualism. Edited by Michel Paradis. Columbia: Hornbeam Press, pp. 250–64. [Google Scholar]
- Litcofsky, Kaitlyn. A., and Janet G. van Hell. 2017. Switching direction affects switching costs: Behavioral, ERP and time-frequency analyses of intra-sentential codeswitching. Neuropsychologia 97: 112–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, Steven. J. 2014. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, Maryellen C. 2013. How language production shapes language form and comprehension. Frontiers in Psychology 4: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macizo, Pedro, and M. Teresa Bajo. 2006. Reading for repetition and reading for translation: Do they involve the same processes? Cognition 99: 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macnamara, John. 1967. The bilingual’s linguistic performance—A psychological overview. Journal of Social Issues 23: 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnamara, John, and Seymour L. Kushnir. 1971. Linguistic independence of bilinguals: The input switch. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 10: 480–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnamara, John, Marcel Krauthammer, and Marianne Bolgar. 1968. Language switching in bilinguals as a function of stimulus and response uncertainty. Journal of Experimental Psychology 78: 208–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacSwan, Jeff. 2009. Generative approaches to code-switching. In The Cambridge Handbook of Linguistic Code-Switching. Edited by Almeida. J. Toribio and Barbara E. Bullock. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 309–35. [Google Scholar]
- Meechan, Marjory, and Shana Poplack. 1995. Orphan categories in bilingual discourse: Adjectivization strategies in Wolof-French and Fongbe-French. Language Variation and Change 7: 169–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuter, Renata F. I., and Alan Allport. 1999. Bilingual language switching in naming: Asymmetrical costs of language selection. Journal of Memory and Language 40: 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, Katherine. 2017. A Neuro-cognitive View of the Bilingual Brain. In Neural Mechanisms of Language. Edited by Maria Mody. Boston: Springer, pp. 129–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Eva M., Kara D. Federmeier, and Marta Kutas. 2002. Switching languages, switching palabras (words): An electrophysiological study of code switching. Brain and Language 80: 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munarriz, Amaia, and Maria del Carmen Parafita Couto. 2014. ¿Cómo estudiar el cambio de código? Incorporación de diferentes metodologías en el caso de varias comunidades bilingües. Lapurdum 18: 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers-Scotton, Carol. 2002. Dueling Languages: Grammatical Structure in Code-switching. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Myers-Scotton, Carol, and Janice L. Jake. 2015. Cross-language asymmetries in code-switching patterns: Implications for bilingual language production. In The Cambridge Handbook of Bilingual Processing. Edited by John Schwieter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 416–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, Sharlene D., Donghoon Lee, and Kristen L. Ratliff. 2009. Off-line sentence processing: What is involved in answering a comprehension probe? Human Brain Mapping 30: 2499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parafita Couto, María del Carmen, and Marianne Gullberg. 2017. Code-switching within the noun phrase: Evidence from three corpora. International Journal of Bilingualism. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafita Couto, María del Carmen, Margaret Deuchar, and Marika Fusser. 2015. How do Welsh–English bilinguals deal with conflict? Adjective-noun order resolution. In Code-Switching between Structural and Sociolinguistic Perspectives. Edited by Gerald Stell and Kofi Yakpo. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, Carol W. 1979. Constraints on language mixing: Intrasentential code-switching and borrowing in Spanish/English. Language 55: 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplack, Shana. 1980. Sometimes I’ll start a sentence in Spanish y termino en español: Toward a typology of codeswitching. Linguistics 18: 581–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplack, Shana. 1988. Contrasting patterns of code-switching in two communities. In Codeswitcing: Anthropological and Sociolinguistic Perspectives. Edited by Monica Heller. Berlin: Mouton, pp. 215–44. [Google Scholar]
- Poplack, Shana. 1989. The care and handling of a mega-corpus: The Ottawa-Hull French project. In Language Change and Variation. Edited by Ralph W. Fasold and Deborah Schiffrin. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 411–51. [Google Scholar]
- Poplack, Shana, and Marjory Meechan. 1998. How languages fit together in codemixing. International Journal of bilingualism 2: 127–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proverbio, Alice M., Giuliana Leoni, and Alberto Zani. 2004. Language switching mechanisms in simultaneous interpreters: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia 42: 1636–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, Keith. 1978. Eye movements in reading and information processing. Psychological Bulletin 85: 618–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, Keith. 1983. The perceptual span and eye movement control during reading. In Eye Movement in Reading: Perceptual and Language Processes. Edited by Keith Rayner. New York: Academic Press, pp. 97–139. [Google Scholar]
- Swaab, Tamara Y., Kerry Ledoux, C. Christine Camblin, and Megan A. Boudewyn. 2012. Language-related ERP components. In Oxford Handbook of Event-Related Potential Components. Edited by Steven J. Luck and Emily S. Kappenman. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 397–440. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, Insup. 1971. How are words from two languages organized in bilinguals’ memory? Canadian Journal of Psychology 25: 228–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, Michael. S. C., and Alan Allport. 2000. Language switching costs in bilingual visual word recognition. Journal of Memory and Language 43: 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Cacoullos, Rena, and Catherine E. Travis. 2015. Gauging convergence on the ground: Code-switching in the community. International Journal of Bilingualism 19: 365–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Cacoullos, Rena, and Catherine E. Travis. 2018. Bilingualism in the Community: Code-Switching and Grammars in Contact. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, Catherine E., and Rena Torres Cacoullos. 2013. Making voices count: Corpus compilation in bilingual communities. Australian Journal of Linguistics 33: 170–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés Kroff, Jorge R. 2016. Mixed NPs in Spanish-English bilingual speech: Using a corpus-based approach to inform models of sentence processing. In Spanish-English Codeswitching in the Caribbean and the US. Edited by Rosa. E. Guzzardo Tamargo, Catherine M. Mazak and M. Carmen Parafita Couto. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés Kroff, Jorge R., and Matías Fernández-Duque. 2017. Experimentally inducing Spanish-English code-switching: A new conversation paradigm. In Multidisciplinary Approaches to Bilingualism in the Hispanic and Lusophone World. Edited by Kate Bellamy, Michael W. Child, Paz González, Antje Muntendam and M. Carmen Parafita Couto. Amsterdam: John Benjamins, pp. 209–31. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés Kroff, Jorge R., Paola E. Dussias, Chip Gerfen, Lauren Perrotti, and M. Teresa Bajo. 2017. Experience with code-switching modulates the use of grammatical gender during sentence processing. Linguistic Approaches to Bilingualism 7: 163–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés Kroff, Jorge R., Rosa E. Guzzardo Tamargo, and Paola E. Dussias. 2018. Experimental contributions of eye-tracking to the understanding of comprehension processes while hearing and reading codeswitches. Linguistic Approaches to Bilingualism 8: 98–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meij, Maartje, Fernando Cuetos, Manuel Carreiras, and Horacio A. Barber. 2011. Electrophysiological correlates of language switching in second language learners. Psychophysiology 48: 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hell, Janet G., Kaitlyn A. Litcofsky, and Caitlin Y. Ting. 2015. Sentential code-switching: Cognitive and neural approaches. In The Cambridge Handbook of Bilingual Processing. Edited by John W. Schwieter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 459–82. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hell, Janet G., Carla B. Fernández, Gerrit Jan Kootstra, Kaitlyn A. Litcofsky, and Caitlin Y. Ting. 2018. Electrophysiological and experimental-behavioral approaches to the study of intra-sentential code-switching. Linguistic Approaches to Bilingualism 8: 134–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, John. N. 2006. Incremental interpretation in second language sentence processing. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 9: 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, Damián V. 2013. One construction, two source languages: Hacer with an English infinitive in bilingual discourse. In Proceedings from the 6th International Workshop on Spanish Sociolinguistics. Edited by Ana M. Carvalho and Sara Beaudrie. Sommerville: Cascadilla Proceedings Project, pp. 123–34. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | For ease of exposition, we adopt a broad definition of codeswitching to include single word and multiword constituents. |
| 2 | We note that the work reviewed here focuses exclusively on Spanish-English data. For a similar perspective focusing on data across different language pairs, we refer the reader to Munarriz and Parafita Couto (2014). |
| 3 | We emphasize that asymmetric preferences described here are not necessarily generalizable across all Spanish-English codeswitching communities. For example, Blokzijl et al. (2017) observed the reverse preference in switching directionality (i.e., mixed NPs with an English determiner and a Spanish noun) in their Spanish-Nicaraguan English Creole data. |
| 4 | For other referential communication tasks that have been employed to study codeswitching, we refer the reader to a comprehensive review by Gullberg et al. (2009). An anonymous reviewer asked whether the codeswitching map task was the same as the director-matcher task reviewed in Gullberg et al. (2009). While both tasks are similar, they differ in two critical ways: First, the codeswitching map task was designed to examine grammatical gender while the director-matcher task additionally manipulated objects’ color and size to prompt the use of complex NPs and examine adjective-noun order resolution. Second, while the two tasks feature conversations between pairs of bilingual speakers, one of the participants in the codeswitching map task is an unscripted confederate who regularly codeswitches. |
| 5 | For illustrative purposes, only electrode Fz is displayed. We refer the reader to the original paper for detailed topographic distribution of the ERPs for each condition. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).