Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminates and Their Application in Variable-Camber Wings
Abstract
1. Introduction
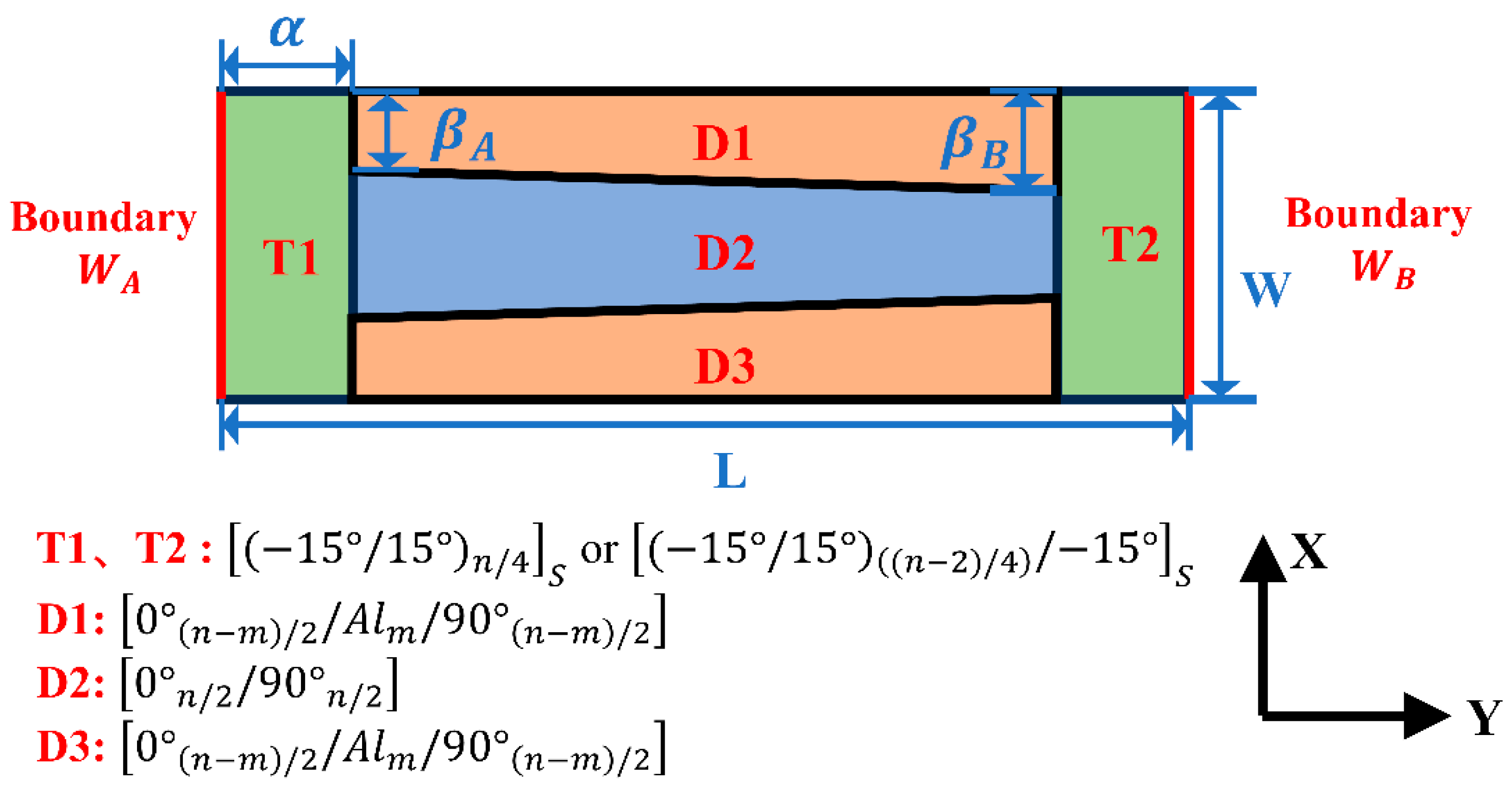
2. Design and Fabrication of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminate
2.1. Structural Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminate
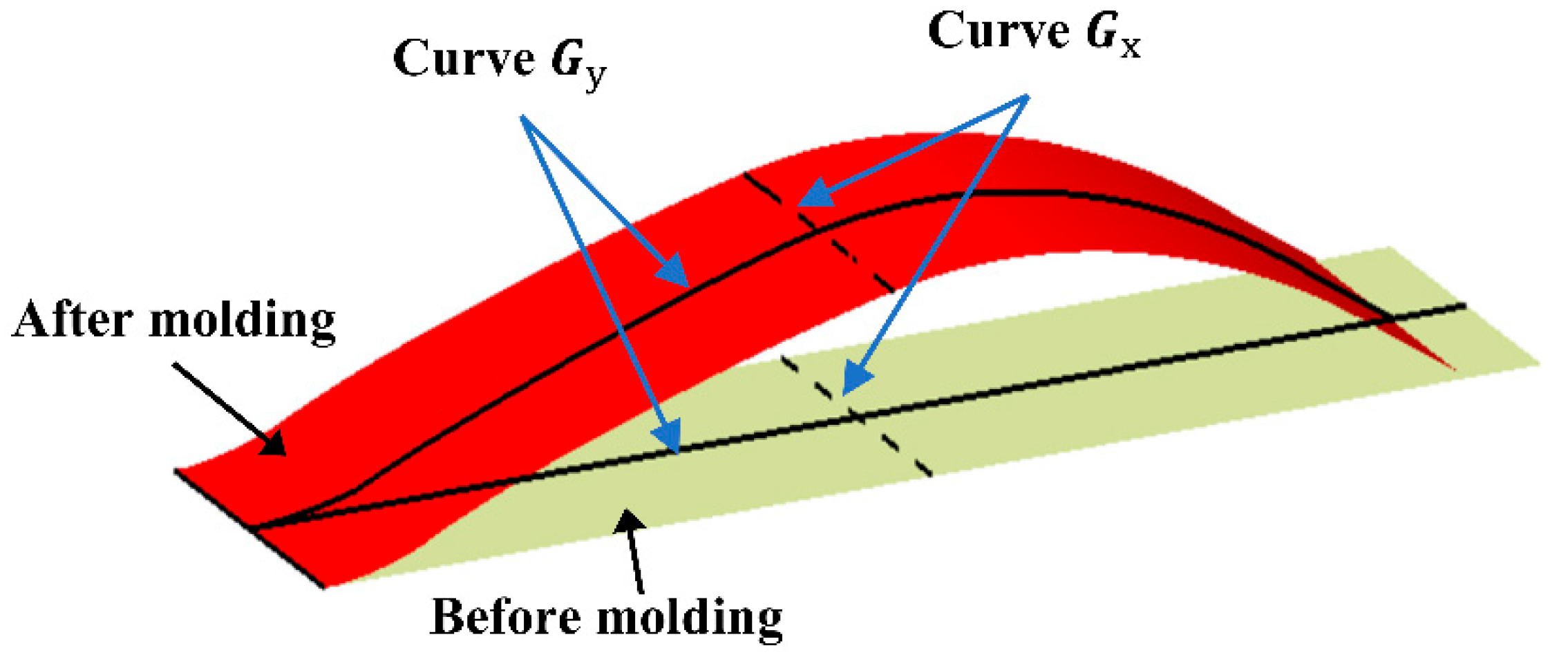
2.2. Physical Model Fabrication and Analysis
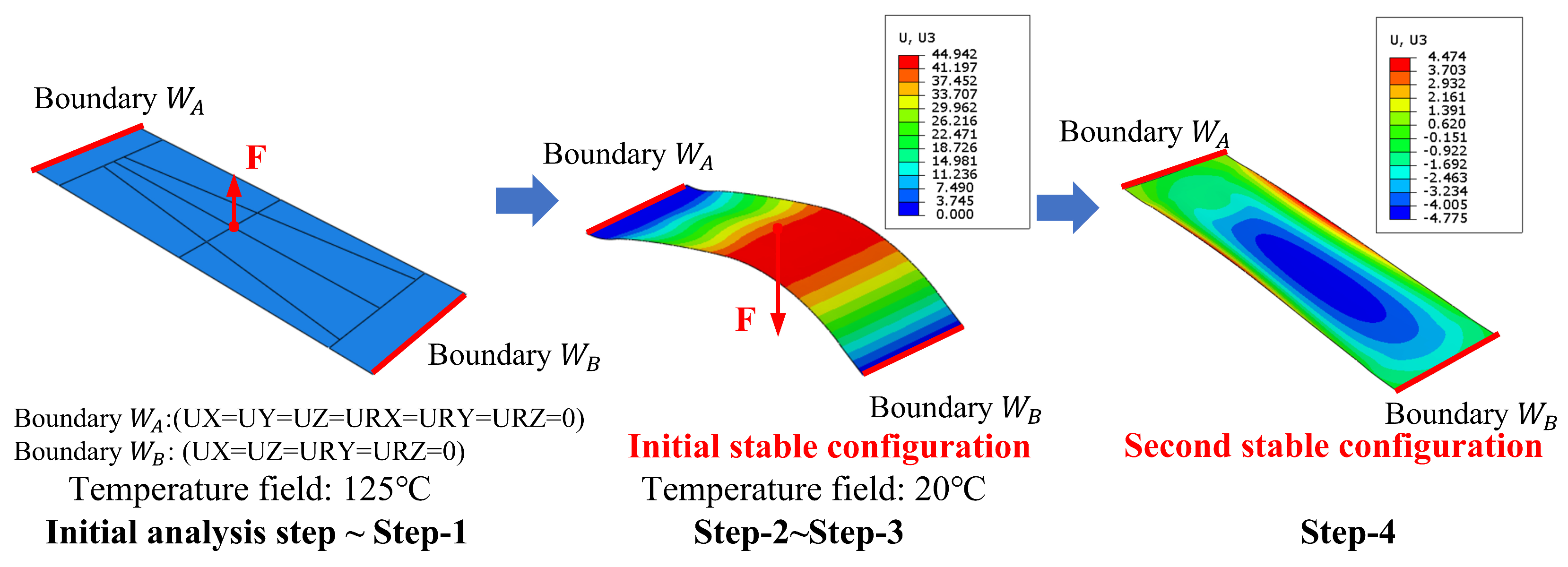
2.3. Finite Element Modeling
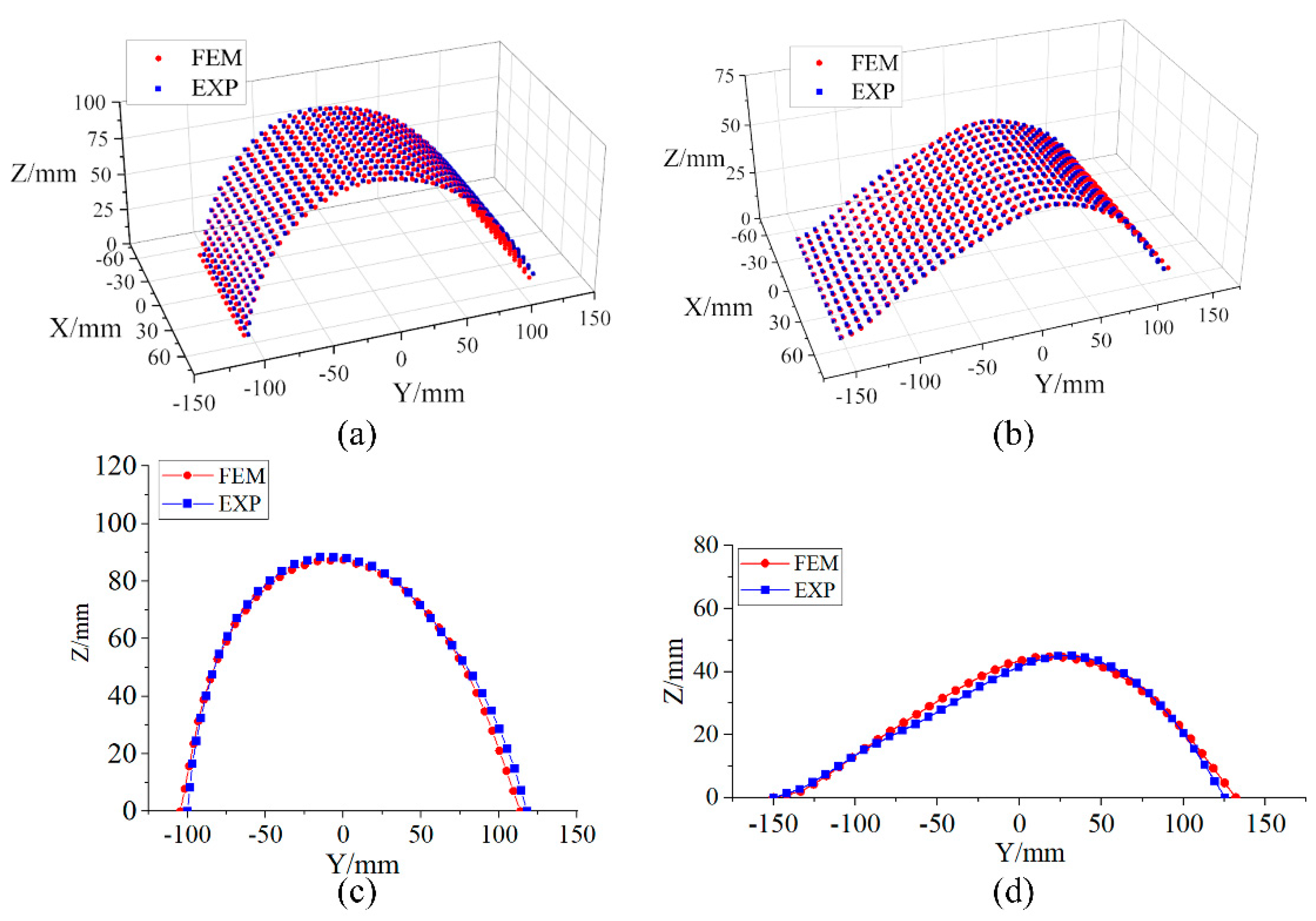
2.4. Initial Stable Configuration Comparison Between Finite Element and Physical Models
3. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Deformation Performances of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Laminates
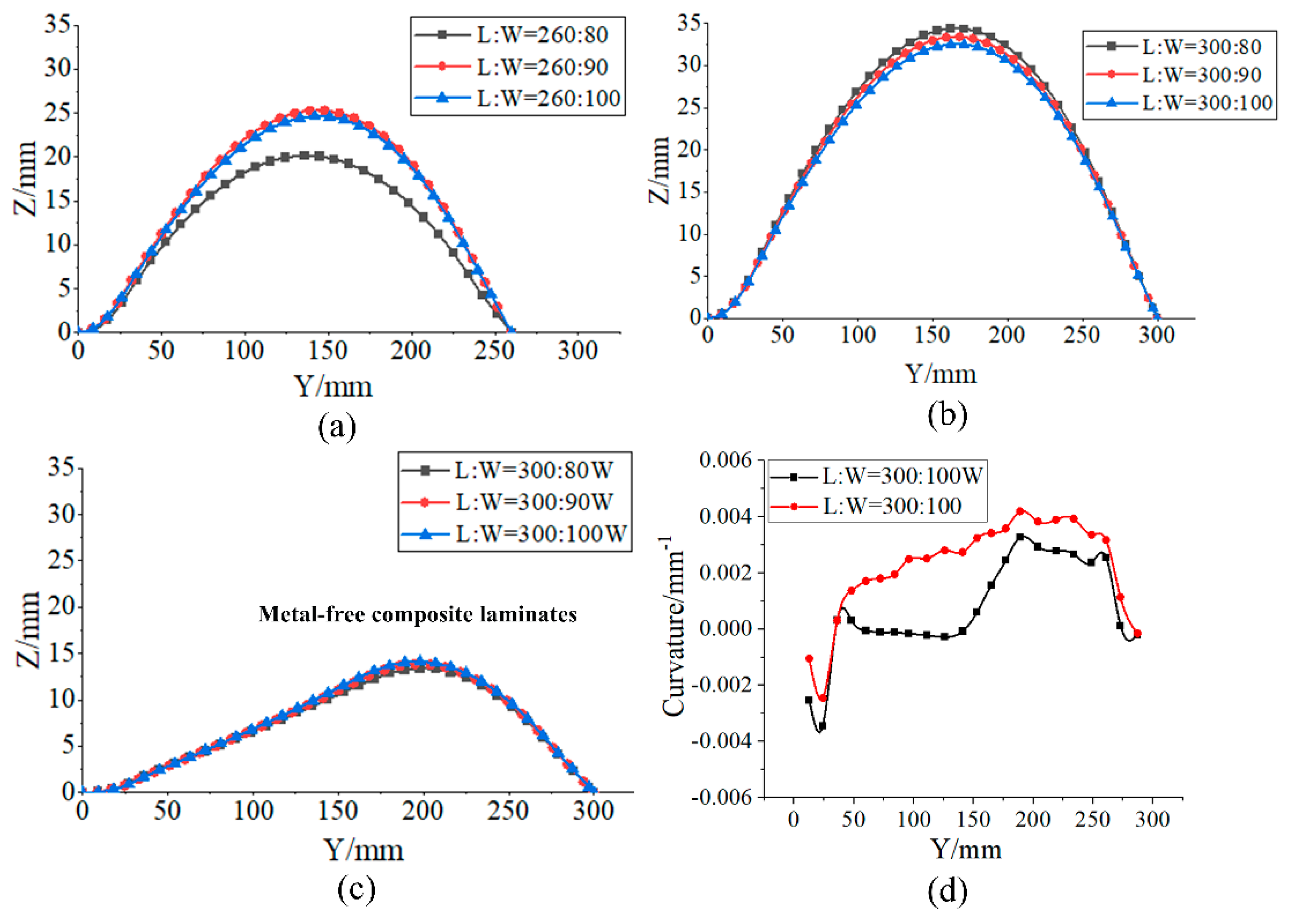
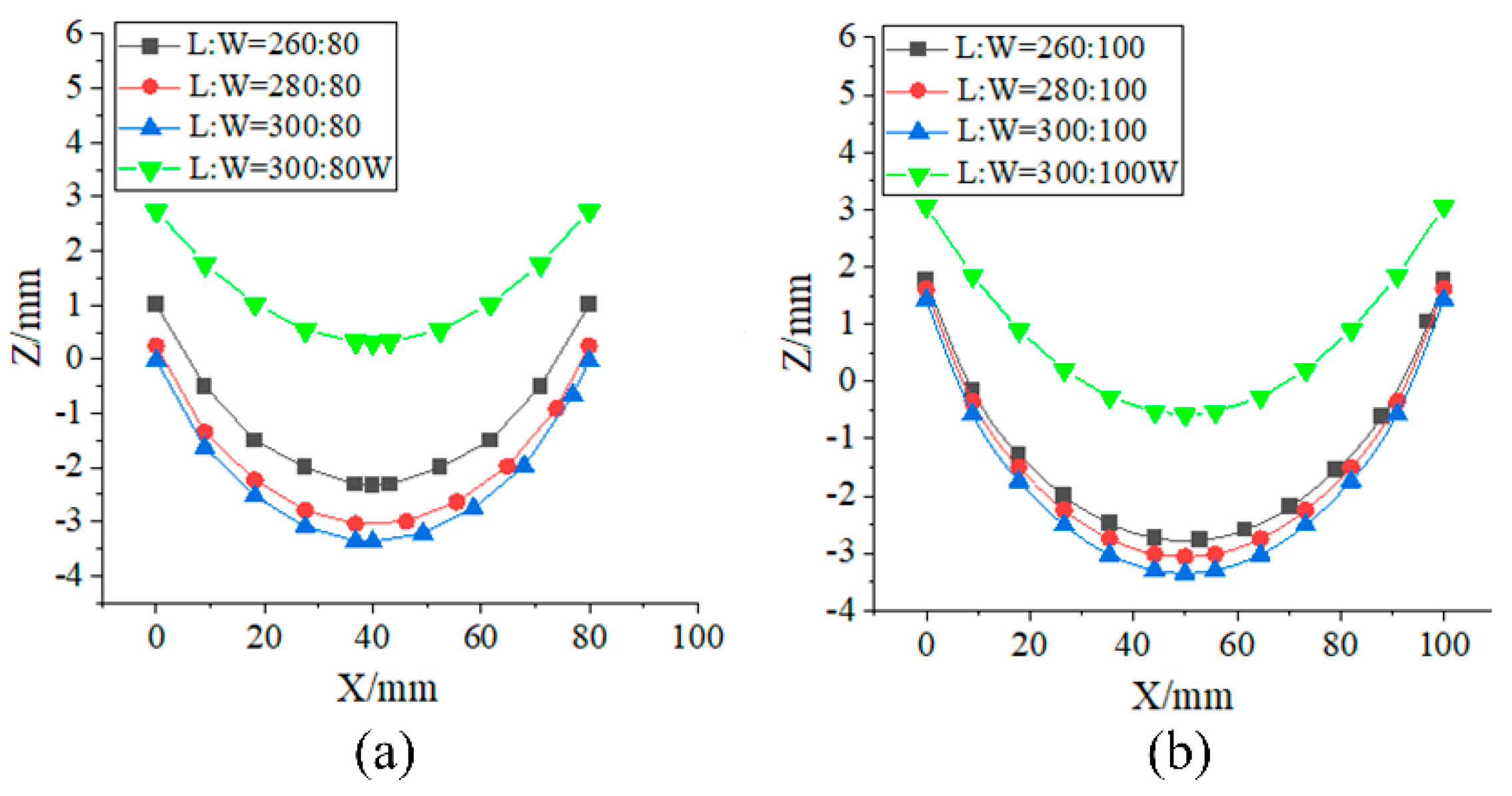
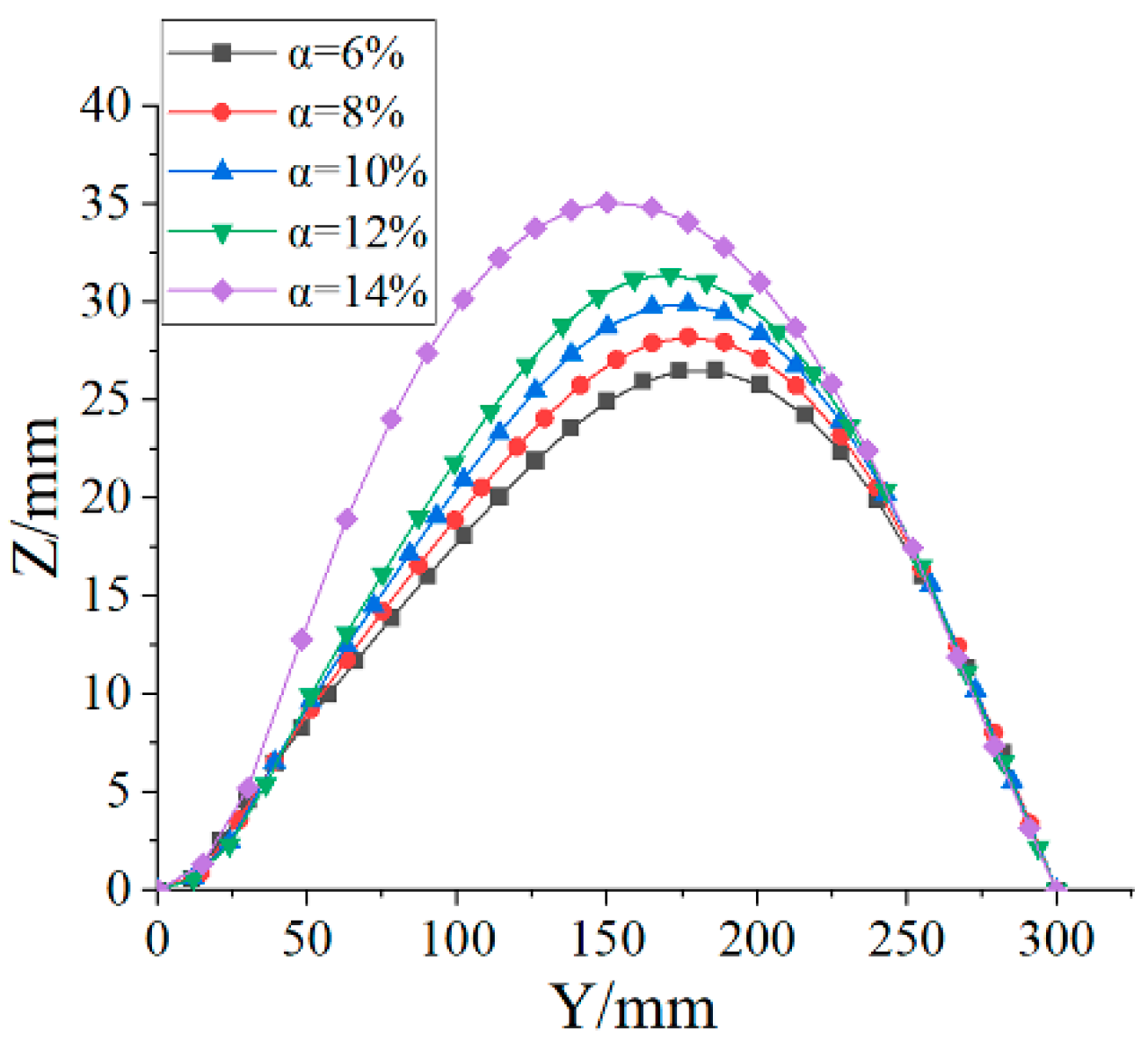
3.1. Influence of the Aspect Ratio on the Deformation Performances of Bistable Laminates
3.2. Influence of Metal Layer Edge Proportions on the Deformation Performances of Bistable Laminates
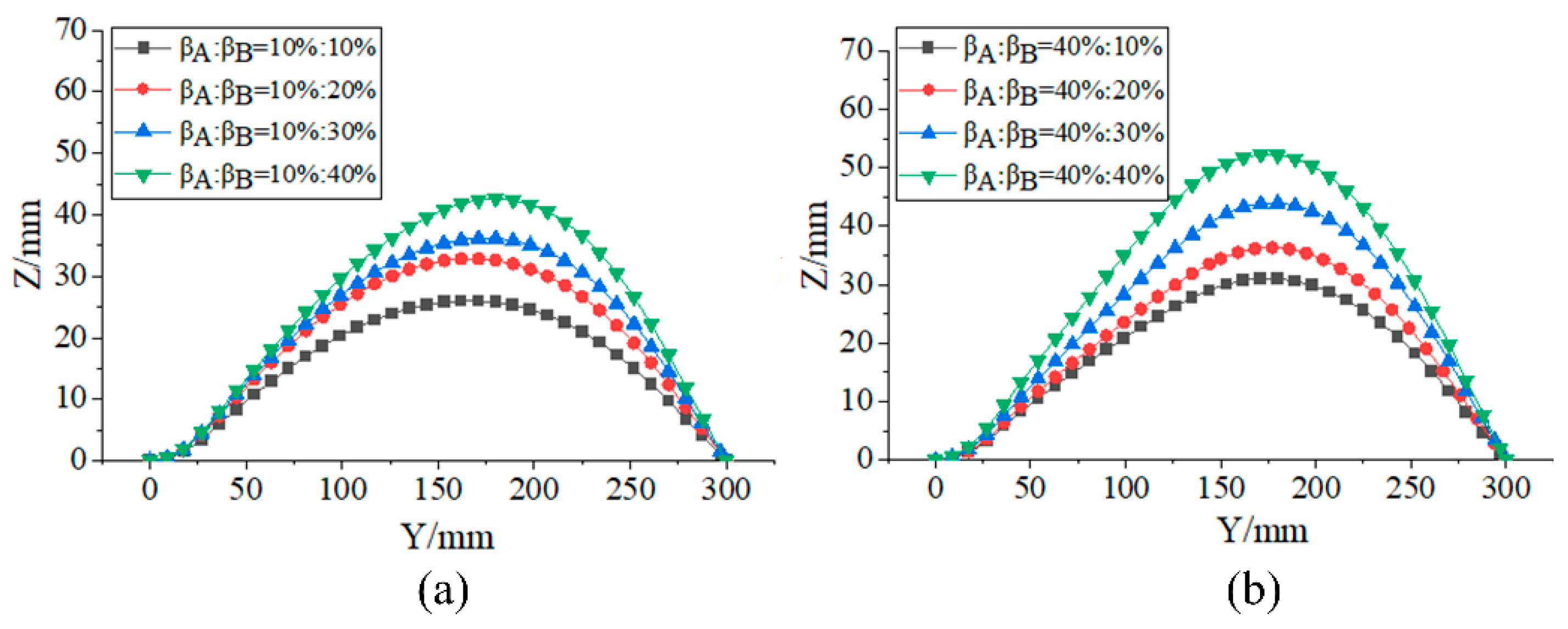
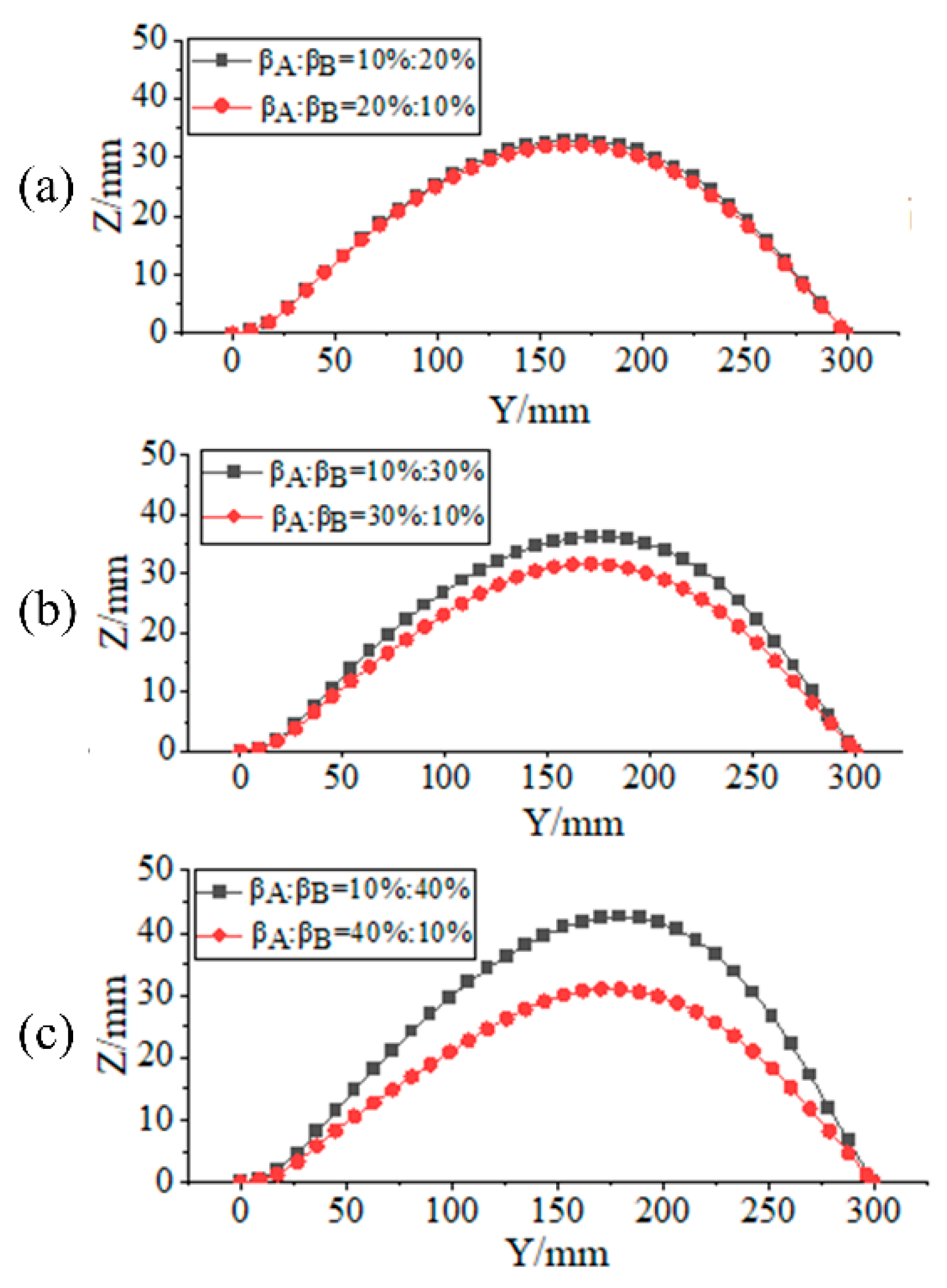
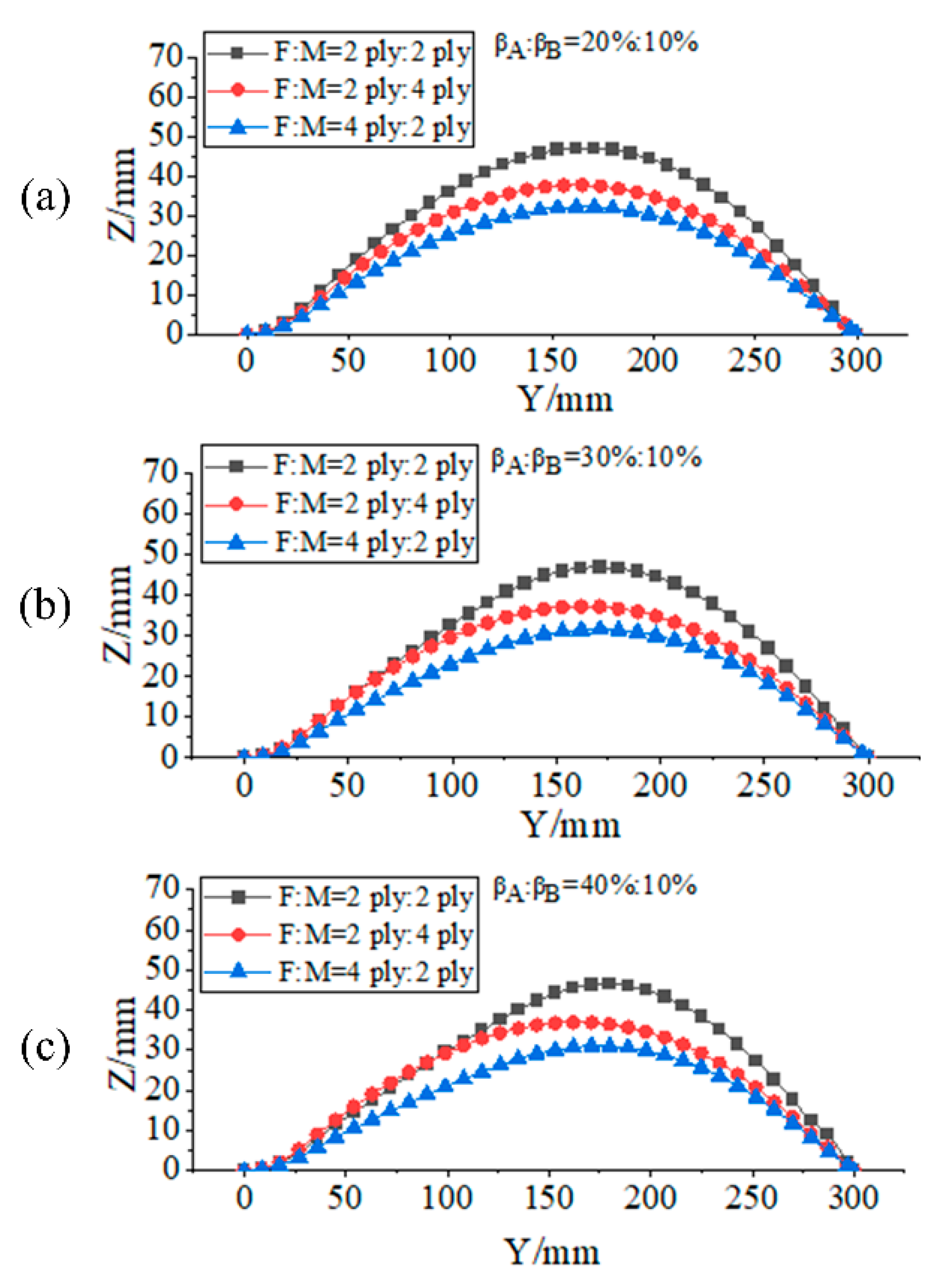
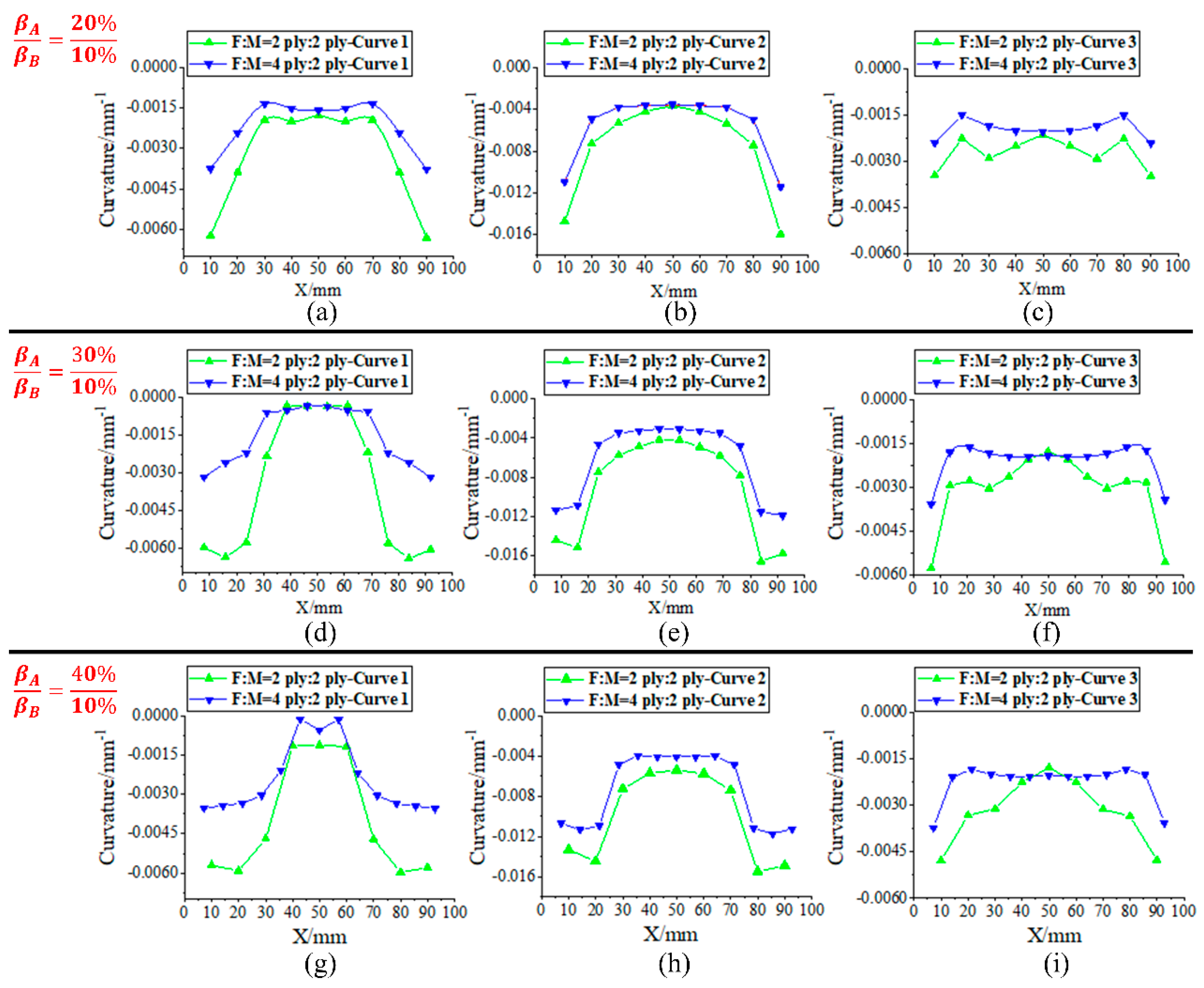
3.3. Influence of the Number of Layers and Layup Ratio of Two Materials on the Deformation Performances of Laminates
3.4. Influence of Transition Element Edge Proportion on Deformation Performances of Laminates
3.5. Analysis and Summary of Influencing Factors on Laminate Deformation
4. Research on Variable-Camber Wing Design Based on Variable-Stiffness Bistable Laminates
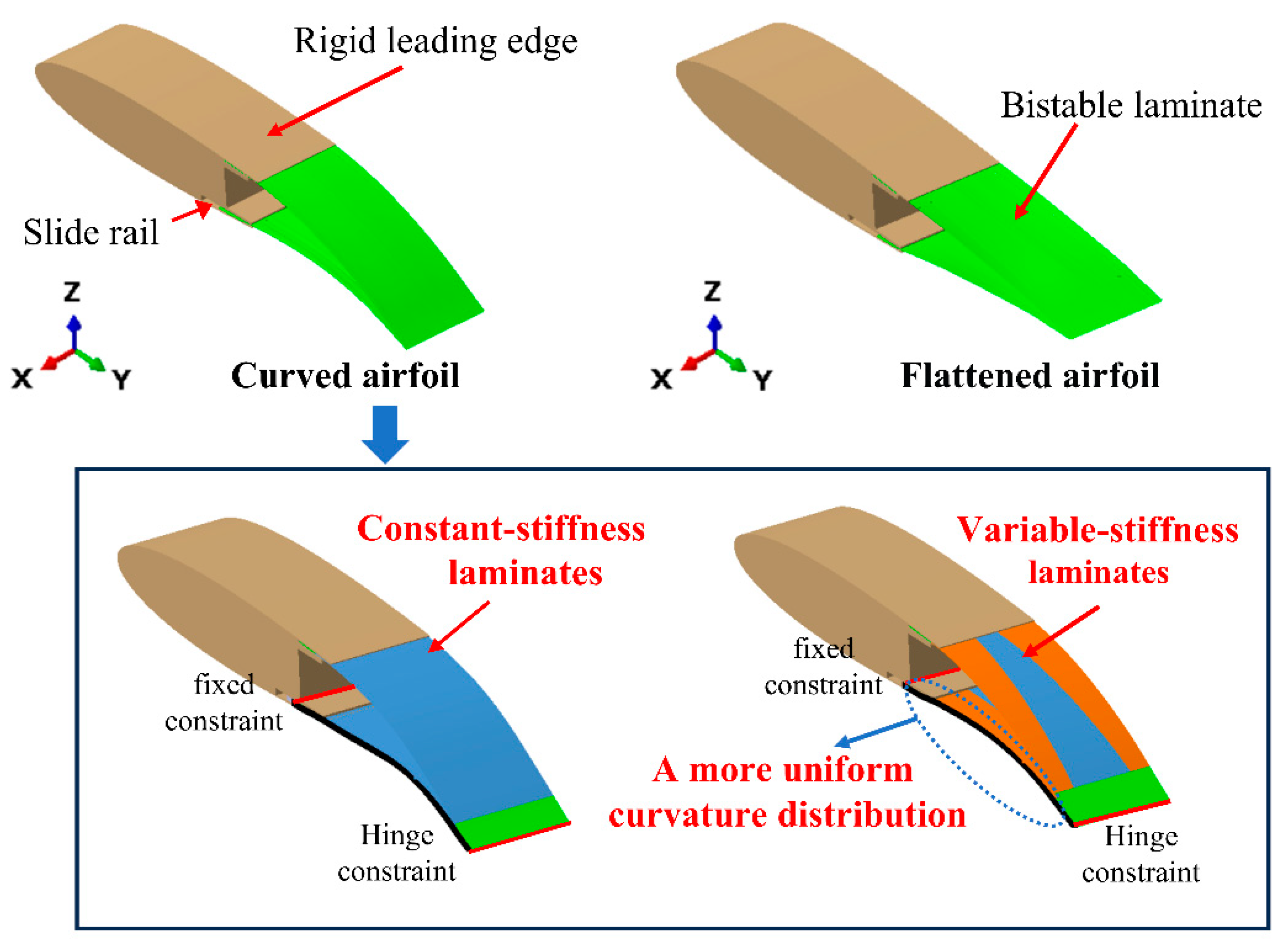
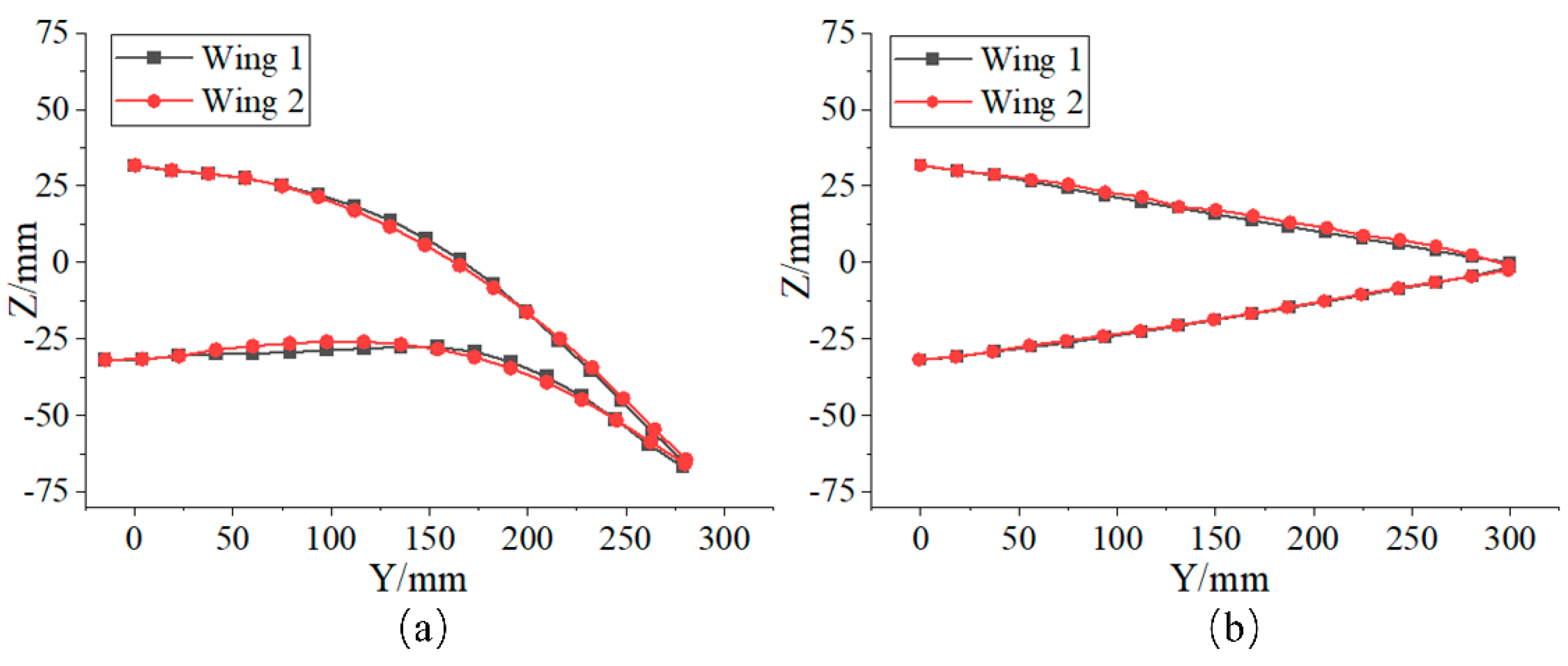
4.1. Conceptual Design of Variable-Camber Wings
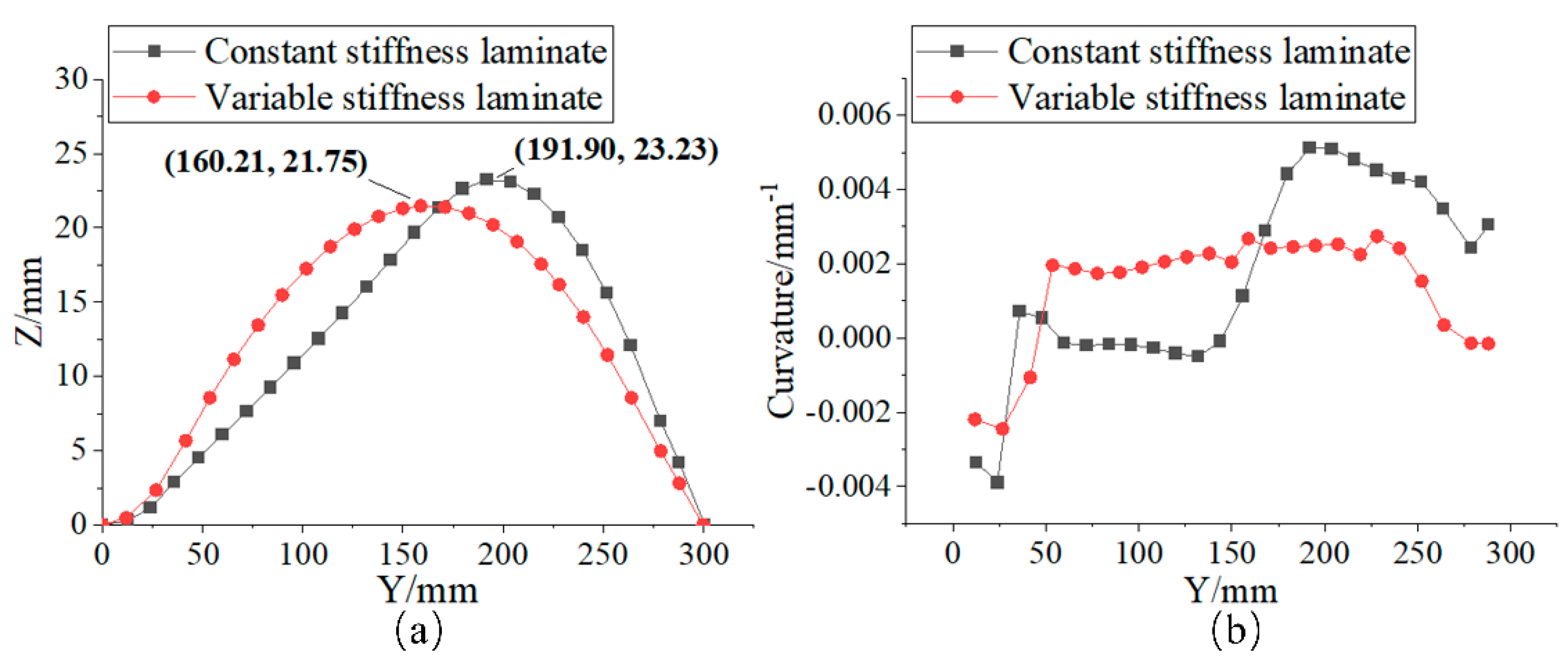
4.2. Comparison of Deformation Properties of Constant-Stiffness and Variable-Stiffness Laminates
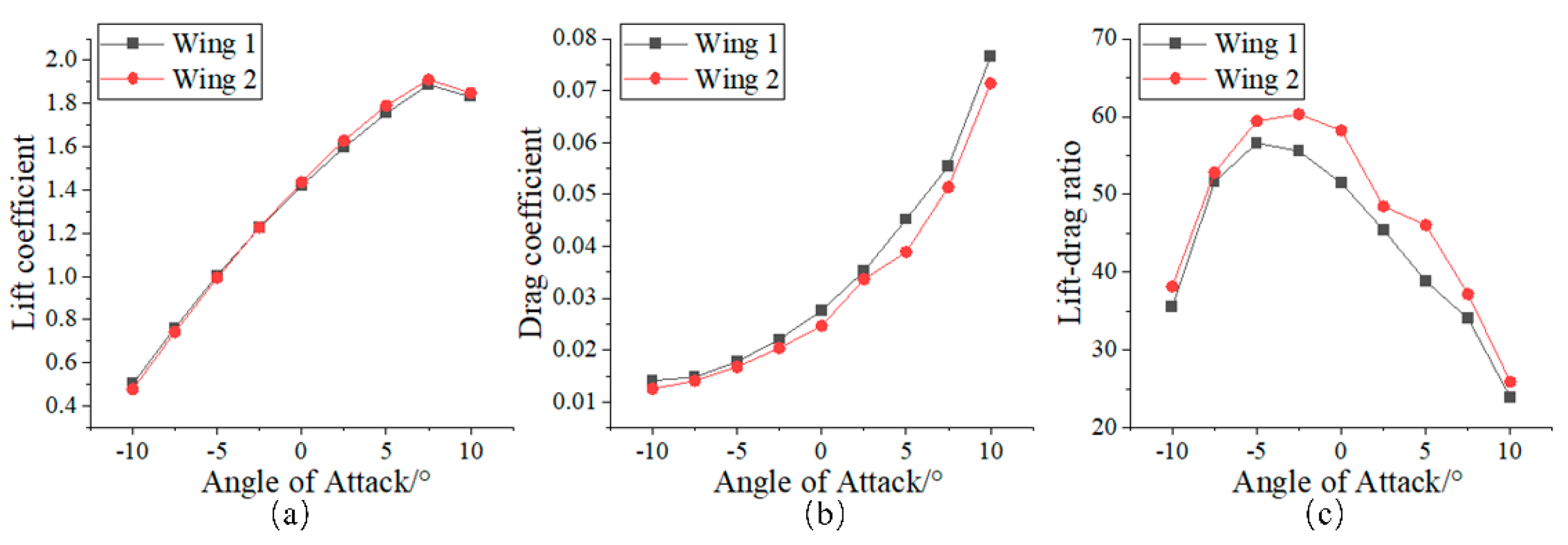
4.3. Aerodynamic Performance Analysis of Variable-CAMBER Wings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.L.; Wu, H.P.; Bao, Y.M.; Chai, G.Z. Bi-stable Characteristics of Orthogonal Unsymmetric Carbon-fiber Composite Structure. Funct. Mater. 2013, 44, 236–239. [Google Scholar]
- Nicassio, F.; Scarselli, G.; Pinto, F.; Ciampa, F.; Iervolino, O.; Meo, M. Low energy actuation technique of bistable composites for aircraft morphing. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarino, S.; Bilgen, O.; Ajaj, R.M.; Friswell, M.I.; Inman, D.J. A Review of Morphing Aircraft. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 823–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, K.D.; Weaver, P.M. A concept for the generation of out-of-plane distortion from tailored FRP laminates. Compos. Part A 2004, 12, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarselli, G.; Nicassio, F.; Pinto, F.; Ciampa, F.; Iervolino, O.; Meo, M. A novel bistable energy harvesting concept. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallol, P.; Mao, H.; Tibert, G. Experiments and simulations of the deployment of a bistable composite boom. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2018, 55, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Hajj, R.M.; Zuo, L. Bio-inspired bi-stable piezoelectric harvester for broadband vibration energy harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 222, 113174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Koh, J.S.; Lee, J.G.; Ryu, J.; Cho, M.; Cho, K.J. Flytrap-inspired robot using structurally integrated actuation based on bistability and a developable surface. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2014, 9, 036004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.W. Some Observations on the Cured Shape of Thin Unsymmetric Laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1981, 15, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.W. The Room-Temperature Shapes of Four-Layer Unsymmetric Cross-Ply Laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Xu, J.L.; Gao, D.X.; Dong, T.; Ma, W.S. The static and dynamic regimes of the bistable asymmetric cross-ply composite laminated plates. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 9005–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.J.; Hong, C.S. Cured Shape of Unsymmetric Laminates with Arbitrary Lay-Up Angles. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1992, 11, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancey, K.S. Viscoelastically prestressed polymeric matrix composites: An overview. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fancey, K.S. A bistable morphing composite using viscoelastically generated prestress. Mater. Lett. 2015, 158, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, D.D.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.P.; Jiang, S.F.; Chai, G.Z. Viscoelastic bistable behaviour of antisymmetric laminated composite shells with time-temperature dependent properties. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 122, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.F.; Hao, Y.X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.N.; Gu, X.J. Cross-well dynamics for vibration energy harvesting of base-excited antisymmetric bi-stable laminate with a point being fixed. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 11010–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.Y. Theory of Nonlinear Vibrations for Antisymmetric Cross-Ply Bistable Laminated Shells. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 3303512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, S.; Potter, K.D.; Weaver, P.M. Bistable prestressed buckled laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 3431–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, F.; Weaver, P.M.; Du, S. Bistable hybrid symmetric laminates. Compos. Struct. 2014, 116, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.H.; Li, H.; Du, S.Y. Cured shape and snap-through of bistable twisting hybrid [0/90/metal]T laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzian-Nejad, A.; Mustapha, S.; Ziaei-Rad, S.; Ghayour, M. Characterization of bi-stable pure and hybrid composite laminates—An experimental investigation of the static and dynamic responses. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzian-Nejad, A.; Bowen, C.; Mustapha, S.; Ghayour, M.; Ziaei-Rad, S. Bi-stable hybrid composite laminates containing metallic strips: An experimental and numerical investigation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 055030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Lou, C.G.; Liang, Y.; Pan, D.K. Bistable hybrid symmetric laminates with a clamped-clamped boundary condition: An experimental and numerical investigation. Compos. Struct. 2024, 327, 117654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.J.; Zhou, Y.S.; Sun, M.; Fu, H.N.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.; Pei, Z.; Chai, H. Magnetorheological elastomer actuated multi-stable gripper reinforced stiffness with twisted and coiled polymer. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 193, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pei, K.; Sun, M.; Wu, H.L.; Wu, H.P.; Jiang, S.F.; Zhang, F. Tessellated multistable structures integrated with new transition elements and antisymmetric laminates. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 170, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lele, A.; Deshpande, V.; Myers, O.; Li, S.Y. Snap-through and stiffness adaptation of a multi-stable Kirigami composite module. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 182, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, R.C. Morphing and Shape Control using Unsymmetrical Composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2007, 18, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuder, K.I.; Arrieta, F.A.; Ermanni, P. Design space of embeddable variable stiffness bi-stable elements for morphing applications. Compos. Struct 2015, 122, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.F.; Kuder, I.K.; Waeber, T.; Ermanni, P. Variable stiffness characteristics of embeddable multi-stable composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 97, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarino, S.; Gandhi, F.; Webster, S.D. Design of Extendable Chord Sections for Morphing Helicopter Rotor Blades. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, W.; Dong, M.M. The novel morphing airfoil based on the bistable composite laminated shell. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 17667–17685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas Padilla, J.R.; Boston, D.M.; Boddapati, K.; Arrieta, A.F. Aero-structural optimization and actuation analysis of a morphing wing section with embedded selectively stiff bistable elements. J. Compos. Mater. 2023, 57, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.R. A Concept for Airfoil-like Active Bistable Twisting Structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008, 19, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, C.G.; Weaver, P.M.; Mattioni, F. Concepts for morphing airfoil sections using bi-stable laminated composite structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2008, 46, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, S.; Nall, S.J.; Weaver, P.M.; Potter, K.D.; Margaris, P.; Mellor, P.H. Bistable Composite Flap for an Airfoil. J. Aircr. 2010, 47, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, S.; Weaver, P.M.; Potter, K.D. Aeroelastic Study of Bistable Composite Airfoils. J. Aircr. 2009, 46, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, S.; Emam, S. Snap-through response of an innovative symmetric bistable composite wing. Acta Mech. Sin. 2024, 40, 423609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ren, L.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Guo, X.T. Chaotic snap-through vibrations of bistable asymmetric deployable composite laminated cantilever shell under foundation excitation and application to morphing wing. Compos. Struct. 2024, 343, 118261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhla, S.; Elruby, A.Y. Applied finite element procedure for morphing wing design. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 1193–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 180 | 10.3 | 5.43 | −1 × 10−7 | 2 × 10−5 | 0.3 |
| 69 | 23 × 10−5 | 0.33 |
| Sample Number | L (mm) | W (mm) | α (%) | Number of Layers of Composite Material | Number of Layers of Metal Material | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 300 | 100 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Sample 2 | 300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 4 | 2 |
| Sample 3 | 300 | 100 | 10 | 40 | 10 | 4 | 2 |
| L (mm) | W (mm) | α (%) | Number of Layers of Composite Material | Number of Layers of Metal Material | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant-stiffness laminates | 300 | 100 | 10 | 50 | 50 | 8 | 2 |
| Variable-stiffness laminates | 300 | 100 | 13 | 40 | 21 | 8 | 2 |
| Constant-Stiffness Laminate | Variable-Stiffness Laminate | Rate of Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum out-of-plane displacement | 23.23 | 21.75 | 6.37% |
| Y-distance from displacement peak point to curve (mm) | 41.90 | 10.21 | 75.63% |
| Turbulence Model | |
|---|---|
| Incoming flow velocity | 0.2 |
| Air viscosity | 1.7894 × 10−5 |
| Temperature | 288 |
| Air mass density | 1.225 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H. Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminates and Their Application in Variable-Camber Wings. Aerospace 2025, 12, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060525
Xie H, Zhang S, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Zhao H. Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminates and Their Application in Variable-Camber Wings. Aerospace. 2025; 12(6):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060525
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Hanqi, Shujie Zhang, Yizhang Yang, Yang Zhou, and Hongxiao Zhao. 2025. "Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminates and Their Application in Variable-Camber Wings" Aerospace 12, no. 6: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060525
APA StyleXie, H., Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y., & Zhao, H. (2025). Design of Variable-Stiffness Bistable Composite Laminates and Their Application in Variable-Camber Wings. Aerospace, 12(6), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12060525






