Abstract
Hollow glass microsphere (HGM) reinforced composites are a suitable alternative to energy absorption materials in the automotive and aerospace industries, because of their high crush efficiency and energy absorption characteristics. In this study, a polyurethane elastomeric matrix was reinforced with HGMs for HGM loadings ranging from 0 to 70 vol% (volume fraction). Quasi-static uniaxial compression tests were performed, subjecting the composite to compressive strains of up to 65%, to assess stress vs. strain and energy absorption characteristics. The results reveal that samples with a higher concentration of spheres generally exhibit better crush efficiency. Specifically, the highest crush efficiency was observed in samples with a 70 vol% HGM loading. A similar relationship was reflected in the energy absorption efficiency results, with the highest energy absorption observed in the 65 vol% sample. A correlation exists between the concentration of HGMs and important metrics such as mean crush stress and energy absorption efficiency. However, it is crucial to note that the optimal choice of sphere concentration varies depending on the desired performance characteristics of the material.
1. Introduction
A hollow glass microsphere (HGM) is a lightweight material consisting of a thin glass shell encapsulating air. The wall thickness of the glass spheres is controlled during their manufacturing process, resulting in a significantly small ratio of the wall thickness to sphere diameter [1]. These spheres have high isostatic strength with a low density (0.1–0.6 g/cc) [2,3], and, thus, HGMs are often used as fillers in composite foams.
The lightweight and high-strength properties of HGM reinforced foam make it highly effective in various applications, including aviation, automotive, and marine industries [4,5,6,7,8,9] with their characteristic of high energy absorption capacity. When the foam is compressed, energy is absorbed as the walls of the spheres come into contact and collapse. Foams with these energy-absorbing properties can be used to protect occupants during impact events. Mei et al. demonstrated that the reinforcing particles break upon compression or impact, effectively absorbing a significant amount of energy [10]. The stress–strain curve obtained from uniaxial compressive testing demonstrates the energy absorption process. This curve typically shows a linear elastic region followed by a non-linear plastic region [11,12,13]. Buddhacosa et al. proposed that the shift from the linear elastic to the non-linear plastic region is mainly caused by the progressive crushing and collapse of microspheres, which greatly increases the syntactic foam’s energy absorption capacity [11]. The collapse of individual spheres leads to the accumulation of localized stress concentrations. When the internal stress exceeds the matrix’s failure strength, the syntactic foam begins to disintegrate, marking the onset of the non-linear plastic region. During this non-linear plastic deformation, the ongoing crushing of the spheres and the disintegration process contribute to energy absorption, resulting in the highest amount of work being performed [11,14].
These energy-absorbing characteristics are evident in the stress–strain profile during crushing events, where energy absorbers in crashworthiness applications typically show an initial elastic response followed by a plastic response. Figure 1A illustrates a typical stress–strain profile of an energy absorber (adapted from Figure 3 in [15]), where the area under the curve represents the energy absorbed. When the material is unloaded, energy stored within the material is released, which in many situations can be detrimental [15]. The horizontal dashed line represents an injury or damage criterion used to ensure crashworthiness. For example, in a seating system designed to protect the lumbar spine, the energy-absorbing material is compressed during a hard or crash landing so that the lumbar spine is in compression, which is desirable [16]. However, if there is energy release at the end of compression, the response of the lumbar spine may lead to tension in the spine, which is clearly undesirable and can even be catastrophic. Certain cellular materials, such as the elastomeric matrix composites reinforced with HGMs under discussion here, can have a stress–strain profile as shown in Figure 1B that is advantageous in the context of crashworthiness. These materials have similar characteristics to elastic-plastic foam under compression (see page 177 of [13]). The elastic response is followed by a plastic response, followed by densification as porosity in the material is eliminated under crush, that is, there is no energy release if the material is designed appropriately. If the HGM loading is too low, then the elastic response of the elastomeric matrix will dominate the response, with an accompanying energy release when the material is unloaded. On the other hand, if the HGM loading is sufficiently high, the desired cellular material response can be achieved [Figure 1B], as the crush response of the HGMs dominates, preventing energy release. Key features of the cellular material response are the peak stress (stress at the boundary between the elastic and plastic response), the plateau stress, and the densification strain.
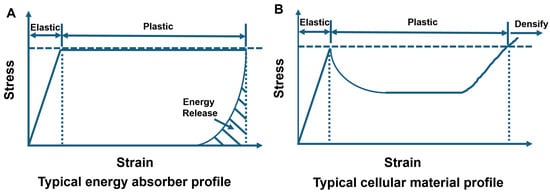
Figure 1.
Typical stress vs. strain profile of (A) a generalized energy absorber, and (B) a cellular material.
HGM-based foams can be grouped into two distinct categories: (1) sintered foams, where particle bonding is achieved via sintering, and (2) syntactic foams.
The first type of HGM-based foam is sintered foam, which is effective when trying to achieve high energy absorption while maintaining low foam density [17]. Foam samples are formed when the consolidated spheres are raised above their glass transition temperature. This allows for the spheres to flow in a viscous manner, leading to consolidation when struts are formed between the spheres, resulting in a closed cellular structure [2,17,18]. These foams have demonstrated superior energy absorption characteristics due to the ability of the spheres to effectively absorb the crush stresses. Individual spheres exhibit gradual collapse, minimizing the effects of dynamic loadings [19]. Ren et. al presented scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of the microstructure of HGMs for foam sintered at different temperatures [20]. The effects of sintering temperature are seen in the deformed HGM. Instead of maintaining their original spherical shape, the spheres were elongated and oval in shape. Also, spheres were shown to have partially or completely fractured during the sintering stages [20]. These early fractures can contribute to spalling that occurs during crush testing [2].
The second type of HGM-based foam is syntactic foam, where a matrix material is reinforced with HGM particles. Syntactic foams are particulate-reinforced materials manufactured by adding inorganic hollow spheres into a matrix material such as polymer, metal, or ceramic [3,4,21,22,23,24]. A typical matrix is a brittle epoxy matrix material. HGM-epoxy composites result in a low volume fraction foam that has a low crush ratio [9,25,26]. It should be noted that a high crush ratio is desired to increase energy absorption capacity. Syntactic foams, or HGM-epoxy composites, were originally developed for buoyancy applications, where the crush ratio was of little importance [27,28,29,30]. Instead, the design objective for these HGM-epoxy syntactic foams was to minimize foam density, while maximizing foam buoyancy.
Prior work in both HGM-based sintered foam and syntactic foam motivates the use of elastomeric matrix material to manufacture a visco-elastic energy absorber. The HGM-reinforced elastomeric matrix composite (EMC) foams investigated here enable a much greater crush ratio than HGM-epoxy syntactic foam because the elastomeric matrix can sustain large deformation with minimal fracture. The HGMs will come into contact and be engaged during the compression of the sample and as they collapse energy absorption capacity is increased [31,32,33]. Previous studies analyzed samples with volume fractions between 0 and 60% and assessed thermal and mechanical properties. For this reason, it is important to find the solids loading that corresponds to the maximum energy absorption to determine if it is feasible to use an HGM-elastomeric composite as an energy absorber.
In this study, energy absorbers (EAs) in the context of a helicopter seating system are investigated, the requirements of which are motivated by the work represented by Farley, et al. [15]. Feasibility of HGM reinforced composites is assessed to address these EA requirements: (1) constant stress versus strain profile, (2) no energy release. Thus, this study examines the effects of HGM loading in an HGM-elastomer matrix composite, which is a polyurethane (PU) elastomeric matrix reinforced by HGMs, which possess low density and high strength. The energy absorption characteristics of these HGM–PU composite foam samples are assessed to determine the relationship between HGM loading and energy absorption metrics such as peak collapse stress, mean crush stress, energy absorption efficiency, and crashworthiness. A key goal is to determine at what HGM loading the crush response changes from an elastic response or a response dominated by the elastomeric matrix to a predominantly plastic response dominated by the crush response of HGMs. These HGM–PU composite foams are also compared to sintered glass foams with 100 vol% HGM loading from our prior work [2,17,18], because they provide a realistic upper bound in the stress–strain profile of HGM–PU composites foams, and, hence, an upper bound on their energy absorption capacity.
2. Experimental Approach
2.1. Materials
HGM-elastomer matrix composite foam was made using K46 microspheres (3M, St. Paul, MN, USA). The composition of these HGMs are soda-lime borosilicate glass, with a density of 0.46 g/cc and a median diameter of 40 μm. The matrix resin system used was Freeman 1035 Polyurethane Elastomer (Avon, OH, USA) with a 35A Shore hardness and a density of 1.02 g/cc.
2.2. Manufacturing
To manufacture the specimen, elastomeric resin was added to a container of HGMs as shown in Figure 2A. Weights of elastomeric resin and HGMs were calculated and then measured to ensure the correct volume fraction was achieved. The elastomeric resin was poured slowly into the powder to minimize the entrained air. The sample was mixed until the mixture was homogeneous (Figure 2B). This step was conducted by gentle hand mixing to minimize damage to the HGMs. The fully mixed sample was then poured into a mold that has a vacuum port on both the near and far end. To ensure the mixture was evenly distributed while being poured into the mold a light force of 1–2 lbs (4–9 N) was applied to its surface using a wooden compactor. The mold was then sealed using Tacky Tape and a bagging film to allow a vacuum to be pulled for 15 min on each side. As mentioned previously, the mold has two ports located on either end. To guarantee that any air introduced into the sample is removed, each port was attached to the vacuum pump while the other side was clamped. This allowed for a more even distribution of suction pressure, and a higher likelihood of a homogeneous sample (Figure 2C). The sample was left to cure for 24 h at room temperature before being removed from the mold.
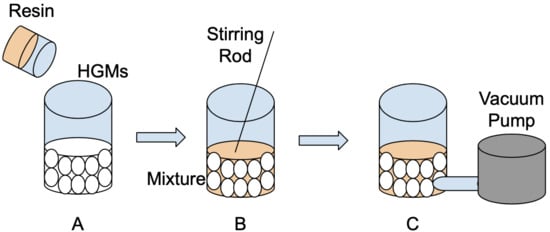
Figure 2.
Schematic of HGM-PU composite foam manufacturing. (A) Combine polyurethane elastomer with K46 HGMs; (B) Create a homogeneous mixture; (C) Pull vacuum to remove air.
To fully characterize the energy absorption behavior at all volume fractions, additional samples were created using 100% HGMs. The 100 vol% samples were sintered HGMs [2,17,18]. The manufacturing process involves filling a mold with K46 HGMs and placing the mold in an oven to be sintered. The temperature was raised to a bonding temperature of 840 °C using a slow ramp rate (0.5 °C/min), followed by a soak time of 20 min.
2.3. Testing
Once the samples were fully cured, test samples were cut into 1 inch (25.4 mm) cubes in order to undergo crush testing. Guidance for this test coupon sizing was taken from two standards for compressive testing of “rigid plastics”. Right prism samples are required by ASTM D695-15 [34] and ISO-604 [35], and typical aspect ratios of 2:1 (height over width of a cubic sample) are suggested when testing “rigid plastics”. However, ISO-604 allows for a reduction in aspect ratio when samples are prone to buckle. These elastomeric samples are much softer than rigid plastics, so that an aspect ratio of 1:1 was selected. A similar approach was taken in Ref. [36], in which syntactic foam using a hard resin matrix was fabricated and crush tested, and where an aspect ratio of 1.67:1 was used. Also, it should be noted that these standards do not encompass crush tests to the point of densification, as was done here and in [36], so that these standards are only used as guidance.
A representative sample from each batch was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to ensure that a homogeneous mixture was achieved. Figure 3A shows one of these SEM images. There appears to be an even distribution of HGMs, with very few that were fractured during manufacturing.

Figure 3.
Samples prepared for testing. (A) An SEM image of a cross-sectional view of HGM-PU composite foam; (B) 40% volume fraction sample, and (C) 65% volume fraction sample (red scale is 6.35 mm).
The samples were tested under uniaxial compression using an MTS servo-hydraulic testing machine (Model 810, Warren, MI, USA) at a strain rate of 1 × 10−3 1/s up to 65% strain. During testing, images were collected every 100 s using a Nikon D5100 camera (Nikon Inc., Melville, NY, USA), so that failure methods could be analyzed later. Figures 3B and 3C show samples with low and high HGM loadings, respectively, during compression testing.
2.4. Metrics for Energy Absorption
A key goal of this study is to assess the feasibility of applying HGM–PU composite foam in crashworthiness applications, so that it is important to measure the energy absorption characteristics of these samples. Energy absorption can be measured using the stress–strain data obtained during compressive or crush testing.
The energy absorbed by the sample can be expressed as follows:
where U(ϵ) is the energy absorbed, is the stress, and is the strain. From this, the crush efficiency (CE) can be determined. The crush efficiency, is the ratio of the energy absorbed over a given strain range, normalized by an ideal (rectangular) constant stress vs. strain profile where the constant stress is the peak stress reached over the strain range:
The mean crush stress, , is the average stress up to the densification point and can be expressed as:
A similar approach is used to determine the energy absorption efficiency (EAE) [37,38]. The energy absorption efficiency, is the ratio of the area under the stress–strain curve divided by the maximum stress value over the whole strain range as below:
As shown in previous studies [37,38,39,40], the densification point is the corresponding strain when a sample reaches its peak value of energy absorption efficiency, .
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Qualitative Results
The HGM–PU composite foams were manufactured by mixing an elastomeric resin with HGMs for different HGM loadings. The elastomeric resin has a low Shore hardness of 35 A. The 1 inch cube samples are compressed under load in the vertical direction and expand (bulge) in the horizontal plane. As discussed above, for low HGM loading, the test sample exhibits an elastic response due to the elastomeric matrix dominating. In this case, the sample can recover allowing energy to be released, which is not desirable for crashworthiness applications. For sufficiently high HGM loadings, as the HGM–PU foam undergoes crush, the HGMs engage with each other and exhibit brittle failure or crush. A key goal is to determine the HGM loading when this transition occurs.
The behavior of the HGM–PU composite foams with different HGM loading can be observed in Figure 4. The modulus, derived from the initial linear region of the curves, demonstrates a dependency on the volume fraction. In this figure, the lower volume fraction sample (40 vol%) exhibits a linear increase in stress up to 50% strain, while the neat resin sample (0 vol%) shows a linear increase up to 40% strain. At 40 vol%, the composite has a lower elastic modulus of about 5 MPa when strained from 0 to 10%. Both samples are predominantly influenced by the elastic properties of the elastomeric (PU) matrix. In contrast, the sample with 70 vol% HGMs shows a modulus of approximately 10 MPa within the 0 to 5% strain range. The modulus increases with higher HGM concentration due to enhanced particle-to-particle interactions, indicating that the composite is reinforced. While low HGM loading samples show a continuous increase of stress over applied strain, the higher HGM loading samples (>60 vol%) experience a peak in the stress–strain curve at around 10% strain. The sample with HGM loading of 55 vol%, positioned between low and high HGM volume fractions, demonstrates a slight bump around 20% strain, indicating a transition in mechanical behavior. This peak is a representation of the transition into the plastic region from the elastic region, which is caused by HGMs interacting during compression. The lack of HGM engagement for the lower HGM loading samples explains their linear-elastic behavior. For an HGM loading of 55 vol% is, HGM engagement initiates at 20% strain, which is reflected in the flattening of the stress–strain curve so that a plateau stress is manifested. As HGM concentration continues to increase, this characterization above becomes more distinct. Increasing the HGMs concentration by 5% from 55 to 60 vol% has a significant increase in sphere engagement. In the 60% stress–strain curve, this can be seen in the change in slope around 15% strain, where a peak stress is becoming visible. This is the point when the HGMs have been engaged, and carry the load, until the spheres have broken within the sample. After a specimen is able to achieve its peak stress, stress vs. strain data progresses into the plateau region, where the stress appears to stabilize. Once the densification strain is reached, the HGMs have been engaged to the point of brittle failure and are mostly crushed and collapsed, so that the stress increases dramatically.
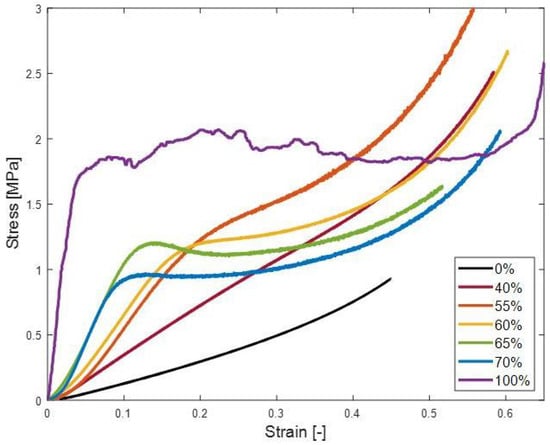
Figure 4.
Stress–strain performance for HGM-PU composite foams manufactured using different HGM loading. The 0% sample has no HGMs and is a neat elastomer, while the 100% sample is manufactured using the sintering process.
Figure 5 presents a series of images depicting uniaxial compression testing on test samples with varying HGM loading. With increased HGM loading, the HGM-elastomer foams show more brittle failure under compression, resulting in material spalling, or breaking into small pieces. Conversely, samples with lower HGM loading do not experience spalling but instead demonstrate elastic behavior. As the 40 vol% sample is compressed to higher strains, the material bulges or is displaced in the lateral direction. Overall, this sample experiences little to no visible damage. Once the force is removed, the sample returns to its original shape within 10 min. This indicates that permanent deformation of the foam is minimal, resulting in its reversible behavior. When reviewing the images from the 70 vol% sample, spalling is immediately noticeable. The image of 70 vol% at 40% strain shows the sample breaking apart into several pieces due to the matrix’s inability to hold the sample together at high strain. For samples at these higher HGM loadings, the response is dominated by the crush response of the HGMs and the low volume fraction of the elastomeric matrix is insufficient to ensure that the HGMs remain bonded, especially under higher strains. As a result, these samples are more prone to spalling. It is important to note that the random packing fraction of polydispersed spherical objects is known to be around 70%, making it hard to achieve a significantly higher HGM loading [41]. Lastly, the 100 vol% samples without the matrix material experienced brittle failure.
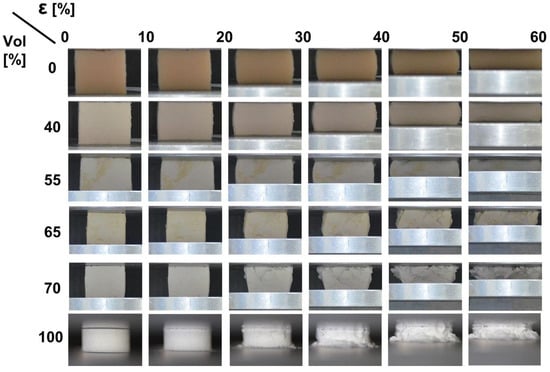
Figure 5.
Images of uniaxial compression testing of samples. The top row represents the applied strain, while the left axis indicates the HGM volume fraction.
The elasticity of HGM-PU composite foams with varying HGM loading was observed when the top platen was removed from the compressed samples. Upon removal, the samples began to decompress and partially return to their original shape. This rebound was noted in most samples with different sphere volume fractions, but to varying degrees. In Figure 6, the rebound of the 40 and 70 vol% samples are shown. As the top platen is being removed after the samples were compressed up to 65% strain, it appears that both samples have some amount of instantaneous recovery. The top row in the Figure, which depicts the 40 vol% sample, has no visible cracks or deformations after the load is entirely removed. This is to be expected because the HGM loading is low, and the rebounding is controlled by the PU matrix. On the other hand, the 70 vol% sample developed permanent deformation, which can be seen by the cracking along the outer surface. However, even with this permanent deformation, these samples are still able to regain some of their original shape. This is due to the elastic matrix being present, even if it is in small quantities.
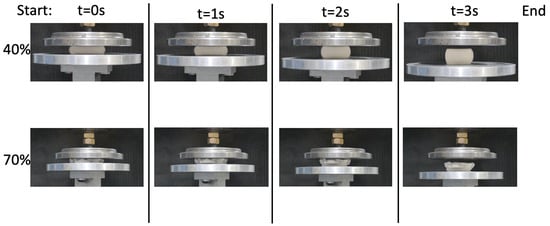
Figure 6.
Behavior of HGM-PU composite foam samples as the load is removed from the sample. Lower volume fractions rebound, while higher volume fractions experience minimal recovery.
The degree of recovery depends on the HGM loading, ranging from 98% in the 0 vol% to 83.5% in the 70 vol%. Although these low HGM loading samples (0 and 40 vol%) have superior rebound characteristics, these samples are unable to hold as much load and are also less crush efficient. When the low HGM sample undergoes compression, the HGMs in the sample are likely not engaged, and instead, the matrix carries the load.
3.2. Mechanical Characteristics
Stress–strain data shown in Figure 4 is used to calculate the energy absorption efficiency (). These curves are nearly linear until a maximum energy absorption efficiency is achieved. The strain at the peak energy absorbed efficiency corresponds to the onset of densification for the samples [37,38,39,40] or when
Figure 7 shows that the HGM loading influences the onset of densification. As HGM loading increases, the strain value at which the onset of densification occurs decreases. As HGM volume fraction increases, the HGMs are packed closer together, so that under compression, the HGMs engage at a lower value of strain, so that the onset of densification occurs at a lower strain level.
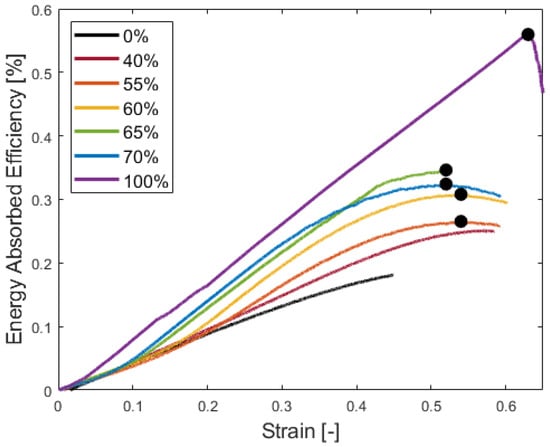
Figure 7.
Energy absorption efficiency for different volume fraction samples. The densification strain for each HGM loading is denoted on its respective curve with a black dot. The 0% sample has no HGMs, while the 100% sample is manufactured using the sintering process.
The second key metric to evaluate the performance of these HGM-elastomer composite foams is crush efficiency (). The useful strain range considered here is defined as the strain range up to the onset of densification. It is desired that the crush efficiency be maximized throughout the useful strain range. Figure 8 shows that when the HGM loading increases, so will the crush efficiency. The peak crush efficiency increases as HGM loading increases, for the simple reason that more HGMs implies a greater load-bearing capacity.
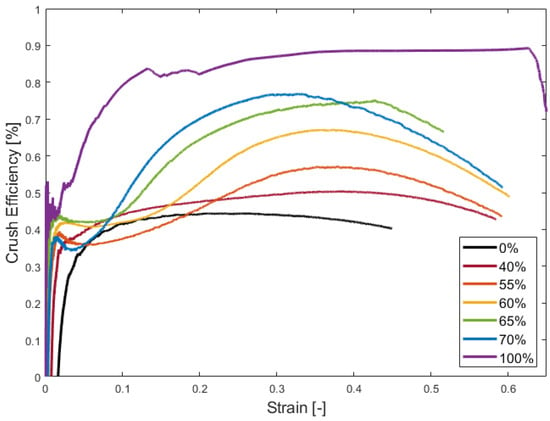
Figure 8.
Crush efficiency of samples at different volume fractions of HGMs. The 0% sample has no HGMs, while the 100% sample is manufactured using the sintering process.
Similarly, as HGM loading increases, the peak energy absorption efficiency also increases. The energy absorption efficiency () increase was measured from 18.78% for the 0 vol% sample to 55.96% for the 100 vol% sample. These two trends emphasize the importance of selecting the desired HGM loading for the given application (Figure 9). The 100 vol% sample exhibits the greatest crush and energy absorption efficiencies, however, the HGM–PU composite is more durable and less prone to brittle fracture.
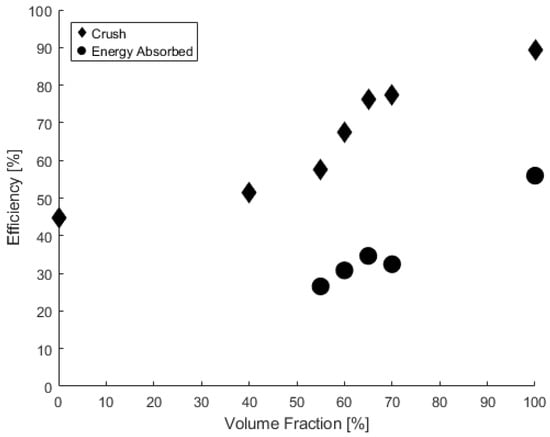
Figure 9.
The crush efficiency and and energy absorption efficiency as a function of HGM loading.
These results are shown in Table 1. The peak crush efficiency, 89%, is recorded in the Table for the 100 vol% sample and the lowest, 44%, for the 0 vol% sample. The neat resin is the least crush-efficient during testing due to its elastic behavior during compression and the absence of crushable spheres. Efficiency increases with higher HGM loading, up to the 100 vol% HGM sample. This demonstrates the feasibility of using HGMs to increase energy absorption and crush efficiencies when used in elastomeric matrix composite systems. As shown in Table 1, the sample with an HGM volume fraction of 40% exhibits a densification strain of = 0.58, which gradually decreases with increasing HGM volume fraction. The densification strain was = 52% for the sample with an HGM volume fraction of 70%. At 40 vol% HGM loading, the densification strain is the highest (0.58) except 100 vol% sample.

Table 1.
Characteristics of HGM–PU foams as a function of HGM volume fraction.
3.3. Analysis of Composite Modulus
The results from this study can be validated using models from the literature. Here, we consider the Paul Model, the Issay-Cohen Model, and the Four-Part Model, as described in [42]. Assumptions used to define the Representative Volume Element (RVE) in these models are:
- Particles are cubic in shape.
- Distribution of matrix volume to each particle is also cubic.
- Particles are uniformly distributed.
- Both matrix material and particles are elastic, isotropic, and homogeneous.
- The particle volume fraction is small enough that particle interactions can be ignored.
- The applied deformation is small, so linearity is maintained.
- The strains do not vary when components are in parallel.
- The stresses do not vary when components are connected in series.
The RVEs used in this study, adopted from Bourkas et al. [42] are shown in Figures 10A, 10B, and 10C, for the Paul, Issay-Cohen, andd Four-Part Model, respectively.
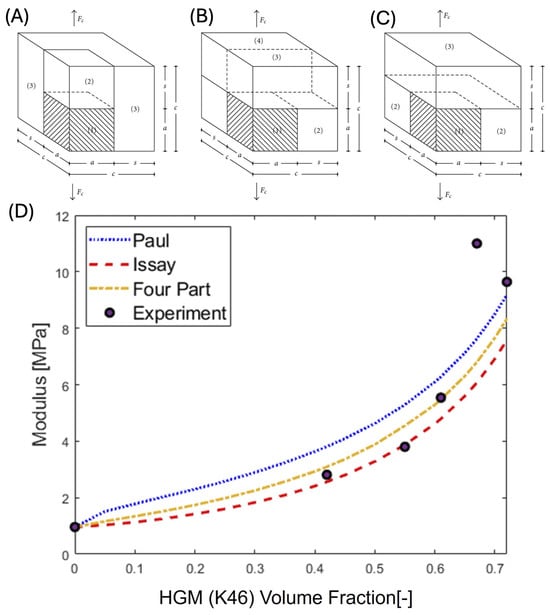
Figure 10.
The Representative Volume Element (RVE) for the analytical models adopted from Bourkas et al. [42]: (A) Paul Model; (B) Issay-Cohen Model; (C) Four-Part Model. (D) The experimental moduli are plotted versus HGM loading along with predictions from the Paul, Issay-Cohen, and Four-Part Models.
First, we examined the Paul Model. It is a three part model that assumes a uniaxial load is applied to the composite. The particle is represented as a cube. A similar cube of matrix is stacked on top of the particle cube. The remaining matrix volume is in parallel with this stack. Using this arrangement, the composite modulus, , can be determined as follows [42]:
where m is the , where , , and are the elastic moduli of the particle, matrix, and composite, respectively, and is the volume fraction. Figure 10D shows the Paul Model plotted using the moduli for the particle and matrix of this system.
The second model considered was the Issay-Cohen model Figure 10B. This also starts with a three-part model and this modulus is combined in parallel with the remaining matrix to determine the composite modulus, or:
As shown in Figure 10D, the Issay-Cohen model tends to underpredict the modulus.
The final model considered was the Four-Part Model Figure 10C. Here, the RVE is divided into four different components, where the modulus is derived from a combination of components in parallel and series [42]. The composite modulus for this RVE is given by:
Figure 10D shows the Four-Part Model plotted using the moduli of this system. The Issay-Cohen model tended to underpredict the composite modulus, while the Paul model tended to overpredict. The composite modulus from the Four-Part model provided a useful middle ground.
These models were applied to a range of HGM loading and presented with the experimental results. There is a marked deviation between the models and the experimental for samples above 65 vol%. Once an HGM loading of 65 vol% is reached, there is an interaction between the spheres and the matrix, as observed in Figure 4. One of the assumptions underlying these models (Assumption 5 above) is that the particle volume fraction is sufficiently small that particle interactions can be ignored. However, examining the stress vs. strain data in Figure 4 for the 60, 65, and 70 vol% curves, there is a noted shoulder in the stress vs. strain data when the cellular nature of the HGM–PU composite foam is evident in that the HGMs interact with each other. This directly violates assumption 5 listed above. In order to use these models, the volume fraction must be low enough such that interactions do not occur, therefore the models cannot be used to determine the moduli of samples with a volume fraction greater than 60%. However, these models did prove to be useful in validating the measured moduli.
3.4. Discussion Summary
Quasi-static compression tests were conducted on samples of various HGM loading in an elastomeric matrix. From these tests, a series of trends were identified. As the HGM loading increases, there is an increase in the crush efficiency and energy absorption efficiency. The densification strain and mean crush stress decrease with increasing HGM loading. These trends can be seen from the data presented in Figure 11. Here, the 0 and 100 vol% were not shown.
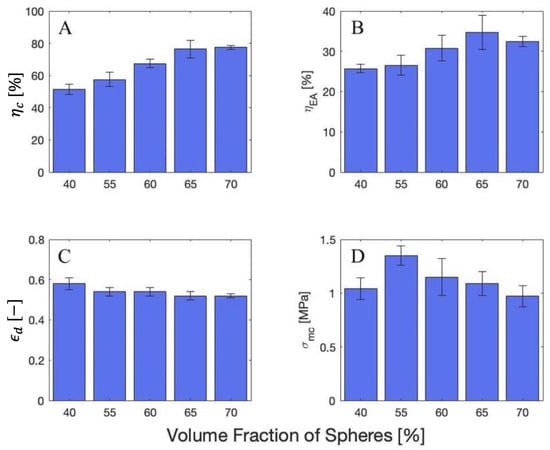
Figure 11.
The average (A) crush efficiency; (B) energy absorption efficiency; (C) densification strain; and (D) mean crush stress for each HGM loading.
Another method for quantifying the performance of the samples in a multi-metric assessment is using a radar plot. The radar plot places the metrics on spokes radiating outwards so that the most ideal values are furthest out. Each sample creates a closed polygon describing the performance of that sample. Figure 12 shows a radar plot with the four best performing samples: 55, 60, 65, and 70 vol%.
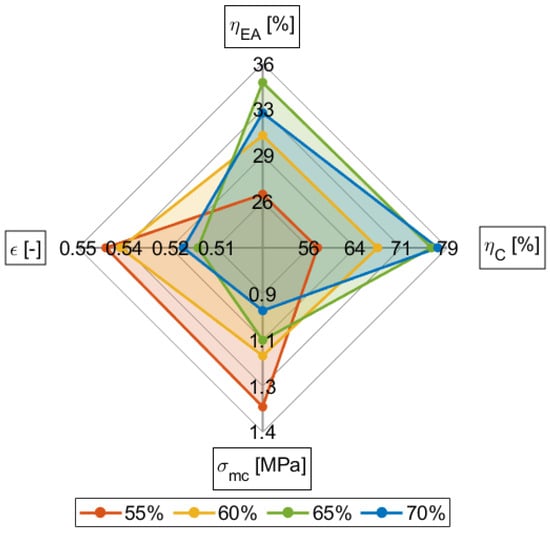
Figure 12.
The best performing HGM loading samples are shown in a radar graph to assist in down selecting optimal HGM loading for a given application.
The radar plot in Figure 12 shows that the optimal HGM loading for these metrics is 60 vol%. This HGM loading shows consistently high values for each metric. Other HGM loadings, like the 65 and 70 vol%, show high crush and energy absorbed efficiencies, but a low mean crush stress and an early densification strain. The 60 vol% is one of the highest densification strains and mean crush stress without compromising on the energy absorbed and crush efficiencies (Figure 12). The 60 vol% sample demonstrates the best performance in both crush efficiency and energy absorption efficiency due to particle engagement through particle collapse. This particle collapse results in the permanent deformation of the composite structure, and thus, shape recovery is not observed.
The purpose of this study was to determine the feasibility of using HGM–PU composite foams in an energy absorption application. According to Farley [15], energy absorption materials are intended to (1) maintain a constant stress versus strain profile and (2) have no energy release. To further demonstrate that these materials meet Farley’s requirements for an energy absorber material, Figure 1 has been reconstructed alongside the samples with 60–70% solids loading in Figure 13. As shown, these HGM–PU composite foam samples exhibit behaviors of those energy absorption materials.
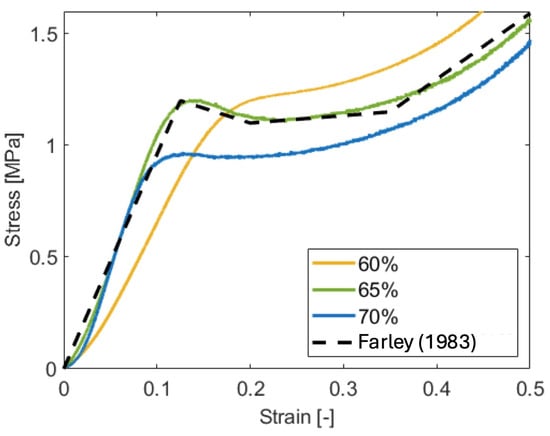
Figure 13.
The Farley Model of a typical cellular material plotted as a stress–strain curve alongside the 60, 65, and 70% samples [13].
4. Conclusions
The goal of this study was to find the optimal HGM loading conditions for a foam using K46 HGMs and a visco-elastic polyurethane matrix, so that it can be used as a protective layer in the event of a low-impact collision. Some key conclusions have been made in the course of this work.
1. As HGM loading increases, the stress–strain behavior of the samples transitions from a linear elastic response to an elastic-plastic response with densification, reflecting the contribution of the HGMs in this cellular material. At low HGM loading (≤40%, the elastomeric matrix dominates the compressive stress vs. strain response. For samples with an HGM loading of 55% or more, the compressive stress vs. strain data exhibited a peak stress, a collapse in stress to a nominal plateau stress, and densification, indicating that HGMs are carrying the compressive load, and collapsing maintain a plateau stress, and densifying once porosity in the HGM–PU composite has been largely eliminated.
2. Increased HGM loading in the HGM–PU composite foam increases both energy absorption efficiency and crush efficiency. HGM–PU composite foams exhibited stress vs. strain behavior required for energy-absorbing materials suitable for crashworthiness or occupant protection applications.
3. The matrix will rebound if there is a sufficient amount of matrix present. In this study, it was determined that samples with less than 55 vol% were able to recover with minimal external deformation, and exhibited energy release. However, such energy-releasing materials do not meet the requirements for occupant protection systems, as in [15].
4. The HGM loading of composites affects spalling behavior under compression. As HGM loading increases, the volume of matrix holding the HGMs decreases. With less matrix, the samples experience an increase in spalling under compression and, thus, an inability to recover after testing, when compared to low HGM loading samples. However, this spalling negates the possibility of energy release, which meets the requirements of minimal energy release expressed in [15].
The behavior of these HGM-reinforced elastomer matrix composites demonstrated the feasibility of these HGM–PU composites as an energy absorber material for occupant protection systems. From the data in this study, it is shown that the 60% HGM–PU composite foam sample is well suited for energy absorber applications.
In our future work, drop tests will be performed using a drop tester modified for testing HGM–PU composite foam samples. This system drops a 5 kg mass onto a sample, atop an anvil, with a specified impact speed, or . We are currently performing impact tests on HGM–PU composite foam samples at speeds ranging up to 5 m/s based on the industrial standard used for automotive crashworthiness testing [43], as well as requirements for helicopter seating systems [16].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: N.M.W. and J.P.; methodology, N.M.W., C.M.M. and J.P.; software, C.M.M. and J.P.; validation, G.S., C.M.M., N.M.W. and J.P.; formal analysis, C.M.M., J.P. and N.M.W.; investigation, G.S. and C.M.M.; resources, N.M.W.; data curation, C.M.M. and J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S. and C.M.M.; writing—review and editing, G.S., C.M.M., J.P. and N.M.W.; visualization, N.M.W. and J.P.; supervision, N.M.W.; project administration, N.M.W.; funding acquisition, N.M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
G.S. was supported under an ASPIRE Research Scholarship from the Maryland Technology Enterprise Institute (MTECH). C.M.M. and J.P. were supported using internal research and development funds of the Dept. of Aerospace Engineering in the Clark School of Engineering at the University of Maryland (UMD). N.M.W. was supported by an endowed Minta Martin Chaired Professorship from the Clark School of Engineering at UMD.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Acronyms | |
| CE | Crush efficiency |
| EA | Energy absorber |
| EAE | Energy absorbed efficiency |
| HGM | Hollow glass microsphere |
| MTS | Materials Test System |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| RVE | Representative Volume Element |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| Notation | |
| Elastic modulus of composite | |
| Elastic modulus of matrix | |
| Elastic modulus of particle | |
| Strain | |
| Densification strain | |
| Crush efficiency | |
| Energy absorbed efficiency | |
| Stress | |
| Mean crush stress | |
| U() | Energy absorbed |
| Volume fraction | |
| vol% | Volume fraction |
References
- Al-Gemeel, A.; Zhuge, Y.; Youssf, O. Use of hollow glass microspheres and hybrid fibres to improve the mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Howard, J.; Edery, A.; DeMay, M.; Wereley, N. Bilayer glass foam with tunable energy absorbing property by localizing voids density. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 29, 2100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Xi, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, B. Preparation and energy absorption of flexible polyurethane foam with hollow glass microsphere. J. Cell. Plast. 2024, 60, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of polymer matrix syntactic foams. JOM 2014, 66, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Ye, F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, B. Co-continuous hollow glass microspheres/epoxy resin syntactic foam prepared by vacuum resin transfer molding. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, Ç.; Akgün, İ.C.; Göksenli, A. On the way to real applications: Aluminum matrix syntactic foams. Eur. Mech. Sci. 2020, 4, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H.; Can, Y.; Guclu, H.; Karen, I.; Yazici, M. Development of lightweight bumper beam and crashbox with thermoplastic composite and syntactic foam based sandwich materials. Automot. Technol. Conf. (Otekon) 2016, 565–570, Bursa, Turkey, 23-24 May. [Google Scholar]
- Swetha, C.; Kumar, R. Quasi-static uni-axial compression behaviour of hollow glass microspheres/epoxy based syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4152–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Q.; Ye, F.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, B. Compressive properties of co-continuous hollow glass microsphere/epoxy resin syntactic foams prepared using resin transfer molding. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2020, 39, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Fu, C.; Fu, Y.; Wang, E.; Yang, Q.; Ding, Y. Effect of particle size and distribution of hollow spheres on the compressive behavior of aluminum matrix syntactic foams. J. Mater. Res. 2023, 38, 4408–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhacosa, N.; Khatibi, A.; Das, R.; Giustozzi, F.; Galos, J.; Kandare, E. Crush behaviour and vibration damping properties of syntactic foam incorporating waste tyre-derived crumb rubber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, H. Constitutive modeling and simulation of polyethylene foam under quasi-static and impact loading. J. Cell. Plast. 2024, 60, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Alteneiji, M.; Krishnan, K.; GUan, Z.; Cantwell, W.; Zhao, Y.; Langdon, G. Dynamic response of aluminium matrix syntactic foams subjected to high strain-rate loading. Compos. Struct. 2023, 303, 116289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, G.L. Energy Absorption of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1983, 17, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, S.P. The evolution of energy absorption systems for crashworthy helicopter seats. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2006, 51, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wereley, N.; Park, J.; Howard, J.; DeMay, M.; Edery, A. Tailorable energy absorbing cellular materials via sintering of dry powder printed hollow glass microspheres. SAMPE J. 2024, 60, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Howard, J.; Edery, A.; Demay, M.; Wereley, N. Tunable energy absorbing property of bilayer amorphous glass foam via dry powder printing. Materials 2022, 15, 9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Wiest, A.; Conner, R. Uniaxial quasistatic and dynamic compressive response of foams made from hollow glass microspheres. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hu, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, M.; Guo, A.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Xian, L. Development of a buoyancy material of hollow glass microspheres/SiO2 for high-temperature applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, M.; Fahr, P.; Shukla, A.; Gunes, S.; Akay, S. Development of a polymer based syntactic foam for high temperature applications. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A 2014, 125, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, A.; Li, Y. Mechanical properties of EPS filled syntactic foams prepared by VARTM. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 136, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, P.K.; Gupta, N.; Schultz, B.F.; Luong, D.D. The synthesis, compressive properties, and applications of metal matrix syntactic foams. JOM 2011, 63, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, E.; Klaeger, S. Advanced new lightweight materials: Hollow-sphere composites (HSCs) for mechanical engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, O.; Mohan, T.; Kanny, K. Processing of low-density HGM-filled epoxy-syntactic foam composites with high specific properties for marine applications. Materials 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, E.; Yu, T.; Yang, J. The effect of strain rate and filler volume fraction on the mechanical properties of hollow glass microsphere modified polymer. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 101, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ying, L.; Fan, Z.; Wei, Y. The failure behavior of syntactic foams as buoyancy materials for deepsea applications. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2024, 105, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobaica, E.; Cook, S. The characteristics of syntactic foams used for buoyancy. J. Cell. Plast. 1968, 4, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Plubrai, P. Manufacturing and failure mechanisms of syntactic foam under compression. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Ali, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, K.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Recent developments on epoxy-based syntactic foams for deep sea exploration. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 2037–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, K.; Chrzaszcz, M.; Ryszkowska, J. Thermal and mechanical properties of ureaurethane elastomer composites with hollow glass spheres. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.; Roh, S.C.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication of novel polyurethane elastomer composites containing hollow glass microspheres and their underwater applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 7305–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Ullas, A. Compressive properties of poly (Dimethylsiloxane)–hollow glass microballoons syntactic foams. Cell. Polym. 2022, 41, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D695-15; Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ISO-604; Plastics—Determination of Compressive Properties. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Gupta, N.; Ricci, W. Comparison of compressive properties of layered syntactic foams having gradient in microballoon volume fraction and wall thickness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Magkiriadis, I.; Harrigan, J.J. Compressive strain at the onset of densification of cellular solids. J. Cell. Plast. 2006, 42, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalle, M.; Belingardi, G.; Montanini, R. Characterization of polymeric structural foams under compressive impact loading by means of energy-absorption diagram. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2001, 25, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.M.; Mao, M.; Park, J.; Howard, J.; Wereley, N.M. Visco-elastic honeycomb structures with increased energy absorption and shape recovery performance using buckling initiators. Polymers 2023, 15, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.; Wise, S.; Wereley, N. Electroplating additively manufactured honeycomb structures to increase energy absorption under quasi-static crush. SAMPE J. 2024, 60, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiso, E.; Müller, E.A. Dense packing of binary and polydisperse hard spheres. Mol. Phys. 2002, 100, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourkas, G.; Prassianakis, I. Kytopoulos, V.; Sideridis, E.; Younis, C. Estimation of elastic moduli of particulate composites by new models and comparison with moduli measured by tension, dynamic, and ultrasonic tests. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 2010, 891824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S.; Beckage, M. Vehicle crash test data acquisition—a review of requirements, technologies and standards. SAE Technical Paper 2009-01-0054, SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).