Figure 1.
Comparison of the gravimetric vacuum specific impulse of the considered amines with 98% HTP.
Figure 1.
Comparison of the gravimetric vacuum specific impulse of the considered amines with 98% HTP.
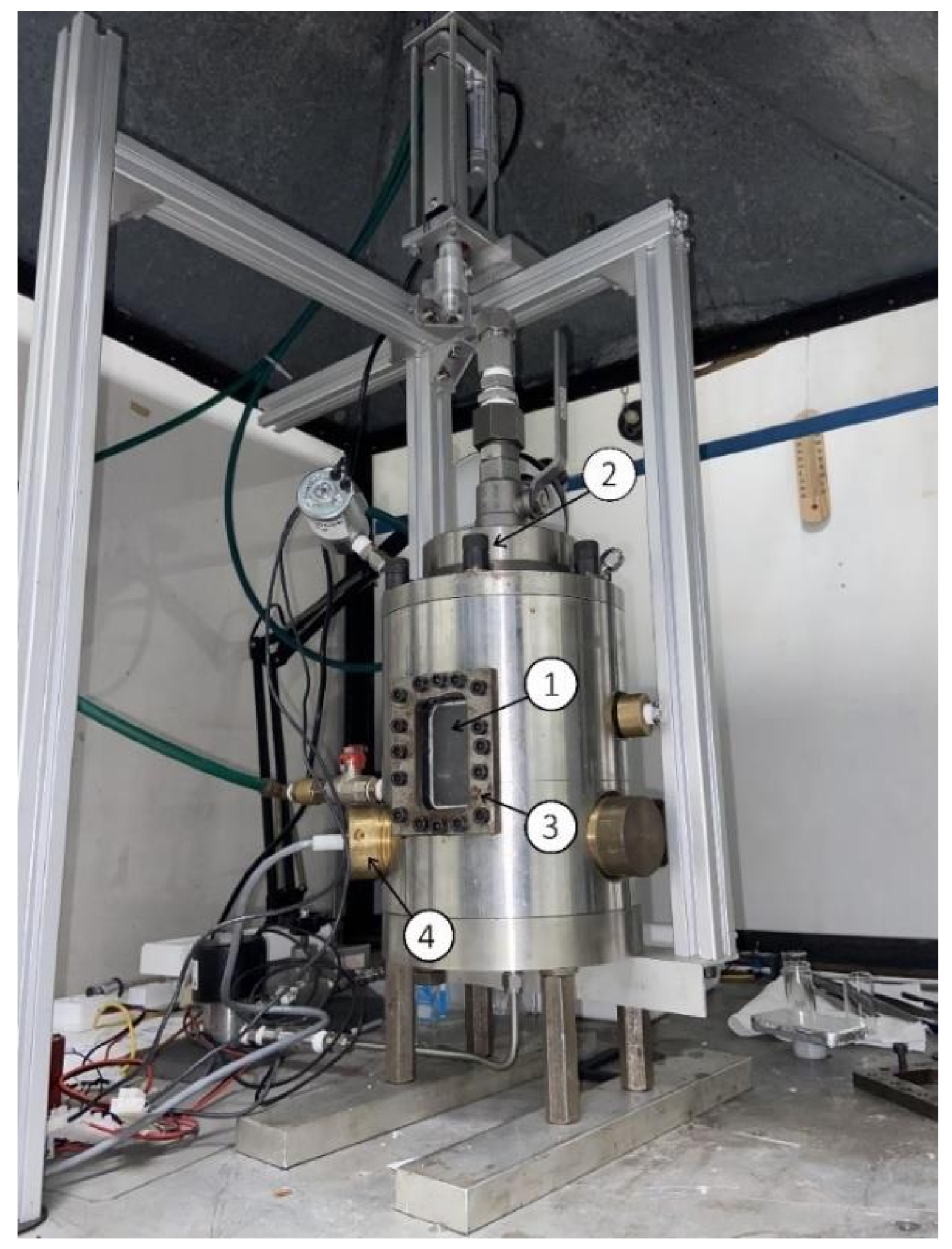
Figure 2.
Drop test reaction chamber: (1) optical access; (2) HTP supply system; (3) combustion chamber body; (4) sensor connections.
Figure 2.
Drop test reaction chamber: (1) optical access; (2) HTP supply system; (3) combustion chamber body; (4) sensor connections.
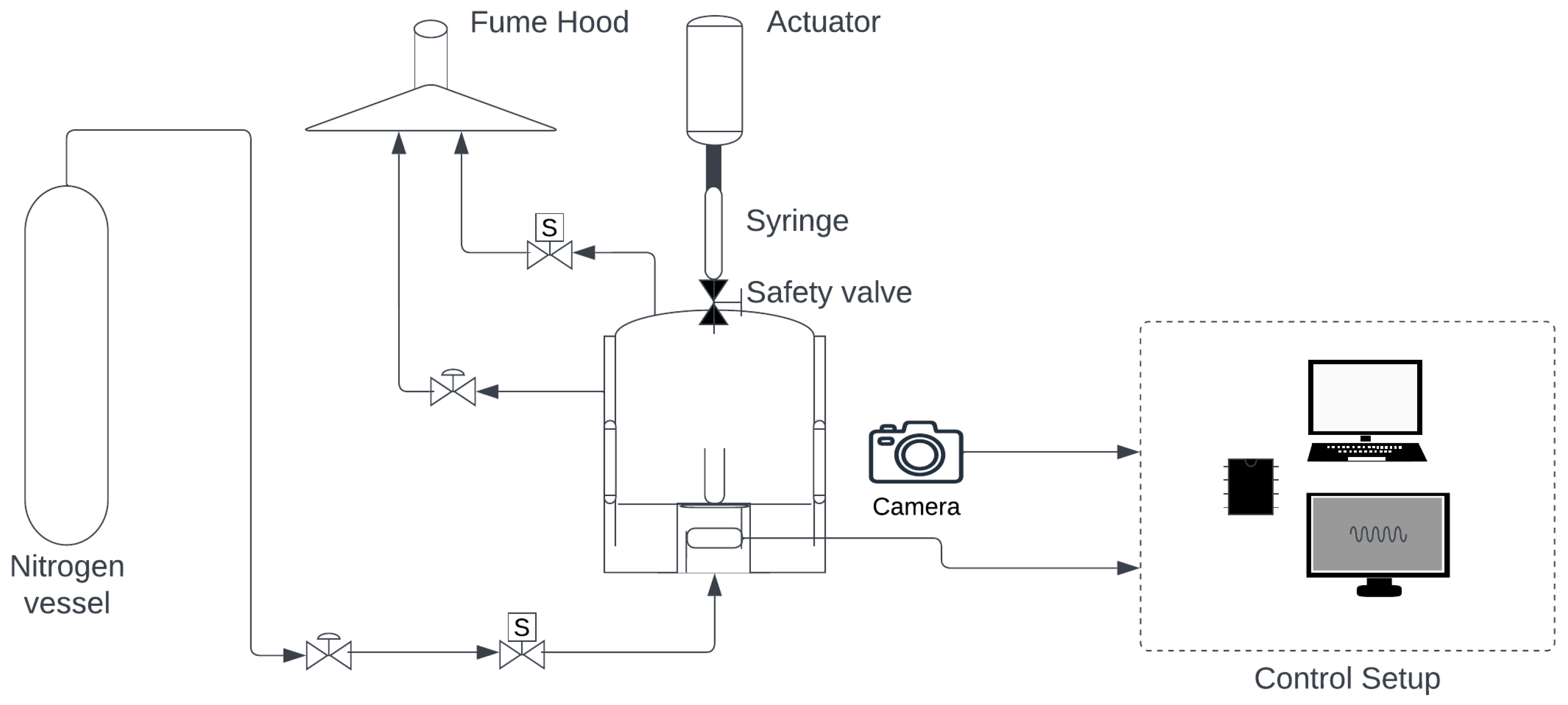
Figure 3.
Drop test apparatus scheme.
Figure 3.
Drop test apparatus scheme.
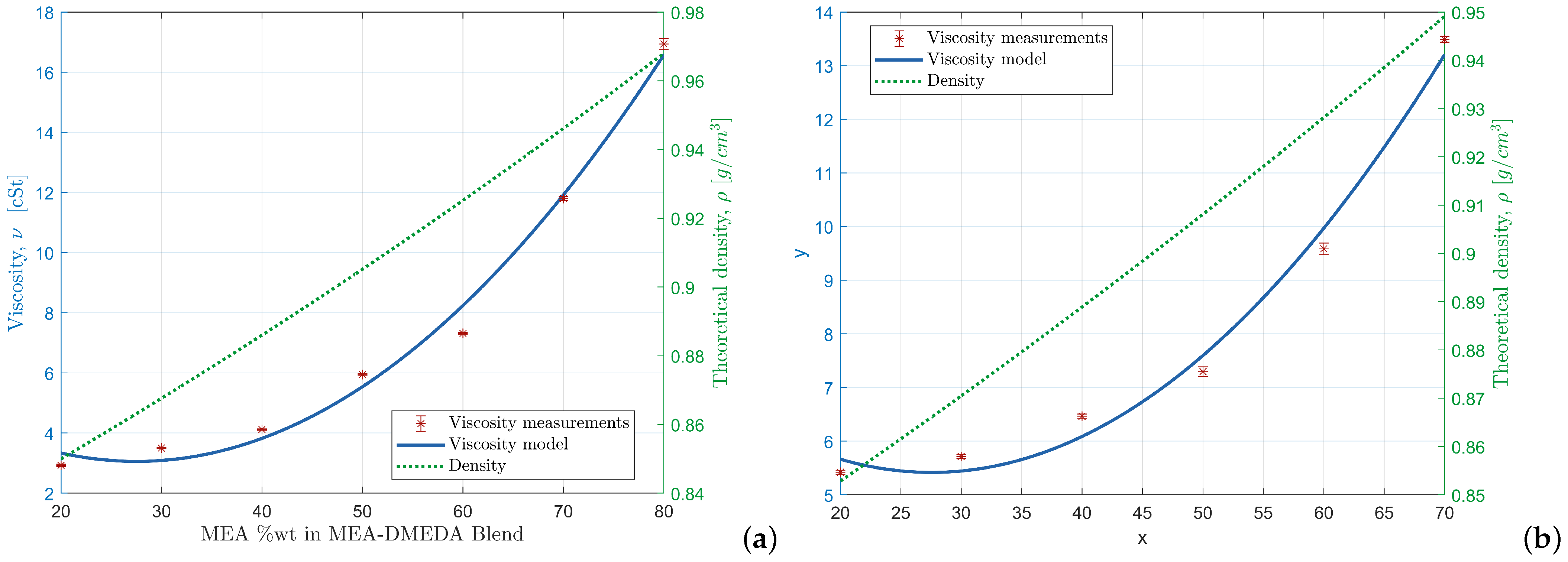
Figure 4.
Theoretical density and measured kinematic viscosity of MEA-based fuels: (a) MEA + CN (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9995 (blue); (b) MEA + CC (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9968 (blue).
Figure 4.
Theoretical density and measured kinematic viscosity of MEA-based fuels: (a) MEA + CN (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9995 (blue); (b) MEA + CC (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9968 (blue).
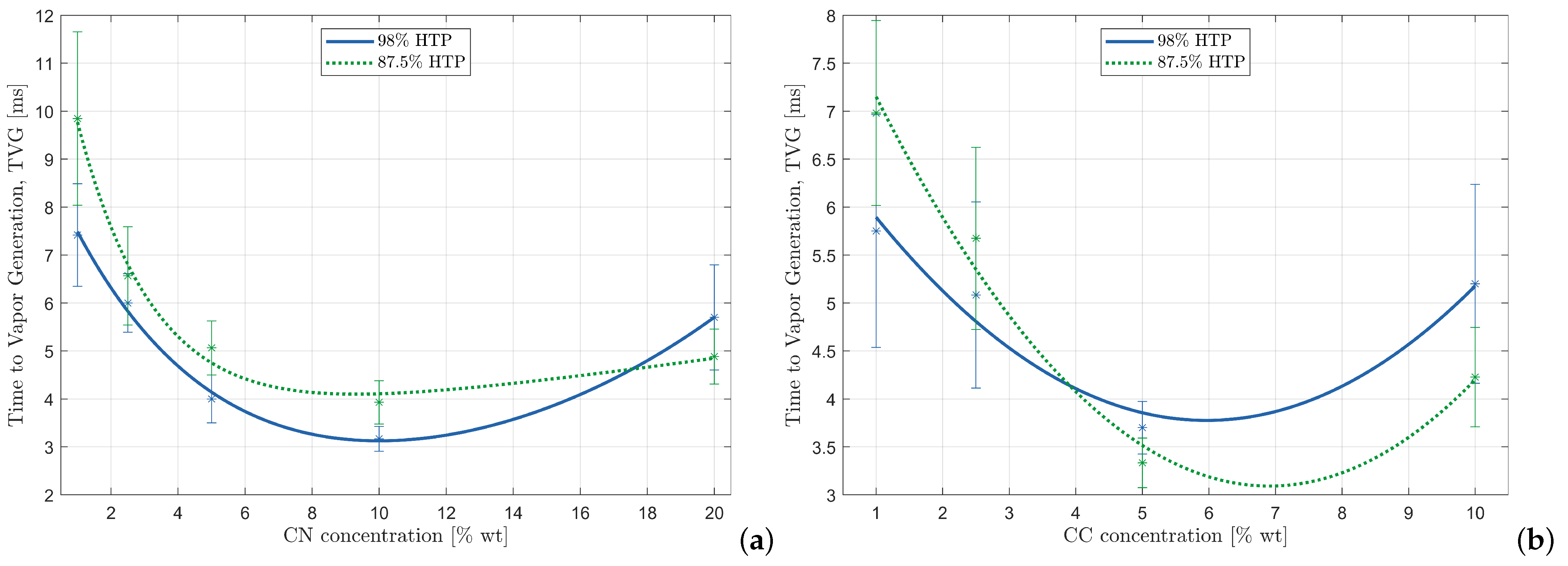
Figure 5.
Measurements with relative standard deviations and fitting of TVG versus additive concentration of MEA-based fuels: (a) TVG of MEA + CN fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9951 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9910 (green); (b) TVG of MEA + CC fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9466 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9785 (green).
Figure 5.
Measurements with relative standard deviations and fitting of TVG versus additive concentration of MEA-based fuels: (a) TVG of MEA + CN fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9951 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9910 (green); (b) TVG of MEA + CC fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9466 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9785 (green).
Figure 6.
Measurements with relative standard deviations and fitting of IDT versus additive concentration of MEA-based fuels: (a) IDT of MEA + CN fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9967 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9957 (green); (b) IDT of MEA + CC fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9424 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9283 (green).
Figure 6.
Measurements with relative standard deviations and fitting of IDT versus additive concentration of MEA-based fuels: (a) IDT of MEA + CN fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9967 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9957 (green); (b) IDT of MEA + CC fuels with (i) 98% HTP, = 0.9424 (blue) and (ii) 87.5%HTP, = 0.9283 (green).
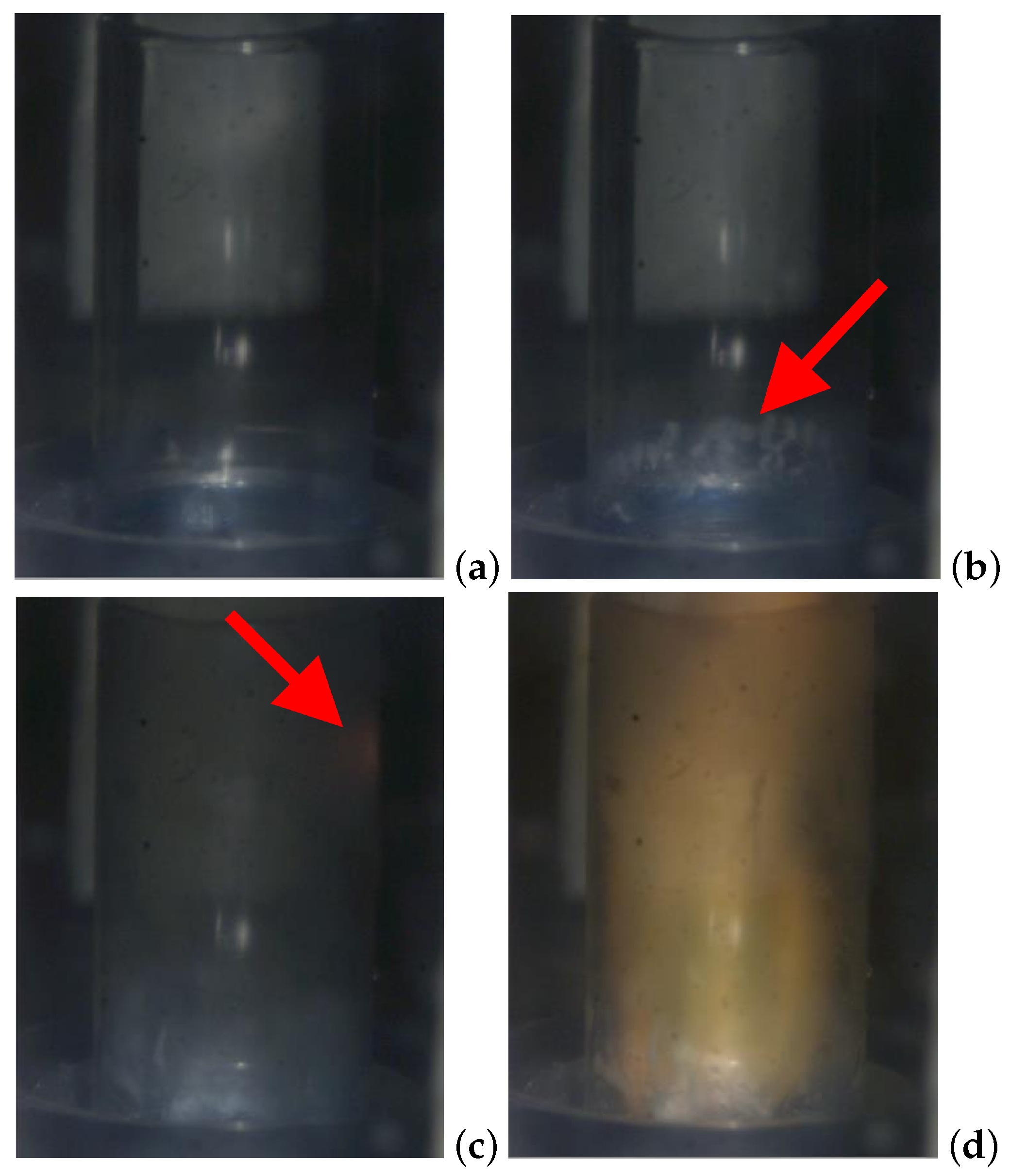
Figure 7.
Example ignition sequence of MEA + CN 10 wt% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, flame kernel enlargement, (e) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
Figure 7.
Example ignition sequence of MEA + CN 10 wt% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, flame kernel enlargement, (e) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
Figure 8.
Theoretical density and measured kinematic viscosity of MEA-DMEDA blends: (a) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 0.5 wt% (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9900 (blue); (b) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 1 wt% (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9874 (blue).
Figure 8.
Theoretical density and measured kinematic viscosity of MEA-DMEDA blends: (a) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 0.5 wt% (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9900 (blue); (b) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 1 wt% (i) theoretical density (green) and (ii) viscosity fitted model = 0.9874 (blue).
Figure 9.
Example ignition sequence of MEA-DMEDA 20:80 + CCH 1% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, flame kernel enlargement; (e) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
Figure 9.
Example ignition sequence of MEA-DMEDA 20:80 + CCH 1% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, flame kernel enlargement; (e) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
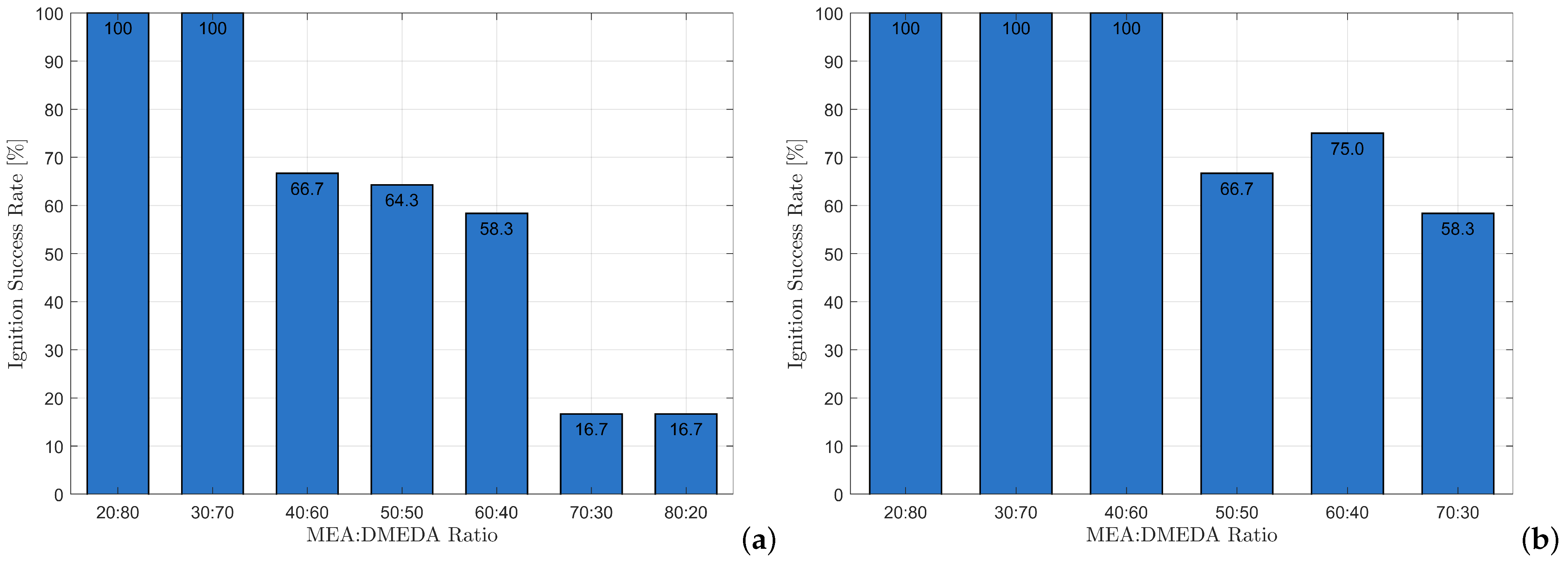
Figure 10.
Ignition success rate of MEA-DMEDA blends with 87.5% HTP: (a) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 0.5%; (b) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 1%. Each formulation was tested 18 times.
Figure 10.
Ignition success rate of MEA-DMEDA blends with 87.5% HTP: (a) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 0.5%; (b) MEA-DMEDA + CCH 1%. Each formulation was tested 18 times.
Figure 11.
Example ignition sequence of MEA-DMEDA 50:50 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
Figure 11.
Example ignition sequence of MEA-DMEDA 50:50 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% with 98% HTP: (a) ms, contact; (b) ms, first vapor generation; (c) ms, ignition; (d) ms, reaction. Red arrows in (b) and (c) point, respectively, at the vapor cloud and ignition kernel to help locating them in the pictures.
Table 1.
Reactions of hydrogen peroxide with amines [
25].
Table 1.
Reactions of hydrogen peroxide with amines [
25].
| | Primary Amines | |
|---|
| RNH2 + H2O2 | → | Vigorous peroxide decomposition; reaction difficult to control; no products isolated. |
| | Secondary Amines | |
| R2NH + H2O2 | → | R2NOH Hydroxylamine |
| | Tertiary Amines | |
| R3N + H2O2 | → | R3NO Amineoxide |
Table 2.
Peak performance values and relative oxidizer-to-fuel mass flow ratio (O/F) for the selected fuels.
Table 2.
Peak performance values and relative oxidizer-to-fuel mass flow ratio (O/F) for the selected fuels.
| Propellant | Is,vac [s] | O/F | Iv [s·g/cm3] | Tc [K] |
|---|
| MMH/NTO | | | | |
| UDMH/NTO | | | | |
| UDMH/WFNA | | | | |
| MEA/HTP () | | | | |
Table 3.
MEA toxicity assessment.
Table 3.
MEA toxicity assessment.
| | Hazard Statements a | NFPA 704 Fire Diamond b | OSHA PEL TWA [ppm] c | ACGIH TLV TWA [ppm] d | IDLH [ppm] b |
|---|
| MEA | H302, H312, H332, H314, H318, H335, H412 | ![Aerospace 11 00309 i001]() | 3 | 3 | 30 |
| H301, H311, H330, H314, H318, H317, H350, H400, H410 | ![Aerospace 11 00309 i002]() | 1 | 0.01 | 50 |
Table 4.
Relevant properties of selected fuels.
Table 4.
Relevant properties of selected fuels.
| Abbreviation | Formula | Molar Mass [g/mol] | Freezing Point [°C] | AIT [°C] | Density [g/cm3] | Viscosity [cP] |
|---|
| MEA monoethanolamine | | 61.08 | 10 | 780 | 1.012 | 18.7440 |
| DMEDA N,N-dimethylethylenediamine | | 88.15 | −70 | 255 | 0.814 | 0.895 |
| TMEDA N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine | | 116.21 | −55 | 150 | 0.772 | 0.586 |
| ETH ethanol | | 46.08 | −114 | 365 | 0.789 | 1.074 |
Table 5.
Fuel toxicity assessment.
Table 6.
Additive toxicity assessment.
Table 6.
Additive toxicity assessment.
| | Hazard Statements a | NFPA 704 Fire Diamond a | OSHA PEL TWA [ppm] | ACGIH TLV TWA [ppm] | IDLH [ppm] |
|---|
| CN copper (II) nitrate trihydrate | H272, H314, H318, H400, H411 | ![Aerospace 11 00309 i006]() | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| CC/CCH copper (II) chloride anhydrous/dihydrate | H302, H312, H315, H318, H400, H411 | ![Aerospace 11 00309 i007]() | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Table 7.
Produced samples.
Table 7.
Produced samples.
| Batch | Subsets | Formulations |
|---|
| MEA-based | MEA + CN | [CN]: 1%; 2.5%; 5%; 10%; 20% |
| | MEA + CC | [CC]: 1%; 2.5%; 5%; 10% |
| | MEA + CCH | [CCH]: 1%; 5% |
| MEA-DMEDA blends | M:D + CCH 0.5% | M:D: 20:80; 30:70; 60:40; 50:50; 40:60; 30:70; 20:80 |
| | M:D + CCH 1% | M:D: 20:80; 30:70; 60:40; 50:50; 40:60; 30:70 |
| ETH blends | M:D + CCH 1% + ETH 10% | M:D: 30:70; 50:50; 70:30; 80:20 |
Table 8.
Oxidizer droplet size.
Table 8.
Oxidizer droplet size.
| Oxidizer (wt%) | Mass [mg] |
|---|
| Avg | Std |
|---|
| HTP 87.5% | 63.6 | 3.4 |
| HTP 98% | 67.3 | 3.5 |
Table 9.
MEA-based fuel maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F, and volumetric specific impulse.
Table 9.
MEA-based fuel maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F, and volumetric specific impulse.
| Formulation | 98% HTP | 87.5% HTP |
|---|
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
|
|---|
| MEA + CN 1 wt% | 304.0 | 3.5 | 400.5 | 291.0 | 4.0 | 374.7 |
| MEA + CN 2.5 wt% | 303.6 | 3.5 | 400.9 | 290.6 | 3.9 | 374.4 |
| MEA + CN 5 wt% | 302.9 | 3.4 | 400.7 | 290.1 | 3.8 | 374.5 |
| MEA + CN 10 wt% | 301.4 | 3.1 | 399.7 | 288.9 | 3.5 | 374.0 |
| MEA + CN 20 wt% | 297.9 | 2.7 | 398.7 | 286.9 | 3.0 | 374.6 |
| MEA + CC 1 wt% | 303.7 | 3.5 | 400.2 | 290.8 | 4.0 | 374.4 |
| MEA + CC 2.5 wt% | 303.2 | 3.5 | 400.4 | 290.2 | 4.0 | 374.4 |
| MEA + CC 5 wt% | 302.1 | 3.4 | 399.6 | 289.2 | 3.9 | 373.8 |
| MEA + CC 10 wt% | 299.7 | 3.2 | 398.1 | 287.1 | 3.7 | 372.6 |
| MEA (reference) | 304.2 | 3.6 | 401.1 | 291.2 | 4.1 | 375.0 |
Table 10.
MEA-based fuel experimental campaign results.
Table 10.
MEA-based fuel experimental campaign results.
| Formulation | TVG 98% HTP [ms] | TVG 87.5% HTP [ms] | IDT 98% HTP [ms] | IDT 87.5% HTP [ms] | Viscosity [cSt] |
|---|
| Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std |
|---|
| MEA + CN 1 wt% | 7.4 | 1.1 | 9.8 | 1.8 | 39.8 | 6.1 | 91.3 | 8.2 | 30.07 | 0.17 |
| MEA + CN 2.5 wt% | 6.0 | 0.6 | 6.6 | 1.0 | 22.3 | 3.4 | 43.9 | 6.7 | 34.07 | 0.36 |
| MEA + CN 5 wt% | 4.0 | 0.5 | 5.1 | 0.6 | 16.4 | 1.5 | 29.1 | 2.7 | 39.78 | 0.55 |
| MEA + CN 10 wt% | 3.2 | 0.3 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 16.3 | 1.3 | 22.4 | 2.0 | 56.74 | 1.65 |
| MEA + CN 20 wt% | 5.7 | 1.1 | 4.9 | 0.3 | 17.0 | 3.5 | 28.5 | 4.8 | 119.14 | 5.68 |
| MEA + CC 1 wt% | 5.8 | 1.2 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 35.3 | 4.4 | 56.8 | 4.8 | 26.14 | 0.35 |
| MEA + CC 2.5 wt% | 5.1 | 1.0 | 5.6 | 0.9 | 30.1 | 1.7 | 48.3 | 7.1 | 35.09 | 0.41 |
| MEA + CC 5 wt% | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 0.3 | 18.5 | 2.9 | 27.3 | 1.8 | 48.25 | 0.42 |
| MEA + CC 10 wt% | 5.2 | 1.0 | 4.2 | 0.5 | 28.9 | 1.2 | 47.1 | 6.2 | 100.71 | 2.16 |
| MEA + CCH 1 wt% | 9.1 * | n/a | 17.8 * | n/a | 52.8 * | n/a | 67.3 | 6.5 | n/a | n/a |
| MEA + CCH 5 wt% | 3.4 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 19.0 | 2.0 | 32.1 | 3.4 | n/a | n/a |
Table 11.
Mass fractions of the combustion products at the exit section for additive-rich formulations and 98% HTP.
Table 11.
Mass fractions of the combustion products at the exit section for additive-rich formulations and 98% HTP.
| Products | MEA + CN 20 wt% | MEA + CC 10 wt% |
|---|
| 0.03% | 0.06% |
| 31.11% | 30.79% |
| 1.83% | 1.13% |
| - | 1.29% |
| 0.05% | 0.13% |
| 61.21% | 61.69% |
| 5.77% | 4.91% |
Table 12.
MEA-DMEDA blend fuel maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F and volumetric specific impulse.
Table 12.
MEA-DMEDA blend fuel maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F and volumetric specific impulse.
| Formulation (MEA:DMEDA) | 98% HTP | 87.5% HTP |
|---|
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
|
|---|
| 20:80 + CCH 0.5% | 324.9 | 4.5 | 415.2 | 312.5 | 5.3 | 392.2 |
| 30:70 + CCH 0.5% | 322.9 | 4.4 | 414.2 | 310.5 | 5.2 | 391.0 |
| 60:40 + CCH 0.5% | 320.8 | 4.3 | 413.0 | 308.4 | 5.0 | 389.2 |
| 50:50 + CCH 0.5% | 318.5 | 4.2 | 411.7 | 306.1 | 4.9 | 387.7 |
| 60:40 + CCH 0.5% | 316.1 | 4.1 | 410.2 | 303.6 | 4.7 | 385.5 |
| 70:30 + CCH 0.5% | 313.4 | 4.0 | 408.5 | 300.9 | 4.6 | 383.7 |
| 80:20 + CCH 0.5% | 310.6 | 3.8 | 405.9 | 298.0 | 4.4 | 381.0 |
| 20:80 + CCH 1% | 324.7 | 4.5 | 415.4 | 312.3 | 5.3 | 392.3 |
| 30:70 + CCH 1% | 322.7 | 4.4 | 414.3 | 310.3 | 5.2 | 391.1 |
| 40:60 + CCH 1% | 320.6 | 4.3 | 413.1 | 308.2 | 5.0 | 389.3 |
| 50:50 + CCH 1% | 318.3 | 4.2 | 411.8 | 305.9 | 4.9 | 387.8 |
| 60:40 + CCH 1% | 315.9 | 4.1 | 410.3 | 303.5 | 4.7 | 385.6 |
| 70:30 + CCH 1% | 313.3 | 3.9 | 407.9 | 300.7 | 4.6 | 383.7 |
Table 13.
MEA-DMEDA blend fuel experimental campaign results.
Table 13.
MEA-DMEDA blend fuel experimental campaign results.
| Formulation | TVG 98% HTP [ms] | TVG 87.5% HTP [ms] | IDT 98% HTP [ms] | IDT 87.5% HTP [ms] | Viscosity [cSt] |
|---|
| (MEA:DMEDA) | Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std | Avg | Std |
| 20:80 + CCH 0.5% | 4.3 | 0.3 | 6.7 | 0.6 | 24.1 | 3.3 | 159.6 | 55.8 | 2.93 | 0.04 |
| 30:70 + CCH 0.5% | 5.2 | 0.7 | 7.0 | 1.1 | 28.7 | 5.1 | 158.6 | 57.5 | 3.50 | 0.02 |
| 40:60 + CCH 0.5% | 6.0 | 0.9 | 9.1 | 2.3 | 30.8 | 1.0 | 195.6 * | 80.4 * | 4.12 | 0.02 |
| 50:50 + CCH 0.5% | 6.0 | 0.8 | 10.4 | 1.9 | 37.3 | 6.3 | 64.8 * | 18.0 * | 5.94 | 0.03 |
| 60:40 + CCH 0.5% | 8.4 | 1.1 | 12.2 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 4.9 | 64.1 * | 4.2 * | 7.31 | 0.03 |
| 70:30 + CCH 0.5% | 8.5 | 1.3 | 14.5 | 1.0 | 47.2 | 8.3 | 134.8 * | 35.7 * | 11.80 | 0.08 |
| 80:20 + CCH 0.5% | 9.8 | 2.0 | 16.6 | 1.6 | 58.4 | 8.3 | 173.3 * | 35.7 * | 16.94 | 0.18 |
| 20:80 + CCH 1% | 3.6 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 18.4 | 1.0 | 27.9 | 5.8 | 5.42 | 0.04 |
| 30:70 + CCH 1% | 3.7 | 0.4 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 21.3 | 0.7 | 55.1 | 18.7 | 5.71 | 0.04 |
| 40:60 + CCH 1% | 4.7 | 0.4 | 5.1 | 0.6 | 24.0 | 1.9 | 71.8 | 23.9 | 6.46 | 0.04 |
| 50:50 + CCH 1% | 5.9 | 0.9 | 7.4 | 1.0 | 30.3 | 4.7 | 60.5 * | 7.3 * | 7.29 | 0.09 |
| 60:40 + CCH 1% | 6.3 | 1.1 | 8.1 | 1.1 | 31.4 | 3.5 | 85.9 * | 28.7 * | 9.59 | 0.11 |
| 70:30 + CCH 1% | 6.8 | 1.3 | 10.5 | 1.6 | 37.6 | 6.2 | 74.0 * | 14.0 * | 13.49 | 0.05 |
Table 14.
Effects of increasing DMEDA mass fraction.
Table 14.
Effects of increasing DMEDA mass fraction.
| Influenced Parameter | Effect |
|---|
| CCH solubility | Reduction |
| Storage Stability | Reduction |
| Viscosity | Reduction |
| Density | Reduction |
| TVG | Reduction |
| IDT | Reduction |
Table 15.
Fuels including ETH maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F, and volumetric specific impulse.
Table 15.
Fuels including ETH maximum gravimetric vacuum specific impulse, corresponding O/F, and volumetric specific impulse.
| Formulation (MEA:DMEDA) | 98% HTP | 87.5% HTP |
|---|
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
| [s]
| O/F | [s·g/cm3]
|
|---|
| 30:70 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 322.6 (322.7) | 4.3 (4.4) | 412.2 (414.3) | 310.3 (310.3) | 5.1 (5.2) | 389.6 (391.1) |
| 50:50 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 318.6 (318.3) | 4.2 (4.2) | 410.6 (411.8) | 306.3 (305.9) | 4.8 (4.9) | 386.4 (387.8) |
| 70:30 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 314.1 (313.3) | 3.9 (3.9) | 406.8 (407.9) | 301.7 (300.7) | 4.6 (4.6) | 383.1 (383.7) |
| 80:20 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 311.6 (310.4) | 3.8 (3.8) | 405.0 (405.6) | 299.1 (297.8) | 4.4 (4.4) | 380.7 (381.0) |
Table 16.
Fuels including ETH ignition test results.
Table 16.
Fuels including ETH ignition test results.
| Formulation (MEA:DMEDA) | IDT 98% HTP [ms] |
|---|
| Avg | Std |
|---|
| 30:70 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 29.1 (21.3) | 4.2 (0.7) |
| 50:50 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 30.3 (30.3) | 4.4 (4.7) |
| 70:30 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 34.2 (37.6) | 1.3 (6.2) |
| 80:20 + ETH 10% + CCH 1% | 35.5 * (n/a) | 2.0 * (n/a) |
Table 17.
Property comparison of the selected samples.
Table 17.
Property comparison of the selected samples.
| Property | MEA + CN 10 wt% | MEA + CC 5 wt% | M:D 20:80 + CCH 1 wt% | M:D 30:70 + ETH 10 wt% + CCH 1 wt% |
|---|
| TVG (98% HTP) [ms] | 3.2 | 3.7 | 3.6 | n/a |
| IDT (98% HTP) [ms] | 16.3 | 18.5 | 18.4 | 29.1 |
| Density | 1.07 | 1.04 | 0.85 | 0.86 |
| Viscosity [cSt] | 56.74 | 48.25 | 5.42 | n/a |
Table 18.
Percent difference between the gravimetric vacuum specific impulse of selected fuel samples with 98% HTP and traditional bipropellant couples.
Table 18.
Percent difference between the gravimetric vacuum specific impulse of selected fuel samples with 98% HTP and traditional bipropellant couples.
| Sample | MEA + CN 10% | MEA + CC 5 wt% | M:D 20:80 +CCH 1 wt% | M:D 30:70 + ETH 10 wt% + CCH 1 wt% |
|---|
| MMH/NTO | −10.5% | −10.3% | −3.6% | −4.2% |
| UDMH/NTO | −9.7% | −9.4% | −2.7% | −3.3% |
| UDMH/WFNA | −3.6% | −3.4% | +3.8% | +3.1% |
Table 19.
Percent difference between the volumetric specific impulse of selected fuel samples with 98% HTP and traditional bipropellant couples.
Table 19.
Percent difference between the volumetric specific impulse of selected fuel samples with 98% HTP and traditional bipropellant couples.
| Sample | MEA + CN 10 wt% | MEA + CC 5 wt% | M:D 20:80 + CCH 1 wt% | M:D 30:70 + ETH 10 wt% + CCH 1 wt% |
|---|
| MMH/NTO | +2.0% | +2.0% | +6.1% | +5.2% |
| UDMH/NTO | +5.2% | +5.2% | +9.3% | +8.5% |
| UDMH/WFNA | +6.8% | +6.8% | +11.0% | +10.1% |