Hydrological Modeling Response to Climate Model Spatial Analysis of a South Eastern Europe International Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
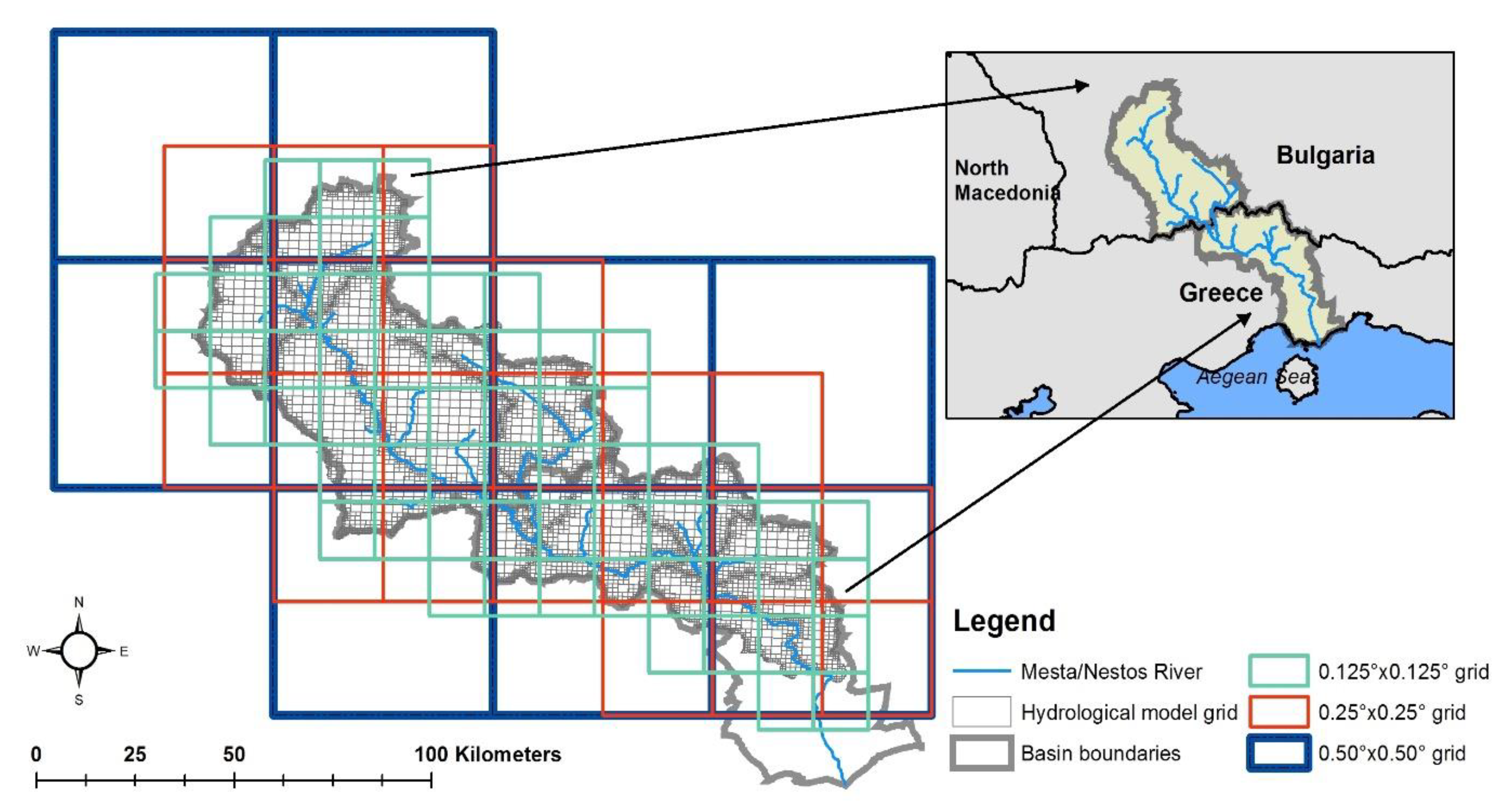
2.1. Case Study Area
2.2. Reanalyis Data and Derived Datasets
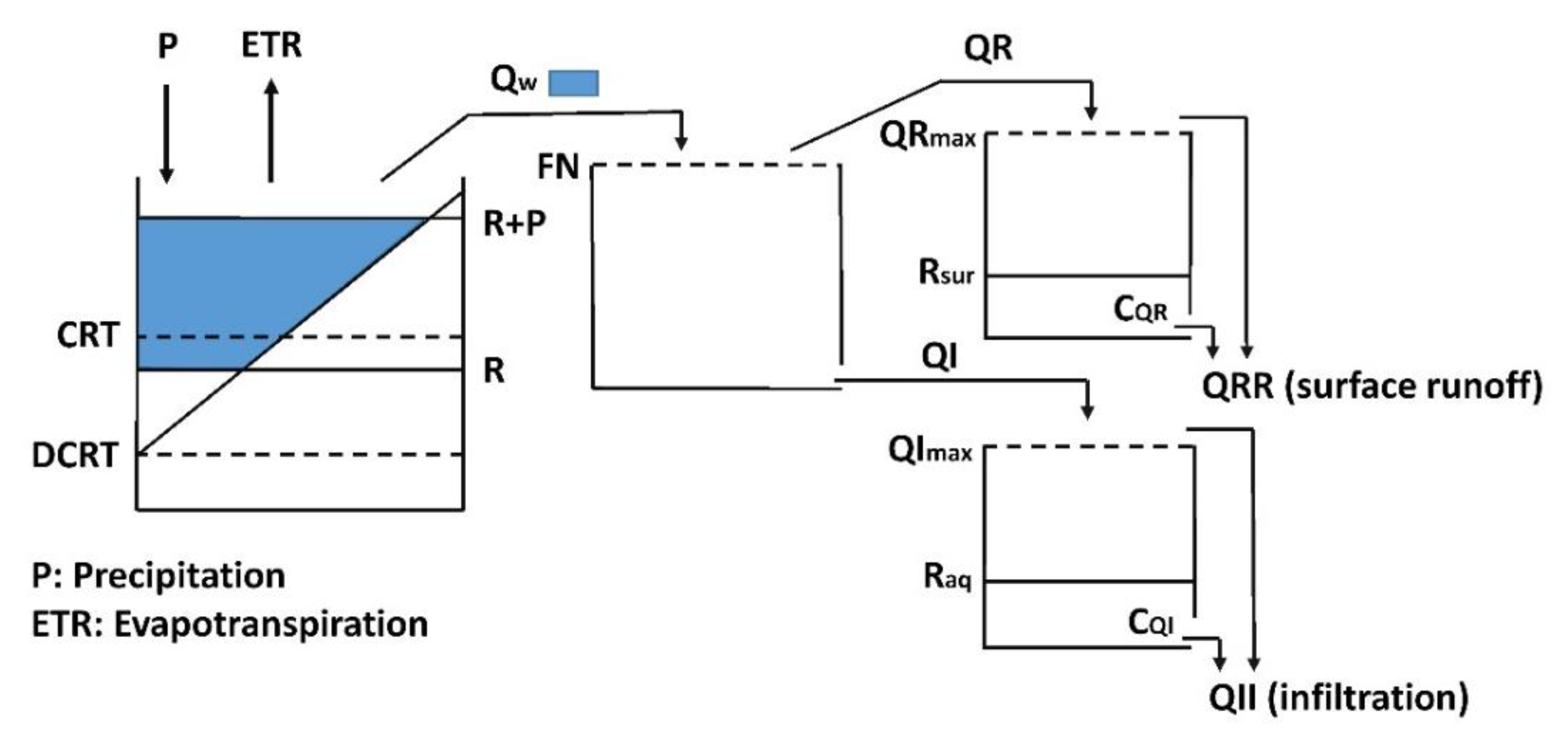
2.3. River Basin Simulation
3. Results
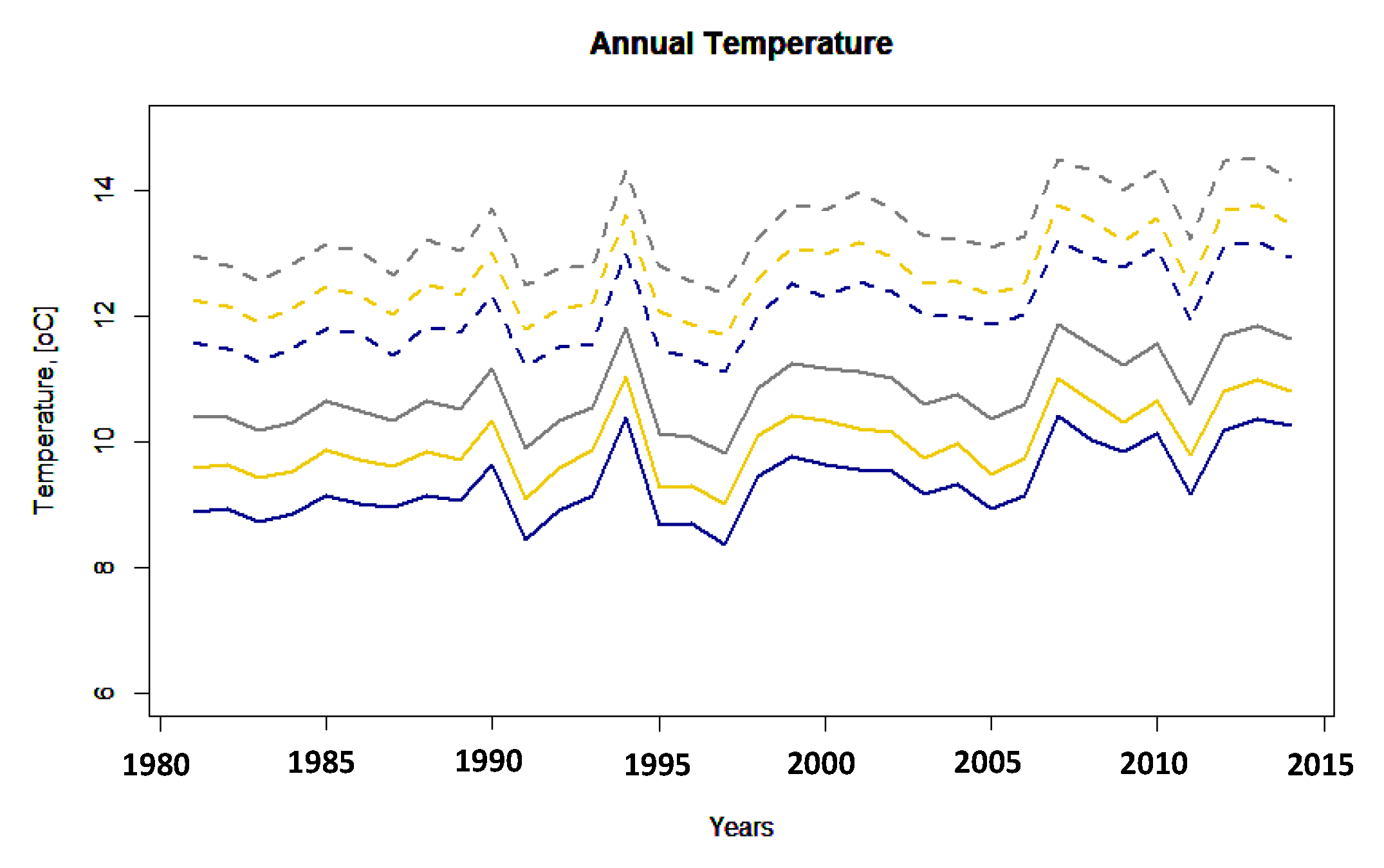
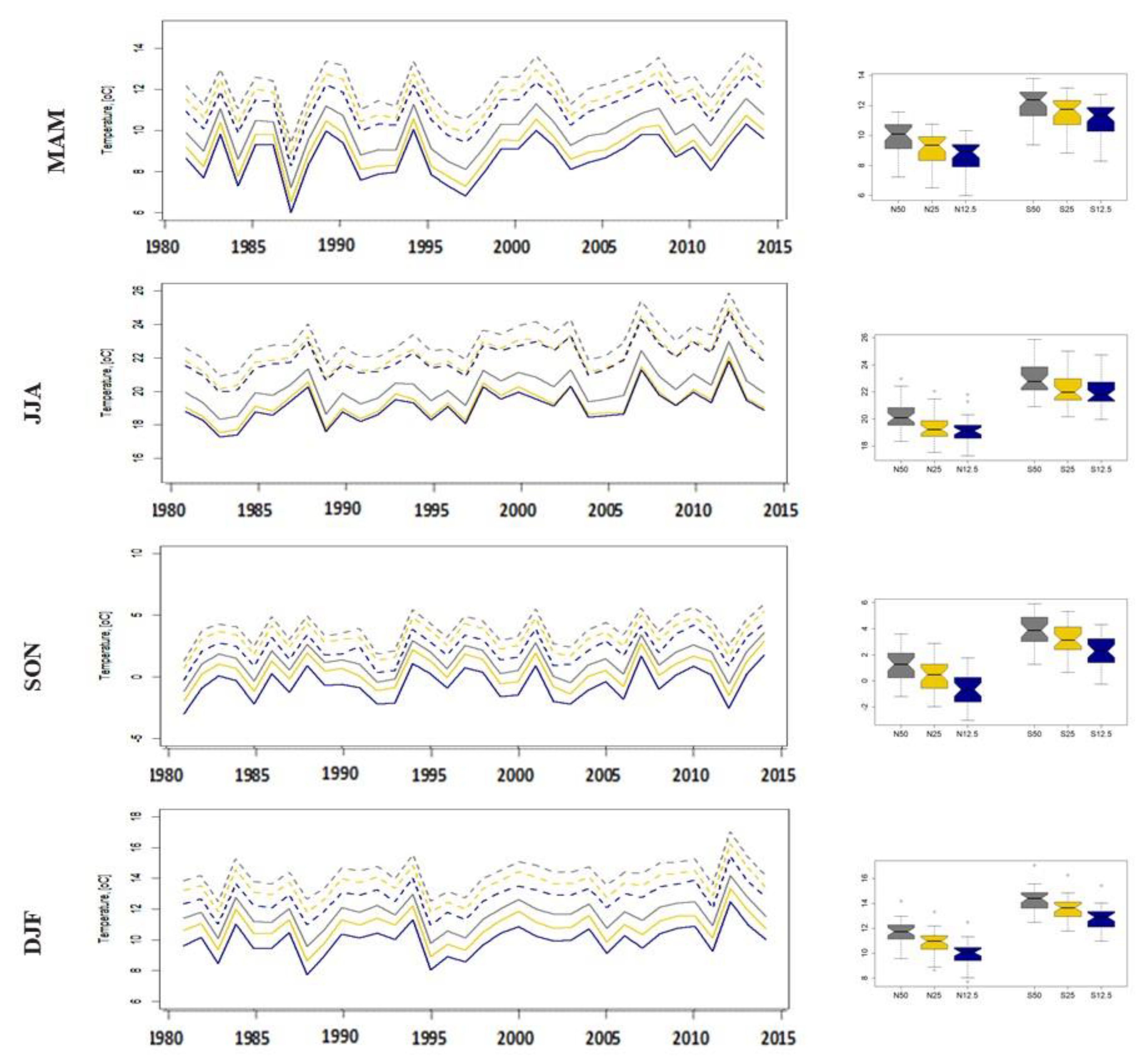
3.1. Climate Analysis of Temperature Data
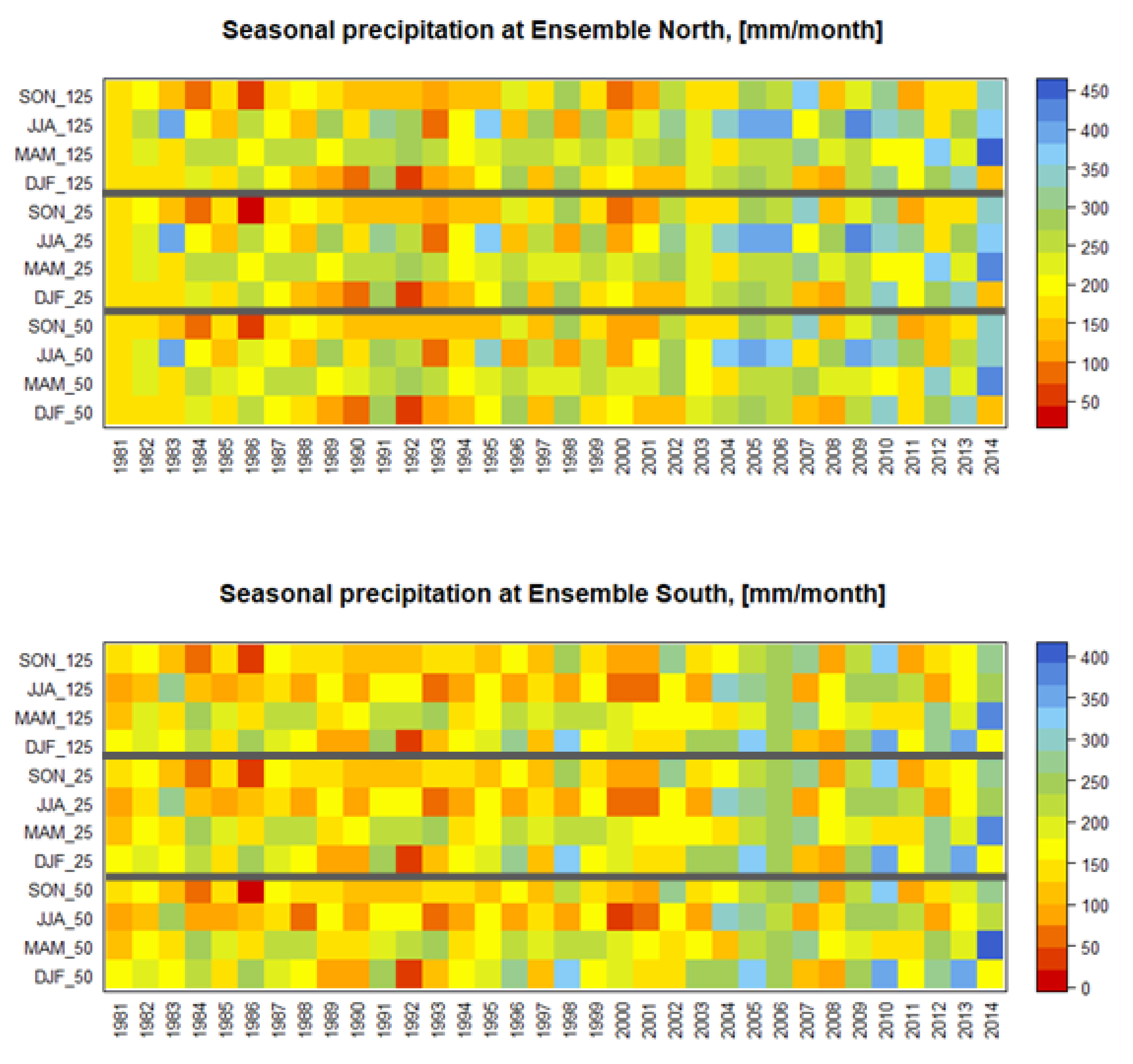
3.2. Climate Analysis of Precipitation Data
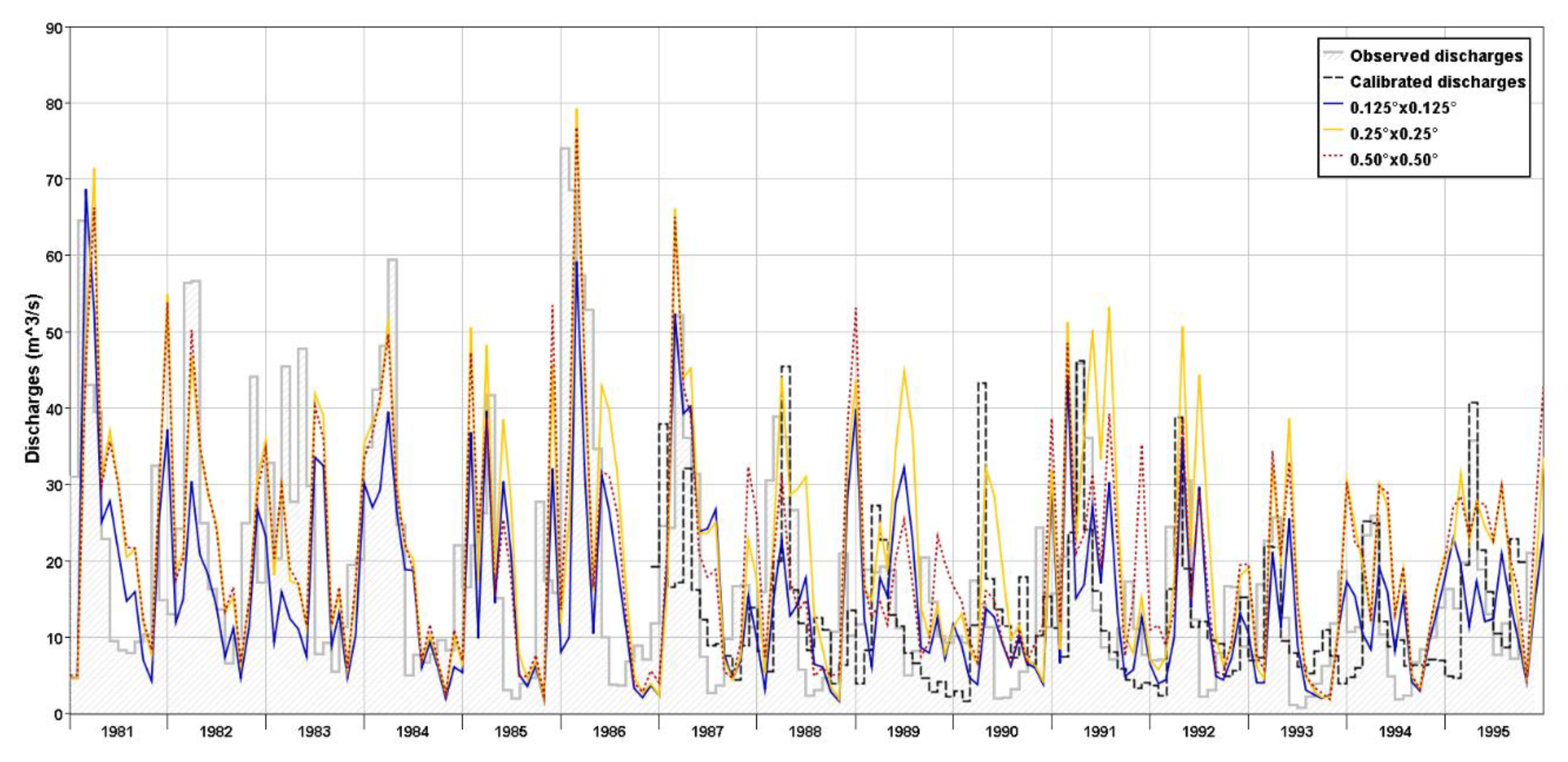
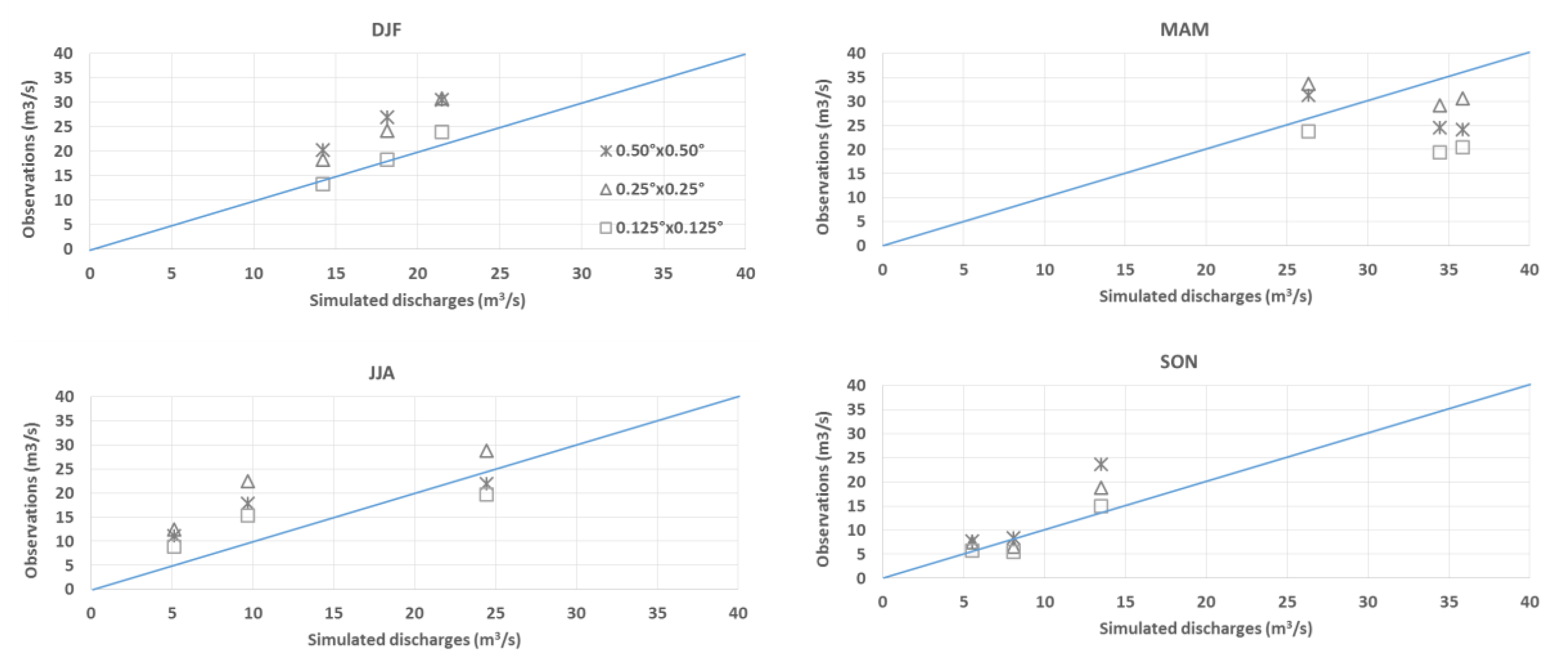
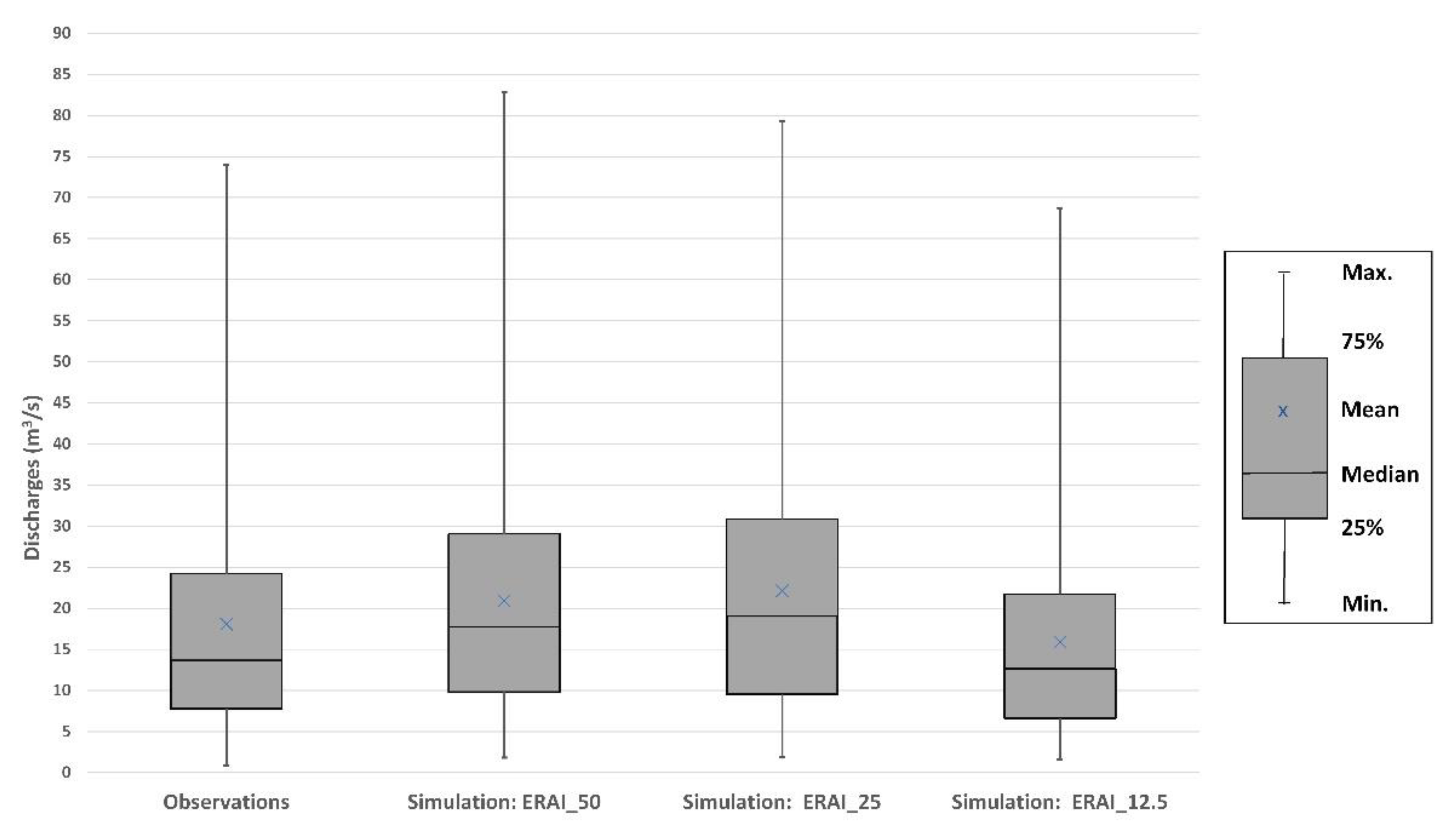
3.3. Hydrologic Model Outputs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brigode, P.; Oudin, L.; Perrin, C. Hydrological model parameter instability: A source of additional uncertainty in estimating the hydrological impacts of climate change? J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Storm, B. Construction, Calibration and Validation of Hydrological Models. In Distributed Hydrological Modelling. Water Science and Technology Library; Abbott, M.B., Refsgaard, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1990; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- O’Riordan, T. Environmental Science for Environmental Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wei, C.; Yeh, H.C. Rainfall network design using kriging and entropy. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Assessing the influence of rain gauge density and distribution on hydrological model performance in a humid region of China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anctil, F.; Lauzon, N.; Andréassian, V.; Oudin, L.; Perrin, C. Improvement of rainfall–runoff forecasts through mean areal rainfall optimization. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.A.; Sivapalan, M.; Duncan, M. Investigating the representative elementary area concept: An approach based on field data. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 6, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C. Physically based distributed modeling of upland catchment using the Systeme Hydrologique Europeen. J. Hydrol. 1986, 87, 79–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Density of stations for a network. In Hydrology—From Measurement to Hydrological Information, Vol 1, Guide to Hydrological Practices, 6th ed.; WMO-168; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.J.; Koch, M.; Chinchilla, K.M. Evaluation of Gridded MultiSatellite Precipitation Estimation (TRMM-3B42-V7) Performance in the Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Climate 2018, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Kirschbaum, D.; Valigi, D.; Mondini, A.; Guzzetti, F. Comparison of Satellite Rainfall Estimates and Rain Gauge Measurements in Italy, and Impact on Landslide Modeling. Climate 2017, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylock, M.R.; Hofstra, N.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Klok, E.J.; Jones, P.D.; New, M. A European daily high-resolution gridded data set of surface temperature and precipitation for 1950–2006. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazoglou, G.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Skoulikaris, C.; Tolika, K. Bias Correction of Climate Model’s Precipitation Using the Copula Method and Its Application in River Basin Simulation. Water 2019, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerini, D.; Zulkafli, Z.; Wang, L.; Onof, C.; Buytaert, W.; Lavado-Casimiro, W.; Guyot, J. A Comparative Analysis of TRMM–Rain Gauge Data Merging Techniques at the Daily Time Scale for Distributed Rainfall–Runoff Modeling Applications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Kapsomenakis, J.; Douvis, K.C. Analysis of precipitation extremes based on satellite and high-resolution gridded data set over Mediterranean basin. Atmos. Res. 2013, 131, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Adjustment of global gridded precipitation for systematic bias. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.A.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Li, M.; Baig, F.; Li, T.; Cui, S. How accurate are the performances of gridded precipitation data products over Northeast China? Atmos. Res. 2018, 211, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstra, N.; Haylock, M.; New, M.; Jones, P.D. Testing E-OBS European high-resolution gridded data set of daily precipitation and surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Schulz, K.; Bernhardt, M. Statistical downscaling of ERA-interim forecast precipitation data in complex terrain using lasso algorithm. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, B.; Mohammadi, B. A comparison between the application of empirical and ANN methods for estimation of daily global solar radiation in Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, D.R.; Walter, M.T.; MacAlister, C.; Degaetano, A.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Easton, Z.M. Using the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis as weather input data for watershed models. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5613–5623. [Google Scholar]
- Essou, G.R.C.; Sabarly, F.; Lucas-Picher, P.; Brissette, F.; Poulin, A. Can precipitation and temperature from meteorological reanalyses be used for hydrological modeling? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilovich, M.G. Regional climate and variability of NASAMERRA and recent reanalyses: U.S. summertime precipitation and temperature. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Kunstmann, H. The hydrological cycle in three state-of-the-art reanalyses: Intercomparison and performance analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1397–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grusson, Y.; Anctil, F.; Sauvage, S.; Sánchez Pérez, J.M. Testing the SWAT Model with Gridded Weather Data of Different Spatial Resolutions. Water 2017, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bernhardt, M.; Schulz, K. Elevation correction of ERA-Interim temperature data in complex terrain. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4661–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppa, S.K.; Anandan, V.K.; Kesarkar, K.A.; Rao, S.V.B.; Reddy, P.N. Study on deep inland penetration of sea breeze over complex terrain in the tropics. Atmospheric. Res. 2012, 104, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Q. Evaluation of reanalysis, spatially interpolated and satellite remotely sensed precipitation data sets in central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5648–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Sillmann, J.; Wild, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Lippmann, T.; Zwiers, F.W. Consistency of Temperature and Precipitation Extremes across Various Global Gridded In Situ and Reanalysis Datasets. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5019–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, H.I.; Dibike, Y.; Prowse, T.; Bonsal, B. Inter-comparison of high-resolution gridded climate data sets and their implication on hydrological model simulation over the Athabasca Watershed, Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4250–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, J.D.; Minder, J.R.; Neiman, P.J.; Sukovich, E. Relationships between Barrier Jet Heights, Orographic Precipitation Gradients, and Streamflow in the Northern Sierra Nevada. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K.; Thorne, R. Snowmelt contribution to discharge from a large mountainous catchment in subarctic Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, T.; Khare, D.; Arora, M. A case study for the assessment of the suitability of gridded reanalysis weather data for hydrological simulation in Beas river basin of North Western Himalaya. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modeling over North-America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulikaris, C.H.; Ganoulis, J. Climate Change Impacts on River Catchment Hydrology Using Dynamic Downscaling of Global Climate Models. In National Security and Human Health Implications of Climate Change, NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Fernando, H., Klaić, Z., McCulley, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bank of Greece. Environmental, Economic and Social Impacts Due to Climate Change in Greece; Bank of Greece: Athens, Greece, 2011; p. 546. [Google Scholar]
- UNECE. Second Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters; UNECE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Balsamo, G.; Albergel, C.; Beljaars, A.; Boussetta, S.; Brun, E.; Cloke, H.; De Rosnay, P. ERA-Interim/Land: A global land surface reanalysis data set. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, E.; Girard, G.; de Marsily, G.; Deschenes, J. Spatially distributed modelling: Conceptual approach, coupling surface water and ground water. In Unsaturated Flow Hydrologic Modelling-Theory and Practice; Morel-Seytoux, H.J., Ed.; NATO ASI Series S 275; Kluwer Academic: Boston, CA, USA, 1989; pp. 435–454. [Google Scholar]
- Violette, S.; Ledoux, E.; Goblet, P.; Carbonnel, J.-P. Hydrologic and thermal modeling of an active volcano: The Piton de la Fournaise, Reunion. J. Hydrol. 1997, 191, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artinyan, E.; Habets, F.; Noilhan, J.; Ledoux, E.; Dimitrov, D.; Martin, E.; Le Moigne, P. Modelling the water budget and the riverflows of the Maritsa basin in Bulgaria. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). National Engineering Handbook, Part 630 Hydrology; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, UAS, 1993; Chapt. 11, Snowmelt.
- Rango, A.; Martinec, J. Revisiting the degree-day method for snowmelt computations. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1995, 31, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchevers, P.; Golaz, C.; Habets, F. Simulation of the water budget and the river flows of the Rhone basin from 1981 to 1994. J. Hydrol. 2001, 244, 60–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchevers, P.; Martin, E. Impact d’un changement climatique sur le manteau neigeux et l’hydrologie des bassins versants de montagne. In Proceedings of the Colloque International «L’eau en montagne», Mégève, France, 6 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrologic. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.R.; Qian, Y. The sensitivity of precipitation and snowpack simulations to model resolution via nesting in regions of complex terrain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, A.; Delrieu, G.; Creutin, J.D.; Obled, C. Temporal and spatial resolution of rainfall measurements required for urban hydrology. J Hydrol. 2004, 299, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Jensen, K.H.; He, X. Impact of Precipitation Spatial Resolution on the Hydrological Response of an Integrated Distributed Water Resources Model. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwen, N. SIMPLE—A Watershed Model for Flood Forecasting. Users’ Manual; Department of Civil Engineering, University of Waterloo: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 1986; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Steinle, P.; Seed, A.; Xiao, Y. The Sensitivity of Heavy Precipitation to Horizontal Resolution, Domain Size, and Rain Rate Assimilation: Case Studies with a Convection-Permitting Model. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunta, G.; Salerno, R.; Ceppi, A.; Ercolani, G.; Mancini, M. Effects of Model Horizontal Grid Resolution on Short- and Medium-Term Daily Temperature Forecasts for Energy Consumption Application in European Cities. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colle, B.A.; Olson, J.B.; Tongue, J.S. Multiseason verification of the MM5. Part II: Evaluation of high-resolution precipitation forecasts over the northeastern United States. Weather. Forecast. 2003, 18, 458–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Bárdossy, A.; Zehe, E.; He, Y. Comparison of conceptual model performance using different representations of spatial variability. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddeland, I.; Matheussen, B.V.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Influence of spatial resolution on simulated streamflow in a macroscale hydrologic model. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 291–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.A.; Moore, R.J. The sensitivity of catchment runoff models to rainfall data at different spatial scales. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdhen, A.; Chahar, B.R.; Sharma, O.P. Snowmelt modelling approaches in watershed models: Computation and comparison of efficiencies under varying climatic conditions. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3439–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Goswami, A.; Saraf, A.K. Assessment of Snowmelt Runoff Using Remote Sensing and Effect of Climate Change on Runoff. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedyk, L.P.; Kingston, D.G. Potential evapotranspiration method influence on climate change impacts on river flow: A mid-latitude case study. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Dugas, W.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Hauck, L.M. Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1169–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J. Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N50 | N25 | N12.5 | S50 | S25 | S12.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Maximum | 60.9 | 60.1 | 59.3 | 72.5 | 69.8 | 69.6 |
| IQR | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| SD | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| Skewness | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| Kurtosis | 18.7 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 31.1 | 30.2 | 30.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skoulikaris, C.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Lazoglou, G. Hydrological Modeling Response to Climate Model Spatial Analysis of a South Eastern Europe International Basin. Climate 2020, 8, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010001
Skoulikaris C, Anagnostopoulou C, Lazoglou G. Hydrological Modeling Response to Climate Model Spatial Analysis of a South Eastern Europe International Basin. Climate. 2020; 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkoulikaris, Charalampos, Christina Anagnostopoulou, and Georgia Lazoglou. 2020. "Hydrological Modeling Response to Climate Model Spatial Analysis of a South Eastern Europe International Basin" Climate 8, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010001
APA StyleSkoulikaris, C., Anagnostopoulou, C., & Lazoglou, G. (2020). Hydrological Modeling Response to Climate Model Spatial Analysis of a South Eastern Europe International Basin. Climate, 8(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010001







