FCVLP: A Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming Model for Municipal Solid Waste Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Fuzzy Linear Programming
2.2. Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk
2.3. Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming
2.4. Solution Method
3. Application
3.1. Overview of the Study System
3.2. Results Analysis
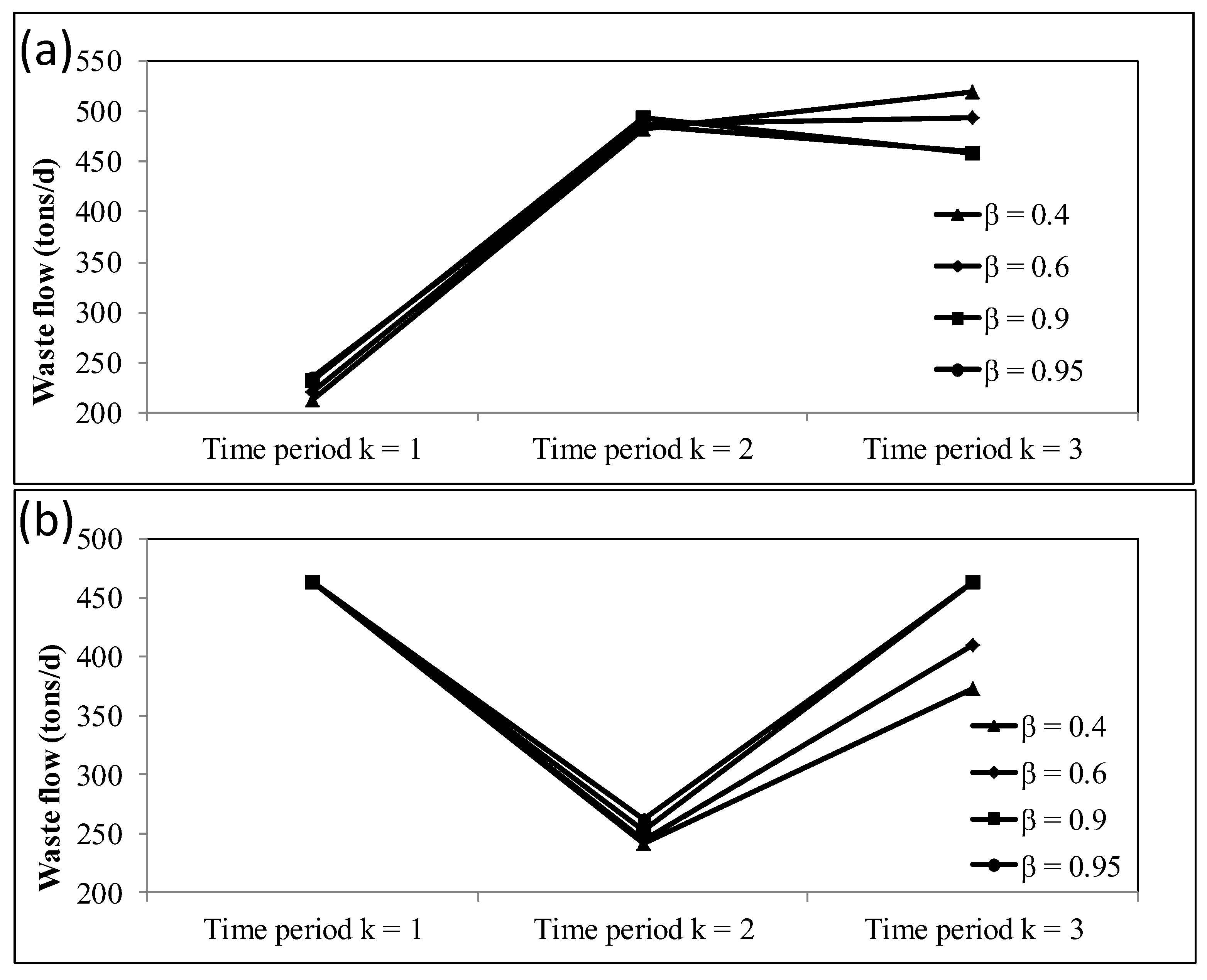
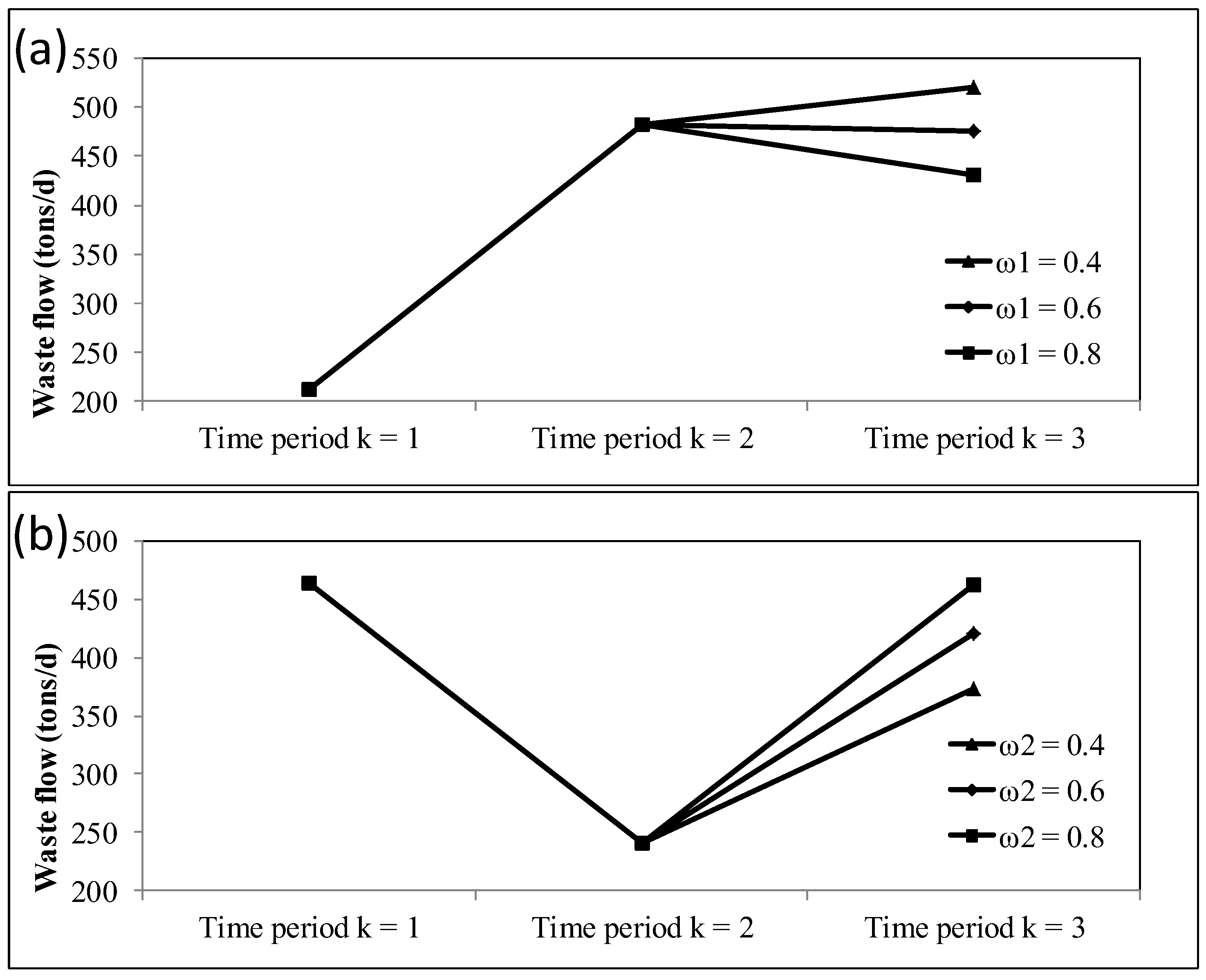
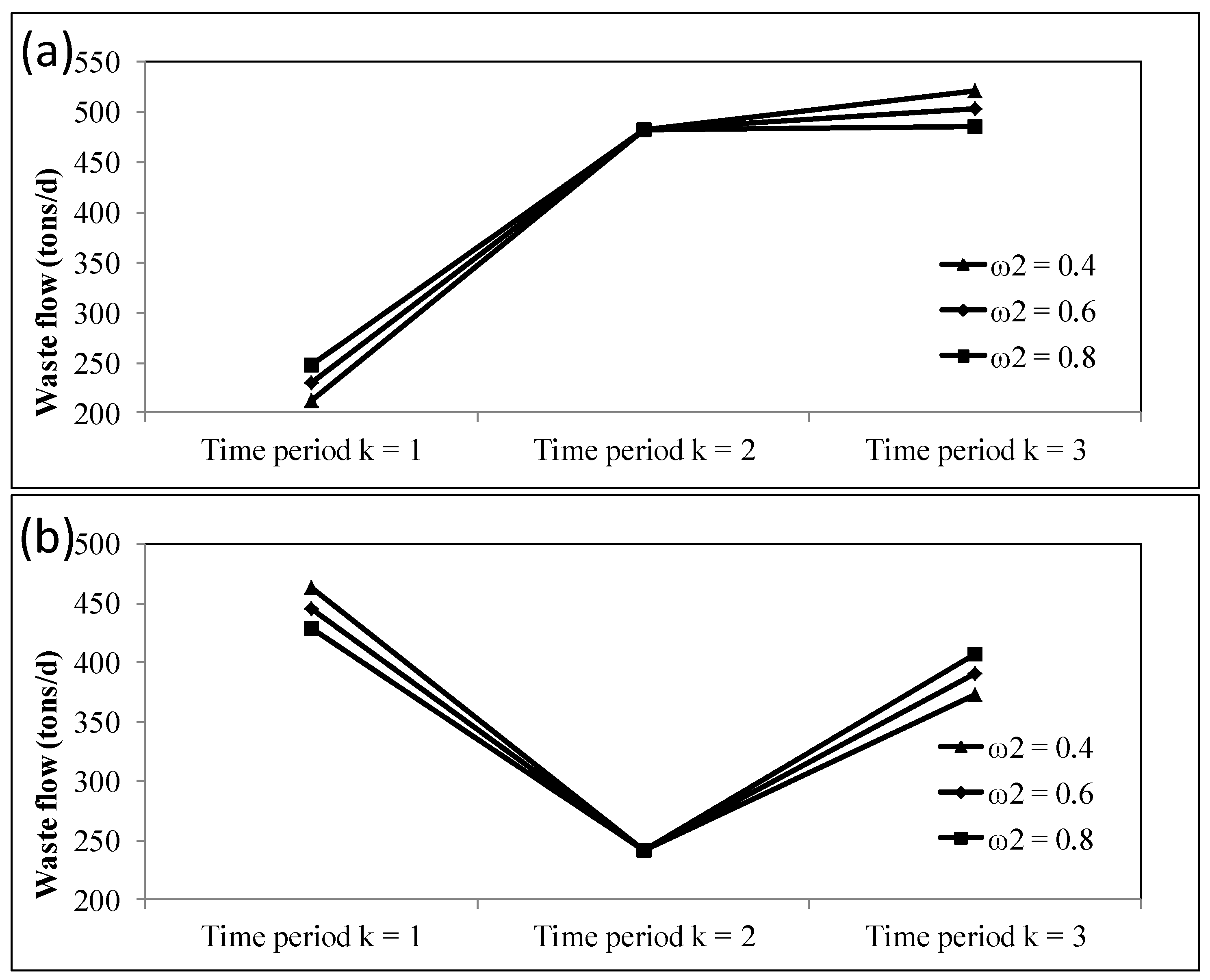
3.2.1. System Cost, Feasibility Degree, and Risk Level Analysis
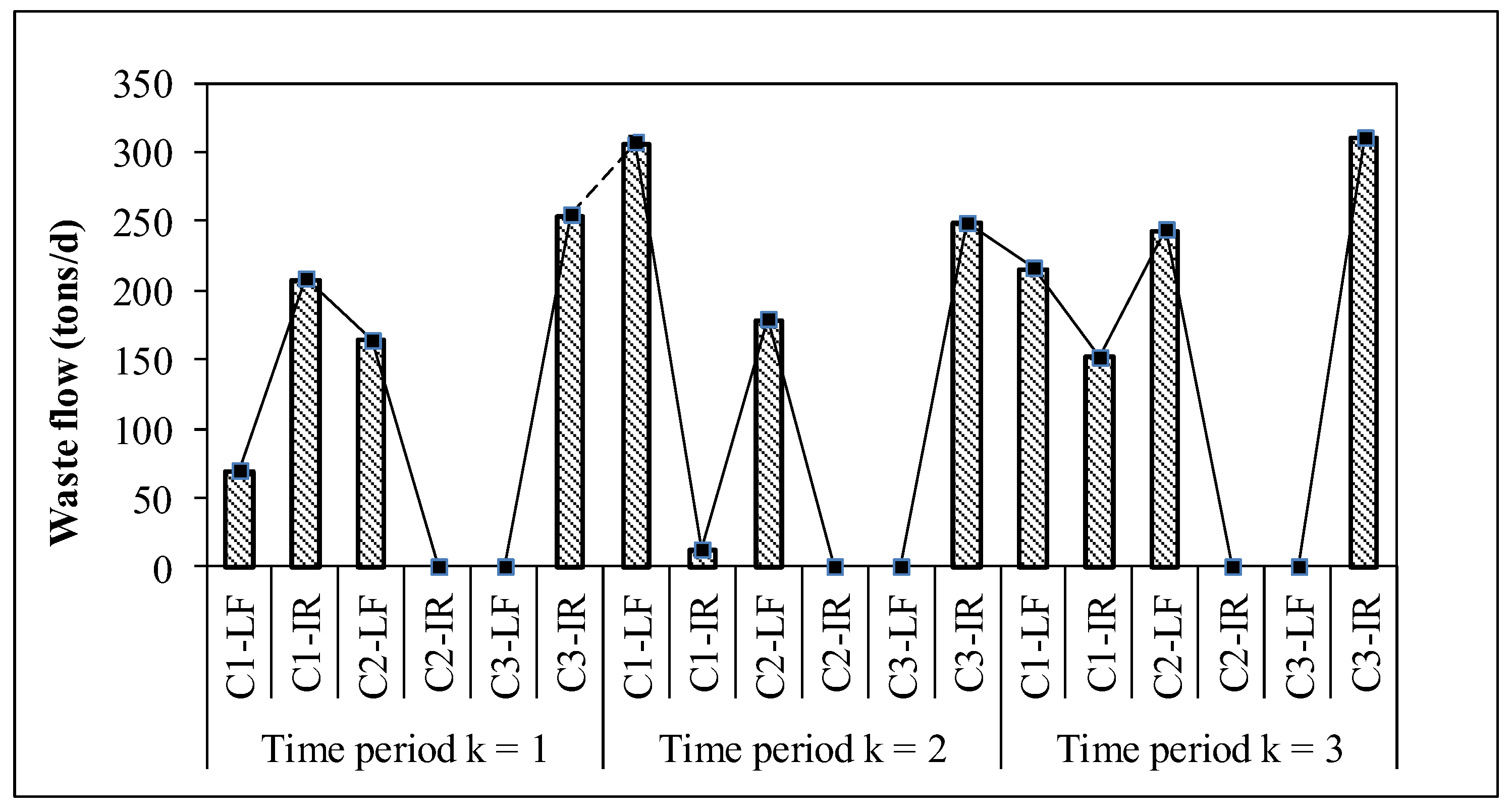
3.2.2. Waste Allocation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Xu, Y.; Huang, G.; Qin, X.; Cao, M. SRCCP: A stochastic robust chance-constrained programming model for municipal solid waste management under uncertainty. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.; Yang, B. An interval-valued fuzzy-stochastic programming approach and its application to municipal solid waste management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 29, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Basak, P. Economic and environmental evaluation of municipal solid waste management system using industrial ecology approach: Evidence from India. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Huang, G.; He, L.; Zeng, G. An inexact dynamic optimization model for municipal solid waste management in association with greenhouse gas emission control. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Jia, R.; Yang, J.; He, S.; Cheng, R. Characterization, quantification and management of China's municipal solid waste in spatiotemporal distributions: A review. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.; Nigam, A. A Mathematical Model for the Optimization of a Waste Management System; SERL Report; University of California at Berkeley, Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Shekdar, A.V.; Bhide, A.D.; Tikekar, A.G. Optimization of route of refuse transportation vehicles. Indian J. Environ. Health. 1987, 1, 1e15. [Google Scholar]
- Baetz, B.W. Optimization/Simulation Modeling for Waste Management Capacity Planning. J. Fuzzy Plan. Dev. 1990, 116, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, I.; Huang, G.H. A Two-Stage Interval-Stochastic Programming Model for Waste Management under Uncertainty. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2003, 53, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.W.; Huang, G.H.; Zeng, G.M.; Maqsood, I.; He, L. An Inexact Two-stage Fuzzy-stochastic Programming Model for Water Resources Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 22, 991–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascione, V.; Mosca, R.; Raggi, A. LCA and linear programming for the environmental optimization of waste management systems: A simulation. In Pathways to Environmental Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Harijani, A.M.; Mansour, S.; Karimi, B. A multi-objective model for sustainable recycling of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Baetz, B.W.; Patry, G.G. Grey fuzzy dynamic programming: Application to municipal solid waste management planning problems. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1994, 11, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.B.; Wang, S.F. A grey fuzzy multiobjective programming approach for the optimal planning of municipal solid waste management systems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 99, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sae-Lim, N.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z. An Interval-Parameter Fuzzy-Stochastic Programming Approach for Municipal Solid Waste Management and Planning. Environ. Model. Assess. 2001, 6, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanat, G. Municipal solid-waste management in Istanbul. Fuzzy Manag. 2010, 30, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G. Interactive two-stage stochastic fuzzy programming for water resources management. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Nie, S. A mathematical model for identifying an optimal waste management policy under uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 2658–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Kankanala, H.R.; Martinsson, R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Uncertainty over techno-economic potentials of biogas from municipal solid waste (MSW): A case study on an industrial process. Appl. Energy 2014, 125, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Huang, G.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y. A duality theorem-based algorithm for inexact quadratic programming problems: Application to waste management under uncertainty. Eng. Optim. 2015, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagoz, S.; Aydin, N.; Isikli, E. Decision-making in Solid Waste Management under Fuzzy Environment. In Intelligence Systems in Environmental Management: Theory and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Huang, G.; Dong, C.; Xu, Y. Distributed mixed-integer fuzzy hierarchical programming for municipal solid waste management. Part I: System identification and methodology development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7236–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Bhurjee, A.; Karmakar, S.; Dikshit, A. A facility location model for municipal solid waste management system under uncertain environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 603, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. The impacts of decision uncertainty on municipal solid waste management. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, H.; Sakawa, M. Interactive fuzzy decision making for generalized multiobjective linear fractional programming problems with fuzzy parameters. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989, 32, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Baetz, B.W.; Patry, G.G. A Grey fuzzy linear programming approach for municipal solid waste management planning under uncertainty. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1992, 10, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciulescu, C.; Fortemps, P.M.; InstalléWertz, V. Multiobjective fuzzy linear programming problems with fuzzy decision variables. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 149, 654–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-F.; Wu, K.-Y. Preference Approach to Fuzzy Linear Inequalities and Optimizations. Fuzzy Optim. Mak. 2005, 4, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fang, H.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Y.-H.; Guo, H.; Zeng, F. Optimal robust position control with input shaping for flexible solar array drive system: A fuzzy-set theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, G.H.; Chan, C.W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Q. A fuzzy-robust stochastic multiobjective programming approach for petroleum waste management planning. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.R.; Huang, G.H.; Veawab, A. A generalized fuzzy linear programming approach for environmental management problem under uncertainty. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, G.; Yang, A. Generalized fuzzy linear programming for decision making under uncertainty: Feasibility of fuzzy solutions and solving approach. Inf. Sci. 2013, 241, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, G.; Jin, L.; Suo, M. Solid waste management under uncertainty: A generalized fuzzy linear programming approach. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2014, 31, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, S.H.; Zavieh, H. A Multi-objective Method for Solving Fuzzy Linear Programming Based on Semi-infinite Model. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 2018, 10, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsmeier, T.J.; Pearson, N.D. Value at Risk. Financ. Anal. 2000, 56, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, A.G.; Zaffaroni, A. Robust optimization of conditional value at risk and portfolio selection. J. Bank. Finance 2008, 32, 2046–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P. Value at risk and tail value at risk in uncertain environment. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Information and Management Sciences, Kunming, China, 20 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Uncertainty Theory; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rockafellar, R.; Uryasev, S. Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J. Bank. Finance 2002, 26, 1443–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.; Arenas, M.; Bilbao, A.; Rodrı´guez, M.V. Linear programming with fuzzy parameters: An interactive method resolution. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 177, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time period | |||
| Operating cost ($/ton) | |||
| (landfill) | (36, 38, 40) | (52, 52.5, 53) | (65, 65.8, 66.6) |
| (incinerator) | (62, 63, 64) | (77, 78, 79) | (86, 86.5, 87) |
| Waste transportation cost ($/ton) | |||
| (17.4, 18.1, 18.8) | (19.3, 19.6, 19.9) | (21.5, 21.8, 22.1) | |
| (15.5, 15.6, 15.7) | (17.6, 17.8, 18) | (21.6, 21.9, 22.2) | |
| (21, 22, 23) | (20.6, 20.8, 21) | (22.7, 22.8, 22.9) | |
| (12.6, 13.3, 14) | (13.6, 14.7, 15.8) | (16.2, 16.5, 16.8) | |
| (13.95, 14, 14.05) | (15.3, 15.5, 15.7) | (16.8, 16.9, 17) | |
| (11.9, 12.1, 12.3) | (12.9, 13.5, 14.1) | (14.3, 14.8, 15.3) | |
| Residue transportation cost from incinerator to landfill ($/ton) | |||
| (6.5, 6.9, 7.3) | (6.6, 7.6, 8.6) | (8.15, 8.4, 8.65) | |
| Time period | ||||
| Waste generation (tons/day) | ||||
| (City 1) | (220, 250, 280) | (380, 400, 420) | (440, 470, 500) | |
| (City 2) | (155, 160, 165) | (244, 254, 264) | (255, 270, 285) | |
| (City 3) | (350, 355, 360) | (335, 350, 365) | (400, 412, 424) | |
| (3.4157, 3.4705, 3.5226) | (3.4164, 3.4714, 3.5236) | (3.4171, 3.4723, 3.5247) | ||
| (3.4437, 3.4985, 3.5504) | (3.4444, 3.4994, 3.5514) | (3.4452, 3.5012, 3.5543) | ||
| (3.4712, 3.5260, 3.5778) | (3.4722, 3.5283, 3.5815) | (3.4731, 3.5307, 3.5853) | ||
| (3.4763, 3.5319, 3.5846) | (3.4770, 3.5328, 3.5857) | (3.4779, 3.5344, 3.5879) | ||
| (3.5043, 3.5599, 3.6125) | (3.5052, 3.5619, 3.6156) | (3.5062, 3.5642, 3.6194) | ||
| (3.5321, 3.5890, 3.6428) | (3.5331, 3.5913, 3.6466) | (3.5340, 3.5937, 3.65.3) | ||
| (3.5673, 3.6242, 3.6780) | (3.5623, 3.6266, 3.6818) | (3.5692, 3.6289, 3.6855) | ||
| (3.5956, 3.6540, 3.7094) | (3.5966, 3.6564, 3.7132) | (3.5975, 3.6587, 3.7169) | ||
| (3.6234, 3.6835, 3.7404) | (3.6245, 3.6858, 3.7442) | (3.6254, 3.6882, 3.7479) | ||
| (3.5825, 3.6400, 3.6942) | (3.5835, 3.6423, 3.6981) | (3.5845, 3.6446, 3.7018) | ||
| (3.6108, 3.6698, 3.7257) | (3.6118, 3.6722, 3.7295) | (3.6397, 3.6745, 3.7332) | ||
| (3.6387, 3.6992, 3.7566) | (3.6397, 3.7016, 3.7604) | (3.6406, 3.7039, 3.7642) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Kong, X.; Zhao, S.; Fan, Y. FCVLP: A Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming Model for Municipal Solid Waste Management. Climate 2019, 7, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7060080
Wang D, Kong X, Zhao S, Fan Y. FCVLP: A Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming Model for Municipal Solid Waste Management. Climate. 2019; 7(6):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7060080
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Donglin, Xiangming Kong, Shan Zhao, and Yurui Fan. 2019. "FCVLP: A Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming Model for Municipal Solid Waste Management" Climate 7, no. 6: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7060080
APA StyleWang, D., Kong, X., Zhao, S., & Fan, Y. (2019). FCVLP: A Fuzzy Random Conditional Value-at-Risk-Based Linear Programming Model for Municipal Solid Waste Management. Climate, 7(6), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7060080





