Temporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature and their Implications on the Streamflow of Rosi River, Central Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
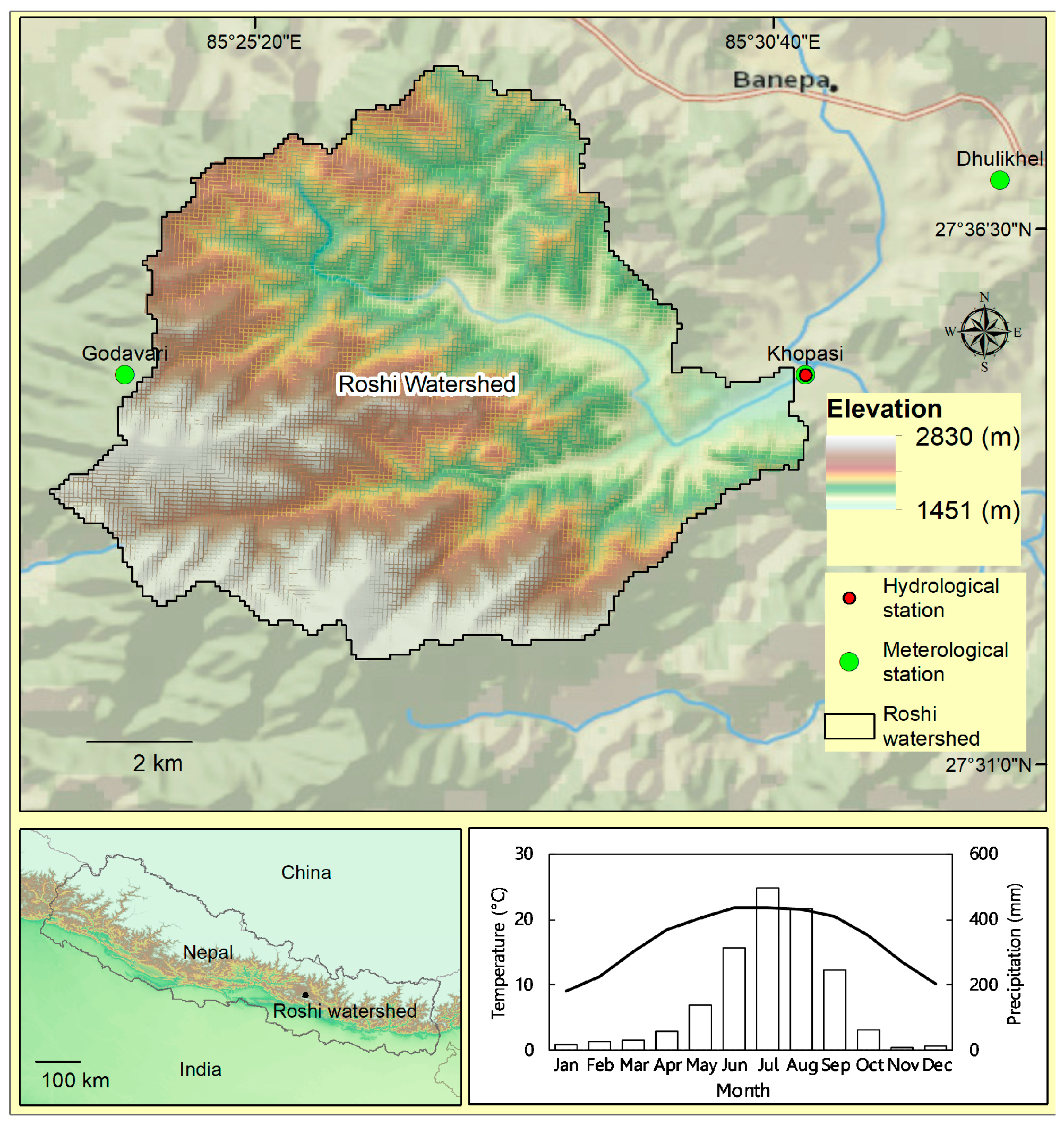
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
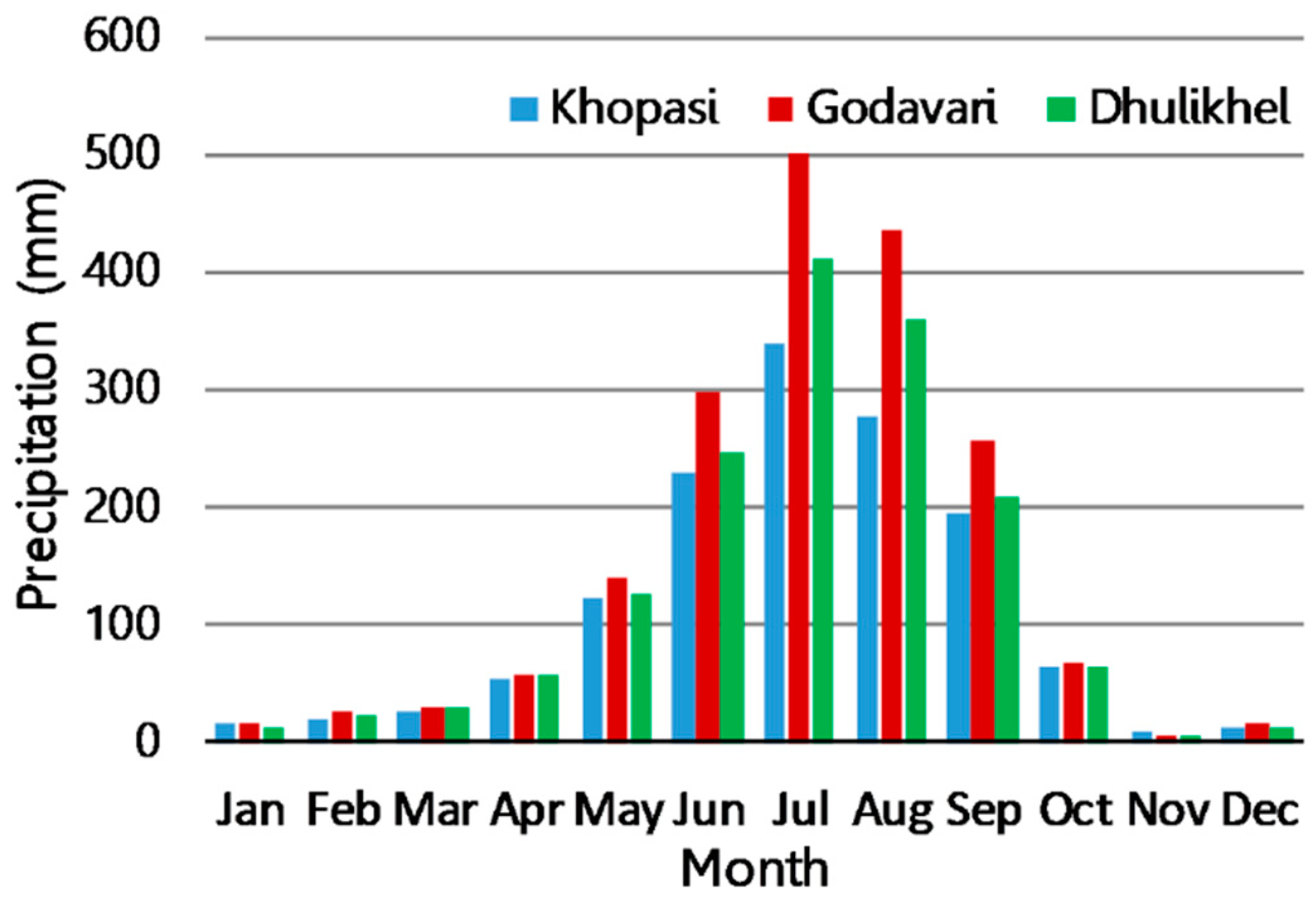
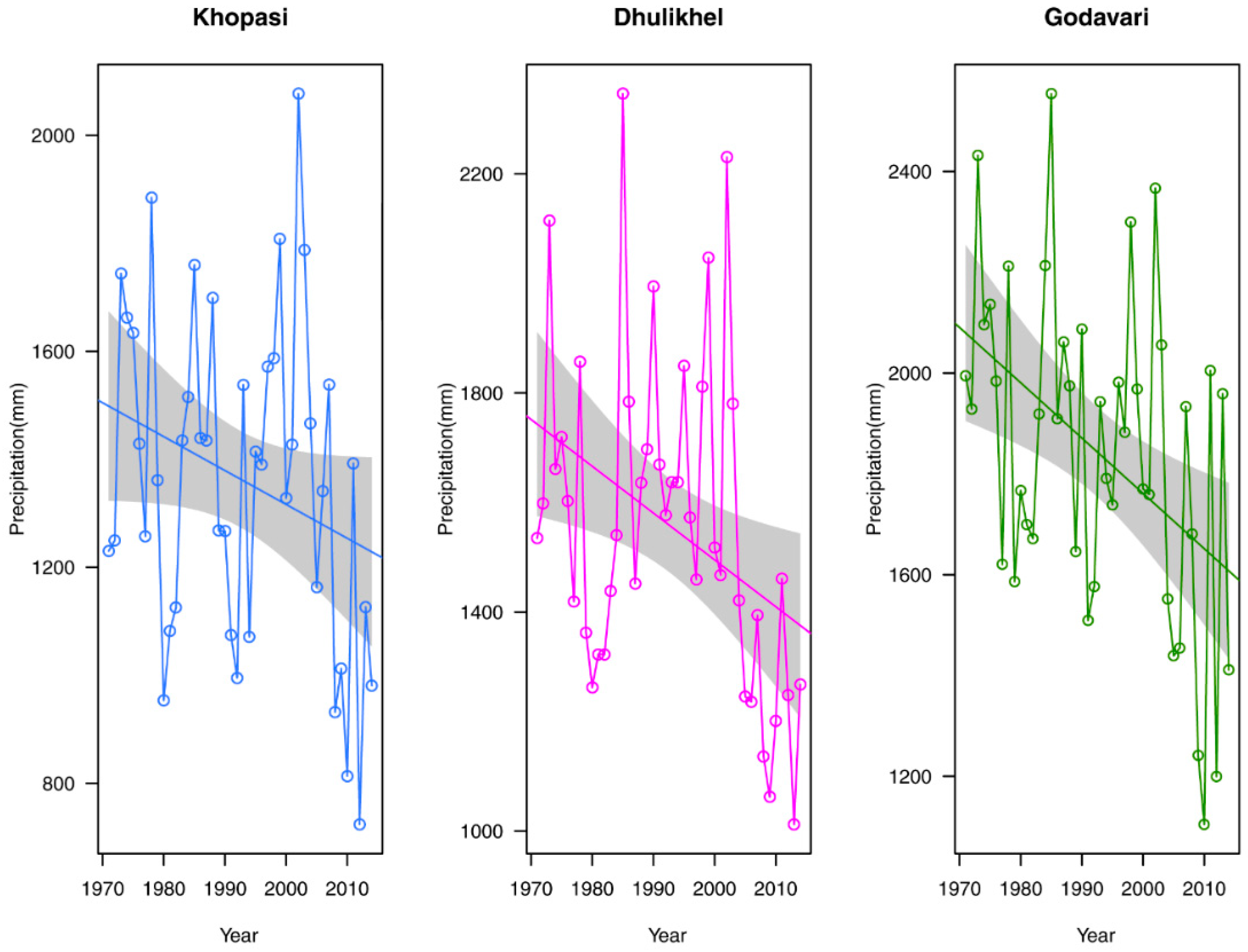
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Precipitation
3.2. Trends in Precipitation Extremes
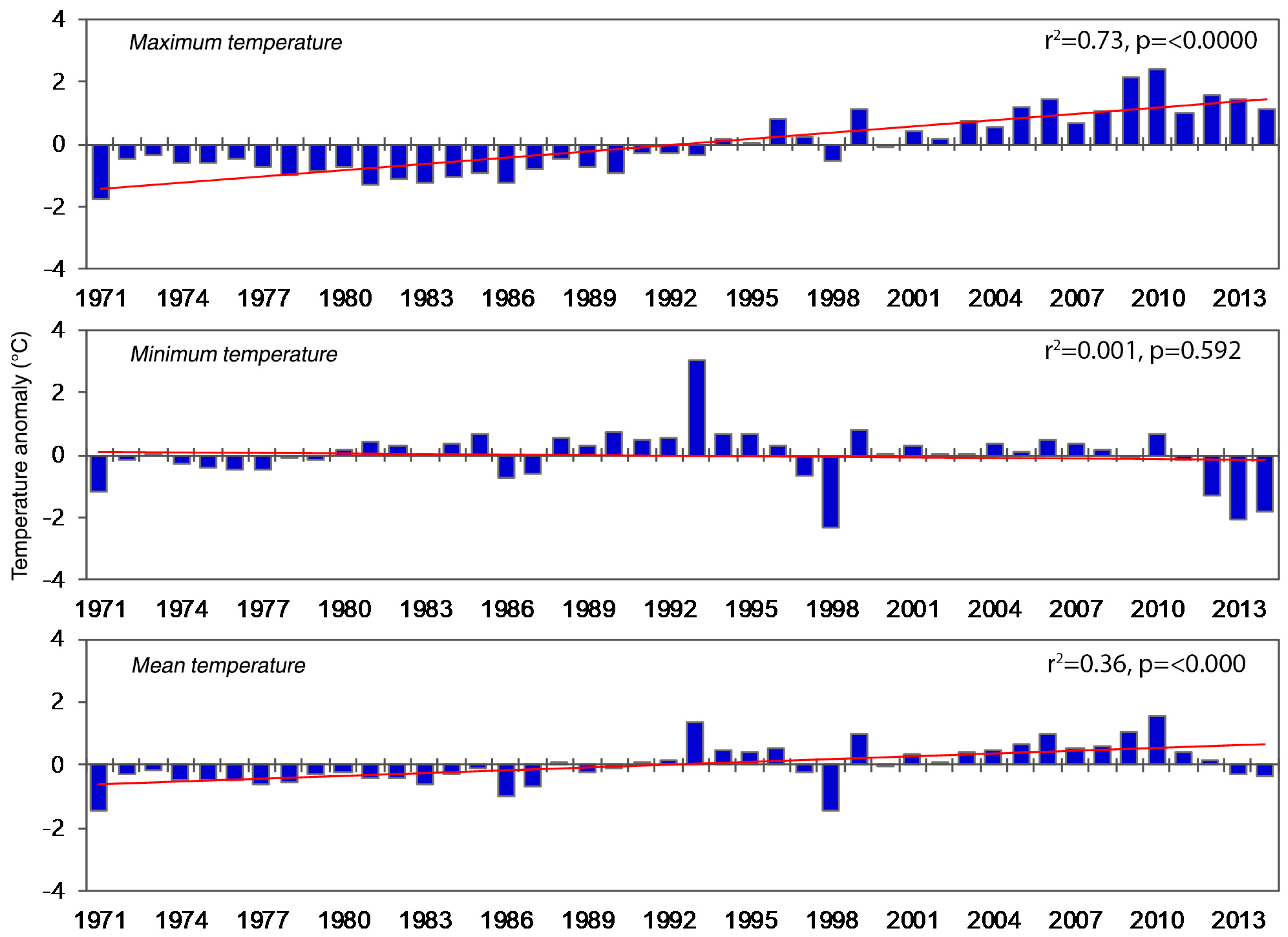
3.3. Temporal Patterns of Temperature
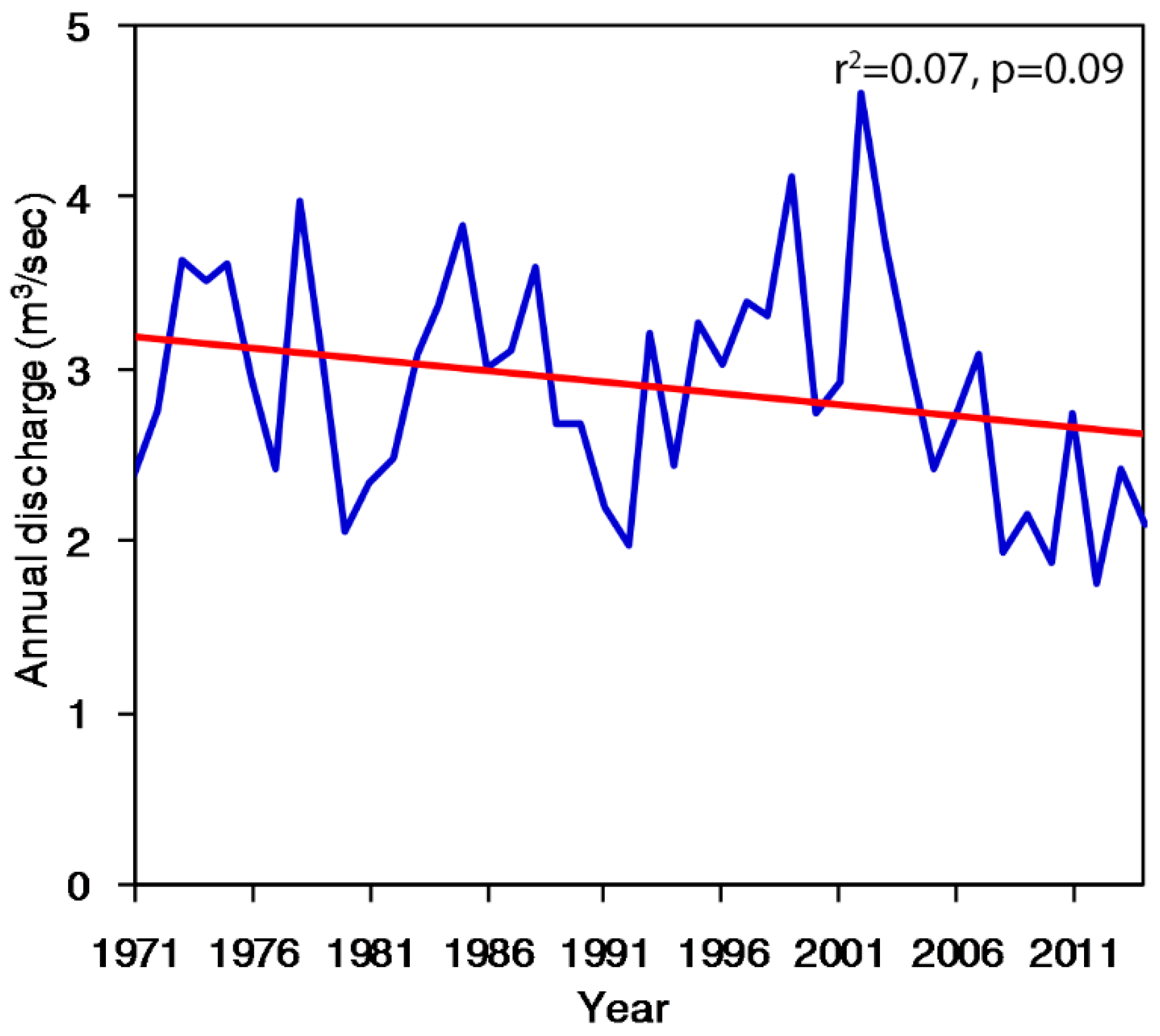
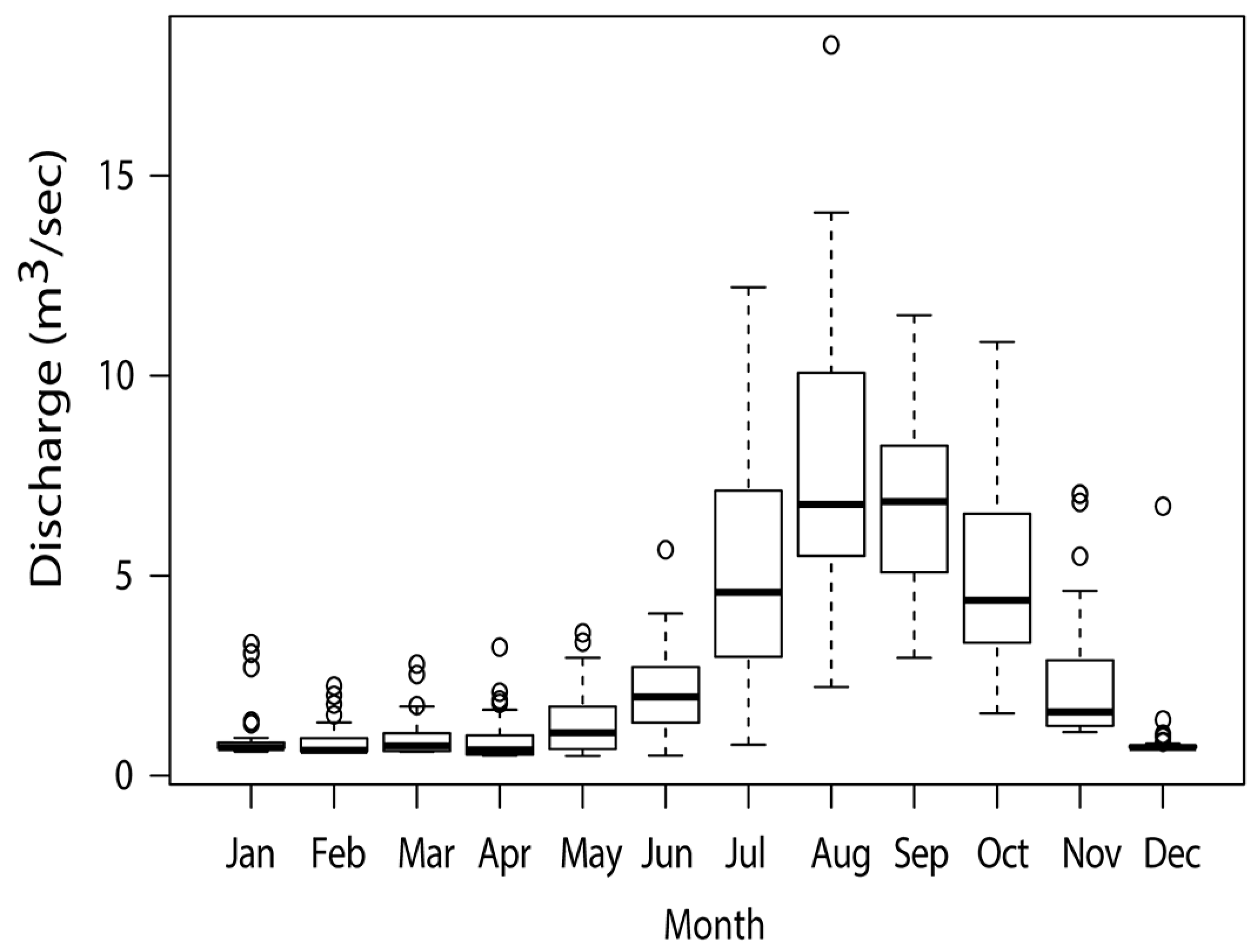
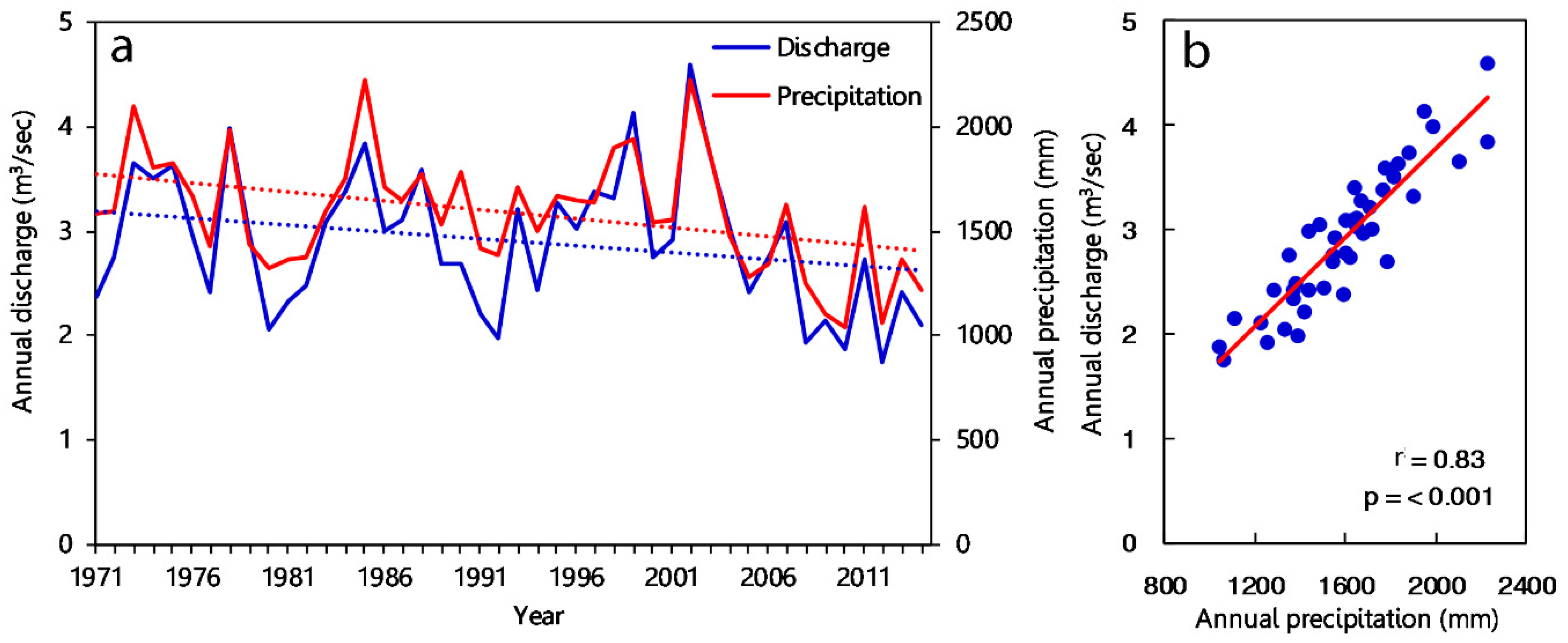
3.4. Hydrological Change and Its Linkage with Precipitation Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnell, N.W.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Isaac, M. The implications of climate policy for the impacts of climate change on global water resources. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P.; De Jong, S.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Large-scale monitoring of snow cover and runoff simulation in Himalayan river basins using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, C.Y.; Beldring, S.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Jain, S.K. Water resources under climate change in Himalayan basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Taylor, R.G.; Xu, Y. Quantifying uncertainty in the impacts of climate change on river discharge in sub-catchments of the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kääb, A.; Huggel, C.; Paul, F.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Kargel, J.S.; Fujita, K.; Scheel, M.; et al. The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science 2012, 336, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.; Bierkens, M.F. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Grumbine, R.E.; Shrestha, A.; Eriksson, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.U.N.; Wilkes, A. The melting Himalayas: Cascading effects of climate change on water, biodiversity, and livelihoods. Conserv. Biol. 2009, 23, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Ahmad, N.; Booij, M.J. The impact of climate change on the water resources of Hindukush–Karakorum–Himalaya region under different glacier coverage scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Aryal, R. Climate change in Nepal and its impact on Himalayan glaciers. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Krause, P.; Flügel, W.A.; Fink, M.; Fischer, C. Understanding the hydrological system dynamics of a glaciated alpine catchment in the Himalayan region using the J2000 hydrological model. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhananga, N.S.; Kayastha, R.B.; Bhattarai, B.C.; Adhikari, T.R.; Pradhan, S.C.; Devkota, L.P.; Shrestha, A.B.; Mool, P.K. Estimation of discharge from Langtang River basin, Rasuwa, Nepal, using a glacio-hydrological model. Ann. Glaciol. 2014, 55, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, H. High and Dry. Kathmandu Post, 21 October 2016. Available online: http://kathmandupost.ekantipur.com/news/2016-10-21/high-and-dry-20161021081608.html (accessed on 14 June 2017).
- Shrestha, U.B.; Gautam, S.; Bawa, K.S. Widespread climate change in the Himalayas and associated changes in local ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.M.; Biggs, E.M.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-temporal trends in precipitation and their implications for water resources management in climate-sensitive Nepal. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 43, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Schickhoff, U.; Scholten, T.; Böhner, J. Rising precipitation extremes across Nepal. Climate 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, D.; Kunzel, V.; Schafer, L. Global Climate Risk Index 2018; Germanwatch e.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2017; Available online: https://germanwatch.org/sites/germanwatch.org/files/publication/20432.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2018).
- The Himalayan Times. Save Water Sources (Editorial). 20 March 2017. Available online: https://thehimalayantimes.com/opinion/editorial-save-water-sources/ (accessed on 16 June 2017).
- Bernet, D. Fleeing Drought D+C Development and Cooperation. 29 April 2013. Available online: https://www.dandc.eu/en/article/climate-change-nepal-entire-villages-must-relocate-because-water-scarcity-getting-worse (accessed on 16 June 2017).
- Tao, H.; Gemmer, M.; Bai, Y.; Su, B.; Mao, W. Trends of streamflow in the Tarim River Basin during the past 50 years: Human impact or climate change? J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Charles, S.P.; Viney, N.R.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.Q. Impacts of climate variability on stream-flow in the Yellow River. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2007, 21, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qiang, H.; Jianxia, C.; Dengfeng, L.; Shengzhi, H.; Xiaoyu, S. Analysis of temporal and spatial trends of hydro-climatic variables in the Wei River Basin. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.R.; Acharya, K. Streamflow trends in Nepal. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Konz, M.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Hydrological response to climate change in a glacierized catchment in the Himalayas. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthi, J.; Dahal, P.; Shrestha, M.L.; Aryal, S.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Lakhankar, T.; Jha, A.; Sharma, M.; Karki, R. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall in the Gandaki River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Climate 2015, 3, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, K.R.; Panthi, J.; Shrestha, M.L.; Nepal, S. Hydro-climatic variability in the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Climate 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, M.; Babel, M.S. Modelling the potential impacts of climate change on hydrology and water resources in the Indrawati River Basin, Nepal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S. Impacts of climate change on the hydrological regime of the Koshi river basin in the Himalayan region. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Babel, M.S.; Maskey, S. Analysis of future precipitation in the Koshi river basin, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, L.P.; Gyawali, D.R. Impacts of climate change on hydrological regime and water resources management of the Koshi River Basin, Nepal. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.H.; Shakya, N.M. Hydrological changes and its impact on water resources of Bagmati watershed, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, M.S.; Bhusal, S.P.; Wahid, S.M.; Agarwal, A. Climate change and water resources in the Bagmati River Basin, Nepal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, V.; Shakya, N.M.; Bhattarai, R. Estimating the impact of climate change on water availability in Bagmati Basin, Nepal. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, R.P.; White, J.D.; Alexander, S.E. Projected hydrologic changes in monsoon-dominated Himalaya Mountain basins with changing climate and deforestation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWIDP. Hydrological Study and Data Collection of Rosi River Catchment; A Technical Report of Department of Water Induced Disaster Prevention; Government of Nepal and Recham Consulting Pvt Ltd.: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2011.
- Costa, A.C.; Soares, A. Trends in extreme precipitation indices derived from a daily rainfall database for the South of Portugal. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1956–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.; Folland, C.; Gruza, G.; Hogg, W.; Mokssit, A.; Plummer, N. Report on the Activities of the Working Group on Climate Change Detection and Related Rapporteurs; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 3, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, Y.; Shrestha, U.B.; Rokaya, M.B.; Shrestha, S.; Chaudhary, R.P.; Thakali, A.; Cockfield, G.; Asselin, H. Perceptions of climate change by highland communities in the Nepal Himalaya. Clim. Dev. 2017, 9, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). National Climate Change Impact Survey 2016; A Statistical Report; Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2017.
- Practical Action. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Climate Change over Nepal (1976–2005); Practical Action Nepal Office: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Merz, J.; Dangol, P.M.; Dhakal, M.P.; Dongol, B.S.; Nakarmi, G.; Weingartner, R. Rainfall-runoff events in a middle mountain catchment of Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, O.; Gassmann, M.; Wegerich, K.; Bauer, M. Identification of the effective water availability from streamflows in the Zerafshan river basin, Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 390, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gong, T.; Uygen, T. Comparative analysis of hydroclimatic changes in glacier-fed rivers in the Tibet-and Bhutan-Himalayas. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Bonell, M.; Dorninger, M.; Goodrich, D.; Gutknecht, D.; Matamoros, D.; Merz, B.; Shand, P.; Szolgay, J. At what scales do climate variability and land cover change impact on flooding and low flows? Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2007, 21, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, W. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the surface runoff in the Tarim River Basin over the last fifty years. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, C.P.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Lubczynski, M.W.; Bonell, M. Rainfall interception by natural and planted forests in the Middle Mountains of Central Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Futter, N.; Bishop, K. On the forest cover–water yield debate: From demand-to supply-side thinking. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICIMOD (International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development). Land cover of Nepal 2010. Available online: http://rds.icimod.org/Home/DataDetail?metadataId=9224 (accessed on 3 March 2016).
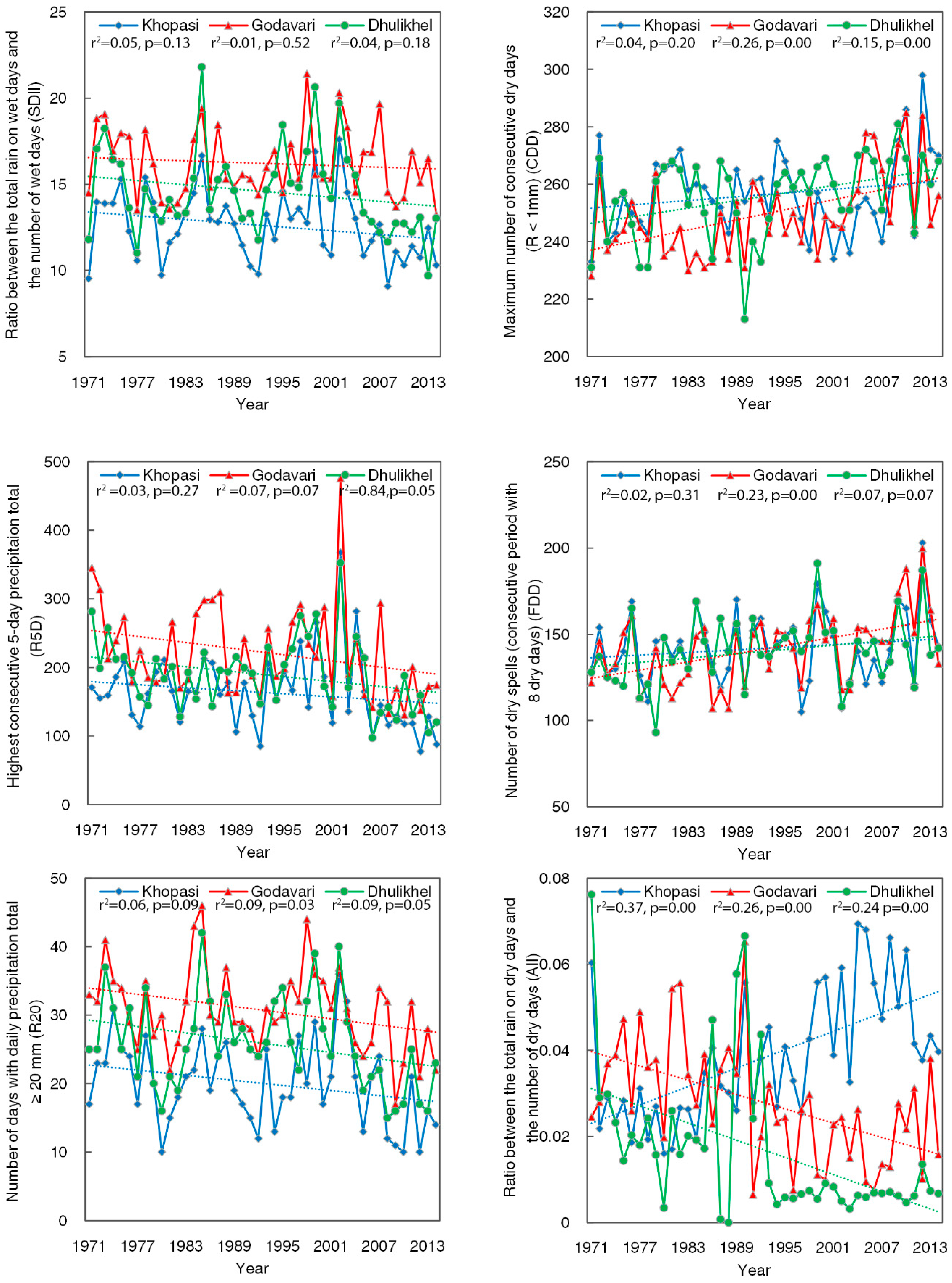
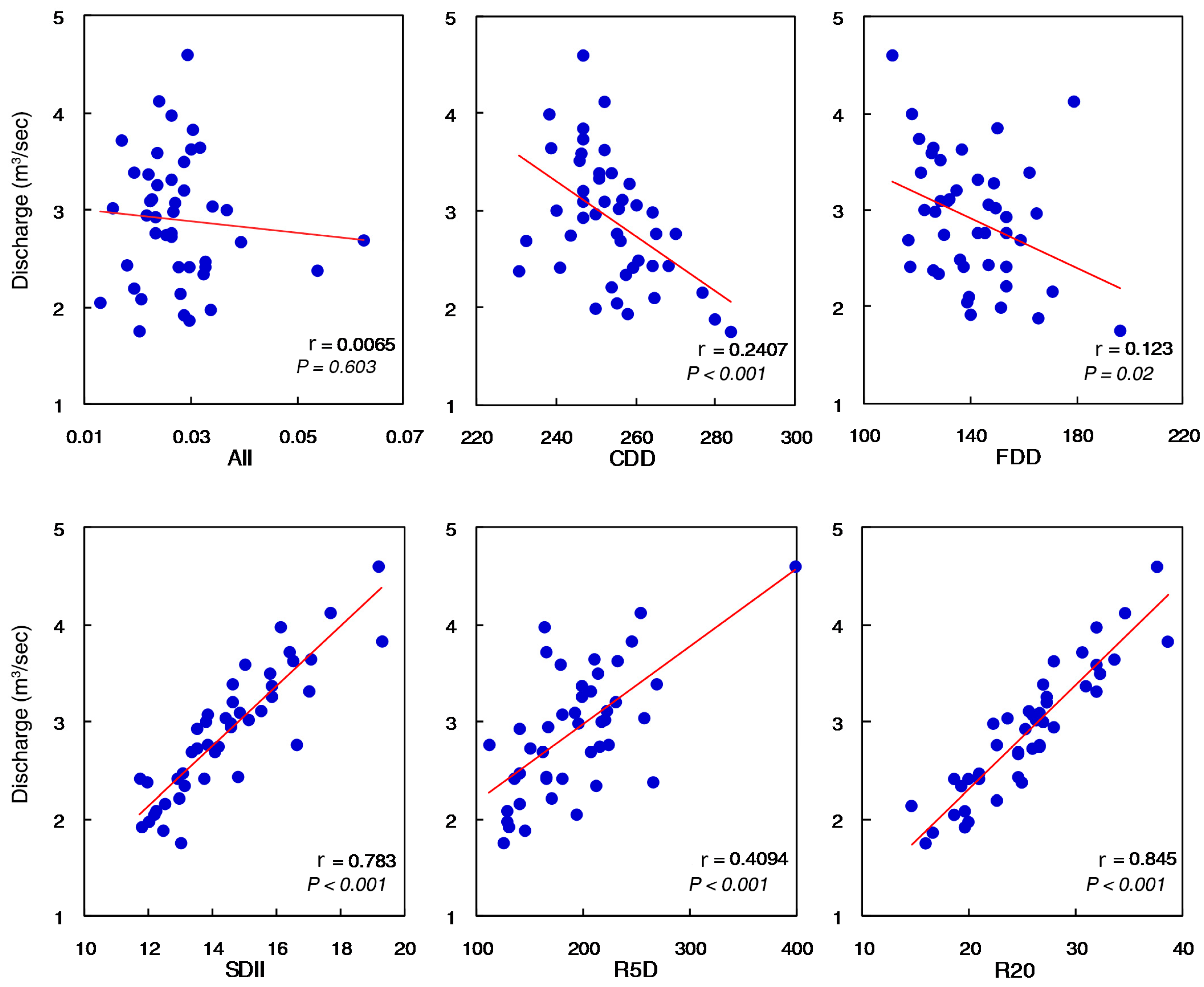
| Indices | Name | Definition | Method of Calculation | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R5D | Number of heavy rainfall days | Annual count of days when days rainfall ≥five mm | RRij ≥ five mm | Days |
| R20 | Number of very heavy rainfall days | Annual count of days when days rainfall ≥ 20 mm | RRij ≥ 20 mm | Days |
| SDII | Simple daily intensity index | Annual mean rainfall when Precipitation ≥one mm | Days | |
| CDD | Maximum length of dry spell | Maximum number of consecutive days with RR <one mm | RRij < one mm | Days |
| FDD | Number of dry spells | Consecutive period with at least eight dry days | R < one mm | Frequency |
| AII | Aridity index | Ratio between the total rain on dry days and the number of dry days | Total rain on days with (R < 10 mm)/number of days with R < 10 mm | mm |
| Weather Stations | Annual | Pre-Monsoon | Monsoon | Post-Monsoon | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khopasi | −6.296 | 0.300 | −6.260 * | −0.386 | −0.215 |
| Godavari | −10.435 * | 0.501 | −10.358 * | −0.207 | −0.117 |
| Dhulikhel | −9.122 * | −0.349 | −7.120 * | −0.922 | −0.162 |
| Khopasi | Godavari | Dhulikhel | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AII | 0.0007 *** | −0.0005 *** | 0.0004 *** |
| CDD | 0.0001 | 0.148 *** | 0.537 *** |
| FDD | 0.250 | 0.707 ** | 0.375 |
| SDII | −0.047 ** | −0.018 | −0.041 * |
| R5D | −1.125 ** | −1.452 ** | −1.363 ** |
| R20 | −0.143 * | −0.149 * | −0.167 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahal, N.; Shrestha, U.B.; Tuitui, A.; Ojha, H.R. Temporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature and their Implications on the Streamflow of Rosi River, Central Nepal. Climate 2019, 7, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010003
Dahal N, Shrestha UB, Tuitui A, Ojha HR. Temporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature and their Implications on the Streamflow of Rosi River, Central Nepal. Climate. 2019; 7(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahal, Ngamindra, Uttam Babu Shrestha, Anita Tuitui, and Hemant Raj Ojha. 2019. "Temporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature and their Implications on the Streamflow of Rosi River, Central Nepal" Climate 7, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010003
APA StyleDahal, N., Shrestha, U. B., Tuitui, A., & Ojha, H. R. (2019). Temporal Changes in Precipitation and Temperature and their Implications on the Streamflow of Rosi River, Central Nepal. Climate, 7(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli7010003






