Mapping Open Data and Big Data to Address Climate Resilience of Urban Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
1. Mapping Open and Big Data in African Cities
1.1. Urban Expansion in African Countries and Its Influence on Informal Settlements
1.2. The Value of Open and Big Data for Fostering Information Processes
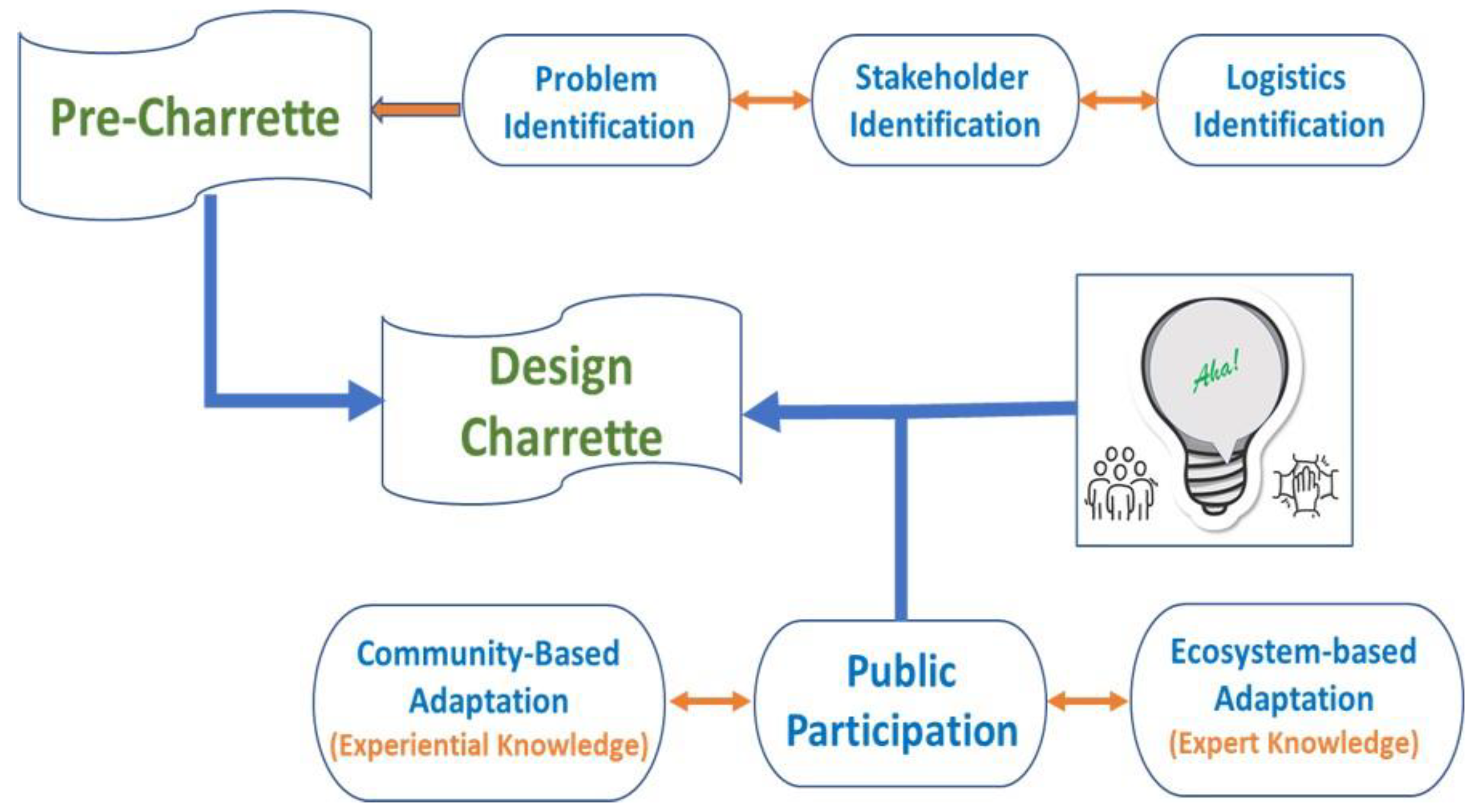
2. The Dreams Project
Charrette Approach
3. Open Data and Big Data as Spatial Information Strategy
3.1. Technical Considerations
3.2. Benefits of Global EO Data for Urban Research
3.3. Barriers in EO Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Revision of World Population Prospects. 2022. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/ (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- UNSTATS. The Sustainable Development Goals Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2019/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2019.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Inkoom, J.N.; Frank, S.; Greve, K.; Fürst, C. A framework to assess landscape structural capacity to provide regulating ecosystem services in West Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleemann, J.; Inkoom, J.N.; Thiel, M.; Shankar, S.; Lautenbach, S.; Fürst, C. Peri-urban land use pattern and its relation to land use planning in Ghana, West Africa. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.C.; Lynch, R.; Boakye-Achampong, S.; Jowaisas, C.; Sam, J.; Norlander, B. Volunteer geographic information in the Global South: Barriers to local implementation of mapping projects across Africa. GeoJournal 2020, 86, 2227–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georganos, S. The Use of Very-High-Resolution Earth Observation Satellite Data for Multi-Thematic Urban Mapping in Sub-Saharan Africa. Applications in Population, Household Wealth and Epidemiological Modeling. Thesis. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348686518_The_use_of_very-high-resolution_earth_observation_satellite_data_for_multi-thematic_urban_mapping_in_sub-Saharan_Africa_Applications_in_population_household_wealth_and_epidemiological_modeling (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- World Wide Web Foundation. Open Data Barometer—Leaders Edition; World Wide Web Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2022a; Available online: https://opendatabarometer.org/4thedition/regional-snapshot/sub-saharan-africa/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Morgner, C.; Ambole, A.; Anditi, C.; Githira, D. Exploring the Dynamics of Social Networks in Urban Informal Settlements: The Case of Mathare Valley, Kenya. Urban Forum 2020, 31, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, B.M.; Cobbinah, P.B. African urbanisation at the confluence of informality and climate change. Urban Stud. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDESA. Revision of World Urbanization Prospects. 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/publications/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Pesaresi, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Siragusa, A.; Kemper, T. Atlas of the Human Planet–Mapping Human Presence on Earth with the Global Human Settlement Layer; JRC103150; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016; European Commission, DG JRC. [Google Scholar]
- Simiyu, S.; Cairncross, S.; Swilling, M. Understanding Living Conditions and Deprivation in Informal Settlements of Kisumu, Kenya. Urban Forum 2019, 30, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Kidokoro, T. Understanding the development patterns of informal settlements in Nairobi. Jpn. Arch. Rev. 2020, 3, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, T.K.; Khirfan, L. Community-based adaptation through ecological design: Lessons from Negril, Jamaica. J. Urban Des. 2016, 21, 234–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Scientific Accomplishments of Earth Observations from Space, National Research Council. Earth Observations from Space: The First 50 Years of Scientific Achievements; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 6. ISBN 978-0-309-11095-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wide Web Foundation. Open Data Barometer—Leaders Edition; World Wide Web Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://opendatabarometer.org (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- BMI. Open-Data-Strategie der Bundesregierung. 2021. Available online: https://www.bmi.bund.de/SharedDocs/downloads/DE/publikationen/themen/moderne-verwaltung/open-data-strategie-der-bundesregierung.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=3 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- European Commission. A European Strategy for Data. 2020. Available online: https://www.assonime.it/Stampa/Documents/SWD_2022_45_1_EN_document_travail_service_part1_v2_tI7BgzIxTJOGvsQzZVHacn6IEVE_83562%20%281%29.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Joubert, A.; Murawski, M.; Bick, M. Big Data Readiness Index—Africa in the Age of Analytics. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society (I3E), Trondheim, Norway, 18–20 September 2019; pp. 101–112. Available online: https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02510093/document (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Wang, X.; Rafa, M.; Moyer, J.D.; Li, J.; Scheer, J.; Sutton, P. Estimation and Mapping of Sub-National GDP in Uganda Using NPP-VIIRS Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, R.; Alexandridis, T.; Amponsah, M.; Ben Khatra, N.; Brockington, D.; Chiconela, T.; Castillo, J.O.; Garba, I.; Gómez-Giménez, M.; Haile, M.; et al. Developing capacity for impactful use of Earth Observation data: Lessons from the AfriCultuReS project. Environ. Dev. 2022, 42, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmugl, M.; Gallaun, H.; Dees, M.; Datta, P.; Deutscher, J.; Koutsias, N.; Schardt, M. Methods for Mapping Forest Disturbance and Degradation from Optical Earth Observation Data: A Review. Curr. For. Rep. 2017, 3, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Lopez, D.; Bachofer, F.; Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Marconcini, M.; Sorichetta, A.; Zeidler, J.; Kuenzer, C.; Dech, S.; et al. New Perspectives for Mapping Global Population Distribution Using World Settlement Footprint Products. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y. Investigating the effects of 3D urban morphology on the surface urban heat island effect in urban functional zones by using high-resolution remote sensing data: A case study of Wuhan, Central China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunyewah, M.; Gajendran, T.; Maund, K. Profiling Informal Settlements for Disaster Risks. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Yokoya, N.; Wang, Q.M.; Hofle, B.; Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F.; Chi, M.M.; Anders, K.; Gloaguen, R.; et al. Multisource and multitemporal data fusion in remote sensing a comprehensive review of the state of the art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 6–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, J.; Frei, C.; Vidale, P.L. Downscaling from GCM precipitation: A benchmark for dynamical and statistical downscaling methods. Int. J. Clim. 2006, 26, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, Y.; Yang, Z. Dynamical downscaling of regional climate: A review of methods and limitations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 62, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T.K.-A. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multisource Remote Sensing Data: Literature Survey, Taxonomy, Principles, Applications, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjya, D.P.; Kauser, A.P. A survey on big data analytics: Challenges, open research issues and tools. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Earth Observation Hub | Data Description | Resolution | Illustration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal [yrs.] | Spatial [m] | No. of Categories | ||||
| 1 | ESA World cover | ESA https://worldcover2020.esa.int (accessed on 26 September 2022) | It is a very high-resolution 11-class land cover map. | 2020 | 10 | 11 | Cape Town |
| 2 | Copernicus Global Land Service: Land Cover | ESA https://land.copernicus.eu/global/products/lc (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The Climate Change Initiative Land Cover (CCI-LC) consists of a time series of 23-class land cover maps on an annual basis. | 2015–2019 | 100 | 23 | Accra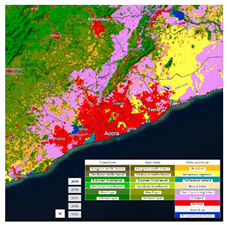 |
| 3 | GlobeLand 30 | Ministry of Natural Resources, China http://www.globallandcover.com (accessed on 26 September 2022) | It is a high-resolution 10-class land cover map. | 2000, 2010, 2020 | 30 | 10 | Kampala |
| 4 | Climate Change Initiative Land Cover (CCI-LC) https://www.esa-landcover-cci.org/?q=node/164 (accessed on 26 September 2022) | A new time series of consistent global LC maps at 300 m spatial resolution on an annual basis | 1992–2019 | 300 | 23 | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town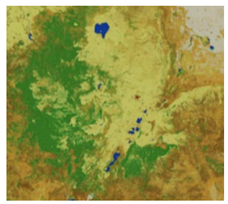 |
| 5 | Africa LC http://maps.elie.ucl.ac.be/CCI/viewer/index.php (accessed on 26 September 2022) | Represents a prototype high resolution LC map at 20m over Africa based on 1 year of Sentinel-2A observations from December 2015 to December 2016 | 2015–2016 | 20 | 38 | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town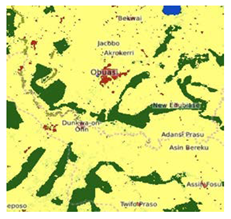 |
| 6 | ESRI LC https://www.arcgis.com/apps/instant/media/index.html?appid=fc92d38533d440078f17678ebc20e8e2 (accessed on 26 September 2022) | It provides access to individual 10-meter resolution GeoTIFF scenes for all land masses on the planet, for each year from 2017-2021 | 2017–2021 | 10 | 9 | Global |
| 7 | ESA WorldCover https://viewer.esa-worldcover.org/worldcover/ (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The product provides a global land cover map for 2020 at 10 m resolution based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data | 2000 | 10 | 11 | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town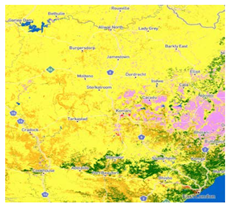 |
| 8 | AFRICOVER https://data.review.fao.org/map/catalog/srv/api/records/22eeb8b6-0158-4be3-a35f-be19e51516b8 (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The full resolution dataset of towns was developed from data from the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA | 1999 | 30 | 23 | Accra, Kampala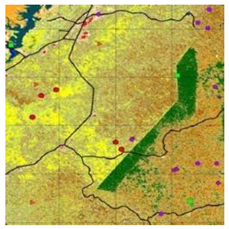 |
| Earth Observation Hub | Data Description | Resolution | Illustration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal [yrs.] | Spatial [m] | No. of Categories | ||||
| 1 | World Settlement Footprint Evolution | DLR https://geoservice.dlr.de/web/maps/eoc:wsfevolution (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The World Settlement Footprint (WSF) Evolution is a 30m resolution dataset outlining the global settlement extent on a yearly basis from 1985 to 2015. | 1985–2015 | 30 | 2 | Kampala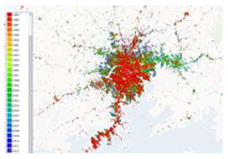 |
| 2 | World Settlement Footprint | DLR https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Mapping_our_human_footprint_from_space (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The World Settlement Footprint (WSF) 2019 is a 10m resolution binary mask outlining the extent of human settlements globally derived by means of 2019 multitemporal Sentinel-1 (S1) and Sentinel-2 (S2) imagery. | 2015 & 2019 | 10 | 2 | Accra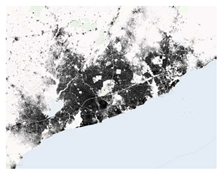 |
| 3 | GHSL - Global Human Settlement Layer https://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/visualisation.php# (accessed on 26 September 2022) | Open and free data and tools for assessing the human presence on the planet. Data created using satellite, in situ (ground) and model data | 1975–2030 | 20 | 12 | |
| 4 | Building Footprints https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/maps/building-footprints (accessed on 26 September 2022) | Building footprints derived with the aid of ML algorithms on available satellite imagery. | 2020–2021 | - | - | Kampala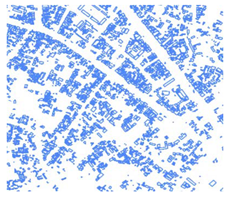 |
| 5 | Open Buildings https://sites.research.google/open-buildings/#download (accessed on 26 September 2022) | This data repository contains an outline of buildings derived from high-resolution satellite imagery. Building footprints are useful for population estimation, urban planning and humanitarian response. | 2021 | - | - | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town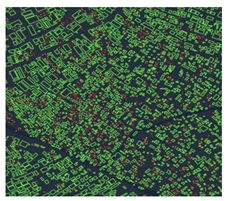 |
| 6 | Open Street Map | Citizen Science https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 26 September 2022) | OpenStreetMap is a map of the world, created by people and freely available | 2022 | 0.04–1000 | >300 | Cape Town |
| Earth Observation Hub | Data Description | Resolution | Illustration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal [yrs.] | Spatial [m] | No. of Categories | ||||
| 1 | Global Urban Heat Island (UHI) | Columbia Universityhttps://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/set/sdei-global-uhi-2013/ (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The product provides a global data set of average summer daytime maximum/nighttime minimum land surface temperatures (LSTs) for urban extents, as well as the LST difference between the urban area and the buffer. | 2013 | 1000 | 4 | Cape Town |
| 2 | Global Surface UHI Explorer | T. Chakraborty, X. Lee (University Yale) https://yceo.yale.edu/research/global-surface-uhi-explorer (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The Global Surface UHI Explorer is an interactive web app to monitor urban heat island (UHI) intensities of practically all urban clusters on Earth. The app is built on the Google Earth Engine platform and allows users to query the UHI data of urban areas using a simple interface. | 2003–2018 | 300 | 6 | Kampala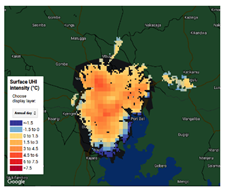 |
| 3 | Digital Earth Africa https://docs.digitalearthafrica.org/en/latest/sandbox/notebooks/Datasets/Digital_Elevation_Models.html (accessed on 26 September 2022) | A collection of four DEM product available from the Open Data Cube. The Copernicus products come from the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) products | >2000 | 30–90 | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town | |
| 4 | Stellenbosch University Digital Elevation Model (SUDEM) https://geosmart.space/products/sudem.html (accessed on 26 September 2022) | The 5 m SUDEM, branded as SUDEM5, is currently the highest resolution DEM covering South Africa | 5 | Cape Town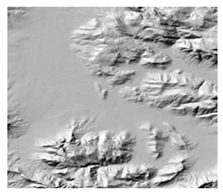 | ||
| 5 | VIIRS Night Lights | Suomi NPP |Satellite Data https://viirsland.gsfc.nasa.gov/Products/NASA/BlackMarble.html (accessed on 26 September 2022) | It is a daily, top-of-atmosphere, at-sensor nighttime radiance product. The product contains 26 Science Data Sets | since 2013 | 500 | - | Accra |
| Earth Observation Hub | Data Description | Resolution | Illustration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal [yrs.] | Spatial [m] | No. of Categories | ||||
| 1 | Gridded Population of the World (GPW), v4 | Center for International Earth Science Information Network | Population Statistics https://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/gpw-v4/sets/browse (accessed on 26 September 2022) | To provide estimates of population density and count for the years 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, based on counts consistent with national censuses and population registers | 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 | 1000 | 2 |  |
| 2 | High Resolution Population Density Maps https://data.humdata.org/ (accessed on 26 September 2022) | Humanitarian data created to respond to humanitarian emergency crises | ||||
| 3 | AfriPolis https://africapolis.org/en/data?country=Angola&keyfigure=totalPop&type=abs&year=2015 (accessed on 26 September 2022) | Africapolis data is based on a large inventory of housing and population censuses, electoral registers and other official population sources | 1950–2015 | - | 2 | Accra, Kampala, Cape Town |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banzhaf, E.; Bulley, H.N.; Inkoom, J.N.; Elze, S. Mapping Open Data and Big Data to Address Climate Resilience of Urban Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa. Climate 2022, 10, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10120186
Banzhaf E, Bulley HN, Inkoom JN, Elze S. Mapping Open Data and Big Data to Address Climate Resilience of Urban Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa. Climate. 2022; 10(12):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10120186
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanzhaf, Ellen, Henry N. Bulley, Justice Nana Inkoom, and Sebastian Elze. 2022. "Mapping Open Data and Big Data to Address Climate Resilience of Urban Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa" Climate 10, no. 12: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10120186
APA StyleBanzhaf, E., Bulley, H. N., Inkoom, J. N., & Elze, S. (2022). Mapping Open Data and Big Data to Address Climate Resilience of Urban Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan Africa. Climate, 10(12), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10120186







