Ginkgo biloba L. Leaf Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
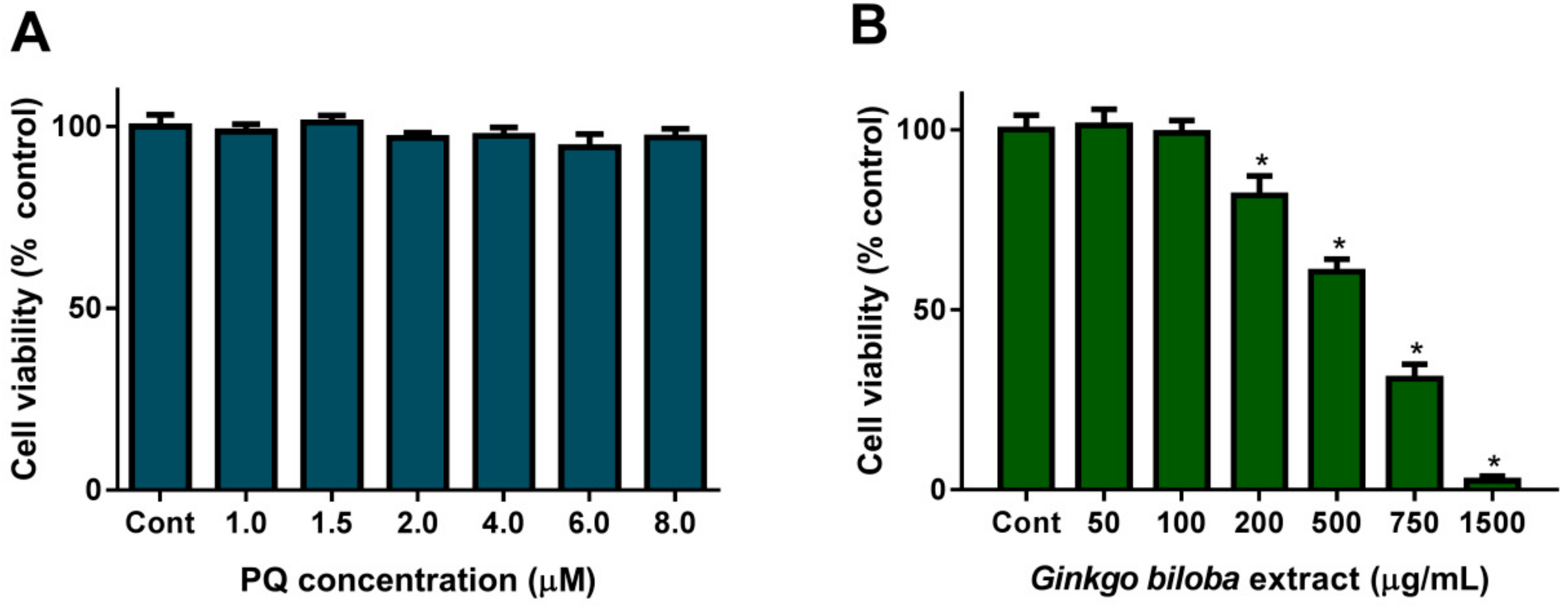
2.1. Cell Viability upon PQ or G. biloba Extract Exposure
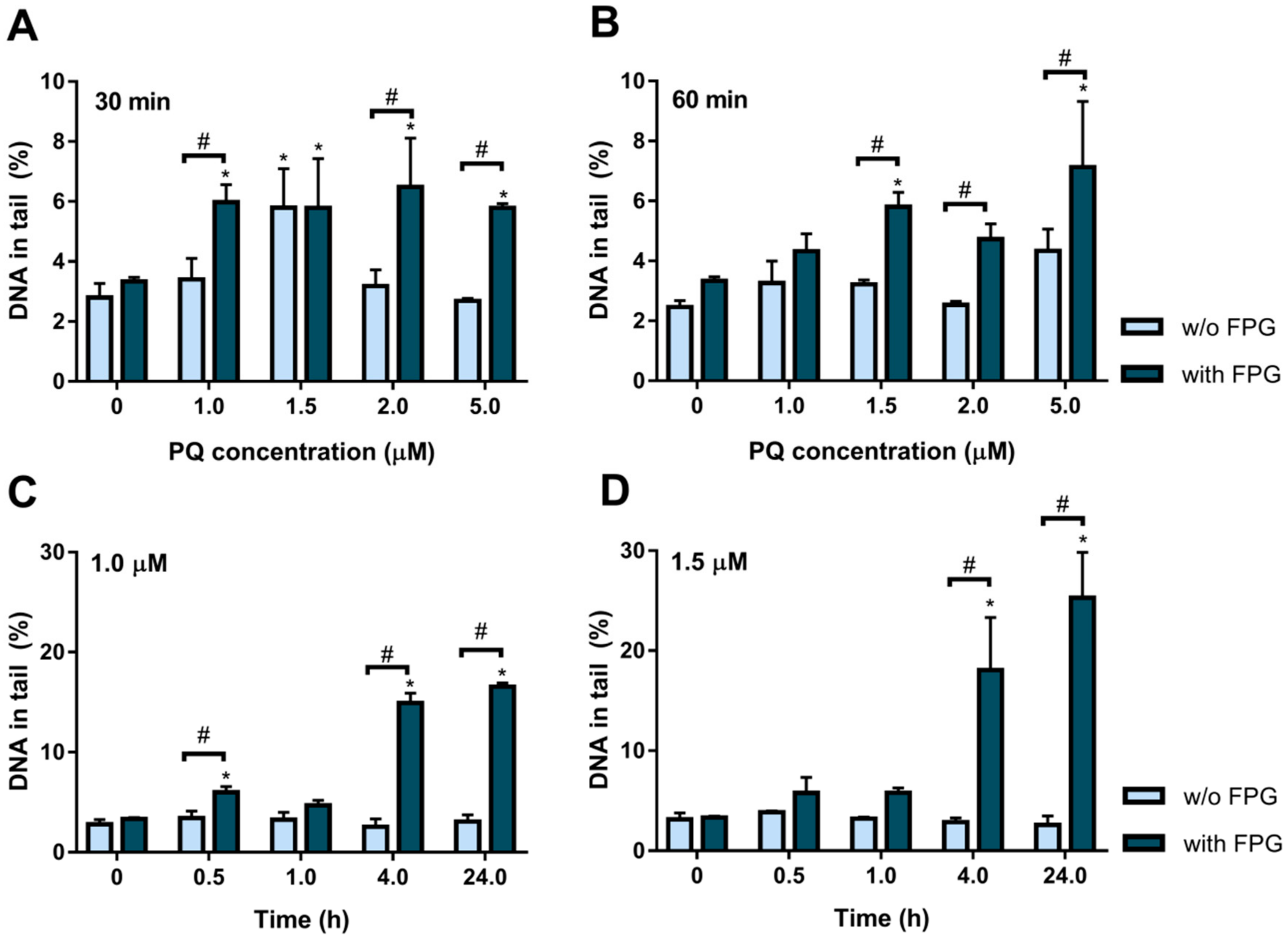
2.2. Paraquat Induces DNA Damage in HepG2 Cells
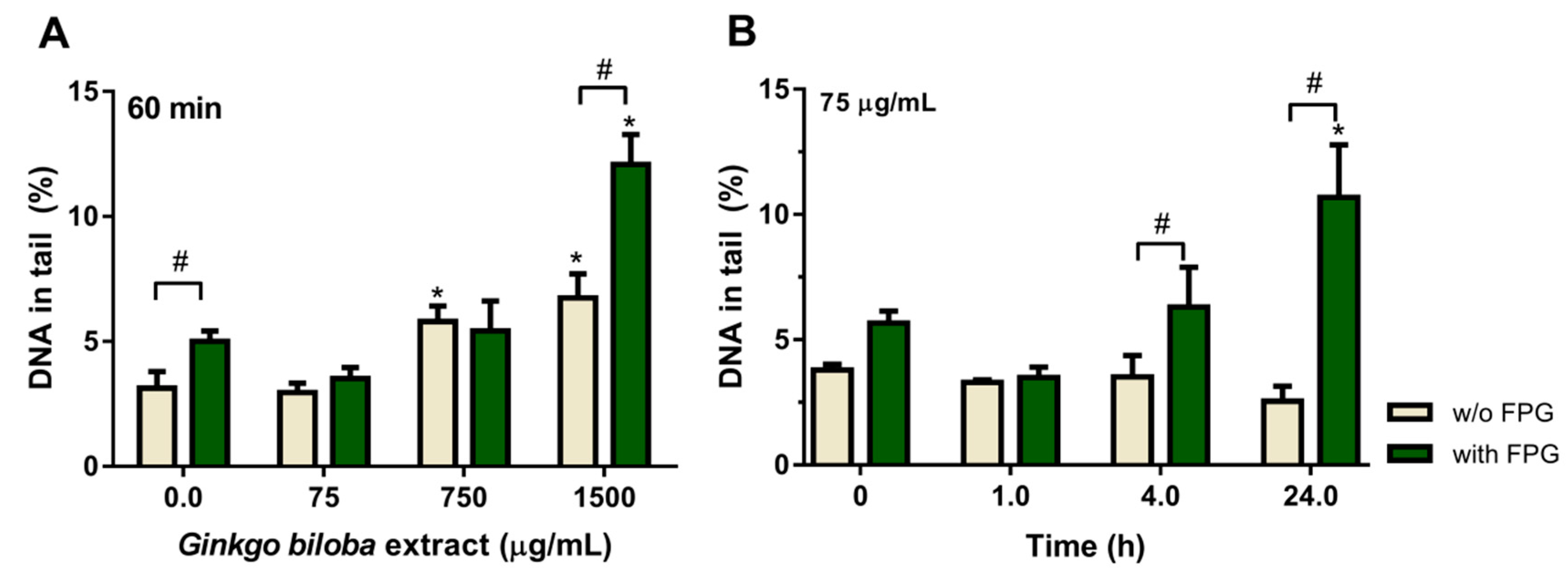
2.3. Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract on DNA Damage
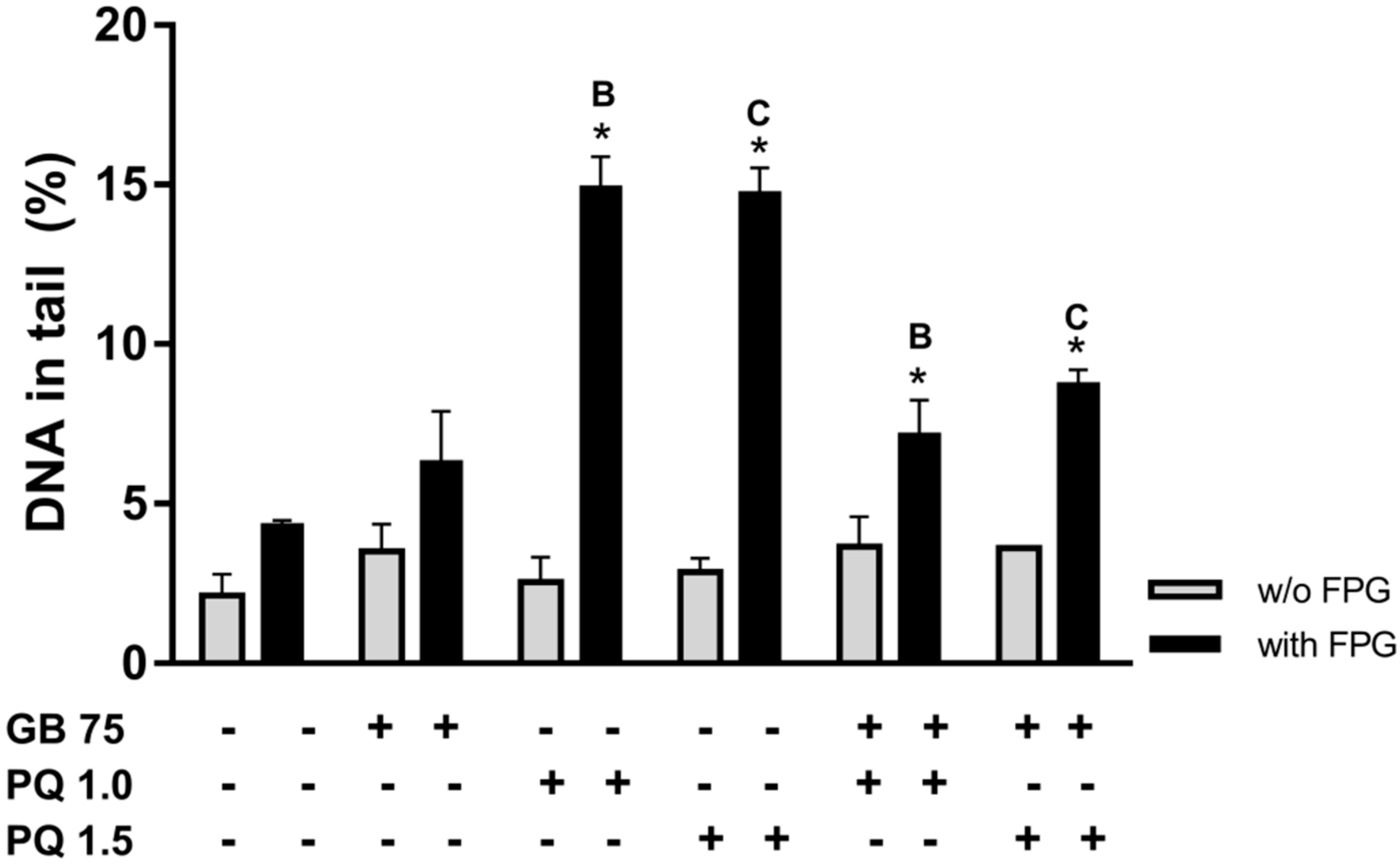
2.4. Ginkgo biloba Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced DNA Damage
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Ginkgo biloba Aqueous Extract
4.2. Cells Culture and Experimental Design
4.2.1. Cell Culture and Maintenance
4.2.2. Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity Assay
4.2.3. Cell Treatment and Experimental Conditions for Comet Assay
4.3. Alkaline Comet Assay
4.3.1. Measurement of Strand Breaks
4.3.2. Measurement of Oxidative DNA Damage
4.3.3. Comet Evaluation
4.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sierpina, V.S.; Wollschlaeger, B.; Blumenthal, M. Ginkgo biloba. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 923–926. [Google Scholar]
- Strømgaard, K.; Nakanishi, K. Chemistry and biology of terpene trilactones from Ginkgo biloba. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1640–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yahya, A.A.; Al-Majed, A.A.; Al-Bekairi, A.M.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Qureshi, S. Studies on the reproductive, cytological and biochemical toxicity of Ginkgo biloba in swiss albino mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, G.; Chandani, S.; Harinarayana Rao, S.; Samuni, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Balasubramanian, D. Molecular and cellular assessment of Ginkgo biloba extract as a possible ophthalmic drug. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 75, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritch, R. Potential role for Ginkgo biloba extract in the treatment of glaucoma. Med. Hypotheses 2000, 54, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, B.; Xia, Z.-M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Rui, W.-J.; Dong, J.-X.; Xiao, F.-J. Anticancer Effects of Five Biflavonoids from Ginkgo Biloba L. Male Flowers In Vitro. Molecules 2019, 24, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-C.; Xia, Q.; Fu, P.P. Ginkgo biloba Leave extract: Biological, medicinal, and toxicological effects. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2007, 25, 211–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekh, A.; Pham, D.L.; Yousem, D.M.; Dizon, M.; Barker, P.B.; Lin, D.D.M. Effects of Ginkgo biloba on cerebral blood flow assessed by quantitative MR perfusion imaging: A pilot study. Neuroradiology 2011, 53, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Zhao, L. Enrichment and Purification of Total Ginkgo Flavonoid O-Glycosides from Ginkgo biloba Extract with Macroporous Resin and Evaluation of Anti-Inflammation Activities In Vitro. Molecules 2018, 23, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, T.A.; Montoro, P. Chemical analysis and quality control of Ginkgo biloba leaves, extracts, and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2002–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoo, H.H. Effects of gut microbiota on the bioavailability of bioactive compounds from Ginkgo biloba leaf extracts. Metabolites 2019, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical characterization of Ginkgo biloba L and antioxidant properties of its extracts and dietary supplements. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 51, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Peng, Q.; Lau, B.H.; Shah, V. Ginkgo biloba inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of nuclear factor kappa B in vascular endothelial cells. Gen. Pharmacol. 1999, 33, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Azevedo, F.; Johansson, B.; Oliveira, R. Stimulation of DNA repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Ginkgo biloba leaf extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Geng, Z.; Lau, B.H. Ginkgo biloba attenuates oxidative stress in macrophages and endothelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, H.; Ackerman, N.J.; Burekhovich, F.; Zuckerbraun, H.L.; Schuck, A.G. Gingko biloba leaf extract induces oxidative stress in carcinoma HSC-2 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, H.; Schuck, A.G.; Weisburg, J.H.; Zuckerbraun, H.L. Research strategies in the study of the pro-oxidant nature of polyphenol nutraceuticals. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Zeng, S. Cytotoxicity of ginkgolic acid in HepG2 cells and primary rat hepatocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 187, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, H.; Johannisson, R.; Koch, E.; Siegers, C.P. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic potential of alkylphenols from Ginkgo biloba L. Toxicology 2002, 177, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Metwally, N.S.; Soliman, M.S.; Ahmed, K.A.; Abdel Moaty, M.M. The chemopreventive effect of Ginkgo biloba and Silybum marianum extracts on hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Cell Int. 2011, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kang, D.; Beane-Freeman, L.; Blair, A.; Hoppin, J.A.; Sandler, D.P.; Lynch, C.F.; Knott, C.; Gwak, J.; Alavanja, M. Cancer incidence among paraquat exposed applicators in the agricultural health study: Prospective cohort study. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2009, 15, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.H.; Li, S.N.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G.N.; Zhuang, H.S. Evaluation of DNA damage in Chinese toad (Bufo bufo gargarizans) after in vivo exposure to sublethal concentrations of four herbicides using the comet assay. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehn, P.F.; White, C.M.; Conners, D.E.; Shipkey, G.; Cumbo, T.A. Characterization of the human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line as an in vitro model for cadmium toxicity studies. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2004, 40, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R.; Oscoz, A.A.; Brunborg, G.; Gaivão, I.; Giovannelli, L.; Kruszewski, M.; Smith, C.C.; Stetina, R. The comet assay: Topical issues. Mutagenesis 2008, 23, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lou, D.; Cai, Q.; Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of paraquat-induced miRNA profiling response in hNPCs undergoing proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18422–18436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Sanchez, R.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Niso-Santano, M.; Soler, G.; Fuentes, J.M.; Gonzalez-Polo, R.A. The neuroprotective effect of talipexole from paraquat-induced cell death in dopaminergic neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Singh, S.V.; Singh, S.P.; Mu, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Saini, S.P.S.; Toma, D.; Ren, S.; Kagan, V.E.; Day, B.W.; et al. Orphan Nuclear Receptor Pregnane X Receptor Sensitizes Oxidative Stress Responses in Transgenic Mice and Cancerous Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Cytotoxicity of paraquat in microglial cells: Involvement of PKCδ- and ERK1/2-dependent NADPH oxidase. Brain Res. 2007, 1167, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusinská, M.; Kovaciková, Z.; Vallová, B.; Collins, A. Responses of alveolar macrophages and epithelial type II cells to oxidative DNA damage caused by paraquat. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.C.J.; Chu, C.C. Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol 2004, 10, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, I.; Suzuki, M.; Imura, N.; Naganuma, A. Involvement of oxidative stress in paraquat-induced metallothionein synthesis under glutathione depletion. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.P.; Silva, A.M.; Oliveira, M.M.; Peixoto, F.; Gaivao, I.; Mota, M.P. Effects of combined physical exercise training on DNA damage and repair capacity: Role of oxidative stress changes. Age 2015, 37, 9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, G.C.; Paniz, C.; Grotto, D.; Valentini, J.; Schott, K.L.; Pomblum, V.J.; Garcia, S.C. General aspects and clinical laboratorial diagnostic of poisoning by paraquat. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2006, 42, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Silva, A.M.; Gaivao, I.; Souto, E.B.; Teixeira, J.P.; Martins-Lopes, P. Comet assay reveals no genotoxicity risk of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Santos, D.L.; Costa, I.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Cationic solid lipid nanoparticles interfere with the activity of antioxidant enzymes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Tanaka, K.; Lim, H.; Moriyama, M. Mechanism of cytotoxicity of Paraquat. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2002, 7, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawara, T.; Fukushima, T.; Hojo, N.; Isobe, A.; Shiwaku, K.; Serogawa, T.; Yamane, Y. Effects of paraquat on mitochondrial electron transport system and catecholamine contents in rat brain. Arch. Toxicol. 1996, 70, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochemé, H.M.; Murphy, M.P. Complex I Is the Major Site of Mitochondrial Superoxide Production by Paraquat. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1786–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grollino, M.G.; Raschellà, G.; Cordelli, E.; Villani, P.; Pieraccioli, M.; Paximadas, I.; Malandrino, S.; Bonassi, S.; Pacchierotti, F. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and gene expression changes elicited by exposure of human hepatic cells to Ginkgo biloba leaf extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sun, C.M.; Chuang, H.H.; Chang, P.T. Studies on the cytotoxic mechanisms of ginkgetin in a human ovarian adenocarcinoma cell line. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2000, 362, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.; Herrmann, S.M.; Heusera, V.; Peres, W.; Possa Marroni, N.; González-Gallego, J.; Erdtmann, B. Evaluation of the genotoxic effect of rutin and quercetin by comet assay and micronucleus test. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Ruppert, G.; Luepke, N.-P. Evidence for toxic effects of alkylphenols from Ginkgo biloba in the hen’s egg test (HET). Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, N.; Guo, X.; Ren, Z.; Kobayashi, D.; Wada, K.; Guo, L. Review of Ginkgo biloba-induced toxicity, from experimental studies to human case reports. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2017, 35, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Chen, E.; Zhou, W.; Lindsay, R.C. A method for extraction and quantification of Ginkgo biloba terpene trilactones. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4332–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Jager, A.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Solid lipid nanoparticles for hydrophilic biotech drugs: Optimization and cell viability studies (Caco-2 & HEPG-2 cell lines). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Andreani, T.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Severino, P.; Souza, A.L.R.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Fernandes, P.M.V.; Calpena, A.C.; Gremiao, M.P.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. The influence of polysaccharide coating on the physicochemical parameters and cytotoxicity of silica nanoparticles for hydrophilic biomolecules delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, T.; Kiill, C.P.; de Souza, A.L.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Fernandes, L.; Doktorovova, S.; Santos, D.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Gremiao, M.P.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Surface engineering of silica nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Characterization and cell toxicity studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R. The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: Principles, applications and limitations. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.P.; Silva, A.M.; Fonseca, S.; Oliveira, M.M.; Peixoto, F.; Gaivao, I.; Mota, M.P. How can age and lifestyle variables affect DNA damage, repair capacity and endogenous biomarkers of oxidative stress? Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 62, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Pashirova, T.N.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B. Soft cationic nanoparticles for drug delivery: Production and cytotoxicity of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.M.; Silva, S.C.; Soares, J.P.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Teixeira, J.P.; Leal, F.; Gaivão, I. Ginkgo biloba L. Leaf Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage. Plants 2019, 8, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120556
Silva AM, Silva SC, Soares JP, Martins-Gomes C, Teixeira JP, Leal F, Gaivão I. Ginkgo biloba L. Leaf Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage. Plants. 2019; 8(12):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120556
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Amélia M., Sandra C. Silva, Jorge P. Soares, Carlos Martins-Gomes, João Paulo Teixeira, Fernanda Leal, and Isabel Gaivão. 2019. "Ginkgo biloba L. Leaf Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage" Plants 8, no. 12: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120556
APA StyleSilva, A. M., Silva, S. C., Soares, J. P., Martins-Gomes, C., Teixeira, J. P., Leal, F., & Gaivão, I. (2019). Ginkgo biloba L. Leaf Extract Protects HepG2 Cells Against Paraquat-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage. Plants, 8(12), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120556






