A Safe Location for a Trip? How the Characteristics of an Area Affect Road Accidents—A Case Study from Poznań
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Road Accidents and Public Health
1.2. Factors Determining Accidents—Literature Review
2. Materials and Methods
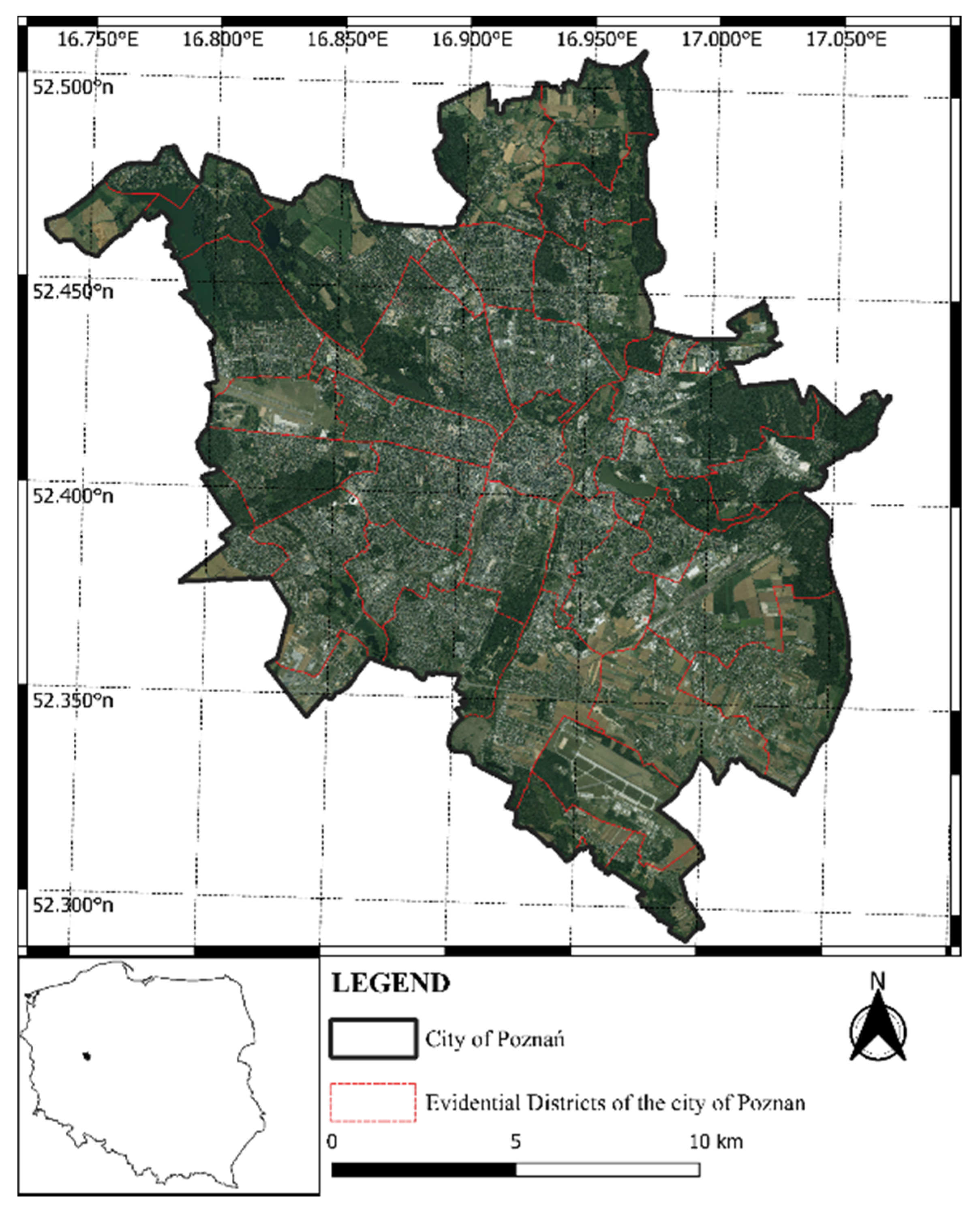
2.1. Characteristics of the Research Area
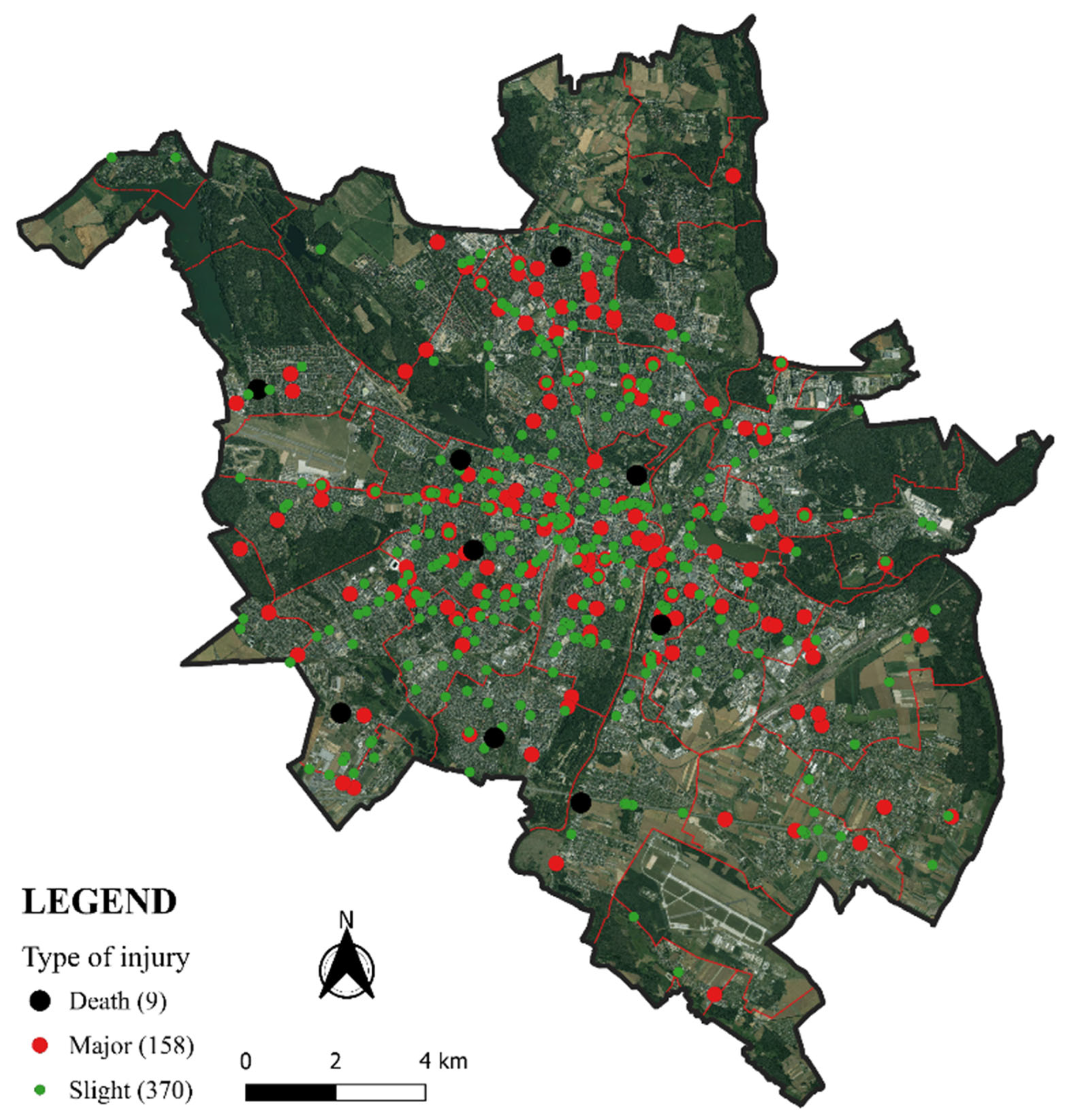
2.2. Research Material
2.3. Methodology
- cov(x,y) = E(x × y) − [E(x) × E(y)],
- —r-Pearson correlation coefficient between applied variables x and y,
- cov(x,y)—covariance between the applied variables x and y,
- σ—standard deviation,
- E—expected value.
- Y—number of road accidents in a cadastral district,
- …… —regression coefficients,
- …… —values of the analyzed parameters,
- —standard error.
- I—Moran’s I global statistics index,
- —value of an attribute of an object i,
- —value of an attribute of an object j,
- —number of objects,
- connection weights of objects i and j.
- Z—Z-score value,
- I—Moran’s I Global Statistics Index,
- —E(I)—expected value I,
- —standard deviation of a random variable I.
- —geographical coordinates of the i-th object,
- —location-specific intersection object,
- —regression coefficient relevant to the location of the given object,
- —variable related to the coefficients ,
- K—number of estimated parameters,
- —standard error.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Variables Included in the Analysis
3.2. OLS Regression
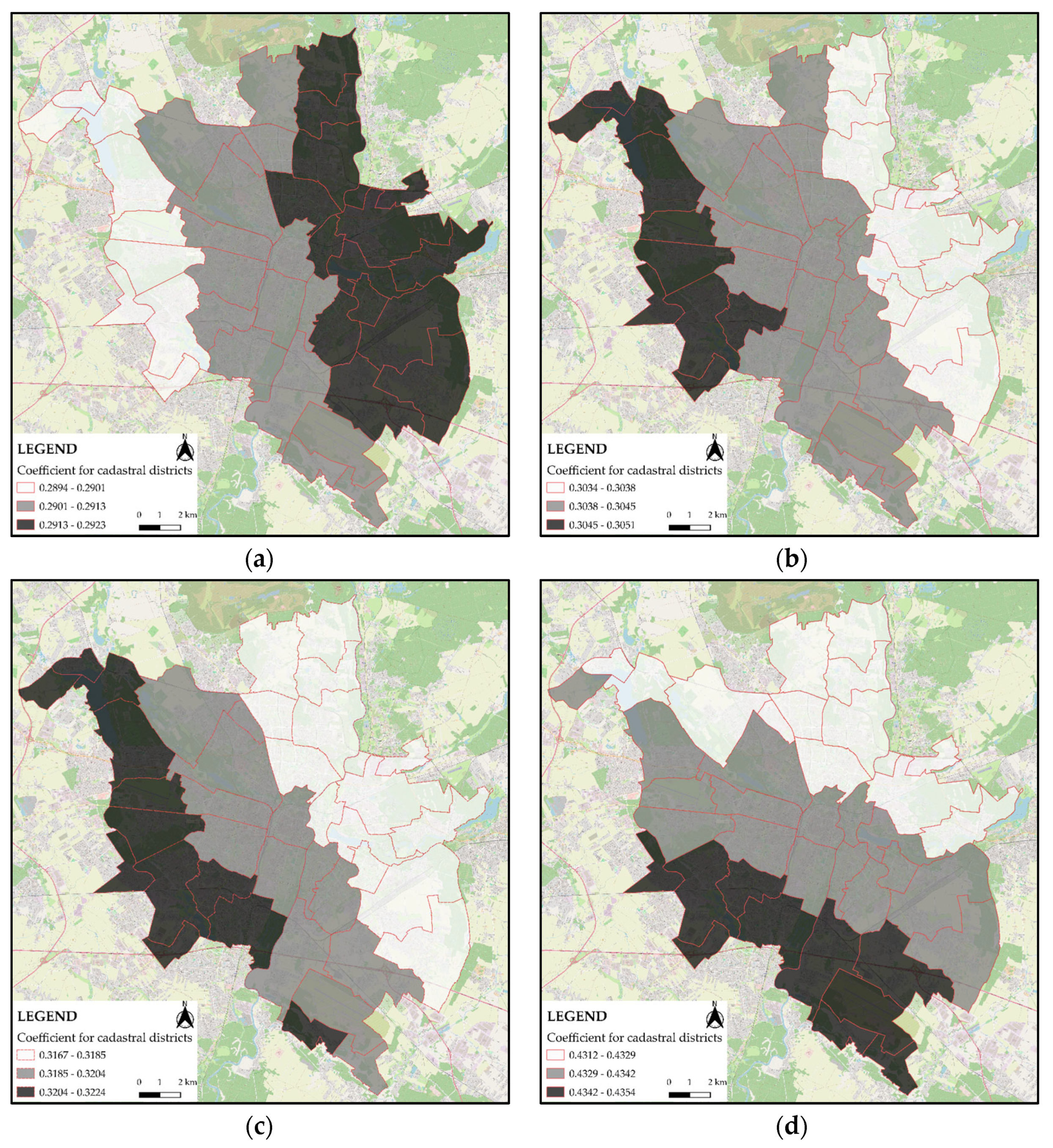
3.3. GWR Regression
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings
4.2. Advantages of the Research—Implications
4.3. Disadvantages of the Study—Directions for Future Research
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEWiK | Accident and Collision Recording System |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares Regression |
| GWR | Geographically Weighted Regression |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- WHO. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240086517 (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- UN. Second Decade of Action for Road Safety: Improving Global Road Safety Global Status Report on Road Safety 2020; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.un.org/en/observances/international-decades (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Sharma, B.R. Road traffic injuries: A major global public health crisis. Public Health 2008, 122, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjuman, T.; Hasanat-E-Rabbi, S.; Siddiqui, C.K.A.; Hoque, M.M. Road traffic accident: A leading cause of the global burden of public health injuries and fatalities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2007 (ICME2007), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 29–31 December 2007; pp. 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Peden, M.; Hyder, A. Road traffic injuries are a global public health problem. BMJ 2002, 324, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevitt, S. Fatal road accidents. Injuries, complications, and causes of death in 250 subjects. Br. J. Surg. 1968, 55, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevitt, S. Fatal road accidents in Birmingham: Times to death and their causes. Injury 1973, 4, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, G.D.; Sayer, I. Road accidents in developing countries. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1983, 15, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kushwaha, V.; Agarwal, A.D.; Sandhu, S.S. Fatal road traffic accidents: Causes and factors responsible. J. Indian Acad. Forensic Med. 2016, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, H.M.; Mayhew, D.R.; Warren, R.A. Epidemiology of road accidents involving young adults: Alcohol, drugs and other factors. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1982, 10, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.; Parsons, R.S.; Davies, N.W.; Chesterman, R.B.; Dineen, R.; Johnson, M.C. Drugs, alcohol and road accidents in Tasmania. Med. J. Aust. 1987, 147, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, A.; Skurtveit, S.; Mørland, J. Risk of road traffic accidents associated with the prescription of drugs: A registry-based cohort study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2007, 17, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, A.S.; Gjerde, H. Prevalence of alcohol and drugs among car and van drivers killed in road accidents in Norway: An overview from 2001 to 2010. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2014, 15, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaabi, K. Identification of hotspot areas for traffic accidents and analyzing drivers’ behaviors and road accidents. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2023, 22, 100929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.S.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Souri, H.; Kalhori, S.M.; Jannatifard, F.; Sepahbodi, G. Personality, driving behavior and mental disorders factors as predictors of road traffic accidents based on logistic regression. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 42, 24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sagberg, F. Road accidents caused by drivers falling asleep. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1999, 31, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Balbissi, A.H. Role of gender in road accidents. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2003, 4, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visby, R.H.; Lundholt, K. Gender differences in Danish road accidents. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pińskwar, I.; Choryński, A.; Graczyk, D. Good weather for a ride (or not?): How weather conditions impact road accidents—A case study from Wielkopolska (Poland). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszweski, D.; McNamara, T. The influence of rainfall on road accidents in urban areas: A weather radar approach. Travel Behav. Soc. 2014, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi-Hassankiadeh, N.; Rad, E.H.; Koohestani, H.S.; Kouchakinejad-Eramsadati, L. The Pattern of Road Accidents in Fog and the Related Factors in North of Iran in 2014–2018. Res. Sq. 2020; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.S.R.; Zareie, A.; Amador-Jiménez, L.E. Climate change modeling and the weather-related road accidents in Canada. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 32, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Alharthi, M.; Alam, M.M. The impacts of climate change on road traffic accidents in Saudi Arabia. Climate 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Minhans, A. Climate change and road safety: A review to assess impacts in Malaysia. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházka, J.; Flimmel, S.; Čamaj, M.; Bašta, M. Modelling the number of road accidents. Applications of Mathematics and Statistics in Economics. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference, Szklarska Poręba, Poland, 30 August–3 September 2017; Conference Proceedings Full Text Papers. pp. 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borucka, A.; Kozłowski, E.; Oleszczuk, P.; Świderski, A. Predictive analysis of the impact of the time of day on road accidents in Poland. Open Eng. 2020, 11, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacasu, M.; Er, A. An analysis on distribution of traffic faults in accidents, based on driver’s age and gender: Eskisehir case. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 20, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Shafiq, M.; Park, Y. Catastrophic factors involved in road accidents: Underlying causes and descriptive analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report: Transport in Poznań (2023). Poznań, Poland. 2024. Available online: https://badam.poznan.pl/transport-w-poznaniu-w-2023-r/ (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Hutcheson, G. GLM Models and OLS Regression; The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Diao, M.; Wu, B. A big data–based geographically weighted regression model for public housing prices: A case study in Singapore. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2019, 109, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellmer, R.; Cichulska, A.; Bełej, M. Spatial Analysis of Housing Prices and Market Activity with the Geographically Weighted Regression. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 2020, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Wen, T.H. Using geographically weighted regression (GWR) to explore spatial varying relationships of immature mosquitoes and human densities with the incidence of dengue. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2798–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, W. Analyzing the impact of urbanization quality on CO2 emissions: What can geographically weighted regression tell us? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzoug, R.; Lakouari, N.; Oubram, O.; Ez-Zahraouy, H.; Khallouk, A.; Limón-Mendoza, M.; Vera-Dimas, J.G. Impact of traffic lights on car accidents at intersections. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2018, 29, 1850121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembuain, A.; Priyanto, S.; Suparma, L. The effect of road infrastructure on traffic accidents. In Proceedings of the 11th Asia Pacific Transportation and the Environment Conference (APTE 2018), Malang, Indonesia, 18–19 October 2018; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, A.H.; Shakoree, A.S.; Ramadan, Z.A. Factors affecting traffic accidents density on selected multilane rural highways. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, L.; Cividino, S.R.; Gubiani, R.; Cecchini, M.; Delfanti, L.M.; Colantoni, A. Urban green spaces activities: A preparatory groundwork for a safety management system. J. Saf. Res. 2016, 56, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Police Report: Road accidents in Poland in 2023. Warsaw, Poland. 2024. Available online: https://statystyka.policja.pl/st/ruch-drogowy/76562,wypadki-drogowe-raporty-roczne.html (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Yang, W. An Extension of Geographically Weighted Regression with Flexible Bandwidths. Ph.D. Thesis, University of St Andrews, St Andrews, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. MGWR: A Python Implementation of Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression for Investigating Process Spatial Heterogeneity and Scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inform. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.T.; Mateos, M.A.; Soto, P.R.; Mezher, A.M.; Igartua, M.A. Smart city for VANETs using warning messages, traffic statistics and intelligent traffic lights. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Madrid, Spain, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 902–907. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, K.A.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, Y.I.; Ulfarsson, G.F. Spatial regression analysis of traffic crashes in Seoul. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 91, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Jamal, A.; Al-Ahmadi, H.M. Examining Hotspots of Traffic Collisions and their Spatial Relationships with Land Use: A GIS-Based Geographically Weighted Regression Approach for Dammam, Saudi Arabia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 2020, 9, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphela, T. Causes of road accidents in Botswana: An econometric model. J. Transp. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Pakgohar, A. Logistic regression approach in road defects impact on accident severity. J. Emerg. Technol. Web Intell. 2013, 5, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majed, V.; Abdoli, G.; Mahdavi, G.; Khodaei, H. Socio-economic factors affecting road accidents. J. Organ. Behav. Res. 2020, 5, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bhavan, T. The economic impact of road accidents: The case of Sri Lanka. S. Asia Econ. J. 2019, 20, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Treibich, C. Socio-economic determinants of road traffic accident fatalities in low and middle income countries. ISS Work. Pap. Ser./Gen. Ser. 2010, 504, 1–44. [Google Scholar]


| Population—Total | Population by Gender | Demographic Structure |
|---|---|---|
| 536,818 | Women—286,333 Men—250,485 | Pre-working age—69,859 Working age—336,968 Post-working age—129,991 |
| Indicator | Classification Criterion | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Only vehicles (cars, trucks, bus) | 183 |
| Vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists | 301 | |
| Other (without cars) | 53 | |
| Part of the year | January–April | 139 |
| May–August | 214 | |
| September–December | 184 | |
| Time of day | 6:00–14:00 | 250 |
| 14:00–22:00 | 253 | |
| 22:00–6:00 | 34 | |
| Type of accident | Alcohol | 27 |
| Speed | 82 | |
| Other | 428 |
| Variable | Max | Min | Me | σ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | 13.38 | 64.00 | 0.00 | 8.50 | 14.97 |
| AR | 6.55 | 13.78 | 0.06 | 5.92 | 3.48 |
| BA | 0.26 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.16 |
| GA | 0.19 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.14 |
| RD | 10.07 | 17.41 | 3.16 | 9.46 | 3.71 |
| PBD | 5.56 | 18.94 | 0.00 | 2.90 | 5.35 |
| RQ | 0.47 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.18 |
| CS | 29.25 | 82.00 | 0.00 | 23.50 | 20.87 |
| PN | 49.75 | 343.00 | 0.00 | 18.00 | 74.98 |
| LN | 34.38 | 203.00 | 0.00 | 15.00 | 47.76 |
| SN | 4.03 | 19.00 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 5.12 |
| LAN | 210.10 | 688.00 | 0.00 | 210.00 | 193.02 |
| RON | 1.40 | 6.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.56 |
| CN | 260.45 | 1106.00 | 0.00 | 172.50 | 264.24 |
| Number of observations | 537 | ||||
| AN | AR | BA | GA | RD | PBD | RQ | CS | PN | LN | SN | LAN | RON | CN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | ||||||||||||||
| AR | 0.140 | |||||||||||||
| BA | 0.666 | −0.176 | ||||||||||||
| GA | −0.228 | 0.278 | −0.391 | |||||||||||
| RD | 0.666 | −0.127 | 0.823 | −0.376 | ||||||||||
| PBD | 0.586 | −0.173 | 0.454 | −0.182 | 0.709 | |||||||||
| RQ | 0.599 | 0.048 | 0.306 | −0.280 | 0.679 | 0.696 | ||||||||
| CS | 0.724 | 0.416 | 0.489 | −0.093 | 0.629 | 0.590 | 0.603 | |||||||
| PN | 0.742 | −0.081 | 0.466 | −0.077 | 0.531 | 0.679 | 0.539 | 0.573 | ||||||
| LN | 0.785 | 0.021 | 0.621 | −0.172 | 0.723 | 0.706 | 0.598 | 0.722 | 0.682 | |||||
| SN | 0.519 | 0.140 | 0.337 | 0.023 | 0.402 | 0.225 | 0.407 | 0.499 | 0.370 | 0.412 | ||||
| LAN | 0.768 | 0.210 | 0.387 | −0.119 | 0.557 | 0.599 | 0.641 | 0.681 | 0.596 | 0.566 | 0.651 | |||
| RON | 0.273 | 0.183 | 0.141 | −0.171 | 0.405 | 0.533 | 0.532 | 0.495 | 0.273 | 0.252 | 0.290 | 0.415 | ||
| CN | 0.876 | 0.193 | 0.617 | −0.105 | 0.696 | 0.686 | 0.597 | 0.801 | 0.776 | 0.872 | 0.582 | 0.770 | 0.319 |
| Coefficient | Standard Error | T-Value | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.1912 | 5.6237 | −0.7453 | 0.4628 | - |
| AR | 0.2307 | 0.5179 | 0.4455 | 0.6596 | 3.3964 |
| BA | 48.8856 | 15.9005 | 3.0745 | 0.0049 * | 6.9797 |
| GA | −2.4309 | 8.8254 | −0.2754 | 0.7851 | 1.6814 |
| RD | −1.6214 | 0.8488 | −1.9102 | 0.0672 | 10.3801 |
| PBD | −0.5473 | 0.4756 | −1.1508 | 0.2603 | 6.7886 |
| RQ | 22.5509 | 11.8570 | 1.9019 | 0.0683 | 4.5927 |
| CS | −0.0135 | 0.1054 | −0.1282 | 0.8990 | 5.0734 |
| PN | 0.0375 | 0.0250 | 1.4989 | 0.1459 | 3.6799 |
| LN | 0.0788 | 0.0534 | 1.4752 | 0.1522 | 6.8255 |
| SN | −0.3092 | 0.3282 | −0.9418 | 0.3549 | 2.9553 |
| LAN | 0.0296 | 0.0106 | 2.8038 | 0.0094 * | 4.3523 |
| RON | 0.0904 | 0.9635 | 0.0938 | 0.9260 | 2.3739 |
| CN | 0.0118 | 0.0143 | 0.8218 | 0.4187 | 14.9729 |
| Number of Observations (cadastral districts) | 40 | ||||
| Multiple R-Squared | 0.8893 | ||||
| Adjusted R-Squared | 0.8340 | ||||
| AICc | 291.9662 | ||||
| Coefficient | Standard Error | T-Value | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −7.4859 | 5.6003 | −1.3367 | 0.1921 | - |
| AR | 0.4778 | 0.4850 | 0.9851 | 0.3330 | 2.7567 |
| BA | 26.6077 | 9.5622 | 2.7826 | 0.0095 * | 2.3364 |
| GA | −4.3855 | 9.1194 | −0.4809 | 0.6343 | 1.6617 |
| PBD | −0.6754 | 0.4660 | −1.4493 | 0.1583 | 6.0327 |
| RQ | 7.7123 | 9.7643 | 0.7898 | 0.4363 | 2.8829 |
| CS | −0.0203 | 0.1094 | −0.1857 | 0.8541 | 5.0537 |
| PN | 0.0608 | 0.0214 | 2.8450 | 0.0082 * | 2.4880 |
| LN | 0.1003 | 0.0442 | 2.2676 | 0.0313 * | 4.3278 |
| SN | −0.2372 | 0.3221 | −0.7365 | 0.4676 | 2.6337 |
| LAN | 0.0335 | 0.0102 | 3.2716 | 0.0028 * | 3.7922 |
| RON | −0.2047 | 0.9808 | −0.2087 | 0.8362 | 2.2765 |
| Number of Observations (cadastral districts) | 40 | ||||
| Multiple R-Squared | 0.8712 | ||||
| Adjusted R-Squared | 0.8206 | ||||
| AICc | 288.0237 | ||||
| Coefficient | Percent of Significant Cases at 95% | Percent of Cases with Local VIF > 7.5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ | Min | Me | Max | ||||
| Intercept | −0.0003 | 0.0004 | −0.0010 | −0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0% | 0% |
| AR | 0.1115 | 0.0008 | 0.1098 | 0.1115 | 0.1128 | 0% | 0% |
| BA | 0.2909 | 0.0007 | 0.2894 | 0.2910 | 0.2923 | 100% | 0% |
| GA | −0.0417 | 0.0010 | −0.0435 | −0.0417 | −0.0397 | 0% | 0% |
| PBD | −0.2428 | 0.0016 | −0.2456 | −0.2429 | −0.2399 | 0% | 0% |
| RQ | 0.0919 | 0.0006 | 0.0908 | 0.0920 | 0.0930 | 0% | 0% |
| CS | −0.0295 | 0.0004 | −0.0303 | −0.0295 | −0.0287 | 0% | 0% |
| PN | 0.3042 | 0.0004 | 0.3034 | 0.3042 | 0.3051 | 100% | 0% |
| LN | 0.3195 | 0.0016 | 0.3167 | 0.3197 | 0.3224 | 100% | 0% |
| SN | −0.0818 | 0.0010 | −0.0835 | −0.0818 | −0.0799 | 0% | 0% |
| LAN | 0.4336 | 0.0011 | 0.4312 | 0.4334 | 0.4354 | 100% | 0% |
| RON | −0.0206 | 0.0014 | −0.0230 | −0.0207 | −0.0174 | 0% | 0% |
| Number of Observations (cadastral districts) | 40 | ||||||
| Multiple R-Squared | 0.872 | ||||||
| Adjusted R-Squared | 0.814 | ||||||
| AIC | 57.637 | ||||||
| AICc | 72.083 | ||||||
| Bandwidth used | 47396.740 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chwiałkowski, C. A Safe Location for a Trip? How the Characteristics of an Area Affect Road Accidents—A Case Study from Poznań. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070249
Chwiałkowski C. A Safe Location for a Trip? How the Characteristics of an Area Affect Road Accidents—A Case Study from Poznań. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(7):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070249
Chicago/Turabian StyleChwiałkowski, Cyprian. 2025. "A Safe Location for a Trip? How the Characteristics of an Area Affect Road Accidents—A Case Study from Poznań" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 7: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070249
APA StyleChwiałkowski, C. (2025). A Safe Location for a Trip? How the Characteristics of an Area Affect Road Accidents—A Case Study from Poznań. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(7), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070249








