A Novel Role of Hyaluronan and Its Membrane Receptors, CD44 and RHAMM, in Obesity-Related Kidney Pathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Renal Function Measurement
2.3. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Cell Culture and Induction of Insulin Resistance
2.7. Tandem Mass Tag (TMT)-Mass Spectrometry (MS) Processing and Analysis
2.8. Human Tissue Procurement and Analysis
2.9. NephroSeq Analysis
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Reduction in HA Attenuated Obesity-Induced Tubular Damage, Renal Dysfunction, and Fibrosis
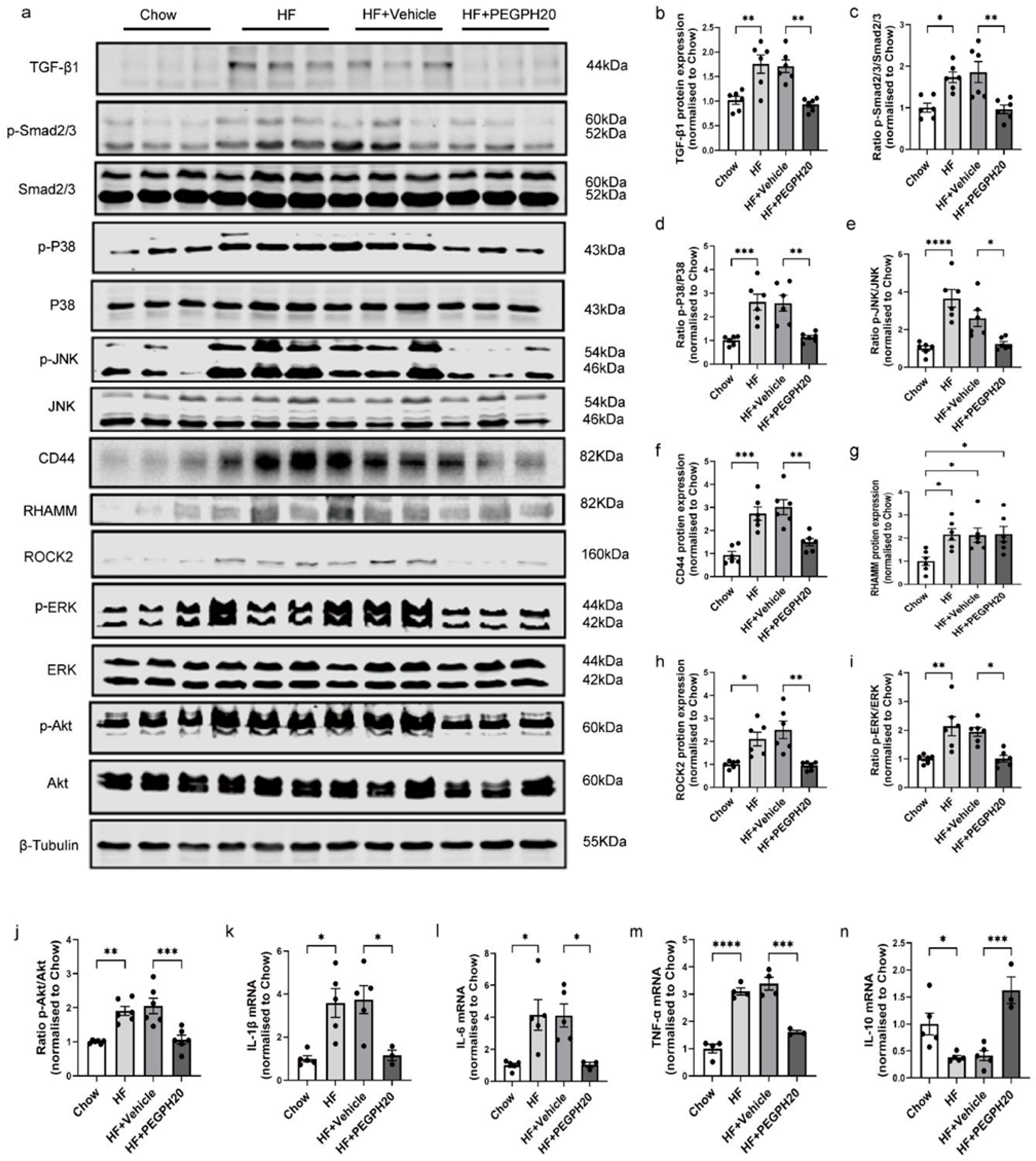
3.2. PEGPH20 Blocked Inflammation and the Activation of TGF-β1/Smad2/3, P38/JNK MAPK, and HA/CD44 Pathways in Obese Mice
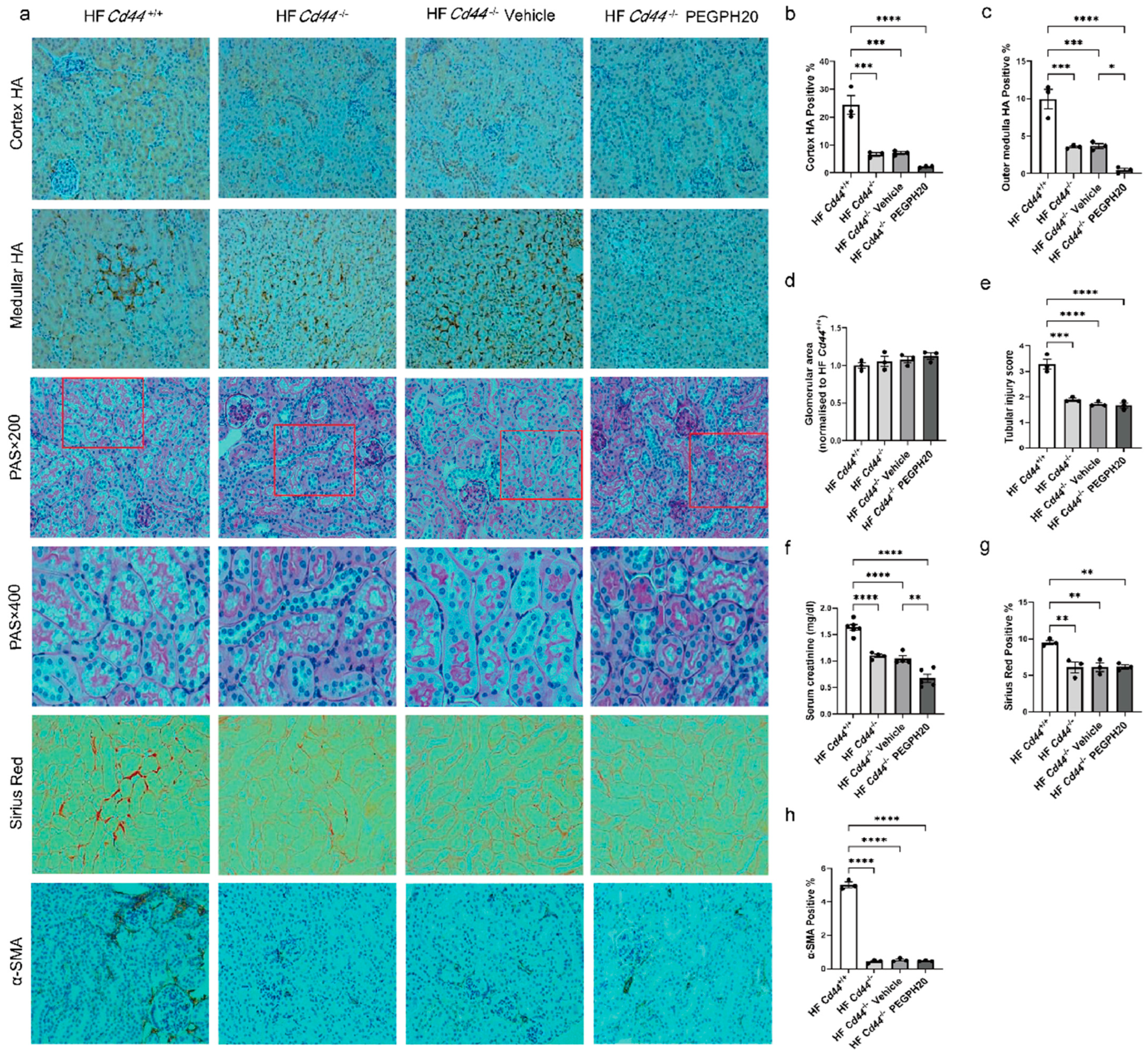
3.3. Global Cd44 Gene Deletion Attenuated Obesity-Induced HA Accumulation, Tubular Damage, Renal Dysfunction, and Fibrosis
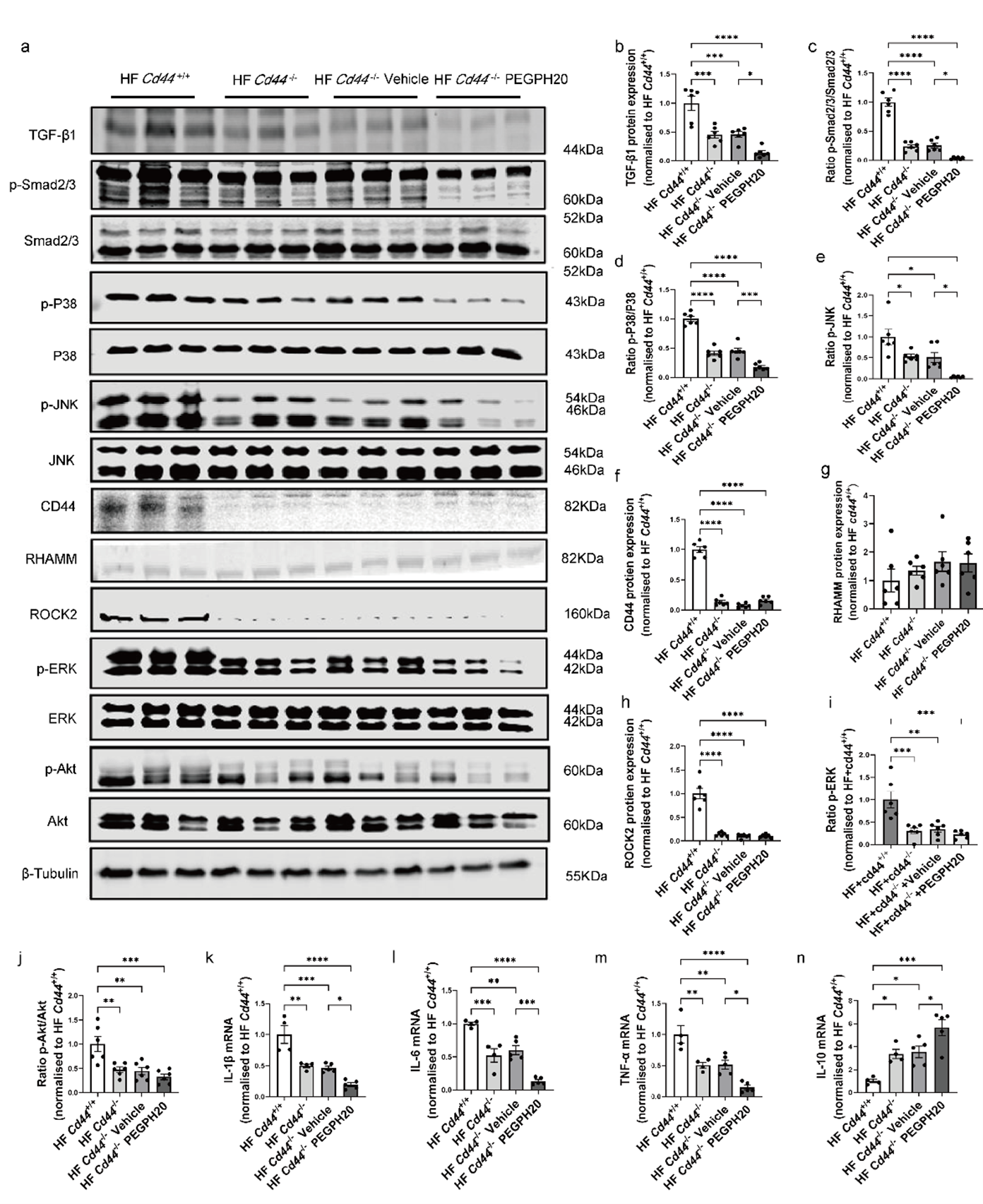
3.4. Global Cd44 Gene Deletion Blocked Inflammation and the Activation of TGF-β1/Smad2/3, P38/JNK MAPK, and HA/CD44 Pathways in Obesity
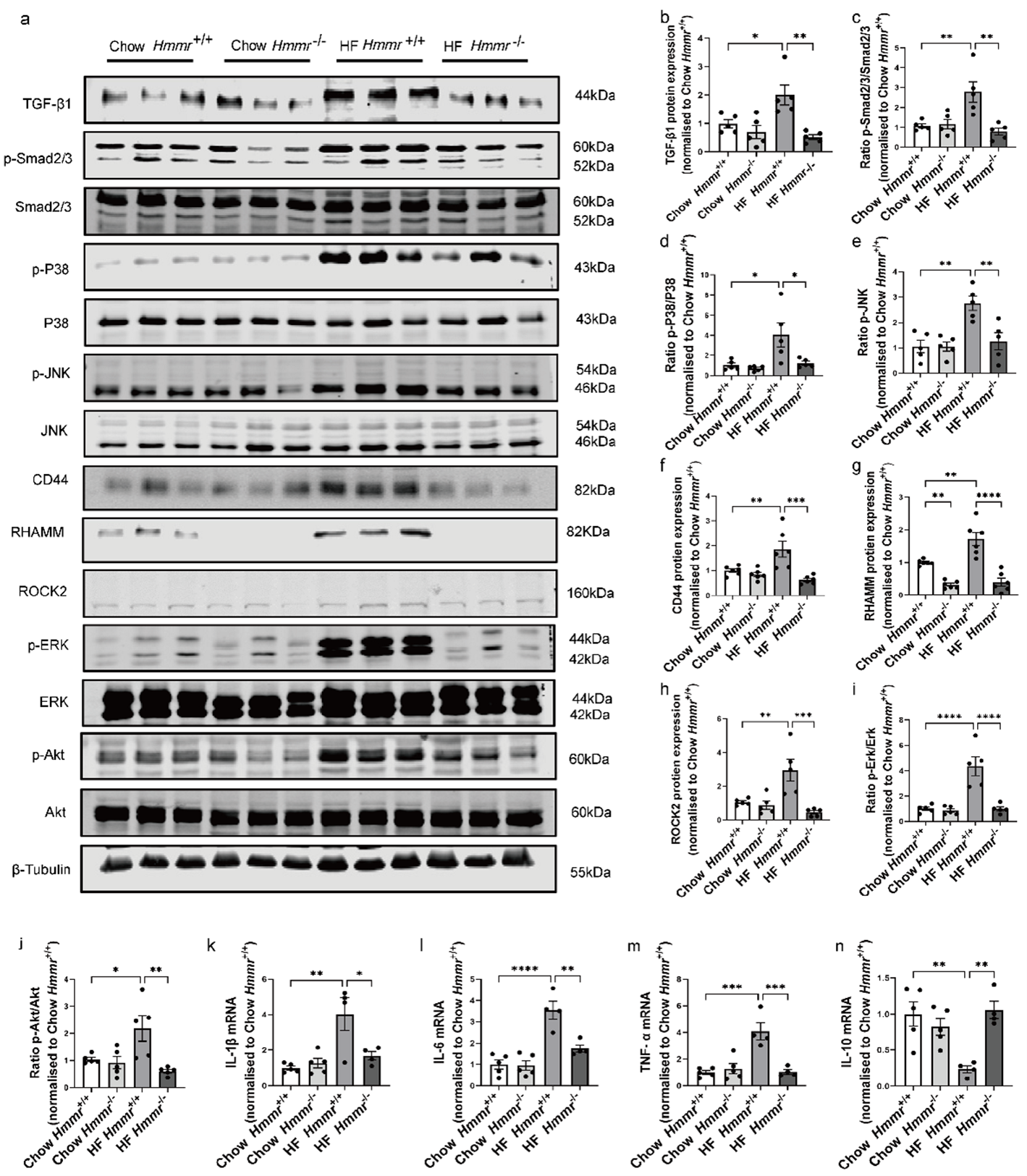
3.5. Global Hmmr Gene Deletion Reduced Obesity-Induced HA Accumulation, Glomerular Expansion, Tubular Damage, Renal Dysfunction, and Fibrosis
3.6. Global Hmmr Gene Deletion Blocked the Activation of TGF-β1/Smad2/3, P38/JNK MAPK, and HA/CD44 Pathways and Prevented Inflammation in the Kidney of Obese Mice
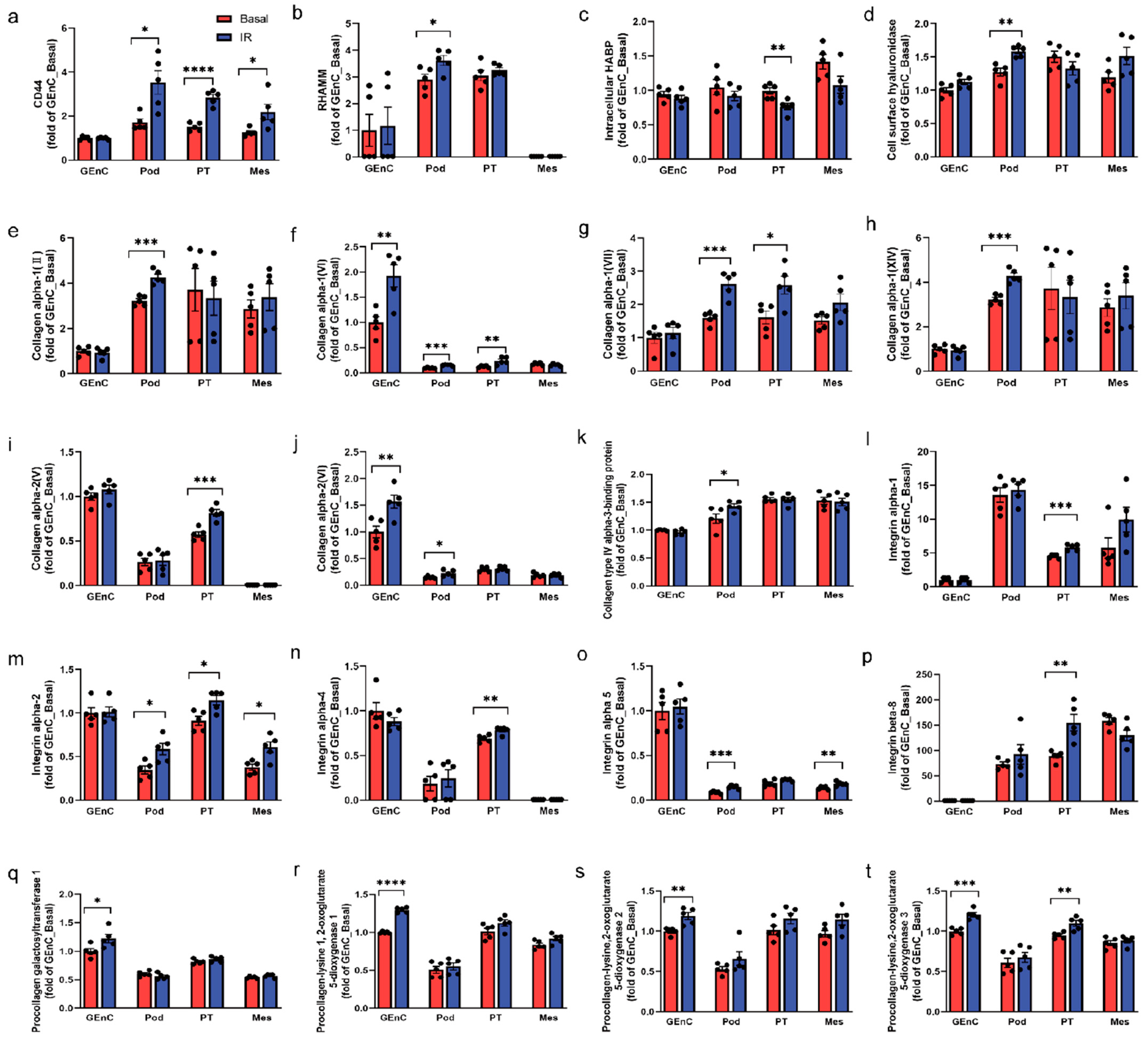
3.7. CD44 and RHAMM Were Upregulated in Insulin-Resistant Human Kidney Cells
3.8. Increased CD44 and RHAMM Expression Correlated with a Decline in Kidney Function in Humans
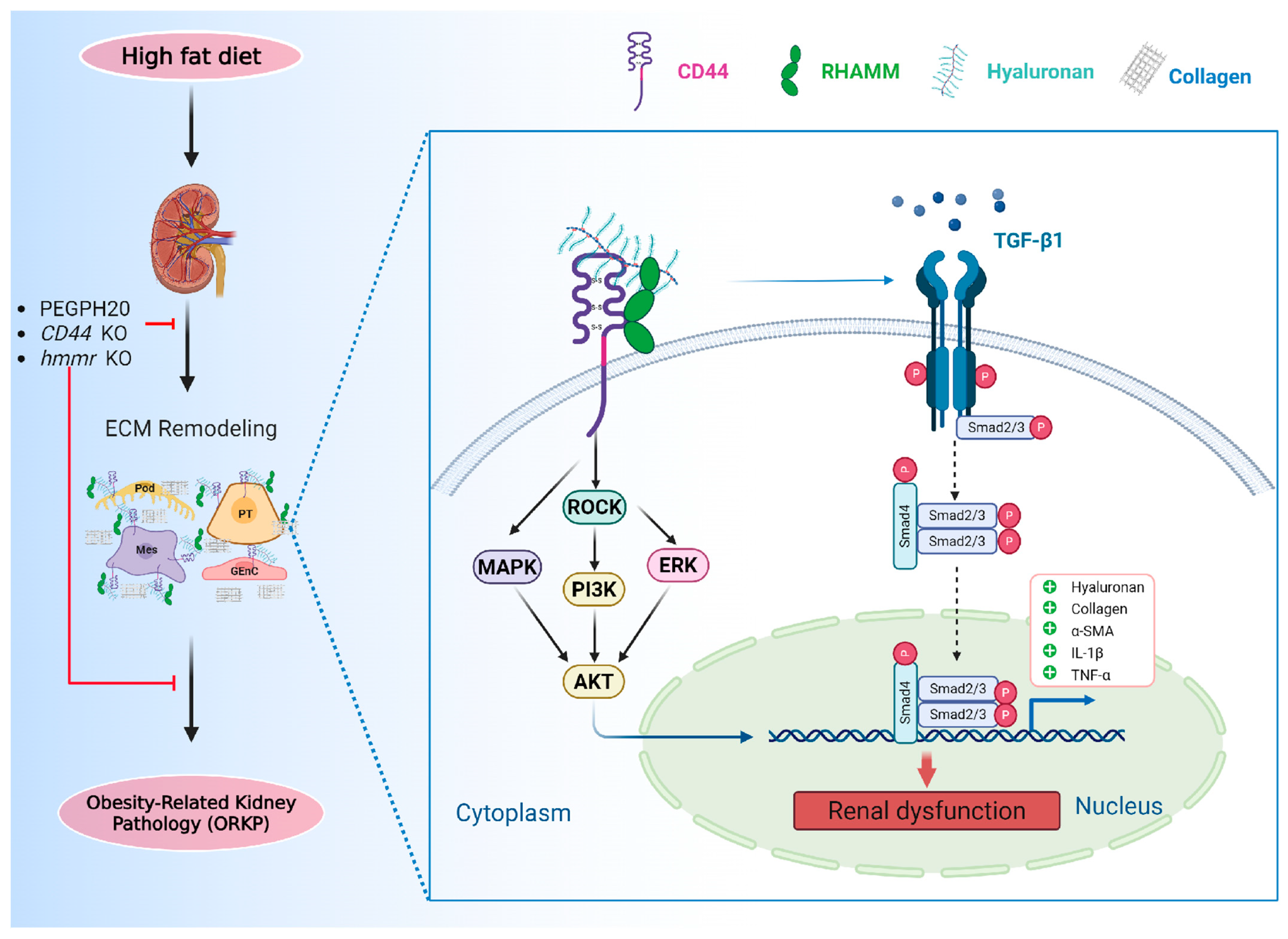
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dogantekin, E.; Akgul, T.; Eser, E.P.; Kotanoglu, M.; Bayburtluoglu, V.; Hucumenoglu, S. The effect of intraurethral hyaluronic acid on healing and fibrosis in rats with experimentally induced urethral trauma. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stridh, S.; Palm, F.; Hansell, P. Renal interstitial hyaluronan: Functional aspects during normal and pathological conditions. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 302, R1235–R1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Singampalli, K.L.; Parikh, U.M.; Yu, L.; Keswani, S.G.; Wang, X. Hyaluronan, a double-edged sword in kidney diseases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Maxwell-Warburton, S.; Hasib, A.; Ma, L.; Kang, L. The membrane receptor CD44: Novel insights into metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decleves, A.E.; Caron, N.; Nonclercq, D.; Legrand, A.; Toubeau, G.; Kramp, R.; Flamion, B. Dynamics of hyaluronan, CD44, and inflammatory cells in the rat kidney after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wu, W.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Lin, S.; Su, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, B.; Duan, S. Increased HA/CD44/TGFβ signaling implicates in renal fibrosis of a Col4a5 mutant Alport mice. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eymael, J.; Sharma, S.; Loeven, M.A.; Wetzels, J.F.; Mooren, F.; Florquin, S.; Deegens, J.K.; Willemsen, B.K.; Sharma, V.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; et al. CD44 is required for the pathogenesis of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis and collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savani, R.C.; Wang, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Kinsella, M.G.; Wight, T.N.; Stern, R.; Nance, D.M.; Turley, E.A. Migration of bovine aortic smooth muscle cells after wounding injury. The role of hyaluronan and RHAMM. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskula, K.; Sacharczuk, M.; Gaciong, Z.; Skiba, D.S. Cardiovascular Effects Mediated by HMMR and CD44. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 4977209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Liu, C.T.; Cheng, C.Y.; Sue, Y.M.; Huang, N.J.; Chen, C.H. Oligosaccharides Ameliorate Acute Kidney Injury by Alleviating Cluster of Differentiation 44-Mediated Immune Responses in Renal Tubular Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, A.; Shirodkar, S.P.; Escudero, D.O.; Ekwenna, O.O.; Yates, T.J.; Ayyathurai, R.; Garcia-Roig, M.; Gahan, J.C.; Manoharan, M.; Bird, V.G.; et al. Molecular characterization of kidney cancer: Association of hyaluronic acid family with histological subtypes and metastasis. Cancer 2012, 118, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Lou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Meng, F.; Pan, Z.; Liu, S.; Yan, G.; Lu, X.; et al. Elevated RHAMM as a biomarker for predicting diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Lantier, L.; Kennedy, A.; Bonner, J.S.; Mayes, W.H.; Bracy, D.P.; Bookbinder, L.H.; Hasty, A.H.; Thompson, C.B.; Wasserman, D.H. Hyaluronan accumulates with high-fat feeding and contributes to insulin resistance. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasib, A.; Hennayake, C.K.; Bracy, D.P.; Bugler-Lamb, A.R.; Lantier, L.; Khan, F.; Ashford, M.L.J.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Wasserman, D.H.; Kang, L. CD44 contributes to hyaluronan-mediated insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of high-fat-fed C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E973–E983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolg, C.; Poon, R.; Fodde, R.; Turley, E.A.; Alman, B.A. Genetic deletion of receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (Rhamm) attenuates the formation of aggressive fibromatosis (desmoid tumor). Oncogene 2003, 22, 6873–6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauet, T.; Mothes, D.; Goujon, J.M.; Caritez, J.C.; Carretier, M.; le Moyec, L.; Eugene, M.; Tillement, J.P. Trimetazidine prevents renal injury in the isolated perfused pig kidney exposed to prolonged cold ischemia. Transplantation 1997, 64, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.A.; O’Hare, M.J.; Reiser, J.; Coward, R.J.; Inward, C.D.; Farren, T.; Xing, C.Y.; Ni, L.; Mathieson, P.W.; Mundel, P. A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrab, R.M.; Lennon, R.; Ni, L.; Wherlock, M.D.; Welsh, G.I.; Saleem, M.A. Establishment of conditionally immortalized human glomerular mesangial cells in culture, with unique migratory properties. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F1131–F1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmer, M.J.; Saleem, M.A.; Masereeuw, R.; Ni, L.; van der Velden, T.J.; Russel, F.G.; Mathieson, P.W.; Monnens, L.A.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Levtchenko, E.N. Novel conditionally immortalized human proximal tubule cell line expressing functional influx and efflux transporters. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchell, S.C.; Tasman, C.H.; Singh, A.; Ni, L.; Geelen, J.; von Ruhland, C.J.; O’Hare, M.J.; Saleem, M.A.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Mathieson, P.W. Conditionally immortalized human glomerular endothelial cells expressing fenestrations in response to VEGF. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, A.C.; Hurcombe, J.A.; Betin, V.M.S.; Barrington, F.; Rollason, R.; Ni, L.; Gillam, L.; Pearson, G.M.E.; Ostergaard, M.V.; Hamidi, H.; et al. Prolonged exposure of mouse and human podocytes to insulin induces insulin resistance through lysosomal and proteasomal degradation of the insulin receptor. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, A.C.; Tran, V.D.T.; Nair, V.; Betin, V.; Hurcombe, J.A.; Barrington, A.F.; Pope, R.J.; Burdet, F.; Mehl, F.; Kryvokhyzha, D.; et al. Profiling of insulin-resistant kidney models and human biopsies reveals common and cell-type-specific mechanisms underpinning Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, J.A.; O’Connor, C.L.; Shi, J.; Wiggins, R.C.; Shedden, K.; Hodgin, J.B.; Bitzer, M. Quantitative morphometrics reveals glomerular changes in patients with infrequent segmentally sclerosed glomeruli. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 75, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Eksi, R.; Yi, D.; Godfrey, B.; Mathew, L.R.; O’Connor, C.L.; Bitzer, M.; Kretzler, M.; Menon, R.; Guan, Y. Micro-dissection and integration of long and short reads to create a robust catalog of kidney compartment-specific isoforms. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippin, J.W.; Kaverina, N.; Wang, Y.; Eng, D.G.; Zeng, Y.; Tran, U.; Loretz, C.J.; Chang, A.; Akilesh, S.; Poudel, C.; et al. Upregulated PD-1 signaling antagonizes glomerular health in aged kidneys and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e156250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Nishihara, K.; Miyata, H.; Shinke, H.; Tomita, E.; Kajiwara, M.; Matsubara, T.; Iehara, N.; Igarashi, Y.; Yamada, H.; et al. Molecular Markers of Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Cell Damage in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Nair, V.; Smith, S.; Zhu, L.; Shedden, K.; Song, P.X.K.; Mariani, L.H.; Eichinger, F.H.; Berthier, C.C.; Randolph, A.; et al. Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 316ra193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, H.; Boucherot, A.; Yasuda, Y.; Henger, A.; Brunner, B.; Eichinger, F.; Nitsche, A.; Kiss, E.; Bleich, M.; Gröne, H.J.; et al. Modular activation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional programs in human diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2993–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, M.S.; Rohacs, T.; Susztak, K. How Many Cell Types Are in the Kidney and What Do They Do? Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Tan, R.J.; Liu, Y. Myofibroblast in Kidney Fibrosis: Origin, Activation, and Regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1165, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Chun, S.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, B.; Yoon, B.; Gil, H.; Han, M.H.; Ha, Y.S.; Lee, J.N.; Kwon, T.G.; et al. IL-10 Deficiency Aggravates Renal Inflammation, Fibrosis and Functional Failure in High-Fat Dieted Obese Mice. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow, R.D.; Boor, P. Extracellular Matrix in Kidney Fibrosis: More Than Just a Scaffold. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2019, 67, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, A.C.; Rogers, M.; Hallett, M.B.; Clayton, A.; Bowen, T.; Phillips, A.O.; Steadman, R. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-stimulated fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation is mediated by hyaluronan (HA)-facilitated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and CD44 co-localization in lipid rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14824–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.; Singleton, P.A.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, B. Hyaluronan promotes signaling interaction between CD44 and the transforming growth factor beta receptor I in metastatic breast tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39703–39712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Chan, T.M. The Role of Hyaluronan and CD44 in the Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis. Autoimmune Dis. 2012, 2012, 207190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoya, H.; Yu, N.; Schiessl, I.M.; Riquier-Brison, A.; Gyarmati, G.; Desposito, D.; Kidokoro, K.; Butler, M.J.; Jacob, C.O.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Essential role and therapeutic targeting of the glomerular endothelial glycocalyx in lupus nephritis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e131252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.H.; Song, H.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, J.H.; Piao, S.G.; Yoon, H.E.; Ghee, J.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, J.; Yang, C.W. Upregulation of hyaluronan and its binding receptors in an experimental model of chronic cyclosporine nephropathy. Nephrology 2010, 15, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Toyoda, T.; Yamada, T.; Morikawa, T.; Ogawa, K. Specific expression of survivin, SOX9, and CD44 in renal tubules in adaptive and maladaptive repair processes after acute kidney injury in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamatani, H.; Eng, D.G.; Hiromura, K.; Pippin, J.W.; Shankland, S.J. CD44 impacts glomerular parietal epithelial cell changes in the aged mouse kidney. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser-Kawaguchi, A.; Luyt, L.G.; Turley, E. Design of peptide mimetics to block pro-inflammatory functions of HA fragments. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.S.; Choe, J.; Hahn, J.H.; Lee, H.; Jeon, J.; Choi, C.; et al. Hyaluronic acid promotes angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFbeta receptor interaction via CD44-PKCdelta. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Pearce, J.D.; Wilson, D.B.; English, W.P.; Edwards, M.S.; Geary, R.L. Loss of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM prevents constrictive artery wall remodeling. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 59, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolg, C.; McCarthy, J.B.; Yazdani, A.; Turley, E.A. Hyaluronan and RHAMM in wound repair and the “cancerization” of stromal tissues. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cha, G.; Xu, X. Effect of receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility inhibition on radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolg, C.; Hamilton, S.R.; Nakrieko, K.A.; Kooshesh, F.; Walton, P.; McCarthy, J.B.; Bissell, M.J.; Turley, E.A. Rhamm−/− fibroblasts are defective in CD44-mediated ERK1,2 motogenic signaling, leading to defective skin wound repair. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.Y.; Kim, S.; Liu, V.M.; Sabino, A.; Minkhorst, K.; Yazdani, A.; Turley, E.A. Function-Blocking RHAMM Peptides Attenuate Fibrosis and Promote Antifibrotic Adipokines in a Bleomycin-Induced Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1482–1492.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.M.; Soares da Costa, D.; Paulo, P.M.R.; Reis, R.L.; Pashkuleva, I. Co-localization and crosstalk between CD44 and RHAMM depend on hyaluronan presentation. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.R.; Fard, S.F.; Paiwand, F.F.; Tolg, C.; Veiseh, M.; Wang, C.; McCarthy, J.B.; Bissell, M.J.; Koropatnick, J.; Turley, E.A. The hyaluronan receptors CD44 and Rhamm (CD168) form complexes with ERK1,2 that sustain high basal motility in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16667–16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, H.; Shigeishi, H.; Kudo, Y.; Higashikawa, K.; Tobiume, K.; Takata, T.; Kamata, N. RHAMM/ERK interaction induces proliferative activities of cementifying fibroma cells through a mechanism based on the CD44-EGFR. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinheimer, J.; de Souza, B.M.; Cardoso, N.S.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. Current role of the NLRP3 inflammasome on obesity and insulin resistance: A systematic review. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Lee, J. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. Reappraisal of Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1460, 297–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Czepiel, K.S.; Kaber, G.; Stefanovski, D.; Hargil, A.; Pennetzdorfer, N.; Targ, R.; Reghupaty, S.C.; Wight, T.N.; Vernon, R.B.; et al. Hymecromone Promotes Longevity and Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Cells 2024, 13, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.S.; Liao, G.; DeGraff, L.M.; Gerrish, K.; Bortner, C.D.; Garantziotis, S.; Jetten, A.M. CD44 plays a critical role in regulating diet-induced adipose inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Ayala, J.E.; Lee-Young, R.S.; Zhang, Z.; James, F.D.; Neufer, P.D.; Pozzi, A.; Zutter, M.M.; Wasserman, D.H. Diet-induced muscle insulin resistance is associated with extracellular matrix remodeling and interaction with integrin alpha2beta1 in mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.S.; Kang, L.; Zheng, J.; Grueter, C.; Bracy, D.P.; James, F.D.; Pozzi, A.; Wasserman, D.H. Integrin alpha1-null mice exhibit improved fatty liver when fed a high fat diet despite severe hepatic insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6546–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugler-Lamb, A.R.; Hasib, A.; Weng, X.; Hennayake, C.K.; Lin, C.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Stimson, R.H.; Ashford, M.L.J.; Wasserman, D.H.; Kang, L. Adipocyte integrin-linked kinase plays a key role in the development of diet-induced adipose insulin resistance in male mice. Mol. Metab. 2021, 49, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, B.; Pisano, A.; Zoccali, C. Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 311, F1087–F1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cao, C.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Z. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy: A Latent Change in Obesity Requiring More Attention. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2020, 45, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunc, F.; Schleicher, E.; Weigert, C.; Fritsche, A.; Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U. The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 721–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liao, J.; Cheong, N.; Longoria, C.; Cao, G.; DeLisser, H.M.; Savani, R.C. The Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility (CD168) promotes inflammation and fibrosis after acute lung injury. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Sun, C. Ablation of CD44 Attenuates Adipogenesis in White Adipocytes via the Tryptophan 5-Hydroxylase 2/5-Hydroxytryptamine Axis to Protect Mice from High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Am. J. Pathol. 2025, 195, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, M.O.; Ham, J.R.; Lee, H.I.; Seo, K.I.; Lee, M.K. Long-term supplementation of umbelliferone and 4-methylumbelliferone alleviates high-fat diet induced hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia in mice. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 216, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, B.; Musale, V.; Weng, X.; Banah, A.K.; Lawlor, A.; Murdoch, C.E.; Lay, A.C.; Heesom, K.J.; Coward, R.J.M.; O’Connor, C.L.; et al. A Novel Role of Hyaluronan and Its Membrane Receptors, CD44 and RHAMM, in Obesity-Related Kidney Pathology. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111598
Qi B, Musale V, Weng X, Banah AK, Lawlor A, Murdoch CE, Lay AC, Heesom KJ, Coward RJM, O’Connor CL, et al. A Novel Role of Hyaluronan and Its Membrane Receptors, CD44 and RHAMM, in Obesity-Related Kidney Pathology. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111598
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Bingxue, Vishal Musale, Xiong Weng, Ayman K. Banah, Alexander Lawlor, Colin E. Murdoch, Abigail C. Lay, Kate J. Heesom, Richard J. M. Coward, Christopher L. O’Connor, and et al. 2025. "A Novel Role of Hyaluronan and Its Membrane Receptors, CD44 and RHAMM, in Obesity-Related Kidney Pathology" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111598
APA StyleQi, B., Musale, V., Weng, X., Banah, A. K., Lawlor, A., Murdoch, C. E., Lay, A. C., Heesom, K. J., Coward, R. J. M., O’Connor, C. L., Ju, W., Bitzer, M., Hills, C. E., Chen, Y., & Kang, L. (2025). A Novel Role of Hyaluronan and Its Membrane Receptors, CD44 and RHAMM, in Obesity-Related Kidney Pathology. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111598





