The Capacities of the Probiotic Strains L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM to Induce Th1-Stimulating Cytokines in Dendritic Cells Are Inversely Correlated with the Thickness of Their S-Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
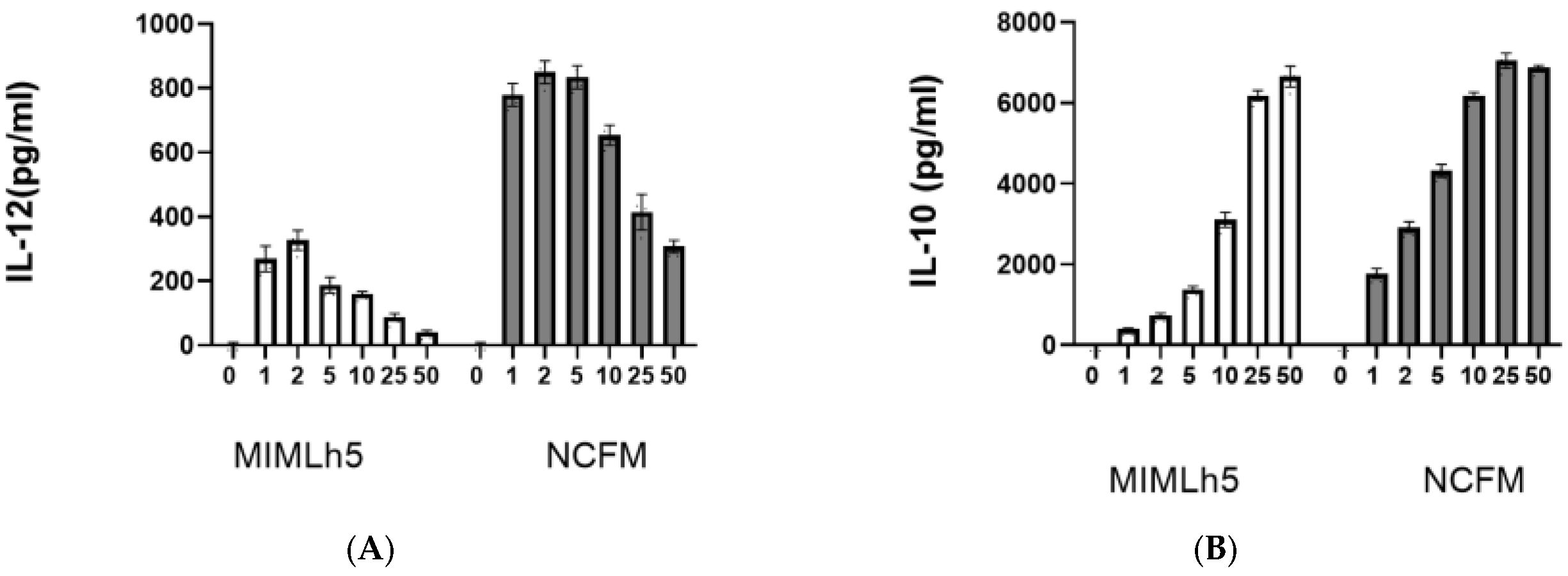
3.1. IL-12 Induction by L. acidophilus NCFM and L. helveticus MIMLh5 Both Peak at MOI 2–5 but Result in Different IL-12 Levels
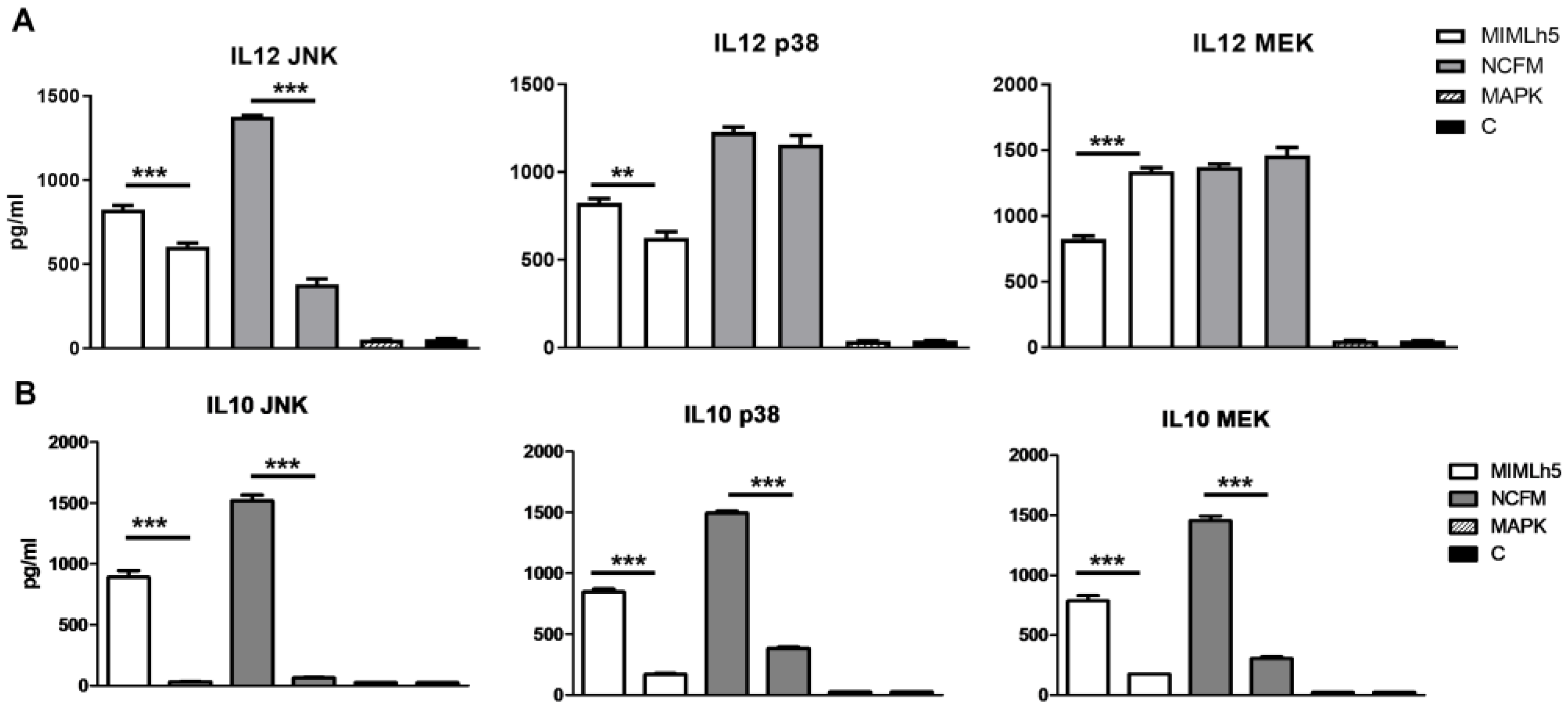
3.2. L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM Differently Activate MAPK Pathways
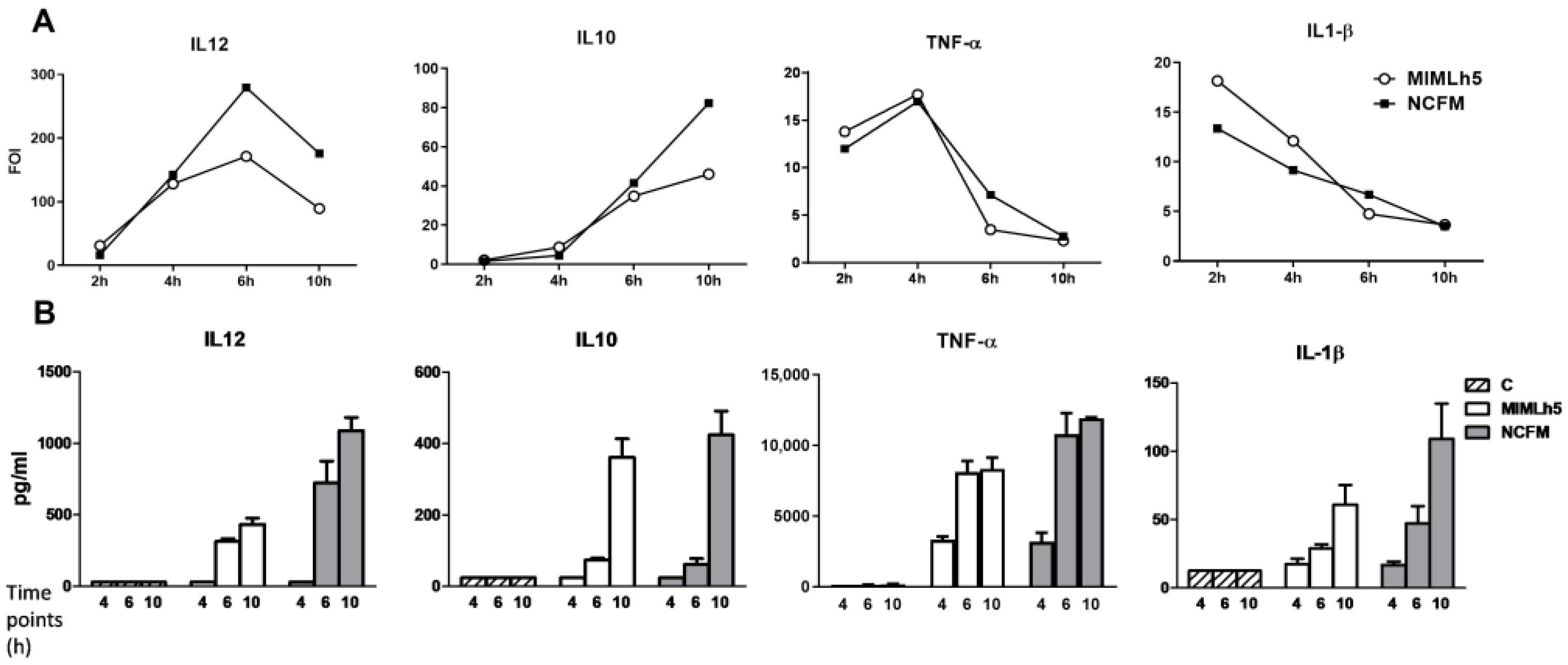
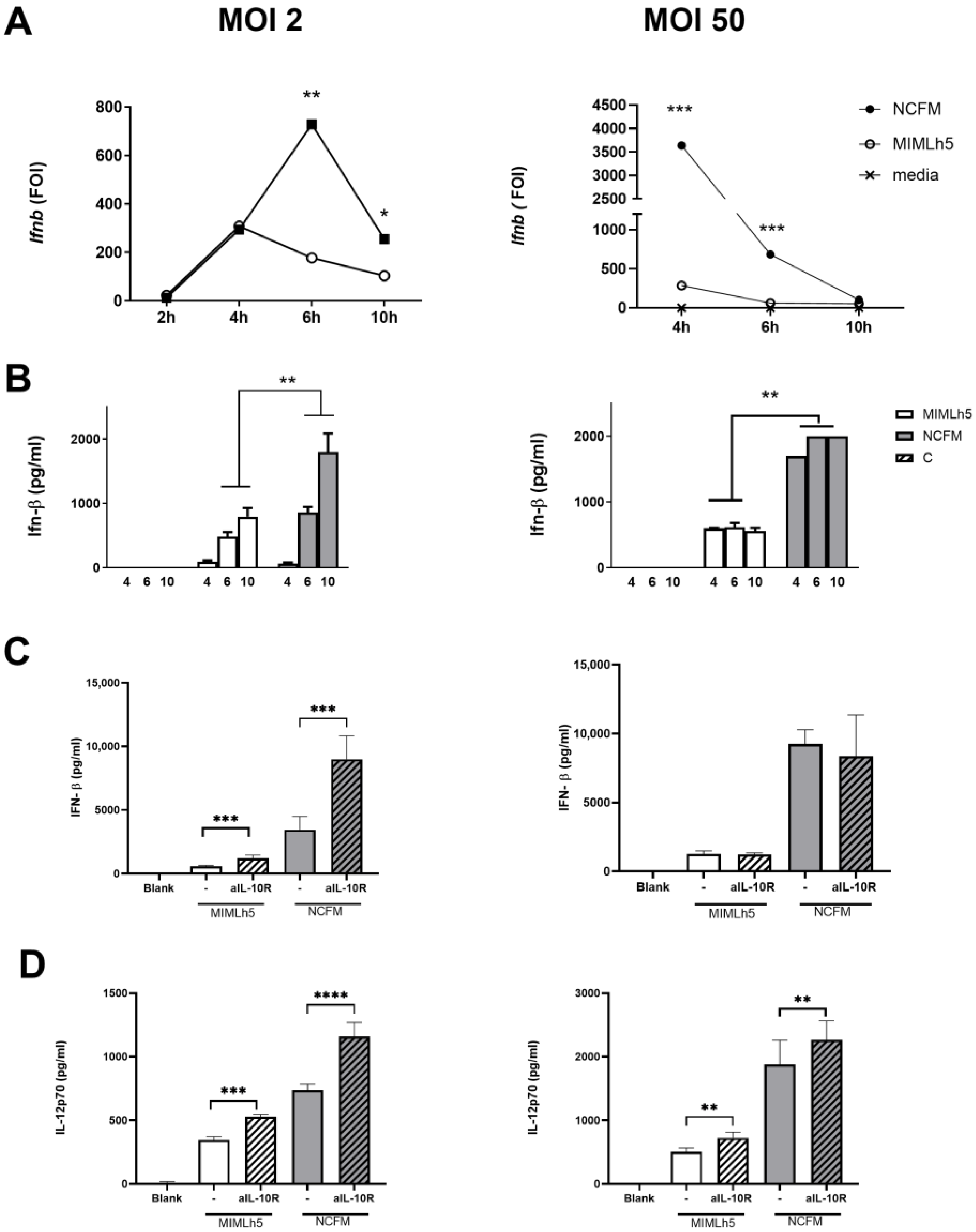
3.3. The Respective Effect of L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM on IL12 Production Correlates with the Ability to Induce IFN-β
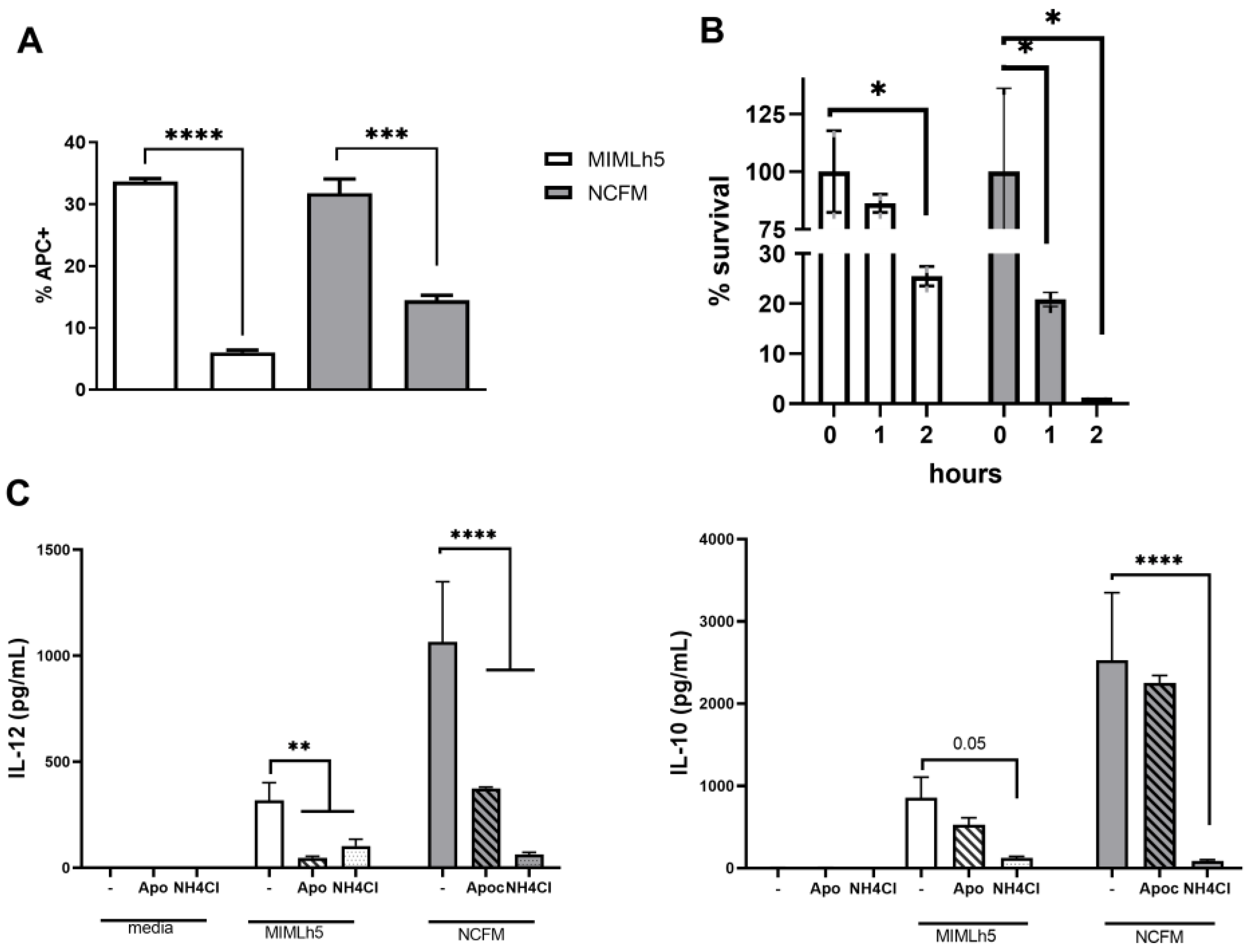
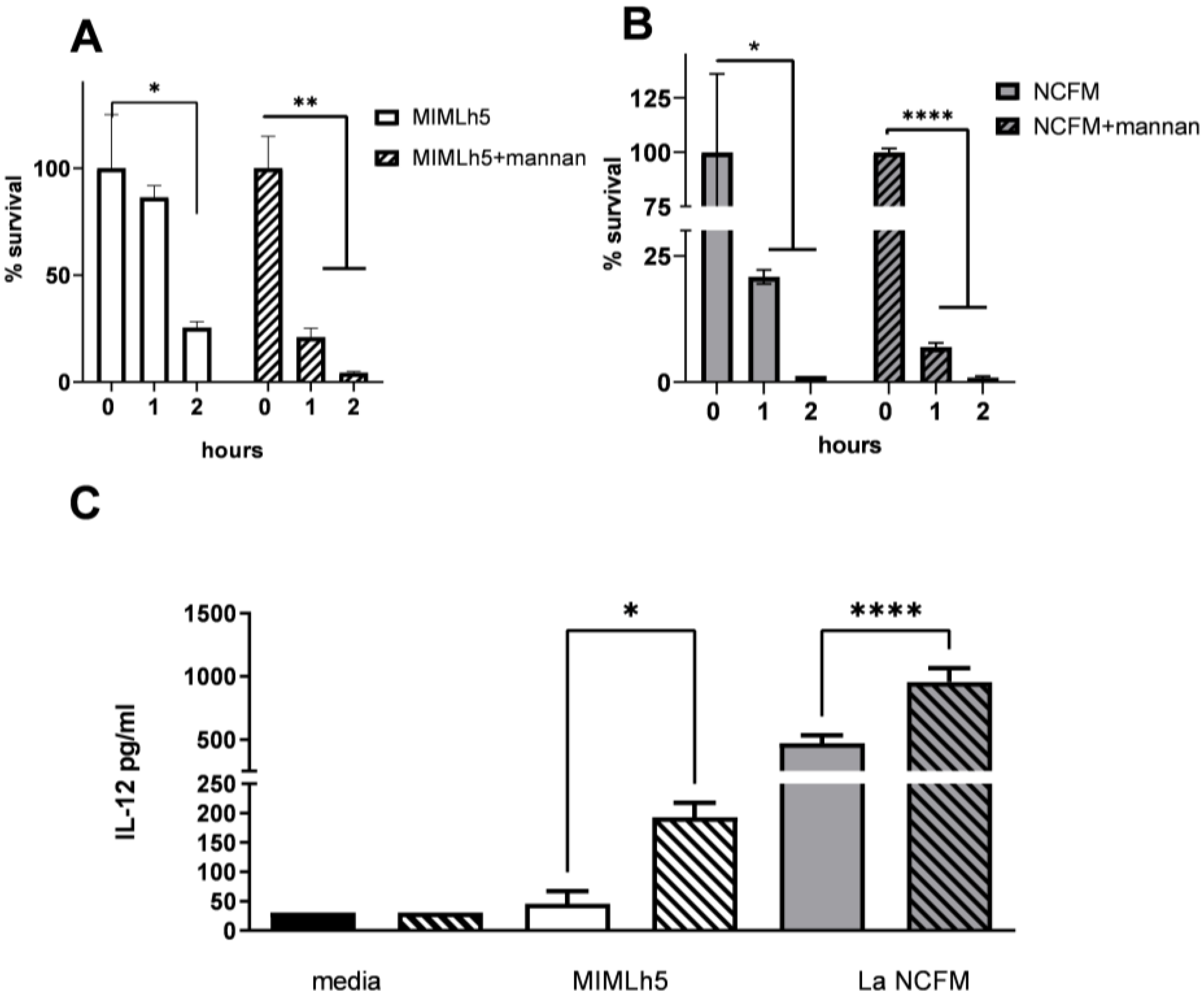
3.4. L. helveticus MIMLh5 Displays a Higher Survival Ability in DCs
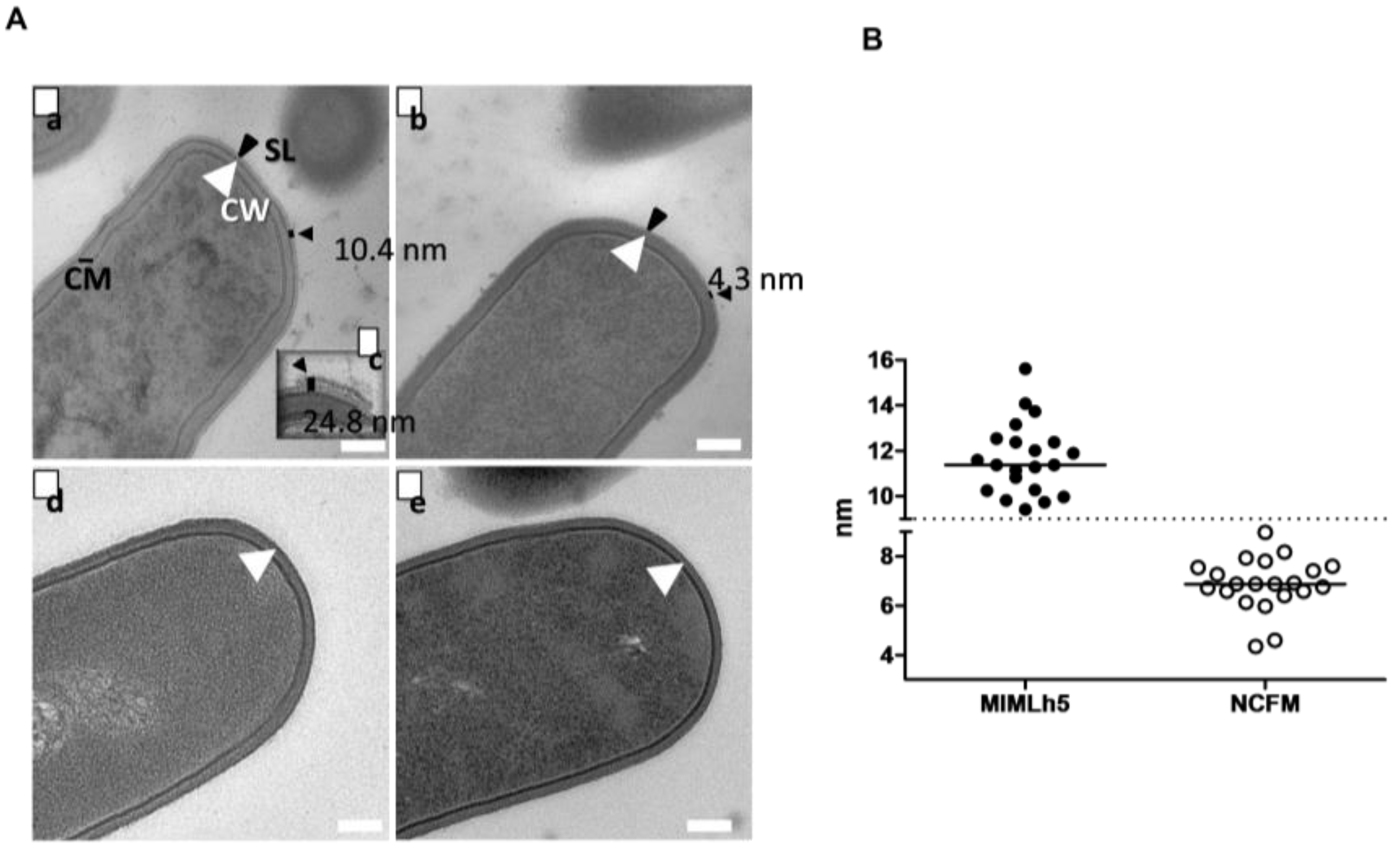
3.5. L. helveticus MIMLh5 Carries a Thicker S-Layer Compared to L. acidophilus NCFM
3.6. Elastic Modulus Measurements by AFM Reveal Higher Stiffness of L. helveticus MIMLh5 Surface Compared to L. acidophilus NCFM
| Sample | Elastic Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|
| MIMLh5 | 5.69 ± 0.12 a |
| MIMLh5_LiCl | 1.11 ± 0.82 b |
| NCFM | 2.88 ± 1.02 b |
| NCFM_LiCl | 1.24 ± 0.50 b |
| L92 | 6.79 ± 3.70 a |
| L92_LiCl | 6.44 ± 0.89 a |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callanan, M.; Kaleta, P.; O’Callaghan, J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Jordan, K.; McAuliffe, O.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; Slattery, L.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Beresford, T.; et al. Genome sequence of Lactobacillus helveticus, an organism distinguished by selective gene loss and insertion sequence element expansion. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sára, M.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layer proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomino, M.M.; Allievi, M.C.; Gordillo, T.B.; Bockor, S.S.; Martin, J.F.; Ruzal, S.M. Surface layer proteins in species of the family Lactobacillaceae. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 1232–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelescu, I.R.; Zamfir, M.; Ionetic, E.C.; Grosu-Tudor, S.S. The Biological Role of the S-Layer Produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 34.9 in Cell Protection and Its Probiotic Properties. Fermentation 2024, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assandri, M.H.; Malamud, M.; Trejo, F.M.; Serradell, M.L.A. S-layer proteins as immune players: Tales from pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2023, 24, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, C.; Goh, Y.J.; O’Flaherty, S.; Barrangou, R. S-layer associated proteins contribute to the adhesive and immunomodulatory properties of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Yokota, K.; Igimi, S.; Kajikawa, A. Comparative analysis of immunological properties of S-layer proteins isolated from Lactobacillus strains. Microbiology 2019, 165, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Sára, M.; Pum, D.; Schuster, B. Characterization and use of crystalline bacterial cell surface layers. Progress Surf. Sci. 2001, 68, 231–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avall-Jääskeläinen, S.; Palva, A. Lactobacillus surface layers and their applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, H.J.; Pouwels, P.H. Expression, secretion and antigenic variation of bacterial S-layer proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuknyte, M.; Brockmann, E.C.; Huovinen, T.; Guglielmetti, S.; Mora, D.; Taverniti, V.; Arioli, S.; De Noni, I.; Lamminmäki, U. Lactobacillus helveticus MIMLh5-specific antibodies for detection of S-layer protein in Grana Padano protected-designation-of-origin cheese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.R.; Hymes, J.; Sanozky-Dawes, R.; Henriksen, E.D.; Barrangou, R.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Conserved S-Layer-Associated Proteins Revealed by Exoproteomic Survey of S-Layer-Forming Lactobacilli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinov, S.R.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Bruijns, S.C.; Singh, S.K.; Valence, F.; Molle, D.; Lortal, S.; Altermann, E.; Klaenhammer, T.R.; et al. S layer protein A of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM regulates immature dendritic cell and T cell functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19474–19479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverniti, V.; Marengo, M.; Fuglsang, E.; Skovsted, H.M.; Arioli, S.; Mantegazza, G.; Gargari, G.; Iametti, S.; Bonomi, F.; Guglielmetti, S.; et al. Surface Layer of Lactobacillus helveticus MIMLh5 Promotes Endocytosis by Dendritic Cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverniti, V.; Stuknyte, M.; Minuzzo, M.; Arioli, S.; De Noni, I.; Scabiosi, C.; Cordova, Z.M.; Junttila, I.; Hämäläinen, S.; Turpeinen, H.; et al. S-layer protein mediates the stimulatory effect of Lactobacillus helveticus MIMLh5 on innate immunity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverniti, V.; Guglielmetti, S. Health-Promoting Properties of Lactobacillus helveticus. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decout, A.; Krasias, I.; Roberts, L.; Molina, B.G.; Charenton, C.; Romero, D.B.; Tee, Q.Y.; Marchesi, J.R.; Ng, S.; Sykes, L.; et al. Lactobacillus crispatus S-layer proteins modulate innate immune response and inflammation in the lower female reproductive tract. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, D.; Kuleaşan, H.; Korkut Altıntaş, A. The importance of the S-layer on the adhesion and aggregation ability of Lactic acid bacteria. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 7, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.P.; Geoghegan, E.M.; Lepenies, B.; Ruzal, S.; Kielian, M.M.; Martinez, M.G. Surface (S) Layer Proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus Block Virus Infection via DC-SIGN Interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 810. [Google Scholar]
- do Carmo, F.L.; Rabah, H.; De Oliveira Carvalho, R.D.; Gaucher, F.; Cordeiro, B.F.; da Silva, S.H.; Le Loir, Y.; Azevedo, V.; Jan, G. Extractable Bacterial Surface Proteins in Probiotic-Host Interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 645. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, G.; Rasmussen, S.; Zeuthen, L.H.; Nielsen, B.N.; Jarmer, H.; Jespersen, L.; Frøkiaer, H. Lactobacillus acidophilus induces virus immune defence genes in murine dendritic cells by a Toll-like receptor-2-dependent mechanism. Immunology 2010, 131, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.; Christensen, H.R.; Zeuthen, L.H.; Vogensen, F.K.; Jakobsen, M.; Frøkiær, H. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria induce differential interferon-β profiles in dendritic cells. Cytokine 2011, 56, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, Y.; Rizzello, V.; Cavaliere, R.; Campana, S.; De Pasquale, C.; Barberi, C.; Oliveri, D.; Pezzino, G.; Costa, G.; Meddah, A.T.; et al. Divergent signaling pathways regulate IL-12 production induced by different species of Lactobacilli in human dendritic cells. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 166, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeuthen, L.H.; Fink, L.N.; Frøkiaer, H. Toll-like receptor 2 and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-2 play divergent roles in the recognition of gut-derived lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in dendritic cells. Immunology 2008, 124, 489–502. [Google Scholar]
- Romani, L.; Puccetti, P.; Bistoni, F. Interleukin-12 in infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 611–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporota, L. Interleukin-12 and the development of atopy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.P.; Zhou, L.; Xu, C.F. Effect of dietary fiber on constipation: A meta analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 7378–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Invited review: The scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic. J. Dairy. Sci. 2001, 84, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, L.; Welsby, I.; Lund, L.D.; Goriely, S.; Frøkiaer, H. Plasma membrane Toll-like receptor activation increases bacterial uptake but abrogates endosomal Lactobacillus acidophilus induction of interferon-β. Immunology 2016, 149, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynönen, U.; Palva, A. Lactobacillus surface layer proteins: Structure, function and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 5225–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, H.R.; Frøkiaer, H.; Pestka, J.J. Lactobacilli differentially modulate expression of cytokines and maturation surface markers in murine dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Maaetoft-Udsen, K.; Stifter, S.A.; Hertzog, P.; Goriely, S.; Thomsen, A.R.; Paludan, S.R.; Frøkiær, H. MyD88 drives the IFN-β response to Lactobacillus acidophilus in dendritic cells through a mechanism involving IRF1, IRF3, and IRF7. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Incecco, P.; Pellegrino, L.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Bassi, D. The late blowing defect of hard cheeses: Behaviour of cells and spores of Clostridium tyrobutyricum throughout the cheese manufacturing and ripening. LWT 2018, 87, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinello, F.; La Storia, A.; Mauriello, G.; Passeri, D. Atomic Force microscopy techniques to investigate activated food packaging materials. Trends in Food Science and Technology 2018, 87, 8493. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Pérez, S.; Chanona-Pérez, J.J.; Méndez-Méndez, J.V.; Arzate-Vázquez, I.; Hernández-Varela, J.D.; Vera, N.G. Recent advances in atomic force microscopy for assessing the nanomechanical properties of food materials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 87, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, R.; Kiyoshima-Shibata, J.; Nagaoka, M.; Nanno, M.; Shida, K. Bacterial teichoic acids reverse predominant IL-12 production induced by certain lactobacillus strains into predominant IL-10 production via TLR2-dependent ERK activation in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejrazka, M.; Mícek, R.; Stípek, S. Apocynin inhibits NADPH oxidase in phagocytes but stimulates ROS production in non-phagocytic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1722, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, R.; Eld, H.M.S.; Sørensen, J.; Fuglsang, E.; Lund, L.D.; Taverniti, V.; Frøkiær, H. Mannan Enhances IL-12 Production by Increasing Bacterial Uptake and Endosomal Degradation in L. acidophilus and S. aureus Stimulated Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Tang, R.; Deng, F.; Kang, W.; Zhao, L. In Vitro Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria with RAW264.7 Macrophages and the Immunoregulatory Mechanism. Processes 2024, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Shen, M.; Yu, H. Two strains of probiotic Lactobacillus enhance immune response and promote naive T cell polarization to Th1. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Chen, P.; Chen, W. Immunomodulatory Effects of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria on Allergic Response and Its Relationship with In Vitro Properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Song, Z. Lactobacillus delbrueckii alleviates depression-like behavior through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling in mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Q.; de Haan, B.; Zhang, H.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Identification of TLR2/TLR6 signalling lactic acid bacteria for supporting immune regulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeer, S.; Bron, P.A.; Marco, M.L.; Van Pijkeren, J.P.; Motherway, M.O.; Hill, C.; Pot, B.; Roos, S.; Klaenhammer, T. Identification of probiotic effector molecules: Present state and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.F.; Kelsey, I.; Forbes, H.; Miller-Jensen, K. Single-cell secretion analysis reveals a dual role for IL-10 in restraining and resolving the TLR4-induced inflammatory response. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Chang, C.H. Negative regulation of MyD88-dependent signaling by IL-10 in dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18327–18332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, G.; Humbert, M.; Deauvieau, F.; Scuiller, M.; Hiscott, J.; Bates, E.E.; Trinchieri, G.; Caux, C.; Garrone, P. A type I interferon autocrine-paracrine loop is involved in Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-12p70 secretion by dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, Z.M.; Henneke, P.; Kolter, J. From Flies to Men: ROS and the NADPH Oxidase in Phagocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 628991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, D.A.; Hines, H.B.; Cheng, R.Y.; Switzer, C.H.; Flores-Santana, W.; Vitek, M.P.; Ridnour, L.A.; Colton, C.A. Nitric oxide and redox mechanisms in the immune response. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalmanach, G.; Saidi, A.; Bigot, P.; Chazeirat, T.; Lecaille, F.; Wartenberg, M. Regulation of the Proteolytic Activity of Cysteine Cathepsins by Oxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shehri, S.S. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and innate immune response. Biochimie 2021, 181, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, K.; Hauri-Hohl, M.; Jaquet, V.; Weyd, H. Unlocking the power of NOX2: A comprehensive review on its role in immune regulation. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eld, H.M.S.; Johnsen, P.R.; Nielsen, E.M.; Jørgensen, F.Z.; Lindstrøm-Svendsen, M.; Baldry, M.; Ingmer, H.; Frøkiær, H. Soluble C-Type Lectin-Receptor Ligands Stimulate ROS Production in Dendritic Cells and Potentiate Killing of MRSA as Well as the MRSA Induced IL-12 Production. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taverniti, V.; D’Incecco, P.; Farris, S.; Jonsen, P.R.; Skovsted Eld, H.; Sørensen, J.; Brunelli, L.; Mantegazza, G.; Arioli, S.; Mora, D.; et al. The Capacities of the Probiotic Strains L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM to Induce Th1-Stimulating Cytokines in Dendritic Cells Are Inversely Correlated with the Thickness of Their S-Layers. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071012
Taverniti V, D’Incecco P, Farris S, Jonsen PR, Skovsted Eld H, Sørensen J, Brunelli L, Mantegazza G, Arioli S, Mora D, et al. The Capacities of the Probiotic Strains L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM to Induce Th1-Stimulating Cytokines in Dendritic Cells Are Inversely Correlated with the Thickness of Their S-Layers. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071012
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaverniti, Valentina, Paolo D’Incecco, Stefano Farris, Peter Riber Jonsen, Helene Skovsted Eld, Juliane Sørensen, Laura Brunelli, Giacomo Mantegazza, Stefania Arioli, Diego Mora, and et al. 2025. "The Capacities of the Probiotic Strains L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM to Induce Th1-Stimulating Cytokines in Dendritic Cells Are Inversely Correlated with the Thickness of Their S-Layers" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071012
APA StyleTaverniti, V., D’Incecco, P., Farris, S., Jonsen, P. R., Skovsted Eld, H., Sørensen, J., Brunelli, L., Mantegazza, G., Arioli, S., Mora, D., Guglielmetti, S., & Frøkiær, H. (2025). The Capacities of the Probiotic Strains L. helveticus MIMLh5 and L. acidophilus NCFM to Induce Th1-Stimulating Cytokines in Dendritic Cells Are Inversely Correlated with the Thickness of Their S-Layers. Biomolecules, 15(7), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071012











