A Type Ia Crustin from the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Antimicrobial and Chemotactic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Shrimp and Tissue Collection
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Cloning
2.3. Bioinformatics and Structural Characterization
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.5. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
2.6. Peptide Design and Synthesis
2.7. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
2.8. Microbial Binding Assay
2.9. Electron Microscopy
2.10. In Vitro Chemotaxis Assay
2.11. RNA Interference Assay and Expression Changes in Immune Genes in the LvCrustinIa-2-Knockdown Shrimp
3. Results
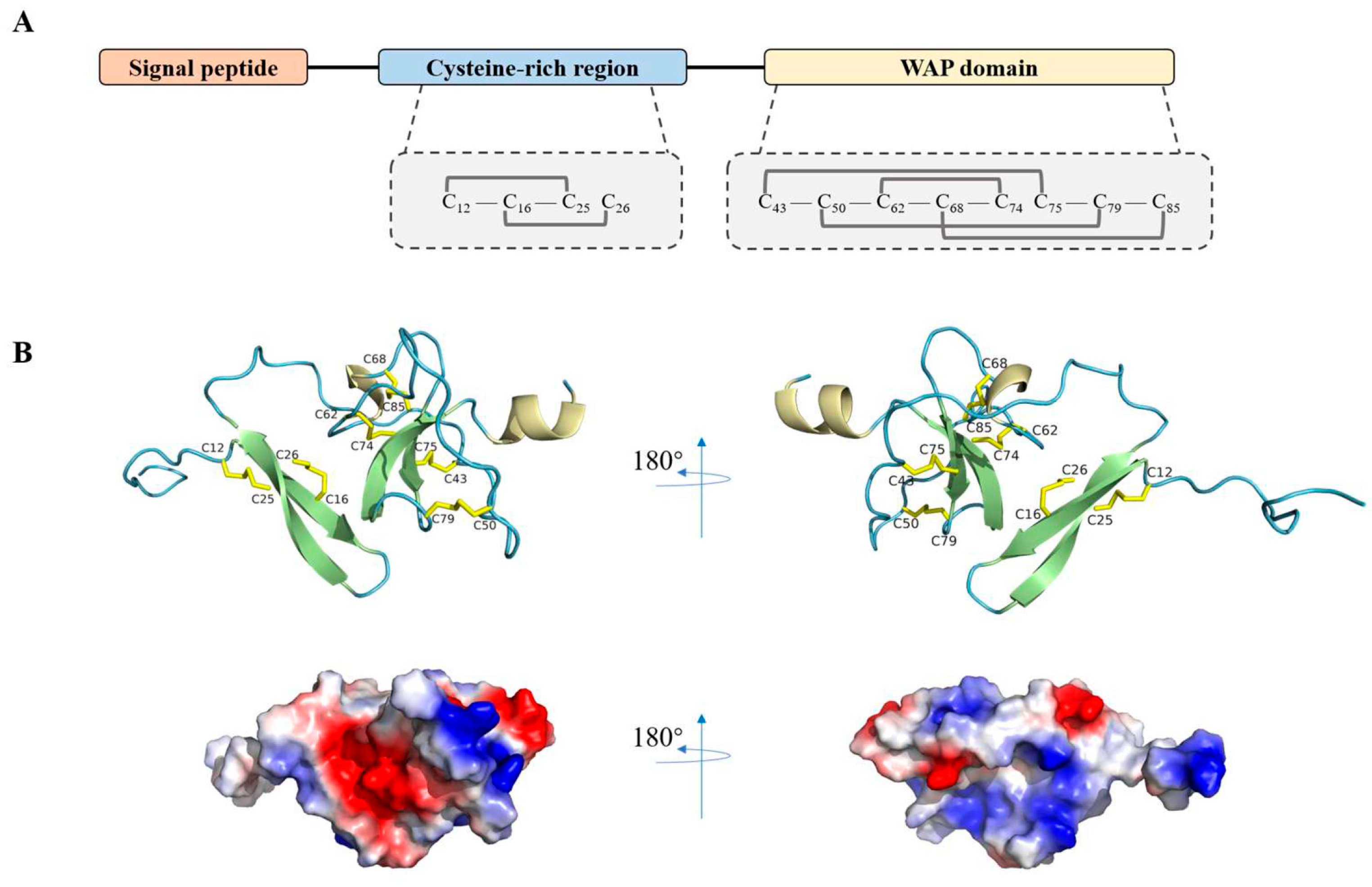
3.1. Characterization of LvCrustinIa-2
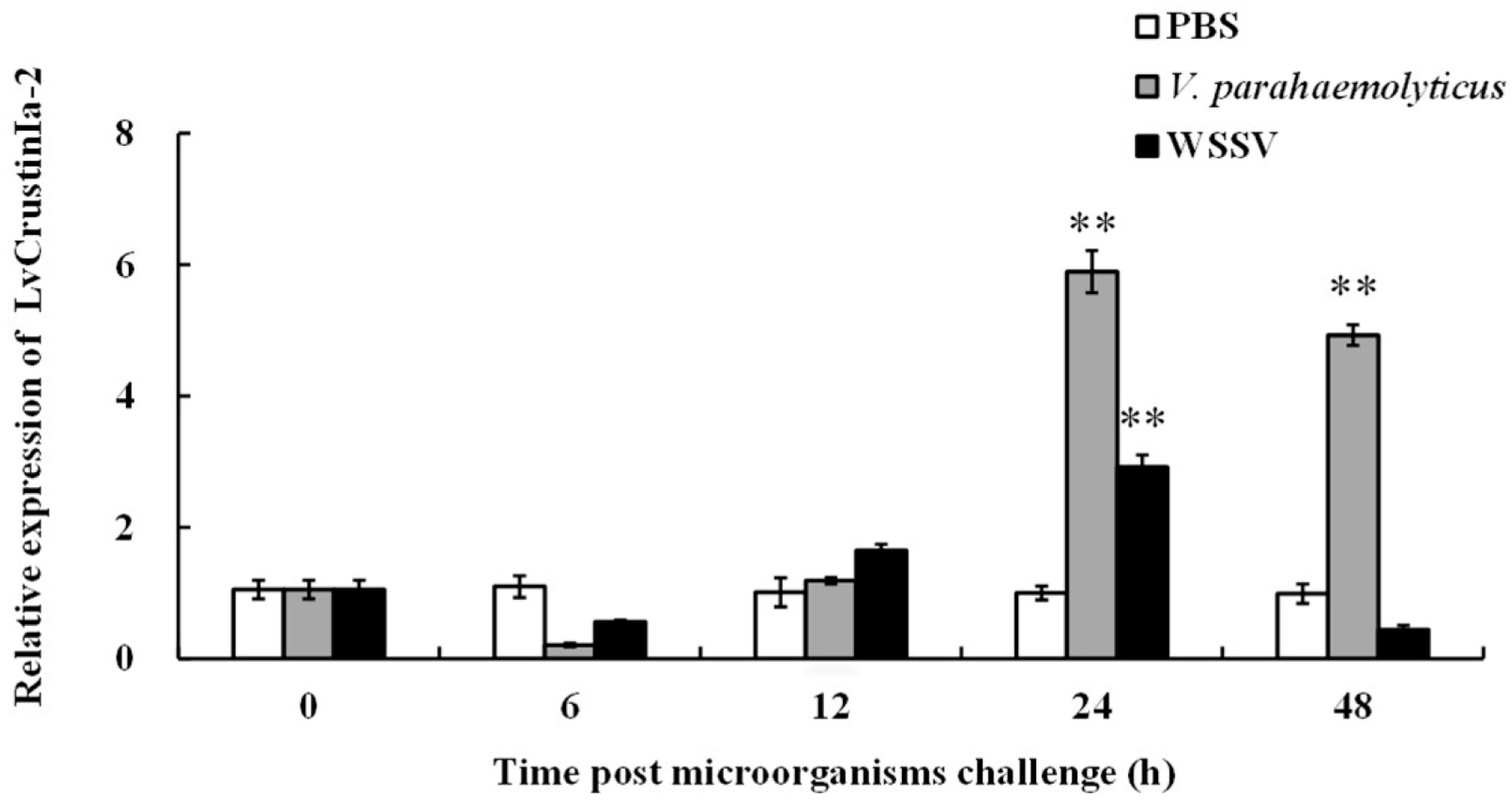
3.2. Expression Pattern Analysis of LvCrustinIa-2 After Pathogen Challenge
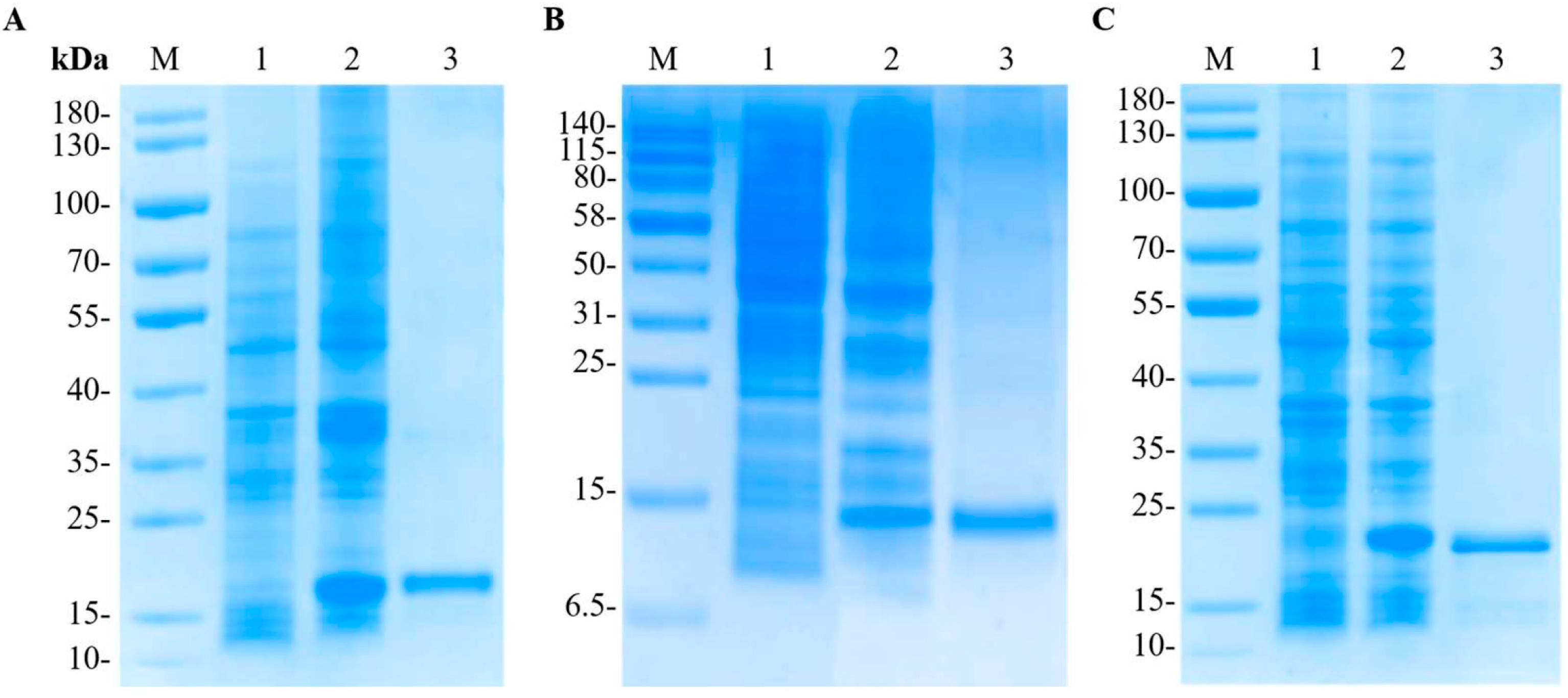
3.3. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant LvCrustinIa-2 and LvCrustinIa-2-WAP
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity of LvCrustinIa-2 Depending on the WAP Domain
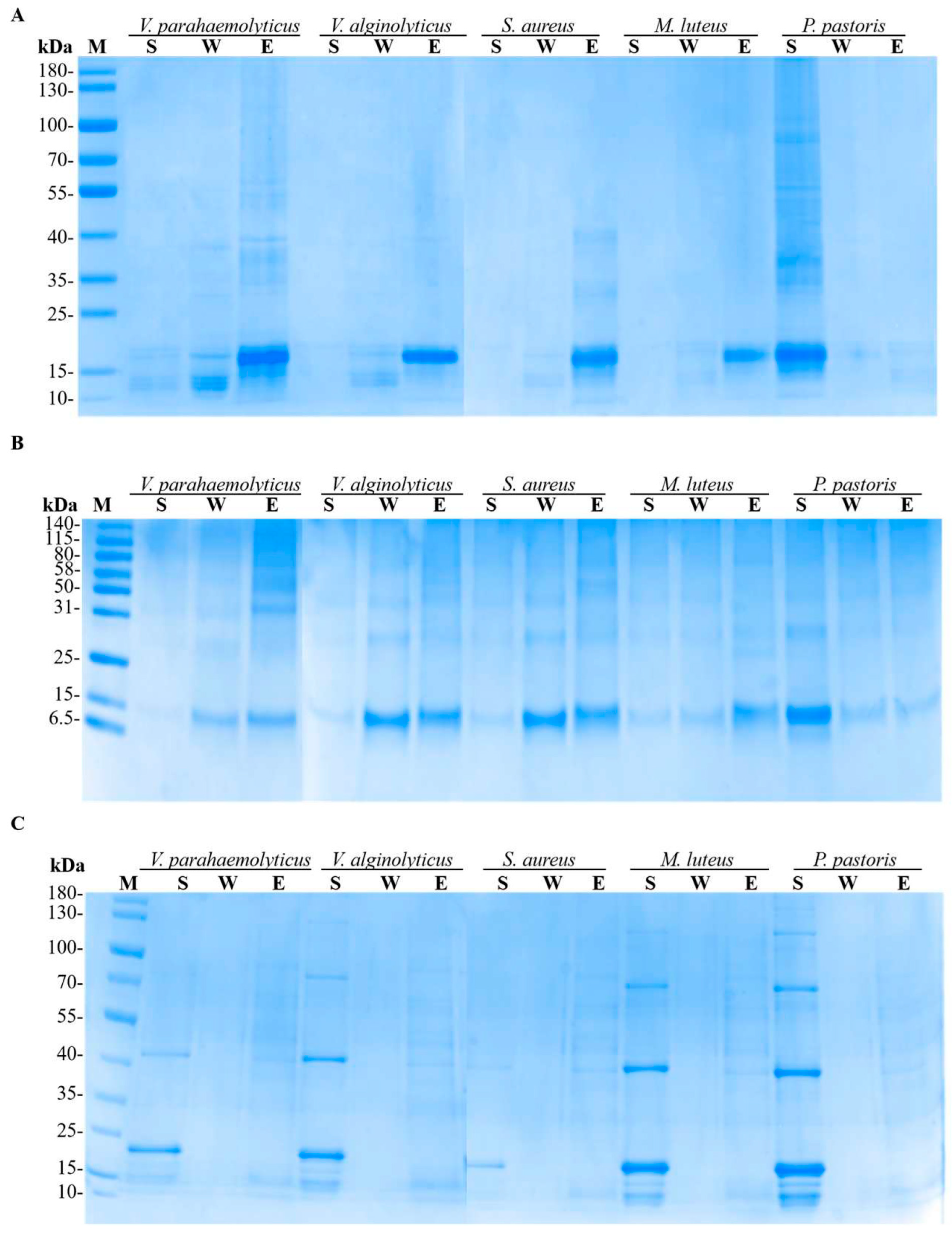
3.5. Microbial Binding Activity of LvCrustinIa-2
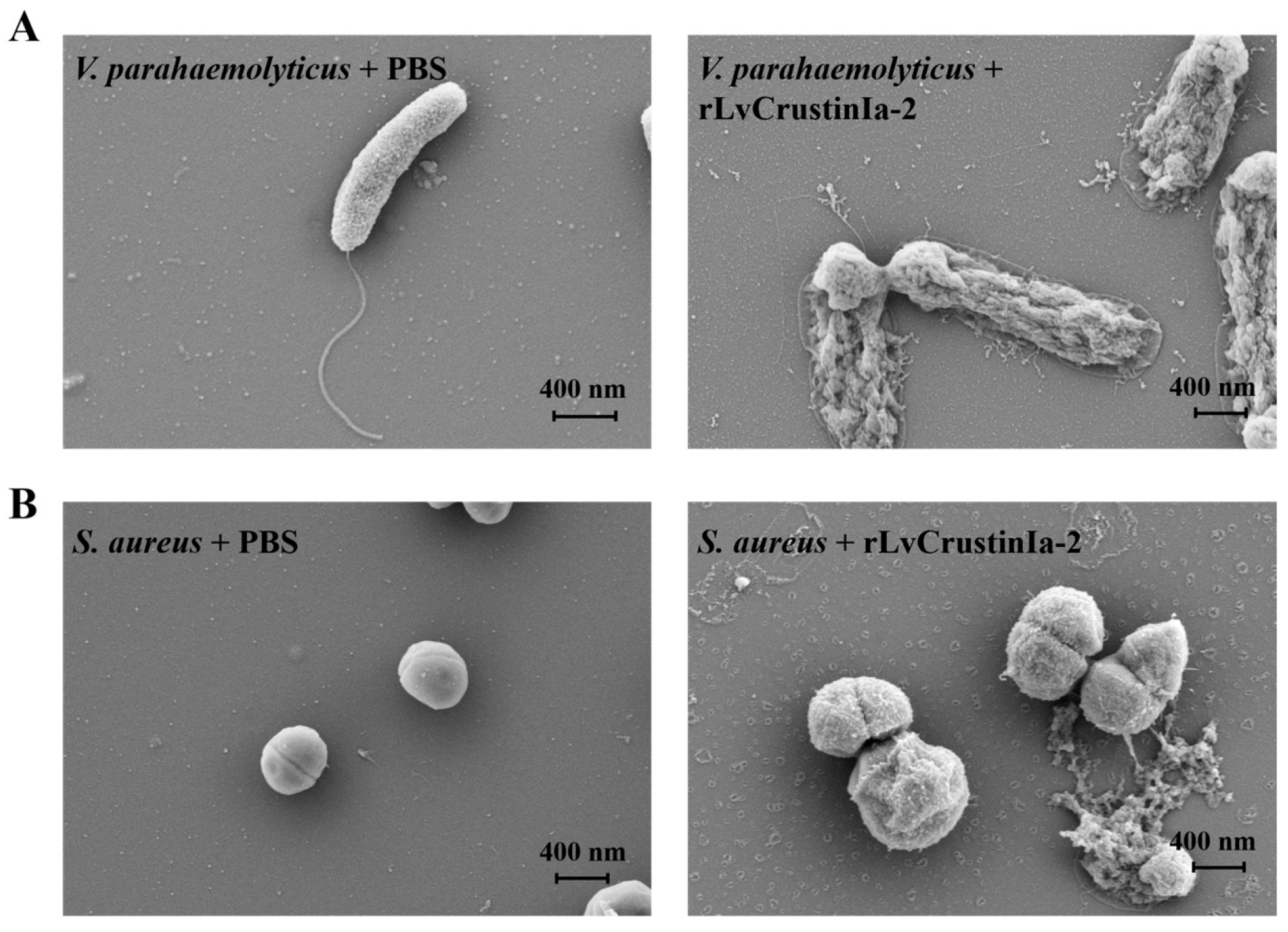
3.6. Effects of LvCrustinIa-2 on Bacterial Morphology and Membrane Integrity
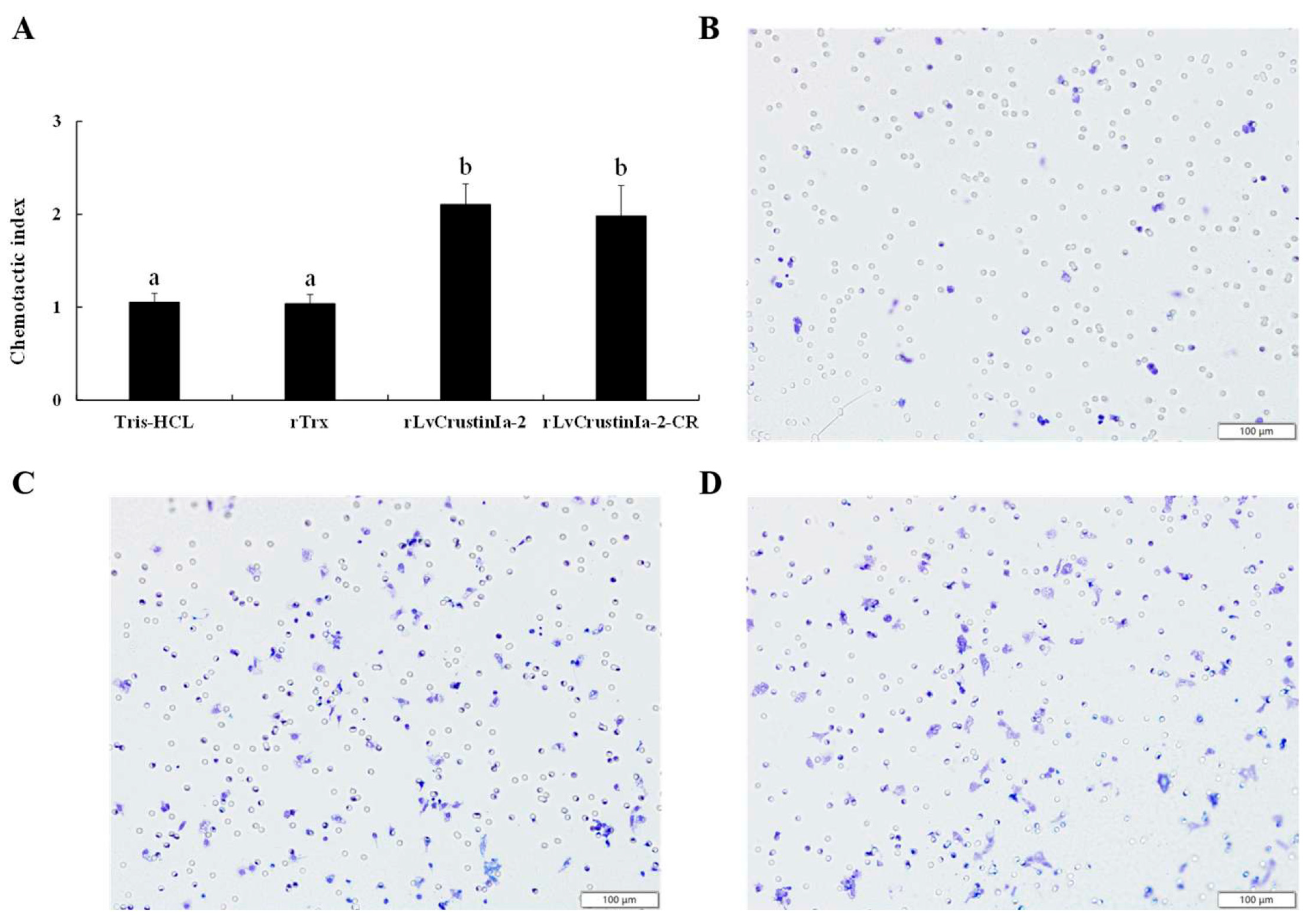
3.7. Chemotactic Activity of LvCrustinIa-2 on Shrimp Hemocytes
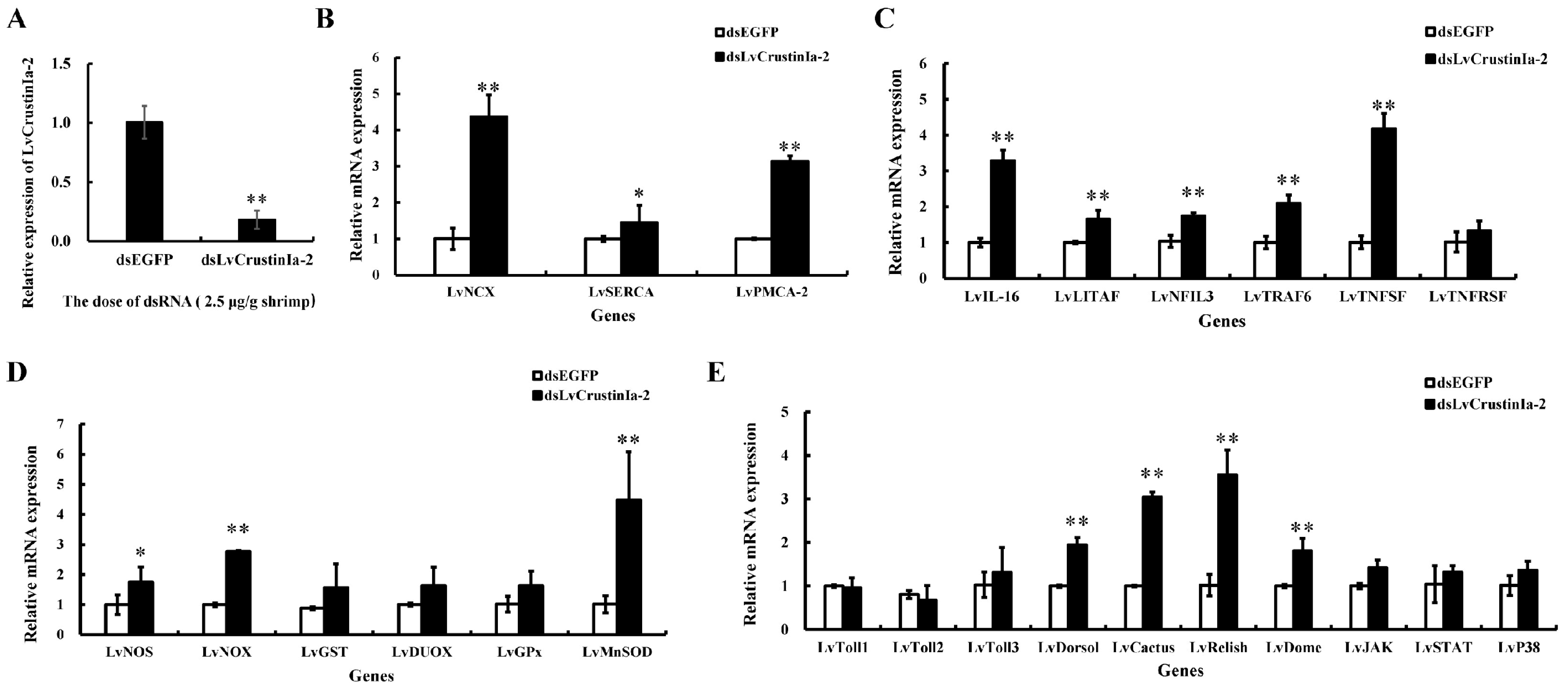
3.8. LvCrustinIa-2 Knockdown and Its Effect on the Expression of Immune Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, H.K.; Kim, C.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. The therapeutic applications of antimicrobial peptides (amps): A patent review. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, A.P.; Mechesso, A.F.; Wang, G. Expanding the landscape of amino acid-rich antimicrobial peptides: Definition, deployment in nature, implications for peptide design and therapeutic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadpanah, A.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial peptides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: Functions and clinical potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Yan, Z.B.; Meng, Y.M.; Hong, X.Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, X.R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dou, X.; Song, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Shan, A. Antimicrobial peptides: Promising alternatives in the post feeding antibiotic era. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 831–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Das, S. Mammalian antimicrobial peptides: Promising therapeutic targets against infection and chronic inflammation. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 99–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Song, Y. Mechanism of antimicrobial peptides: Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antibiofilm activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, T.; Kristensen, H.H. Using antimicrobial host defense peptides as anti-infective and immunomodulatory agents. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Nijnik, A.; Philpott, D.J. Modulating immunity as a therapy for bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chertov, O.; Oppenheim, J.J. Participation of mammalian defensins and cathelicidins in anti-microbial immunity: Receptors and activities of human defensins and cathelicidin (ll-37). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.L.; Poon, G.F.; Birkenhead, D.; Pena, O.M.; Falsafi, R.; Dahlgren, C.; Karlsson, A.; Bylund, J.; Hancock, R.E.; Johnson, P. Host defense peptide ll-37 selectively reduces proinflammatory macrophage responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5497–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cañadillas, J.M.; Zaballos, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Varona, R.; Roncal, F.; Albar, J.P.; Márquez, G.; Bruix, M. Nmr solution structure of murine ccl20/mip-3alpha, a chemokine that specifically chemoattracts immature dendritic cells and lymphocytes through its highly specific interaction with the beta-chemokine receptor ccr6. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28372–28379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrl, J.; Yang, D.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Hehlgans, T. Human beta-defensin 2 and 3 and their mouse orthologs induce chemotaxis through interaction with CCR2. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6688–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Molecular and functional characterization of the gilthead seabream β-defensin demonstrate its chemotactic and antimicrobial activity. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Xiao, X.; Jakovlić, I.; Liu, X.; Su, J.; Yuan, G. Chemotactic effect of β-defensin 1 on macrophages in Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Chi, H.; Tang, X.; Xing, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhan, W. The functions of β-defensin in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): Antibiosis, chemotaxis and modulation of phagocytosis. Biology 2021, 10, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Han, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Mu, C. Antibacterial activities and mechanisms of action of a defensin from manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Ruan, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Tian, X.; Yang, D.; et al. Molecular characterization, expression and antibacterial function of a macin, hdmac, from Haliotis discus hannai. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 204, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Han, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, L.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J. Identification, antibacterial activities and action mode of two macins from manila clam Venerupis philippinarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 118, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Rosa, R.; Schmitt, P.; Vieira, C.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Mitta, G.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E. Antimicrobial peptides in marine invertebrate health and disease: Table 1. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Amparyup, P. Sequence diversity and evolution of antimicrobial peptides in invertebrates. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Amparyup, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Supungul, P. Cationic antimicrobial peptides in penaeid shrimp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.J.; Dyrynda, E.A. Antimicrobial proteins: From old proteins, new tricks. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Molecular and functional diversity of crustin-like genes in the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, C.; Matos, G.M.; Rosa, R.D. On the wave of the crustin antimicrobial peptide family: From sequence diversity to function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 3, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.J.; Fernandes, J.M.; Kemp, G.D.; Hauton, C. Crustins: Enigmatic wap domain-containing antibacterial proteins from crustaceans. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, C.; Zhu, P.; Yang, Y.; Lei, A.; Chen, X.; Liang, W.; Chen, M.; Xiong, J.; Li, C. A new crustin is involved in the innate immune response of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visetnan, S.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Donpudsa, S.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. A single wap domain-containing protein from Litopenaeus vannamei possesses antiproteinase activity against subtilisin and antimicrobial activity against ahpnd-inducing vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lan, J.F.; Sun, J.J.; Jia, W.M.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. A novel crustin from Marsupenaeus japonicus promotes hemocyte phagocytosis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Yu, Y.B.; Choi, J.H.; Jo, A.H.; Hong, S.M.; Kang, J.C.; Kim, J.H. Viral shrimp diseases listed by the oie: A review. Viruses 2022, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorriehzahra, M.; Banaederakhshan, R. Early mortality syndrome (EMS) as new emerging threat in shrimp industry. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Crustin defense against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection by regulating intestinal microbial balance in Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Boulo, V.; Mialhe, E.; Bachere, E. Characterisation of shrimp haemocytes and plasma components by monoclonal antibodies. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108 Pt 3, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinakumar, R.; Walkenhorst, W.F.; Wimley, W.C. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides by rational combinatorial design and high-throughput screening: The importance of interfacial activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7609–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100 (ISBN 978-1-68440-170-3 [Print]; ISBN 978-1-68440-171-0 [Electronic]); Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Söderhäll, K. Characterization of a pattern recognition protein, a masquerade-like protein, in the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7319–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Sun, L. A fish galectin-8 possesses direct bactericidal activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justus, C.R.; Marie, M.A.; Sanderlin, E.J.; Yang, L.V. Transwell in vitro cell migration and invasion assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2644, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipolito, S.G.; Shitara, A.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Role of Marsupenaeus japonicus crustin-like peptide against Vibrio penaeicida and white spot syndrome virus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiaraj, J.; Gnanam, A.J.; Muthukrishnan, D.; Gudimella, R.; Milton, J.; Singh, A.; Muthupandian, S.; Kasi, M.; Bhassu, S. Crustin, a wap domain containing antimicrobial peptide from freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii: Immune characterization. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Andrén, T.; Söderhäll, I. Antibacterial peptides in hemocytes and hematopoietic tissue from freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus: Characterization and expression pattern. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gai, Y.; Song, L. A novel type iii crustin (cruses2) identified from chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.W.; Cheng, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; Feng, J.; Su, Y.L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.X. Molecular characterization, expression and antimicrobial activities of a c-type lysozyme from the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 98, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, L.; Gai, Y.; Song, L. Molecular characterization and expression of a crustin-like gene from chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donpudsa, S.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A.; Söderhäll, I.; Söderhäll, K. Characterization of two crustin antimicrobial peptides from the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 104, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperstad, S.V.; Haug, T.; Paulsen, V.; Rode, T.M.; Strandskog, G.; Solem, S.T.; Styrvold, O.B.; Stensvåg, K. Characterization of crustins from the hemocytes of the spider crab, Hyas araneus, and the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.Q.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, Q. Characterisation of a novel type i crustin involved in antibacterial and antifungal responses in the red claw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 48, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Song, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Crustins from eyestalk cdna library of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus: Molecular characterization, genomic organization and expression analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.-P.; Sun, Y.-D.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.-W.; Zhao, X.-F.; Wang, J.-X. A single whey acidic protein domain (swd)-containing peptide from fleshy prawn with antimicrobial and proteinase inhibitory activities. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, J. Cloning and recombinant expression of a crustin-like gene from chinese shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L. A crustin from hydrothermal vent shrimp: Antimicrobial activity and mechanism. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Biragyn, A.; Kwak, L.W.; Oppenheim, J.J. Mammalian defensins in immunity: More than just microbicidal. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, Y.; Chen, Q.; Schmidt, A.P.; Anderson, G.M.; Wang, J.M.; Wooters, J.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Chertov, O. Ll-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (fprl1) as a receptor to chemoattract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes, and t cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Moser, B. Antimicrobial activities of chemokines: Not just a side-effect? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieshima, K.; Ohtani, H.; Shibano, M.; Izawa, D.; Nakayama, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Shiba, F.; Shiota, M.; Katou, F.; Saito, T.; et al. Ccl28 has dual roles in mucosal immunity as a chemokine with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Palazzo, R.; Marinari, B.; Pietraforte, I.; Santos, G.S.; Mattenberger, Y.; Spadaro, F.; Stefanantoni, K.; Iannace, N.; et al. Cxcl4 assembles DNA into liquid crystalline complexes to amplify tlr9-mediated interferon-α production in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.R.; Meyer, T. Calcium flickers lighting the way in chemotaxis? Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 160–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, S.F.; Serrano, A.; Hernanz-Falcón, P.; Martín de Ana, A.; Monterrubio, M.; Martínez, C.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M. Chemokines integrate jak/stat and g-protein pathways during chemotaxis and calcium flux responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumoza-Toledo, A.; Lange, I.; Cortado, H.; Bhagat, H.; Mori, Y.; Fleig, A.; Penner, R.; Partida-Sánchez, S. Dendritic cell maturation and chemotaxis is regulated by TRPM2-mediated lysosomal Ca2+ release. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3529–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Lin, H.J.; Lin, W.F.; Wu, J.L.; Gong, H.Y. A potent tilapia secreted granulin peptide enhances the survival of transgenic zebrafish infected by Vibrio vulnificus via modulation of innate immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.C.; Chen, J.Y. Epinecidin-1: An orange-spotted grouper antimicrobial peptide that modulates Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid-induced inflammation in macrophage cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R14–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Sun, L. A Type Ib crustin from deep-sea shrimp possesses antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primers Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | PCR Objective |
|---|---|---|
| LvCrustinIa-2-F | AGACAACATGCAGGGTCTCG | Gene cloning |
| LvCrustinIa-2-R | CCCTTCTCAACCGAACTGG | Gene cloning |
| dsLvCrustinIa-2-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGACAACATGCAGGGTCTCG | dsRNA |
| dsLvCrustinIa-2-R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCCCTTCTCAACCGAACTGG | dsRNA |
| LvCrustinIa-2-qF | CCCACAAGTCCGTCCCACCT | Real-time PCR |
| LvCrustinIa-2-qR | CTCCCAGACACCTGTCGAAGCAG | Real-time PCR |
| rLvCrustinIa-2-F | AATGGGTCGCGGATCCAGCTTCCCCGGCGCCACAGCC | Recombinant expression |
| r LvCrustinIa-2-R | CTCGAGTGCGGCCGCAAGCTTACCGAACTGGTTGTAG | Recombinant expression |
| rLvCrustinIa-2-WAP-F | AATGGGTCGCGGATCCAAGCCCCTCGACTGCCCACAA | Recombinant expression |
| rLvCrustinIa-2-WAP-R | GTGCGGCCGCAAGCTTGGAAGGGGGCTTGCACACGT | Recombinant expression |
| 18S-F | TATACGCTAGTGGAGCTGGAA | Real-time PCR |
| 18S-R | GGGGAGGTAGTGACGAAAAAT | Real-time PCR |
| dsEGFP-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAGTGCTTCAGCCGCTACCC | dsRNA |
| dsEGFP-R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGTTCACCTTGATGCCGTTCTT | dsRNA |
| T7 promoter | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG | Sequencing |
| T7 terminator | GCTAGTTATTGCTCAGCGGT | Sequencing |
| M13-47 | CGCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACGAC | Sequencing |
| RV-M | GAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGG | Sequencing |
| LvNCX-qF | ATCGGTCTGAAGGACTCGG | Real-time PCR |
| LvNCX-R | TGGACATTGTGGTAGATAGCA | Real-time PCR |
| LvPMCA-2-qF | CGGAGGCTACCGCATTTAT | Real-time PCR |
| LvPMCA-2-qR | CACTTCAGGACGCACAGGA | Real-time PCR |
| LvSERCA-qF | CCGTATTGGTGTGTTTGGTG | Real-time PCR |
| LvSERCA-qR | TGGATTTGTGGAAAGGCTCG | Real-time PCR |
| LvLITAF-qF | GCAGTCAACGCACATGATCT | Real-time PCR |
| LvLITAF-qR | TTGTATTTGCCCAGGAAAGC | Real-time PCR |
| LvIL-16-qF | AGCAAGAGCCTCGTGTCAGAC | Real-time PCR |
| LvIL-16-qR | CCTCCAGAGAAAAGCCCAGT | Real-time PCR |
| LvNIFL3-qF | ATTATGGTTGCTGAGACGGTGA | Real-time PCR |
| LvNIFL3-qR | GATGTGGGGCGAGTAGTTGG | Real-time PCR |
| LvTRAF6-qF | ACATCACCAATCCCAGAG | Real-time PCR |
| LvTRAF6-qR | GTCAGCACCGCCTTTATC | Real-time PCR |
| LvTNFSF-qF | CAGAGCCGTCAAGAAGATCC | Real-time PCR |
| LvTNFSF-qR | TGAGGGAGTACTTCCGGTTG | Real-time PCR |
| LvTNFRSF-qF | AAAGAGGAACGTGGTCATGG | Real-time PCR |
| LvTNFRSF-qR | CACTCCTTTCCCCACTGTGT | Real-time PCR |
| LvMnSOD-qF | ATTGCCGCTACGAAGAAG | Real-time PCR |
| LvMnSOD-qR | AGATGGTGTGGTTCAAGTG | Real-time PCR |
| LvGPx-qF | GCACCAGGAGAACACTAC | Real-time PCR |
| LvGPx-qR | TTCCAGGCAATGTCAGAG | Real-time PCR |
| LvGST-qF | AGAAAAACTACCCTGTCGG | Real-time PCR |
| LvGST-qR | CCTTGCTCTGCGTTATCTT | Real-time PCR |
| LvDUOX-qF | GACTTGGCAGCAAACCTA | Real-time PCR |
| LvDUOX-qR | TGCGGGAAAGGTCGTAGAT | Real-time PCR |
| LvNOX-qF | CCAACGATGTGCCTGATAGTG | Real-time PCR |
| LvNOX-qR | ATGTCGGTCTTCTGAAGGGCT | Real-time PCR |
| LvNOS-qF | GAGCAAGTTATTCGGCAAGGC | Real-time PCR |
| LvNOS-qR | TCTCTCCCAGTTTCTTGGCGT | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll1-qF | CTATTGTGGTGCTTTCGT | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll1-qR | TGGAGATGTACAGTCGTAAC | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll2-qF | CATGCCTGCAGGACTGTTTA | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll2-qR | GGCCTGAGGGTAAGGTCTTC | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll3-qF | GTGAATCTGACCCGAGTTGA | Real-time PCR |
| LvToll3-qR | TGCTGCCTTCGGTGTTCTA | Real-time PCR |
| LvCactus-qF | GCCTGTCTTACGCCCCT | Real-time PCR |
| LvCactus-qR | CCGTCCGACCACTCTTG | Real-time PCR |
| LvRelish-qF | CATGCAAGACTTCGCAA | Real-time PCR |
| LvRelish-qR | CTGGTAATGTAACAGGACG | Real-time PCR |
| LvDorsal-qF | TGGGGAAGGAAGGATGC | Real-time PCR |
| LvDorsal-qR | CGTAACTTGAGGGCATCTTC | Real-time PCR |
| LvDOME-qF | CTCAGGCTATGTTTCTCAGGATTCA | Real-time PCR |
| LvDOME-qR | CACGGCAGTTCCTTTATGGTCT | Real-time PCR |
| LvJAK-qF | CCTTAATTCGAGCGCAATGGG | Real-time PCR |
| LvJAK-qR | CTAGCGACAGAGGGTTTAGCG | Real-time PCR |
| LvSTAT-qF | TATATCCGAATGTGCCTAAG | Real-time PCR |
| LvSTAT-qR | ATAGTTTGTGGTGTGTTGGG | Real-time PCR |
| Lvp38-qF | GTCGGCTCGCAACTACATAC | Real-time PCR |
| Lvp38-qR | CCGTTACACGCCTTTCACT | Real-time PCR |
| Microorganism | MIC (µM) | |
|---|---|---|
| rLvCrustinIa-2 | rLvCrustinIa-2-WAP | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus Pa6 | 21.4 | 7.7 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus L59 | 21.4 | 7.7 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa P25 | >21.4 | >30.7 |
| Edwardsiella tarda E3 | >21.4 | >30.7 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus S7 | 10.7 | 7.7 |
| Staphylococcus delphini Sd2 | 10.7 | 15.4 |
| Micrococcus luteus M2 | 10.7 | 15.4 |
| Fungus | ||
| Pichia pastoris GS115 | >21.4 | >30.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Z.; Sun, M.; Li, F. A Type Ia Crustin from the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Antimicrobial and Chemotactic Activities. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071015
Gao X, Liu Y, Huang X, Yang Z, Sun M, Li F. A Type Ia Crustin from the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Antimicrobial and Chemotactic Activities. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiuyan, Yuan Liu, Xiaoyang Huang, Zhanyuan Yang, Mingzhe Sun, and Fuhua Li. 2025. "A Type Ia Crustin from the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Antimicrobial and Chemotactic Activities" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071015
APA StyleGao, X., Liu, Y., Huang, X., Yang, Z., Sun, M., & Li, F. (2025). A Type Ia Crustin from the Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Antimicrobial and Chemotactic Activities. Biomolecules, 15(7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15071015






