Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD: Harnessing Epigenetic and Gut Microbiota Pathways for Targeted Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
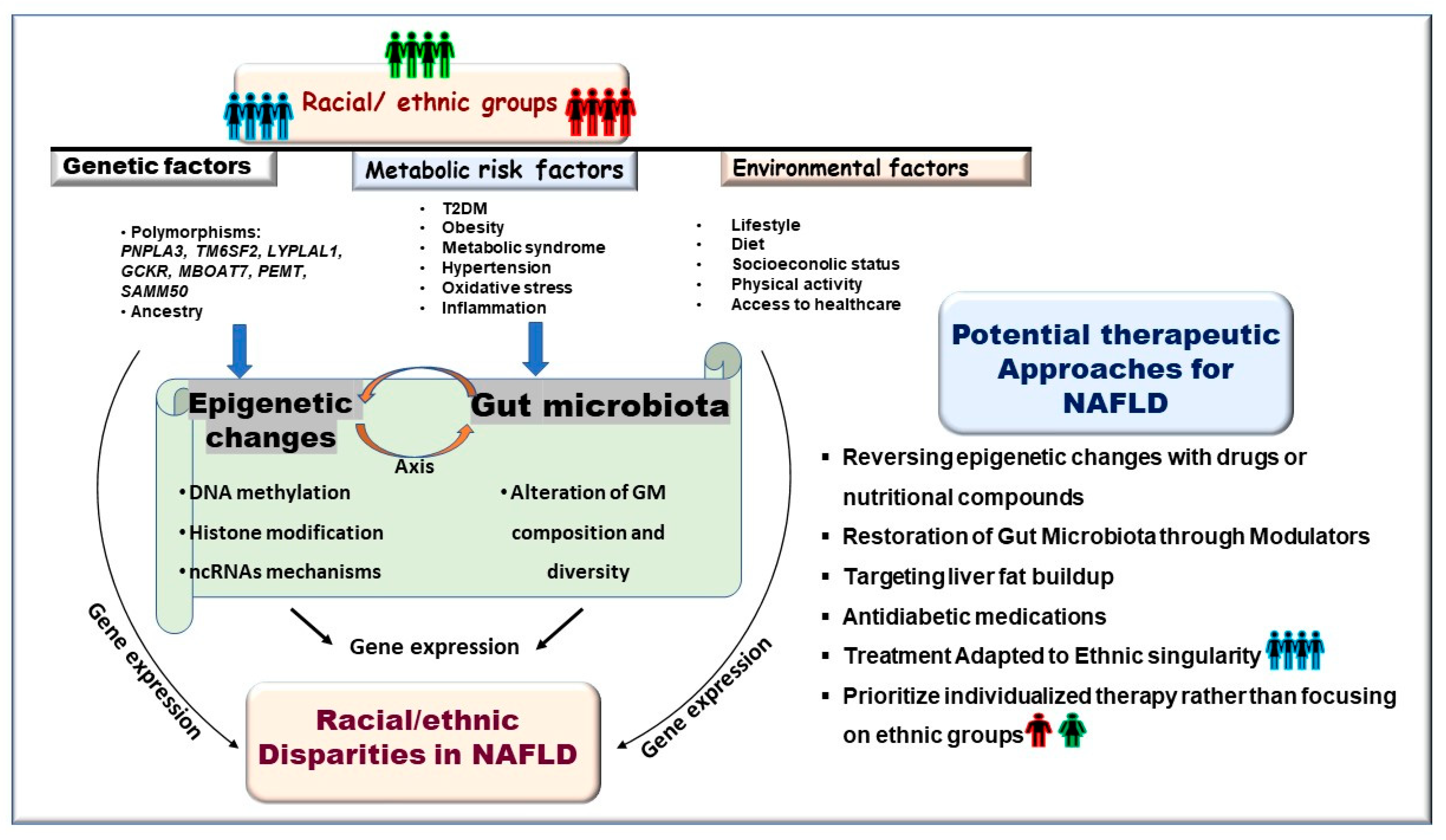
1. Introduction
2. Race/Ethnic Health Disparities in Susceptibility to NAFLD
3. The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD
4. Epigenetic Determinants of Racial/Ethnic Disparity in NAFLD
5. Therapy for NAFLD: Exploiting the Reversibility of Gut Microbiota Composition and Epigenetic Changes for Potential Treatment
5.1. Restoring Dysbiosis in Gut Microbiota Alleviates NAFLD
5.2. Reversibility of Epigenetic Mechanisms
5.2.1. Potential Epigenetic Drugs in Clinical Trials for NAFLD
5.2.2. Potential Epigenetic Targets for the Treatment of NAFLD
| Drug | Class | Mechanism of Action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-Aza-CdR + Curcumin | DNMTi | Reverse PPAR-α DNA methylation involved in NAFLD | [135] |
| Givinostat | HDACi | Potential drug for treatment of NASH and liver fibrosis | [136] |
| GLP-1RAs | SIRT activator | Sirt activator ameliorates hepatic steatosis and may serve as a potential drug for NAFLD | [139] |
| Resveratol | SIRT1 activator | Prevents HFD-induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis by suppressing miR-34a-induced activation of SIRT1 | [140] |
| Quercetin | SIRT1 activator | Significant therapeutic benefits for the prevention of NASH | [141] |
| Metformin+ Quercetin | SIRT1 activator | Alleviate hepatic steatosis by activating autophagy through the cAMP/AMPK/SIRT1 pathway | [142] |
| Target | KDM1A | Histone demethylase KDM1A promotes hepatic steatosis and inflammation by increasing chromatin accessibility in NAFLD | [143] |
5.2.3. Development of Epigenetic Biomarkers for NAFLD
6. Perspectives on Future Research and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview. Heptol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Schattenberg, J.M. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approaches. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Hellerbrand, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Vessby, J.; Ekstedt, M.; Shang, Y. 99% of patients with NAFLD meet MASLD criteria and natural history is therefore identical. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e76–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.P.; Dodge, J.L.; Terrault, N.A. National prevalence estimates for steatotic liver disease and subclassifications using consensus nomenclature. Hepatology 2024, 79, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tao, X.; Zeng, M.; Mi, Y.; Xu, L. Clinical and histological features under different nomenclatures of fatty liver disease: NAFLD, MAFLD, MASLD and MetALD. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e64–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, W.R.; Kim, H.J.; Therneau, T.M. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.L.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Chan, K.E.; Tan, D.J.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.D.; Tan, E.; Muthiah, M.D. Global incidence and prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S32–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.E.; Shah, V.H. Pathogenesis and pathways: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease & alcoholic liver disease. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallwitz, E.R.; Daviglus, M.L.; Allison, M.A.; Emory, K.T.; Zhao, L.; Kuniholm, M.H.; Chen, J.; Gouskova, N.; Pirzada, A.; Talavera, G.A.; et al. Prevalence of suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Hispanic/Latino individuals differs by heritage. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control [CDC]; National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2008; With Chartbook; Center for Disease Control: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus08.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2015).
- Zhou, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.J.; Ji, Y.X.; Zhang, P.; She, Z.G.; Zhu, L.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Unexpected Rapid Increase in the Burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zou, X.; Wen, X.; Zhou, X.; Ji, L. NAFLD or MAFLD: Which Has Closer Association With All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality?-Results from NHANES III. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 693507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, N.E.; Oji, S.; Mufti, A.R.; Browning, J.D.; Parikh, N.D.; Odewole, M.; Mayo, H.; Singal, A.G. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Prevalence, Severity, and Outcomes in the United States: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 198–210.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, M.; Kanwal, F.; El-Serag, H.B.; Thrift, A.P. Acculturation and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Risk Among Hispanics of Mexican Origin: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Le, I.; Ha, A.; Le, R.H.; Rouillard, N.A.; Fong, A.; Gudapati, S.; Park, J.E.; Maeda, M.; Barnett, S.; et al. Differences in liver and mortality outcomes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by race and ethnicity: A longitudinal real-world study. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Le, M.H.; Cheung, R.C.; Nguyen, M.H. Differential Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Outcomes in Persons with NAFLD and/or MAFLD. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2172–2181.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Feng, Y.; Stave, C.D.; Zhu, Q.; et al. The epidemiology of NAFLD in Mainland China with analysis by adjusted gross regional domestic product: A meta-analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zou, B.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Huang, D.Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Global NAFLD Prevalence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2809–2817.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Sawada, K.; Tatsuta, M.; Maeshiro, T.; Tobita, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Akahane, T.; Hasebe, C.; Kawanaka, M.; et al. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2014 to 2018 in Japan: A large-scale multicenter retrospective study. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Pavlopoulou, I.; Papatheodoridi, M.; Markakis, G.E.; Bouras, E.; Haidich, A.B.; Papatheodoridis, G. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Vilar-Gomez, E.; Petta, S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Wong, G.L.; Adams, L.A.; de Lédinghen, V.; Sookoian, S.; Wong, V.W. Geographical similarity and differences in the burden and genetic predisposition of NAFLD. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1404–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Schnabl, B. Microbiota and Fatty Liver Disease-the Known, the Unknown, and the Future. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 28, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Jin, X.; Wu, M. Diet-gut microbiota-epigenetics in metabolic diseases: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, M.; Ohtake, N.; Kaneko, A.; Tsuchiya, N.; Imamura, S.; Iizuka, S.; Ishizawa, S.; Nishi, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Taketomi, A.; et al. Increase of Akkermansia muciniphila by a Diet Containing Japanese Traditional Medicine Bofutsushosan in a Mouse Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P. The Microbiome in Hepatobiliary and Intestinal Disease. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 893074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Rehman, A.; Dittrich, M.; Groen, A.K.; Hermanns, H.M.; Seyfried, F.; Beyersdorf, N.; Dandekar, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Geier, A. Fecal SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria in gut microbiome of human NAFLD as a putative link to systemic T-cell activation and advanced disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. A Metagenome-Wide Association Study of the Gut Microbiome and Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 682721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Dimitriadis, G.; Triantafyllou, K. Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2015, 14, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallott, E.K.; Sitarik, A.R.; Leve, L.D.; Cioffi, C.; Camargo, C.A.; Hasegawa, K., Jr.; Bordenstein, S.R. Human microbiome variation associated with race and ethnicity emerges as early as 3 months of age. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.W.; Priya, S.; Blekhman, R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut microbiota diversity across ethnicities in the United States. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.J.; et al. Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in a population with varied ethnic origins but shared geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Jenkins, I.C.; Randolph, T.W.; Curtis, K.R.; Monroe, K.R.; Ernst, T.; Shepherd, J.A.; Stram, D.O.; Cheng, I.; Kristal, B.S.; et al. Associations of the gut microbiome with hepatic adiposity in the Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1965463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, V.W.; Stram, D.O.; Porcel, J.; Lu, S.C.; Le Marchand, L.; Noureddin, M. Prevalence of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis by underlying cause in understudied ethnic groups: The multiethnic cohort. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, K.R.; Arrieta, M.C.; Azad, M.B.; Bailey, M.T.; Broussard, J.L.; Bruggeling, C.E.; Claud, E.C.; Costello, E.K.; Davenport, E.R.; Dutilh, B.E.; et al. The human gut microbiome and health inequities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017947118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrello, K.; Lim, U.; Park, S.Y.; Monroe, K.R.; Maskarinec, G.; Boushey, C.J.; Wilkens, L.R.; Randolph, T.W.; Le Marchand, L.; Hullar, M.A.; et al. Dietary Intake Mediates Ethnic Differences in Gut Microbial Composition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Sun, Y.; Wan, Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Zhang, F.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N.; Luo, J.; Wang, W.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Human-Gut-DNA Virome Variations across Geography, Ethnicity, and Urbanization. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 741–751.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangay, P.; Johnson, A.J.; Ward, T.L.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Hillmann, B.M.; Lucas, S.K.; Beura, L.K.; Thompson, E.A.; Till, L.M.; et al. US Immigration Westernizes the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell 2018, 175, 962–972.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Shadike, Q.; Wang, M.; Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Tuerdi, R.; Zhou, W.; Li, L. A low abundance of genus Bacteroides in gut microbiota is negatively correlated with blood phenylalanine levels in Uygur patients with phenylketonuria. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, W.; Wu, S.; Zheng, H.M.; Li, P.; Sheng, H.F.; Chen, M.X.; Chen, Z.H.; Ji, G.Y.; Zheng, Z.D.; et al. Linking gut microbiota, metabolic syndrome and economic status based on a population-level analysis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.T.; Zhao, B.; Jose, P.O.; Azar, K.M.; Fortmann, S.P.; Palaniappan, L.P. Racial/ethnic differences in dyslipidemia patterns. Circulation 2024, 129, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balvers, M.; de Goffau, M.; van Riel, N.; van den Born, B.J.; Galenkamp, H.; Zwinderman, K.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Levin, E. Ethnic variations in metabolic syndrome components and their associations with the gut microbiota: The HELIUS study. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warmbrunn, M.V.; Boulund, U.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; de Goffau, M.C.; Abeka, R.E.; Davids, M.; Bresser, L.R.F.; Levin, E.; Clement, K.; Galenkamp, H.; et al. Networks of gut bacteria relate to cardiovascular disease in a multi-ethnic population: The HELIUS study. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallwitz, E.R.; Tayo, B.O.; Kuniholm, M.H.; Cai, J.; Daviglus, M.; Cooper, R.S.; Cotler, S.J. American Ancestry Is a Risk Factor for Suspected Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Hispanic/Latino Adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Stokowski, R.P.; Kershenobich, D.; Ballinger, D.G.; Hinds, D.A. Variant in PNPLA3 is associated with alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.A.; Larrieta, E.; Kershenobich, D.; Torre, A. The Expression of PNPLA3 Polymorphism could be the Key for Severe Liver Disease in NAFLD in Hispanic Population. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Palmer, N.D.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Langefeld, C.D.; Norris, J.M.; Wang, N.; Xiang, A.H.; Guo, X.; Williams, A.H.; Chen, Y.I.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Loci for Liver Enzyme Concentrations in Mexican Americans: The GUARDIAN Consortium. Obesity 2019, 27, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, M.; Patel, P.; Dunn-Valadez, S.; Dao, C.; Khan, V.; Ali, H.; El-Serag, L.; Hernaez, R.; Sisson, A.; Thrift, A.P.; et al. Women Have a Lower Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease but a Higher Risk of Progression vs Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 61–71.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, M.; Pan, D.; Schrode, K.M.; Kermah, D.; Puri, V.; Zarrinpar, A.; Elisha, D.; Najjar, S.M.; Friedman, T.C. Reassessment of the Hispanic Disparity: Hepatic Steatosis Is More Prevalent in Mexican Americans Than Other Hispanics. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Heredia, N.I.; Balakrishnan, M.; Thrift, A.P. Prevalence and factors associated with NAFLD detected by vibration controlled transient elastography among US adults: Results from NHANES 2017-2018. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaiou, M.; Amrani, R.; Rihn, B.; Hajri, T. Dietary Patterns Influence Target Gene Expression through Emerging Epigenetic Mechanisms in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, R.M.; Krushkal, J.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Thomas, F. Racial differences in gene-specific DNA methylation levels are present at birth. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2011, 91, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanter, J.M.; Gignoux, C.R.; Oh, S.S.; Torgerson, D.; Pino-Yanes, M.; Thakur, N.; Eng, C.; Hu, D.; Huntsman, S.; Farber, H.J.; et al. Differential methylation between ethnic sub-groups reflects the effect of genetic ancestry and environmental exposures. eLife 2017, 6, e20532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, H.R.; Burrows, K.; Min, J.L.; Tillin, T.; Mason, D.; Wright, J.; Santorelli, G.; Davey Smith, G.; Lawlor, D.A.; Hughes, A.D.; et al. Characterisation of ethnic differences in DNA methylation between UK-resident South Asians and Europeans. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.A.; Ciaccio, C.E.; Gigliotti, N.; Rezaiekhaligh, M.; Siedlik, J.A.; Kennedy, K.; Barnes, C.S. DNA methylation levels associated with race and childhood asthma severity. J. Asthma 2017, 54, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwabi-Addo, B.; Wang, S.; Chung, W.; Jelinek, J.; Patierno, S.R.; Wang, B.D.; Andrawis, R.; Lee, N.H.; Apprey, V.; Issa, J.P.; et al. Identification of differentially methylated genes in normal prostate tissues from African American and Caucasian men. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Jung, Y. DNA Methylation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachher, M.; Bansal, S.; Kumar, B.; Yadav, S.; Burman, A. Deciphering the role of aberrant DNA methylation in NAFLD and NASH. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, T.; Zaiou, M.; Fungwe, T.V.; Ouguerram, K.; Besong, S. Epigenetic Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Mediates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Nano, J.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hennein, R.; Liu, C.; Speliotes, E.K.; Huan, T.; Song, C.; Mendelson, M.M.; et al. A Peripheral Blood DNA Methylation Signature of Hepatic Fat Reveals a Potential Causal Pathway for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moylan, C.A.; Mavis, A.M.; Jima, D.; Maguire, R.; Bashir, M.; Hyun, J.; Cabezas, M.N.; Parish, A.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Diehl, A.M.; et al. Alterations in DNA methylation associate with fatty liver and metabolic abnormalities in a multi-ethnic cohort of pre-teenage children. Epigenetics 2022, 17, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Selvaraju, V.; Babu, J.R.; Wang, X.; Geetha, T. Racial Disparities in Methylation of NRF1, FTO, and LEPR Gene in Childhood Obesity. Genes 2022, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.A.; Seffernick, A.E.; Archer, K.J.; Mori, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Chang, L.; Ernst, T.; Tiirikainen, M.; Peplowska, K.; Wilkens, L.R.; et al. Race/ethnicity-associated blood DNA methylation differences between Japanese and European American women: An exploratory study. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegermann, K.; Suzuki, A.; Mavis, A.M.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Diehl, A.M.; Moylan, C.A. Tackling Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Three Targeted Populations. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, D.R.; Vaucher, Y.; Yamamoto, T.R. Diabetes in pregnancy in Mexican Americans. Diabetes Care 1991, 14, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Huang, R.; Xiang, M. SIRT1: Harnessing multiple pathways to hinder NAFLD. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Wieser, V.; Gerner, R.R.; Bichler, A.; Enrich, B.; Moser, P.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Kaser, S.; Tilg, H. Adipose tissue and liver expression of SIRT1, 3, and 6 increase after extensive weight loss in morbid obesity. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Wei, X. Berberine alleviates non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis partially by promoting SIRT1 deacetylation of CPT1A in mice. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 11, goad032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.B.; Bao, J.; Deng, C.X. Emerging roles of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushotham, A.; Schug, T.T.; Xu, Q.; Surapureddi, S.; Guo, X.; Li, X. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of SIRT1 alters fatty acid metabolism and results in hepatic steatosis and inflammation. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.J. Single Gene Inactivation with Implications to Diabetes and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome. J. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuanping, Z.; Rifang, L.; Qing, C.; Sidong, C. The Association between SIRT1 Genetic Variation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Is Influenced by Dietary Intake in Elderly Chinese. Iran. J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Feng, J.; Befroy, D.; Dziura, J.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Shulman, G.I. Increased prevalence of insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian-Indian men. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18273–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibian, J.H.; Lazo, M.; Durazo, F.A.; Yeh, H.C.; Tong, M.J.; Clark, J.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease across ethno-racial groups: Do Asian-American adults represent a new at-risk population? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepke, M.L.; Hansen, S.B.; Limborg, M.T. Unraveling host regulation of gut microbiota through the epigenome-microbiome axis. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Song, A.; Son, A.; Shin, Y. Gut microbiota and epigenetic choreography: Implications for human health: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e39051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Wong, V.W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Interplay between gut microbiome, host genetic and epigenetic modifications in MASLD and MASLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2024, 74, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lezana, T.; Raurell, I.; Bravo, M.; Torres-Arauz, M.; Salcedo, M.T.; Santiago, A.; Schoenenberger, A.; Manichanh, C.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M.; et al. Restoration of a healthy intestinal microbiota normalizes portal hypertension in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, T.; Fan, G. Gut mycobiome and metabolic diseases: The known, the unknown, and the future. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, V.; Figueroa, F.; González-Pizarro, K.; Jopia, P.; Ibacache-Quiroga, C. Probiotics and Prebiotics as a Strategy for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, a Narrative Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Seyfried, N.; Hartmann, D.; Hartmann, P. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 325, G42–G61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano-García, L.; Trepiana, J.; Martínez, J.A.; Portillo, M.P.; Milton-Laskibar, I. Beneficial Effects of Viable and Heat-Inactivated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Administration on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Diet-Induced NAFLD in Rats. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Li, H. Bacteroides and NAFLD: Pathophysiology and therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1288856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, T.; Barve, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is required for the therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG against fructose-induced fatty liver in mice. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kononenko, L.; Boccuto, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Dynnyk, O. A Multi-strain Probiotic Reduces the Fatty Liver Index, Cytokines and Aminotransferase levels in NAFLD Patients: Evidence from a Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2018, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshimoghaddam, F.; Shateri, K.; Sina, M.; Hashemian, M.; Alizadeh, M. Daily Consumption of Synbiotic Yogurt Decreases Liver Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Maurizi, V.; Boccuto, L.; Di Berardino, A.; Giostra, N.; Santori, P.; Scarcella, M.L.; Procopio, A.C.; Rasetti, C.; Scarpellini, E. Nutritional Support in Acute Liver Failure. Diseases 2022, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos-Trejo, A.; Nuño-Lambarri, N.; Barbero-Becerra, V.; Uribe-Esquivel, M.; Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Chávez-Tapia, N. Prebiotics and Probiotics: Therapeutic Tools for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Jia, R.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Mei, L.; Bai, L.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, P. Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 and fructooligosaccharides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Feng, H.; Mao, X.L.; Deng, Y.J.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, S.M. The effects of probiotics supplementation on glycaemic control among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamikkannu, D.M.; Dasarapu, S.; Siva, R.V.; Nallam, J.; Pabba, S. The gut-liver nexus: Exploring gut microbiota dysbiosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its therapeutic implications. Egypt. Liver J. 2024, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, N.M.J.; de Vos, W.M.; Nieuwdorp, M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in human metabolic diseases: From a murky past to a bright future? Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Schnabl, B. Modulating the microbiome in chronic liver diseases—Current evidence on the role of fecal microbiota transplantation. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajili?-Stojanovi?, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A.; et al. European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut 2017, 66, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayyedi, P.; Surette, M.G.; Kim, P.T.; Libertucci, J.; Wolfe, M.; Onischi, C.; Armstrong, D.; Marshall, J.K.; Kassam, Z.; Reinisch, W.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Induces Remission in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 102–109.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. The gut microbiota and obesity: From correlation to causality. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.R.; Yang, W.; Tan, Q.H.; Bai, S.; Zhong, H.; Tai, Y.; Tong, H. Gut microbiota therapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from randomized clinical trials. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1004911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, M.; Santopaolo, F.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Gut microbiota modulation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Effects of current treatments and future strategies. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stols-Gonçalves, D.; Mak, A.L.; Madsen, M.S.; van der Vossen, E.W.J.; Bruinstroop, E.; Henneman, P.; Mol, F.; Scheithauer, T.P.M.; Smits, L.; Witjes, J.; et al. Faecal Microbiota transplantation affects liver DNA methylation in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multi-omics approach. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2223330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Modulating Gut Microbiota to Improve Severity? Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kootte, R.S.; Levin, E.; Salojärvi, J.; Smits, L.P.; Hartstra, A.V.; Udayappan, S.D.; Hermes, G.; Bouter, K.E.; Koopen, A.M.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity after Lean Donor Feces in Metabolic Syndrome Is Driven by Baseline Intestinal Microbiota Composition. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 611–619.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamah, S.; Iatcu, O.C.; Covasa, M. Dietary Influences on Gut Microbiota and Their Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Nutrients 2024, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, J.; Díaz-Alvarez, C.B.; Alfonso, C.; O’Neill, H.J.; Ríos-Bedoya, C.F.; Malik, V.S.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Cheng, C.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Design and Implementation of a Culturally-Tailored Randomized Pilot Trial: Puerto Rican Optimized Mediterranean-Like Diet. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2022, 7, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Modern epigenetics methods in biological research. Methods 2021, 187, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Rönn, T. Epigenetics in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Epigenetic drugs in cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025, 44, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, L.J.; Ulloa, E.V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lizano, M.; De La Cruz-Hernández, E.; Contreras-Paredes, A. Modulating epigenetic modifications for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2023, 49, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y.; Song, J.H.; Lee, J.; Shin, E.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J.T.; Choi, H.K. Tannic acid, a novel histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease both in vivo and in vitro model. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Dahlin, J.L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F.; Walters, M.A. The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1620–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Malik, M. Effects of curcumin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Liver J. 2024, 7, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Kianpour, P.; Mohtashami, R.; Jafari, R.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Sahebkar, A. Efficacy and Safety of Phytosomal Curcumin in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Drug Res. 2017, 67, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcu, M.G.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Chung, E.J.; Lee, M.J.; Trepel, J.; Neckers, L. Curcumin is an inhibitor of p300 histone acetylatransferase. Med. Chem. 2006, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Mansour, A.; Yari, Z.; Poustchi, H.; Hedayati, M.; Hatami, B.; Hekmatdoost, A. Curcumin and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, N.; Wang, P.; Xia, Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, G.; Gonzalez, F.J. Herbal drug discovery for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2020, 10, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Adibi, P.; Rafiei, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Resveratrol supplementation improves inflammatory biomarkers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.K.; Nellemann, B.; Bibby, B.M.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Pedersen, S.B.; Grønbaek, H.; Nielsen, S. No effect of resveratrol on VLDL-TG kinetics and insulin sensitivity in obese men with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2504–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, K.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kałduńska, J.; Stachowska, E.; Gutowska, I.; Janda, K. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, D.; Karwatowska-Prokopczuk, E.; Baum, S.J.; Hurh, E.; Kingsbury, J.; Bartlett, V.J.; Figueroa, A.L.; Piscitelli, P.; Singleton, W.; Witztum, J.L.; et al. Vupanorsen, an N-acetyl galactosamine-conjugated antisense drug to ANGPTL3 mRNA, lowers triglycerides and atherogenic lipoproteins in patients with diabetes, hepatic steatosis, and hypertriglyceridaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3936–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Hao, C.; Yu, L.; Zeng, S.; Xu, H.; Fang, M.; Shen, A.; et al. The Histone Methyltransferase Suv39h2 Contributes to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1904–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Tang, D.; Du, Y.L.; Cao, C.Y.; Nie, Y.Q.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.J. Fatty liver mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-? DNA methylation can be reversed by a methylation inhibitor and curcumin. J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.M.; Fan, S.J.; Zhou, X.R.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, X.; Liao, L.P.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.C.; Yu, L.; Fu, R.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, A.F.; Anjum, M.B.; Rehman, R.U. Unleashing the Potential of Givinostat: A Novel Therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Cur. Ther. Res. 2025, 102, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X. The Ameliorating Effects of Apple Polyphenol Extract on High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis Are SIRT1-Dependent: Evidence from Hepatic-Specific SIRT1 Heterozygous Mutant C57BL/6 Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5579–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, K.; Weng, J. SIRT1 mediates the effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide on ameliorating hepatic steatosis. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BinMowyna, M.N.; AlFaris, N.A.; Al-Sanea, E.A.; AlTamimi, J.Z.; Aldayel, T.S. Resveratrol attenuates against high-fat-diet-promoted non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats mainly by targeting the miR-34a/SIRT1 axis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 130, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.Z.; Liu, Y.H.; Yu, B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zang, J.N.; Yu, C.H. Dietary quercetin ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by a high-fat diet in gerbils. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, H.; Noori, S.; Zarghi, A. Hepatic Steatosis Alleviated by a Novel Metformin and Quercetin Combination Activating Autophagy Through the cAMP/AMPK/SIRT1 Pathway. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 22, e136952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Shu, R.; Shi, W.; Qu, W.; Liu, D.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM1A promotes hepatic steatosis and inflammation by increasing chromatin accessibility in NAFLD. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Gianotti, T.F.; Burgueño, A.L.; Rey-Funes, M.; Loidl, C.F.; Mallardi, P.; Martino, J.S.; Castaño, G.O.; Sookoian, S. Epigenetic modification of liver mitochondrial DNA is associated with histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2013, 62, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.D.; Wu, X.; Still, C.D.; Chu, X.; Petrick, A.T.; Gerhard, G.S.; Conneely, K.N.; DiStefano, J.K. Differential DNA methylation and changing cell-type proportions as fibrotic stage progresses in NAFLD. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhartova, D.; Cahova, M.; Dankova, H.; Heczkova, M.; Mikova, I.; Sticova, E.; Spicak, J.; Seda, O.; Trunecka, P. Serum miR-33a is associated with steatosis and inflammation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease after liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Qian, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Gao, R.; Shen, M.; Chen, S.; Fu, Q.; Yang, T. Circulating microRNA 135a 3p in serum extracellular vesicles as a potential biological marker of non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdizadeh, F.; Sobhi, P.; Banaei, S. A class of MicroRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic strategies in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2025, 49, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiou, M. The Emerging Role and Promise of Circular RNAs in Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. Cells 2020, 9, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Liu, C.H.; Ampuero, J.; Wu, D.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Bai, L.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Tang, H. Circular RNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Functions and clinical significance. RNA Biol. 2024, 21, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Chen, J.N.; Sun, F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pan, Q.; Fan, J.G. circRNA_0046367 Prevents Hepatoxicity of Lipid Peroxidation: An Inhibitory Role against Hepatic Steatosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 3960197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Sun, F.; Chen, J.N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Pan, Q.; Fan, J.G. circRNA_0046366 inhibits hepatocellular steatosis by normalization of PPAR signaling. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qi, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, K.; Dai, Z.; Yuan, L.; Sun, C. A nanodrug system overexpressed circRNA_0001805 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via miR-106a-5p/miR-320a and ABCA1/CPT1 axis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, H. Prevalence of steatotic liver disease and associated fibrosis in the United States: Results from NHANES 2017-March 2020. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e70–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stronks, K.; Snijder, M.B.; Peters, R.J.; Prins, M.; Schene, A.H.; Zwinderman, A.H. Unravelling the impact of ethnicity on health in Europe: The HELIUS study. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. Race and Ethnicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, F.; Kacprowski, T.; Rühlemann, M.; Pietzner, M.; Bang, C.; Franke, A.; Nauck, M.; Völker, U.; Völzke, H.; Dörr, M.; et al. Long-term instability of the intestinal microbiome is associated with metabolic liver disease, low microbiota diversity, diabetes mellitus and impaired exocrine pancreatic function. Gut 2021, 70, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Trial ID/Phase | Class | Compound | Clinical Trial.gov/Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02908152 | HATi | Curcumin | https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02908152 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Phase 2/3 | The effect of curcumin supplement on metabolic factors and hepatic fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver patients. Curcumin may reverse PPARα methylation and suppress FOXO1 acetylation. | ||
| NCT03864783 | HATi | Curcumin | https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT03864783 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Not applicable | The effect of curcumin on liver fat content in obese subjects with NAFLD. Curcumin reduces TG in NAFLD, inhibits NAFLD progression. | ||
| NCT04315350 | HATi | Curcumin | https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04315350 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Not applicable | The effect of curcumin on the development of prednisolone-induced hepatic insulin resistance. | ||
| NAFLD/Insulin resistance | |||
| NCT01446276 | STAC | Resveratrol | https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT01446276 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Not applicable | Long-term investigation of resveratrol on fat metabolism in obese men with NAFLD. | ||
| NCT02030977 | STAC | Resveratrol | https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT02030977 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Phase 2/3 | The effects of resveratrol supplement on lipid profile, liver enzymes, inflammatory factors, and hepatic fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. | ||
| NCT05419765 | - | - | https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT05419765 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: crosstalk between genetic predisposition and epigenetic lysosomal acid lipase activity reduction in blood, plasma, and platelets. | |||
| NCT02148471 | - | - | https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=%20NCT02148471 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Fatty acids, genes, and microbiota in fatty liver. Study of gene expression and regulation by miRNA. Role of microbiota composition in NAFLD. | |||
| NCT03371355 | ASO | - | https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT03371355 (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Phase 2 | Study of ISIS 703,802 in participants with hypertriglyceridemia, T2DM, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. | ||
| NCT03915002 | - | - | https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?intr=NCT03915002 Observational (accessed on 28 April 2025) |
| Integrated approaches for identifying molecular targets in liver disease. | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaiou, M.; Joubert, O. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD: Harnessing Epigenetic and Gut Microbiota Pathways for Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050669
Zaiou M, Joubert O. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD: Harnessing Epigenetic and Gut Microbiota Pathways for Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(5):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050669
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaiou, Mohamed, and Olivier Joubert. 2025. "Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD: Harnessing Epigenetic and Gut Microbiota Pathways for Targeted Therapeutic Approaches" Biomolecules 15, no. 5: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050669
APA StyleZaiou, M., & Joubert, O. (2025). Racial and Ethnic Disparities in NAFLD: Harnessing Epigenetic and Gut Microbiota Pathways for Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Biomolecules, 15(5), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15050669








