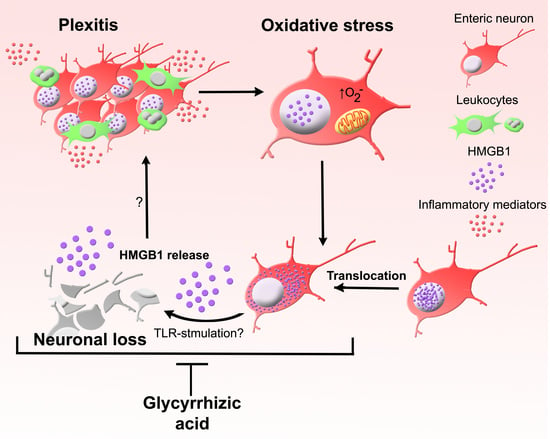
Oxidative Stress-Induced HMGB1 Translocation in Myenteric Neurons Contributes to Neuropathy in Colitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Organotypic Culture of Myenteric Ganglia
2.3. Glycyrrhizic Acid Administration
2.4. Evaluation of Colitis
2.5. Histology
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. MitoSOX Red Fluorescent Staining
2.8. Imaging and Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HMGB1 Is an Endogenous TLR Agonist Highly Expressed in the ENS
3.2. Chronic Intestinal Inflammation Associates with HMGB1 Translocation in Enteric Neurons
3.3. HMGB1 Translocation in Enteric Neurons and Neuropathy Is Mediated by Oxidative Stimuli
3.4. Inhibition of HMGB1 Alleviates Clinical Symptoms and Myenteric Neuropathy Independent of Plexitis in Chronic Colitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voss, U.; Ekblad, E. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Loss of Cultured Rat Myenteric Neurons—Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Xiang, L.; Yuan, L.; Hu, L.; Wu, W.; Cai, L.; Yin, L.; Dong, H. Protective effect of glycyrrhizin, a direct HMGB1 inhibitor, on focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stavely, R.; Fraser, S.; Sharma, S.; Rahman, A.A.; Stojanovska, V.; Sakkal, S.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Bertrand, P.; Nurgali, K. The onset and progression of chronic colitis parallels increased mucosal serotonin release via enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia and downregulation of the serotonin reuptake transporter. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippone, R.T.; Dargahi, N.; Eri, R.; Uranga, J.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Nurgali, K. Potent CCR3 Receptor Antagonist, SB328437, Suppresses Colonic Eosinophil Chemotaxis and Inflammation in the Winnie Murine Model of Spontaneous Chronic Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.M.; Rahman, A.A.; Carbone, S.E.; Randall-Demllo, S.; Filippone, R.; Bornstein, J.C.; Eri, R.; Nurgali, K. Alterations of colonic function in the Winnie mouse model of spontaneous chronic colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G85–G102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stavely, R.; Robinson, A.M.; Miller, S.; Boyd, R.; Sakkal, S.; Nurgali, K. Allogeneic guinea pig mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate neurological changes in experimental colitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stavely, R.; Robinson, A.M.; Miller, S.; Boyd, R.; Sakkal, S.; Nurgali, K. Human adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue and bone marrow attenuate enteric neuropathy in the guinea-pig model of acute colitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.L.; Partridge, T.A. A New Blocking Method for Application of Murine Monoclonal Antibody to Mouse Tissue Sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1998, 46, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbransen, B.D.; Bashashati, M.; Hirota, S.A.; Gui, X.; Roberts, J.A.; MacDonald, J.A.; Muruve, D.A.; McKay, D.M.; Beck, P.L.; Mawe, G.M.; et al. Activation of neuronal P2X7 receptor-Pannexin-1 mediates death of enteric neurons during colitis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.A.; Robinson, A.M.; Jovanovska, V.; Eri, R.; Nurgali, K. Alterations in the distal colon innervation in Winnie mouse model of spontaneous chronic colitis. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 362, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuade, R.M.; Carbone, S.E.; Stojanovska, V.; Rahman, A.; Gwynne, R.M.; Robinson, A.M.; Goodman, C.A.; Bornstein, J.C.; Nurgali, K. Role of oxidative stress in oxaliplatin-induced enteric neuropathy and colonic dysmotility in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 3502–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeisel, A.; Hochgerner, H.; Lönnerberg, P.; Johnsson, A.; Memic, F.; van der Zwan, J.; Häring, M.; Braun, E.; Borm, L.E.; La Manno, G.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the Mouse Nervous System. Cell 2018, 174, 999–1014.e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Svetkauskaite, D.; He, Q.; Kim, J.Y.; Strassheim, D.; Ishizaka, A.; Abraham, E. Involvement of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box 1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7370–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.A.; Robinson, A.M.; Brookes, S.J.; Eri, R.; Nurgali, K. Rectal prolapse in Winnie mice with spontaneous chronic colitis: Changes in intrinsic and extrinsic innervation of the rectum. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 366, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janko, C.; Filipović, M.; Munoz, L.E.; Schorn, C.; Schett, G.; Ivanović-Burmazović, I.; Herrmann, M. Redox Modulation of HMGB1-Related Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, W.; Hu, Y.-C.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Li, W.-D.; Ma, B.; Zhu, J.-H.; et al. Early release of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from neurons in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in vivo and in vitro. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Törnblom, H.; Lindberg, G.; Nyberg, B.; Veress, B. Full-thickness biopsy of the jejunum reveals inflammation and enteric neuropathy in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, M.D.; Mullaney, T.; Karasek, S.; Yamini, B. Diarrhea associated with myenteric ganglionitis in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1988, 193, 346–348. [Google Scholar]
- Jodal, M.; Holmgren, S.; Lundgren, O.; Sjoqvist, A. Involvement of the myenteric plexus in the cholera toxin-induced net fluid secretion in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Yang, H.; Harris, H. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) operates as an alarmin outside as well as inside cells. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raucci, A.; Palumbo, R.; Bianchi, M.E. HMGB1: A signal of necrosis. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Livesey, K.M.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Activates an Autophagic Response to Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Antoine, D.; Xiao, X.; Wang, H.; Andersson, U.; Billiar, T.R.; Tracey, K.J.; Lu, B. Regulation of Posttranslational Modifications of HMGB1 During Immune Responses. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Haig, A.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Jevnikar, A.M. Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates HMGB1-mediated cell death and inflammation after renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Jin, Y.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, I.-D.; Lee, H.-K.; Park, S.; Han, P.-L.; Lee, J.-K. Glycyrrhizic acid affords robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting HMGB1 phosphorylation and secretion. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Katsuki, H.; Fukutomi, C.; Takahashi, M.; Motomura, M.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Isohama, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Kume, T.; et al. HMGB1 inhibitor glycyrrhizin attenuates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced injury in rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, G.-Y.; Moon, T.G.; Lee, D.H.; Yoo, B.C. Glycyrrhizin attenuates HMGB1-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the p38-dependent mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Takagi, Y.; Iwazaki, A.; Nakanishi, K. Radical scavenging ability of glycyrrhizin. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2013, 3, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollica, L.; De Marchis, F.; Spitaleri, A.; Dallacosta, C.; Pennacchini, D.; Zamai, M.; Agresti, A.; Trisciuoglio, L.; Musco, G.; Bianchi, M.E. Glycyrrhizin binds to high-mobility group box 1 protein and inhibits its cytokine activities. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldt, B.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Ikeda, K.; Verhey, E.; Suzuki, H.; Schalm, S.W. Long-term clinical outcome and effect of glycyrrhizin in 1093 chronic hepatitis C patients with non-response or relapse to interferon. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuma, Y.; Liu, K.; Wake, H.; Liu, R.; Nishimura, Y.; Hui, Z.; Teshigawara, K.; Haruma, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Glycyrrhizin inhibits traumatic brain injury by reducing HMGB1–RAGE interaction. Neuropharmacology 2014, 85, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Yuan, L.-b.; Hu, L.; Wu, W.; Yin, L.; Hou, J.-l.; Liu, Y.-h.; Zhou, L.-s. Glycyrrhizin attenuates rat ischemic spinal cord injury by suppressing inflammatory cytokines and HMGB1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 33, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauley, J.; Pisetsky, D.S. The translocation of HMGB1 during cell activation and cell death. Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-M.; Gregersen, H.; Zhao, J.-B. Advanced glycation end-product expression is upregulated in the gastrointestinal tract of type 2 diabetic rats. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgueño, J.F.; Barba, A.; Eyre, E.; Romero, C.; Neunlist, M.; Fernández, E. TLR2 and TLR9 modulate enteric nervous system inflammatory responses to lipopolysaccharide. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venereau, E.; Casalgrandi, M.; Schiraldi, M.; Antoine, D.J.; Cattaneo, A.; De Marchis, F.; Liu, J.; Antonelli, A.; Preti, A.; Raeli, L.; et al. Mutually exclusive redox forms of HMGB1 promote cell recruitment or proinflammatory cytokine release. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakovlev, A.G.; Faden, A.I. Mechanisms of neural cell death: Implications for development of neuroprotective treatment strategies. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negroni, A.; Cucchiara, S.; Stronati, L. Apoptosis, Necrosis, and Necroptosis in the Gut and Intestinal Homeostasis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 250762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, L.; Ghoreishi, M.; Templeman, V.; Vallance, B.A.; Buchan, A.M.; Jevon, G.; Jacobson, K. Myenteric plexus injury and apoptosis in experimental colitis. Auton. Neurosci. 2005, 117, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotze, M.T.; Tracey, K.J. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, R.; Stronati, L.; Negroni, A.; Di Nardo, G.; Pierdomenico, M.; Del Giudice, E.; Rossi, P.; Cucchiara, S. Fecal HMGB1 is a novel marker of intestinal mucosal inflammation in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palone, F.; Vitali, R.; Cucchiara, S.; Pierdomenico, M.; Negroni, A.; Aloi, M.; Nuti, F.; Felice, C.; Armuzzi, A.; Stronati, L. Role of HMGB1 as a suitable biomarker of subclinical intestinal inflammation and mucosal healing in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davé, S.H.; Tilstra, J.S.; Matsuoka, K.; Li, F.; DeMarco, R.A.; Beer-Stolz, D.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Fink, M.P.; Lotze, M.T.; Plevy, S.E. Ethyl pyruvate decreases HMGB1 release and ameliorates murine colitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitali, R.; Palone, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Negroni, A.; Cavone, L.; Costanzo, M.; Aloi, M.; Dilillo, A.; Stronati, L. Dipotassium Glycyrrhizate Inhibits HMGB1-Dependent Inflammation and Ameliorates Colitis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamasaki, H.; Mitsuyama, K.; Masuda, J.; Kuwaki, K.; Takedatsu, H.; Sugiyama, G.; Yamada, S.; Sata, M. Roles of high-mobility group box 1 in murine experimental colitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2009, 2, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhave, S.; Arciero, E.; Baker, C.; Ho, W.L.; Stavely, R.; Goldstein, A.M.; Hotta, R. Enteric neuronal cell therapy reverses architectural changes in a novel diphtheria toxin-mediated model of colonic aganglionosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, H.-Z.; Liu, S.; Ren, J.; Zafirov, D.H.; Wood, J.D. IL-1β and IL-6 excite neurons and suppress nicotinic and noradrenergic neurotransmission in guinea pig enteric nervous system. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelles, A.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. IL-1β and IL-6 excite neurones and suppress cholinergic neurotransmission in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2000, 12, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downen, M.; Amaral, T.D.; Hua, L.L.; Zhao, M.L.; Lee, S.C. Neuronal death in cytokine-activated primary human brain cell culture: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Glia 1999, 28, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaginella, T.S.; Grisham, M.B.; Thomas, D.B.; Walsh, R.; Moummi, C. Oxidant-evoked release of acetylcholine from enteric neurons of the rat colon. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 263, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Wada-Takahashi, S.; Tamura, K. Actions of reactive oxygen species on AH/type 2 myenteric neurons in guinea pig distal colon. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G893–G902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A.; Durnin, L.; Sharkey, K.A.; Mutafova-Yambolieva, V.N.; Mawe, G.M. Oxidative stress disrupts purinergic neuromuscular transmission in the inflamed colon. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 3725–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.D.; Jia, H.; Eyer, B.; Good, M.; Guerriero, C.J.; Sodhi, C.P.; Afrazi, A.; Prindle, T., Jr.; Ma, C.; Branca, M.; et al. Discovery and Validation of a New Class of Small Molecule Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stavely, R.; Sahakian, L.; Filippone, R.T.; Stojanovska, V.; Bornstein, J.C.; Sakkal, S.; Nurgali, K. Oxidative Stress-Induced HMGB1 Translocation in Myenteric Neurons Contributes to Neuropathy in Colitis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121831
Stavely R, Sahakian L, Filippone RT, Stojanovska V, Bornstein JC, Sakkal S, Nurgali K. Oxidative Stress-Induced HMGB1 Translocation in Myenteric Neurons Contributes to Neuropathy in Colitis. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121831
Chicago/Turabian StyleStavely, Rhian, Lauren Sahakian, Rhiannon T. Filippone, Vanesa Stojanovska, Joel C. Bornstein, Samy Sakkal, and Kulmira Nurgali. 2022. "Oxidative Stress-Induced HMGB1 Translocation in Myenteric Neurons Contributes to Neuropathy in Colitis" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121831
APA StyleStavely, R., Sahakian, L., Filippone, R. T., Stojanovska, V., Bornstein, J. C., Sakkal, S., & Nurgali, K. (2022). Oxidative Stress-Induced HMGB1 Translocation in Myenteric Neurons Contributes to Neuropathy in Colitis. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121831