MDM2-Driven Ubiquitination Rapidly Removes p53 from Its Cognate Promoters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Transfections
2.4. Immunoblot Analysis
2.5. Chromatin Immunopreciptitation (ChIP)
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
2.7. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Software
3. Results
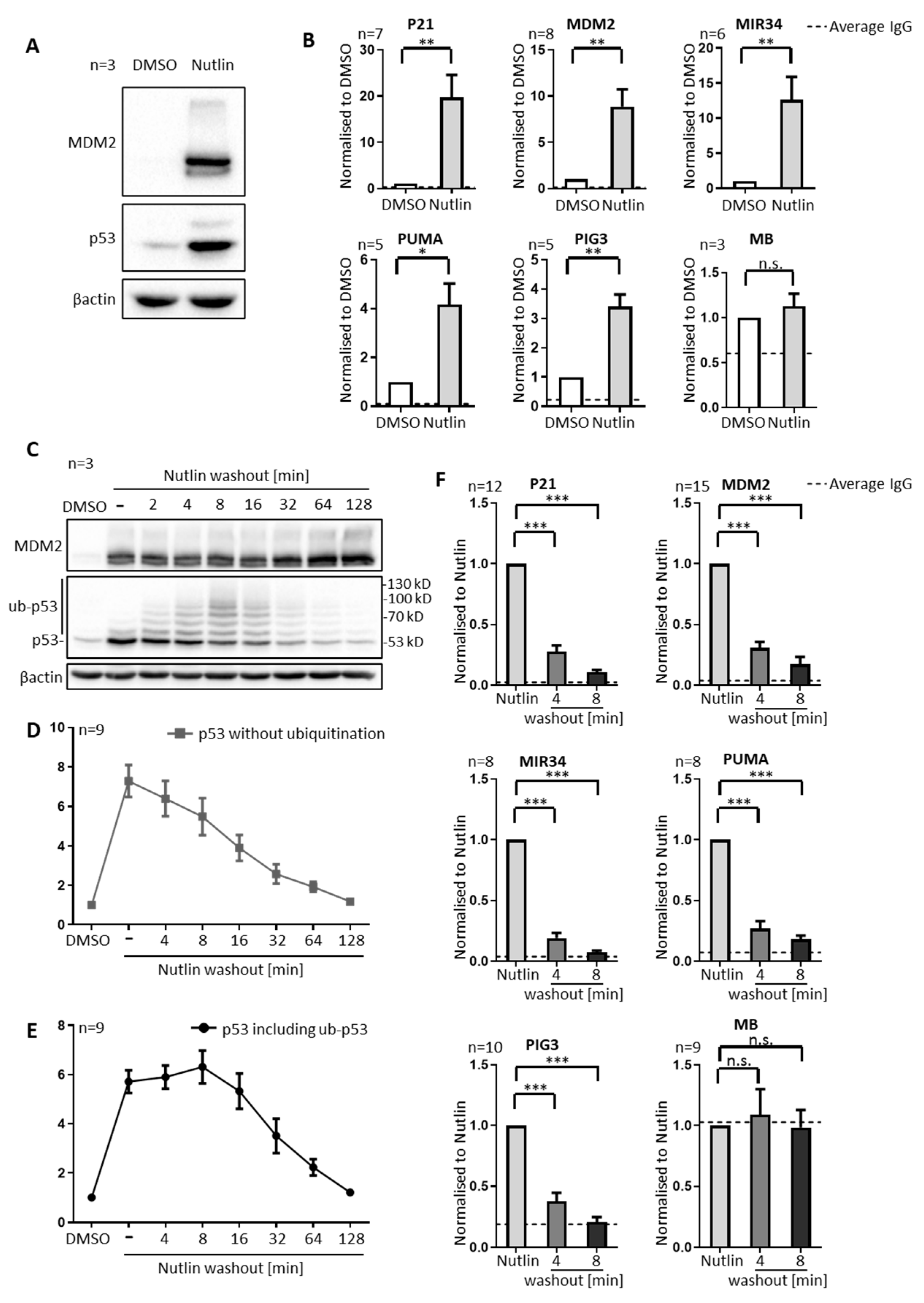
3.1. P53 Is Rapidly Removed from Promoters upon Nutlin Washout, in Parallel to Its Ubiquitination, but Prior to Its Degradation
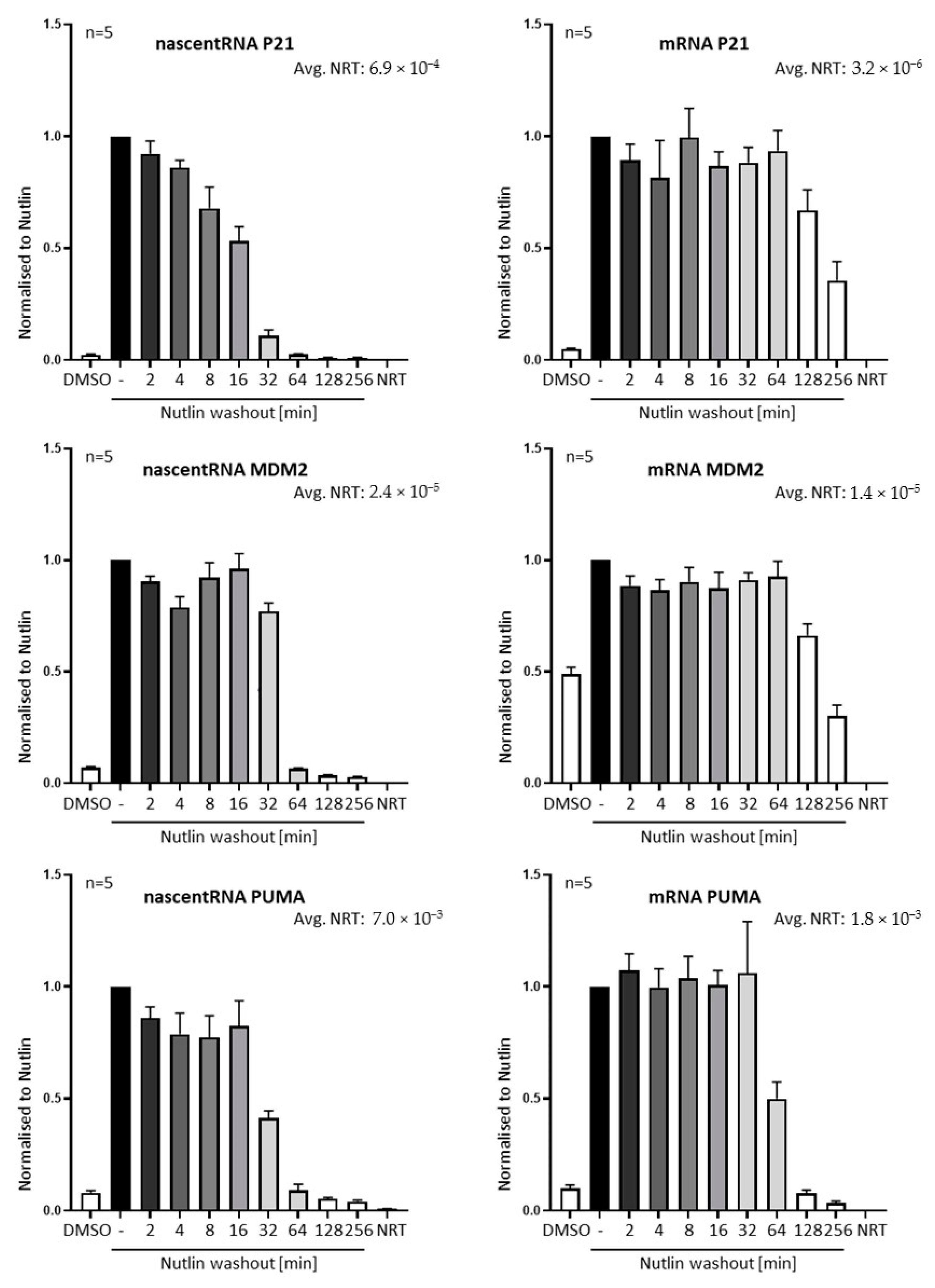
3.2. Nutlin Washout Diminishes p53-Mediated Transcription within an Hour
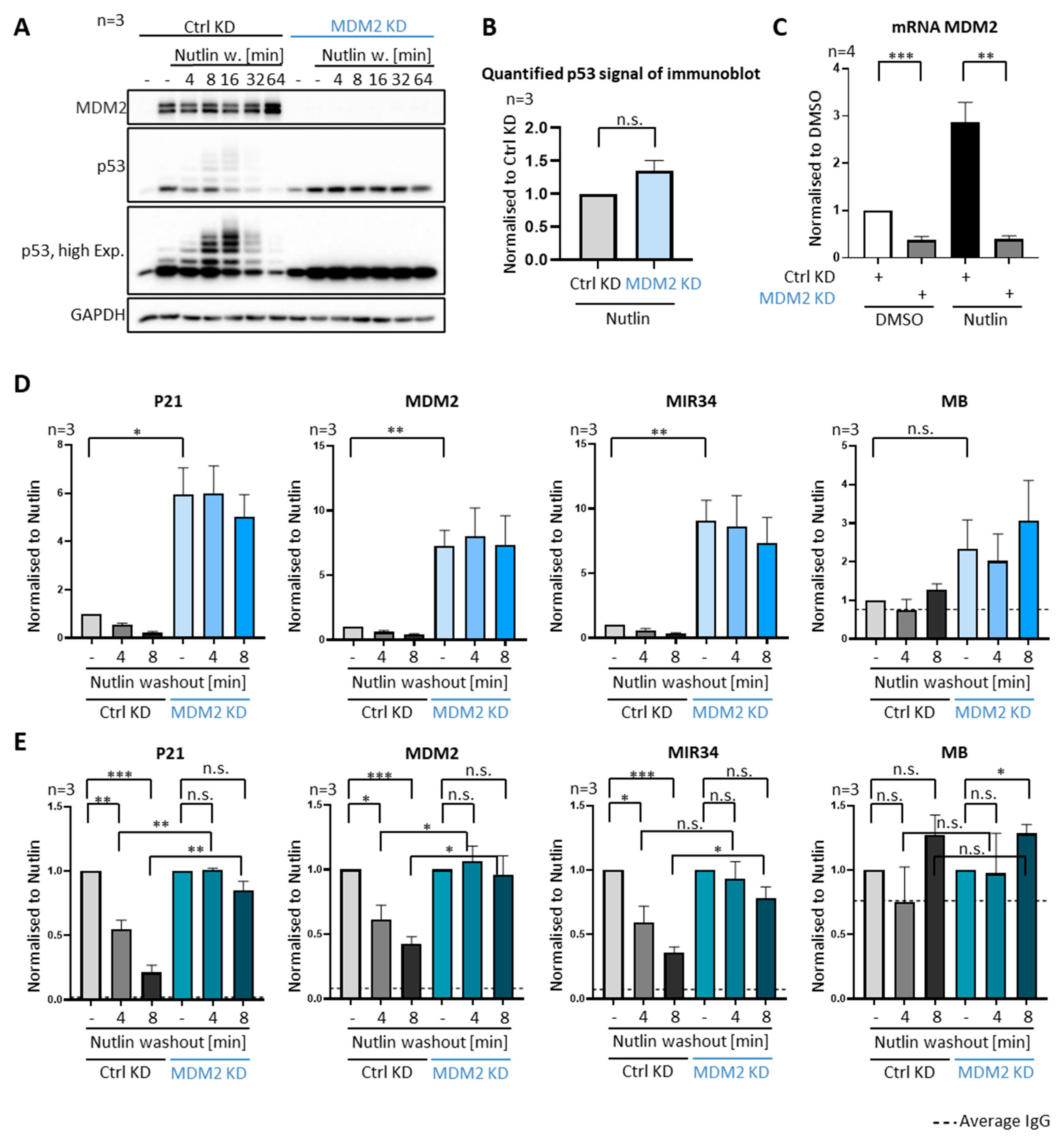
3.3. P53 Removal from Promoters Strictly Depends on MDM2
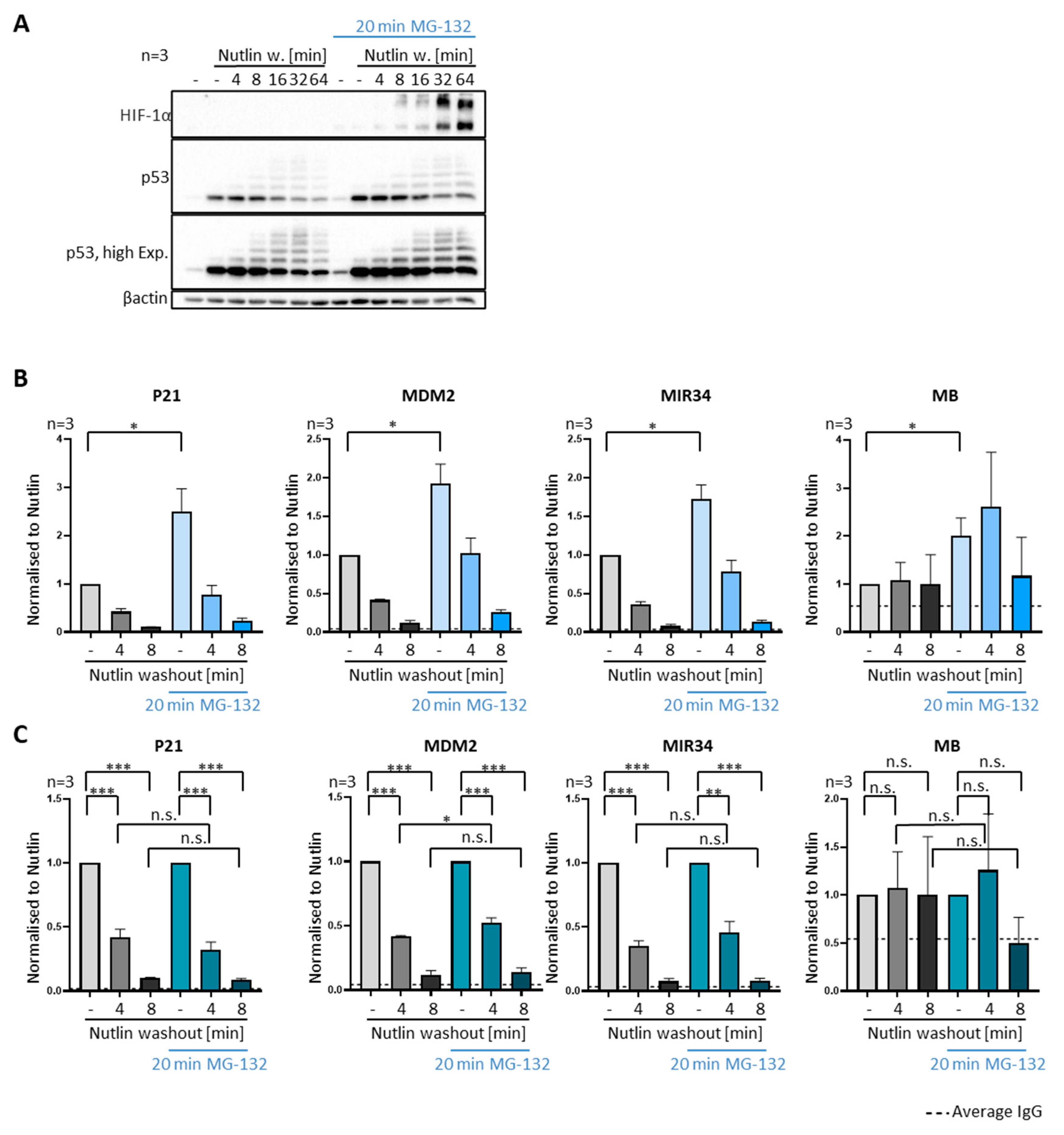
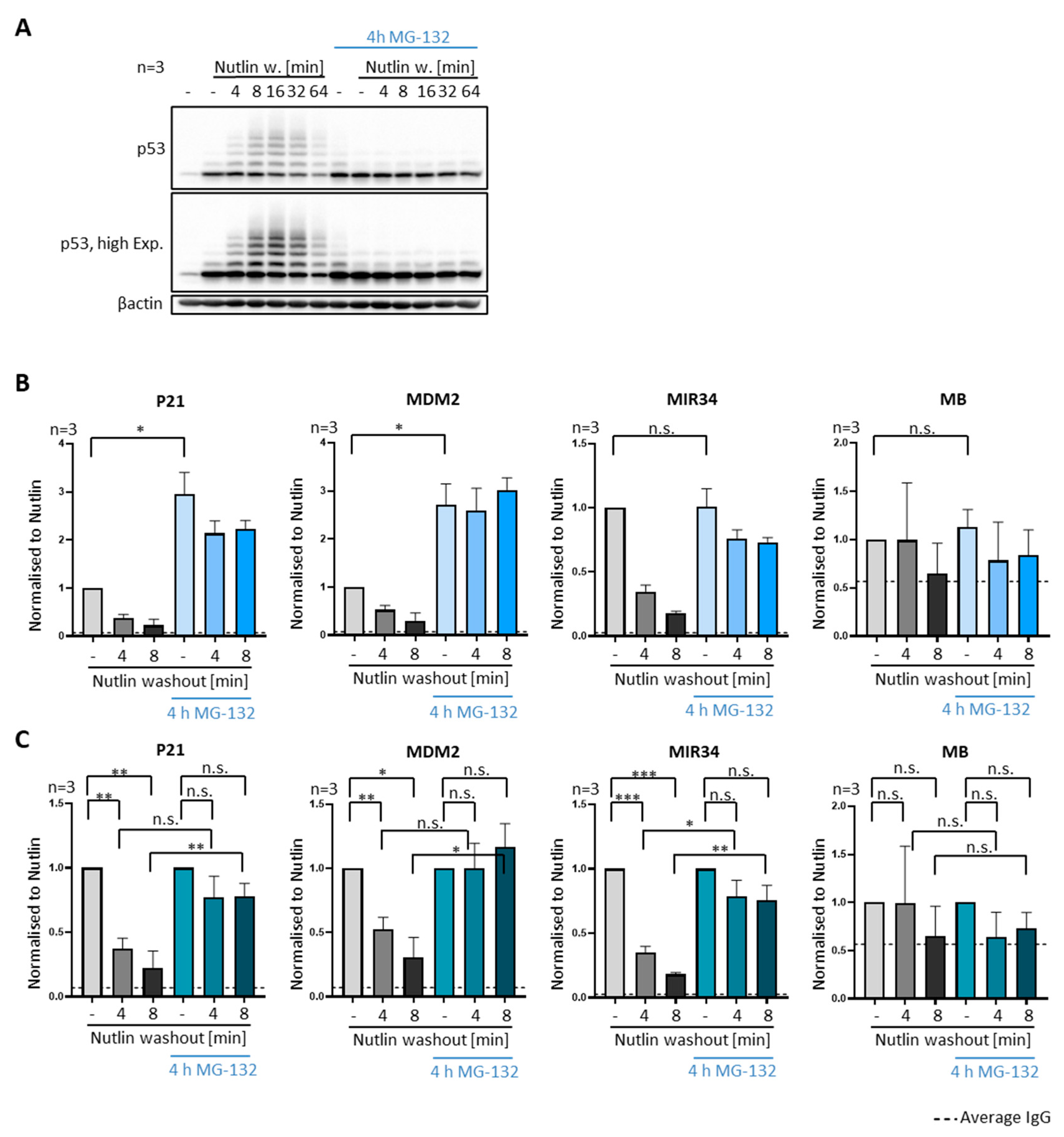
3.4. P53 Removal from Promoters Does Not Require Proteasomal Activity
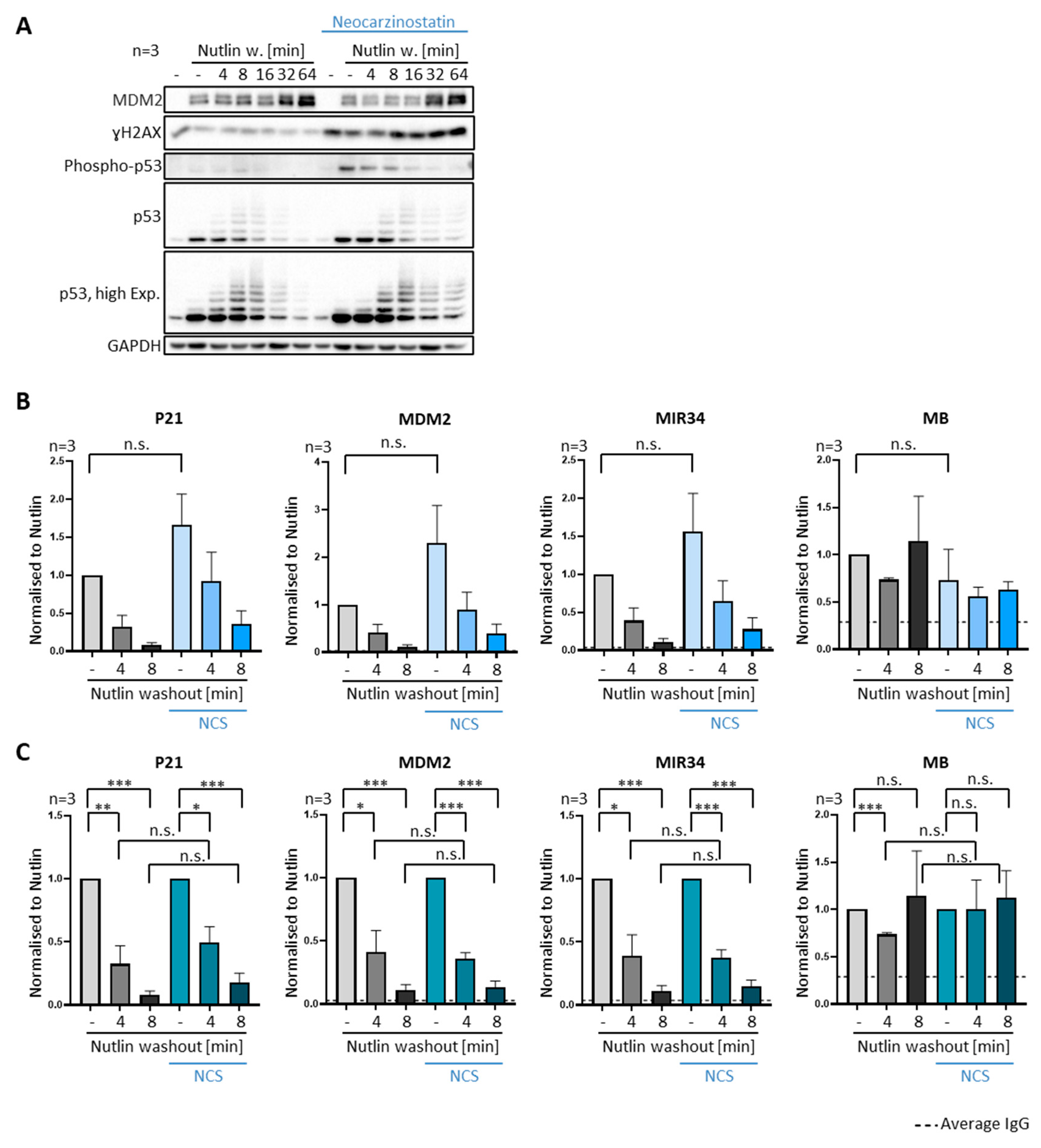
3.5. DNA Damage Does Not Compromise Dissociation of Prebound P53 from Promoter Sites
3.6. Ubiquitin Is Required for the Removal of P53 from Promoters
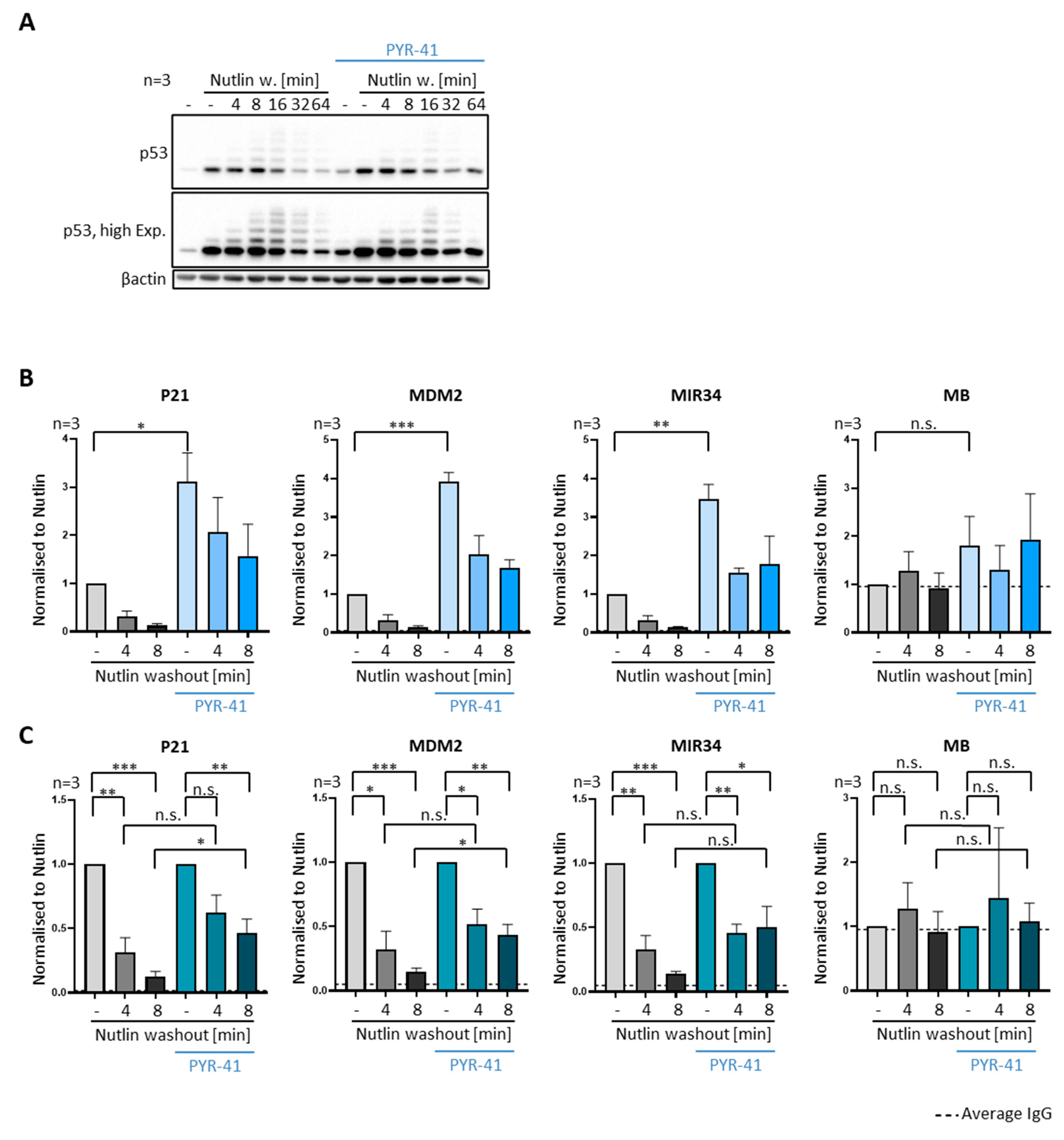
3.7. Inhibiting E1 Ubiquitin Ligases Delays the Removal of P53 from Promoters
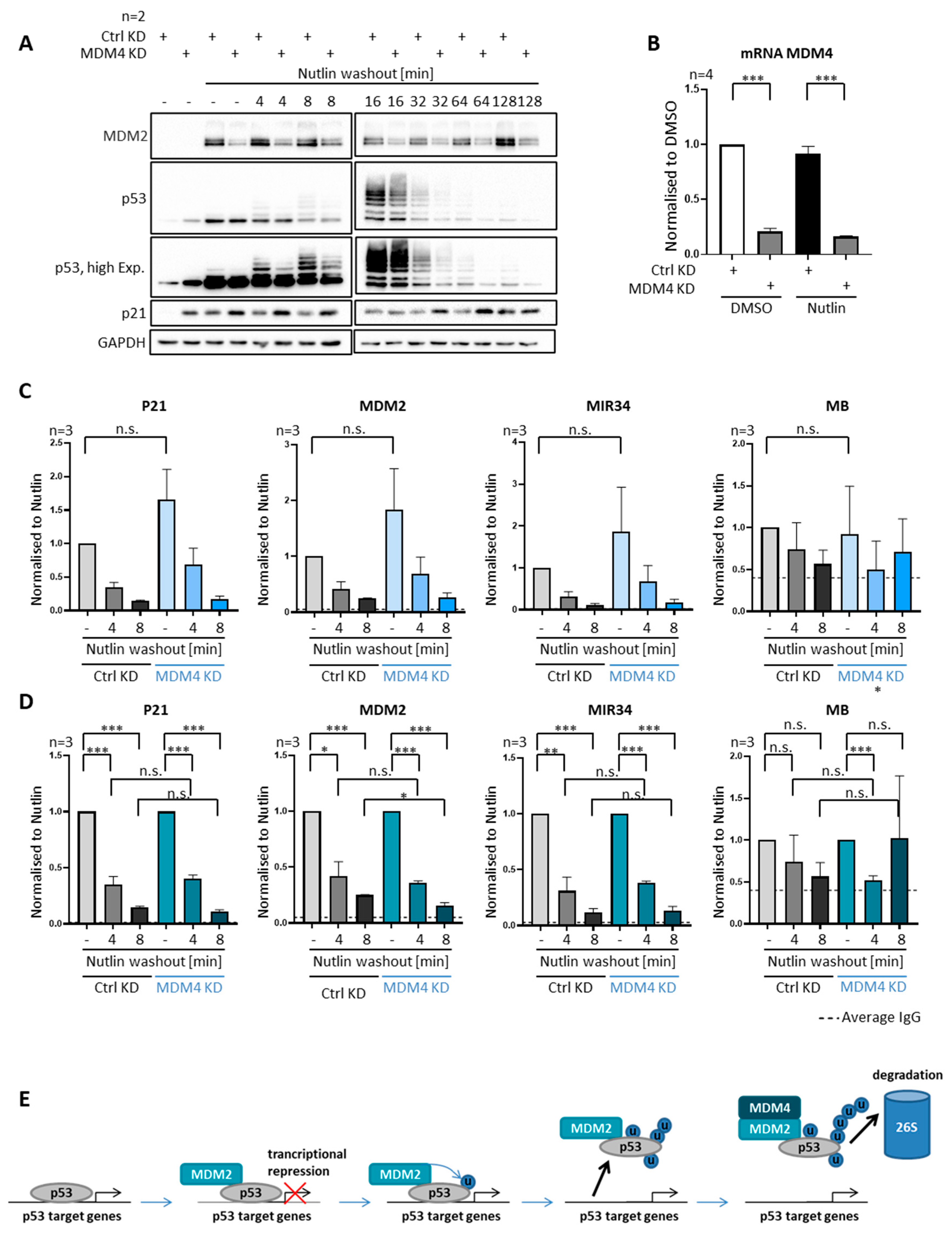
3.8. MDM4 Is Not Required for Removing P53 from Promoters, despite Its Requirement for Polyubiquitination
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, C.L.; Gu, W. P53 Ubiquitination: Mdm2 and Beyond. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobbelstein, M.; Levine, A.J. Mdm2: Open Questions. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, M.; Li, Y.-C.; Wahl, G.M. MDM2, MDMX and P53 in Oncogenesis and Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In Vivo Activation of the P53 Pathway by Small-Molecule Antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leslie, P.L.; Zhang, Y. MDM2 Oligomers: Antagonizers of the Guardian of the Genome. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6157–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barboza, J.A.; Iwakuma, T.; Terzian, T.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Lozano, G. Mdm2 and Mdm4 Loss Regulates Distinct P53 Activities. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X. MdmX Protein Is Essential for Mdm2 Protein-Mediated P53 Polyubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23725–23734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Levine, A.J. Differential Regulation of the P21/WAF-1 and Mdm2 Genes after High-Dose UV Irradiation: P53-Dependent and P53-Independent Regulation of the Mdm2 Gene. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, F.W.; Chen, L.; Madura, K. Catalytically Active Proteasomes Function Predominantly in the Cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18765–18777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kito, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Hatano, A.; Takami, T.; Oshikawa, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Nakayama, K.I. Cell Cycle–Dependent Localization of the Proteasome to Chromatin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, B.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Q.; Li, B.; Yuan, Z.-M.; Chen, J. Inhibition of P53 DNA Binding Function by the MDM2 Protein Acidic Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16018–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, C.L.; Li, M.; Gu, W. Mechanistic Studies of MDM2-Mediated Ubiquitination in P53 Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22804–22815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.T.; Gu, W. The Multiple Levels of Regulation by P53 Ubiquitination. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thut, C.J.; Goodrich, J.A.; Tjian, R. Repression of P53-Mediated Transcription by MDM2: A Dual Mechanism. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Kovacs, J.J.; Higashimoto, Y.; Appella, E.; Yao, T.-P. MDM2-HDAC1-Mediated Deacetylation of P53 Is Required for Its Degradation. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienken, M.; Dickmanns, A.; Nemajerova, A.; Kramer, D.; Najafova, Z.; Weiss, M.; Karpiuk, O.; Kassem, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lozano, G.; et al. MDM2 Associates with Polycomb Repressor Complex 2 and Enhances Stemness-Promoting Chromatin Modifications Independent of P53. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlberedt, K.; Klusmann, I.; Derevyanko, P.K.; Henningsen, K.; Choo, J.A.M.Y.; Manzini, V.; Magerhans, A.; Giansanti, C.; Eischen, C.M.; Jochemsen, A.G.; et al. Mdm4 Supports DNA Replication in a P53-Independent Fashion. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4828–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Ferry, K.V.; Diamond, M.A.; Wee, K.E.; Kim, Y.B.; Ma, J.; Yang, T.; Benfield, P.A.; Copeland, R.A.; Auger, K.R. Human Mdm2 Mediates Multiple Mono-Ubiquitination of P53 by a Mechanism Requiring Enzyme Isomerization*. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31357–31367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Lane, W.S.; Chen, J. ATM Activates P53 by Regulating MDM2 Oligomerization and E3 Processivity. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3857–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, Y.F.; Stad, R.; Attema, J.; Peltenburg, L.T.; van der Eb, A.J.; Jochemsen, A.G. Aberrant Expression of HDMX Proteins in Tumor Cells Correlates with Wild-Type P53. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Poyurovsky, M.V.; Katz, C.; Laptenko, O.; Beckerman, R.; Lokshin, M.; Ahn, J.; Byeon, I.-J.L.; Gabizon, R.; Mattia, M.; Zupnick, A.; et al. The C Terminus of P53 Binds the N-Terminal Domain of MDM2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V. The VHL Tumor Suppressor: Master Regulator of HIF. CPD 2009, 15, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povirk, L.F. DNA Damage and Mutagenesis by Radiomimetic DNA-Cleaving Agents: Bleomycin, Neocarzinostatin and Other Enediynes. Mutat. Res. 1996, 355, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, S.; Moyal, L.; Shieh, S.; Taya, Y.; Anderson, C.W.; Chessa, L.; Smorodinsky, N.I.; Prives, C.; Reiss, Y.; Shiloh, Y.; et al. Enhanced Phosphorylation of P53 by ATM in Response to DNA Damage. Science 1998, 281, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canman, C.E.; Lim, D.S.; Cimprich, K.A.; Taya, Y.; Tamai, K.; Sakaguchi, K.; Appella, E.; Kastan, M.B.; Siliciano, J.D. Activation of the ATM Kinase by Ionizing Radiation and Phosphorylation of P53. Science 1998, 281, 1677–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, J. Mechanism of P53 Stabilization by ATM after DNA Damage. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maya, R.; Balass, M.; Kim, S.T.; Shkedy, D.; Leal, J.F.; Shifman, O.; Moas, M.; Buschmann, T.; Ronai, Z.; Shiloh, Y.; et al. ATM-Dependent Phosphorylation of Mdm2 on Serine 395: Role in P53 Activation by DNA Damage. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melikova, M.S.; Kondratov, K.A.; Kornilova, E.S. Two Different Stages of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Receptor Endocytosis Are Sensitive to Free Ubiquitin Depletion Produced by Proteasome Inhibitor MG132. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kitagaki, J.; Dai, R.-M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lorick, K.L.; Ludwig, R.L.; Pierre, S.A.; Jensen, J.P.; Davydov, I.V.; Oberoi, P.; et al. Inhibitors of Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme (E1), a New Class of Potential Cancer Therapeutics. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9472–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X. Mdm2 and MdmX Partner to Regulate P53. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, C.L.; Gu, W. P53 Regulation by Ubiquitin. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Dey, R.; Chen, L. Crystal Structure of the P53 Core Domain Bound to a Full Consensus Site as a Self-Assembled Tetramer. Structure 2010, 18, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Schulz, R.; Edmunds, S.; Krüger, E.; Markert, E.; Gaedcke, J.; Cormet-Boyaka, E.; Ghadimi, M.; Beissbarth, T.; Levine, A.J.; et al. MicroRNA-101 Suppresses Tumor Cell Proliferation by Acting as an Endogenous Proteasome Inhibitor via Targeting the Proteasome Assembly Factor POMP. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohrum, M.A.E.; Woods, D.B.; Ludwig, R.L.; Bálint, É.; Vousden, K.H. C-Terminal Ubiquitination of P53 Contributes to Nuclear Export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8521–8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, J.; Dobbelstein, M.; Freedman, D.A.; Shenk, T.; Levine, A.J. Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Shuttling of the Hdm2 Oncoprotein Regulates the Levels of the P53 Protein via a Pathway Used by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Rev Protein. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stommel, J.M.; Marchenko, N.D.; Jimenez, G.S.; Moll, U.M.; Hope, T.J.; Wahl, G.M. A Leucine-Rich Nuclear Export Signal in the P53 Tetramerization Domain: Regulation of Subcellular Localization and P53 Activity by NES Masking. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narita, M.; Nũnez, S.; Heard, E.; Narita, M.; Lin, A.W.; Hearn, S.A.; Spector, D.L.; Hannon, G.J.; Lowe, S.W. Rb-Mediated Heterochromatin Formation and Silencing of E2F Target Genes during Cellular Senescence. Cell 2003, 113, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, C.L.; Gu, W. The Impact of Acetylation and Deacetylation on the P53 Pathway. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawara, Y.; Kishishita, S.; Obata, T.; Isazawa, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Masuyama, N.; Gotoh, Y. Akt Enhances Mdm2-Mediated Ubiquitination and Degradation of P53. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21843–21850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.P.; Liao, Y.; Xia, W.; Zou, Y.; Spohn, B.; Hung, M.-C. HER-2/Neu Induces P53 Ubiquitination via Akt-Mediated MDM2 Phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Target | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| P21 | CTTTCTGGCCGTCAGGAACA | CTTCTATGCCAGAGCTCAACATGT |
| MDM2 | TTCAGTGGGCAGGTTGACTC | CCAGCTGGAGACAAGTCAGG |
| MIR34 | ATTCTTCCCCTTACGGAGGC | GAAGGAGGCGGGAACTAGAC |
| PUMA | CCCTGCTCTGGTTTGGTGAG | AGTCACTCTGGTGAGGCGAT |
| PIG3 | CCCTGGGTACCTGCATTAAG | TAGCCGTGCACTTTGACAAG |
| MB | CTCATGATGCCCCTTCTTCT | GAAGGCGTCTGAGGACTTAAA |
| Primer Target | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| nascent RNA P21 | AGACCAGCATGACAGGTGCG | GCCTGGCATAATGAACATTCCCA |
| mRNA P21 | TAGGCGGTTGAATGAGAGG | AAGTGGGGAGGAGGAAGTAG |
| nascent RNA MDM2 | CATTGGTTTGTGGACTTGAGGAT | TAAAGGCAGTCACTTCTGGGA |
| mRNA MDM2 | CCGGATTAGTGCGTACGAG | GTCTCTTGTTCCGAAGCTGGA |
| nascent RNA PUMA | ATTTCCGGGTGCGCTCT | CCTCAACACTCCCTAGCAACT |
| mRNA PUMA | GACGACCTCAACGCACAGTA | TAATTGGGCTCCATCTCGGG |
| mRNA MDM4 | CTCAGACTCTCGCTCTCGCA | CTCAAATCCAAGGTCCAGCC |
| mRNA 36B4 | GATTGGCTACCCAACTGTTG | CAGGGGCAGCAGCCACAAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henningsen, K.M.; Manzini, V.; Magerhans, A.; Gerber, S.; Dobbelstein, M. MDM2-Driven Ubiquitination Rapidly Removes p53 from Its Cognate Promoters. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010022
Henningsen KM, Manzini V, Magerhans A, Gerber S, Dobbelstein M. MDM2-Driven Ubiquitination Rapidly Removes p53 from Its Cognate Promoters. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenningsen, Kester Mo, Valentina Manzini, Anna Magerhans, Sabrina Gerber, and Matthias Dobbelstein. 2022. "MDM2-Driven Ubiquitination Rapidly Removes p53 from Its Cognate Promoters" Biomolecules 12, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010022
APA StyleHenningsen, K. M., Manzini, V., Magerhans, A., Gerber, S., & Dobbelstein, M. (2022). MDM2-Driven Ubiquitination Rapidly Removes p53 from Its Cognate Promoters. Biomolecules, 12(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010022






