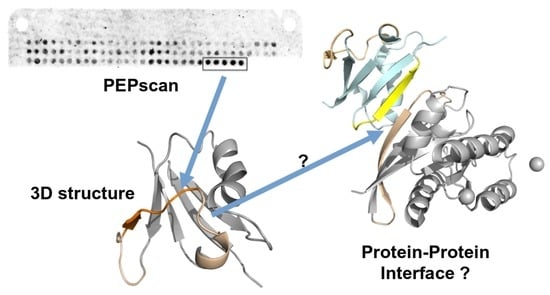
Pepscan Approach for the Identification of Protein–Protein Interfaces: Lessons from Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. PEPscan Protocol
2.2.1. Binding Assay on Cellulose-Bound Peptides
2.2.2. Peptide Synthesis and Sequence
2.3. Candidate Peptide Identification from Membranes
2.4. Structurally Validated Patches of Interaction
3. Results
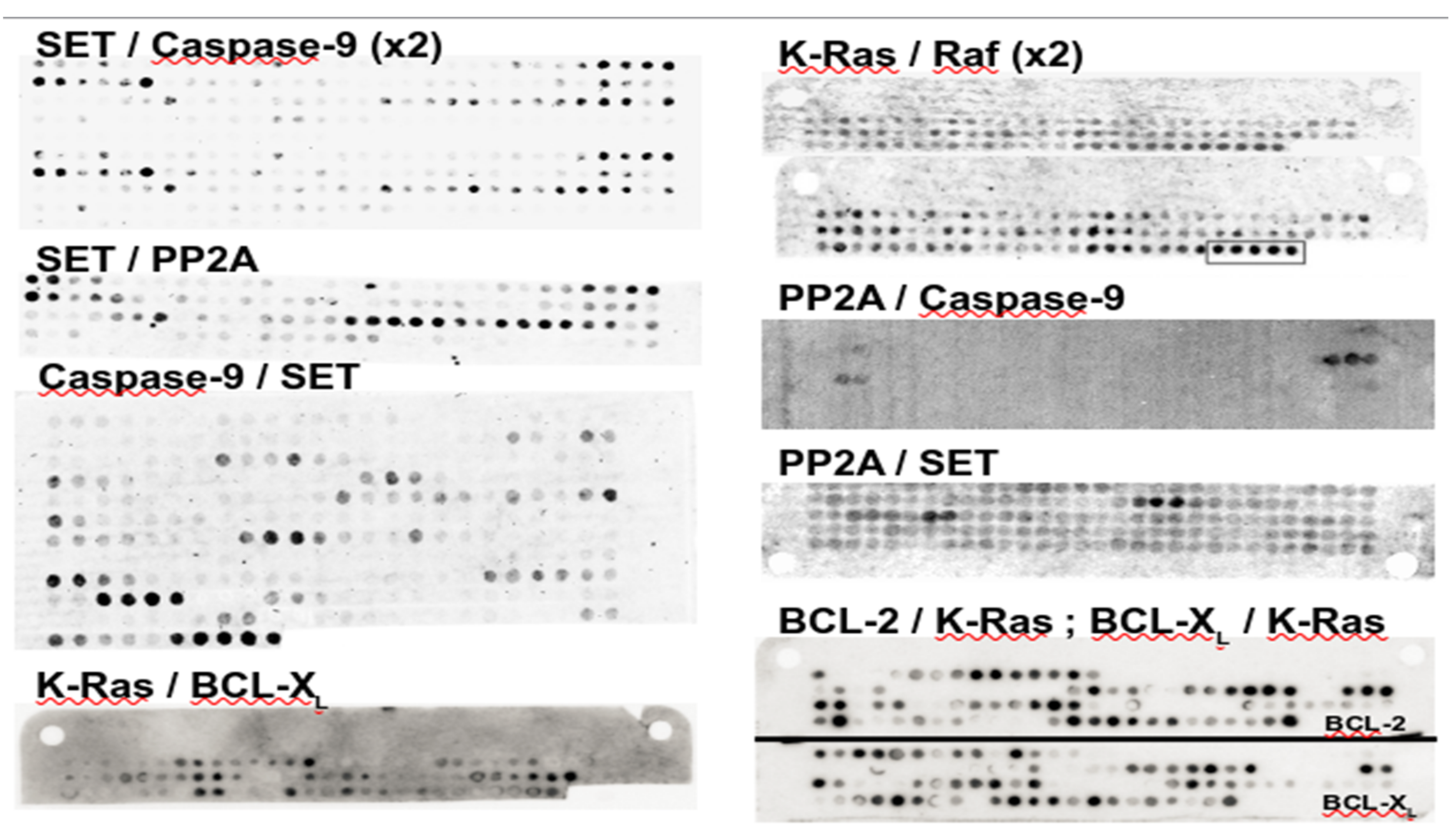
3.1. A Note on PEPscan Experiment Reproducibility
3.2. Confronting PEPscan Positive Fragments with Structural Data
3.3. PEPscan Identifies a Limited Number of IPs
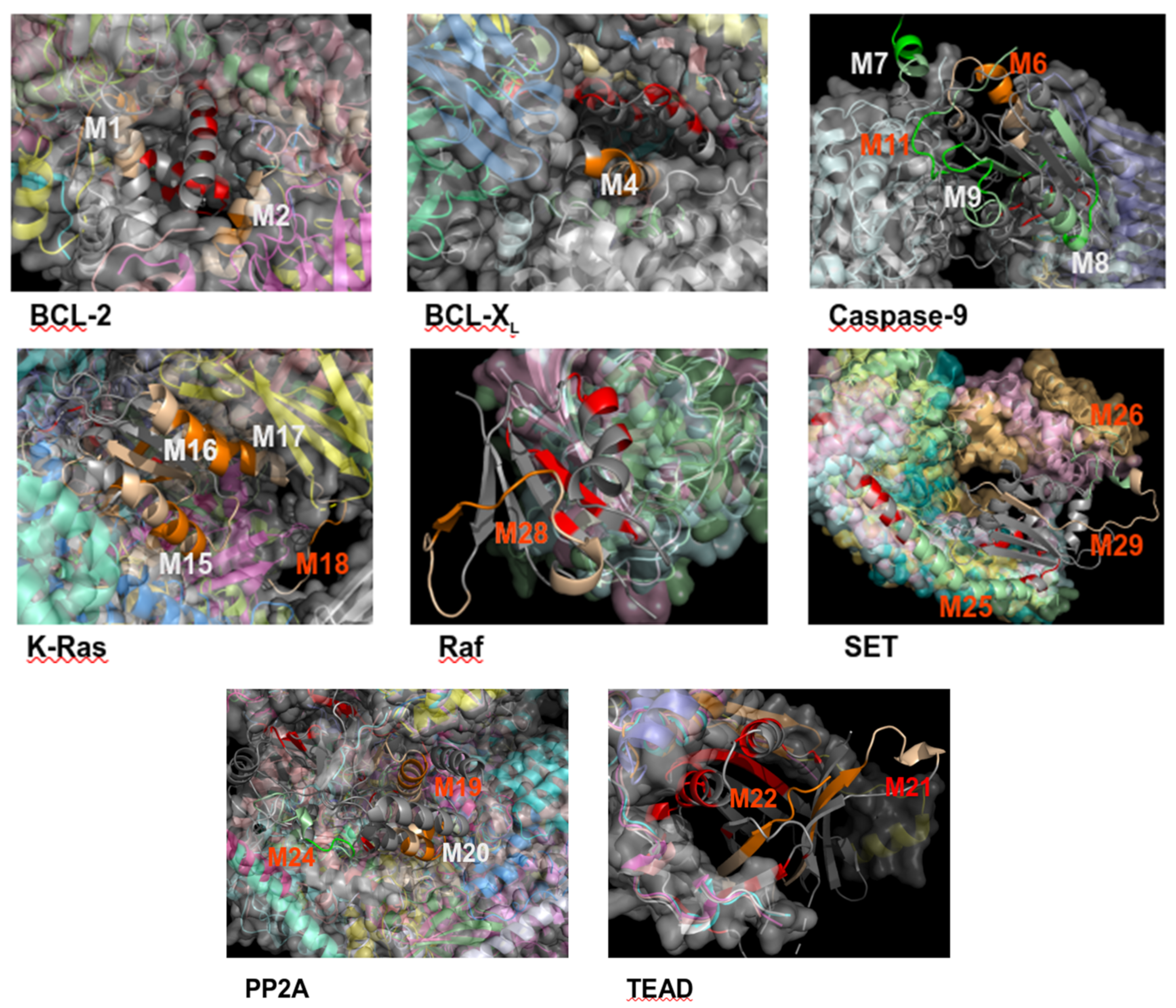
3.4. Can MOFs Correspond to Fragments at the PPI Interface?
3.5. Can Candidate IPs Target Specific Patches on the Partner Protein?
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frank, R.; Overwln, H. SPOT Synthesis: Epitope Analysis with Arrays of Synthetic Peptides Prepared on Cellulose Membranes. Methods Mol. Biol. 1996, 66, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reineke, U.; Sabat, R.; Volk, H.-D.; Schneider-Mergener, J. Mapping of the interleukin-10/interleukin-10 receptor combining site. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geysen, H.M.; Meloen, R.H.; Barteling, S.J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3998–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, G.; Kostyal, D.A.; Reisert, P.S.; Humphreys, R.E.; Sairenji, T. Synthetic Peptides to Identify Antigenic Determinants on Epstein-Barr Virus Gp350/220. Intervirology 1990, 31, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.; Frank, R.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Weiss, S. T Cell Epitope Analysis with Peptides Simultaneously Synthesized on Cellu-lose Membranes: Fine Mapping of Two DQ Dependent Epitopes. FEBS Lett. 1994, 352, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, R.; Kaga, C.; Kunimatsu, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Honda, H. Peptide array-based interaction assay of solid-bound peptides and anchorage-dependant cells and its effectiveness in cell-adhesive peptide design. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askoxylakis, V.; Zitzmann, S.; Mier, W.; Graham, K.; Krämer, S.; Von Wegner, F.; Fink, R.H.; Schwab, M.; Eisenhut, M.; Haberkorn, U. Preclinical Evaluation of the Breast Cancer Cell-Binding Peptide, p160. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6705–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Pérez, P.M.; Grimsey, E.; Bourne, L.; Mikut, R.; Hilpert, K. Screening and Optimizing Antimicrobial Peptides by Using SPOT-Synthesis. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, T.; Heiss, K.; Fischer, N.; Geiger, C.; Bischoff, F.R.; Moldenhauer, G.; Rychlewski, L.; Sié, A.; Coulibaly, B.; Seeberger, P.H.; et al. High-density Peptide Arrays Help to Identify Linear Immunogenic B-cell Epitopes in Individuals Naturally Exposed to Malaria Infection. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Souma, T.; Wei, A.Z.-S.; Xie, X.; Luo, X.; Jin, J. Personalized Peptide Arrays for Detection of HLA Alloantibodies in Organ Transplantation. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 56278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.S.; Birgisdottir Å, B.; Johansen, T. Use of peptide arrays for identification and characterization of LIR motifs. In Autophagy; Methods in Molecular Biology, 1980; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gausepohl, H.; Boulin, C.; Kraft, M.; Frank, R.W. Automated multiple peptide synthesis. Pept. Res. 1992, 5, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, T.; Pham, S.; Deshpande, S. Automated multiple peptide synthesis: Improvements in obtaining quality peptides. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1996, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R. The SPOT-Synthesis Technique: Synthetic Peptide Arrays on Membrane Supports—Principles and Applications. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 267, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.; Heikens, W.; Heisterberg-Moutsis, G.; Blöcker, H. A New General Approach for the Simultaneous Chemical Syn-thesis of Large Numbers of Oligonucleotides: Segmental Solid Supports. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 4365–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxinger, C.; Conrads, T.P.; Goldstein, D.J.; Veenstra, T.D. Fully Automated Synthesis of (Phospho) Peptide Arrays in Micro-titer Plate Wells Provides Efficient Access to Protein Tyrosine Kinase Characterization. BMC Immunol. 2005, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dikmans, A.J.; Morr, M.; Zander, N.; Adler, F.; Türk, G.; Frank, R. A new compact disc format of high density array synthesis applied to peptide nucleic acids and in situ MALDI analysis. Mol. Divers. 2004, 8, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleux, F.; Dubois, P. Novel Version of Multiple Antigenic Peptide Allowing Incorporation on a Cysteine Functionalized Ly-sine Tree. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1992, 40, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, L.C.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Mrksich, M. Peptide Arrays: Development and Application. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molony, R.D.; Rice, J.M.; Yuk, J.S.; Shetty, V.; Dey, D.; Lawrence, D.A.; Lynes, M.A. Mining the Salivary Proteome with Grating-Coupled Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging and Surface Plasmon Coupled Emission Microarrays. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2012, 53, 18.16.1–18.16.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkes, R.; Niday, E.; Gordon, J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 119, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, M.S.; Johnston, K.H.; Russell-Jones, G.J.; Gotschlich, E.C. A Rapid, Sensitive Method for Detection of Alkaline Phos-phatase-Conjugated Anti-Antibody on Western Blots. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 136, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verastegui, M.; Moro, P.; Guevara, A.; Rodriguez, T.; Miranda, E.; Gilman, R.H. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot test for diagnosis of human hydatid disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landgraf, C.; Panni, S.; Montecchi-Palazzi, L.; Castagnoli, L.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Volkmer-Engert, R.; Cesareni, G. Pro-tein Interaction Networks by Proteome Peptide Scanning. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dürauer, A.; Kopecky, E.; Berger, E.; Seifert, M.; Hahn, R.; Jungbauer, A. Evaluation of a sensitive detection method for peptide arrays prepared by SPOT synthesis. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2006, 66, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reineke, U.; Sabat, R.; Kramer, A.; Stigler, R.D.; Seifert, M.; Michel, T.; Volk, H.D.; Schneider-Mergener, J. Mapping Pro-tein-Protein Contact Sites Using Cellulose-Bound Peptide Scans. Mol. Divers. 1996, 1, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.K.; Smith, G.P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science 1990, 249, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiertz, E.J.; Van Gaans-van den Brink, J.A.; Gausepohl, H.; Prochnicka-Chalufour, A.; Hoogerhout, P.; Poolman, J.T. Identi-fication of T Cell Epitopes Occurring in a Meningococcal Class 1 Outer Membrane Protein Using Overlapping Peptides As-sembled with Simultaneous Multiple Peptide Synthesis. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, F.S.; de Almeida Lima, S.; De Ávila, G.R.; Castro, K.L.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Sanchez, E.F.; Nguyen, C.; Granier, C.; Molina, F.; Chávez-Olortegui, C. Identification of Protective B-Cell Epitopes of Atroxlysin-I: A Metalloproteinase from Both-rops Atrox Snake Venom. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, M.; Lewinsohn, D.M. T-Cell Epitope Mapping in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using PepMixes Created by Mi-cro-Scale SPOTTM- Synthesis. In Epitope Mapping Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology, 524; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 369–382. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Alezra, V.; Wolff, N.; Dong, C.-Z.; Tuffery, P.; Rebollo, A. Interfering Peptides Targeting Protein–Protein Interactions: The next Generation of Drugs? Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, N.; Movshovitz-Attias, D.; Schueler-Furman, O. The Structural Basis of Peptide-Protein Binding Strategies. Structure 2010, 18, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, D.; Liu, N.; Sheng, C. Allosteric Modulators of Protein–Protein Interactions (PPIs). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1163, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrouss, I.; Nemati, F.; Roncal, F.; Wislez, M.; Dorgham, K.; Vallerand, D.; Rabbe, N.; Karboul, N.; Carlotti, F.; Bravo, J. Spe-cific Targeting of Caspase-9/PP2A Interaction as Potential New Anti-Cancer Therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrouss, I.; Decaudin, D.; Choquet, S.; Azar, N.; Parizot, C.; Zini, J.M.; Nemati, F.; Rebollo, A. Cell Penetrating Peptides as a Therapeutic Strategy in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Protein Pept. Lett. 2015, 22, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.H.; Rebollo, A.; Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Schinella, G.; Piazzon, I.; Duarte, A.; Errecalde, J. T cell leukemia control via Ras-Raf pathway inhibition with peptides. J. Med. Life 2017, 10, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Nemati, F. Identification of Ras/Raf Binding Site and Design of Interfering Peptide with Potential Clinical Application. Integr. Mol. Med. 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Berrocal, L.; Cirri, E.; Zhang, X.; Andrini, L.; Marin, G.H.; Lebel-Binay, S.; Rebollo, A. New Therapeutic Ap-proach for Targeting Hippo Signalling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrini, L.; Marin, G.H.; Inda, A.M.; Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Garcia, M.; Errecalde, J.; Rebollo, A. Anti-tumoral Effect of a Cell Penetrating and Interfering Peptide Targeting PP2A/SET Interaction. Folia Med. 2020, 62, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Haesen, D.; Bravo, J.; Fominaya, J.; Choquet, S.; Zini, J.M.; Loisel, S.; Waelkens, E.; Janssens, V. Identifi-cation of PP2A/Set Binding Sites and Design of Interacting Peptides with Potential Clinical Applications. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2018, 24, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhangi, G.; Fréville, A.; Rebollo, A.; Khalife, J. Peptides Derived from Plasmodium Falciparum Leu-cine-Rich Repeat 1 Bind to Serine/Threonine Phosphatase Type 1 and Inhibit Parasite Growth In Vitro. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.Z.; Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Yu, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Parizot, C.; Zini, J.M.; Brossas, J.Y.; Tuffery, P.; Rebollo, A. Identification of peptides interfering with the LRRK2/PP1 interaction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Reineke, U.; Dong, L.; Hoffmann, B.; Hoffmüller, U.; Winkler, D.; Volkmer-Engert, R.; Schneider-Mergener, J. Spot synthesis: Observations and optimizations. J. Pept. Res. 1999, 54, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reineke, U.; Kramer, A.; Schneider-Mergener, J. Antigen sequence- and library-based mapping of linear and discontinuous protein-protein-interaction sites by spot synthesis. Comb. Chem. Biol. 1999, 243, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gouw, M.; Michael, S.; Sámano-Sánchez, H.; Pancsa, R.; Glavina, J.; Diakogianni, A.; Valverde, J.A.; Bukirova, D.; Čalyševa, J.; et al. ELM—the eukaryotic linear motif resource in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D296–D306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karami, Y.; Guyon, F.; De Vries, S.; Tufféry, P. DaReUS-Loop: Accurate loop modeling using fragments from remote or unrelated proteins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, Y.; Rey, J.; Postic, G.; Murail, S.; Tufféry, P.; De Vries, S.J. DaReUS-Loop: A web server to model multiple loops in homology models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W423–W428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Debulpaep, M.; Kuemmerer, N.; De La Paz, M.L.; Martins, I.C.; Reumers, J.; Morris, K.L.; Copland, A.; Serpell, L.; Serrano, L.; et al. Exploring the sequence determinants of amyloid structure using position-specific scoring matrices. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, R.; Céol, A.; Aloy, P. Interactome3D: Adding structural details to protein networks. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, D.; Petrey, D.; Honig, B. Integrating 3D structural information into systems biology. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Gracia, L.; Savier, E.; Parizot, C.; Brossas, J.Y.; Loisel, S.; Teesalu, T.; Conti, F.; Charlotte, F.; Scatton, O.; Aoudjehane, L.; et al. Bifunctional Therapeutic Peptides for Targeting Malignant B Cells and Hepatocytes: Proof of Concept in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 2000131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein | UniProt | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| BCL-2 | P10415 | 2xa0 |
| BCL-XL | Q8SQ42 | 4qnq/1bxl |
| Caspase-9 | P55211/Q8C3Q9 | 1jxq/2ar9 |
| K-Ras | P32883-2 | 5uk9 |
| PP2A | P67775 | 5w0w |
| Raf | P04049 | 3omv/4g0n |
| SET | Q01105-2 | 2e50 |
| TEAD | Q15562 | 3kys/3l15 |
| YAP | P46937 | 3kys |
| TAZ | Q9GZV5 | 5gn0 |
| PEPscan | IPs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | |||||||||
| Lbl | Seq | s2 | z-sc | Val. | Lbl | Seq | s2 | z-sc | Val | |
| BCL-2/K-Ras (×1) | M1 | 19-IHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDVG | αc | −0.33 | - | - | ||||
| M2 | 187-TWIQDNGGWDAFVELYGP | αc | −0.14 | |||||||
| BCL-XL/K-Ras (×1) | M3 | 27-FSDVEENRTEAPEGTESE (*) | - | - | - | M23 | 111-MVLVGNKCDLPSRTVDTK | βc | −0.53 | - |
| M4 | 163-VSRIAAWMATYLNDHLEP | α | –0.44 | |||||||
| M5 | 195-YGNNAAAESRKGQERFNRWFLTGM (*) | - | 0.58 | |||||||
| Caspase-9/PP2A (×2) | M6 | 401-YIETLDGILEQWARSEDL (†+) | αc | −0.28 | cpm, cell, aff | M24 | 175-DTLDHIRALDRLQEVPHEGP (†+) | αc | −0.36 | cell |
| Caspase-9/SET (×2) | M7 | 133-SGGFGDVGALESLRGN (n) | α | −0.39 | cell | cell | ||||
| M8 | 199-FMVEVKGDLTAKKMVLAL (n) | βα | −0.2 | |||||||
| M9 | 267-FNGTSCPSLGGKPKLFFI (n) | cβ | −0.39 | M25 | 53-ILKVEQKYNKLRQPFFQKRSEL (†+) | α | 0.94 | |||
| M10 | 348-FPGFVSWRDPKSGSWYVE (n) | cα | 1.88 | M26 | 169-RSSQTQNKASRKRQHEEP (†-) | cα | −0.22 | |||
| M11 | 399-QMPGCFNFLRKKLFFKTS (†+) | βc | 0 | |||||||
| K-Ras/Raf (×2) | M12 | 1-MTEYKLVVVGAGGVGK (n) | βc | −0.19 | cpm, cell | cell | ||||
| M13 | 31-EYDPTIEDSYRKQVVIDG (3D site) (n) | cβ | 1.74 | |||||||
| M14 | 61-QEEYSAMRDQYMRTGEGFLCVF (n) | cαβ | 0.19 | M27 | 1-MEHIQGAWKTISNGFGLK (*†+) | - | - | |||
| M15 | 91-EDIHHYREQIKRVKDSED (n) | αc | −0.46 | M28 | 103-HEHKGKKARLDWNTDAAS (†+) | cβc | −0.42 | |||
| M16 | 127-TKQAQELARSYGIPFI (n) | αc | −0.34 | |||||||
| M17 | 155-AFYTLVREIRKHKEKMSK (n) | α | −0.4 | |||||||
| M18 | 169-KMSKDGKKKKKKSRTRCTVM (†+) | αc | −0.34 | |||||||
| PP2A / SET (×1) | M19 | 95-ETVTLLVALKVRYRERIT (†+) | αc | −0.28 | cpm, cell | M29 | 151-PSSKSTEIKWKSGKDLTKRSSQ (†+) | Βcα | −0.59 | cell |
| M20 | 133-CLRKYGNANVWKYF (n) | α | −0.37 | M30 | 165-DLTKRSSQTQNKASRKRQHEEP (n) | αcα | −0.28 | |||
| TEAD / YAP (×1) | M21 | 227-RLQLVEFSAFVEPPDAVD (†+) | βc | −0.52 | cpm, cell | M31 | 76-KTANVPQTVPMRLRKLPD (†+, 3D site) | c | - | cell |
| TEAD / TAZ (×1) | M22 | 293-PPHAFFLVKFWADLNWGPSGEEAGAG (†+, 3D site) | ββ | −0.24 | cell | cell | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebollo, A.; Savier, E.; Tuffery, P. Pepscan Approach for the Identification of Protein–Protein Interfaces: Lessons from Experiment. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060772
Rebollo A, Savier E, Tuffery P. Pepscan Approach for the Identification of Protein–Protein Interfaces: Lessons from Experiment. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(6):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060772
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebollo, Angelita, Eric Savier, and Pierre Tuffery. 2021. "Pepscan Approach for the Identification of Protein–Protein Interfaces: Lessons from Experiment" Biomolecules 11, no. 6: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060772
APA StyleRebollo, A., Savier, E., & Tuffery, P. (2021). Pepscan Approach for the Identification of Protein–Protein Interfaces: Lessons from Experiment. Biomolecules, 11(6), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060772