Identification and Target-Modification of SL-BBI: A Novel Bowman–Birk Type Trypsin Inhibitor from Sylvirana latouchii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Sylvirana latouchii Skin Secretions
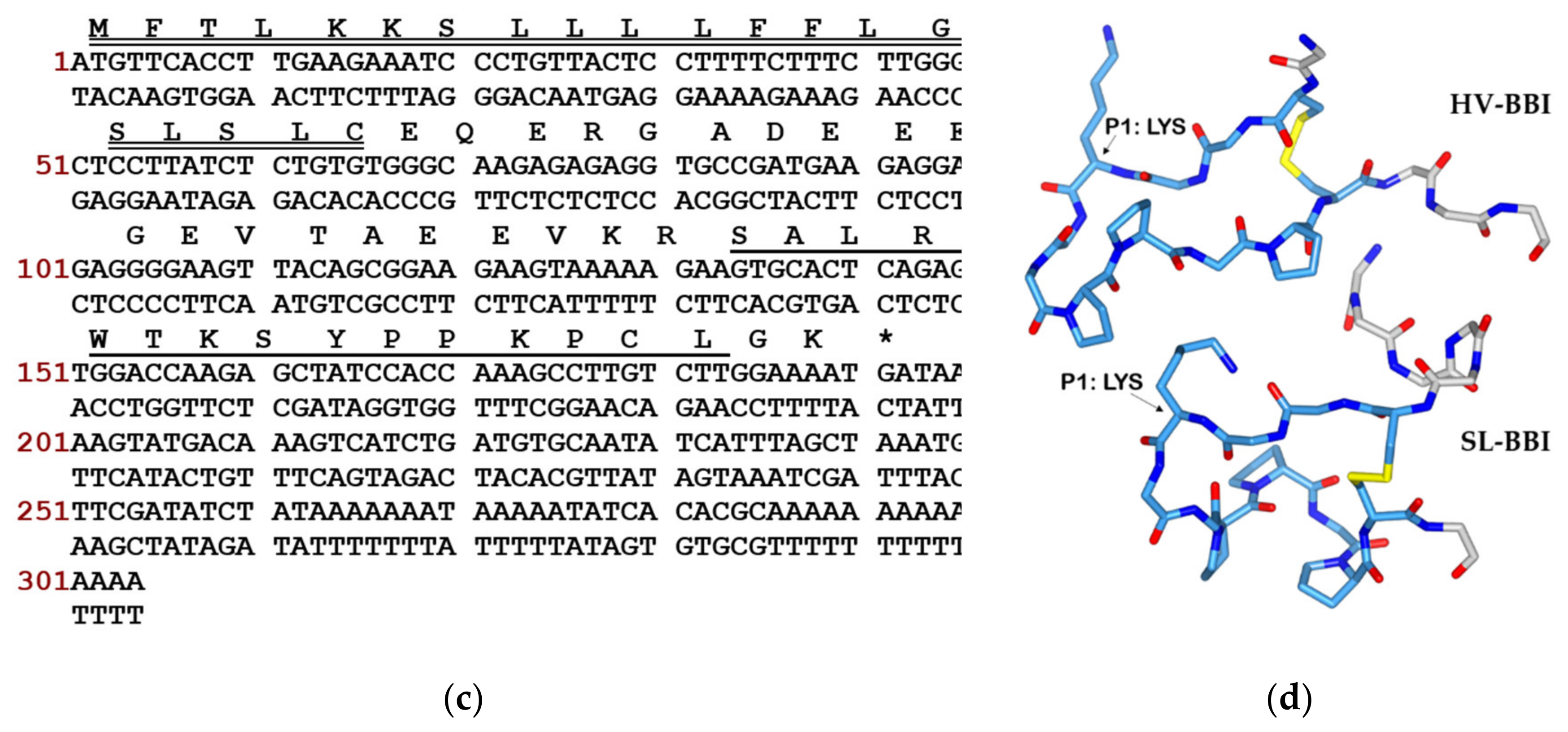
2.2. “Shot-gun” Cloning of SL-BBI Precursor-Encoding cDNA
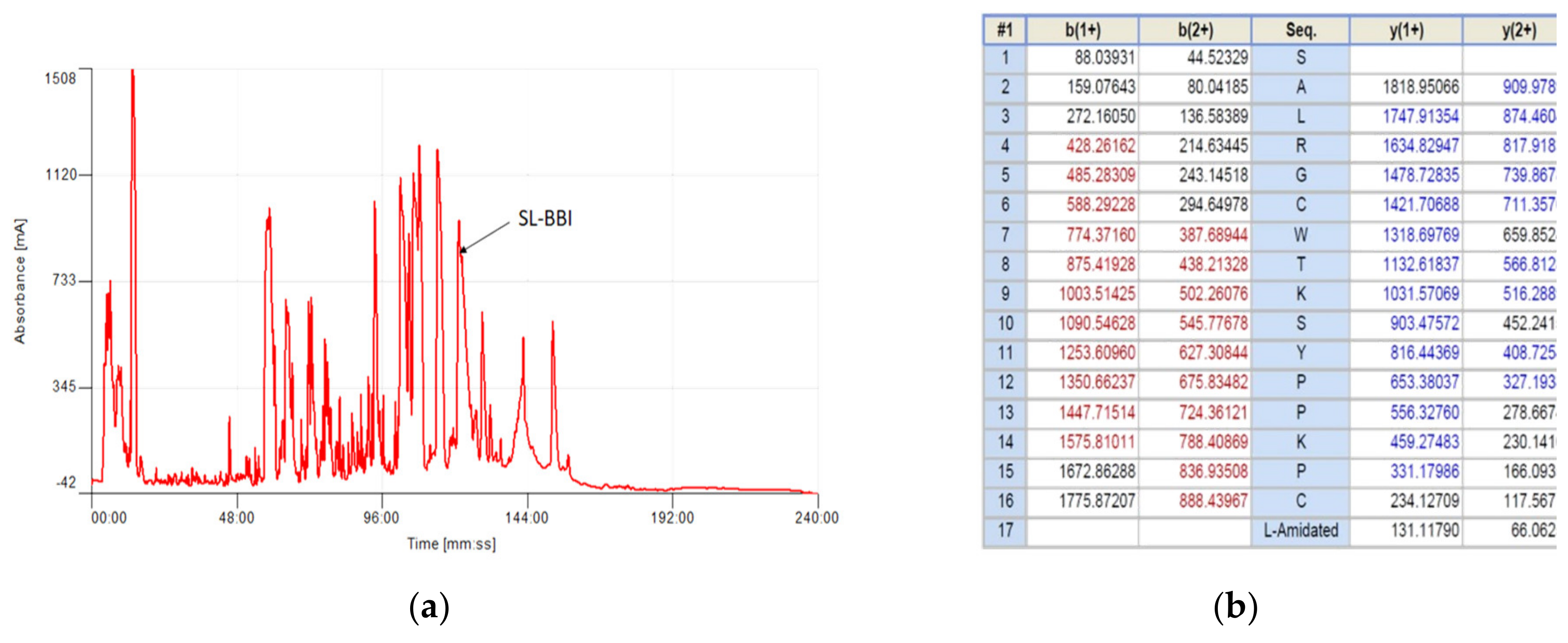
2.3. Isolation and Structural Analysis of SL-BBI
2.4. Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis of SL-BBI and Its Analogues
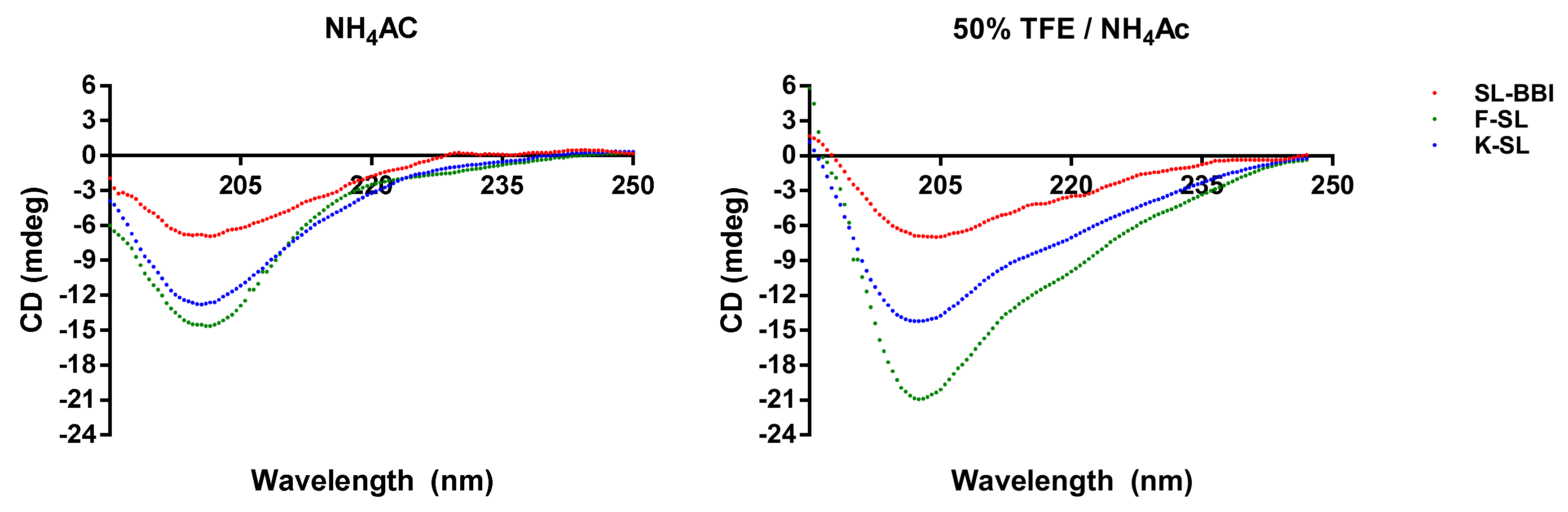
2.5. Secondary Structure Analysis through Circular Dichroism (CD)
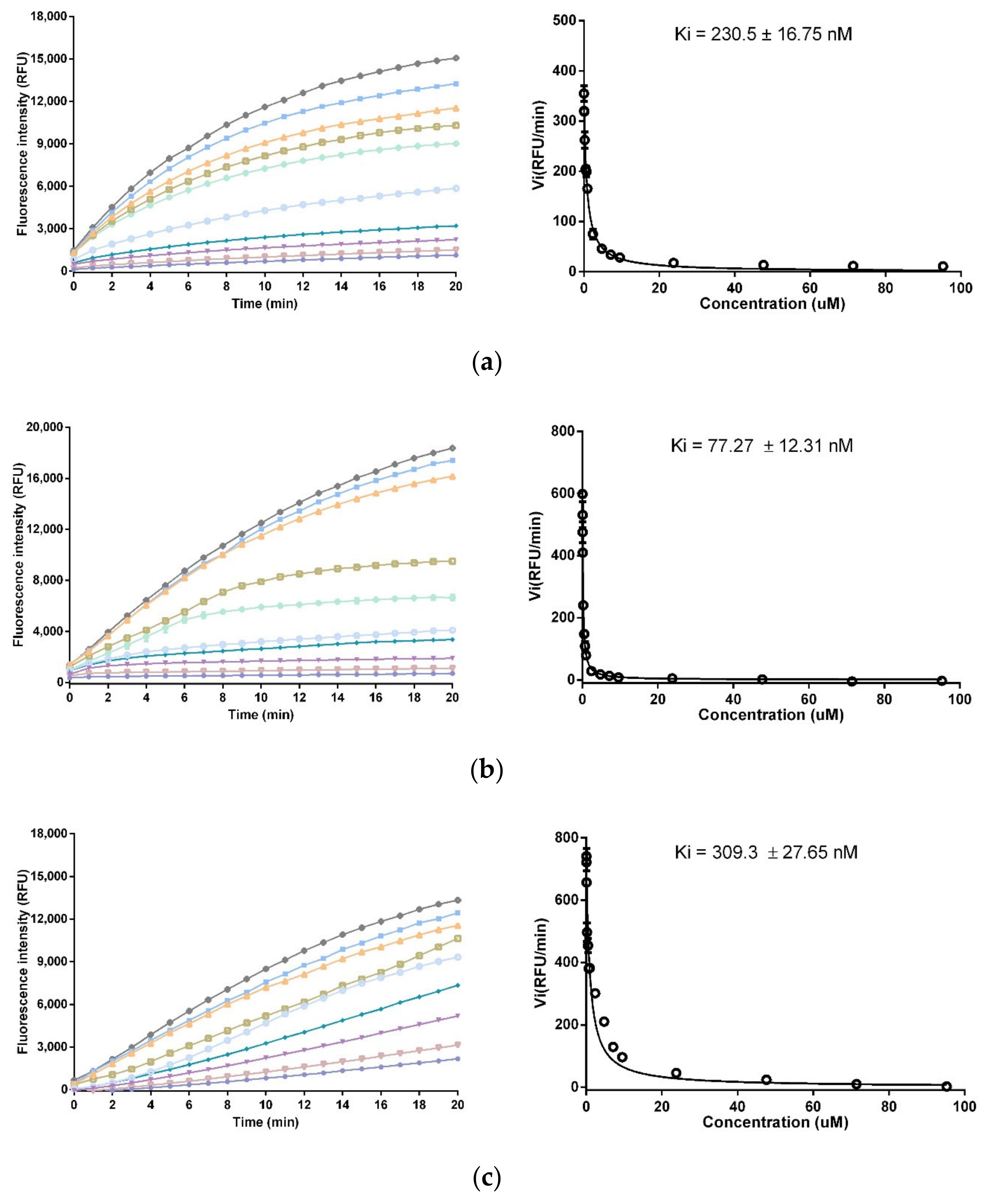
2.6. Trypsin and Chymotrypsin Inhibition Assay
2.7. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Assays
2.8. MTT Cell Viability and LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) Cytotoxicity Assay
2.9. Haemolysis Activity Assay
2.10. Cells Apoptosis Detection
2.11. Caspase 3/7 Activity Assay
2.12. Modelling and Molecular Docking Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Structural Characterisation of SL-BBI
3.2. Motif-Targeted Peptide Design and Synthesis
3.3. Secondary Structure Prediction of SL-BBI and Its Analogues
3.4. Trypsin and Chymotrypsin Inhibitory Activity
3.5. Antimicrobial and Haemolytic Activity
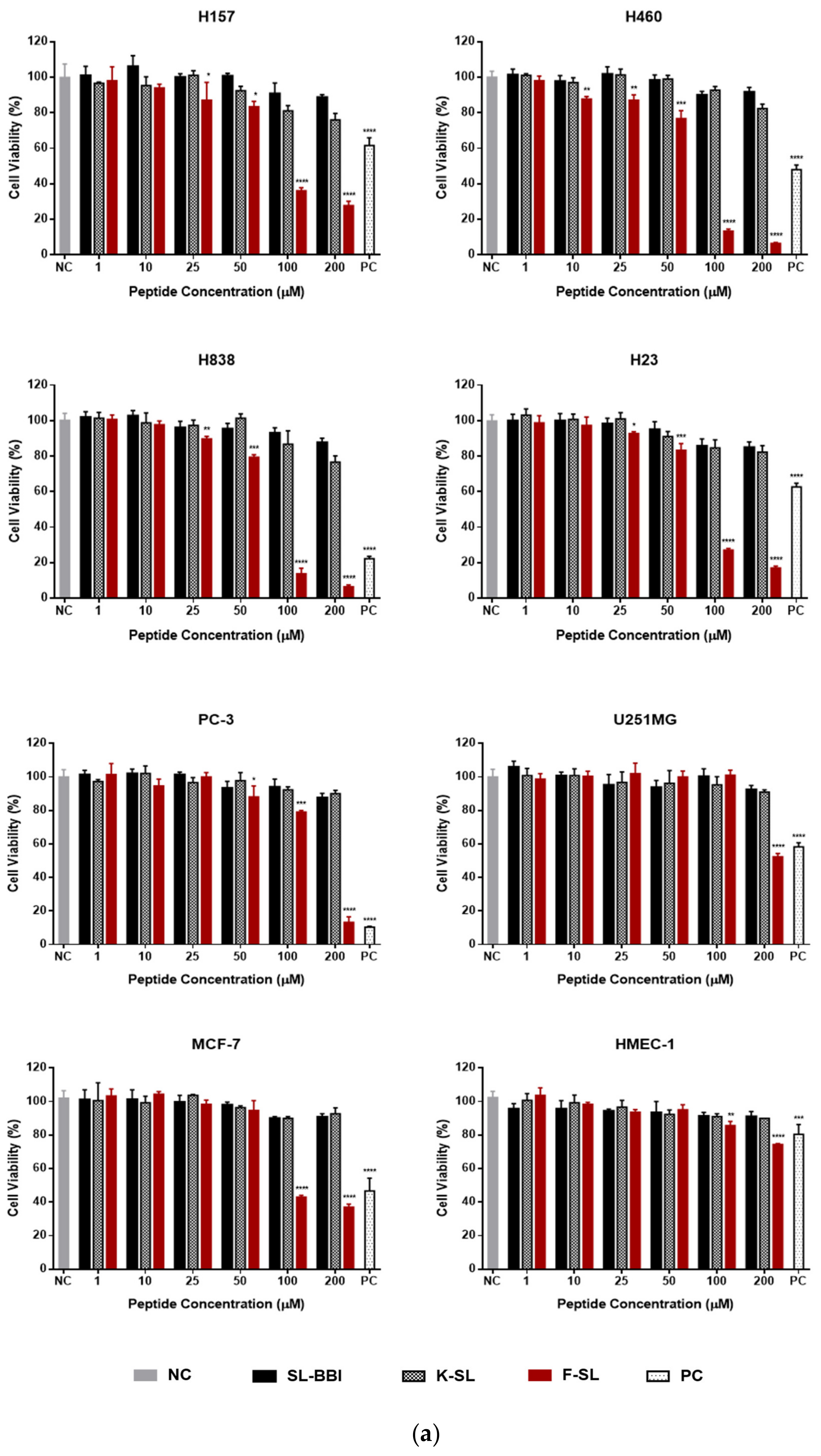
3.6. Anti-Proliferation Activity on Human Cancer and Normal Cells
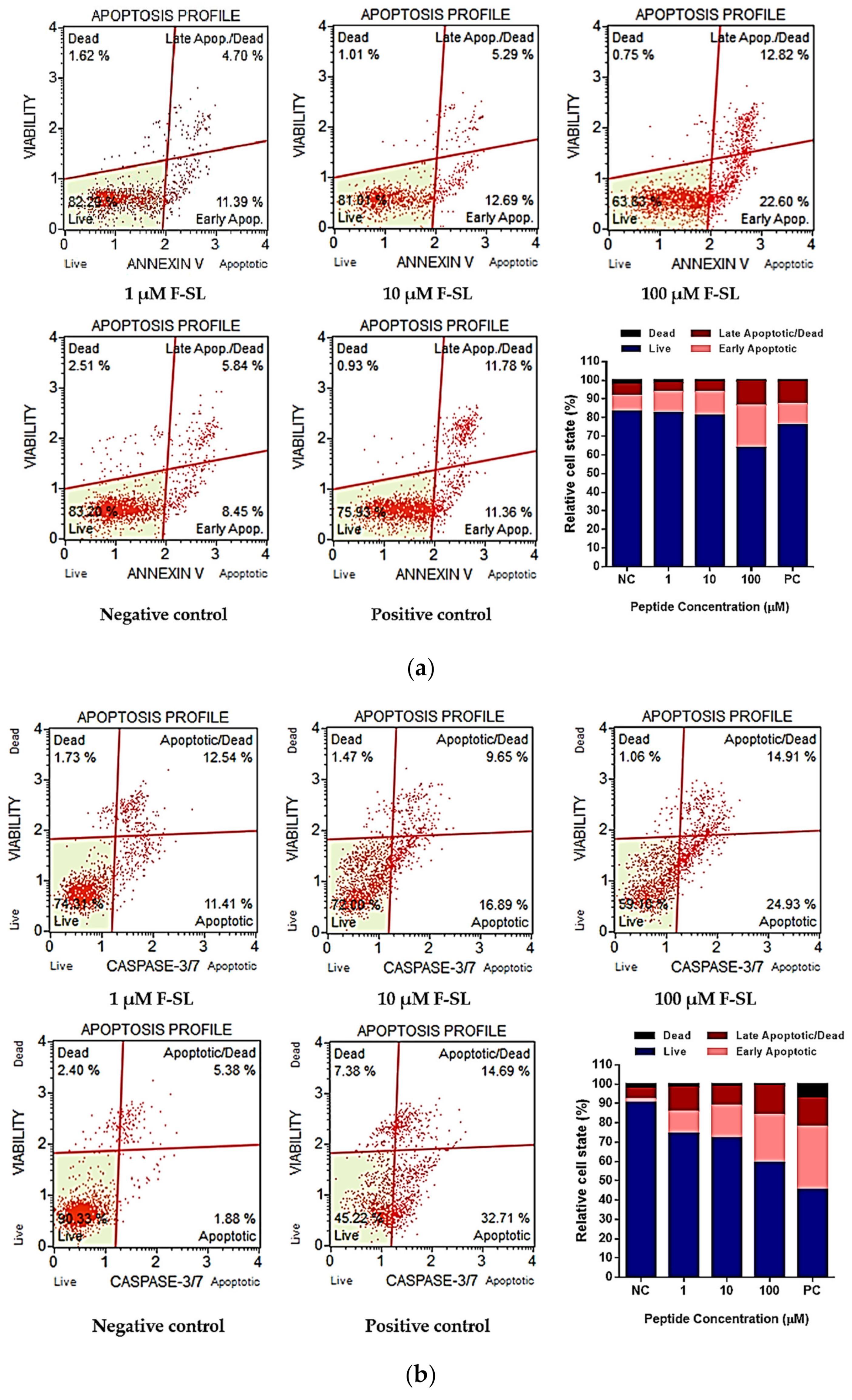
3.7. F-SL Exerts Anti-Cancer Effect by Apoptosis
3.8. Molecular Docking Simulation of F-SL
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brauer, A.B.E.; Nievo, M.; McBride, J.D.; Leatherbarrow, R.J. The Structural Basis of a Conserved P2 Threonine in Canonical Serine Proteinase Inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2003, 20, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Papo, N.; Mignogna, G.; Andreu, D.; Shai, Y.; Barra, D.; Simmaco, M. Ranacyclins, a New Family of Short Cyclic Antimicrobial Peptides: Biological Function, Mode of Action, and Parameters Involved in Target Specificity. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14023–14035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Shi, D.; Ying, Y.; Xi, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, T. A Novel Kunitzin-Like Trypsin Inhibitor Isolated from Defensive Skin Secretion of Odorrana versabilis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilosi, G.; Caruso, C.; Caporale, C.; Leonardi, L.; Bertini, L.; Buzi, A.; Nobile, M.; Magro, P.; Buonocore, V. Antifungal Activity of a Bowman-Birk-type Trypsin Inhibitor from Wheat Kernel. J. Phytopathol. 2000, 148, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Chen, T.; Walker, B.; Shaw, C.; Wang, L. A Bowman-Birk type chymotrypsin inhibitor peptide from the amphibian, Hylarana erythraea. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, A.; Moreno, F.J.; Marín-Manzano, M.d.C.; Jiménez, E.; Domoney, C. The cytotoxic effect of Bowman-Birk isoinhibitors, IBB1 and IBBD2, from soybean (Glycine max) on HT29 human colorectal cancer cells is related to their intrinsic ability to inhibit serine proteases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidunian, A.; Sadeghalvad, M.; Oscoie, M.O.; Mostafaie, A. Soybean Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor (BBI): Identification of the Mechanisms of BBI Suppressive Effect on Growth of Two Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines: AGS and HT29. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Wan, X.S. Effects of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor on growth, invasion, and clonogenic survival of human prostate epithelial cells and prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2002, 50, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogyo, M.; Souza, L.d.C.; Camargo, R.; Demasi, M.; Santana, J.M.; Sá, C.M.d.; de Freitas, S.M. Effects of an Anticarcinogenic Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor on Purified 20S Proteasome and MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.; Irvine, A.E.; McClean, S.; Richter, S.C.; Flatt, P.R.; Shaw, C. Peptide Tyrosine Arginine, a potent immunomodulatory peptide isolated and structurally characterized from the skin secretions of the dusky gopher frog, Rana sevosa. Peptides 2005, 26, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Che, Q.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; You, D.; Wang, A.; Li, J.; et al. Bi-functional peptides with both trypsin-inhibitory and antimicrobial activities are frequent defensive molecules in Ranidae amphibian skins. Amino Acids 2011, 43, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakash, S. Role of proteases in cancer: A review. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 7, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Chen, G.; Xi, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Burrows, J.F.; Duan, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T. Discovery and Rational Design of a Novel Bowman-Birk Related Protease Inhibitor. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdad, A.; Brumana, G.; Souza, A.A.; Barbosa, J.; Ventura, M.M.; de Freitas, S.M. A Bowman–Birk inhibitor induces apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma through mitochondrial impairment and oxidative damage following proteasome 20S inhibition. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joanitti, G.A.; Azevedo, R.B.; Freitas, S.M. Apoptosis and lysosome membrane permeabilization induction on breast cancer cells by an anticarcinogenic Bowman–Birk protease inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata seeds. Cancer Lett. 2010, 293, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, W.B.; Wan, X.S.; Kennedy, A.R.; Taylor, T.H.; Meyskens, F.L. Development of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor for oral cancer chemoprevention and analysis of neu immunohistochemical staining intensity with Bowman-Birk inhibitor concentrate treatment. Laryngoscope 2010, 113, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R. The Bowman-Birk inhibitor from soybeans as an anticarcinogenic agent. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1406S–1412S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Rodemann, H. Radioprotection of Normal Tissue to Improve Radiotherapy: The Effect of the Bowman Birk Protease Inhibitor. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti Cancer Agents 2003, 3, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. The radioprotector Bowman–Birk proteinase inhibitor stimulates DNA repair via epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation and nuclear transport. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 86, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, W.B.; Taylor, T.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Melrose, R.J.; Messadi, D.V.; Gu, M.; Le, A.D.; Perloff, M.; Civantos, F.; Goodwin, W.J.; et al. Bowman Birk Inhibitor Concentrate and Oral Leukoplakia: A Randomized Phase IIb Trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Huang, S.-C.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Lin, J.-K. Bowman–Birk inhibitor abates proteasome function and suppresses the proliferation of MCF7 breast cancer cells through accumulation of MAP kinase phosphatase-1. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, A.; Gee, J.M.; Johnson, I.T.; MacKenzie, D.A.; Domoney, C. Pea (Pisum sativumL.) Protease Inhibitors from the Bowman–Birk Class Influence the Growth of Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma HT29 Cellsin Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8979–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.R. Prevention of carcinogenesis by protease inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1999s–2005s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Álvares, A.; Schwartz, E.; Amaral, N.; Trindade, N.; Pedrino, G.; Silva, L.; de Freitas, S. Bowman-Birk Protease Inhibitor from Vigna unguiculata Seeds Enhances the Action of Bradykinin-Related Peptides. Molecules 2014, 19, 17536–17558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Xi, X.; Ma, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, T. Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Antimicrobial and Anticancer Peptide, Dermaseptin-PS4(Der-PS4), from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa sauvagii. Molecules 2019, 24, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Long, Q.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shaw, C.; Walker, B. A structural and functional analogue of a Bowman–Birk-type protease inhibitor from Odorrana schmackeri. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.G.; Wiehe, K.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.H.; Vreven, T.; Weng, Z. ZDOCK server: Interactive docking prediction of protein-protein complexes and symmetric multimers. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintseris, J.; Pierce, B.; Wiehe, K.; Anderson, R.; Chen, R.; Weng, Z. Integrating statistical pair potentials into protein complex prediction. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 69, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Lai, R. Peptidomics and genomics analysis of novel antimicrobial peptides from the frog, Rana nigrovittata. Genomics 2010, 95, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Isolation, characterization and molecular cloning of new antimicrobial peptides belonging to the brevinin-1 and temporin families from the skin of Hylarana latouchii (Anura: Ranidae). Biochimie 2009, 91, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Su, S.; Shaw, C. Ranatensin-HL: A Bombesin-Related Tridecapeptide from the Skin Secretion of the Broad-Folded Frog, Hylarana latouchii. Molecules 2017, 22, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, K.; Yuan, W.; Ma, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Hong, M.; Xi, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T. Modification Targeting the “Rana Box” Motif of a Novel Nigrocin Peptide From Hylarana latouchii Enhances and Broadens Its Potency Against Multiple Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Hang, H.; Chen, T.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Shaw, C. pLR-HL: A Novel Amphibian Bowman-Birk-type Trypsin Inhibitor from the Skin Secretion of the Broad-folded Frog, Hylarana latouchii. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Pirri, G.; Nicoletto, S. Antimicrobial peptides: An overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Open Life Sci. 2007, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariani, T.; McBride, J.D.; Leatherbarrow, R.J. The role of the P2′ position of Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor in the inhibition of trypsin: Studies on P2′ variation in cyclic peptides encompassing the reactive site loop. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1999, 1431, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Lai, R.; Gong, W. Trypsin inhibitory loop is an excellent lead structure to design serine protease inhibitors and antimicrobial peptides. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, A.L.; Cross, L.J.M.; Irvine, A.E.; Lappin, T.R.J.; Dathe, M.; Krause, G.; Canning, P.; Thim, L.; Beyermann, M.; Rothemund, S.; et al. Peptide Leucine Arginine, a Potent Immunomodulatory Peptide Isolated and Structurally Characterized from the Skin of the Northern Leopard Frog, Rana pipiens. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10145–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.W.; Donahue, J.J.; Wan, X.S. Effects of the bowman-Birk protease inhibitor on survival of fibroblasts and cancer cells exposed to radiation andcis-platinum. Nutr. Cancer 1996, 26, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.S.; Hamilton, T.C.; Ware, J.H.; Donahue, J.J.; Kennedy, A.R. Growth inhibition and cytotoxicity induced by Bowman-Birk inhibitor concentrate in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 1998, 31, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.H.; Gueven, N.; Mayer, C.; Rodemann, H.-P. Characterization of the amino acids essential for the photo- and radioprotective effects of a Bowman–Birk protease inhibitor-derived nonapeptide. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2001, 14, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Billings, P.C.; Wan, X.S.; Newberne, P.M. Effects of Bowman-Birk Inhibitor on Rat Colon Carcinogenesis. Nutr. Cancer 2002, 43, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witschi, H.; Espiritu, I. Development of tobacco smoke-induced lung tumors in mice fed Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor concentrate (BBIC). Cancer Lett. 2002, 183, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombella, V.J.; Rando, O.J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Maniatis, T. The ubiquitinproteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-κB1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-κB. Cell 1994, 78, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coux, O.; Tanaka, K.; Goldberg, A.L. Structure and Functions of the 20S and 26S Proteasomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 801–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J. The proteasome: A suitable antineoplastic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.; Berkers, C.R.; Ploegh, H.L.; Ovaa, H. Crystal Structure of the Boronic Acid-Based Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib in Complex with the Yeast 20S Proteasome. Structure 2006, 14, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccadoro, M.; Morgan, G.; Cavenagh, J. Preclinical evaluation of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cancer therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2005, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Frezza, M.; Schmitt, S.; Kanwar, J.; Dou, Q.P. Bortezomib as the First Proteasome Inhibitor Anticancer Drug: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Mechanisms of Caspase Activation and Inhibition during Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, H.; Chaudhary, P.M. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.A.; Chacko, A.; Mutti, L. BCL-2 family regulation by the 20S proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Oncogene 2007, 27, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Peptides | Sequence | Net Charge | GRAVY 1 | Theoretical Mass (Da) | Observed Mass (Da) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL-BBI | SALRGCWTKSYPPKPCL-NH2 | +4 | −0.447 | 1904.34 | 1904.60 |
| K-SL | AALRGCWTKSIPPKPCK-NH2 | +5 | −0.406 | 1853.33 | 1851.88 |
| F-SL | SALRGCWTFSIPPKPCL-NH2 | +3 | 0.288 | 1873.32 | 1873.82 |
| Peptides | NH4AC | 50%TFE/NH4AC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helix | Antiparallel | Others | Helix | Antiparallel | Others | |
| SL-BBI | 13 | 33 | 54 | 23 | 32 | 45 |
| K-SL | 15 | 38 | 47 | 29 | 26 | 45 |
| F-SL | 13 | 40 | 47 | 13 | 36 | 51 |
| Peptides | MIC/MBC (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | C. albicans | MRSA | |
| SL-BBI | 256/256 | 128/128 | 256/256 | >512 |
| K-SL | 64/64 | 128/128 | 64/64 | >512 |
| F-SL | >512 | >512 | >512 | >512 |
| Peptides | IC50 (μM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H157 | H460 | H838 | H23 | PC-3 | MCF-7 | HMEC-1 | |
| F-SL | 101.4 ± 1.74 | 65.99 ± 2.64 | 59.74 ± 2.72 | 79.06 ± 6.41 | 158.6 ± 6.44 | 201.7 ± 10.6 | 573.5 ± 9.41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Xi, X.; Ma, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, L. Identification and Target-Modification of SL-BBI: A Novel Bowman–Birk Type Trypsin Inhibitor from Sylvirana latouchii. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091254
Chen X, Chen D, Huang L, Chen X, Zhou M, Xi X, Ma C, Chen T, Wang L. Identification and Target-Modification of SL-BBI: A Novel Bowman–Birk Type Trypsin Inhibitor from Sylvirana latouchii. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(9):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091254
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Dong Chen, Linyuan Huang, Xiaoling Chen, Mei Zhou, Xinping Xi, Chengbang Ma, Tianbao Chen, and Lei Wang. 2020. "Identification and Target-Modification of SL-BBI: A Novel Bowman–Birk Type Trypsin Inhibitor from Sylvirana latouchii" Biomolecules 10, no. 9: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091254
APA StyleChen, X., Chen, D., Huang, L., Chen, X., Zhou, M., Xi, X., Ma, C., Chen, T., & Wang, L. (2020). Identification and Target-Modification of SL-BBI: A Novel Bowman–Birk Type Trypsin Inhibitor from Sylvirana latouchii. Biomolecules, 10(9), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091254






