Quasars: From the Physics of Line Formation to Cosmology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Quasar Spectra: Emission from Mildly Ionized Gas
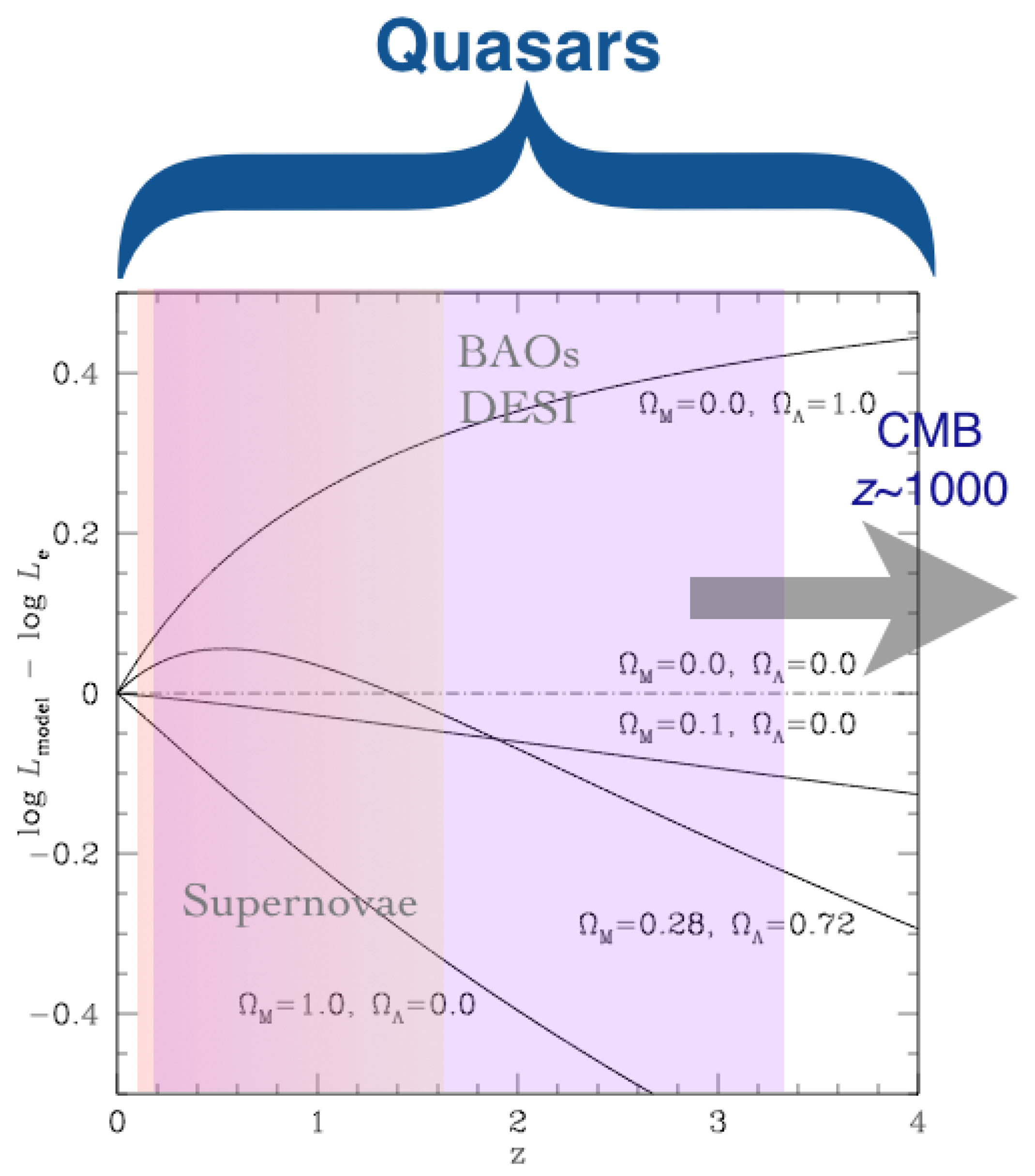
1.2. Quasars for Cosmology: An Open Issue
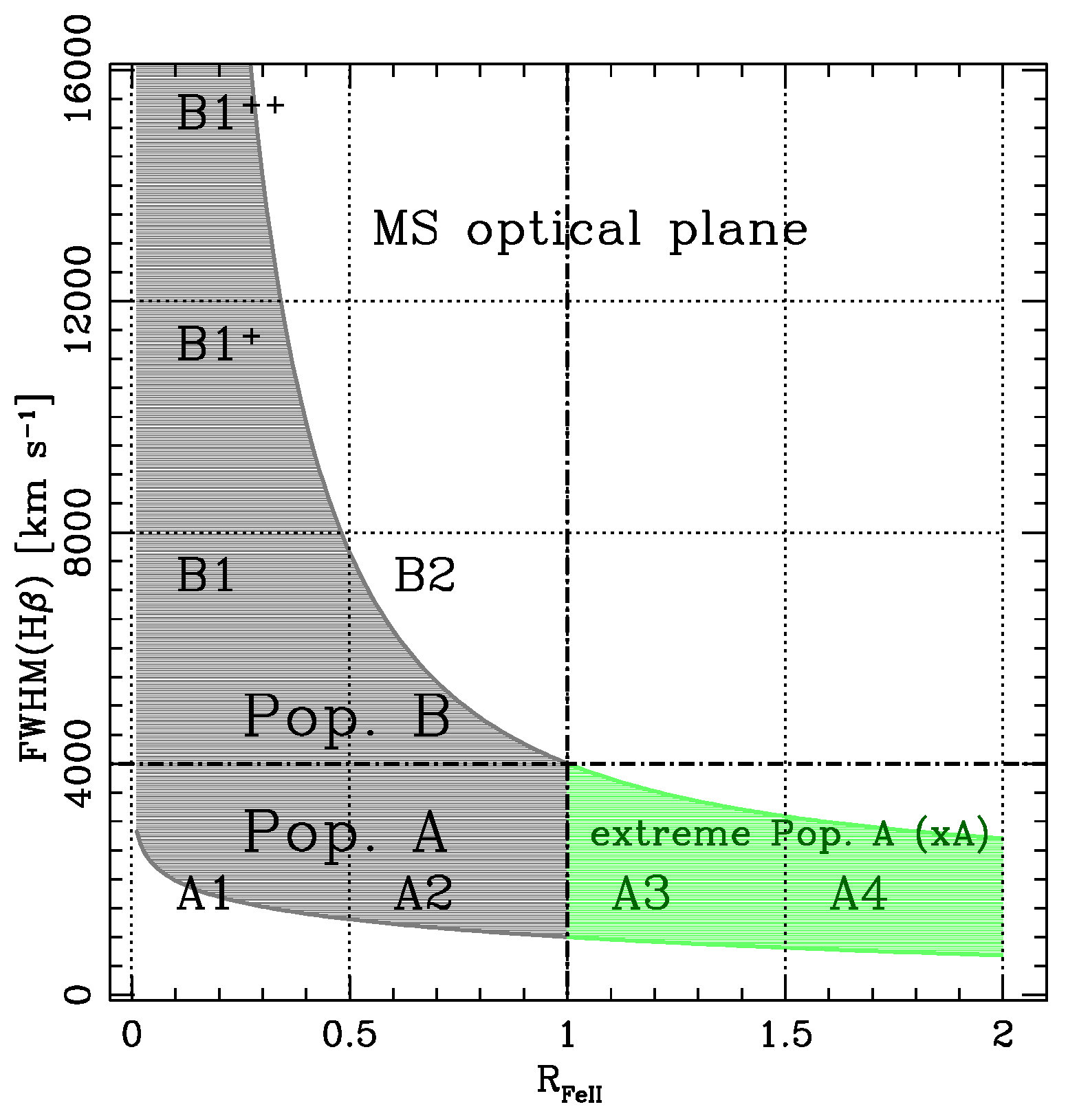
2. Definition of a Class of Type-1 Quasars with Properties of Eddington Standard Candles
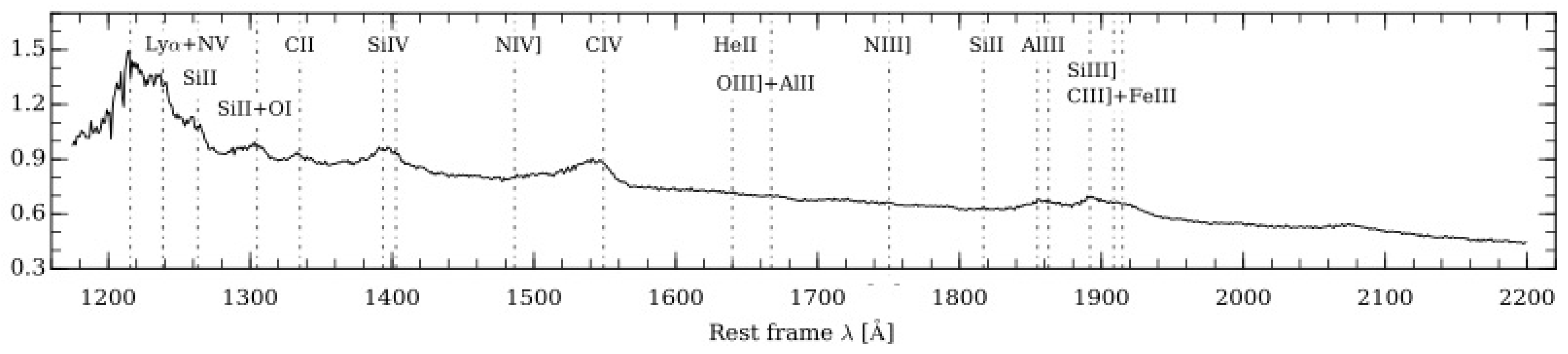
3. Diagnostics of Mildly-Ionized Gases
4. xA Quasars as Eddington Standard Candles
Virial Luminosity
- The first step is the actual estimate of the accretion luminosity via a virial broadening estimator (VBE). The luminosity can be written asassuming virial motions of the low-ionionization part of the broad-line region (BLR). The stands for a suitable VBE, usually the width of a convenient LIL (in practice, the FWHM of H or even Pa, [65]).
- The can be estimated from the inversion of Equation (1) [51,52], again taking advantage of the fact that the ionizing photon flux shows a small scatter around a well defined value. In addition, another key assumption is thatEquation (3) implies that scales with the square root of the luminosity. This is needed to preserve the U parameter. If U were going to change, then the spectrum would also change as a function of luminosity. This is not evident comparing spectra over a wide luminosity range (4.5 dex), although some second order effects are possible.1
- We can therefore write the virial luminosity asMaking explicit the dependence of the number of ionizing photons on the SED, the virial luminosity becomes:where is the fraction of ionizing luminosity scaled to 0.5, the average frequency of ionizing photons scaled to Hz, and to .
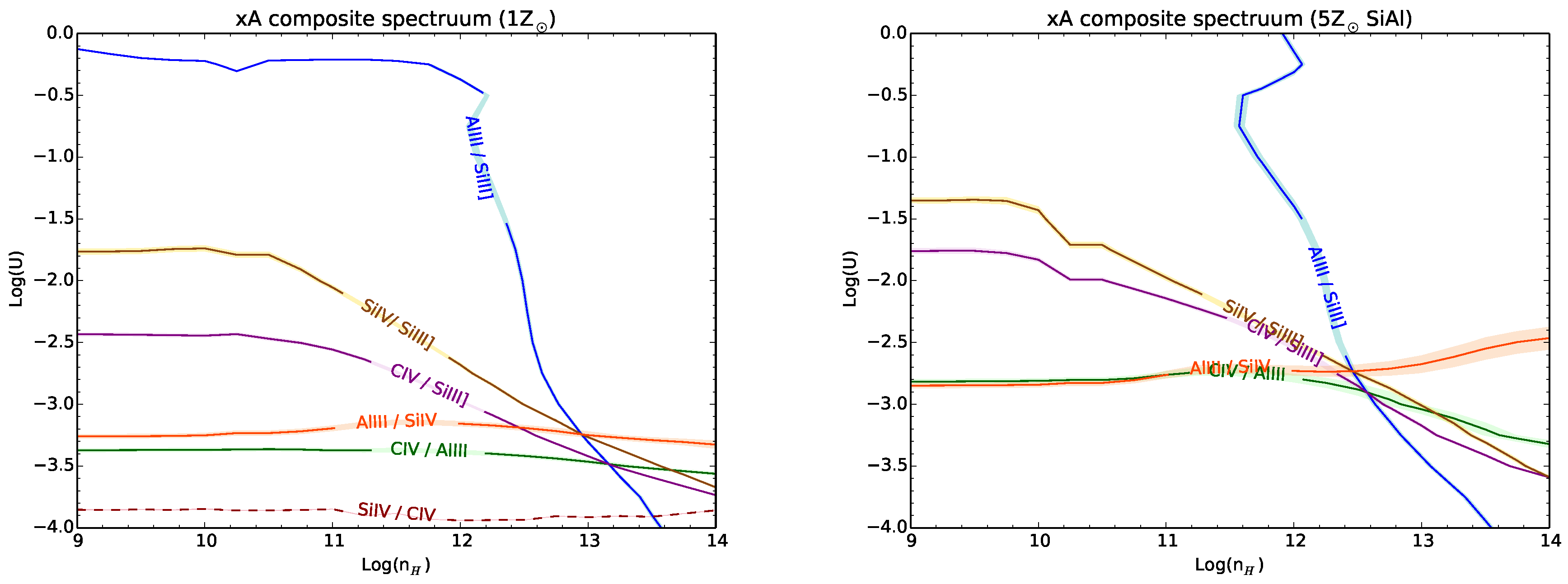
5. Selection of Eddington Standard Candles
- ,
- UV AlIII1860/SiIII]1892 ,
- SiIII]1892/CIII]1909 .
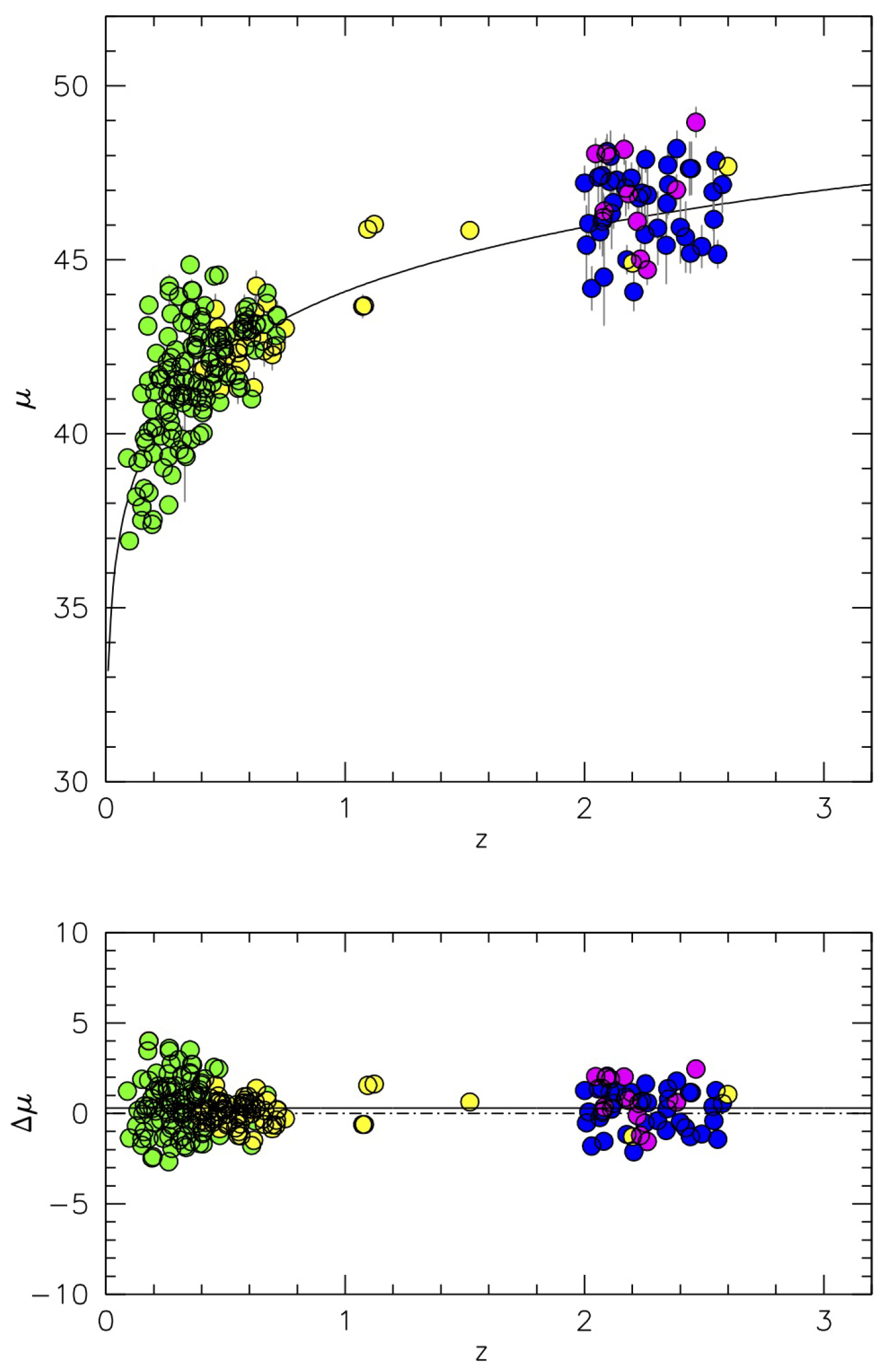
6. Tentative Applications to Cosmology and the Future Perspectives
Error Budget
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGN | Active Galactic Nucleus |
| BLR | Broad Line Region |
| DESI | Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument |
| ESC | Eddington Standard Candles |
| FWHM | Full Width Half-Maximum |
| HIL | High-Ionization Line |
| LIL | Low-Ionization Line |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| MS | Main Sequence |
| NLSy1 | Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 |
| SDSS | Sloan Digital Sly Survey |
| VBE | Virial Broadening Estimator |
References
- Vanden Berk, D.E.; Richards, G.T.; Bauer, A.; Strauss, M.A.; Schneider, D.P.; Heckman, T.M.; York, D.G.; Hall, P.B.; Fan, X.; Knapp, G.R.; et al. Composite Quasar Spectra from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Dultzin-Hacyan, D.; Sulentic, J.W. Accretion onto Supermassive Black Holes in Quasars: Learning from Optical/UV Observations. In New Developments in Black Hole Research; Kreitler, P.V., Ed.; Nova Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Netzer, H. AGN emission lines. In Active Galactic Nuclei; Blandford, R.D., Netzer, H., Woltjer, L., Courvoisier, T.J.-L., Mayor, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 57–160. [Google Scholar]
- Marinello, A.O.M.; Rodriguez-Ardila, A.; Garcia-Rissmann, A.; Sigut, T.A.A.; Pradhan, A.K. The FeII emission in active galactic nuclei: Excitation mechanisms and location of the emitting region. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1602.05159. [Google Scholar]
- Antonucci, R. Unified models for active galactic nuclei and quasars. Annu. R. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 473–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Burigana, C. Questions of Modern Cosmology: Galileo’s Legacy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pâris, I.; Petitjean, P.; Aubourg, É.; Myers, A.D.; Streblyanska, A.; Lyke, B.W.; Anderson, S.F.; Armengaud, É.; Bautista, J.; Blanton, M.R.; et al. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Quasar Catalog: Fourteenth data release. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 613, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Dultzin, D.; Sulentic, J.W.; Del Olmo, A.; Negrete, C.A.; Martinez-Aldama, M.L.; D’Onofrio, M.; Bon, E.; Bon, N.; Stirpe, G.M. A main sequence for quasars. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Marziani, P.; Esparza, D.; Sulentic, J.W.; del Olmo, A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; García López, A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Bon, N.; et al. Highly accreting quasars: The SDSS low-redshift catalog. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, D.R.; Gu, M.F. The Jet Power, Radio Loudness, and Black Hole Mass in Radio-loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2006, 637, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, E.; Zucker, S.; Netzer, H.; Marziani, P.; Bon, N.; Jovanović, P.; Shapovalova, A.I.; Komossa, S.; Gaskell, C.M.; Popović, L.Č.; et al. Evidence for Periodicity in 43 year-long Monitoring of NGC 5548. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2016, 225, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, E.; Marziani, P.; Bon, N. Periodic optical variability of AGN. IAU Symp. 2017, 324, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, H. Meeting Summary: A 2017 View of Active Galactic Nuclei. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; D’Onofrio, M.; del Olmo, A.; Dultzin, D. (Eds.) Quasars at All Cosmic Epochs; Frontiers Media: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; Marziani, P.; Dultzin-Hacyan, D. Phenomenology of Broad Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 38, 521–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, J.A.; Burke, W.L.; Gaskell, C.M.; Wampler, E.J. Relative quasar luminosities determined from emission line strengths. Nature 1978, 273, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerikorpi, P. On Öpik’s distance evaluation method in a cosmological context. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 531, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Du, P.; Valls-Gabaud, D.; Hu, C.; Netzer, H. Super-Eddington Accreting Massive Black Holes as Long-Lived Cosmological Standards. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 081301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Du, P.; Li, Y.R.; Ho, L.C.; Hu, C.; Bai, J.M. A New Approach to Constrain Black Hole Spins in Active Galaxies Using Optical Reverberation Mapping. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 792, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W. Highly accreting quasars: Sample definition and possible cosmological implications. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 1211–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, B.; Beaton, R.; Bejger, M.; Cackett, E.; Dall’Ora, M.; Holanda, R.F.L.; Jensen, J.B.; Jha, S.W.; Lusso, E.; Minezaki, T.; et al. Astronomical Distance Determination in the Space Age. Secondary Distance Indicators. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; Zamfir, S.; Marziani, P.; Dultzin, D. Our Search for an H-R Diagram of Quasars. Revista Mexicana de Astronomia y Astrofisica Conference Series 2008, 32, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Boroson, T.A.; Green, R.F. The emission-line properties of low-redshift quasi-stellar objects. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1992, 80, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; Marziani, P.; Zamanov, R.; Bachev, R.; Calvani, M.; Dultzin-Hacyan, D. Average Quasar Spectra in the Context of Eigenvector 1. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 566, L71–L75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, S.; Sulentic, J.W.; Marziani, P.; Dultzin, D. Detailed characterization of Hβ emission line profile in low-z SDSS quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 403, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ho, L.C. The diversity of quasars unified by accretion and orientation. Nature 2014, 513, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, K.X.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.R.; Bai, J.M.; Bian, W.H.; et al. Supermassive Black Holes with High Accretion Rates in Active Galactic Nuclei. IX. 10 New Observations of Reverberation Mapping and Shortened Hβ Lags. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultzin-Hacyan, D.; Schuster, W.J.; Parrao, L.; Pena, J.H.; Peniche, R.; Benitez, E.; Costero, R. Optical variability of the Seyfert nucleus NGC 7469 in timescales from days to minutes. Astron. J. 1992, 103, 1769–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giveon, U.; Maoz, D.; Kaspi, S.; Netzer, H.; Smith, P.S. Long-term optical variability properties of the Palomar-Green quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 306, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.; Marziani, P.; Zamfir, S. The Case for Two Quasar Populations. Balt. Astron. 2011, 20, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraszkiewicz, J.K.; Green, P.J.; Crenshaw, D.M.; Dunn, J.; Forster, K.; Vestergaard, M.; Aldcroft, T.L. Emission Line Properties of Active Galactic Nuclei from a Post-COSTAR Hubble Space Telescope Faint Object Spectrograph Spectral Atlas. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2004, 150, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Y. Dissecting the Quasar Main Sequence: Insight from Host Galaxy Properties. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 804, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultzin, D.; Martinez, M.L.; Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W.; Negrete, A. Narrow-Line Seyfert 1s: A luminosity dependent definition. In Proceedings of the Conference “Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies and Their Place in the Universe”, Milano, Italy, 4–6 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fraix-Burnet, D.; Marziani, P.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dultzin, D. The Phylogeny of Quasars and the Ontogeny of Their Central Black Holes. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2017, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighly, K.M. Hubble Space Telescope STIS Ultraviolet Spectral Evidence of Outflow in Extreme Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies. II. Modeling and Interpretation. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; del Olmo, A.; Marziani, P.; Martínez-Carballo, M.A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dultzin, D.; Perea, J.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; Negrete, C.A.; Stirpe, G.M.; et al. What does Civλ1549 tell us about the physical driver of the Eigenvector Quasar Sequence? arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.03187. [Google Scholar]
- Elvis, M. A Structure for Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogni, S.; di Serego Alighieri, S.; Goldoni, P.; Ho, L.C.; Marconi, A.; Ponti, G.; Risaliti, G. Simultaneous detection and analysis of optical and ultraviolet broad emission lines in quasars at z 2.2. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1702.08046. [Google Scholar]
- Vietri, G.; Piconcelli, E.; Bischetti, M.; Duras, F.; Martocchia, S.; Bongiorno, A.; Marconi, A.; Zappacosta, L.; Bisogni, S.; Bruni, G.; et al. The WISSH Quasars Project IV. BLR versus kpc-scale winds. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1802.03423. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; Del Olmo, A.; Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W.; Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; D’Onofrio, M.; Perea, J. Extreme quasars at high redshift. Astron. Astroph. 2018, 618, A179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Lu, K.X.; Hu, C.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y.R.; Huang, Y.K.; Wang, F.; Bai, J.M.; Bian, W.H.; Yuan, Y.F.; et al. Supermassive Black Holes with High Accretion Rates in Active Galactic Nuclei. VI. Velocity-resolved Reverberation Mapping of the Hβ Line. Astrophys. J. 2016, 820, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, C.H.; Shlosman, I. Fueling nuclear activity in disk galaxies: Starbursts and monsters. Astrophys. J. 1994, 424, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Zahn, J.P. Star formation and evolution in accretion disks around massive black holes. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 344, 433–449. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J.R.; Baker, A.C.; Perry, J.J. Symbiotic starburst-black hole active galactic nuclei—I. Isothermal hydrodynamics of the mass-loaded interstellar medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 310, 913–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Marziani, P. A Multimessenger View of Galaxies and Quasars From Now to Mid-century. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2018, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Pounds, K. Powerful Outflows and Feedback from Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. R. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 53, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; Del Olmo, A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Stirpe, G.M. Quasar massive ionized outflows traced by CIV λ1549 and [OIII]λλ4959,5007. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, E.; Reeves, J.N.; Gofford, J.; Harrison, F.A.; Risaliti, G.; Braito, V.; Costa, M.T.; Matzeu, G.A.; Walton, D.J.; Behar, E.; et al. Black hole feedback in the luminous quasar PDS 456. Science 2015, 347, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetarenko, B.E.; Lasota, J.P.; Heinke, C.O.; Dubus, G.; Sivakoff, G.R. Strong disk winds traced throughout outbursts in black-hole X-ray binaries. Nature 2018, 554, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, A.; Laor, A. Metal enrichment by radiation pressure in active galactic nucleus outflows - theory and observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 426, 1144–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, A.; Dultzin, D.; Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J. BLR Physical Conditions in Extreme Population A Quasars: A Method to Estimate Central Black Hole Mass at High Redshift. Astrophys. J. 2012, 757, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W. Reverberation and Photoionization Estimates of the Broad-line Region Radius in Low-z Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 771, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferland, G.J.; Porter, R.L.; van Hoof, P.A.M.; Williams, R.J.R.; Abel, N.P.; Lykins, M.L.; Shaw, G.; Henney, W.J.; Stancil, P.C. The 2013 Release of Cloudy. Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica 2013, 49, 137–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ferland, G.J.; Chatzikos, M.; Guzmán, F.; Lykins, M.L.; van Hoof, P.A.M.; Williams, R.J.R.; Abel, N.P.; Badnell, N.R.; Keenan, F.P.; Porter, R.L.; et al. The 2017 Release Cloudy. Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica 2017, 53, 385–438. [Google Scholar]
- Punsly, B.; Marziani, P.; Bennert, V.N.; Nagai, H.; Gurwell, M.A. Revealing the Broad Line Region of NGC 1275: The Relationship to Jet Power. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Woo, J.H.; Nagao, T.; Kim, S.C. The Chemical Properties of Low-redshift QSOs. Astrophys. J. 2013, 763, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; Marziani, P.; del Olmo, A.; Dultzin, D.; Perea, J.; Alenka Negrete, C. GTC spectra of z ≈ 2.3 quasars: Comparison with local luminosity analogs. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 570, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.M.; Wandel, A. Evidence for Supermassive Black Holes in Active Galactic Nuclei from Emission-Line Reverberation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 540, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.M.; Wandel, A. Keplerian Motion of Broad-Line Region Gas as Evidence for Supermassive Black Holes in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 521, L95–L98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, C.M. What broad emission lines tell us about how active galactic nuclei work. New Astron. Rev. 2009, 53, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, E.; Lutz, D.; Risaliti, G.; Netzer, H.; Gallo, L.C.; Trakhtenbrot, B.; Sturm, E.; Boller, T. Enhanced star formation in narrow-line Seyfert 1 active galactic nuclei revealed by Spitzer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 403, 1246–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Czerny, B.; Lasota, J.P.; Szuszkiewicz, E. Slim accretion disks. Astrophys. J. 1988, 332, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineshige, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Hayashida, K. Slim-Disk Model for Soft X-Ray Excess and Variability of Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 Galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 52, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Straub, O. Accretion discs. Scholarpedia 2014, 9, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Franca, F.; Bianchi, S.; Ponti, G.; Branchini, E.; Matt, G. A New Cosmological Distance Measure Using Active Galactic Nucleus X-Ray Variability. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 787, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Fisher, J.R. A new method of determining distances to galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1977, 54, 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, S.M.; Jackson, R.E. Velocity dispersions and mass-to-light ratios for elliptical galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1976, 204, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; Del Olmo, A.; Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W.; Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Perea, J.; D’Onofrio, M. Highly Accreting Quasars at High Redshift. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2018, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Martinez-Aldama, M.L.; Del Olmo, A.; Esparza, D.; Sulentic, J.W.; D’Onofrio, M.; Stirpe, G.M.; Bon, E.; et al. Highly accreting quasars: A tool for cosmology? IAU Symp. 2017, 324, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Sulentic, J.W. Quasars and their emission lines as cosmological probes. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Bebek, C.; Beers, T.; Blum, R.; Cahn, R.; Eisenstein, D.; Flaugher, B.; Honscheid, K.; Kron, R.; Lahav, O.; et al. The DESI Experiment, a whitepaper for Snowmass 2013. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:1308.0847. [Google Scholar]
- Shemmer, O.; Lieber, S. Weak Emission-line Quasars in the Context of a Modified Baldwin Effect. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, M.J.; McLure, R.J. Orientation dependency of broad-line widths in quasars and consequences for black hole mass estimation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Olmo, A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.; Dultzin, D.; Negrete, A.; Bon, E.; Bon, N.; D’Onofrio, M. Quasar Black Hole Mass Estimates from High-Ionization Lines: Breaking a Taboo? Atoms 2017, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risaliti, G.; Lusso, E. A Hubble Diagram for Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | The maximum temperature of the accretion disk is ; the SED is expected to become softer at high , but this effect has not been detected yet at a high confidence level. |
| 2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marziani, P.; Bon, E.; Bon, N.; del Olmo, A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dultzin, D.; Negrete, C.A.; Stirpe, G.M. Quasars: From the Physics of Line Formation to Cosmology. Atoms 2019, 7, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7010018
Marziani P, Bon E, Bon N, del Olmo A, Martínez-Aldama ML, D’Onofrio M, Dultzin D, Negrete CA, Stirpe GM. Quasars: From the Physics of Line Formation to Cosmology. Atoms. 2019; 7(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarziani, Paola, Edi Bon, Natasa Bon, Ascension del Olmo, Mary Loli Martínez-Aldama, Mauro D’Onofrio, Deborah Dultzin, C. Alenka Negrete, and Giovanna M. Stirpe. 2019. "Quasars: From the Physics of Line Formation to Cosmology" Atoms 7, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7010018
APA StyleMarziani, P., Bon, E., Bon, N., del Olmo, A., Martínez-Aldama, M. L., D’Onofrio, M., Dultzin, D., Negrete, C. A., & Stirpe, G. M. (2019). Quasars: From the Physics of Line Formation to Cosmology. Atoms, 7(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7010018






