Stopping Power of Iron for Protons: Theoretical Calculations from Very Low to High Energies
Abstract
1. Introduction
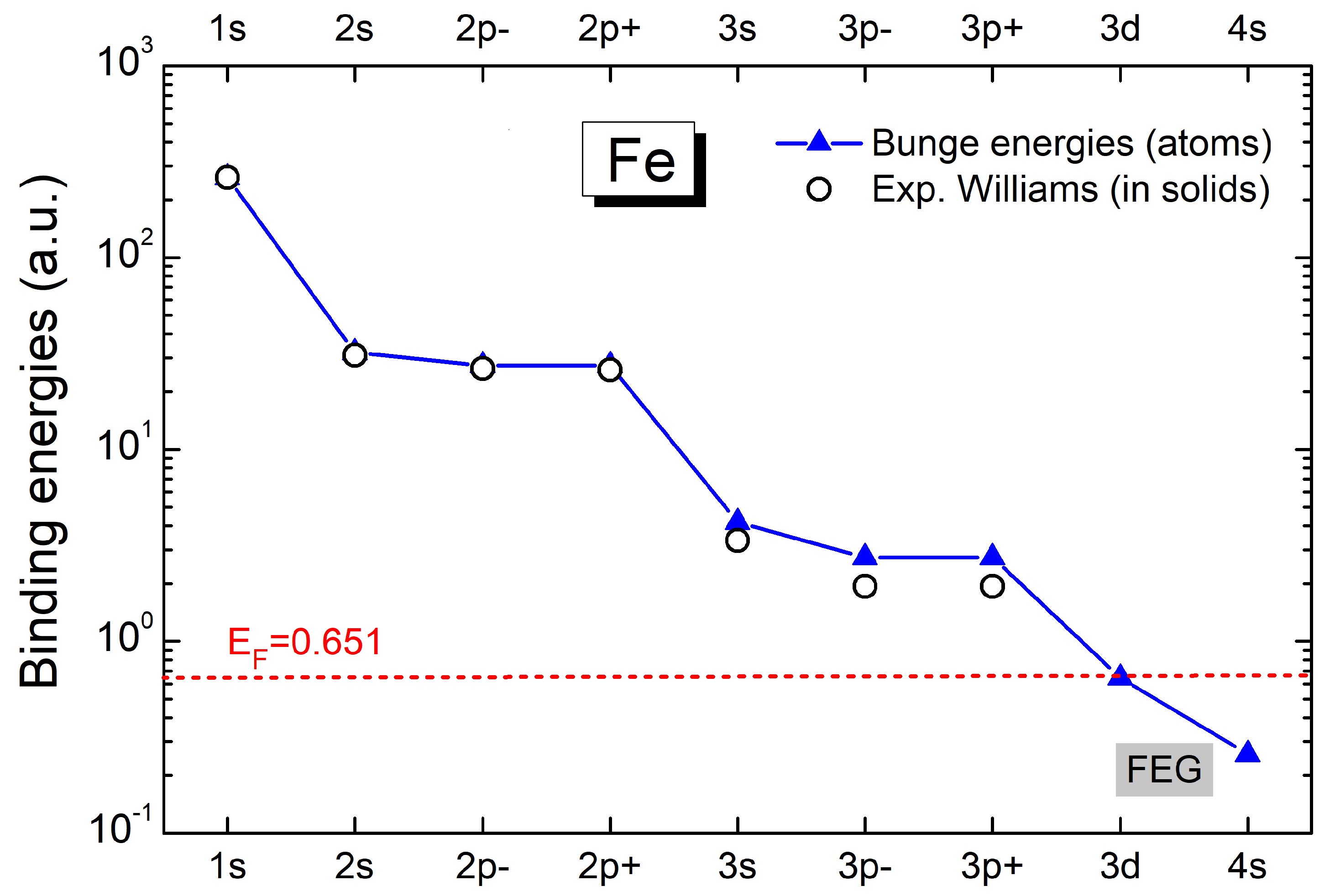
2. Theoretical Models
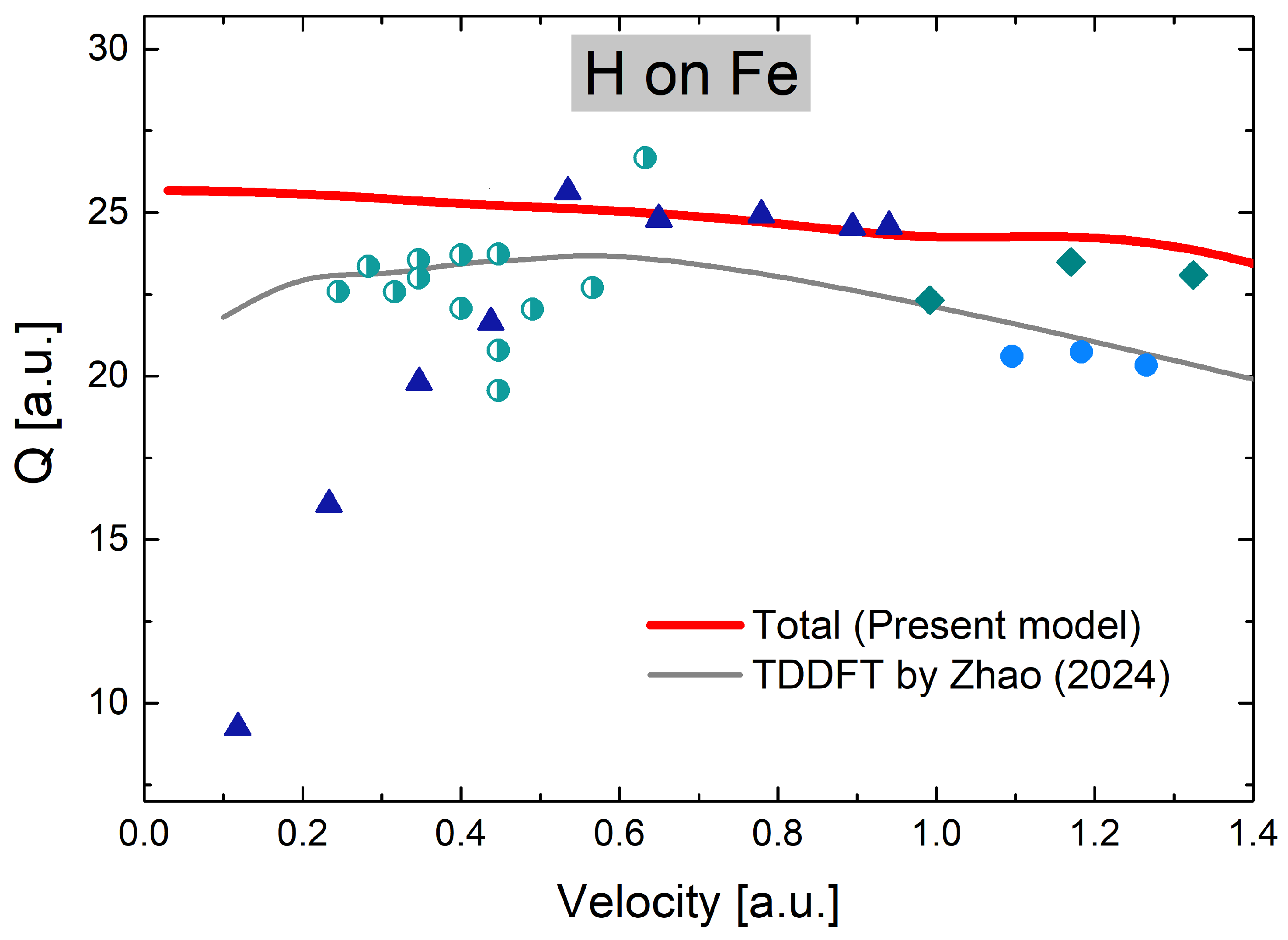
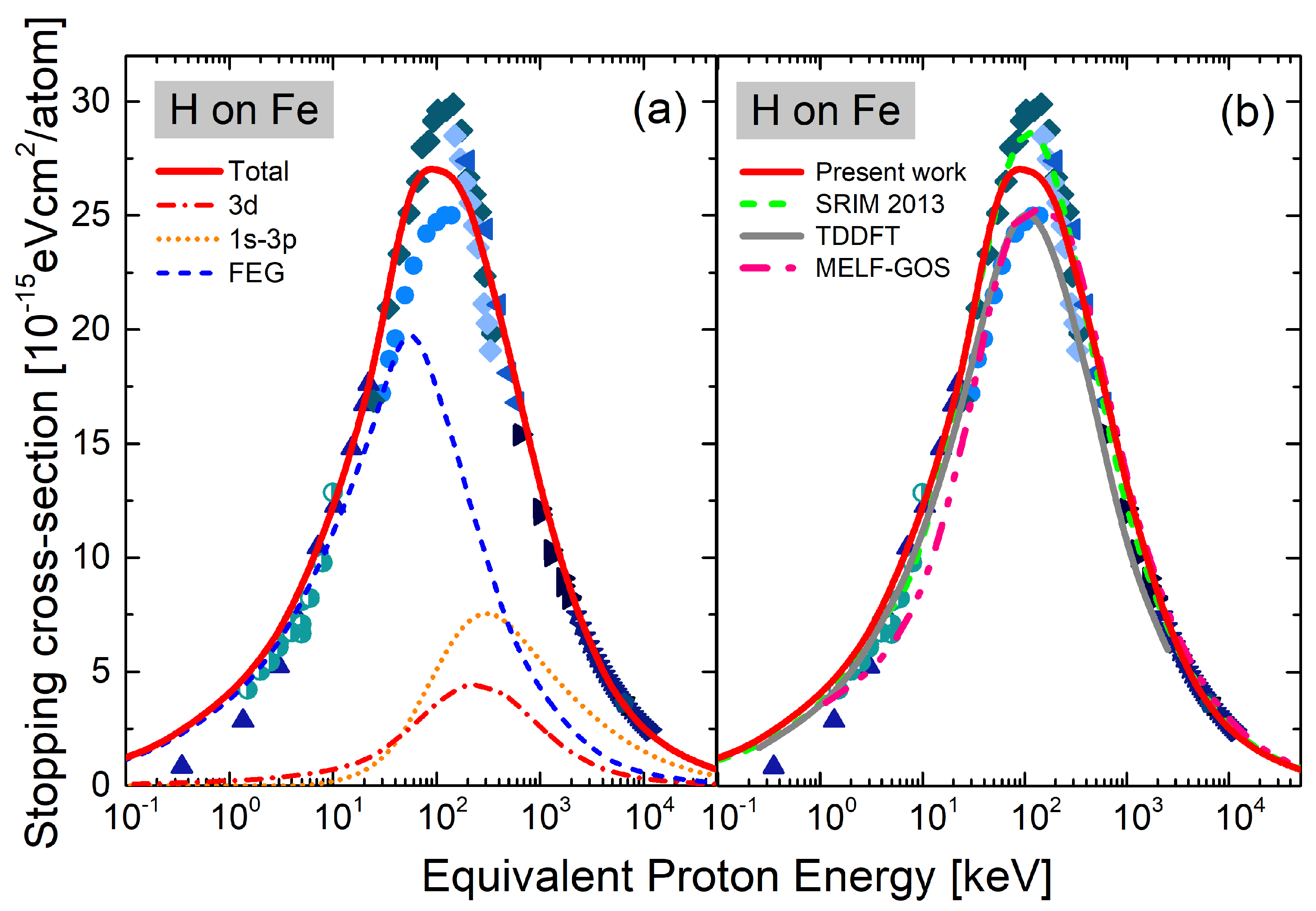
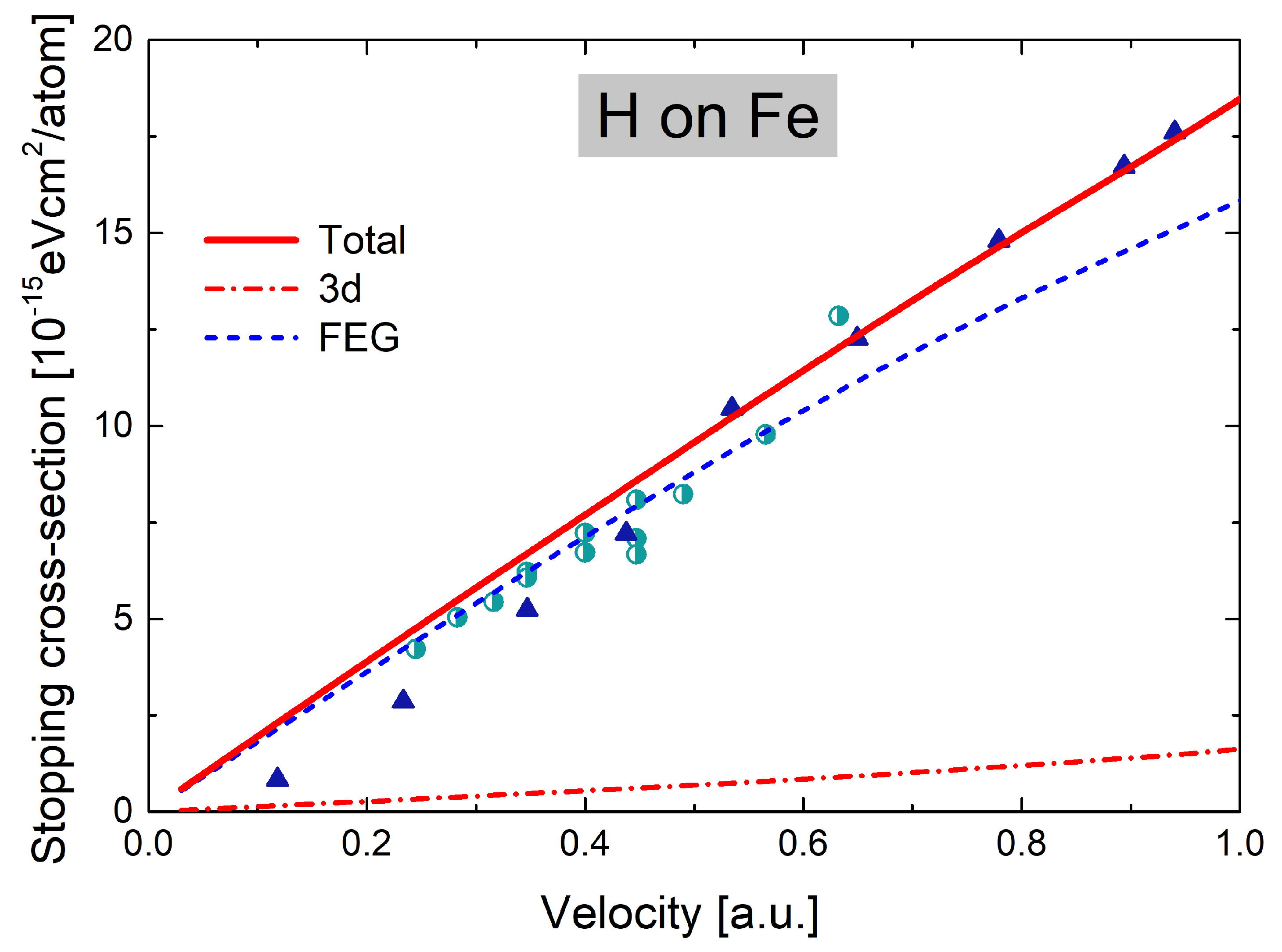
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montanari, C.; Dimitriou, P.; Marian, L.; Mendez, A.; Peralta, J.; Bivort-Haiek, F. The IAEA electronic stopping power database: Modernization, review, and analysis of the existing experimental data. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2024, 551, 165336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethe, H. Zur Theorie des Durchgangs schneller Korpuskularstrahlen durch Materie. Ann. Phys. 1930, 397, 325–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, N. The Penetration of Atomic Particles Through Matter; Munksgaard: Copenhagen, Danmark, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund, P.; Schinner, A. Progress in understanding heavy-ion stopping. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2016, 382, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, N.W.; Mermin, N.D. Solid State Physics; Holt, Rinehart and Winston: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, R.H. Interaction of Charged Particles with a Degenerate Fermi-Dirac Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1959, 114, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, T.L.; Ritchie, R.H. Energy losses by slow ions and atoms to electronic excitation in solids. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echenique, P.M.; Flores, F.; Ritchie, R.H. Dynamic Screening of Ions in Condensed Matter. In Solid State Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 43, pp. 229–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quashie, E.E.; Saha, B.C.; Correa, A.A. Electronic band structure effects in the stopping of protons in copper. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 155403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Guo, X.; Xue, J.M.; Zhang, F.S. Electronic stopping power of protons in platinum: Direct valence and inner-shell-electron excitations from first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 107, 052814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.D.; Mao, F.; Deng, H. Electronic stopping of iron for protons and helium ions from first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 109, 032807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, F.; Grande, P.L.; Koval, N.E.; Shorto, J.M.B.; Silva, T.F.; Arista, N.R. Deeper-band electron contributions to stopping power of silicon for low-energy ions. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 064310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Trujillo, R.; Sabin, J.; Deumens, E.; Öhrn, Y. Dynamical Processes in Stopping Cross Sections. In Theory of the Interaction of Swift Ions with Matter. Part 1; Advances in Quantum Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 45, pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiwietz, G.; Grande, P. Stopping of protons–Improved accuracy of the UCA model. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2012, 273, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schinner, A.; Sigmund, P. Expanded PASS stopping code. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2019, 460, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer-Ávila, M.E.; Quinto, M.A.; Monti, J.M.; Rivarola, R.D.; Champion, C. Proton transport modeling in a realistic biological environment by using TILDA-V. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril, I.; Garcia-Molina, R.; Denton, C.D.; Pérez-Pérez, F.J.; Arista, N.R. Dielectric description of wakes and stopping powers in solids. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 58, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, C.C.; Miraglia, J.E. The Dielectric Formalism for Inelastic Processes in High-Energy Ion–Matter Collisions. In Advances in Quantum Chemistry: Theory of Heavy Ion Collision Physics in Hadron Therapy; Belkic, D., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 2, Chapter 7; pp. 165–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vera, P.; Abril, I.; Garcia-Molina, R. Energy Spectra of Protons and Generated Secondary Electrons around the Bragg Peak in Materials of Interest in Proton Therapy. Radiat. Res. 2018, 190, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhard, J. On the properties of a gas of charged particles. K. Dan. Vidensk. Selsk. Mat.-Fys. Medd. 1954, 28, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Mermin, N.D. Lindhard Dielectric Function in the Relaxation-Time Approximation. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 1, 2362–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, P.; Krist, T. Electronic stopping cross sections for 30–300 keV protons in materials with 23 ≤ Z2 ≤ 30. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 1982, 194, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, P.; Krist, T. Stopping ratios for 30–330 keV ions with 1 ≤ Z1 ≤ 5. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 7343–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.; Mueller, R.M. Electronic Stopping Cross Sections for 1H and 4He Particles in Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Cu at Energies near 100 keV. Phys. Rev. 1969, 187, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglin, J.; Chu, W. Stopping power of 0.3–2.6 MeV 4He ions in Fe and Ni. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1978, 149, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.K.; Powers, D. Alpha-Particle Stopping Cross Section in Solids from 400 keV to 2 MeV. Phys. Rev. 1969, 187, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, E.D.; Lantschner, G.H.; Eckardt, J.C.; Arista, N.R. Velocity dependence of the energy loss of very slow proton and deuteron beams in Cu and Ag. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 80, 032904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, S.N.; Primetzhofer, D.; Prusa, S.; Brunmayr, M.; Kowarik, G.; Aumayr, F.; Bauer, P. Electronic interaction of very slow light ions in Au: Electronic stopping and electron emission. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 195122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, E.; Valdés, P.V.; Esaulov, V.A. Energy losses of slow ions traveling through crystalline solids and scattered on crystalline surfaces. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2016, 171, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebl, D.; Roth, D.; Bauer, P. Role of d electrons in electronic stopping of slow light ions. Phys. Rev. A-At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 87, 062903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.P.; Mendez, A.M.P.; Mitnik, D.M.; Montanari, C.C. The d-electron contribution to the stopping power of transition metals. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Electronic Stopping Power of Matter for Ions. 1928–2024. Available online: https://www-nds.iaea.org/stopping/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Shams-Latifi, J.; Pitthan, E.; Primetzhofer, D. Experimental electronic stopping cross-section of EUROFER97 for slow protons, deuterons and helium ions. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 224, 112073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E.; Teller, E. The Capture of Negative Mesotrons in Matter. Phys. Rev. 1947, 72, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, C.C.; Miraglia, J.E. Low- and intermediate-energy stopping power of protons and antiprotons in solid targets. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 012707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, I.; Bergara, A. A model for the velocity-dependent screening. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1996, 115, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.P.; Fiori, M.; Mendez, A.M.P.; Montanari, C.C. Stopping-power calculations and the Levine-Mermin dielectric function for inner shells. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 062814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, C.; Barrientos, J.; Bunge, A. Roothaan-Hartree-Fock Ground-State Atomic Wave Functions: Slater-Type Orbital Expansions and Expectation Values for Z = 2–54. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1993, 53, 113–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, M.R.; Levy, H., II. Simple Analytic Expression for General Two-Center Coulomb Integrals. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 50, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, W.S.M.; Glantschnig, K.; Ambrosch-Draxl, C. Optical Constants and Inelastic Electron-Scattering Data for 17 Elemental Metals. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2009, 38, 1013–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P. Electron Binding Energies of the Elements. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Chapter 10; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipov, E.P.; Gott, Y.V. Slowing down of 0.5–30 keV protons in some materials. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1969, 29, 615. [Google Scholar]
- de Vera, P.; Abril, I.; Garcia-Molina, R. Electronic cross section, stopping power and energy-loss straggling of metals for swift protons, alpha particles and electrons. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1249517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F. SRIM. 2013. Available online: http://www.srim.org/ (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Bader, M.; Pixley, R.E.; Mozer, F.S.; Whaling, W. Stopping Cross Section of Solids for Protons, 50–600 KeV. Phys. Rev. 1956, 103, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwari, R.; Shiomi, N.; Shirai, S.; Uemura, U. Stopping powers of Al, Ti, Fe, Cu, Mo, Ag, Sn, Ta and Au for 7.2 MeV protons. Phys. Lett. A 1974, 48, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwari, R.; Shiomi, N.; Sakamoto, N. Stopping powers of Be, Al, Ti, V, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mo, Rh, Ag, Sn, Ta, Pt and Au for 6.75 MeV protons. Phys. Lett. A 1979, 75, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.H.; Hanke, C.C.; Simonsen, H.; Sørensen, H.; Vajda, P. Stopping Power of the Elements Z = 20 Through Z = 30 for 5–12-MeV Protons and Deuterons. Phys. Rev. 1968, 175, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leminen, E.; Anttila, A. Energy Loss and Straggling of 0.6–2.0 MeV Protons in Fe, Co and Sb. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. Phys. Ser. A VI Phys. 1971, 370, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi-Tsuda, N.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishiwari, R. Stopping powers of Be, Al, Ti, V, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mo, Rh, Ag, Sn, Ta, Pt and Au for 13 MeV deuterons. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1994, 93, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peralta, J.P.; Mendez, A.M.P.; Mitnik, D.M.; Montanari, C.C. Stopping Power of Iron for Protons: Theoretical Calculations from Very Low to High Energies. Atoms 2025, 13, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13030022
Peralta JP, Mendez AMP, Mitnik DM, Montanari CC. Stopping Power of Iron for Protons: Theoretical Calculations from Very Low to High Energies. Atoms. 2025; 13(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13030022
Chicago/Turabian StylePeralta, Jesica P., Alejandra M. P. Mendez, Dario M. Mitnik, and Claudia C. Montanari. 2025. "Stopping Power of Iron for Protons: Theoretical Calculations from Very Low to High Energies" Atoms 13, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13030022
APA StylePeralta, J. P., Mendez, A. M. P., Mitnik, D. M., & Montanari, C. C. (2025). Stopping Power of Iron for Protons: Theoretical Calculations from Very Low to High Energies. Atoms, 13(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13030022