Abstract
Type II supernovae (SNe II), which show abundant hydrogen in their spectra, belong to a class of SNe with diverse observed properties. It is commonly accepted that SNe II are produced by core collapse and explosion of massive stars. However, the large photometric and spectroscopic diversity of SNe II and the mechanisms responsible for this diversity are not thoroughly understood. In this review, we first briefly introduce the optical characteristics and possible progenitors of each subtype of SNe II. We then highlight the role of the Chinese Space Station Telescope in future SN studies. With a deep limiting magnitude, the main survey project could detect SN IIP-like objects as distant as and obtain UV-optical follow-up for peculiar transients, especially those long-lived events. With a high resolution and a large field of view, the main survey camera is powerful in linking a nearby SN with its progenitor, while the integral field spectrograph is powerful in revealing the SN environment. All this information has the potential to help enrich our understanding of supernova physics.
1. Introduction
Supernovae are huge explosions that take place at the end of the evolution of stars. They exhibit great diversity and can be divided into different subclasses based on their observational characteristics. The first-order classification of supernovae is based on whether hydrogen lines are shown in their spectra. Those that do not contain hydrogen in their spectra are classified as type I supernovae (SNe I), while those that show clear hydrogen are divided into the class of Type II supernovae (SNe II) [1]. With more and more supernovae detected by modern techniques, the classification scheme was extended according to additional spectral or photometrical properties. SNe I were divided into SNe Ia, SNe Ib, and SNe Ic, while SNe II were divided into more subcategories, i.e., SNe IIP, SNe IIL, SNe IIb, SNe IIn, and SN 1987A-like objects [2,3]. The difference in observational properties reflects the difference in stellar state (e.g., type, mass, metallicity, rotation, whether in binary system, etc.) and circumstellar environment of the progenitor star [4,5,6,7,8].
It is commonly accepted that SNe Ia come from the thermonuclear explosions of white dwarfs [9], while SNe Ib, SNe Ic, and SNe II are produced by core collapse and explosion of massive stars (≥8–10M) [10,11,12]. However, the exact connection between a supernova and its progenitor is not understood thoroughly. Therefore, an important topic in the study of supernovae is to map the observed SN type to the progenitor type and to test the theory of star evolution in the meantime. Several indirect ways based on the analysis of the resultant supernovae are used to derive information on progenitor stars. Modeling of the nebular-phase spectra can be used to constrain the progenitor masses since spectra at this phase permit a direct view into the inner layers and contain information of nucleosynthesis yields which differ in different progenitors [13,14,15]. Furthermore, many efforts have been made in modeling the light curve, which can be used to estimate the explosion energy, ejecta mass, progenitor radius, and the mass of nickel produced by the explosion [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. However, the most reliable method is to observe the progenitor itself directly. This can be achieved by searching the SN progenitor in pre-SN images in archives of imaging surveys. Such a method is successful for a few of SNe, e.g., 1987A [27,28,29], SN IIb 1993J [30,31], and a dozen of SNe IIP [32], and so on. However, SNe with conclusive progenitors detected are still rare, and sometimes an SN site may not be covered due to the small Field of View (FoV) of recent space telescopes. The wield-field space telescope, e.g., the 2 m Chinese Space Station Telescope (CSST), which has a resolution of 0.15″ and a large FoV of 1.1 deg, is therefore expected to be powerful in identifying nearby progenitors.
2. Observational Diversity of SNe II
2.1. SN IIP
The most common type of SNe II is Type IIP supernovae, which could account for nearly 60% of the total SNe II [33]. The relative ratios of each subtype are shown in Figure 1. SNe IIP are characterized by a plateau (the luminosity declines very slowly) of ∼100 days after the maximum in their light curve [34]. As shown in Figure 2, the V-band light curve of the prototypical SN IIP, 1999em, remains almost constant for nearly 80 days, after which the light curve displays a much steeper declination of ∼2 mag within the following 40 days [35]. Such a plateau stage is the consequence of the hydrogen recombination wave receding inward into the expanding SN ejecta [22,23]. Once the recombination front reaches the base of the massive hydrogen envelope, the plateau ends and the light curve shows a significant flux drop entering the radioactive decay tail. At this phase, the light curve is powered by radioactive decay of 56Ni and its decay product 56Co [36].
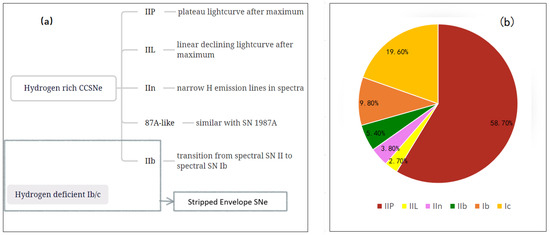
Figure 1.
Panel (a): Subtypes of SNe II and defining properties of each subtype. Panel (b): Relative frequency of SNe II subtypes [32].
The spectra of SN 1999em at different phases are shown in Figure 3. At early phases, the spectra of SNe IIP are characterized by a blackbody continuum, with P-Cgyni profile of Balmer series and He i 5876 supposed on it. With rapid-response transient surveys, spectroscopy can be obtained in just a few days or even hours after the explosion. Narrow emission lines of ionized species, which disappear quickly and are referred to as Flash-Ionized (FI) features [37], can be caught [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] (see the spectra of 2013fs in Figure 3). As the ejecta expands and the photosphere recedes (in mass), material in deeper layers is exposed. At photospheric phases, spectra are formed by a series of radiative-transfer processes, i.e., photon emissions, absorptions, and scatterings [46,47]. The spectra show the P-Cgyni profile of different species, such as Fe ii and Na I D. As the ejecta becomes totally transparent to optical photons, the spectra evolve to the nebular phase. Optical lines are mainly formed by recombination, collisional excitation, and fluorescence [48]. The characteristic line profile is emission lines that peak near the rest wavelength [47].
2.2. SN IIL
SNe IIL is a rare subclass and in general, they are brighter than SNe IIP. Different from SN IIP, the light curve of SN IIL declines linearly after maximum [49]. The absorptions of H in the spectra of SNe IIL are shallower [50,51,52] (see the light curve and spectra of SN 1979C in Figure 2 and Figure 3). Both theoretical and observational evidence suggests that the hydrogen envelope is a main factor to affect the observed properties of SNe IIP/L. The progenitor of an SN IIL is supposed to retain a lower mass of hydrogen envelope at the time of the explosion so that they cannot sustain a plateau in its light curve [22,53,54,55]. Additionally, the interaction between SN ejecta and circumstellar material (CSM) could produce SNe IIL-like properties as well, e.g., a fast-declining light curve and a weak or absent H absorption during the recombination phase [56]. However, there are no exact classification criteria for SNe IIL and SNe IIP, and whether they form two distinct populations is still debated [34,54,55,57,58,59,60,61].
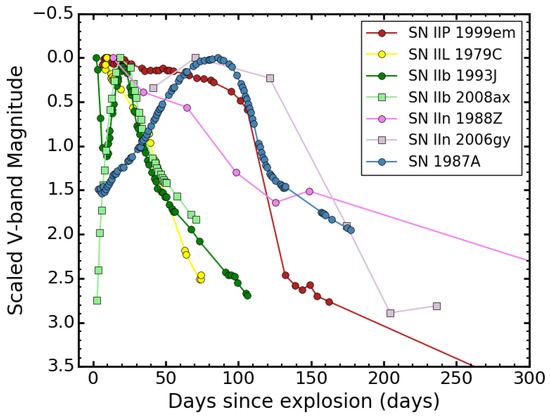
Figure 2.
V-band light curves of typical individuals of each SN II subtype, including SN IIP 1999em [35,62], SN IIL 1979C [63], SN IIb 1993J [64], SN IIb 2008ax [65], SN IIn 1988Z [66,67], SN IIn 2006gy [12], and SN 1987A [68]. Magnitudes are normalized to peak SN magnitudes for comparison.
2.3. SN IIb
The spectra of SN IIb show an evolution from that of SN II to that of SN Ib [69,70]. At first, the spectra of SNe IIb show clear hydrogen lines. However, hydrogen lines weaken at later phases and helium lines become dominant (see the spectra evolution of SN 1993J in Figure 3), resembling the spectra of SN Ib. Such spectral transition is associated with the progenitors which are partially stripped of their hydrogen enveloped. SN IIb, together with hydrogen deficient SN Ib [71] (the progenitor is supposed to lose all its hydrogen envelope) and SN Ic [72] (hydrogen deficient and helium deficient, the progenitor loses both H and He envelope), are called stripped envelope supernovae (SESNe) [73].
The light curves of part of SNe IIb, e.g., SN 1993J, show two peaks [64]. The first peak is supposed to be in the shock cooling phase, while the second peak is powered by 56Ni decay chain [74]. A low mass but extended envelope is required for the initial peak. Such a density structure is suggested to be produced in a binary system with the progenitor losing most of its hydrogen envelope through mass transfer to a companion star [75,76,77]. Another part of SNe IIb, e.g., SN 2008ax, shows only one peak in their optical light curves [65,78]. The lack of shock cooling phase points to a compact progenitor. In conclusion, as proposed by Chevalier and Soderberg, there may exist two subtypes of SNe IIb, i.e., cIIb and eIIb [79].
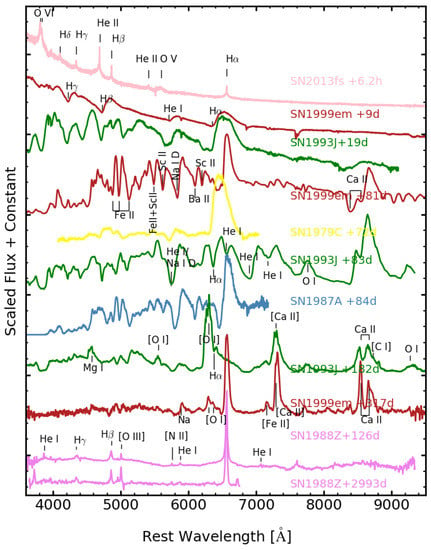
Figure 3.
Optical spectra of SN IIP 2013fs [41], SN IIP 1999em [62,80], SN IIL 1979C [81], SN IIb 1993J [82,83], SN IIn 1988Z [67,84], and SN 1987A [85], shifted vertically for clarity. The numbers on the right side mark the epochs since SNe explosion.
2.4. SN IIn
Massive progenitors of SNe II lose mass and then produce CSM by means of stellar winds, impulsive eruptions, or mass transfer between interacting binaries [86]. As SN explodes in CSM, hydrodynamic and radiative interactions between SN ejecta and CSM will lead to distinct observable properties, e.g., hydrogen emission lines [87,88]. Therefore, SNe II with narrow (or intermediate-width) emission lines of hydrogen in spectra (see the spectra of SN 1988Z) are classified as SNe IIn [89]. In fact, SN IIn as a group show large diversities, since parameters associated with CSM, e.g., density, geometric distribution, and CSM composition, need to be considered in addition to the explosion parameters of their progenitors [90].
2.5. SN 1987A-Like
SN 1987A, with many peculiar properties, was one of the best-studied SNe objects (see the review of [91] and references therein). Its light curve shows a long rise (∼90 days) before coming to the primary maximum [68]. The rapid initial decline of the bolometric light curve indicated a relatively compact progenitor, while the long rise to the second peak is mainly powered by slower diffusion of radioactive decay energy [92]. Several objects with similar long-rising light curves have since been identified and classified as 87A-like objects [93,94,95,96,97,98]. Most of the 87A-like events appear in slightly low-metallicity environments [99]. This type is intrinsically rare and consists of less than 3% of core-collapse supernovae (CCSNe) [33].
3. Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae
The identifications of the progenitors of SNe provide direct information on their explosion mechanisms, which is a key point in SN studies. Detections of progenitors at pre-SN images suggested that SNe IIP come from red supergiants (RSG) with initial mass of ∼8–17 [32,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110]. For instance, the effective temperature and luminosity of the progenitor of SN IIP 2017eaw are most consistent with the endpoint of 15M track (see Figure 4) [110]. For SNe IIL, observations of progenitors are rare and analysis results present significant uncertainties. A luminous yellow supergiant (YSG) with initial mass ∼18–24 M could be the progenitor of SN IIL 2009kr (see Figure 4) [111]. However, it is difficult to determine if the object is a single star, a binary system, or a compact cluster [112,113]. The progenitor of SN 2009hd could be an RSG or YSG with an initial mass smaller than 20M [114]. In conclusion, the progenitors of SNe IIL and their mass range are still in debate.
Stripped envelope SNe IIb, whose progenitor stars are supposed to be partially stripped of their hydrogen envelope, may arise from two different channels. For SN IIb 1993J, the detection of the signatures of the companion star 10 years after SN 1993J exploded supported the binary scenario of a pair of K-type supergiant primary star () plus B-type supergiant companion star () [31]. On the other hand, Crockett et al. found that both a single Wolf–Rayet (WR) star and an interacting binary could be the progenitor of SN 2008ax [115]. However, Folatelli et al. suggested that a single WR star was not compatible with the new, revisited photometry [116].
SNe Ib/c, which are cousins of SNe IIb, may be produced by multiple channels as well. Theoretically, a star above 25–30M is supposed to evolve to a WR star, lose its hydrogen (and helium) envelope by stellar winds, and then explode as SN Ib/c [117]. Such a scenario is supported by the evidence that SNe Ib/c trace the star formation of their host galaxies more accurately than SNe II [118]. However, smaller ejecta masses for stripped envelope SNe are inconsistent with those expected from very massive stars [119]. Alternatively, it has been suggested that stripped-envelope SNe may come from moderately massive progenitors (8∼20M) in binaries. In such a channel, the progenitor could shed its hydrogen (and helium) envelope through interaction with a binary companion [4,120]. It is suggested that a large ratio of massive stars (more than 70%) could be in binaries [121]. The explosion rate of SN Ib/c, which is higher than the single WR stars channel expected [122], can be explained with binary population models [123] as well. Thus, binary systems could constitute a significant fraction of SNe Ib/c progenitors. Successful detections of progenitor for SN Ib/c are rare. For SNe Ib, the late time observations (+740 d) of iPTF13bvn favor a helium giant progenitor in binary [124] rather than a WR star [125]. SN 2019yvr was the second SN Ib with progenitor detected, and its progenitor could be in a binary system as well [126,127]. For SN Ic, the progenitor candidate of SN 2017ein found in archival Hubble Space Telescope (HST) images could be the first time that a progenitor candidate of SN Ic has ever been identified. The very blue and hot candidate would have to be very massive (see Figure 4) [128,129].
Luminous Blue Variable stars (LBV) are the possible progenitor candidates for the majority of SNe IIn since giant eruptions of LBV can produce CSM which are dense enough [90]. Gal-Yam et al. identified a luminous point source, which is likely an LBV, as the possible progenitor of SN 2005gl [130]. A series of LBV-like giant eruptions was also observed for the progenitor of SN 2009ip [131,132,133]. However, we must notice that SNe IIn are defined by external features associated with circumstellar interaction and thus, they cannot be linked to a singular progenitor type.
The Progenitor of SN 1987A, known as Sk-69202, was detected in archival images. It was a compact blue supergiant (BSG) with a ZAMS mass of 14–20M [27,28,29,134]. It is surprising that Sk-69202 was not a RSG when it exploded. Additionally, Nitrogen-enhanced circumstellar material with a triple-ring structure [135] was supposed to be ejected from the progenitor of SN 1987A about 20,000 years before the explosion [136]. Many theoretical models, such as mass transfer in binaries, binary merger, a rapidly rotating single-star, extensive mass loss, and so on, are proposed to explain why the progenitor of SN 1987A ends as a compact BSG [91,134,137,138,139,140,141]. However, progenitors of 87A-like SNe are not settled yet and there is much to learn about this type.
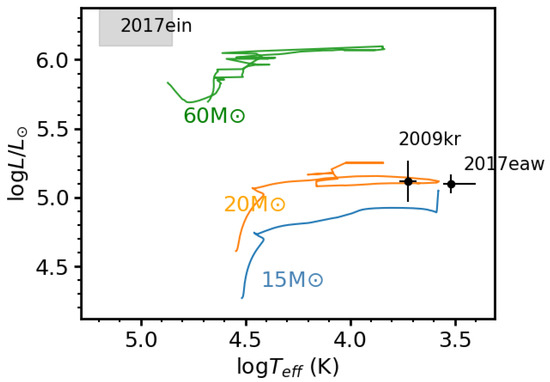
Figure 4.
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram showing the locus of the progenitor of SN IIP 2017eaw [110], SN IIL 2009kr [111], and SN Ic 2017ein (gray shadow) [128,129]. Blue, orange, and green solid lines show the single-star evolutionary tracks for 15M (with rotation at ), 20M (), and 60M () at solar metallicity from the Geneva model, respectively [142,143].
Linking the types and mass ranges of progenitor stars with the characteristic of SN is one of the major goals in studies of SNe explosions. Since the late 1990s, efforts have been made in the systematic search for progenitor stars of all nearby SNe. However, we still do not have a complete picture of the progenitor channels of core-collapse supernovae. RSG with an initial mass between 8 and 17M was confirmed to be the progenitor of SNe IIP. However, the reason for the “red supergiant problem”, related to lacking detected RSG progenitors with initial masses between 17 and 25M, is still unclear. High-mass RSG () with sufficiently low metallicity could explode as SN IIP, however such progenitors in low-luminosity, low-metallicity galaxies are not easy to detect [144]. Inadequate bolometric correction [145], additional extinction resulting from the dust [146], limited wavelength coverage [110], and so on, would all underestimate the luminosity and thus the initial mass of progenitor stars. On the other hand, Smartt proposed that stars in the mass range between 17 and 25M might collapse to form black holes with failed SNe, as theoretically expected [147]. Such a scenario was supported by Adams et al. since they identified a failed supernovae candidate, N6946-BH1, a ∼25M red supergiant which experienced a weak optical outburst [148] and has since disappeared in the optical [149]. Its bolometric luminosity is fading as ∼, consistent with the models of fallback accretion onto a black hole as well [148].
For other core-collapse supernovae, e.g., SNe IIL, IIb, and IIn, there are only a few of progenitor detections, which are insufficient to draw conclusions for the whole class. The progenitors of CCSNe are suggested to experience larger amount of mass loss with the sequence of SNe IIP–IIL–IIb–Ib/c, since the hydrogen envelope is decreasing with this sequence. Mass loss, rotation, metallicity, and binary interaction are all factors that will influence the evolution of massive stars and thus the observed properties of SNe [11,120]. In conclusion, the mapping of massive stars (especially those above 17) with their death product, as well as the role of rotation, metallicity, mass loss, and binary interaction still need to be determined, while there is only a very limited number of clear progenitor detection.
4. Roles of CSST in SNe II Studies
4.1. Chinese Space Station Telescope
The 2 m Chinese Space Station Telescope (CSST), which will be launched at the end of 2023, is expected to be a powerful tool in revealing the diversity of SNe II. The main survey project, which is capable of performing both photometric imaging and spectroscopic slitless surveys, will cover a survey area of 17,500 deg in 10 years and obtain high-quality photometric and spectral data for hundreds of millions of targets. Its photometric survey, with an average limiting magnitude of 25.5 mag, is designed to cover a wavelength range of 255–1000 nm in NUV, u, g, r, i, z, and y bands, while the spectroscopic survey will cover GU, GV, and GI bands down to a limiting magnitude of about 21 mag [150,151]. In addition to the multicolor imaging and slitless spectroscopy survey camera, a multichannel imager (MCI), an integral field spectrograph (IFS), a cool planet imaging coronagraph, and a terahertz receiver are equipped in CSST as well. With FoV of and limiting magnitude of mag, MCI is designed to provide flux calibration for the main survey, as well as UV-optical ultradeep field observations (observations in three bands, 250–400 nm, 400–700 nm, and 700–1100 nm, could be performed simultaneously). IFS is designed to obtain two-dimensional spectra that contain both spatial and spectral information. Designed parameters of the main survey camera, MCI, and IFS are listed in Table A1.
4.2. CSST for Mapping SNe II with Progenitors
With an average limit magnitude of 25.5 mag, the photometric survey could probe the brightest RSG (, mag [152]) within ∼30 Mpc. With a resolution of 0.15″, extra information, such as color and spectral energy distribution (SED), is needed to distinguish progenitor stars and clusters in some cases. Such information could be obtained by CSST as well. If an SN is located with a coeval cluster, SED and multiband photometry could be used for studying the stellar population, thus, the turn-off mass, which provides clues of the initial mass of the progenitor, could be estimated [102]. Furthermore, deep and high-resolution images taken after SNe fading away are also critical to distinguish between different progenitor scenarios.
Consider the local rate of CCSNe [153] and the average luminosity density of galaxies [154], CCSNe will appear within 30 Mpc. Such a rate is consistent with the volume rate calculated from Lick Observatory Supernova Search (LOSS) [155] and the number of CCSNe (i.e., 92) found within 28 Mpc in a 10.5-year period. In these 92 CCSNe, only 26% of them have a pre-SN image in the HST archive, partly because the SN position is missed due to the small FoV of the HST camera [33]. With a large FoV of 1.1 deg, which is ∼300 times that of Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS)/Wide Field Channel (WFC) of HST, the coverage of host galaxies, and then, the detection rate of SN progenitors, will be improved.
4.3. CSST for Revealing the Environment of SNe II
Due to the rarity of sufficient deep and high-resolution pre-images of nearby SN explosions, the environmental properties in the vicinity of the SN site, e.g., metallicity, star formation, and radial position, could provide additional statistical constraints for progenitor systems of different SN types. Both photometric, e.g., H+[N II]+R-band images, and spectroscopic observations have been used for environment analysis [118,156,157]. Considering the ambiguities of SN classification, Anderson believes that using specific SN features to investigate environment trends in future works will significantly increase insight on SN progenitors [158]. They also strengthen the importance of wide-field integral field units (IFU) observations, which enables simultaneous spatial and spectral information for SN site. The IFS equipped in CSST, with a spatial resolution of 0.2″ and FoV of 6″ × 6″, could provide a detailed environment structure within a radius of ∼2 kpc for supernovae within 40 Mpc. One of the main scientific goals of the CCST is to understand galaxy formation and evolution by scrutinizing the star formation and stellar population of nearby galaxies. Once this information is provided, it can be used to estimate SN environment properties.
4.4. CSST for Observing Peculiar Transients
Recent surveys have revealed new classes of peculiar transients, e.g., the bright, long-lived multipeak iPTF14hls and Fast Blue Optical Transients (FBOT). A series of models have been proposed for iPTF14hls [159,160,161,162,163] and FBOT 2018cow [164,165,166,167,168], however, their true nature is still under debate. These peculiar transients, which pose significant challenges to conventional supernova explosion physics, are critical for understanding the stellar evolution theory. Considering the FoV of all seven filters and the exposure time of 150 s, the multiband main survey camera will take about 90 days to cover the whole 17,500 deg. Such a survey strategy is powerful in observing the long-lived supernova, as well as pre-SN activities. In Figure 5, we simulate the observation results (each mock sampling randomly selects a certain filter) taken by the multiband camera for iPTF14hls-like events and 2018cow-like events. The bright iPTF14hls-like events at z = 0.05 could be observed for years. However, a survey strategy with a high cadence (e.g., covering 500 square degrees in one year) should be conducted for those fast-evolving events.
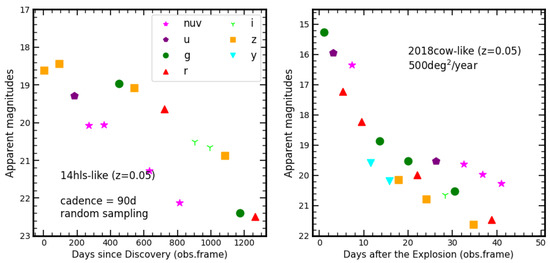
Figure 5.
Simulated light curves for iPTF14hls and 2018cow with a cadence of 90 days and 3 days, separately. Different colors and shapes represent different bands. In our simulation, the target randomly falls on a certain filter in each observation.
The collapse of iron core may not be the only mechanism through which a massive star can die and create a supernova. It is suggested that extremely massive stars could explode as pair-instability SNe (PISNe). The oxygen cores of these extremely massive stars may reach a high-temperature but low-density condition, in which electron–positron pairs are copiously produced. The radiation pressure is reduced and the star contracts, leading to a runaway thermonuclear explosion to completely disrupt the star [169,170]. Additionally, massive stars may undergo pulsational pair instability and eject massive shells [171]. Most of these PISNe are supposed to occur in the early universe, thus, they could be the target of the ultradeep field observations of MCI. At the low-mass end (8–10M) of SNe II progenitor, electron capture by 20Ne and 24Mg is supposed to trigger the collapse and produce electron-capture supernovae (ECSNe) [172,173,174]. Several transients are ECSNe candidates [175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182] but no unequivocal observations have been obtained. With the survey project of CSST and ground-based telescopes, new peculiar transients may be discovered and monitored, and thus, progress will be made in stellar evolution theory.
A supernova first shines in X-ray and UV at shock breakout. After the breakout, the hot ejecta expands and cools, and the SN is radiated mainly in UV and optical [183]. Radiation during the shock breakout and shock cooling phase contains information about the progenitor star, e.g., density structure. Moreover, ultraviolet flux accounts for a large part of the total bolometric luminosity for SN II [184]. All massive stars lose their mass with different rates and mechanisms, leading to different density structures of CSM. When CSI happened, both the shocked region and the unshocked region could radiate in the UV and optical [88]. Such emission could be used to derive the mass loss history of the progenitor star, which, in turn, could help to determine the progenitor type. Thus, UV observations are paramount for both detecting objects with shock breakout or CSI, and estimating the bolometric luminosity especially at early phases. However, instruments which could performed UV obervations, e.g., and HST, are scarce. CSST, equipped with a multiband survey camera and MCI, could be one of the few instruments that are able to provide near-UV observations in the future.
4.5. CSST for SNe II Cosmology
The intrinsic high luminosity and the relation between peak brightness and the shape of the light curve (e.g., the Phillips relation [185]) make SNe Ia the best “standardizable candle” for cosmological distance measurement. The magnitude/distance-redshift relation of SNe Ia can be used to constrain the cosmological parameters, e.g., the Hubble constant (H0), the mass density, the cosmological constant, and the deceleration parameter. Based on SN Ia cosmology, both the High-z Supernova Search Team and the Supernova Cosmology Project favored the universe model with a positive cosmological constant and a current accelerated expansion [186,187,188]. Using 42 Cepheid-calibrated SNe Ia, the uncertainty in the local determination of H0 has been decreased to 1.4% [189]. However, to date, there is no explanation found for the “H0 tension”, which refers to the discrepancy between the value derived from Cepheid-calibrated SNe Ia and that inferred via the cosmic microwave background [189]. While H0 can be measured locally, high-redshift objects are critical for distinguishing different universe models. However, only a small number of SN Ia are detected at z > 1.4 due to a long time delay between the formation of the progenitor star and the explosion of the supernova [190]. Other independent distance measurements are needed as much as possible. Although SN II is less luminous than SN Ia, its intrinsic explosion rate is higher than SN Ia, especially at high redshift [191]. Unlike the relatively homogeneous appearance of SNe Ia, SNe II exhibit a large diversity, making their standardization more difficult than that of the former. However, several methods have been proposed using theoretical or empirical relation of SNe II to measure distance, mainly including the “Expanding Photosphere Method” (EPM) [192], the “Standard Candle Method” (SCM) [193], and the “Photometric Color Method” (PCM) [194]. The dispersions in the Hubble diagram obtained for PCM and SCM are 0.44 and 0.29 mag, respectively [194], still larger than the 0.15 mag precision yielded by SNe Ia [195]. New knowledge and insight about Type II supernovae and their progenitors from CSST observation are essential to improve their accuracy as distance indicators.
We assess the detectability of SNe II by mock observations of the multiband imaging survey of CSST. The volume rate of SNe II is calculated following the method in [191] and references therein. Considering the heterogeneity of SNe II, a mean spectra energy distribution of SNe IIP [196] ( scaled to −16.7 mag) is assumed for simplification. The observer-frame light curve is then generated using [197]. Considering the FoV and an exposure time of 150 s, a regular cadence of 90 days is assumed for mock observations. The result is shown in the left panel of Figure 6. In our simulations, the photometric survey could detect SN IIP at z∼1.2. However, a higher cadence (e.g., 10 days, see the right panel of Figure 6) must be conducted to obtain a relatively intact light curve that could be utilized in PCM.
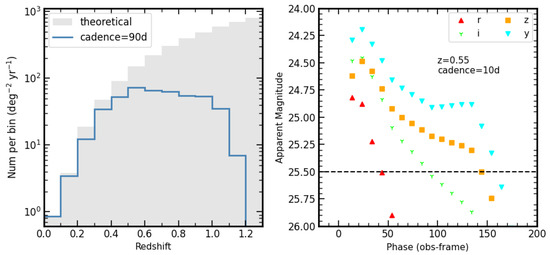
Figure 6.
Left: Redshift distribution of SNe II simulated for multiband imaging survey. Right: Simulated light curve for average SNe IIP with a regular cadence of 10 days at .
5. Conclusions
SNe II, produced by core collapse and explosion of massive stars, are the most common type of explosion in the universe. In this review, we briefly introduce the classification scheme, the observational diversities and possible progenitor stars of SNe II, and the role that CSST can play in this field.
Although SNe have been studied extensively for decades and remarkable achievements have been accomplished, a host of scientific questions still exist. The basic questions are which kinds of progenitor stars explode to which kinds of SNe and the physical mechanisms lead to the explosions. The main survey camera of CSST, with high resolution and large FoV, could obtain deep, high-resolution pre-SN and post-SN images, thus, it is expected to be powerful in identifying progenitors and distinguishing between different progenitor scenarios. Moreover, spatial and spectral information of the SN environment obtained by the IFS module could provide additional constraints for progenitor systems. Supernovae are involved in many relevant objectives of the research, e.g., mass loss and its influence on the evolution of massive stars, cosmology, and so on. Well-observed individuals, especially those with peculiar properties, are critical for stellar physics, while those at a cosmological distance are possible to serve as distance indicators. With CSST and rapid-response surveys by ground-based telescope, a large number of transients with intense multiwavelength follow-up could be obtained and thus help to enrich our understanding in these fields.
Author Contributions
H.L. is the first author who is responsible for this paper; J.Z. supervised/ supported H.L. for this paper and simulated light curves of peculiar transients. X.Z. gave useful comments for this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China with No. 2021YFA1600404, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 12173082), and science research grants from the China Manned Space Project with No. CMS-CSST-2021-A12, the Yunnan Province Foundation (202201AT070069), the Top-notch Young Talents Program of Yunnan Province, and the Light of West China Program provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This work is supported by International Centre of Supernovae, Yunnan Key Laboratory (No. 202302AN360001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some data were obtained from the Open Supernova Catalog at https://github.com/astrocatalogs, accessed on 23 October 2022, and the Weizmann Interactive Supernova Data Repository (WISeREP) at https://wiserep.weizmann.ac.il/, accessed on 23 October 2022. Some data used in this work are available from the published literature.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SN/SNe | supernova/supernovae |
| CCSNe | Core-Collapse Supernovae |
| SESNe | Stripped Envelope Supernovae |
| SLSNe | Superluminous Supernovae |
| PISNe | Pair-instability Supernovae |
| ECSNe | Electron-capture Supenovae |
| CSM | Circumstellar Material |
| CSI | Circumstellar Interaction |
| RSG | Red Supergiant |
| BSG | Blue Supergiant |
| YSG | Yellow Supergiant |
| WR | Wolf-Rayet stars |
| LBV | Luminous Blue Varible |
| FBOT | Fast Blue Optical Transients |
| FoV | Field of View |
| SED | spectral energy distribution |
| FI | Flash-Ionized |
| CSST | Chinese Space Station Telescope |
| MCI | multichannel imager |
| IFS | integral field spectrograph |
| IFU | integral field units |
| LOSS | Lick Observatory Supernova Search |
| HST | Hubble Space Telescope |
| ACS | Advanced Camera for Surveys |
| WFC | Wide Field Channel |
| EPM | Expanding Photosphere Method |
| PCM | Photometric Color Method |
| SCM | Standard Candle Method |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Parameters of multicolor imaging and slitless spectroscopy survey, MCI and IFS.
Table A1.
Parameters of multicolor imaging and slitless spectroscopy survey, MCI and IFS.
| Multicolor Imaging and Slitless Spectroscopy Survey | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV | 1.1 deg | |||
| Survey area | ≥17,500 | |||
| Photometric survey | Spectroscopic survey | |||
| Bands | NUV (255 nm–317 nm), u (322 nm–396 nm), g (403 nm–545 nm), r (554 nm–684 nm), i (695 nm–833 nm), z (846 nm–1000 nm) and y (937 nm–1000 nm) | Bands | GU (255 um–420 nm), GV (400 nm–650 nm), GI (620 nm–1000 nm) | |
| Spatial resolution | ∼0.15″ | Spectral resolution | R ≥ 200 | |
| Limit magnitude | 25.5 on average (S/N > 5, AB mag) | Limit magnitude | GU, GI 20; GV 21 (S/N > 5) | |
| MCI | ||||
| FOV | ||||
| Survey area | ≥300 arcmin | |||
| Bands | 250 nm–400 nm, 400 nm–700 nm, 700 nm–1100 nm | |||
| Spatial resolution | 0.18″ | |||
| Limit magnitude | 29–30 mag (SN>5) | |||
| IFS | ||||
| FOV | ≥6″ × 6″ | |||
| Wavelength coverage | 0.35–1.0 um | |||
| Spatial resolution | ≤0.2″ | |||
| Spectral resolution | R ≥ 1000 | |||
| Limit magnitude | 17 mag/arcsec (B band, 200 s × 20, SN = 10) | |||
References
- Minkowski, R. Spectra of Supernovae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1941, 53, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V. Optical Spectra of Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 35, 309–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turatto, M. Classification of Supernovae. In Supernovae and Gamma-ray Bursters; Weiler, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 598, pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlowski, P.; Joss, P.C.; Hsu, J.J.L. Presupernova Evolution in Massive Interacting Binaries. Astrophys. J. 1992, 391, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, A.; Langer, N. Presupernova Evolution of Rotating Massive Stars. II. Evolution of the Surface Properties. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, 1016–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M. Supernova Types and Rates. In Proceedings of the The Influence of Binaries on Stellar Population Studies; Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Vanbeveren, D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 264, p. 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, J.J.; Tout, C.A. The progenitors of core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 353, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, R.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A. Stellar evolution with rotation. XII. Pre-supernova models. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 425, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.; Iben, I., Jr. Binaries and Supernovae of Type I. Astrophys. J. 1973, 186, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Weaver, T.A. The physics of supernova explosions. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 24, 205–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, A.; Fryer, C.L.; Woosley, S.E.; Langer, N.; Hartmann, D.H. How Massive Single Stars End Their Life. Astrophys. J. 2003, 591, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletto, I.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Mazzali, P.; Pastorello, A.; Della Valle, M.; Bufano, F.; Harutyunyan, A.; et al. SN 2006gy: Was it Really Extraordinary? Astrophys. J. 2009, 691, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, K.; Jerkstrand, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Fransson, C.; Pastorello, A.; Benetti, S.; Valenti, S.; Bufano, F.; Leloudas, G. Constraining the physical properties of Type II-Plateau supernovae using nebular phase spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 3451–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkstrand, A.; Fransson, C.; Maguire, K.; Smartt, S.; Ergon, M.; Spyromilio, J. The progenitor mass of the Type IIP supernova SN 2004et from late-time spectral modeling. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, A28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkstrand, A.; Ertl, T.; Janka, H.T.; Müller, E.; Sukhbold, T.; Woosley, S.E. Emission line models for the lowest mass core-collapse supernovae—I. Case study of a 9 M⊙ one-dimensional neutrino-driven explosion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberg, E.K.; Imshennik, V.S.; Nadyozhin, D.K. On the Theory of the Light Curves of Supernovae. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1971, 10, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, S.W.; Arnett, W.D. Radiation Dynamics, Envelope Ejection, and Supernova Light Curves. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1977, 33, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D. Analytic solutions for light curves of supernovae of Type II. Astrophys. J. 1980, 237, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinova, I.Y.; Nadezhin, D.K. Determination of Integrated Parameters for Type-II Supernovae. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1985, 11, 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- Chugai, N.N. Duration of the Plateau Stage in Type-II Supernovae. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1991, 17, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Blinnikov, S.I.; Popov, D.V. Analytic models for low-mass supernovae of type II. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 274, 775. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, D.V. An Analytical Model for the Plateau Stage of Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1993, 414, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Woosley, S.E. Type II Supernovae: Model Light Curves and Standard Candle Relationships. Astrophys. J. 2009, 703, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, M.L.; Zampieri, L. Radiation-hydrodynamical Modeling of Core-collapse Supernovae: Light Curves and the Evolution of Photospheric Velocity and Temperature. Astrophys. J. 2011, 741, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Hillier, D.J.; Li, C.; Woosley, S. On the nature of supernovae Ib and Ic. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 2139–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, V.; Piro, A.L.; Renzo, M.; Ott, C.D.; Clausen, D.; Couch, S.M.; Ellis, J.; Roberts, L.F. Light Curves of Core-collapse Supernovae with Substantial Mass Loss Using the New Open-source SuperNova Explosion Code (SNEC). Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.L.; Malin, D.F. Possible binary star progenitor for SN1987A. Nature 1987, 327, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmozzi, R.; Cassatella, A.; Clavel, J.; Fransson, C.; Gonzalez, R.; Gry, C.; Panagia, N.; Talavera, A.; Wamsteker, W. The progenitor of SN1987A. Nature 1987, 328, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walborn, N.R.; Prevot, M.L.; Prevot, L.; Wamsteker, W.; Gonzalez, R.; Gilmozzi, R.; Fitzpatrick, E.L. The spectrograms of Sanduleak - 69º202, precursor to supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 219, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Aldering, G.; Humphreys, R.M.; Richmond, M. SN 1993J: The Optical Properties of its Progenitor. Astron. J. 1994, 107, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Kudritzki, R.P.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Gilmore, G.F. The massive binary companion star to the progenitor of supernova 1993J. Nature 2004, 427, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smartt, S.J. Progenitors of Core-Collapse Supernovae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 63–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, S.J.; Eldridge, J.J.; Crockett, R.M.; Maund, J.R. The death of massive stars—I. Observational constraints on the progenitors of Type II-P supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 1409–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Gal-Yam, A.; Cenko, S.B.; Fox, D.B.; Leonard, D.C.; Moon, D.S.; Sand, D.J.; Soderberg, A.M.; Kiewe, M.; Yaron, O.; et al. Caltech Core-Collapse Project (CCCP) Observations of Type II Supernovae: Evidence for Three Distinct Photometric Subtypes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 756, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmhamdi, A.; Danziger, I.J.; Chugai, N.; Pastorello, A.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Altavilla, G.; Benetti, S.; Patat, F.; Salvo, M. Photometry and spectroscopy of the Type IIP SN 1999em from outburst to dust formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 338, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D. Supernovae and Nucleosynthesis: An Investigation of the History of Matter from the Big Bang to the Present; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Khazov, D.; Yaron, O.; Gal-Yam, A.; Manulis, I.; Rubin, A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Arcavi, I.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Ofek, E.O.; Cao, Y.; et al. Flash Spectroscopy: Emission Lines from the Ionized Circumstellar Material around <10-day-old Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Yam, A.; Arcavi, I.; Ofek, E.O.; Ben-Ami, S.; Cenko, S.B.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Cao, Y.; Yaron, O.; Tal, D.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A Wolf-Rayet-like progenitor of SN 2013cu from spectral observations of a stellar wind. Nature 2014, 509, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Cenko, S.B.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Silverman, J.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Gal-Yam, A.; Clubb, K.I.; Graham, M.L.; Leonard, D.C.; et al. PTF11iqb: Cool supergiant mass-loss that bridges the gap between Type IIn and normal supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 1876–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivvers, I.; Groh, J.H.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Fox, O.D.; Leonard, D.C.; Filippenko, A.V. Early Emission from the Type IIn Supernova 1998S at High Resolution. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, O.; Perley, D.A.; Gal-Yam, A.; Groh, J.H.; Horesh, A.; Ofek, E.O.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Sollerman, J.; Fransson, C.; Rubin, A.; et al. Confined dense circumstellar material surrounding a regular type II supernova. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, T.; Kawabata, K.S.; Maeda, K.; Tanaka, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Moriya, T.J.; Tominaga, N.; Morokuma, T.; Takaki, K.; Kawabata, M.; et al. The Low-luminosity Type IIP Supernova 2016bkv with Early-phase Circumstellar Interaction. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, G.; Valenti, S.; McCully, C.; Howell, D.A.; Arcavi, I.; Jerkstrand, A.; Guevel, D.; Tartaglia, L.; Rui, L.; Mo, J.; et al. Short-lived Circumstellar Interaction in the Low-luminosity Type IIP SN 2016bkv. Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; József, V.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, T.; Filippenko, A.V.; Brink, T.G.; Zheng, W.; Wyrzykowski, Ł.; Mikołajczyk, P.; et al. SN 2018zd: An unusual stellar explosion as part of the diverse Type II Supernova landscape. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terreran, G.; Jacobson-Galán, W.V.; Groh, J.H.; Margutti, R.; Coppejans, D.L.; Dimitriadis, G.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Matthews, D.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Angus, C.R.; et al. The Early Phases of Supernova 2020pni: Shock Ionization of the Nitrogen-enriched Circumstellar Material. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, D.J.; Branch, D. Analysis of Supernova Spectra. In Proceedings of the Supernovae, Jerusalem Winter School for Theoretical Physics; Wheeler, J.C., Piran, T., Weinberg, S., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 1990; Volume 6, p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, D.; Baron, E.; Jeffery, D.J. Optical Spectra of Supernovae. arXiv 2001, arXiv:astro-ph/astro-ph/0111573. [Google Scholar]
- Kozma, C.; Fransson, C. Gamma-Ray Deposition and Nonthermal Excitation in Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1992, 390, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbon, R.; Ciatti, F.; Rosino, L. Photometric properties of type II supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 72, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Patat, F.; Barbon, R.; Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M. Light curves of type II supernovae. II. The analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 282, 731–741. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, E.M. On the Early Spectroscopic Distinction of Type II Supernovae. Astron. J. 1996, 111, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, C.P.; Anderson, J.P.; Hamuy, M.; González-Gaitán, S.; Folatelli, G.; Morrell, N.I.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Phillips, M.M.; McCarthy, P.; Suntzeff, N.B.; et al. Hα Spectral Diversity of Type II Supernovae: Correlations with Photometric Properties. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 786, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinova, I.I.; Nadezhin, D.K. Hydrodynamical Models of Type-II Supernovae. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1983, 89, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; González-Gaitán, S.; Hamuy, M.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Olivares E., F.; Phillips, M.M.; Schulze, S.; Antezana, R.; Bolt, L.; et al. Characterizing the V-band Light-curves of Hydrogen-rich Type II Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, C.P.; Anderson, J.P.; Hamuy, M.; González-Gaitan, S.; Galbany, L.; Dessart, L.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Phillips, M.M.; Morrell, N.; Folatelli, G. Type II Supernova Spectral Diversity. II. Spectroscopic and Photometric Correlations. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.J.; Dessart, L. Photometric and spectroscopic diversity of Type II supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 631, A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faran, T.; Poznanski, D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.J.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Leonard, D.C.; Li, W.; Modjaz, M.; Nakar, E.; et al. Photometric and spectroscopic properties of Type II-P supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faran, T.; Poznanski, D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.J.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Leonard, D.C.; Li, W.; Modjaz, M.; Serduke, F.J.D.; et al. A sample of Type II-L supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.E.; Soderberg, A.M.; Gezari, S.; Betancourt, M.; Chornock, R.; Berger, E.; Foley, R.J.; Challis, P.; Drout, M.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Toward Characterization of the Type IIP Supernova Progenitor Population: A Statistical Sample of Light Curves from Pan-STARRS1. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, S.; Howell, D.A.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Graham, M.L.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Arcavi, I.; Bildsten, L.; Jerkstrand, A.; McCully, C.; Pastorello, A.; et al. The diversity of Type II supernova versus the similarity in their progenitors. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3939–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaeger, T.; Anderson, J.P.; Galbany, L.; González-Gaitán, S.; Hamuy, M.; Phillips, M.M.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Contreras, C.; Folatelli, G.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; et al. Observed Type II supernova colours from the Carnegie Supernova Project-I. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 4592–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, D.C.; Filippenko, A.V.; Gates, E.L.; Li, W.; Eastman, R.G.; Barth, A.J.; Bus, S.J.; Chornock, R.; Coil, A.L.; Frink, S.; et al. The Distance to SN 1999em in NGC 1637 from the Expanding Photosphere Method. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2002, 114, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vaucouleurs, G.; de Vaucouleurs, A.; Buta, R.; Ables, H.D.; Hewitt, A.V. The bright SN 1979 C in M 100. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1981, 93, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, M.W.; Treffers, R.R.; Filippenko, A.V.; Paik, Y.; Leibundgut, B.; Schulman, E.; Cox, C.V. UBVRI Photometry of SN 1993J in M81: The First 120 Days. Astron. J. 1994, 107, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Crockett, R.M.; Valenti, S.; Arbour, R.; Itagaki, K.; Kaspi, S.; Gal-Yam, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Griffith, R.; et al. The Type IIb SN 2008ax: Spectral and light curve evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathakis, R.A.; Sadler, E.M. What was supernova 1988Z? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 250, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Danziger, I.J.; Benetti, S.; Gouiffes, C.; della Valle, M. The type II supernova 1988Z in MCG +03-28-022: Increasingevidence of interaction of supernova ejecta with a circumstellar wind. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1993, 262, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamuy, M.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Martin, G. SN 1987A in the LMC: UBVRI Photometry at Cerro Tololo. Astron. J. 1988, 95, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V. Supernova 1987K: Type II in Youth, Type Ib in Old Age. Astron. J. 1988, 96, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V.; Matheson, T.; Ho, L.C. The “Type IIb” Supernova 1993J in M81: A Close Relative of Type Ib Supernovae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1993, 415, L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.C.; Levreault, R. The peculiar type I supernova in NGC 991. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1985, 294, L17–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V.; Barth, A.J.; Matheson, T.; Armus, L.; Brown, M.; Espey, B.R.; Fan, X.M.; Goodrich, R.W.; Ho, L.C.; Junkkarinen, V.T.; et al. The Type IC Supernova 1994I in M51: Detection of Helium and Spectral Evolution. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 450, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clocchiatti, A.; Wheeler, J.C.; Benetti, S.; Frueh, M. SN 1983N and the Nature of Stripped Envelope–Core Collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1996, 459, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.C.; Barker, E.; Benjamin, R.; Boisseau, J.; Clocchiatti, A.; de Vaucouleurs, G.; Gaffney, N.; Harkness, R.P.; Khokhlov, A.M.; Lester, D.F.; et al. Early Observations of SN 1993J in M81 at McDonald Observatory. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1993, 417, L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shigeyama, T.; Kumagai, S.; Yamaoka, H.; Saio, H. A type IIb model for supernova 1993J. Nature 1993, 364, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlowski, P.; Hsu, J.J.L.; Joss, P.C.; Ross, R.R. The progenitor of supernova 1993J: A stripped supergiant in a binary system? Nature 1993, 364, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Eastman, R.G.; Weaver, T.A.; Pinto, P.A. SN 1993J: A Type IIb Supernova. Astrophys. J. 1994, 429, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenberger, S.; Navasardyan, H.; Maurer, J.I.; Zampieri, L.; Chugai, N.N.; Benetti, S.; Agnoletto, I.; Bufano, F.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Turatto, M.; et al. The He-rich stripped-envelope core-collapse supernova 2008ax. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A.; Soderberg, A.M. Type IIb Supernovae with Compact and Extended Progenitors. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 711, L40–L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuy, M.; Pinto, P.A.; Maza, J.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Phillips, M.M.; Eastman, R.G.; Smith, R.C.; Corbally, C.J.; Burstein, D.; Li, Y.; et al. The Distance to SN 1999em from the Expanding Photosphere Method. Astrophys. J. 2001, 558, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, D.; Falk, S.W.; McCall, M.L.; Rybski, P.; Uomoto, A.K.; Wills, B.J. The type II SN 1979c in M 100 and the distance to the Virgo cluster. Astrophys. J. 1981, 244, 780–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippenko, A.V.; Matheson, T.; Barth, A.J. The Peculiar Type II Supernova 1993J in M81: Transition to the Nebular Phase. Astron. J. 1994, 108, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, T.; Filippenko, A.V.; Barth, A.J.; Ho, L.C.; Leonard, D.C.; Bershady, M.A.; Davis, M.; Finley, D.S.; Fisher, D.; González, R.A.; et al. Optical Spectroscopy of Supernova 1993J During Its First 2500 Days. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretxaga, I.; Benetti, S.; Terlevich, R.J.; Fabian, A.C.; Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M.; della Valle, M. SN 1988Z: Spectro-photometric catalogue and energy estimates*. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 309, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pun, C.S.J.; Kirshner, R.P.; Sonneborn, G.; Challis, P.; Nassiopoulos, G.; Arquilla, R.; Crenshaw, D.M.; Shrader, C.; Teays, T.; Cassatella, A.; et al. Ultraviolet Observations of SN 1987A with the IUE Satellite. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1995, 99, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Mass Loss: Its Effect on the Evolution and Fate of High-Mass Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 487–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A. The radio and X-ray emission from type II supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1982, 259, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A.; Fransson, C. Supernova Interaction with a Circumstellar Medium. In Supernovae and Gamma-Ray Bursters; Weiler, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 598, pp. 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, E.M. A new subclass of type II supernovae ? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1990, 244, 269–271. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, N. Interacting Supernovae: Types IIn and Ibn. In Handbook of Supernovae; Alsabti, A.W., Murdin, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; p. 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, W.D.; Bahcall, J.N.; Kirshner, R.P.; Woosley, S.E. Supernova 1987A. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 27, 629–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E. SN 1987A: After the Peak. Astrophys. J. 1988, 330, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Baron, E.; Branch, D.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Ramina, M.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Salvo, M.; Patat, F.; et al. SN 1998A: Explosion of a blue supergiant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Pumo, M.L.; Navasardyan, H.; Zampieri, L.; Turatto, M.; Sollerman, J.; Taddia, F.; Kankare, E.; Mattila, S.; Nicolas, J.; et al. SN 2009E: A faint clone of SN 1987A. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddia, F.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Sollerman, J.; Phillips, M.M.; Anderson, J.P.; Ergon, M.; Folatelli, G.; Fransson, C.; Freedman, W.; Hamuy, M.; et al. The Type II supernovae 2006V and 2006au: Two SN 1987A-like events. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddia, F.; Sollerman, J.; Fremling, C.; Migotto, K.; Gal-Yam, A.; Armen, S.; Duggan, G.; Ergon, M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Fransson, C.; et al. Long-rising Type II supernovae from Palomar Transient Factory and Caltech Core-Collapse Project. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sahu, D.K.; Anupama, G.C.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, H.; Yamanaka, M.; Baklanov, P.V.; Tominaga, N.; Blinnikov, S.I.; Maeda, K.; et al. SN 2018hna: 1987A-like Supernova with a Signature of Shock Breakout. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 882, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sai, H.; Zhang, J.; Brink, T.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Mo, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; et al. SN 2018hna: Adding a piece to the puzzles of the explosion of blue supergiants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddia, F.; Sollerman, J.; Razza, A.; Gafton, E.; Pastorello, A.; Fransson, C.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Leloudas, G.; Ergon, M. A metallicity study of 1987A-like supernova host galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V. On the Progenitor of the Type II-Plateau Supernova 2003gd in M74. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, M.A.; Smartt, S.J.; Maund, J.R.; Pastorello, A.; Zampieri, L.; Benetti, S.; Turatto, M.; Cappellaro, E.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Kotak, R.; et al. A study of the Type II-P supernova 2003gd in M74. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 359, 906–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maíz-Apellániz, J.; Bond, H.E.; Siegel, M.H.; Lipkin, Y.; Maoz, D.; Ofek, E.O.; Poznanski, D. The Progenitor of the Type II-P SN 2004dj in NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2004, 615, L113–L116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Cuillandre, J.C. On the Progenitor of the Type II Supernova 2004et in NGC 6946. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Smartt, S.J.; Danziger, I.J. The progenitor of SN 2005cs in the Whirlpool Galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 364, L33–L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Filippenko, A.V.; Cuillandre, J.C.; Jha, S.; Bloom, J.S.; Riess, A.G.; Livio, M. Identification of the Red Supergiant Progenitor of Supernova 2005cs: Do the Progenitors of Type II-P Supernovae Have Low Mass? Astrophys. J. 2006, 641, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.; Kotak, R.; Fraser, M.; Mattila, S.; Pietrzyński, G.; Prieto, J.L. Revisiting the progenitor of the low-luminosity type II-plateau supernova, SN 2008bk. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Cenko, S.B.; Poznanski, D.; Arcavi, I.; Gal-Yam, A.; Filippenko, A.V.; Silverio, K.; Stockton, A.; Cuillandre, J.C.; Marcy, G.W.; et al. The Red Supergiant Progenitor of Supernova 2012aw (PTF12bvh) in Messier 95. Astrophys. J. 2012, 756, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Fraser, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Botticella, M.T.; Barbarino, C.; Childress, M.; Gal-Yam, A.; Inserra, C.; Pignata, G.; Reichart, D.; et al. Supernova 2012ec: Identification of the progenitor and early monitoring with PESSTO. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, L102–L106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J. The dusty progenitor star of the Type II supernova 2017eaw. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Zheng, W.; Maund, J.R.; Brink, T.G.; Srinivasan, S.; Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N.; Leonard, D.C.; Morozova, V.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. The Type II-plateau Supernova 2017eaw in NGC 6946 and Its Red Supergiant Progenitor. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Miller, A.A.; Silverman, J.M.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Boden, A.F.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Vinkó, J.; Cuillandre, J.C.; et al. The Massive Progenitor of the Type II-linear Supernova 2009kr. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 714, L254–L259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Takáts, K.; Pastorello, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Mattila, S.; Botticella, M.T.; Valenti, S.; Ergon, M.; Sollerman, J.; Arcavi, I.; et al. On the Progenitor and Early Evolution of the Type II Supernova 2009kr. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 714, L280–L284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maund, J.R.; Fraser, M.; Reilly, E.; Ergon, M.; Mattila, S. Whatever happened to the progenitors of supernovae 2008cn, 2009kr and 2009md? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias-Rosa, N.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Li, W.; Silverman, J.M.; Foley, R.J.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Kankare, E.; Jha, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. The Massive Progenitor of the Possible Type II-Linear Supernova 2009hd in Messier 66. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, R.M.; Eldridge, J.J.; Smartt, S.J.; Pastorello, A.; Gal-Yam, A.; Fox, D.B.; Leonard, D.C.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Mattila, S.; Maund, J.R.; et al. The type IIb SN 2008ax: The nature of the progenitor. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folatelli, G.; Bersten, M.C.; Kuncarayakti, H.; Benvenuto, O.G.; Maeda, K.; Nomoto, K. The Progenitor of the Type IIb SN 2008ax Revisited. Astrophys. J. 2015, 811, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, C.M.; Cappellaro, E.; Dinerstein, H.L.; Garnett, D.R.; Harkness, R.P.; Wheeler, J.C. Type Ib Supernovae 1983n and 1985f: Oxygen-rich Late Time Spectra. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1986, 306, L77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; James, P.A. Constraints on core-collapse supernova progenitors from correlations with Hα emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 390, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lyman, J.D.; Bersier, D.; James, P.A.; Mazzali, P.A.; Eldridge, J.J.; Fraser, M.; Pian, E. Bolometric light curves and explosion parameters of 38 stripped-envelope core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K.I.; Iwamoto, K.; Suzuki, T. The evolution and explosion of massive binary stars and Type Ib-Ic-IIb-IIL supernovae. physrep 1995, 256, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, H.; de Mink, S.E.; de Koter, A.; Langer, N.; Evans, C.J.; Gieles, M.; Gosset, E.; Izzard, R.G.; Le Bouquin, J.B.; Schneider, F.R.N. Binary Interaction Dominates the Evolution of Massive Stars. Science 2012, 337, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Chornock, R. Observed fractions of core-collapse supernova types and initial masses of their single and binary progenitor stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 412, 1522–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, J.J.; Fraser, M.; Smartt, S.J.; Maund, J.R.; Crockett, R.M. The death of massive stars - II. Observational constraints on the progenitors of Type Ibc supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 774–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, J.J.; Maund, J.R. The disappearance of the helium-giant progenitor of the Type Ib supernova iPTF13bvn and constraints on its companion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, L117–L121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Arcavi, I.; Horesh, A.; Hancock, P.; Valenti, S.; Cenko, S.B.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Gal-Yam, A.; Gorbikov, E.; et al. Discovery, Progenitor and Early Evolution of a Stripped Envelope Supernova iPTF13bvn. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 775, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Auchettl, K.; Dimitriadis, G.; Foley, R.J.; Jones, D.O.; DeMarchi, L.; French, K.D.; Gall, C.; Hjorth, J.; et al. A cool and inflated progenitor candidate for the Type Ib supernova 2019yvr at 2.6 yr before explosion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 2073–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.C.; Maund, J.R.; Crowther, P.A.; Hirai, R.; Kashapov, A.; Liu, J.F.; Liu, L.D.; Zapartas, E. An environmental analysis of the Type Ib SN 2019yvr and the possible presence of an inflated binary companion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 510, 3701–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, S.D.; Zheng, W.; Brink, T.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Milisavljevic, D.; Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N.; Cignoni, M.; Fox, O.D.; Kelly, P.L.; et al. SN 2017ein and the Possible First Identification of a Type Ic Supernova Progenitor. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wang, X.; Mo, J.; Wang, L.; Smartt, S.; Fraser, M.; Ehgamberdiev, S.A.; Mirzaqulov, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Observations of SN 2017ein Reveal Shock Breakout Emission and a Massive Progenitor Star for a Type Ic Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Yam, A.; Leonard, D.C.; Fox, D.B.; Cenko, S.B.; Soderberg, A.M.; Moon, D.S.; Sand, D.J.; Caltech Core Collapse Program; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. On the Progenitor of SN 2005gl and the Nature of Type IIn Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2007, 656, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Miller, A.; Li, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; Silverman, J.M.; Howard, A.W.; Nugent, P.; Marcy, G.W.; Bloom, J.S.; Ghez, A.M.; et al. Discovery of Precursor Luminous Blue Variable Outbursts in Two Recent Optical Transients: The Fitfully Variable Missing Links UGC 2773-OT and SN 2009ip. Astron. J. 2010, 139, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Smith, N.; Filippenko, A.V.; Blanchard, K.B.; Blanchard, P.K.; Casper, C.F.E.; Cenko, S.B.; Clubb, K.I.; Cohen, D.P.; Fuller, K.L.; et al. The unprecedented 2012 outburst of SN 2009ip: A luminous blue variable star becomes a true supernova. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, A.; Cappellaro, E.; Inserra, C.; Smartt, S.J.; Pignata, G.; Benetti, S.; Valenti, S.; Fraser, M.; Takáts, K.; Benitez, S.; et al. Interacting Supernovae and Supernova Impostors: SN 2009ip, is this the End? Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlowski, P. The Progenitor of SN 1987A. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1992, 104, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, P.; Fransson, C. The Line Emission from the Circumstellar Gas around SN 1987A. Astrophys. J. 1996, 464, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotts, A.P.S.; Heathcote, S.R. SN 1987A’s Circumstellar Envelope. II. Kinematics of the Three Rings and the Diffuse Nebula. Astrophys. J. 2000, 528, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saio, H.; Kato, M.; Nomoto, K. Why Did the Progenitor of SN 1987A Undergo the Blue-Red-Blue Evolution? Astrophys. J. 1988, 331, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrandt, W.; Hoeflich, P.; Weiss, A.; Truran, J.W. Explosion of a blue supergiant: A model for supernova SN1987A. Nature 1987, 327, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Pinto, P.A.; Ensman, L. Supernova 1987A: Six Weeks Later. Astrophys. J. 1988, 324, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Heger, A. The quest for blue supergiants: Binary merger models for the evolution of the progenitor of SN 1987A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 4649–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrobin, V.P.; Wongwathanarat, A.; Janka, H.T.; Müller, E.; Ertl, T.; Menon, A.; Heger, A. Supernova 1987A: 3D Mixing and Light Curves for Explosion Models Based on Binary-merger Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2021, 914, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgy, C.; Ekström, S.; Granada, A.; Meynet, G.; Mowlavi, N.; Eggenberger, P.; Maeder, A. Populations of rotating stars. I. Models from 1.7 to 15 M⊙ at Z = 0.014, 0.006, and 0.002 with Ω/Ωcrit between 0 and 1. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Hirschi, R.; Eggenberger, P.; Ekström, S.; Georgy, C.; Sibony, Y.; Crowther, P.A.; Meynet, G.; Kassim, H.A.; Harun, W.A.W.; et al. Grids of stellar models with rotation VII: Models from 0.8 to 300 M⊙ at supersolar metallicity (Z = 0.020). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 511, 2814–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; Dessart, L.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; Krühler, T.; Galbany, L.; Jerkstrand, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Contreras, C.; Morrell, N.; Phillips, M.M.; et al. The lowest-metallicity type II supernova from the highest-mass red supergiant progenitor. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Beasor, E.R. The initial masses of the red supergiant progenitors to Type II supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmswell, J.J.; Eldridge, J.J. Circumstellar dust as a solution to the red supergiant supernova progenitor problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhbold, T.; Ertl, T.; Woosley, S.E.; Brown, J.M.; Janka, H.T. Core-collapse Supernovae from 9 to 120 Solar Masses Based on Neutrino-powered Explosions. Astrophys. J. 2016, 821, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Gerke, J.R.; Stanek, K.Z.; Dai, X. The search for failed supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: Confirmation of a disappearing star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 4968–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinger, C.M.; Kochanek, C.S.; Adams, S.M.; Dai, X.; Stanek, K.Z. The search for failed supernovae with the Large Binocular Telescope: N6946-BH1, still no star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H. Consideration for a large-scale multi-color imaging and slitless spectroscopy survey on the Chinese space station and its application in dark energy research. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 41, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Z.; Li, R.; Li, X.D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, H. Cosmology from the Chinese Space Station Optical Survey (CSS-OS). Astrophys. J. 2019, 883, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, P.; Neugent, K.F.; Ekstrom, S.; Georgy, C.; Meynet, G. The Time-Averaged Mass-Loss Rates of Red Supergiants As Revealed by their Luminosity Functions in M31 and M33. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellaro, E.; Evans, R.; Turatto, M. A new determination of supernova rates and a comparison with indicators for galactic star formation. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 351, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, N.; Driver, S.P.; Couch, W.; Baugh, C.M.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; Bridges, T.; Cannon, R.; Cole, S.; Colless, M.; Collins, C.; et al. The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: The number and luminosity density of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 324, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chornock, R.; Leaman, J.; Filippenko, A.V.; Poznanski, D.; Wang, X.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Mannucci, F. Nearby supernova rates from the Lick Observatory Supernova Search - III. The rate-size relation, and the rates as a function of galaxy Hubble type and colour. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 412, 1473–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.A.; Anderson, J.P. The Hα Galaxy Survey. III. Constraints on supernova progenitors from spatial correlations with Hα emission. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 453, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; Covarrubias, R.A.; James, P.A.; Hamuy, M.; Habergham, S.M. Observational constraints on the progenitor metallicities of core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 2660–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anderson, J.P.; James, P.A.; Habergham, S.M.; Galbany, L.; Kuncarayakti, H. Statistical Studies of Supernova Environments. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2015, 32, e019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.E.; Smith, N. Strong late-time circumstellar interaction in the peculiar supernova iPTF14hls. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Gilkis, A. Explaining iPTF14hls as a common-envelope jets supernova. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L. A magnetar model for the hydrogen-rich super-luminous supernova iPTF14hls. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 610, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, K.; Maeda, K. A Wind-driven Model: Application to Peculiar Transients AT2018cow and iPTF14hls. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, T.J.; Mazzali, P.A.; Pian, E. iPTF14hls as a variable hyper-wind from a very massive star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perley, D.A.; Mazzali, P.A.; Yan, L.; Cenko, S.B.; Gezari, S.; Taggart, K.; Blagorodnova, N.; Fremling, C.; Mockler, B.; Singh, A.; et al. The fast, luminous ultraviolet transient AT2018cow: Extreme supernova, or disruption of a star by an intermediate-mass black hole? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 1031–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, R.; Metzger, B.D.; Chornock, R.; Vurm, I.; Roth, N.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Savchenko, V.; Cartier, R.; Steiner, J.F.; Terreran, G.; et al. An Embedded X-Ray Source Shines through the Aspherical AT 2018cow: Revealing the Inner Workings of the Most Luminous Fast-evolving Optical Transients. Astrophys. J. 2019, 872, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M.; Toonen, S. Fast-rising blue optical transients and AT2018cow following electron-capture collapse of merged white dwarfs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 5618–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuin, N.P.M.; Wu, K.; Oates, S.; Lien, A.; Emery, S.; Kennea, J.A.; de Pasquale, M.; Han, Q.; Brown, P.J.; Tohuvavohu, A.; et al. Swift spectra of AT2018cow: A white dwarf tidal disruption event? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 2505–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.; Blinnikov, S.; Nomoto, K.; Baklanov, P.; Sorokina, E.; Tolstov, A. A Model for the Fast Blue Optical Transient AT2018cow: Circumstellar Interaction of a Pulsational Pair-instability Supernova. Astrophys. J. 2020, 903, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, Z.; Rakavy, G.; Sack, N. Dynamics of Supernova Explosion Resulting from Pair Formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 18, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakavy, G.; Shaviv, G. Instabilities in Highly Evolved Stellar Models. Astrophys. J. 1967, 148, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Blinnikov, S.; Heger, A. Pulsational pair instability as an explanation for the most luminous supernovae. Nature 2007, 450, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaji, S.; Nomoto, K.; Yokoi, K.; Sugimoto, D. Supernova triggered by electron captures. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 32, 303–329. [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto, K. Evolution of 8–10 solar mass stars toward electron capture supernovae. I—Formation of electron-degenerate O + NE + MG cores. Astrophys. J. 1984, 277, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K. Evolution of 8–10 Msun Stars toward Electron Capture Supernovae. II. Collapse of an O + NE + MG Core. Astrophys. J. 1987, 322, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticella, M.T.; Pastorello, A.; Smartt, S.J.; Meikle, W.P.S.; Benetti, S.; Kotak, R.; Cappellaro, E.; Crockett, R.M.; Mattila, S.; Sereno, M.; et al. SN 2008S: An electron-capture SN from a super-AGB progenitor? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 1041–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, T.A.; Prieto, J.L.; Stanek, K.Z.; Kistler, M.D.; Beacom, J.F.; Kochanek, C.S. A New Class of Luminous Transients and a First Census of their Massive Stellar Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1364–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, D.; Howell, D.A.; Van Dyk, S.D.; Goldberg, J.A.; Maeda, K.; Moriya, T.J.; Tominaga, N.; Nomoto, K.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Arcavi, I.; et al. The electron-capture origin of supernova 2018zd. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhan, J.C.; Smith, N.; Silverman, J.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; Morgan, A.N.; Cenko, S.B.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Clubb, K.I.; Bloom, J.S.; Matheson, T.; et al. SN 2011ht: Confirming a class of interacting supernovae with plateau light curves (Type IIn-P). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, T.J.; Tominaga, N.; Langer, N.; Nomoto, K.; Blinnikov, S.I.; Sorokina, E.I. Electron-capture supernovae exploding within their progenitor wind. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Reguitti, A.; Valerin, G.; Wang, X. Gap Transients Interacting with Circumstellar Medium. Universe 2022, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Gall, C.; Arcavi, I.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Harmanen, J.; et al. AT 2017be—A new member of the class of intermediate-luminosity red transients. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3424–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-Z.; Pastorello, A.; Fraser, M.; Botticella, M.T.; Elias-Rosa, N.; Wang, L.-Z.; Kotak, R.; Benetti, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Turatto, M.; et al. Intermediate-luminosity red transients: Spectrophotometric properties and connection to electron-capture supernova explosions. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 654, A157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, S.W. Shock steepening and prompt thermal emission in supernovae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1978, 225, L133–L136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, X.F.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Brown, P.J.; Mo, J.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, K.C.; Zhang, T.M.; Howell, D.A.; Arcavi, I.; et al. SN 2016X: A type II-P supernova with a signature of shock breakout from explosion of a massive red supergiant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 3959–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.M. The Absolute Magnitudes of Type IA Supernovae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1993, 413, L105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.P.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Phillips, M.M.; Schommer, R.A.; Clocchiatti, A.; Kirshner, R.P.; Garnavich, P.; Challis, P.; Leibundgut, B.; Spyromilio, J.; et al. The High-Z Supernova Search: Measuring Cosmic Deceleration and Global Curvature of the Universe Using Type IA Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1998, 507, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Casertano, S.; Jones, D.O.; Murakami, Y.; Anand, G.S.; Breuval, L.; et al. A Comprehensive Measurement of the Local Value of the Hubble Constant with 1 km s−1 Mpc−1 Uncertainty from the Hubble Space Telescope and the SH0ES Team. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 934, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, T.; Strolger, L.G.; Riess, A.G. The Extended HST Supernova Survey: The Rate of SNe Ia at z > 1.4 Remains Low. Astrophys. J. 2008, 681, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melinder, J.; Dahlen, T.; Mencía Trinchant, L.; Östlin, G.; Mattila, S.; Sollerman, J.; Fransson, C.; Hayes, M.; Kankare, E.; Nasoudi-Shoar, S. The rate of supernovae at redshift 0.1-1.0. The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey III. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 545, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshner, R.P.; Kwan, J. Distances to extragalactic supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1974, 193, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuy, M.; Pinto, P.A. Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 566, L63–L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaeger, T.; González-Gaitán, S.; Anderson, J.P.; Galbany, L.; Hamuy, M.; Phillips, M.M.; Stritzinger, M.D.; Gutiérrez, C.P.; Bolt, L.; Burns, C.R.; et al. A Hubble Diagram from Type II Supernovae Based Solely on Photometry: The Photometric Color Method. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuy, M.; Phillips, M.M.; Suntzeff, N.B.; Schommer, R.A.; Maza, J.; Antezan, A.R.; Wischnjewsky, M.; Valladares, G.; Muena, C.; Gonzales, L.E.; et al. BVRI Light Curves for 29 Type IA Supernovae. Astron. J. 1996, 112, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, R.L.; Nugent, P.E.; Phillips, M.M. High-Redshift Supernovae in the Hubble Deep Field. Astrophys. J. 1999, 521, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbary, K.; Bailey, S.; Barentsen, G.; Barclay, T.; Biswas, R.; Boone, K.; Craig, M.; Feindt, U.; Friesen, B.; Goldstein, D.; et al. SNCosmo. Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/6363879#.ZEOCc85BxPY (accessed on 20 February 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).