MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis in the Identification of Urine Proteomic Patterns of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
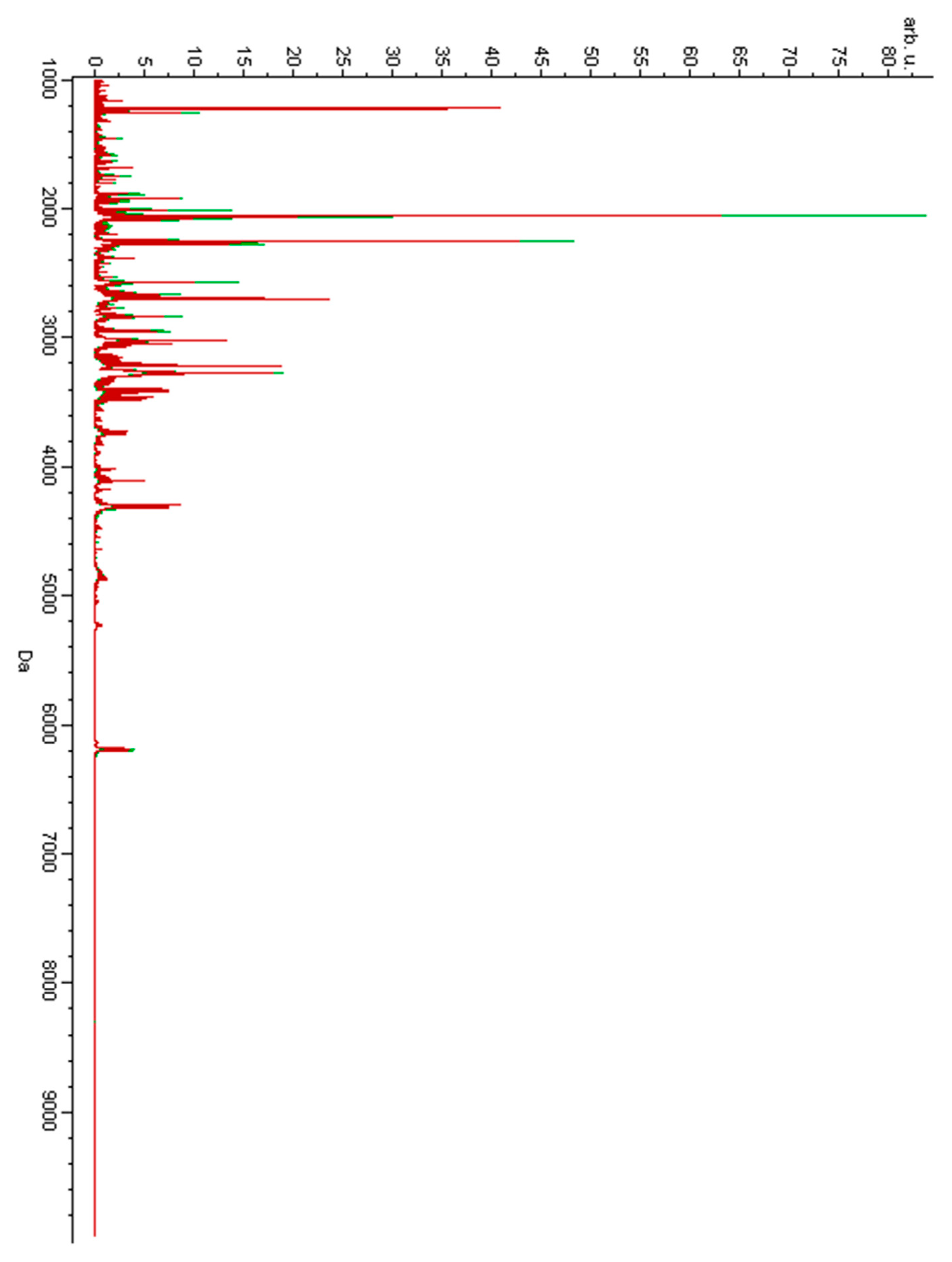
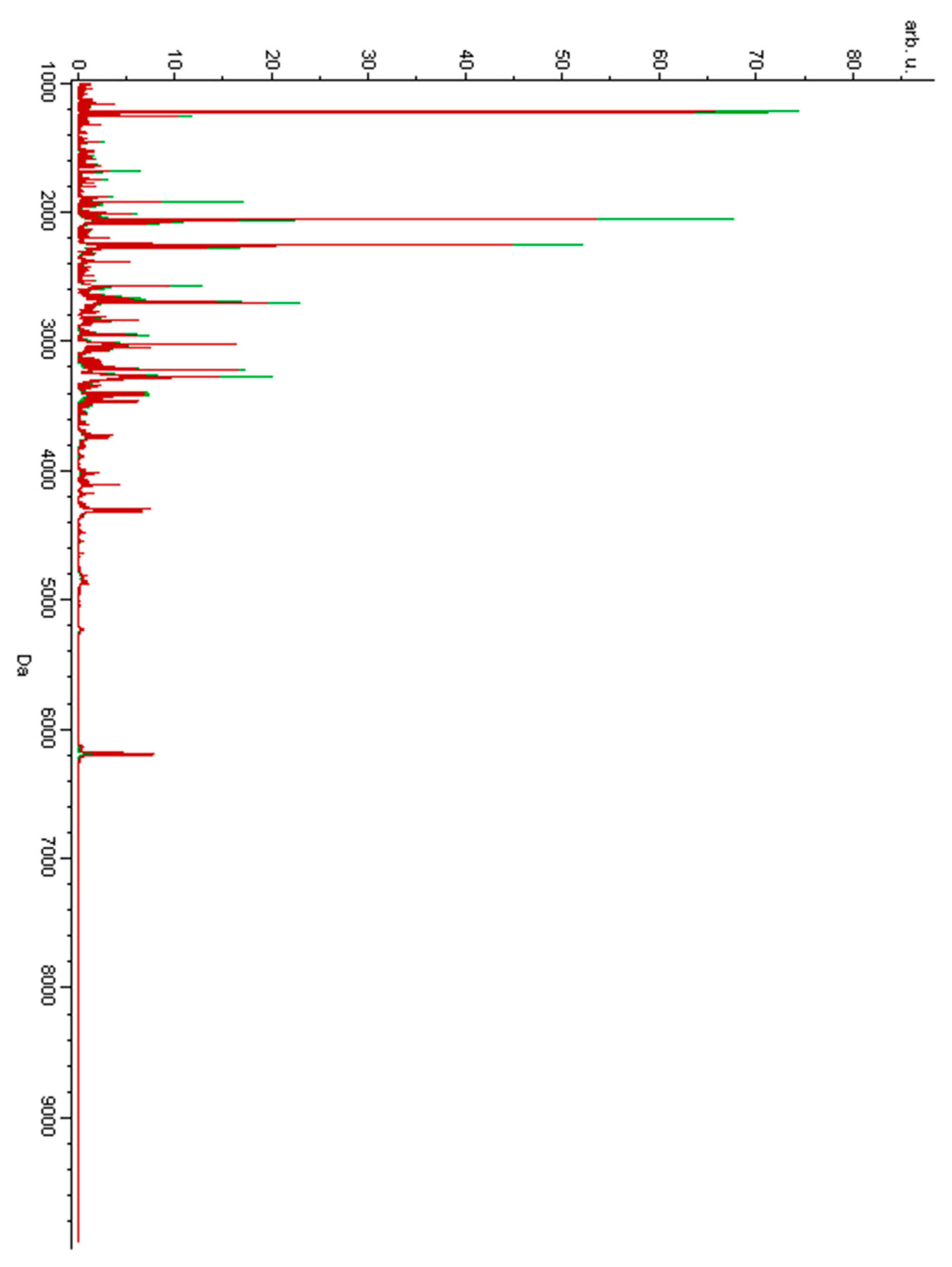
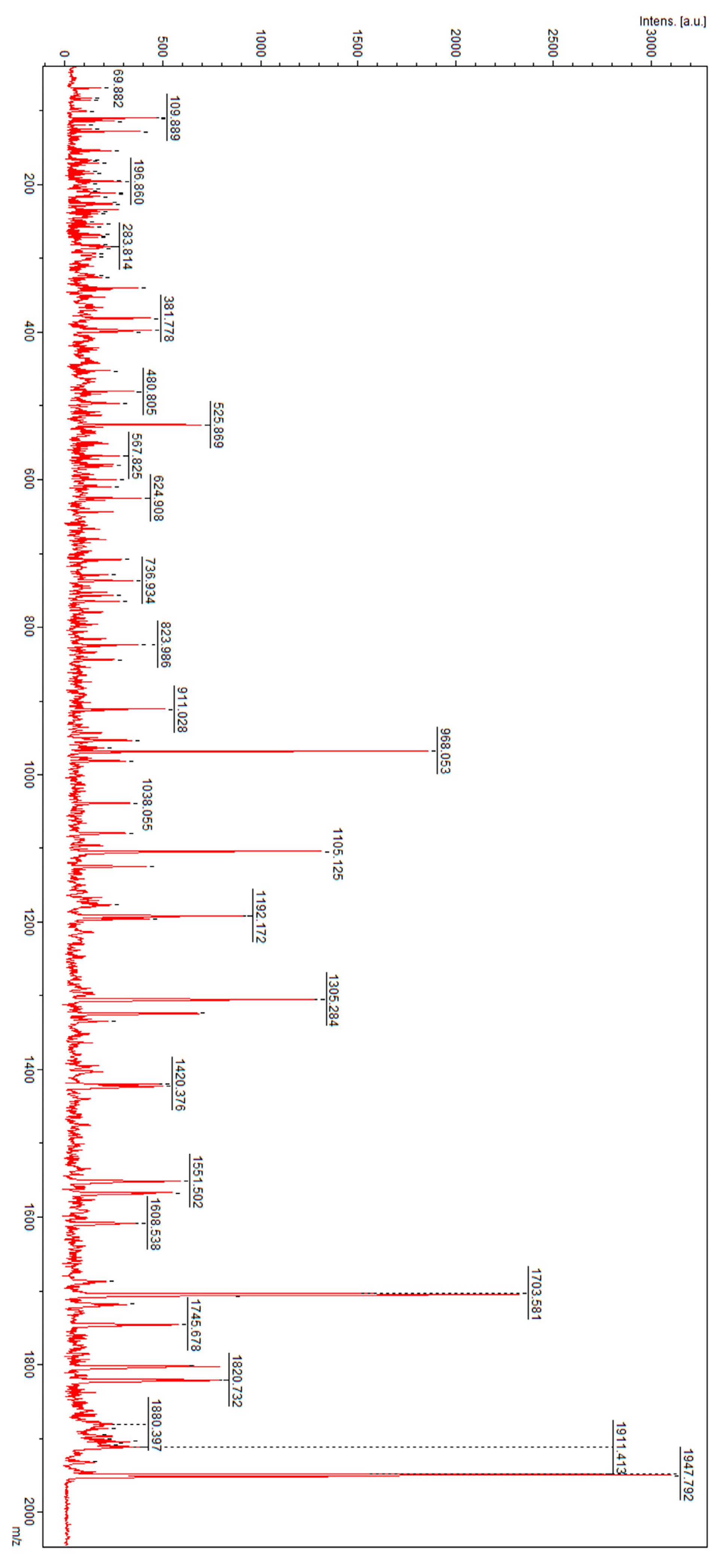
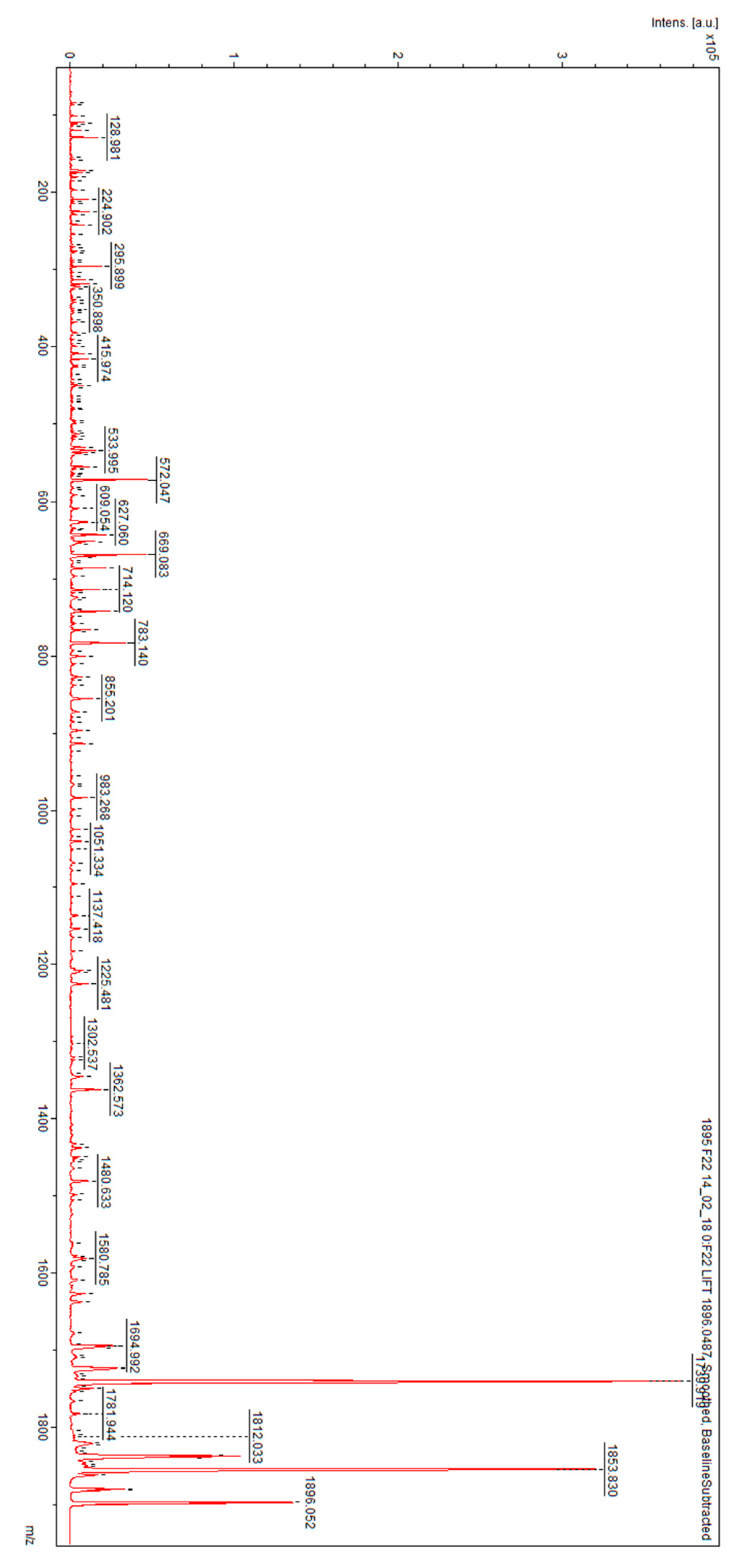
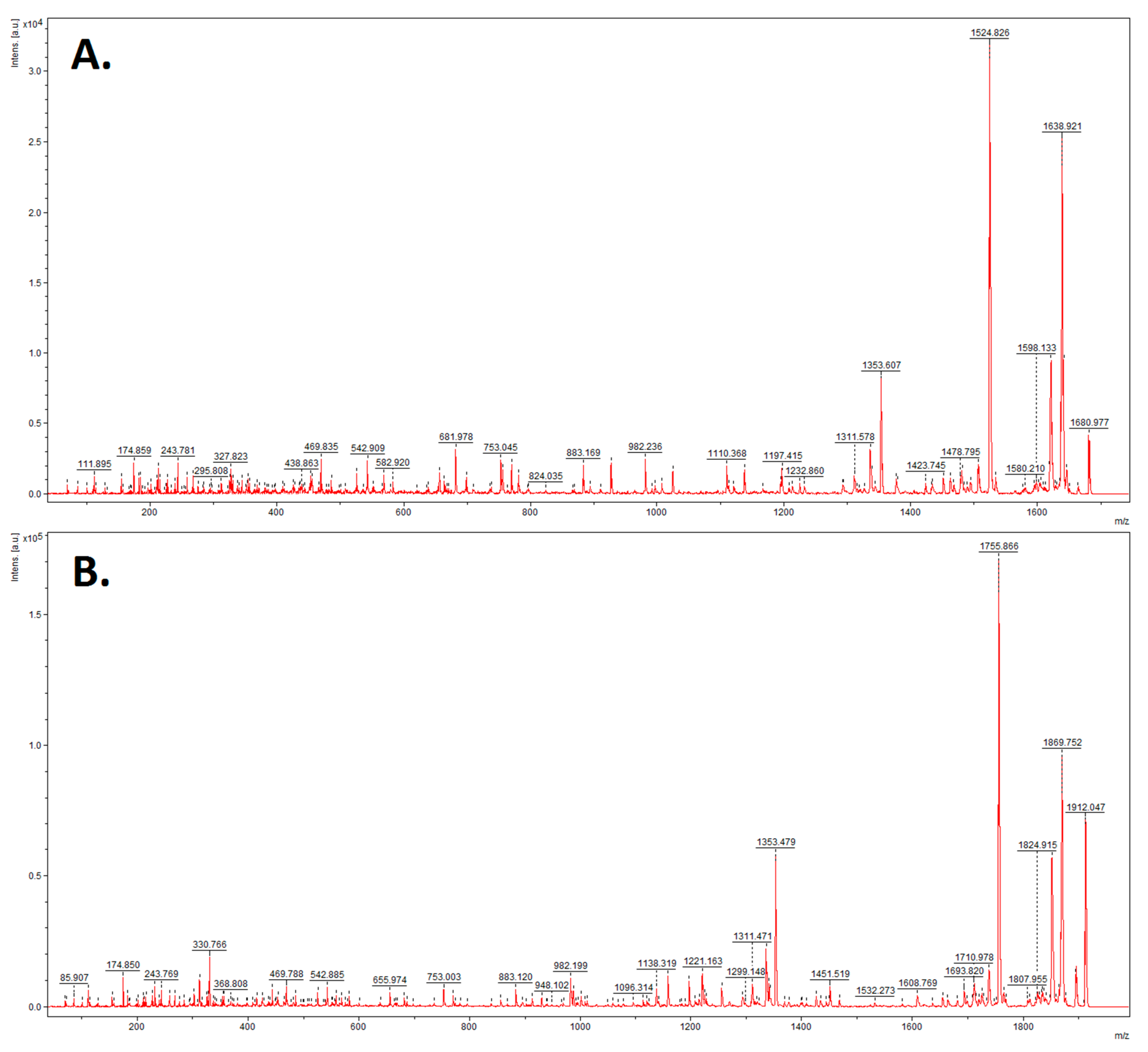
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banach, P.; Suchy, W.; Dereziński, P.; Matysiak, J.; Kokot, Z.J.; Nowak-Markwitz, E. Mass spectrometry as a tool for biomarkers searching in gynecological oncology. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, P.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Arentz, G.; Zhang, C.; Kaur, G.; Oehler, M.K.; Hoffmann, P. Proteomics of endometrial cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckl, M.J.; Sebire, N.J.; Berkowitz, R.S. Gestational trophoblastic disease. Lancet 2010, 376, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaro, A.; Braga, A.; Berkowitz, R.S. Diagnosis, classification and treatment of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obs. 2015, 37, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Gao, Y.H.; Jiang, C.G.; Tian, Y.P.; Zhang, X.J. Serum proteomic profile analysis for endometrial carcinoma detection with MALDI-ToF MS. Arch. Med. Sci. 2010, 6, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.W.; Lai, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiou, J.Y.; Shui, H.A.; Chang, C.C.; Yu, M.H.; Chu, T.Y. Plasma proteomic profiling for detecting and differentiating in situ and invasive carcinomas of the uterine cervix. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2006, 16, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Arentz, G.; Winderbaum, L.; Lokman, N.A.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Mittal, P.; Carter, C.; Oehler, M.K.; Hoffmann, P. MALDI mass spectrometry imaging reveals decreased CK5 levels in vulvar squamous cell carcinomas compared to the precursor lesion differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.; Moore, K.; Phillips, L.; Boyle, F.M.; Marsh, D.J.; Baxter, R.C. Novel serum protein biomarker panel revealed by mass spectrometry and its prognostic value in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batorfi, J.; Ye, B.; Mok, S.C.; Cseh, I.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Fulop, V. Protein profiling of complete mole and normal placenta using ProteinChip analysis on laser capture microdissected cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 88, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Feng, F.; Wan, X. Comparative proteomic analysis between benign and malignant-transformed hydatidiform mole. J. Reprod. Med. 2008, 53, 623–628. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.H.; Zhao, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.M. CLIC1 protein: A candidate prognostic biomarker for malignant-transformed hydatidiformmoles. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2011, 21, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, F.T.; Katzorke, N.; Tempfer, C.; Kreimer, U.; Bizjak, G.I.; Fleisch, M.C.; Fehm, T.N. Gestational Trophoblastic Disorders: An Update in 2015. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2015, 75, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.; Turner, G.A. Elevated levels of abnormally-fucosylated haptoglobins in cancer sera. Br. J. Cancer 1987, 56, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodorescu, D.; Schiffer, E.; Bauer, H.W.; Douwes, F.; Eichhorn, F.; Polley, R.; Schmidt, T.; Schöfer, W.; Zürbig, P.; Good, D.M.; et al. Discovery and validation of urinary biomarkers for prostate cancer. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2008, 2, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Leng, W.; Sun Ch Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Men, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhen, B.; Qin, J. Urine Proteome Profiling Predicts Lung Cancer from Control Cases and Other Tumors. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Jing, X.Y.; Wang, N.N.; Zhang, T.; Hu, C.J. Detection and Identification of Serum Peptides Biomarker in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.D.; Gu, W. Urinary proteomics as a novel tool for biomarker discovery in kidney diseases. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Subramanian, S.; Hwang, S.J.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Fox, C.S.; Courchesne, P.; Muntendam, P.; Gordon, N.; Adourian, A.; Juhasz, P.; et al. Protein biomarkers of new-onset cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar-Kharghan, V. The role of the complement system in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosens, I.; Pijnenborg, R.; Vercruysse, L.; Romero, R. The “Great Obstetrical Syndromes” are associated with disorders of deep placentation. Obs. Gynecol 2011, 204, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buurma, A.; Cohen, D.; Veraar, K.; Schonkeren, D.; Claas, F.H.; Bruijn, J.A.; Bloemenkamp, K.W.; Baelde, H.J. Preeclampsia is characterized by placental complement dysregulation. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, W.; Lee, Y.; Wong, P.; Chung, M.; Lee, K.; Yeung, W.S. Complement 3 deficiency impairs early pregnancy in mice. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2009, 76, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Mao, D.; Holers, V.M.; Palanca, B.; Cheng, A.M.; Molina, H. A critical role for murine complement regulator crry in fetomaternal tolerance. Science 2000, 287, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohlin, F.C.; Mercier, E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Liszewski, M.K.; Atkinson, J.P.; Gris, J.C.; Blom, A.M. Analysis of genes coding for CD46, CD55, and C4b-binding protein in patients with idiopathic, recurrent, spontaneous pregnancy loss. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierli, J.A.; Ng, Y.C.; Peters, D.K. The role of complement and its receptor in the elimination of immune complexes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 488–495. [Google Scholar]
- Pio, R.; Ajona, D.; Lambris, J.D. Complement inhibition in cancer therapy. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuzzi, M.; Marelli, C.; Bagnati, R.; Colombi, A.; Fanelli, R.; Saieva, C.; Ceroti, M.; Bendinelli, B.; Caini, S.; Airoldi, L.; et al. Plasma clusterin as a candidate pre- diagnosis marker of colorectal cancer risk in the Florence cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition: A pilot study. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajona, D.; Pajares, M.J.; Corrales, L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Agorreta, J.; Lozano, M.D.; Torre, W.; Massion, P.P.; de-Torres, J.P.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; et al. Investigation of complement activation product C4d as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broek, I.; Sparidans, R.W.; Schellens, J.H.; Beijinen, J.H. Quantitative assay for six potential breast cancer biomarker peptides in human serum by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyletal, P.; Bleyer, A.J.; Kmoch, S. Uromodulin Biology and Pathophysiology—An Update. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 456–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchmore, A.V. Uromodulin: An Immunoregulatory Glycoprotein Isolated From Pregnancy Urine That Binds to and Regulates the Activity of Interleukin 1. AJRI 1986, 11, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst, O.; Olinger, E.; Rampoldi, L. Uromodulin: From physiology to rare and complex kidney disorders. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhotta, K. Uromodulin and Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottini, A.; Berruti, A.; Brizzi, M.P.; Bersiga, A.; Generali, D.; Allevi, G.; Aguggini, S.; Bolsi, G.; Bonardi, S.; Bertoli, G.; et al. Pretreatment hemoglobin levels significantly predict the tumor response to primary chemotherapy in human breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woong-Shick, A.; Sung-Pil, P.; Su-Mi, B.; Joon-Mo, L.; Sung-Eun, N.; Gye-Hyun, N.; Young-Lae, C.; Ho-Sun, C.; Heung-Jae, J.; Chong-Kook, K.; et al. Identification of hemoglobin-α and -β subunits as potential serum biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Cross Validation (%) | Recognition Capability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| GA | 68.2 | 94.4 |
| SNN | 50 | 54 |
| QC | 61.8 | 84.4 |
| Model | Cross Validation (%) | Recognition Capability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| GA | 56.7 | 97.1 |
| SNN | 50 | 52.9 |
| QC | 33.6 | 84 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banach, P.; Dereziński, P.; Matuszewska, E.; Matysiak, J.; Bochyński, H.; Kokot, Z.J.; Nowak-Markwitz, E. MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis in the Identification of Urine Proteomic Patterns of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Metabolites 2019, 9, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9020030
Banach P, Dereziński P, Matuszewska E, Matysiak J, Bochyński H, Kokot ZJ, Nowak-Markwitz E. MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis in the Identification of Urine Proteomic Patterns of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Metabolites. 2019; 9(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanach, Paulina, Paweł Dereziński, Eliza Matuszewska, Jan Matysiak, Hubert Bochyński, Zenon J. Kokot, and Ewa Nowak-Markwitz. 2019. "MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis in the Identification of Urine Proteomic Patterns of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease" Metabolites 9, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9020030
APA StyleBanach, P., Dereziński, P., Matuszewska, E., Matysiak, J., Bochyński, H., Kokot, Z. J., & Nowak-Markwitz, E. (2019). MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis in the Identification of Urine Proteomic Patterns of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Metabolites, 9(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9020030





