Metabolomic Profiles of a Midge (Procladius villosimanus, Kieffer) Are Associated with Sediment Contamination in Urban Wetlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sediment Contaminants
2.2. Annotated Untargeted Metabolite Analysis of P. Villosimanus
2.3. Targeted Amine-Containing Metabolite Analysis of P. villosimanus
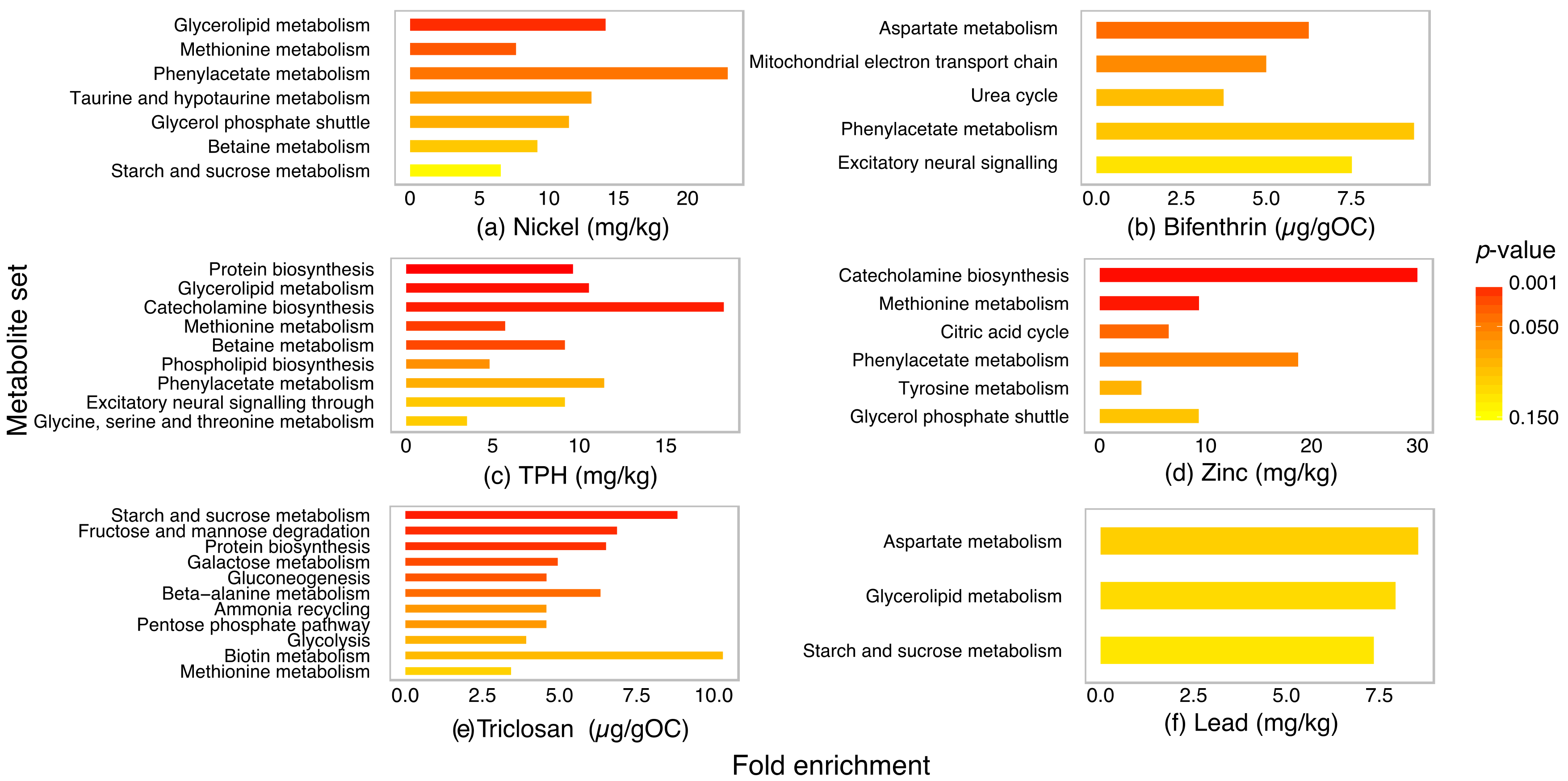
2.4. Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis of P. villosimanus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area and Procladius Collection
4.2. Sediment Chemical Analyses
4.3. Species Identification of P. villosimanus
4.4. Metabolomic Analysis
4.4.1. Metabolite Extraction
4.4.2. Annotated Untargeted Metabolite Analysis and Data Processing (GC-MS)
4.4.3. Targeted Amine-Containing Metabolomic Analysis and Data Processing (LC-MS)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, P.M.; Wang, F.Y.; Janssen, C.; Persoone, G.; Allen, H.E. Ecotoxicology of metals in aquatic sediments: Binding and release, bioavailability, risk assessment and remediation. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Mauceri, A.; Corsaro, C.; Maisano, M.; Parrino, V.; Lo Paro, G.; Messina, G.; Fasulo, S. Impact of environmental pollution on caged mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis using NMR-based metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandao, F.; Cappello, T.; Raimundo, J.; Santos, M.A.; Maisano, M.; Mauceri, A.; Pacheco, M.; Pereira, P. Unravelling the mechanisms of mercury hepatotoxicity in wild fish (Liza aurata) through a triad approach: Bioaccumulation, metabolomic profiles and oxidative stress. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.M.; Tull, D.L.; Jeppe, K.J.; De Souza, D.P.; Dayalan, S.; Pettigrove, V.J.; McConville, M.J.; Hoffmann, A.A. A multi-platform metabolomics approach demonstrates changes in energy metabolism and the transsulfuration pathway in Chironomus tepperi following exposure to zinc. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 162, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.K.; Primicerio, R.; Amundsen, P.A. Diversity and structure of Chironomidae (Diptera) communities along a gradient of heavy metal contamination in a subarctic watercourse. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 307, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharley, D.J.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Pettigrove, V. Effects of sediment quality on macroinvertebrates in the Sunraysia region of the Murray-Darling Rivers, Australia. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, K.R.; Pettigrove, V.J.; Carew, M.E.; Hoffmann, A.A. The effects of sediment quality on benthic macroinvertebrates in the River Murray, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 60, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrove, V. Larval mouthpart deformities in Procladius paludicola Skuse (Diptera, Chironomidae) from the Murray and Darling Rivers, Australia. Hydrobiologia 1989, 179, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.G.; Davey, M.P.; Viant, M.R. Environmental metabolomics: A critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sevillano, M.A.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L. Environmental metabolomics: Biological markers for metal toxicity. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 2348–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skelton, D.M.; Ekman, D.R.; Martinovic-Weigelt, D.; Ankley, G.T.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Teng, Q.; Collette, T.W. Metabolomics for in situ environmental monitoring of surface waters impacted by contaminants from both point and nonpoint sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargiela, R.; Herbst, F.A.; Martinez-Martinez, M.; Seifert, J.; Rojo, D.; Cappello, S.; Genovese, M.; Crisafi, F.; Denaro, R.; Chernikova, T.N.; et al. Metaproteomics and metabolomics analyses of chronically petroleum-polluted sites reveal the importance of general anaerobic processes uncoupled with degradation. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3508–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, A.; Staff, F.J.; Widdows, J.; Compton, R.M.; Falciani, F.; Viant, M.R. Discovery of metabolic signatures for predicting whole organism toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.S.; Kirwan, J.A.; Johnson, C.; Yan, N.D.; Viant, M.R.; Gunn, J.M.; McGeer, J.C. Predicting chronic copper and nickel reproductive toxicity to Daphnia pulex-pulicaria from whole-animal metabolic profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T.; Fernandes, D.; Maisano, M.; Casano, A.; Bonastre, M.; Bebianno, M.J.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S.; Porte, C. Sex steroids and metabolic responses in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to drospirenone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, Y.; Kashiba, M.; Maruyama, K.; Hoshikawa, K.; Sasaki, R.; Saito, K.; Kimura, H.; Goda, N.; Suematsu, M. Cadmium exposure alters metabolomics of sulfur-containing amino acids in rat testes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. 1H NMR-based metabolomics investigation on the effects of petrochemical contamination in posterior adductor muscles of caged mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisano, M.; Cappello, T.; Natalotto, A.; Vitale, V.; Parrino, V.; Giannetto, A.; Oliva, S.; Mancini, G.; Cappello, S.; Mauceri, A.; et al. Effects of petrochemical contamination on caged marine mussels using a multi-biomarker approach: Histological changes, neurotoxicity and hypoxic stress. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasulo, S.; Iacono, F.; Cappello, T.; Corsaro, C.; Maisano, M.; D’Agata, A.; Giannetto, A.; De Domenico, E.; Parrino, V.; Lo Paro, G.; et al. Metabolomic investigation of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819) caged in aquatic environments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundy, J.G.; Sidhu, J.K.; Rana, F.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Svendsen, C.; Wren, J.F.; Sturzenbaum, S.R.; Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P. ‘Systems toxicology’ approach identifies coordinated metabolic responses to copper in a terrestrial non-model invertebrate, the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. BMC Biol. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.N.; Samuelsson, L.; Bernardi, G.; Gooneratne, R.; Larsson, D.G.J. Aqueousandlipid nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomic profiles of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa show potential as an indicator species for environmental metabolomics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Meyer, K.A.; Jackson, T.M.; Schock, T.B.; Johnson, W.E.; Bearden, D.W. Application of NMR-based metabolomics for environmental assessment in the Great Lakes using zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T.; Pereira, P.; Maisano, M.; Mauceri, A.; Pacheco, M.; Fasulo, S. Advances in understanding the mechanisms of mercury toxicity in wild golden grey mullet (Liza aurata) by 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaling, M.; Kanawati, B.; Ghirardo, A.; Albert, A.; Winkler, J.B.; Heller, W.; Barta, C.; Loreto, F.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Schnitzler, J.P. UV-B mediated metabolic rearrangements in poplar revealed by non-targeted metabolomics. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Reig, M.; Jaumot, J.; Pina, B.; Moyano, E.; Galceran, M.T.; Tauler, R. Metabolomic analysis of the effects of cadmium and copper treatment in Oryza sativa L. using untargeted liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry and all-ion fragmentation. Metallomics 2017, 9, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viant, M.R.; Rosenblum, E.S.; Tjeerdema, R.S. NMR-based metabolomics: A powerful approach for characterizing the effects of environmental stressors on organism health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4982–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halama, A.; Kulinski, M.; Kader, S.A.; Satheesh, N.J.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Suhre, K.; Mohammad, R.M. Measurement of 1,5-anhydroglucitol in blood and saliva: From non-targeted metabolomics to biochemical assay. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.Z.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, L.L.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, M.C.; Pan, H.Z.; Zou, L.N.; Chang, D. Long-chain unsaturated fatty acids as possible important metabolites for primary angle-closure glaucoma based on targeted metabolomic analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppe, K.J.; Yang, J.H.; Long, S.M.; Carew, M.E.; Zhang, X.W.; Pettigrove, V.; Hoffmann, A.A. Detecting copper toxicity in sediments: From the subindividual level to the population level. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.L.; Bundy, J.G.; Want, E.J.; Kille, P.; Sturzenbaum, S.R. The metabolomic responses of Caenorhabditis elegans to cadmium are largely independent of metallothionein status but dominated by changes in cystathionine and phytochelatins. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.; Jones, O.; Beale, D.; Boughton, B.; Benheim, D.; Kouremenos, K.; Wolfender, J.-L.; Wishart, D. Current and future perspectives on the structural identification of small molecules in biological systems. Metabolites 2016, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Wang, P.; Xu, H.Y.; Chen, L.P.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Y.J. Metabolomics analysis and biomarker identification for brains of rats exposed subchronically to the mixtures of low-dose cadmium and chlorpyrifos. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluender, C.; Sans-Piche, F.; Riedl, J.; Altenburger, R.; Hartig, C.; Laue, G.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. A metabolomics approach to assessing phytotoxic effects on the green alga Scenedesmus vacuolatus. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Sharley, D.J.; Jeppe, K.J.; Sharp, S.; Rose, G.; Pettigrove, V. Potentially toxic concentrations of synthetic pyrethroids associated with low density residential land use. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharley, D.J.; Sharp, S.M.; Marshall, S.; Jeppe, K.; Pettigrove, V.J. Linking urban land use to pollutants in constructed wetlands: Implications for stormwater and urban planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppe, K.J.; Kellar, C.R.; Marshall, S.; Colombo, V.; Sinclair, G.M.; Pettigrove, V. Bifenthrin causes toxicity in urban stormwater wetlands: Field and laboratory assessment using Austrochiltonia (Amphipoda). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7254–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amweg, E.L.; Weston, D.P.; Ureda, N.M. Use and toxicity of pyrethroid pesticides in the Central Valley, California, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, K.D.; Kuivila, K.M.; Hladik, M.L.; Haluska, T.; Cole, M.B. Storm-event-transport of urban-use pesticides to streams likely impairs invertebrate assemblages. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, R.W.; Anderson, B.S.; Phillips, B.M.; Hunt, J.W.; Crane, D.B.; Mekebri, A.; Connor, V. Statewide investigation of the role of pyrethroid pesticides in sediment toxicity in California’s Urhan waterways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7003–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehler, W.T.; Li, H.Z.; Lydy, M.J.; You, J. Identifying the causes of sediment-associated toxicity in urban waterways of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantwell, M.G.; Wilson, B.A.; Zhu, J.; Wallace, G.T.; King, J.W.; Olsen, C.R.; Burgess, R.M.; Smith, J.P. Temporal trends of triclosan contamination in dated sediment cores from four urbanized estuaries: Evidence of preservation and accumulation. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.H.; Iwata, H. Risk assessment of triclosan in the global environment using a probabilistic approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemec, A.; Drobne, D.; Tisler, T.; Sepcic, K. Biochemical biomarkers in environmental studies-lessons learnt from enzymes catalase, glutathione S-transferase and cholinesterase in two crustacean species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, P.L.; Reynoldson, T.B.; Dixon, D.G. Metallothionein-like protein and tissue metal concentrations in invertebrates (Oligochaetes and Chironomids) collected from reference and metal contaminated field sediments. J. Great Lakes Res. 2006, 32, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahashi, T. Nerve membrane ionic channels as the primary target of pyrethroids. Neurotoxicology 1985, 6, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marshall, S.; Pettigrove, V.; Carew, M.; Hoffmann, A. Isolating the impact of sediment toxicity in urban streams. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carew, M.E.; Marshall, S.E.; Hoffmann, A.A. A combination of molecular and morphological approaches resolves species in the taxonomically difficult genus Procladius Skuse (Diptera: Chironomidae) despite high intra-specific morphological variation. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2011, 101, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Phys. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, S.; De Souza, D.P.; Isaac, A.; Wang, Q.; Hodkinson, L.; Olshansky, M.; Erwin, T.; Appelbe, B.; Tull, D.L.; Roessner, U.; et al. PyMS: A Python toolkit for processing of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) data. Application and comparative study of selected tools. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bearden, D.; Bundy, J.; Collette, T.; Currie, F.; Davey, M.P.; Field, D.; Haigh, N.S.; Hancock, D.; Jones, O.; Morrison, N.; et al. CIMR: Environmental Analysis Context—Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Available online: http://msi-workgroups.sourceforge.net/bio-metadata/ (accessed on 9 November 2017).
- Boughton, B.A.; Callahan, D.L.; Silva, C.; Bowne, J.; Nahid, A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Tull, D.L.; McConville, M.J.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Comprehensive profiling and quantitation of amine group containing metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7523–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council (ANZECC), Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand (ARMCANZ). Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Freshwater and Marine Water Quality; Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand: Canberra, Australia, 2000.
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, L.H.; Norman, J.E.; Moran, P.W.; Martin, J.D.; Stone, W.W. Pesticide Toxicity Index: A tool for assessing potential toxicity of pesticide mixtures to freshwater aquatic organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. VSURF: An R package for variable selection using random forests. R J. 2015, 7, 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Loh, P.R.; Barker, N.D.; Tucker, G.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.H.; Escalon, B.L.; Berger, B.; Perkins, E.J. Building quantitative prediction models for tissue residue of two explosives compounds in earthworms from microarray gene expression data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehoe, M.J.; Chun, K.P.; Baulch, H.M. Who smells? Forecasting taste and odor in a drinking water reservoir. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10984–10992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, B.T.; Gronberg, J.M.; Faunt, C.C.; Eberts, S.M.; Belitz, K. Modeling nitrate at domestic and public-supply well depths in the Central Valley, California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5643–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.G.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.G.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst 3.0-making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
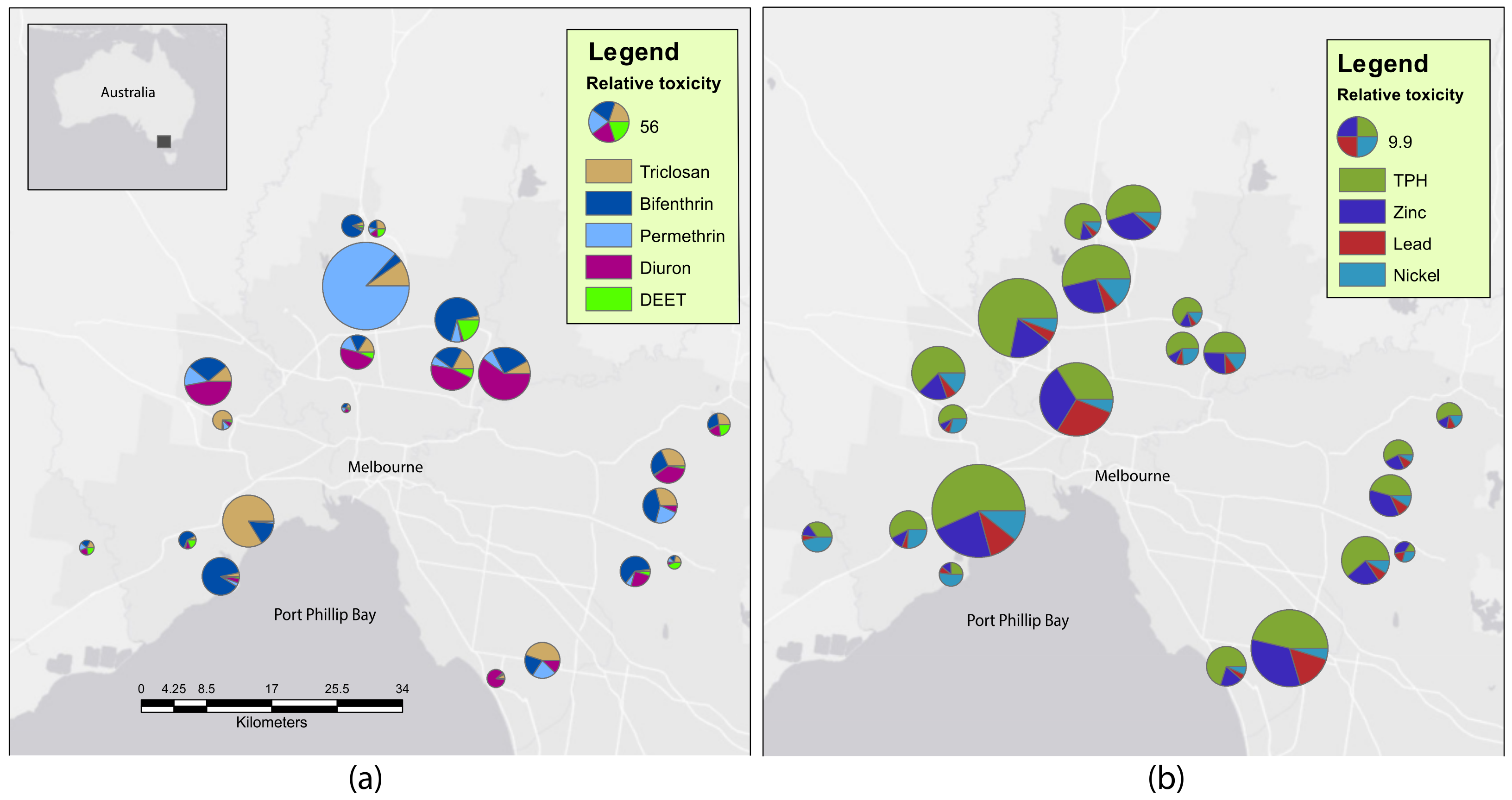
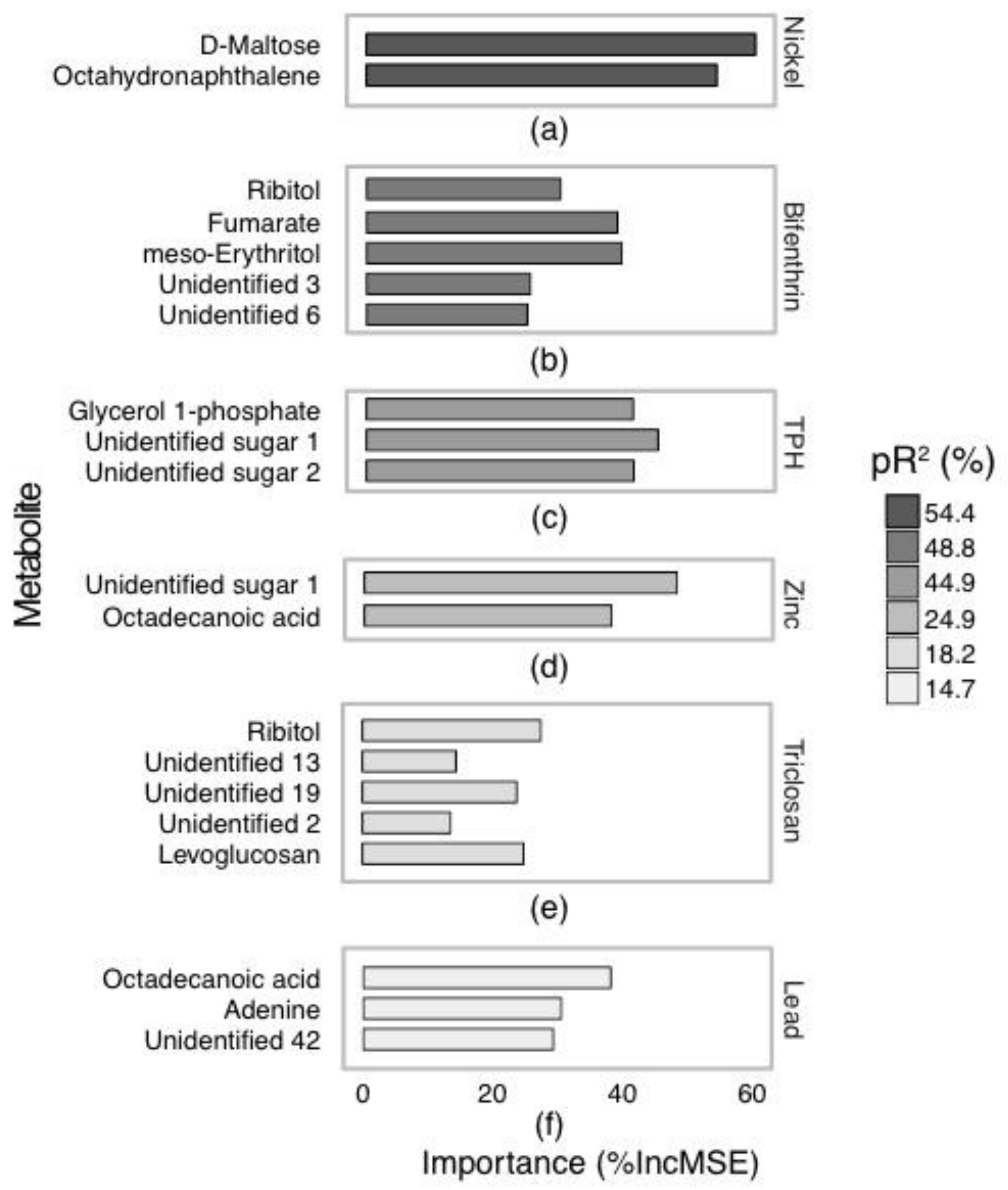

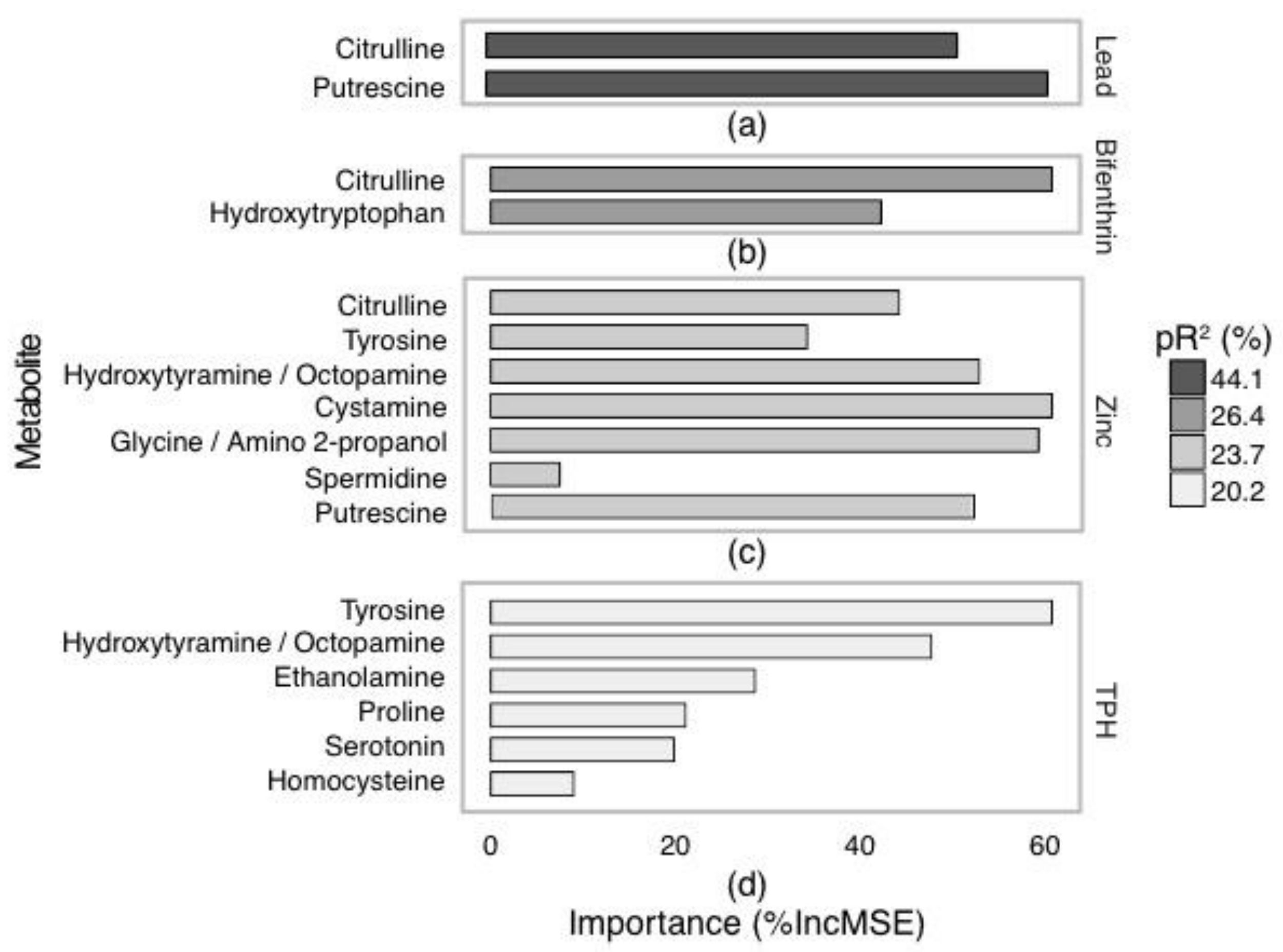
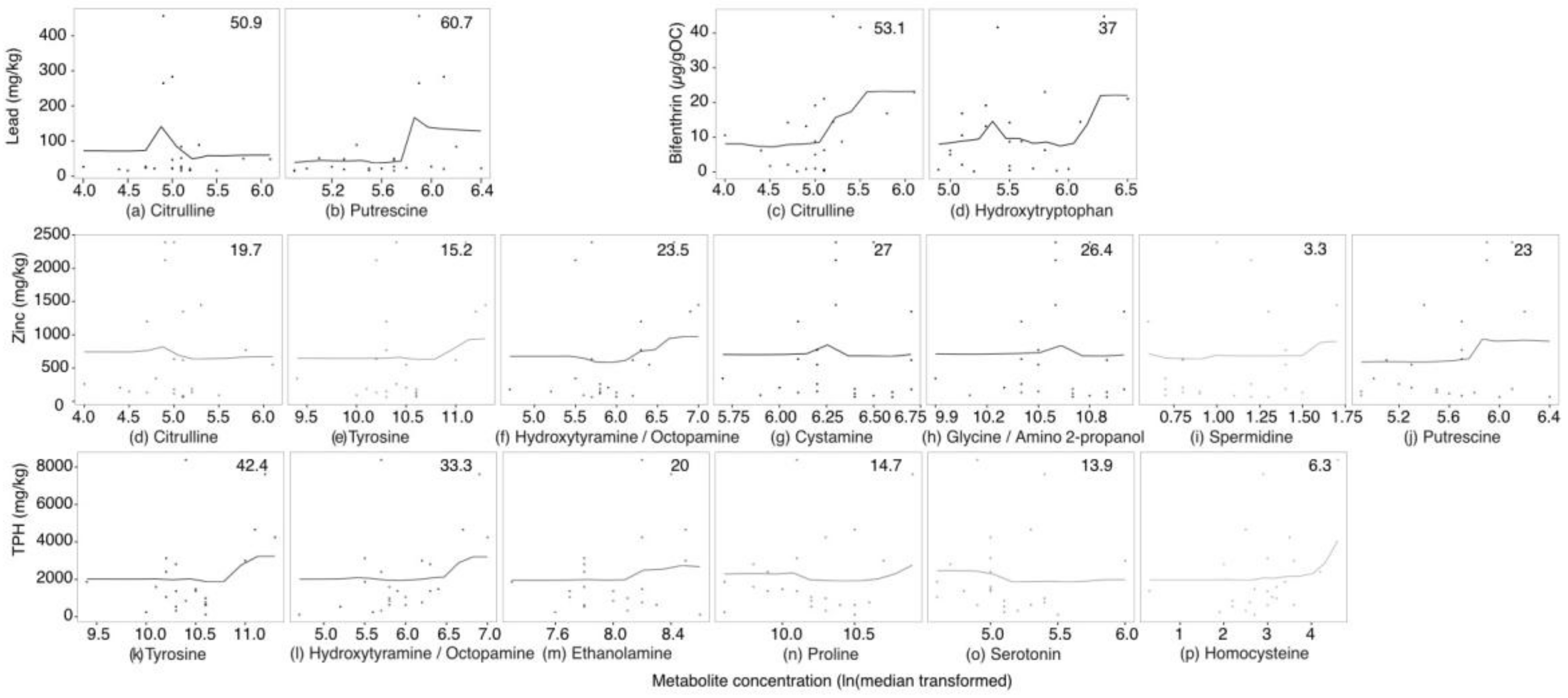
| Chemical Class | Contaminant | Detection Frequency (%) | <LOR | LOR < LT | LT < HT | >HT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbon | TPH * | 100 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 18 |
| Metal | Zinc * | 100 | 0 | 8 | 3 | 10 |
| Metal | Lead * | 100 | 0 | 14 | 4 | 3 |
| Metal | Nickel * | 100 | 0 | 7 | 11 | 3 |
| Metal | Copper | 100 | 0 | 12 | 8 | 1 |
| Metal | Chromium | 100 | 0 | 19 | 2 | 0 |
| Insecticide | Bifenthrin * | 90.5 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 18 |
| Metalloid | Arsenic | 76.2 | 5 | 14 | 2 | 0 |
| Insecticide | DEET * | 57.1 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| Antimicrobial | Triclosan * | 52.4 | 10 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Herbicide | Diuron * | 47.6 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| Metal | Mercury | 42.9 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| Metal | Cadmium | 33.3 | 14 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Insecticide | Permethrin * | 33.3 | 14 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Fungicide | Pyrimethanil | 19 | 17 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Metal | Silver | 9.5 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Metalloid | Antimony | 9.5 | 19 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Fungicide | Trifloxystrobin | 9.5 | 19 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Insecticide | Fenamiphos | 4.8 | 20 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Herbicide | Prometryn | 4.8 | 20 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeppe, K.J.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Townsend, K.R.; MacMahon, D.F.; Sharley, D.; Tull, D.L.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Pettigrove, V.; Long, S.M. Metabolomic Profiles of a Midge (Procladius villosimanus, Kieffer) Are Associated with Sediment Contamination in Urban Wetlands. Metabolites 2017, 7, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7040064
Jeppe KJ, Kouremenos KA, Townsend KR, MacMahon DF, Sharley D, Tull DL, Hoffmann AA, Pettigrove V, Long SM. Metabolomic Profiles of a Midge (Procladius villosimanus, Kieffer) Are Associated with Sediment Contamination in Urban Wetlands. Metabolites. 2017; 7(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeppe, Katherine J., Konstantinos A. Kouremenos, Kallie R. Townsend, Daniel F. MacMahon, David Sharley, Dedreia L. Tull, Ary A. Hoffmann, Vincent Pettigrove, and Sara M. Long. 2017. "Metabolomic Profiles of a Midge (Procladius villosimanus, Kieffer) Are Associated with Sediment Contamination in Urban Wetlands" Metabolites 7, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7040064
APA StyleJeppe, K. J., Kouremenos, K. A., Townsend, K. R., MacMahon, D. F., Sharley, D., Tull, D. L., Hoffmann, A. A., Pettigrove, V., & Long, S. M. (2017). Metabolomic Profiles of a Midge (Procladius villosimanus, Kieffer) Are Associated with Sediment Contamination in Urban Wetlands. Metabolites, 7(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7040064







