Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes—A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hypothalamic and Pituitary Dysfunction
2.1. Growth Hormone (GH)
2.1.1. Adult GH Deficiency
2.1.2. Acromegaly
2.2. Hyperprolactinemia
2.3. Vasopressin Disturbances
3. Phosphocalcic Metabolism Disturbances
3.1. Vitamin D Deficiency
3.2. Other Disturbances of Bone Metabolism
4. Thyroid Dysfunction
5. Reproductive System Dysfunction and NAFLD
5.1. Hypogonadism
5.2. Impact of Menopause on Liver Disease
5.3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
5.4. Important Sex Differences in NAFLD Development and Severity
6. Adrenal Gland Disorders and NAFLD
6.1. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS)
6.2. Cushing’s Syndrome and NAFLD
6.3. Pheochromocytoma
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Personalizing care for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: What are the research priorities? Pers. Med. 2014, 11, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singeap, A.M.; Stanciu, C.; Huiban, L.; Muzica, C.M.; Cuciureanu, T.; Girleanu, I.; Chiriac, S.; Zenovia, S.; Nastasa, R.; Sfarti, C.; et al. Association between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrinopathies: Clinical Implications. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 6678142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, L.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Endocrine causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11053–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlehurst, J.M.; Tomlinson, J.W. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in common endocrine disorders. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, R27–R37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebe, R.; Esposito, I.; Bock, H.H.; Vom Dahl, S.; Stindt, J.; Baumann, U.; Luedde, T.; Keitel, V. Diagnosis and management of secondary causes of steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1455–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, A.Y.; Merriam, G.R. Diagnosis and treatment of growth hormone deficiency in adults. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y. The Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Gola, M.; Karamouzis, I.; Giubbini, R.; Giustina, A. Cardiovascular risk in adult patients with growth hormone (GH) deficiency and following substitution with GH--an update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Monson, J.P. Adult GH deficiency throughout lifetime. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161 (Suppl. 1), S97–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nguyen, A.; Ricolfi, F.; Lemogne, B.; Aho, S.; Lemaire, S.; Bouillet, B.; Duvillard, L.; Denimal, D.; Fourmont, C.; Loffroy, R.; et al. Liver Fat Content in People with Pituitary Diseases: Influence of Serum IGF1 Levels. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, H.; Iguchi, G.; Murawaki, A.; Fukuoka, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Kaji, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Seo, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adult hypopituitary patients with GH deficiency and the impact of GH replacement therapy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Hamasaki, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Ejima, E.; Eguchi, K.; Nakao, K. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic steatosis in patients with adult onset growth hormone deficiency. Gut 2003, 52, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, E.; Swain, J.; Sanderson, S.; Krishnan, A.; Watt, K.; Charlton, M. Growth hormone, dehydroepiandrosterone and adiponectin levels in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An endocrine signature for advanced fibrosis in obese patients. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Loria, P.; Leonardi, F.; Ganazzi, D.; Carulli, N. Growth hormone plasma levels in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z.; Ginsberg, S.; Webb, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver in patients with Laron syndrome and GH gene deletion—Preliminary report. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2008, 18, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, M.; Krusenstjerna-Hafstrom, T.; Moller, L.; Christensen, B.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Pedersen, S.B.; Frystyk, J.; Jessen, N.; Hansen, T.K.; Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H.; et al. Fat content in liver and skeletal muscle changes in a reciprocal manner in patients with acromegaly during combination therapy with a somatostatin analog and a GH receptor antagonist: A randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, C.J.; Irwin, A.J.; Daousi, C.; McFarlane, I.A.; Joseph, F.; Bell, J.D.; Thomas, E.L.; Adams, V.L.; Kemp, G.J.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Hepatic steatosis, GH deficiency and the effects of GH replacement: A Liverpool magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sos, B.C.; Harris, C.; Nordstrom, S.M.; Tran, J.L.; Balazs, M.; Caplazi, P.; Febbraio, M.; Applegate, M.A.; Wagner, K.U.; Weiss, E.J. Abrogation of growth hormone secretion rescues fatty liver in mice with hepatocyte-specific deletion of JAK2. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, J.L.; Nelson, C.N.; Ishikawa, M.; Murray, L.A.; Kerr, L.M.; McPhee, T.R.; Powell, E.E.; Waters, M.J. GH-dependent STAT5 signaling plays an important role in hepatic lipid metabolism. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Fukuoka, H.; Iguchi, G.; Kitazawa, R.; Takahashi, Y. GH-independent IGF-I action is essential to prevent the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a GH-deficient rat model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoba-Chacon, J.; Majumdar, N.; List, E.O.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Frank, S.J.; Manzano, A.; Bartrons, R.; Puchowicz, M.; Kopchick, J.J.; Kineman, R.D. Growth Hormone Inhibits Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis in Adult Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3093–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.B.; Carmichael, J.D.; Kleinberg, D.L. Effects of low dose versus high dose human growth hormone on body composition and lipids in adults with GH deficiency: A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. Pituitary 2015, 18, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, P.; Griffin, S.; Nicoue-Beglah, M.; Haddad, N.; Balkau, B.; Chanson, P.; Metaanalysis of Blinded, R.P.-C.T. Impact of growth hormone (GH) treatment on cardiovascular risk factors in GH-deficient adults: A Metaanalysis of Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Iida, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Fukuoka, H.; Takeno, R.; Imanaka, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Seo, Y.; et al. Growth hormone reverses nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a patient with adult growth hormone deficiency. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Lora, A.L.; Zamora-Nava, L.E.; Marin-Rosas, D.L.; Klunder-Klunder, M.; Sanchez-Curiel, M.; Dies-Suarez, P. Resolution of fatty liver disease after growth hormone replacement in a pediatric survivor of thyroid cancer. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2019, 76, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, S.; Kanzaki, S.; Sato, M.; Kubo, T.; Seino, Y. Effect of growth hormone on fatty liver in panhypopituitarism. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 76, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujio, A.; Kawagishi, N.; Echizenya, T.; Tokodai, K.; Nakanishi, C.; Miyagi, S.; Sato, K.; Fujimori, K.; Ohuchi, N. Long-term survival with growth hormone replacement after liver transplantation of pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis complicating acquired hypopituitarism. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2015, 235, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roith, D.; Bondy, C.; Yakar, S.; Liu, J.L.; Butler, A. The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufinatscha, K.; Ress, C.; Folie, S.; Haas, S.; Salzmann, K.; Moser, P.; Dobner, J.; Weiss, G.; Iruzubieta, P.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; et al. Metabolic effects of reduced growth hormone action in fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichelaar, M.M.; Charlton, M.R. Decreased muscle mass in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New evidence of a link between growth hormone and fatty liver disease? Hepatology 2014, 59, 1668–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, K.; Imachi, H.; Lyu, J.; Dong, T.; Sato, S.; Ibata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yonezaki, K.; Matsunaga, T.; et al. IGF1 suppresses cholesterol accumulation in the liver of growth hormone-deficient mice via the activation of ABCA1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E1232–E1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, S.; Pucilowska, J.B.; Liu, S.; Rodriguez-Ortigosa, C.M.; Lund, P.K.; Brenner, D.A.; Fuller, C.R.; Simmons, J.G.; Pardo, A.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor I by activated hepatic stellate cells reduces fibrogenesis and enhances regeneration after liver injury. Gut 2005, 54, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Yonei, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Mori, K.; Kanemasa, K.; Imai, S.; Taketani, H.; Hara, T.; Seko, Y.; Ishiba, H.; et al. Lower levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 standard deviation score are associated with histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukropec, J.; Penesova, A.; Skopkova, M.; Pura, M.; Vlcek, M.; Radikova, Z.; Imrich, R.; Ukropcova, B.; Tajtakova, M.; Koska, J.; et al. Adipokine protein expression pattern in growth hormone deficiency predisposes to the increased fat cell size and the whole body metabolic derangements. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arturi, F.; Succurro, E.; Procopio, C.; Pedace, E.; Mannino, G.C.; Lugara, M.; Procopio, T.; Andreozzi, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Hribal, M.L.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with low circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1640–E1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.S.; Weiss, J.J.; Fourman, L.T.; Buckless, C.; Branch, K.L.; Lee, H.; Torriani, M.; Misra, M.; Stanley, T.L. Effect of recombinant human growth hormone on liver fat content in young adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2021, 94, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, H.; Iguchi, G.; Fukuoka, H.; Takahashi, M.; Suda, K.; Bando, H.; Matsumoto, R.; Yoshida, K.; Odake, Y.; Ogawa, W.; et al. IGF-I induces senescence of hepatic stellate cells and limits fibrosis in a p53-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.; Cabello-Verrugio, C.; Solis, N.; San Martin, D.; Cofre, C.; Pizarro, M.; Arab, J.P.; Abrigo, J.; Campos, F.; Irigoyen, B.; et al. Somatotropic Axis Dysfunction in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Beneficial Hepatic and Systemic Effects of Hormone Supplementation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrossians, P.; Daly, A.F.; Natchev, E.; Maione, L.; Blijdorp, K.; Sahnoun-Fathallah, M.; Auriemma, R.; Diallo, A.M.; Hulting, A.L.; Ferone, D.; et al. Acromegaly at diagnosis in 3173 patients from the Liege Acromegaly Survey (LAS) Database. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, N.; Jorgensen, J.O. Effects of growth hormone on glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism in human subjects. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winhofer, Y.; Wolf, P.; Krssak, M.; Wolfsberger, S.; Tura, A.; Pacini, G.; Gessl, A.; Raber, W.; Kukurova, I.J.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; et al. No evidence of ectopic lipid accumulation in the pathophysiology of the acromegalic cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4299–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsou-Tassopoulou, A.; Papapostoli-Sklavounou, I.; Krawczyk, M.; Friesenhahn-Ochs, B.; Weber, S.N.; Lammert, F.; Stokes, C.S. Hepatic steatosis in patients with acromegaly. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 2, e00090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, W.M.; Rowles, S.V.; Roberts, M.E.; Fode, F.K.; Besser, G.M.; Monson, J.P.; Trainer, P.J. Insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance improve in patients with acromegaly converted from depot octreotide to pegvisomant. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.C.; Doyle, N.; Ballesteros, M.; Waters, M.J.; Ho, K.K. Insulin regulation of human hepatic growth hormone receptors: Divergent effects on biosynthesis and surface translocation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4712–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neggers, S.J.; Kopchick, J.J.; Jorgensen, J.O.; van der Lely, A.J. Hypothesis: Extra-hepatic acromegaly: A new paradigm? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubeck, K.Z.; Madsen, M.; Andreasen, C.M.; Fisker, S.; Frystyk, J.; Jorgensen, J.O. Conventional and novel biomarkers of treatment outcome in patients with acromegaly: Discordant results after somatostatin analog treatment compared with surgery. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 163, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, A.; Bennett, W.F.; Rasch, R.; Kopchick, J.J.; Scarlett, J.A. Inhibitory effect of a growth hormone receptor antagonist (G120K-PEG) on renal enlargement, glomerular hypertrophy, and urinary albumin excretion in experimental diabetes in mice. Diabetes 1999, 48, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, L.; Norrelund, H.; Jessen, N.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Pedersen, S.B.; Gaylinn, B.D.; Liu, J.; Thorner, M.O.; Moller, N.; Lunde Jorgensen, J.O. Impact of growth hormone receptor blockade on substrate metabolism during fasting in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4524–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Droste, M.; Domberg, J.; Buchfelder, M.; Mann, K.; Schwanke, A.; Stalla, G.; Strasburger, C.J. Therapy of acromegalic patients exacerbated by concomitant type 2 diabetes requires higher pegvisomant doses to normalise IGF1 levels. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szendroedi, J.; Zwettler, E.; Schmid, A.I.; Chmelik, M.; Pacini, G.; Kacerovsky, G.; Smekal, G.; Nowotny, P.; Wagner, O.; Schnack, C.; et al. Reduced basal ATP synthetic flux of skeletal muscle in patients with previous acromegaly. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciresi, A.; Guarnotta, V.; Campo, D.; Giordano, C. Hepatic Steatosis Index in Acromegaly: Correlation with Insulin Resistance Regardless of the Disease Control. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 5421961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Young, J.; Binart, N. Prolactin—A pleiotropic factor in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macotela, Y.; Triebel, J.; Clapp, C. Time for a New Perspective on Prolactin in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemark, M.; Avril, I.; Fleenor, D.; Driscoll, P.; Petro, A.; Opara, E.; Kendall, W.; Oden, J.; Bridges, S.; Binart, N.; et al. Targeted deletion of the PRL receptor: Effects on islet development, insulin production, and glucose tolerance. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Herrera, X.; de Los Rios, E.A.; Diaz, J.M.; Lerma-Alvarado, R.M.; Martinez de la Escalera, L.; Lopez-Barrera, F.; Lemini, M.; Arnold, E.; Martinez de la Escalera, G.; Clapp, C.; et al. Prolactin Promotes Adipose Tissue Fitness and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Males. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serri, O.; Li, L.; Mamputu, J.C.; Beauchamp, M.C.; Maingrette, F.; Renier, G. The influences of hyperprolactinemia and obesity on cardiovascular risk markers: Effects of cabergoline therapy. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2006, 64, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berinder, K.; Nystrom, T.; Hoybye, C.; Hall, K.; Hulting, A.L. Insulin sensitivity and lipid profile in prolactinoma patients before and after normalization of prolactin by dopamine agonist therapy. Pituitary 2011, 14, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos Silva, C.M.; Barbosa, F.R.; Lima, G.A.; Warszawski, L.; Fontes, R.; Domingues, R.C.; Gadelha, M.R. BMI and metabolic profile in patients with prolactinoma before and after treatment with dopamine agonists. Obesity 2011, 19, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, M.; Kelly, P.A. Tissue distribution and regulation of rat prolactin receptor gene expression. Quantitative analysis by polymerase chain reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13337–13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ge, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Sun, X.; Chu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Prolactin improves hepatic steatosis via CD36 pathway. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Yao, Z.; Lu, J.; Song, Y.; He, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L. Ablation of prolactin receptor increases hepatic triglyceride accumulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Lv, Z.; Xia, T.; Chen, S.; Li, K.; Du, Y.; et al. PRLR regulates hepatic insulin sensitivity in mice via STAT5. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, G.M.; Lopez-Vicchi, F.; Ornstein, A.M.; Brie, B.; De Winne, C.; Fiore, E.; Perez-Millan, M.I.; Mazzolini, G.; Rubinstein, M.; Becu-Villalobos, D. Chronic hyperprolactinemia evoked by disruption of lactotrope dopamine D2 receptors impacts on liver and adipocyte genes related to glucose and insulin balance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E974–E988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Daily, J.W.; Kim, S.H. Serum prolactin concentrations determine whether they improve or impair beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2011, 27, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ-Crain, M. Vasopressin and Copeptin in health and disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Velho, G.; Bouby, N. Vasopressin and metabolic disorders: Translation from experimental models to clinical use. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhorning, S.; Melander, O. The Vasopressin System in the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiorenal Disease, and Hydration as a Potential Lifestyle Intervention. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72 (Suppl. 2), 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Enhorning, S.; Cimini, F.A.; Capoccia, D.; Chiappetta, C.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Leonetti, F.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Elevated plasma copeptin levels identify the presence and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hems, D.A.; Whitton, P.D. Stimulation by vasopressin of glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem. J. 1973, 136, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.A.; Robertson, S.M.; Olson, M.S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and vasoconstriction in the perfused rat liver by the thromboxane A2 analogue U-46619. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 4631–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.C.; Bardis, C.N.; Jansen, L.T.; Adams, J.D.; Kirkland, T.W.; Kavouras, S.A. Reduced water intake deteriorates glucose regulation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyama, M.; Aoyagi, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Birumachi, J.; Shigematsu, Y.; Kiwaki, K.; Tasaki, R.; Endo, F.; Tanoue, A. Hypermetabolism of fat in V1a vasopressin receptor knockout mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofe, A.M.; Williamson, D.H. Metabolic effects of vasopressin infusion in the starved rat. Reversal of ketonaemia. Biochem. J. 1983, 212, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Moustaid, N.; Wilkison, W.O.; Zemel, M.B. The agouti gene product inhibits lipolysis in human adipocytes via a Ca2+-dependent mechanism. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N.; Caldecourt, M.A.; Watts, D.I.; Sugden, M.C. Inhibition of lipogenesis by vasopressin and angiotensin II in glycogen-depleted hepatocytes. Biosci. Rep. 1983, 3, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taveau, C.; Chollet, C.; Waeckel, L.; Desposito, D.; Bichet, D.G.; Arthus, M.F.; Magnan, C.; Philippe, E.; Paradis, V.; Foufelle, F.; et al. Vasopressin and hydration play a major role in the development of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis in obese rats. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, F.; Aljohani, N. Vitamin D: Deficiency, sufficiency and toxicity. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3605–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, H.F. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1689S–1696S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, F.A.; Barchetta, I.; Carotti, S.; Bertoccini, L.; Baroni, M.G.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Cavallo, M.G.; Morini, S. Relationship between adipose tissue dysfunction, vitamin D deficiency and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3407–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Associations of vitamin D with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.; Kochhar, A. Interplay of vitamin D and metabolic syndrome: A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2016, 10, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovitch, S.; Dahan-Bachar, L.; Sharvit, E.; Weisman, Y.; Ben Tov, A.; Brazowski, E.; Reif, S. Vitamin D inhibits proliferation and profibrotic marker expression in hepatic stellate cells and decreases thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Gut 2011, 60, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilfuss, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Sydor, S.; Beste, M.; Bechmann, L.P.; Schlattjan, M.; Syn, W.K.; Wedemeyer, I.; Mathe, Z.; Jochum, C.; et al. Vitamin D counteracts fibrogenic TGF-beta signalling in human hepatic stellate cells both receptor-dependently and independently. Gut 2015, 64, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Scott, J.; Kim, K.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gonzales, N.M.; Wu, H.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Activation in Liver Macrophages Ameliorates Hepatic Inflammation, Steatosis, and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Hepatology 2019, 71, 1559–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, M.; Guzman, C.; Benet, M.; Sanchez-Campos, S.; Garcia-Monzon, C.; Gari, E.; Gatius, S.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Jover, R. Hepatocyte vitamin D receptor regulates lipid metabolism and mediates experimental diet-induced steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliades, M.; Spyrou, E.; Agrawal, N.; Lazo, M.; Brancati, F.L.; Potter, J.J.; Koteish, A.A.; Clark, J.M.; Guallar, E.; Hernaez, R. Meta-analysis: Vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S.; Chalasani, N. Serum vitamin D concentrations and unexplained elevation in ALT among US adults. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, M.; Spyrou, E. Vitamin D: A new player in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Scala, L.; Cigolini, M.; Zenari, L.; Falezza, G.; Arcaro, G. Associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 concentrations and liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 17, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wan, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, N.; Lin, S.; et al. Association between Vitamin D Status and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Study. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 2019, 65, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Neves, J.S.; Mendonça, F.; Silva, M.M.; Costa, C.; Cabral, P.M.; Guerreiro, V.; Lourenço, R.; Meira, P.; Salazar, D.; et al. The Impact of Vitamin D in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in Patients with Morbid Obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Hwang, S.G.; Rim, K.S. The Association between Vitamin D Insufficiency and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, C.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; Xia, F.; Cheng, J.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y. Vitamin D and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Bi-directional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. EBioMedicine 2018, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Del Ben, M.; Angelico, F.; Di Martino, M.; Fraioli, A.; La Torre, G.; Saulle, R.; Perri, L.; Morini, S.; Tiberti, C.; et al. No effects of oral vitamin D supplementation on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cui, M.; You, X.; Chen, M.; Piao, X.; Jin, G. A role of 1,25(OH)2D3 supplementation in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by choline-deficient diet. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, J.T.; Elangovan, H.; Stokes, R.A.; Gunton, J.E. Vitamin D and the Liver-Correlation or Cause? Nutrients 2018, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Danafar, F.; Eshraghian, A.; Omrani, G.R. Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Cavallo, M.G. Vitamin D Supplementation and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Present and Future. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Bjelakovic, M.; Gluud, C. Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD011564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, L.; Osborn, J.F.; Bonci, E.; Pierimarchi, P.; Chiesa, C. Association between Vitamin D Levels and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Potential Confounding Variables. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 310–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, R.; Radzki, R.P.; Bienko, M. Novel insights into the relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and osteoporosis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Lonardo, A.; Rossini, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and decreased bone mineral density: Is there a link? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggiogalle, E.; Donini, L.M.; Lenzi, A.; Chiesa, C.; Pacifico, L. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease connections with fat-free tissues: A focus on bone and skeletal muscle. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.F.; Lin, H.D.; Yan, H.M.; Bian, H.; Chang, X.X.; Zhang, L.S.; He, W.Y.; Gao, X. The association of liver fat content and serum alanine aminotransferase with bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly Chinese men and postmenopausal women. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Dai, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and osteoporotic fracture in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yun, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, Y.G.; Min, H.; Chung, E.; Bae, Y.S.; Ryou, I.S.; Cho, B. Association between bone mineral density and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Sheng, H.; Rui, X.F.; Cheng, X.Y.; Sheng, C.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Qu, S. Low bone mineral density in chinese adults with nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 396545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.W. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with low bone mass in postmenopausal women. Endocrine 2012, 42, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.P.; Nigam, P.; Misra, A.; Guleria, R.; Qadar Pasha, M.A. Independent associations of low 25 hydroxy vitamin D and high parathyroid hormonal levels with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian Indians residing in north India. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upala, S.; Jaruvongvanich, V.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Sanguankeo, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2017, 35, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, P.; Carulli, L.; Bertolotti, M.; Lonardo, A. Endocrine and liver interaction: The role of endocrine pathways in NASH. Nat Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Bonora, E.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Targher, G. Association Between Primary Hypothyroidism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Han, B.; Qi, X. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with thyroid function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Mantovani, A.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. NAFLD in Some Common Endocrine Diseases: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Principles of Diagnosis and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD: Evidence for a distinct disease entity? Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Viscarra, J.; Kim, S.J.; Sul, H.S. Transcriptional regulation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohinc, B.N.; Michelotti, G.; Xie, G.; Pang, H.; Suzuki, A.; Guy, C.D.; Piercy, D.; Kruger, L.; Swiderska-Syn, M.; Machado, M.; et al. Repair-related activation of hedgehog signaling in stromal cells promotes intrahepatic hypothyroidism. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4591–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Bruinstroop, E.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.F.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Chen, L.M.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Huang, W.; Xie, Z.X.; Tang, X.; Sun, J. Myricetin alleviated hepatic steatosis by acting on microRNA-146b/thyroid hormone receptor b pathway in high-fat diet fed C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Yamamoto, N.; Inoue, A.; Morisawa, S. Fatty acyl-CoAs are potent inhibitors of the nuclear thyroid hormone receptor in vitro. J. Biochem. 1990, 107, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, M.D.; Cable, E.E.; Ito, B.R.; Jiang, H.; Fujitaki, J.M.; Finn, P.D.; Zhang, B.H.; Hou, J.; Boyer, S.H.; van Poelje, P.D.; et al. Targeting thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonists to the liver reduces cholesterol and triglycerides and improves the therapeutic index. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15490–15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, E.E.; Finn, P.D.; Stebbins, J.W.; Hou, J.; Ito, B.R.; van Poelje, P.D.; Linemeyer, D.L.; Erion, M.D. Reduction of hepatic steatosis in rats and mice after treatment with a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor agonist. Hepatology 2009, 49, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, M.P.; Lionetti, L.; Moreno, M.; Lombardi, A.; De Lange, P.; Antonelli, A.; Lanni, A.; Cavaliere, G.; Barletta, A.; Goglia, F. 3,5-diiodo-l-thyronine, by modulating mitochondrial functions, reverses hepatic fat accumulation in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinstroop, E.; Dalan, R.; Cao, Y.; Bee, Y.M.; Chandran, K.; Cho, L.W.; Soh, S.B.; Teo, E.K.; Toh, S.A.; Leow, M.K.S.; et al. Low-Dose Levothyroxine Reduces Intrahepatic Lipid Content in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and NAFLD. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Guy, C.D.; Zhou, R.; Moylan, C.A.; Frias, J.P.; Alkhouri, N.; Bansal, M.B.; Baum, S.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Qi, X. Thyroid Function and Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Euthyroid Subjects. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, E.H.; van Tienhoven-Wind, L.J.; Amini, M.; Schreuder, T.C.; Faber, K.N.; Blokzijl, H.; Dullaart, R.P. Higher free triiodothyronine is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in euthyroid subjects: The Lifelines Cohort Study. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2017, 67, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Neves, J.S.; Mendonca, F.; Silva, M.M.; Costa, C.; Cabral, P.M.; Guerreiro, V.; Lourenco, R.; Meira, P.; Salazar, D.; et al. Thyroid Function and the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Morbid Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 572128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Not Associated with Thyroid Hormone Levels and Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delitala, A.P.; Scuteri, A.; Maioli, M.; Mangatia, P.; Vilardi, L.; Erre, G.L. Subclinical hypothyroidism and cardiovascular risk factors. Minerva Med. 2019, 110, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Chaker, L.; Plompen, E.P.; Hofman, A.; Dehghan, A.; Franco, O.H.; Janssen, H.L.; Darwish Murad, S.; Peeters, R.P. Thyroid Function and the Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Rotterdam Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, M.A.; Puliga, E.; Cabras, L.; Sulas, P.; Petrelli, A.; Perra, A.; Ledda-Columbano, G.M.; Morandi, A.; Merlin, S.; Orru, C.; et al. Thyroid hormone inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via induction of differentiation and metabolic reprogramming. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, T.; Matsuura, B.; Furukawa, S.; Todo, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshida, O.; Imai, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirooka, M.; et al. Hyperthyroidism Improves the Pathological Condition of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Case of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis with Graves’ Disease. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 2019–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Filippi, S.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M.; Corona, G. Metabolic Syndrome in Male Hypogonadism. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 49, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, A.A.; Quinton, R. The Metabolic Syndrome in Central Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 49, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, R. Metabolic Syndrome in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 49, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, A.A.; Pownall, H.J.; Hamilton, D.J. Estrogen: An emerging regulator of insulin action and mitochondrial function. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 916585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Samuel, V.T.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2014, 510, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Shi, H. Sex Hormones and Their Receptors Regulate Liver Energy Homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 294278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, J.S.; Lee, H.; Burnett-Bowie, S.A.; Pallais, J.C.; Yu, E.W.; Borges, L.F.; Jones, B.F.; Barry, C.V.; Wulczyn, K.E.; Thomas, B.J.; et al. Gonadal steroids and body composition, strength, and sexual function in men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Rahman, N.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Li, N.; et al. Differential effects of estrogen/androgen on the prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the male rat. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kur, P.; Kolasa-Wolosiuk, A.; Misiakiewicz-Has, K.; Wiszniewska, B. Sex Hormone-Dependent Physiology and Diseases of Liver. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.; Sprung, V.S.; Pugh, C.J.; Daousi, C.; Irwin, A.; Aziz, N.; Adams, V.L.; Thomas, E.L.; Bell, J.D.; Kemp, G.J.; et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome with hyperandrogenism is characterized by an increased risk of hepatic steatosis compared to nonhyperandrogenic PCOS phenotypes and healthy controls, independent of obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, L.; Kempegowda, P.; Arlt, W.; O’Reilly, M.W. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: The sexually dimorphic role of androgens in human metabolic disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, R125–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Alvarez-Blasco, F.; Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Luque-Ramirez, M. The striking similarities in the metabolic associations of female androgen excess and male androgen deficiency. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintziori, G.; Poulakos, P.; Tsametis, C.; Goulis, D.G. Hypogonadism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017, 42, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbonetti, A.; Caterina Vassallo, M.R.; Cotugno, M.; Felzani, G.; Francavilla, S.; Francavilla, F. Low testosterone and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence for their independent association in men with chronic spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2016, 39, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.K.; Koo, H.S.; Haam, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Park, K.C.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.S. Prediction of prevalent but not incident non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by levels of serum testosterone. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, M.; Angulo, P.; Chalasani, N.; Merriman, R.; Viker, K.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Sanderson, S.; Gawrieh, S.; Krishnan, A.; Lindor, K. Low circulating levels of dehydroepiandrosterone in histologically advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2008, 47, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.M.; Zhou, Y.C.; Ram, P.A.; Lee, S.S.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Waxman, D.J. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha required for gene induction by dehydroepiandrosterone-3 beta-sulfate. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, H.F.; Hussein, A.M.; Eid, E.A.; AlKhateeb, M. Possible mechanisms underlying fatty liver in a rat model of male hypogonadism: A protective role for testosterone. Steroids 2018, 135, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yanase, T.; Nomura, M.; Okabe, T.; Goto, K.; Sato, T.; Kawano, H.; Kato, S.; Nawata, H. Androgen receptor null male mice develop late-onset obesity caused by decreased energy expenditure and lipolytic activity but show normal insulin sensitivity with high adiponectin secretion. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traish, A.M.; Haider, A.; Doros, G.; Saad, F. Long-term testosterone therapy in hypogonadal men ameliorates elements of the metabolic syndrome: An observational, long-term registry study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.B.; Guerra-Junior, G.; Baptista, M.T.; Marques-de-Faria, A.P.; Lemos-Marini, S.H.; Maciel-Guerra, A.T. Turner syndrome: A pediatric diagnosis frequently made by non-pediatricians. J. Pediatr. 2010, 86, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elsheikh, M.; Hodgson, H.J.; Wass, J.A.; Conway, G.S. Hormone replacement therapy may improve hepatic function in women with Turner’s syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2001, 55, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, O.; Ostberg, J.; Conway, G.S. Liver dysfunction in Turner’s syndrome: Prevalence, natural history and effect of exogenous oestrogen. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2008, 69, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Kiso, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Chatani, N.; Kizu, T.; Hamano, M.; Tsubakio, M.; Takemura, T.; Ezaki, H.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Estrogen deficiency worsens steatohepatitis in mice fed high-fat and high-cholesterol diet. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G1031–G1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambliss, K.L.; Barrera, J.; Umetani, M.; Umetani, J.; Kim, S.H.; Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Huang, L.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Mineo, C.; et al. Nonnuclear Estrogen Receptor Activation Improves Hepatic Steatosis in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klair, J.S.; Yang, J.D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Guy, C.D.; Gill, R.M.; Yates, K.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Lavine, J.E.; Clark, J.M.; Diehl, A.M.; et al. A longer duration of estrogen deficiency increases fibrosis risk among postmenopausal women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2016, 64, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Watanabe, N.; Numata, M.; Ogawa, T.; Matsuzaki, S. Increase in the prevalence of fatty liver in Japan over the past 12 years: Analysis of clinical background. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Grobe, Y.; Ponciano-Rodriguez, G.; Ramos, M.H.; Uribe, M.; Mendez-Sanchez, N. Prevalence of non alcoholic fatty liver disease in premenopausal, posmenopausal and polycystic ovary syndrome women. The role of estrogens. Ann. Hepatol. 2010, 9, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Gualtieri, M.R.; Cahoon, S.S.; Jung, C.E.; Paulson, R.J.; Shoupe, D.; Muderspach, L.I.; Wakatsuki, A.; Wright, J.D.; Roman, L.D. Surgical menopause and increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in endometrial cancer. Menopause 2016, 23, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Keach, J.C.; Batts, K.P.; Lindor, K.D. Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Pang, H.; Guy, C.D.; Smith, A.D.; Diehl, A.M.; Suzuki, A. Gender and menopause impact severity of fibrosis among patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Abdelmalek, M.F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in women. Womens Health (Lond.) 2009, 5, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotterdam, E.A.-S.P.c.w.g. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, B.O.; Bozdag, G.; Yapici, Z.; Esinler, I.; Yarali, H. Prevalence, phenotype and cardiometabolic risk of polycystic ovary syndrome under different diagnostic criteria. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Rossini, M.; Lonardo, A. Evidence that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and polycystic ovary syndrome are associated by necessity rather than chance: A novel hepato-ovarian axis? Endocrine 2016, 51, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, X.Y.; Shi, R.X.; Liu, S.F.; Wang, X.Y. A potential link between polycystic ovary syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update meta-analysis. Reprod. Health 2018, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setji, T.L.; Holland, N.D.; Sanders, L.L.; Pereira, K.C.; Diehl, A.M.; Brown, A.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarendran, B.; O’Reilly, M.W.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Toulis, K.A.; Gokhale, K.M.; Sitch, A.J.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Coomarasamy, A.; Arlt, W.; Nirantharakumar, K. Polycystic ovary syndrome, androgen excess, and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in women: A longitudinal study based on a United Kingdom primary care database. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, W.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Tao, T. Role of Androgen in Liver Fat Content in Women: Metabolically Advantageous or Disadvantageous? Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, D.; Yim, J.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Han, K.H.; Kim, S.M.; Hwang, K.R.; Ku, S.Y.; Suh, C.S.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome with hyperandrogenism as a risk factor for non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z. The clinical characteristics and etiological study of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese women with PCOS. Iran J. Reprod. Med. 2013, 11, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Legro, R.S.; Arslanian, S.A.; Ehrmann, D.A.; Hoeger, K.M.; Murad, M.H.; Pasquali, R.; Welt, C.K.; Endocrine, S. Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4565–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossing, S.; Nylander, M.; Chabanova, E.; Frystyk, J.; Holst, J.J.; Kistorp, C.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J. Effect of liraglutide on ectopic fat in polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, D.T.; Glasier, A.F. Hormonal contraception. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Lazo, M.; Koteish, A.; Kao, W.H.; Shih, M.H.; Bonekamp, S.; Hernaez, R.; Clark, J.M. Oral contraceptive pill use is associated with reduced odds of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in menstruating women: Results from NHANES III. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; LEAN trial team; Abouda, G.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Suzuki, A. Sexual Dimorphism of NAFLD in Adults. Focus on Clinical Aspects and Implications for Practice and Translational Research. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex Differences in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: State of the Art and Identification of Research Gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, B.B.; Carroll, H.A.; Lustyk, M.K. Gender Differences in Exercise Habits and Quality of Life Reports: Assessing the Moderating Effects of Reasons for Exercise. Int. J. Lib. Arts Soc. Sci. 2014, 2, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Castellanos, M.; Aller-de la Fuente, R.; Metwally, M.; Eslam, M.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Alvarez-Quinones Sanz, M.; Conde-Martin, A.F.; et al. Fibrosis Severity as a Determinant of Cause-Specific Mortality in Patients With Advanced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multi-National Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 443–457.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Chow, P.K.H.; Suzuki, A. Sex disparity in hepatocellular carcinoma owing to NAFLD and non-NAFLD etiology: Epidemiological findings and pathobiological mechanisms. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascha, M.S.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Feldstein, A.F.; Zein, N.N. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Komorizono, Y.; Koike, K.; Arii, S.; Imai, Y.; Shima, T.; Kanbara, Y.; Saibara, T.; Mori, T.; et al. Characteristics of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis who develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Marriott, I.; Fish, E.N. Sex-based differences in immune function and responses to vaccination. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugler, W.E.; Sakurai, T.; Kim, S.; Maeda, S.; Kim, K.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Karin, M. Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science 2007, 317, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itagaki, T.; Shimizu, I.; Cheng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Oshio, A.; Tamaki, K.; Fukuno, H.; Honda, H.; Okamura, Y.; Ito, S. Opposing effects of oestradiol and progesterone on intracellular pathways and activation processes in the oxidative stress induced activation of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells. Gut 2005, 54, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.; Meinert Larsen, T.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.; Macdonald, I.; Martinez, J.A.; Handjiev, S.; Poppitt, S.; Hansen, S.; Ritz, C.; Astrup, A.; et al. Men and women respond differently to rapid weight loss: Metabolic outcomes of a multi-centre intervention study after a low-energy diet in 2500 overweight, individuals with pre-diabetes (PREVIEW). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2840–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Tsiaousi, E. The role of adiponectin in the pathogenesis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneman, P.; Janssens, A.C.; Zillikens, M.C.; Frolich, M.; Frants, R.R.; Oostra, B.A.; van Duijn, C.M.; van Dijk, K.W. Menopause impacts the relation of plasma adiponectin levels with the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 267, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemke, F.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: Lessons from translational research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 258S–261S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin and leptin in the diagnosis and therapy of NAFLD. Metabolism 2020, 103, 154028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Toulis, K.A.; Goulis, D.G.; Zavos, C.; Kountouras, J. Serum total adiponectin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2011, 60, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin as a target for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with thiazolidinediones: A systematic review. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elasy, T.A.; Griffin, M. Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: A consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association: Response to Nesto. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, E.; Adachi, H.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Hirai, Y.; Enomoto, M.; Fukami, A.; Otsuka, M.; Kumagae, S.; Nanjo, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; et al. Plasma aldosterone levels and development of insulin resistance: Prospective study in a general population. Hypertension 2011, 58, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.A.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Habibi, J.; Wei, Y.; Lastra, G.; Manrique, C.; Stas, S.; Sowers, J.R. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and oxidative stress in cardiovascular insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H2009–H2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Muntner, P.; Hamm, L.L.; Fonseca, V.; Batuman, V.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Insulin resistance and risk of chronic kidney disease in nondiabetic US adults. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastra-Lastra, G.; Sowers, J.R.; Restrepo-Erazo, K.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.; Lastra-Gonzalez, G. Role of aldosterone and angiotensin II in insulin resistance: An update. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2009, 71, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Yu, C. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypokalemia in Primary Aldosteronism Among Chinese Population. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 565714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, R.; Yoshiji, H.; Ikenaka, Y.; Kaji, K.; Shirai, Y.; Aihara, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Namisaki, T.; Kitade, M.; Yoshii, J.; et al. Selective aldosterone blocker ameliorates the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Zafeiriadou, E.; Patsiaoura, K.; Katsiki, E.; Deretzi, G.; Zavos, C.; Tsarouchas, G.; Rakitzi, P.; Slavakis, A. Effect of spironolactone and vitamin E on serum metabolic parameters and insulin resistance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2011, 12, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, M.; Solis, N.; Quintero, P.; Barrera, F.; Cabrera, D.; Rojas-de Santiago, P.; Arab, J.P.; Padilla, O.; Roa, J.C.; Moshage, H.; et al. Beneficial effects of mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Blackshear, C.; Subauste, J.S.; Esfandiari, N.H.; Oral, E.A.; Subauste, A.R. Fatty Liver Disease, Women, and Aldosterone: Finding a Link in the Jackson Heart Study. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wu, C.; Howatt, D.A.; Balakrishnan, A.; Moorleghen, J.J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, M.; Graham, M.J.; Mullick, A.E.; Crooke, R.M.; et al. Angiotensinogen Exerts Effects Independent of Angiotensin II. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, T.W. Treating the metabolic syndrome: Telmisartan as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activator. Acta Diabetol. 2005, 42 (Suppl. 1), S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Tomita, K.; Kawai, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Shimada, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Hirose, H.; Ebinuma, H.; Irie, J.; Ojiro, K.; et al. Effect of Telmisartan or Losartan for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Fatty Liver Protection Trial by Telmisartan or Losartan Study (FANTASY). Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 587140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokohama, S.; Yoneda, M.; Haneda, M.; Okamoto, S.; Okada, M.; Aso, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Tokusashi, Y.; Miyokawa, N.; Nakamura, K. Therapeutic efficacy of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallo, F.; Dalla Pozza, A.; Tecchio, M.; Tona, F.; Sonino, N.; Ermani, M.; Catena, C.; Bertello, C.; Mulatero, P.; Sabato, N.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in primary aldosteronism: A pilot study. Am. J. Hypertens 2010, 23, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Su, T.; Li, M.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Ning, G. Serum potassium level is associated with metabolic syndrome: A population-based study. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockall, A.G.; Sohaib, S.A.; Evans, D.; Kaltsas, G.; Isidori, A.M.; Monson, J.P.; Besser, G.M.; Grossman, A.B.; Reznek, R.H. Hepatic steatosis in Cushing’s syndrome: A radiological assessment using computed tomography. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Cui, S.; Pang, C.; Lu, L.; Pang, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Xing, B. Demographic Characteristics, Etiology, and Comorbidities of Patients with Cushing’s Syndrome: A 10-Year Retrospective Study at a Large General Hospital in China. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 7159696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppini, G.; Targher, G.; Venturi, C.; Zamboni, C.; Muggeo, M. Relationship of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis to overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test in obese individuals. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2004, 61, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Zenari, L.; Falezza, G. Associations between liver histology and cortisol secretion in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2006, 64, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, M.K.; Stalla, G.K.; Stieg, M.R. Investigating the role of cortisol and growth hormone in fatty liver development: Fatty liver index in patients with pituitary adenomas. Pituitary 2016, 19, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza A., M.; Beaudry, J.L.; Szigiato, A.A.; Trumble, S.J.; Snook, L.A.; Bonen, A.; Giacca, A.; Riddell, M.C. Consumption of a high-fat diet rapidly exacerbates the development of fatty liver disease that occurs with chronically elevated glucocorticoids. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G850–G863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, R.; Okuno, Y.; Mukai, K.; Kitamura, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Onodera, T.; Murata, M.; Fukuhara, A.; Imamura, R.; Miyagawa, Y.; et al. Adipocyte GR Inhibits Healthy Adipose Expansion Through Multiple Mechanisms in Cushing Syndrome. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, C.E.; Renquist, B.J. Hepatic lipid accumulation: Cause and consequence of dysregulated glucoregulatory hormones. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, R1–R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia, R.; Riquelme, A.; Baudrand, R.; Carvajal, C.A.; Morales, M.; Solis, N.; Pizarro, M.; Escalona, A.; Carrasco, G.; Boza, C.; et al. Overexpression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in visceral adipose tissue and portal hypercortisolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad Sakamuri, S.S.; Sukapaka, M.; Prathipati, V.K.; Nemani, H.; Putcha, U.K.; Pothana, S.; Koppala, S.R.; Ponday, L.R.; Acharya, V.; Veetill, G.N.; et al. Carbenoxolone treatment ameliorated metabolic syndrome in WNIN/Ob obese rats, but induced severe fat loss and glucose intolerance in lean rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hernandez-Ono, A.; Crooke, R.M.; Graham, M.J.; Ginsberg, H.N. Effects of antisense-mediated inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.E.; Barat, P.; Di Rollo, E.M.; Rees, G.A.; Weldin, B.A.; Rog-Zielinska, E.A.; MacFarlane, D.P.; Walker, B.R.; Andrew, R. 5alpha-Reductase type 1 deficiency or inhibition predisposes to insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and liver fibrosis in rodents. Diabetes 2015, 64, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Rabbitt, E.; Brady, T.; Brown, C.; Guest, P.; Bujalska, I.J.; Doig, C.; Newsome, P.N.; Hubscher, S.; Elias, E.; et al. A switch in hepatic cortisol metabolism across the spectrum of non alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigala, B.; McKee, C.; Soeda, J.; Pazienza, V.; Morgan, M.; Lin, C.I.; Selden, C.; Vander Borght, S.; Mazzoccoli, G.; Roskams, T.; et al. Sympathetic nervous system catecholamines and neuropeptide Y neurotransmitters are upregulated in human NAFLD and modulate the fibrogenic function of hepatic stellate cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, M.; Arab, J.P.; Barrera, F.; Kaufmann, B.; Valenti, L.; Feldstein, A.E. Insights into Nonalcoholic Fatty-Liver Disease Heterogeneity. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Arab, J.P.; Arrese, M. Perspectives on Precision Medicine Approaches to NAFLD Diagnosis and Management. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 2130–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
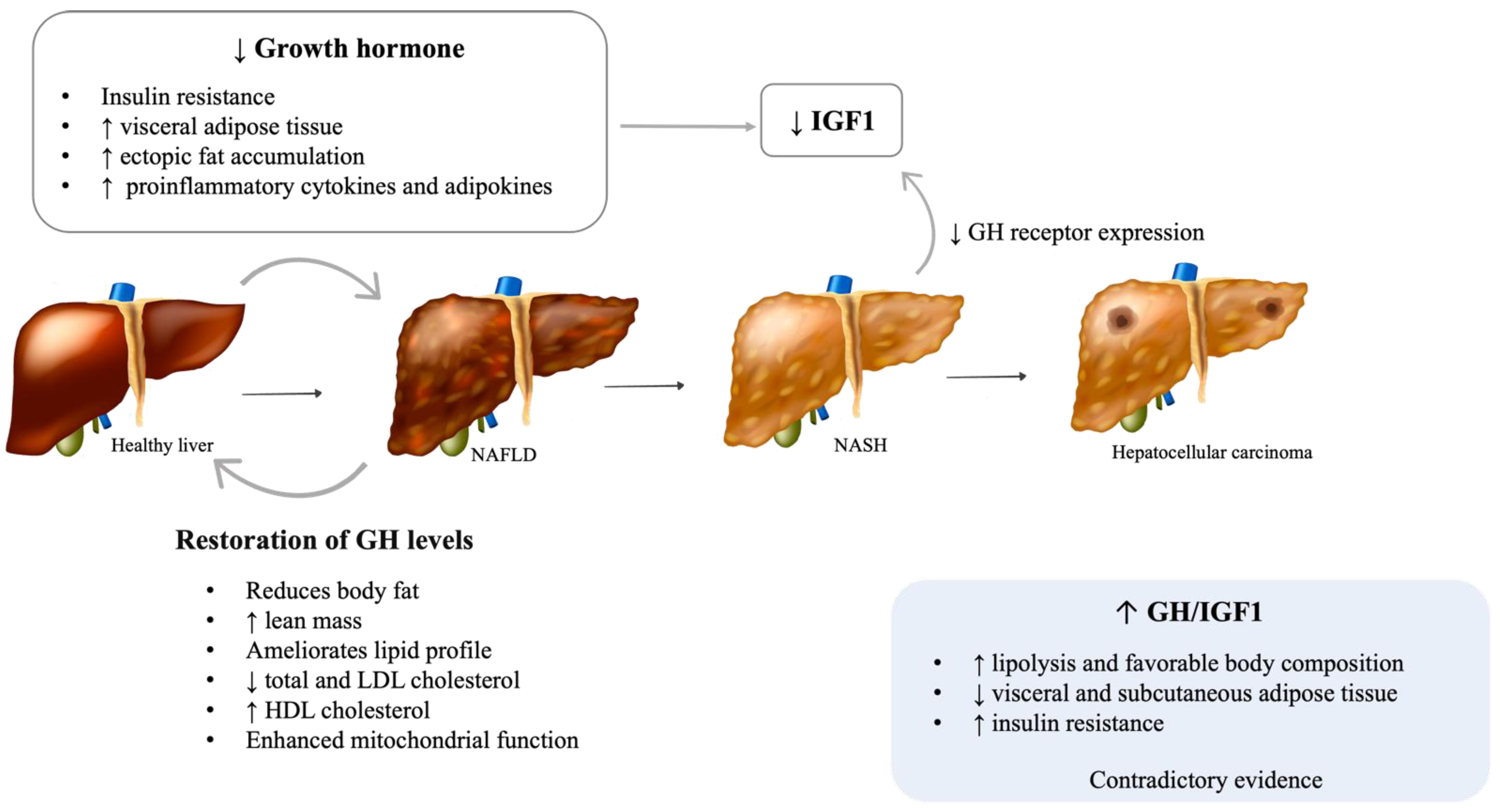

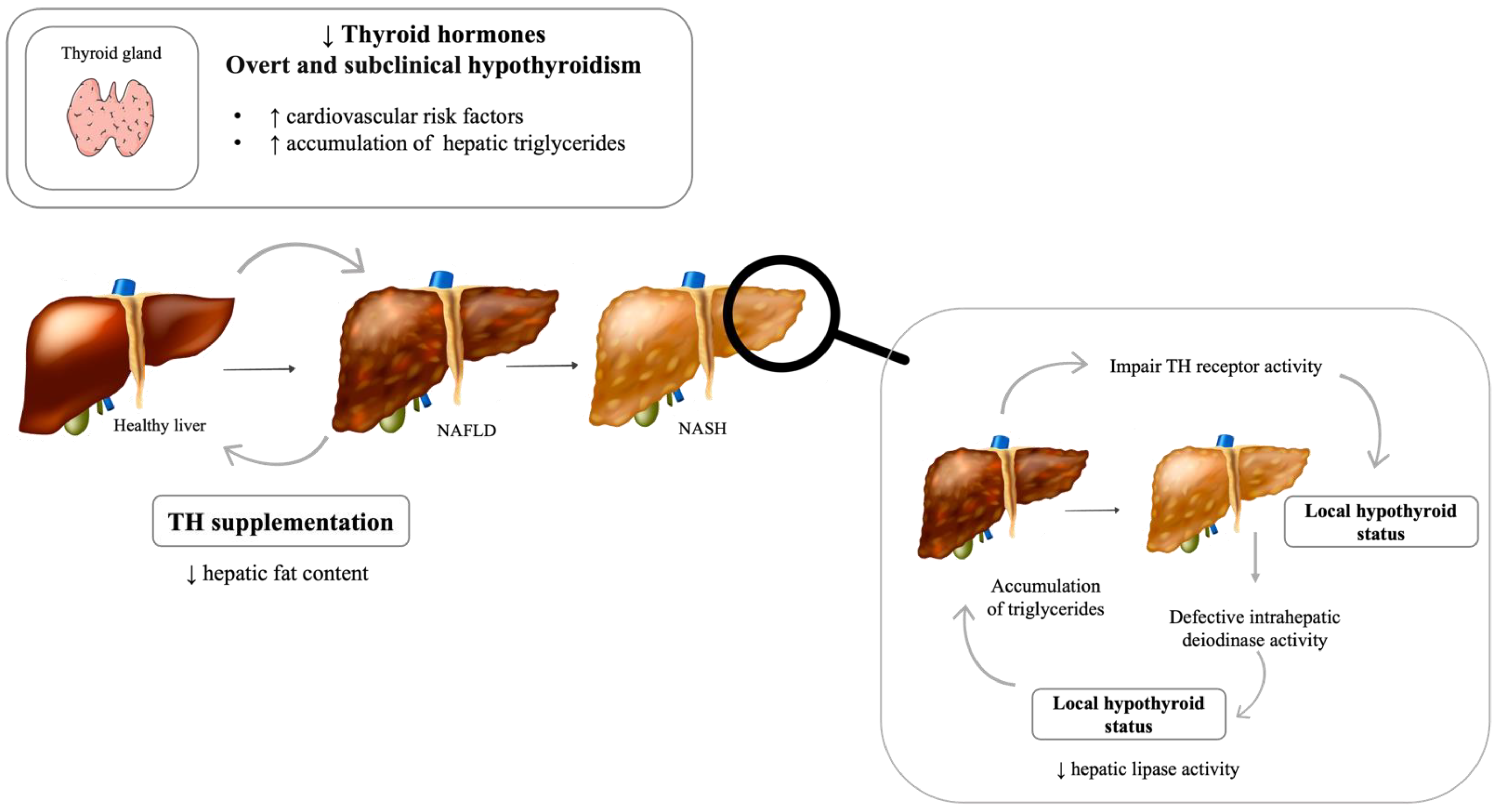
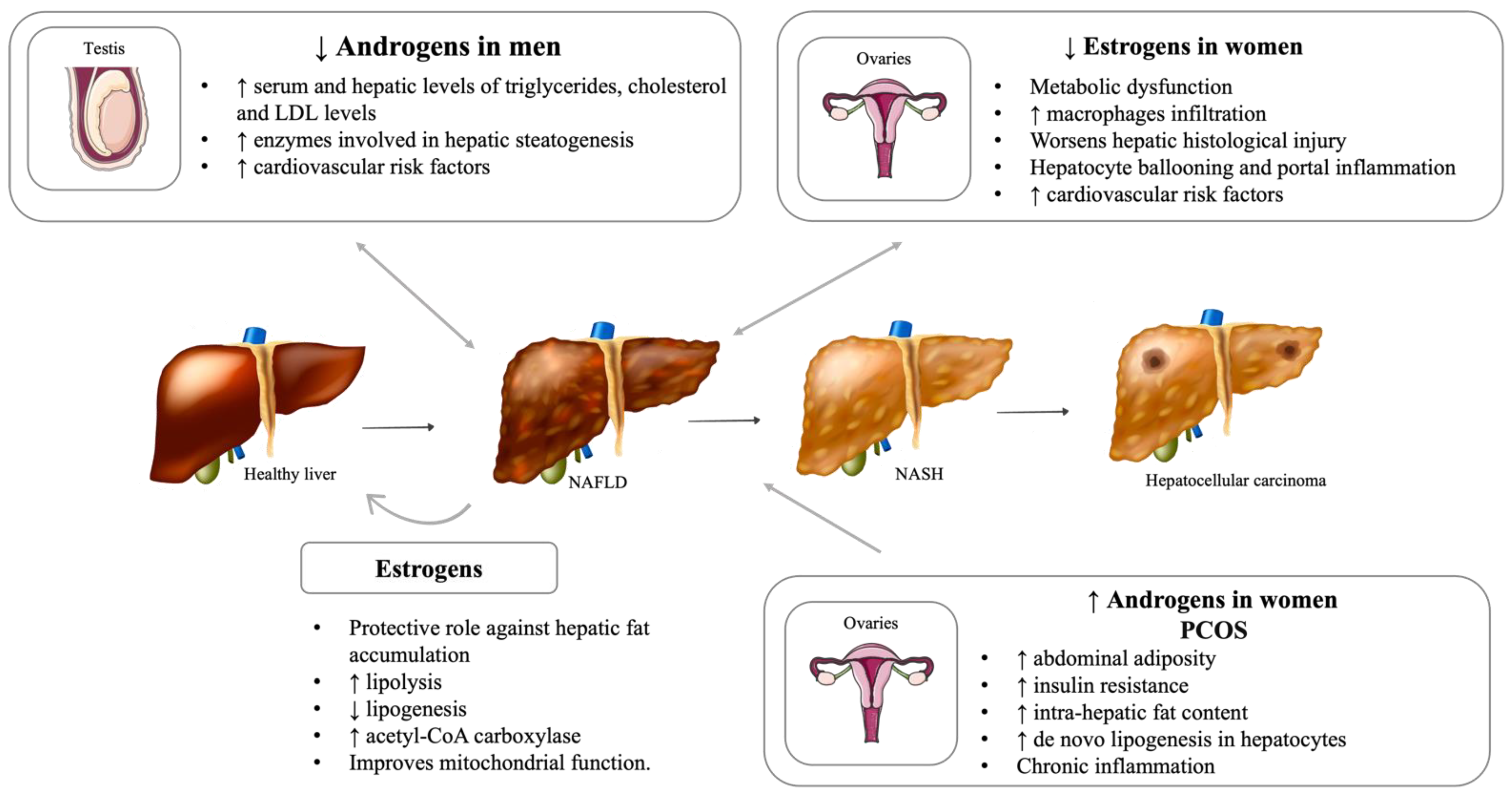

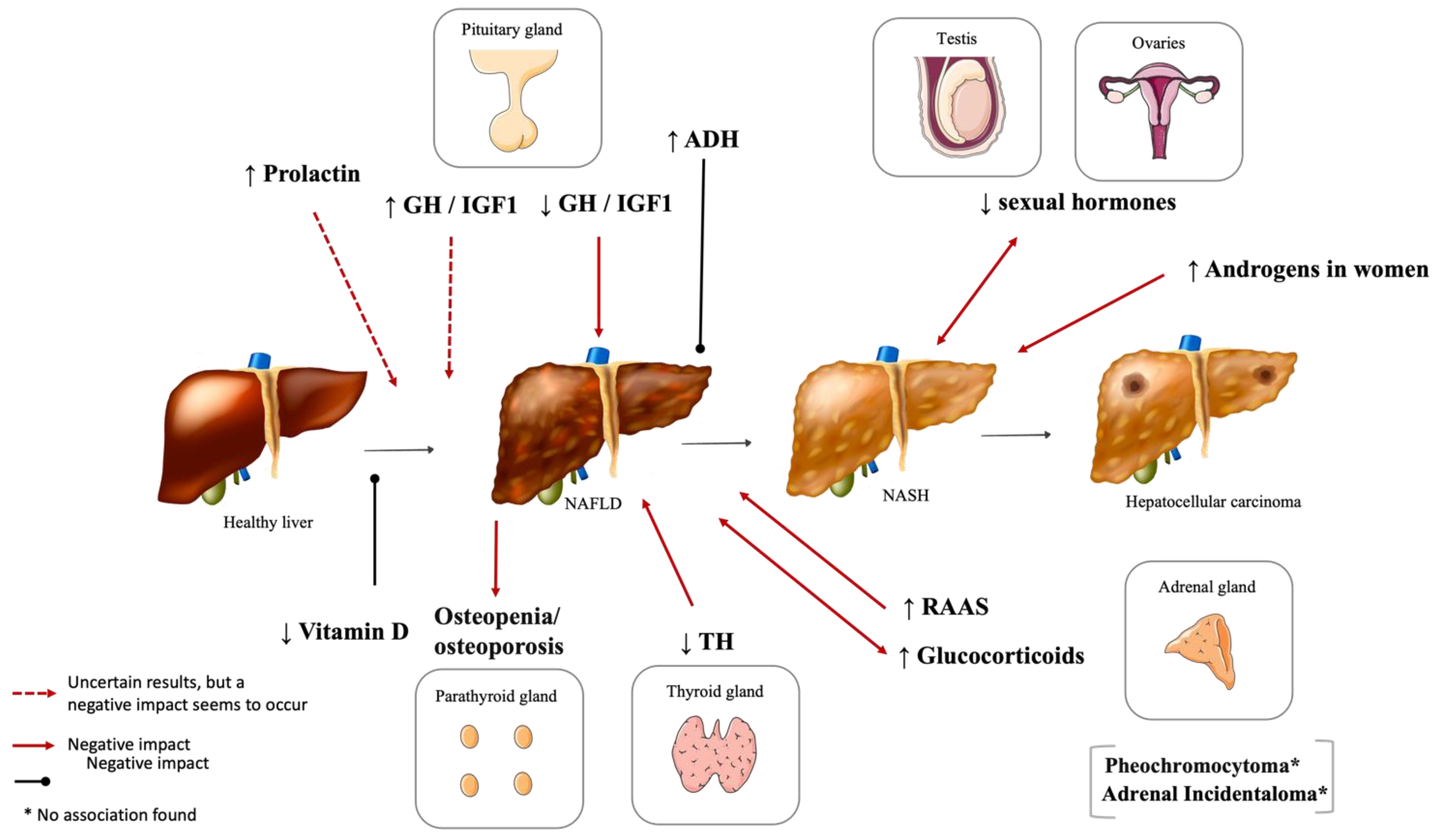
| Hormone | Plasmatic Levels | Effect | Human Studies | Animal Studies | In Vitro Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth hormone/IGF1 | Increased | ↑ lipolysis and lean body mass | Maison, Griffin et al. 2004, Petrossians, Daly et al. 2017 | ||
| ↓ visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue | Petrossians, Daly et al. 2017, Koutsou-Tassopoulou, Papapostoli-Sklavounou et al. 2019 | ||||
| Impairment of lipid profile and ↑ insulin resistance | Moller and Jorgensen 2009 | ||||
| Decreased | Hepatic steatosis | Ichikawa, Hamasaki et al. 2003, Laron, Ginsberg et al. 2008, Nishizawa, Iguchi et al. 2012, Nguyen, Ricolfi et al. 2018 | Sos, Harris et al. 2011, Nishizawa, Takahashi et al. 2012, Cordoba-Chacon, Majumdar et al. 2015 | ||
| ↓ Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis | Sumida, Yonei et al. 2015 | ||||
| ↑ proinflammatory cytokines and adipokines | Ukropec, Penesova et al. 2008 | ||||
| Restoration of GH levels | ↑ lean body mass and ↓ body fat | Newman, Carmichael et al. 2015 | |||
| Improvement of lipid profile | Newman, Carmichael et al. 2015 | ||||
| Improvement of hepatic injury | Nishizawa, Iguchi et al. 2012, Takahashi, Iida et al. 2007 | Nishizawa, Takahashi et al. 2012 | |||
| Prolactin | Increased | Weight gain | Serri, Li et al. 2006 | ||
| ↓ insulin sensitivity and hyperinsulinemia | Serri, Li et al. 2006 | ||||
| ↑ hepatic triglyceride content and de novo lipogenesis | Park, Kim et al. 2011, Luque, Lopez-Vicchi et al. 2016 | ||||
| Decreased | ↓ hepatic cholesterol and triacylglycerol | Zhang, Ge et al. 2018 | |||
| ↓ expression of genes involved in lipogenesis Hepatic steatosis | Zhang, Ge et al. 2018 | ||||
| Restoration of prolactin levels | Weight loss | Berinder, Nystrom et al. 2011 | |||
| ↑ insulin sensitivity and glycemic control | dos Santos Silva, Barbosa et al. 2011 | ||||
| Improvement of lipid profile | dos Santos Silva, Barbosa et al. 2011 | ||||
| Vitamin D | Normal/Increased | ↓ hepatic fibrogenesis | Beilfuss, Sowa et al. 2015 | ||
| Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, and anti-fibrotic effects in liver | Abramovitch, Dahan-Bachar et al. 2011 | ||||
| Thyroid Hormones | TH supplementation | ↓ Hepatic steatosis | Bruinstroop, Dalan et al. 2018, Harrison, Bashir et al. 2019 | Erion, Cable et al. 2007 Cable, Finn et al. 2009, Mollica, Lionetti et al. 2009 | Erion, Cable et al. 2007 |
| Decreased | ↓ hepatic lipase activity and ↑ triglyceride accumulation | Erion, Cable et al. 2007 Cable, Finn et al. 2009, Mollica, Lionetti et al. 2009 | Erion, Cable et al. 2007 | ||
| Estrogens | Increased | Improves hepatic function | Chambliss, Barrera et al. 2016: ♀ | ||
| ↓ IL-6 levels | Naugler, Sakurai et al. 2007: ♂ | ||||
| ↓ collagen synthesis in stellate cells | Itagaki, Shimizu et al. 2005 | ||||
| Decreased | Worsens the hepatic histological injury, ↑ macrophage infiltration, and enhanced expression of hepatic inflammatory genes | Kamada, Kiso et al. 2011 | |||
| Estrogen replacement therapy | Ameliorates hepatic histological injury | Kamada, Kiso et al. 2011 | |||
| ↓ macrophage infiltration and enhanced expression of inflammatory genes | Kamada, Kiso et al. 2011 | ||||
| Improves hepatic function | Elsheikh, Hodgson et al. 2001♀ | ||||
| Androgens | Decreased levels (♂) | ↑ serum and hepatic levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDL | Sakr, Hussein et al. 2018 | ||
| ↑ enzymes involved in hepatic steatogenesis (SREBP-1 and SREBP-2) | Sakr, Hussein et al. 2018 | ||||
| ↑ hepatic fat accumulation and NAFLD development and progression | Fan, Yanase et al. 2005 | ||||
| ↑ late-onset obesity | Fan, Yanase et al. 2005 | ||||
| Increased levels (♀) | ↑ intra-hepatic fat content | Wang, Guo et al. 2020 | |||
| Testosterone replacement therapy | Improvement of metabolic syndrome | Traish, Haider et al. 2014 | |||
| RAAS | Increased | ↑ insulin resistance | Kumagai, Adachi et al. 2011) | ||
| ↑ ROS formation and endothelial dysfunction | Chen, Muntner et al. 2003 | ||||
| ↑ weigh gain and hepatic steatosis | Lu, Wu et al. 2016 | ||||
| Decreased/Pharmacological block | ↓ hepatic fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis | Noguchi, Yoshiji et al. 2010 | |||
| ↓ insulin resistance in NAFLD | Polyzos, Kountouras et al. 2011 | ||||
| ↓ Steatosis and hepatic fibrosis | Hirata, Tomita et al. 2013 | Pizarro, Solis et al. 2015 | |||
| ↓ serum free fatty acid level and improved the liver/spleen ratio | Hirata, Tomita et al. 2013 | ||||
| ↓ serum liver enzyme and TGF-1 levels, ↓ hepatic necroinflammation | Yokohama, Yoneda et al. 2004 | ||||
| Glucocorticoids | Increased | Hepatic steatosis | D’Souza A, Beaudry et al. 2012, Auer, Stalla et al. 2016 | ||
| Insulin resistance | Hayashi, Okuno et al. 2019 | ||||
| Possibly limits hepatic inflammation in NASH patients | Ahmed, Rabbitt et al. 2012 | ||||
| Catecholamines | Normal/Increased | ↑ Fibrogenic α/β-adrenoreceptor and neuropeptide Y receptors in human cirrhotic NAFLD | Sigala, McKee et al. 2013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Von-Hafe, M.; Borges-Canha, M.; Vale, C.; Leite, A.R.; Sérgio Neves, J.; Carvalho, D.; Leite-Moreira, A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes—A Scoping Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040298
Von-Hafe M, Borges-Canha M, Vale C, Leite AR, Sérgio Neves J, Carvalho D, Leite-Moreira A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes—A Scoping Review. Metabolites. 2022; 12(4):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040298
Chicago/Turabian StyleVon-Hafe, Madalena, Marta Borges-Canha, Catarina Vale, Ana Rita Leite, João Sérgio Neves, Davide Carvalho, and Adelino Leite-Moreira. 2022. "Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes—A Scoping Review" Metabolites 12, no. 4: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040298
APA StyleVon-Hafe, M., Borges-Canha, M., Vale, C., Leite, A. R., Sérgio Neves, J., Carvalho, D., & Leite-Moreira, A. (2022). Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes—A Scoping Review. Metabolites, 12(4), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040298






