Drought Stress Responses in Context-Specific Genome-Scale Metabolic Models of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
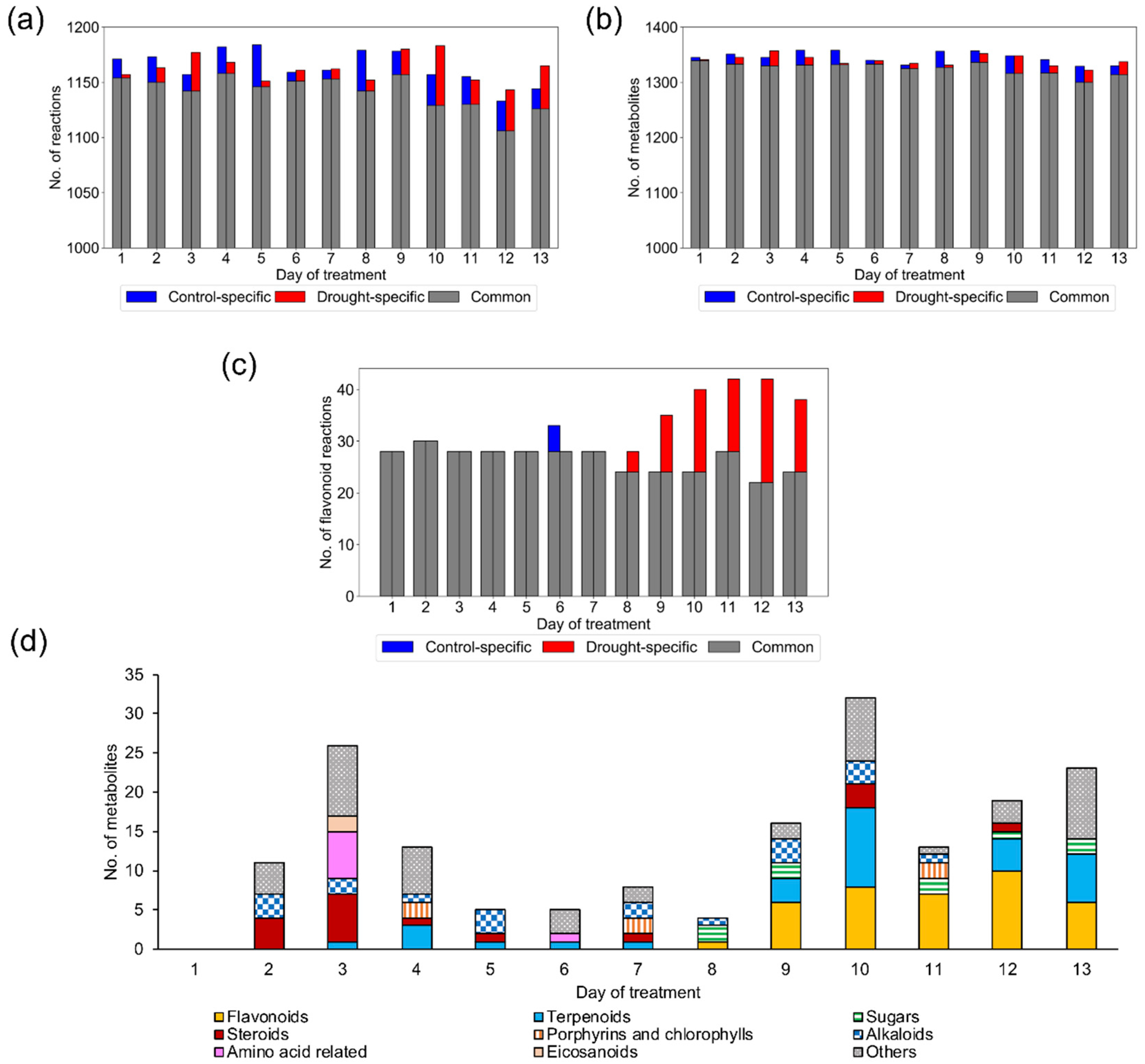
2.1. Reconstruction and Examination of Context-Specific GEMs
2.1.1. Reconstruction of Context-Specific GEMs
2.1.2. Model Examination Based on Occurrence Percentage of Metabolites
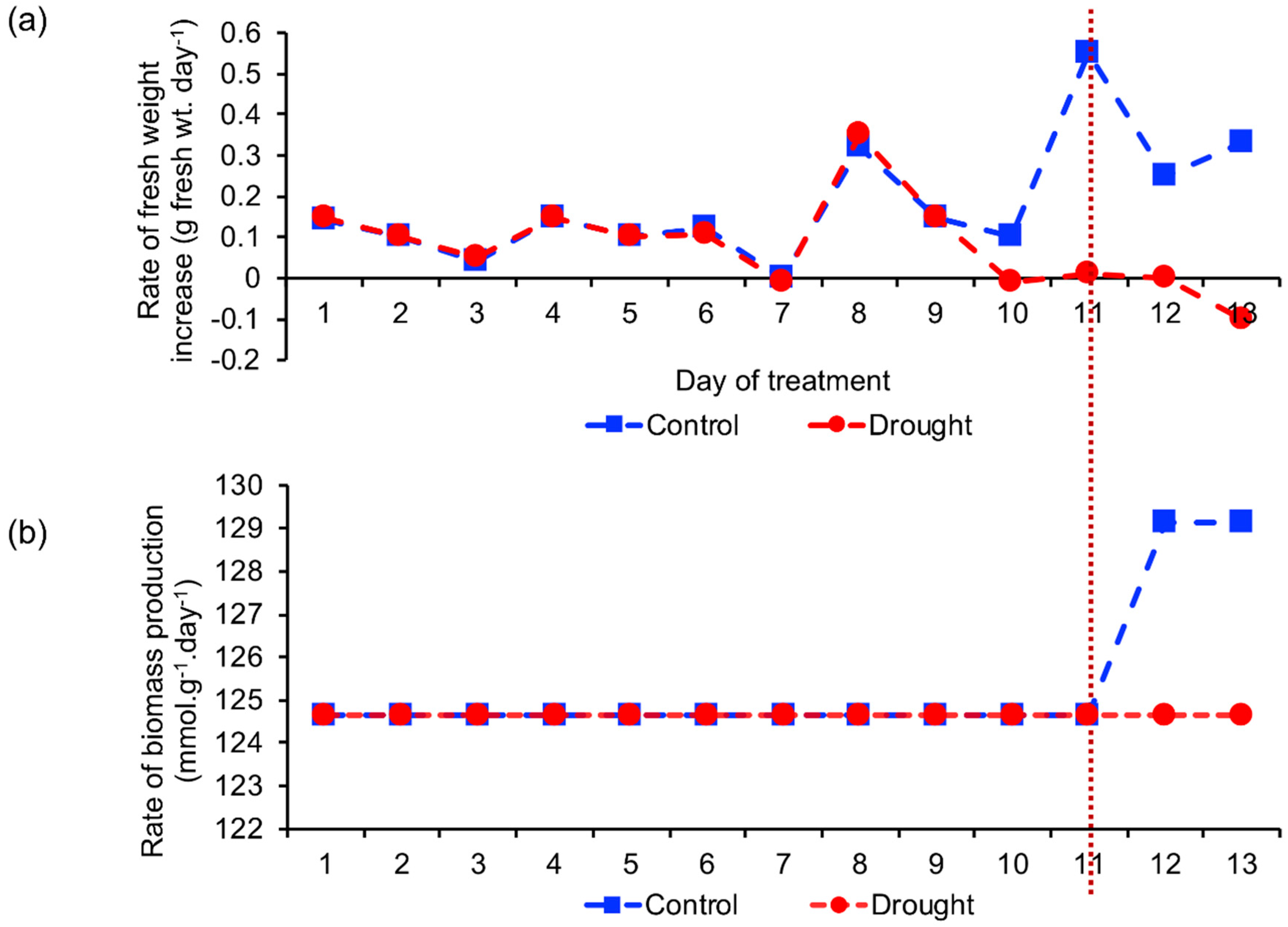
2.2. Biomass Production Rate
2.2.1. Comparison of Estimated and Actual Biomass Production Rate
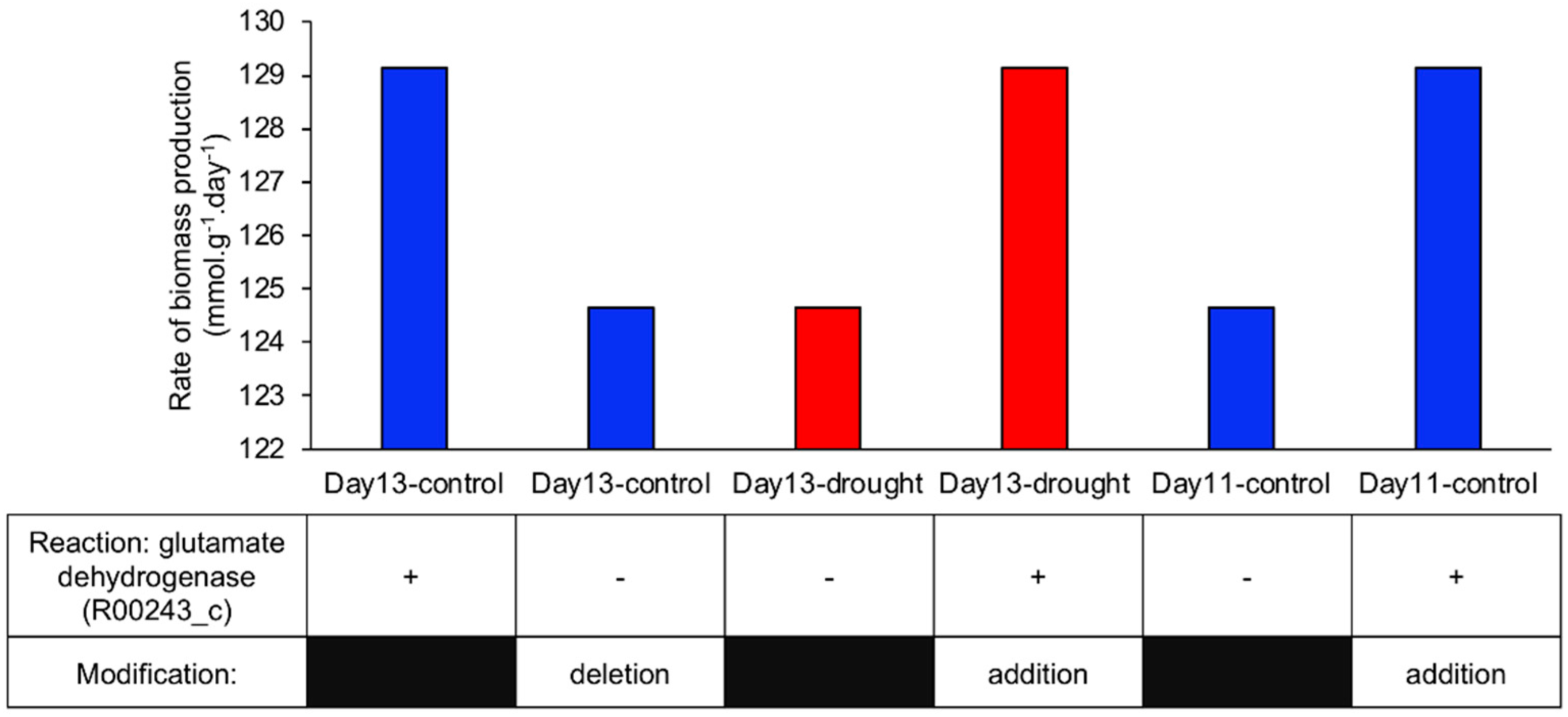
2.2.2. Identification of the Reaction Involved in Increasing Biomass Production Rate
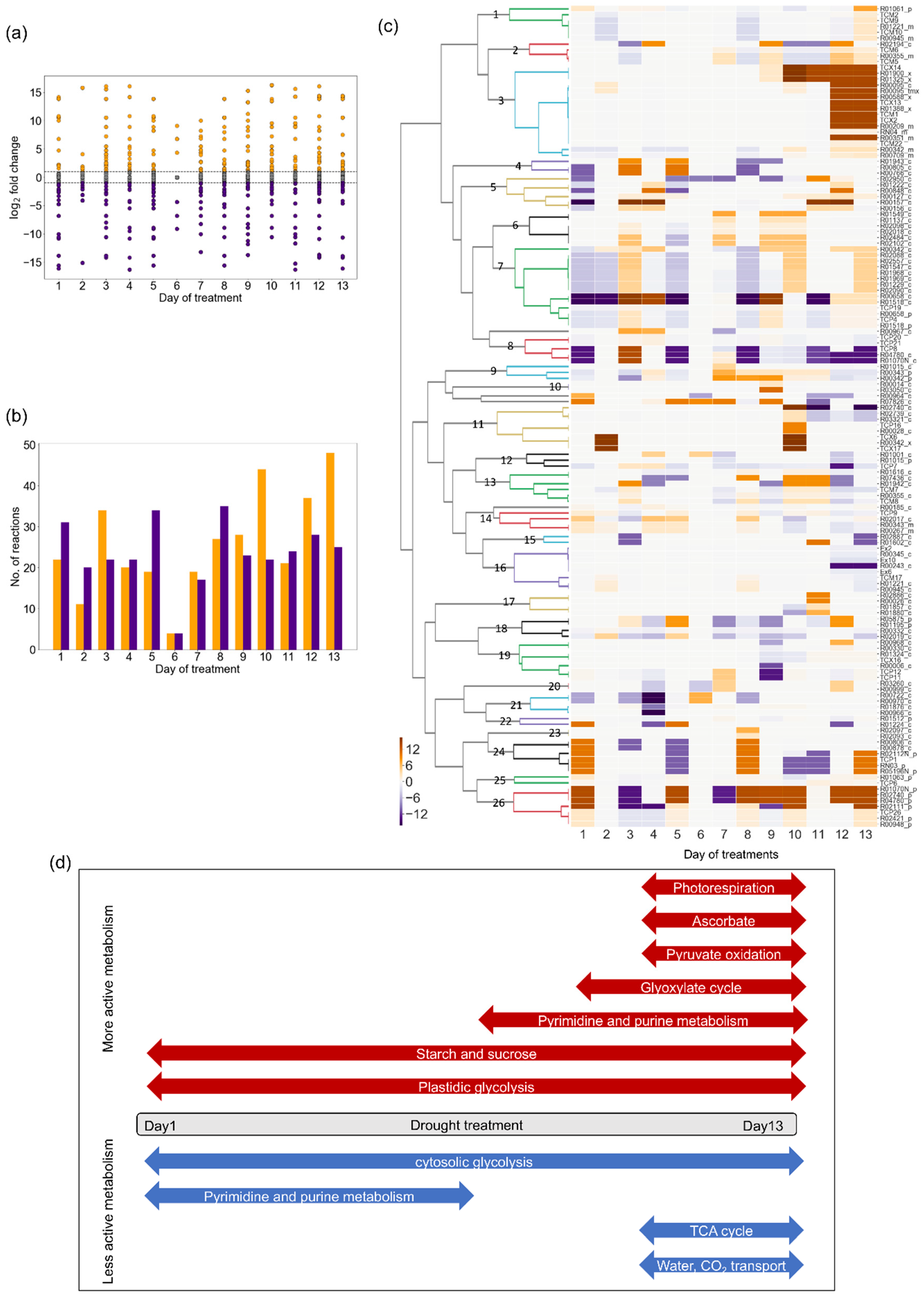
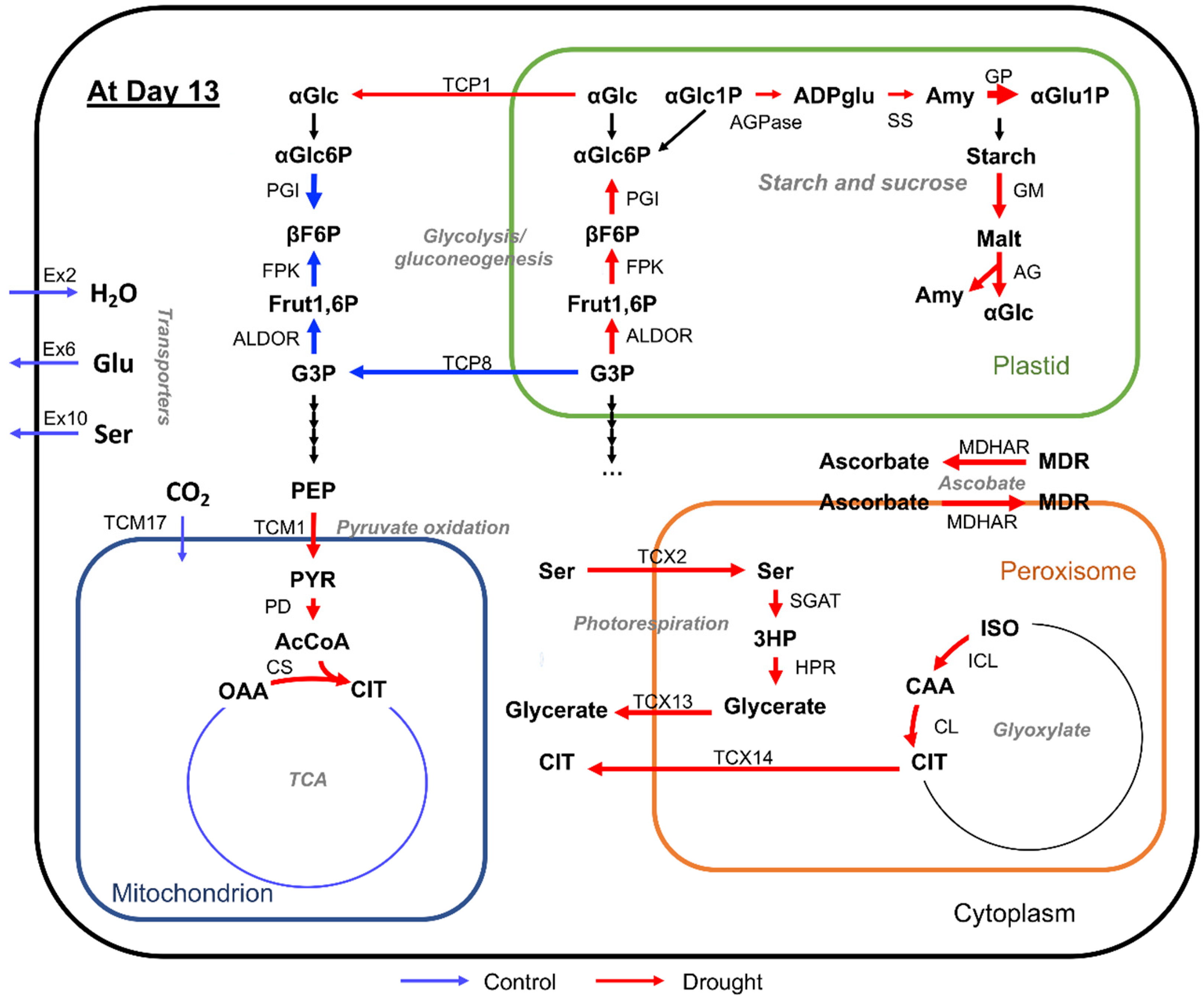
2.3. Changes in Flux Distribution Under Drought Stress
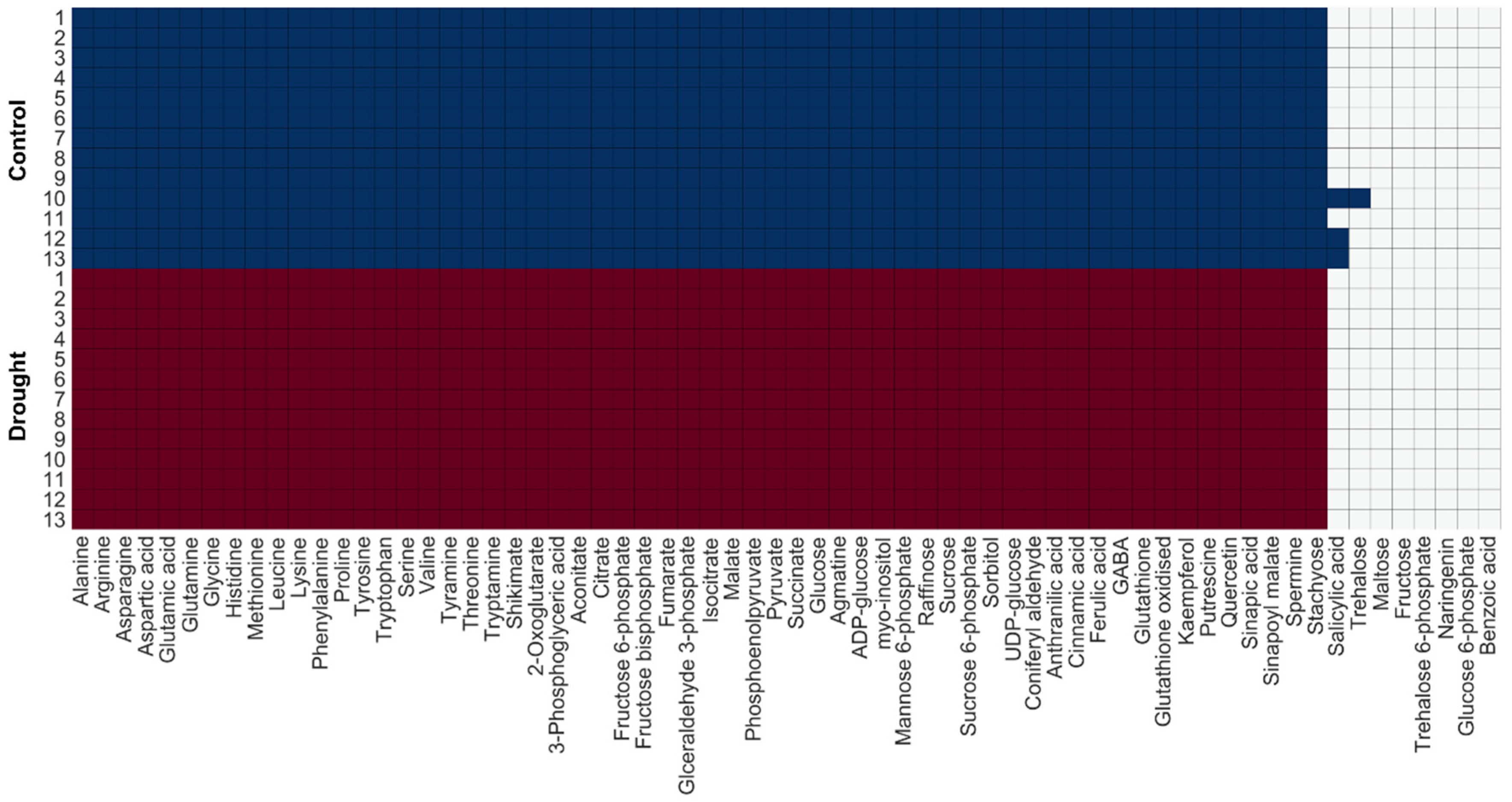
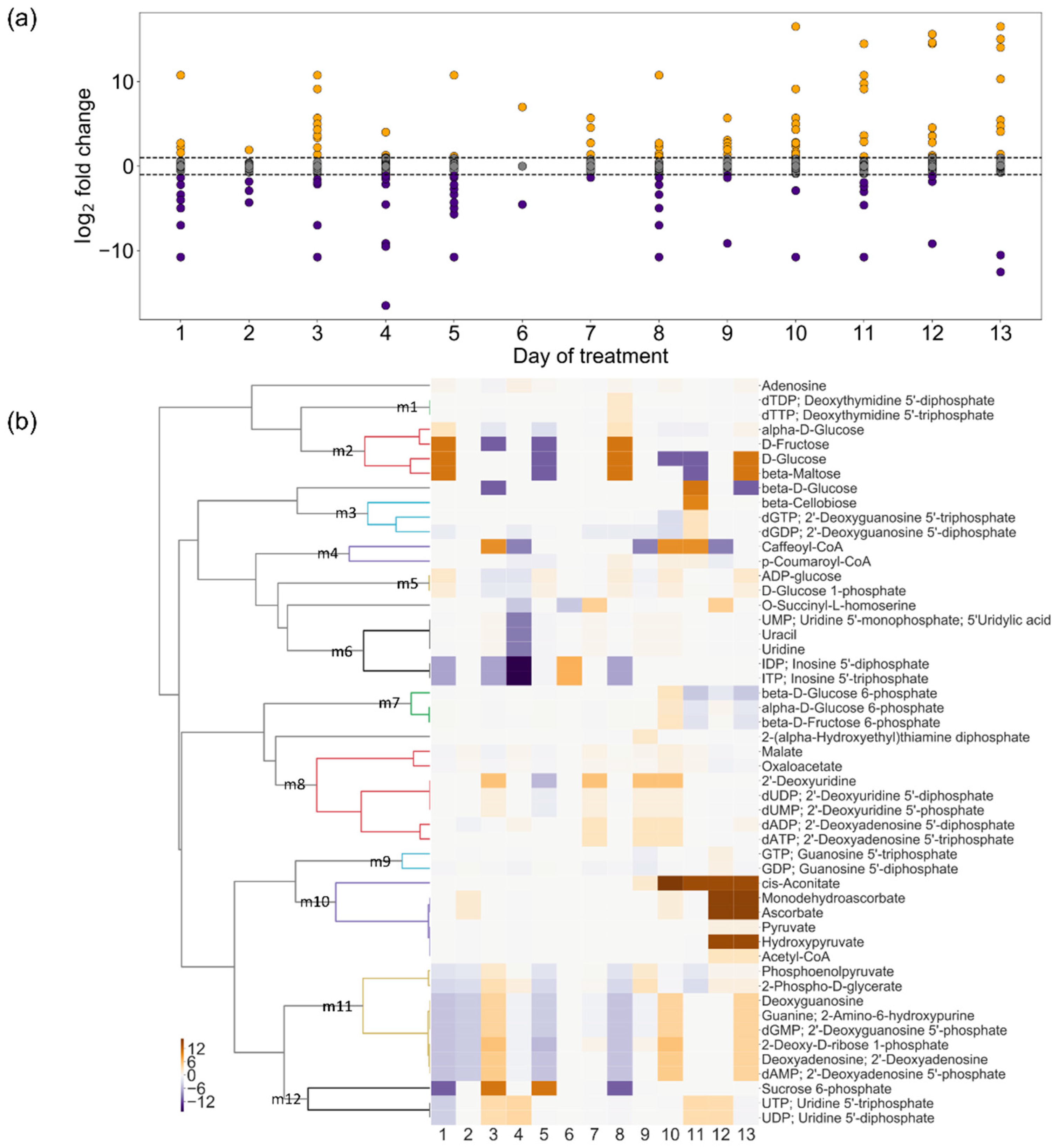
2.4. Change in Turnover Rate of Metabolites Under Drought Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome-Scale Metabolic Model
4.2. Transcriptome Data Processing
4.3. Calculation of the Rate of Fresh Weight Increase
4.4. Flux Balance Analysis (FBA)
4.5. Reconstruction of Context-Specific GEMs Using GIMME
4.6. Occurrence Percentage
4.7. Single Reaction Deletion
4.8. Flux-Sum
4.9. Comparative Analysis of Flux and Flux-Sum
4.9.1. Fold-Change in Flux
4.9.2. Fold-Change in Flux-Sum
4.9.3. Cluster Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrão, H.; Naumann, G.; Barbosa, P. Mapping global patterns of drought risk: An empirical framework based on sub-national estimates of hazard, exposure and vulnerability. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 39, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B. The World’s Water 2006–2007: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources. Environ. Pract. 2017, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, R. Abscisic Acid synthesis and response. Arab. Book 2013, 11, e0166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, H.; Inze, D. The agony of choice: How plants balance growth and survival under water-limiting conditions. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Ito, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxa, M.; Liebthal, M.; Telman, W.; Chibani, K.; Dietz, K.J. The role of the plant antioxidant system in drought tolerance. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, A.; Monk, J.M.; King, Z.A.; Palsson, B.O. Constraint-based models predict metabolic and associated cellular functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.J.; Monk, J.M.; Palsson, B.O. Using genome-scale models to predict biological capabilities. Cell 2015, 161, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Boele, J.; Teusink, B. A practical guide to genome-scale metabolic models and their analysis. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 500, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, J.D.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.O. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Current status and applications of genome-scale metabolic models. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toya, Y.; Shimizu, H. Flux analysis and metabolomics for systematic metabolic engineering of microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opdam, S.; Richelle, A.; Kellman, B.; Li, S.; Zielinski, D.C.; Lewis, N.E. A systematic evaluation of methods for tailoring genome-scale metabolic models. Cell Syst. 2017, 4, 318–329.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Dal’Molin, C.G.; Quek, L.E.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Brumbley, S.M.; Nielsen, L.K. AraGEM, a genome-scale reconstruction of the primary metabolic network in Arabidopsis. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 152, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, U.; Penfold, C.A.; Jenkins, D.J.; Legaie, R.; Moore, J.D.; Lawson, T.; Matthews, J.S.; Vialet-Chabrand, S.R.; Baxter, L.; Subramaniam, S.; et al. Time-series transcriptomics reveals that AGAMOUS-LIKE22 affects primary metabolism and developmental processes in drought-stressed Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.A.; Palsson, B.O. Context-specific metabolic networks are consistent with experiments. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, R.; Mori, T.; Saito, K. Alternation of flavonoid accumulation under drought stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e29518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungur, R.; Wood, A.J.; Lightfoot, D.A. Water potential is maintained during water deficit in Nicotiana tabacum expressing the Escherichia coli glutamate dehydrogenase gene. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 50, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot, D.A.; Mungur, R.; Ameziane, R.; Nolte, S.; Long, L.; Bernhard, K.; Colter, A.; Jones, K.; Iqbal, M.J.; Varsa, E.; et al. Improved drought tolerance of transgenic Zea mays plants that express the glutamate dehydrogenase gene (gdhA) of E-coli. Euphytica 2007, 156, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.K.; Lee, D.Y. Flux-sum analysis: A metabolite-centric approach for understanding the metabolic network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, J.M.; Kim, T.Y.; Yun, H.; Lee, S.Y. The genome-scale metabolic network analysis of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 explains physiological features and suggests ethanol and succinic acid production strategies. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tang, X.; Huo, Y.; Xu, R.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zheng, C.; Wu, C.A. Identification and characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase genes in Arabidopsis reveal a gene family with diverse responses to abiotic stresses. Gene 2012, 503, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Xie, L.P.; Xie, C.G.; Zhang, X.H.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tang, Y.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Guo, A.G.; et al. Molecular characterization, gene evolution, and expression analysis of the fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Cloning and molecular characterization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase gene regulated by high-salinity and drought in Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingler, A.; Quick, W.P.; Bungard, R.A.; Bailey, K.J.; Lea, P.J.; Leegood, R.C. The role of photorespiration during drought stress: An analysis utilizing barley mutants with reduced activities of photorespiratory enzymes. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingler, A.; Lea, P.J.; Quick, W.P.; Leegood, R.C. Photorespiration: Metabolic pathways and their role in stress protection. Philos Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, J. Using co-expression analysis and stress-based screens to uncover Arabidopsis peroxisomal proteins involved in drought response. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaina Estevez, S.; Nikoloski, Z. Generalized framework for context-specific metabolic model extraction methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collakova, E.; Yen, J.Y.; Senger, R.S. Are we ready for genome-scale modeling in plants? Plant Sci. 2012, 191–192, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cokelaer, T.; Pultz, D.; Harder, L.M.; Serra-Musach, J.; Saez-Rodriguez, J. BioServices: A common Python package to access biological Web Services programmatically. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3241–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Kerr, M.K.; Cui, X.; Churchill, G.A. MAANOVA: A Software Package for the Analysis of Spotted cDNA Microarray Experiments. In The Analysis of Gene Expression Data; Parmigiani, G., Garrett, E.S., Irizarry, R.A., Zeger, S.L., Eds.; Statistics for Biology and Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 313–341. [Google Scholar]
- Heirendt, L.; Arreckx, S.; Pfau, T.; Mendoza, S.N.; Richelle, A.; Heinken, A.; Haraldsdóttir, H.S.; Wachowiak, J.; Keating, S.M.; Vlasov, V.; et al. Creation and analysis of biochemical constraint-based models using the COBRA Toolbox v.3.0. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 639–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python; ScienceOpen: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Waskom, M.; Botvinnik, O.; O’Kane, D.; Hobson, P.; Ostblom, J.; Lukauskas, S.; Gemperline, D.C.; Augspurger, T.; Halchenko, Y.; Cole, J.B.; et al. mwaskom/seaborn: v0.9.0 (July 2018). 2018. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1313201#.XpqPyZkRVPY (accessed on 20 March 2020). [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siriwach, R.; Matsuda, F.; Yano, K.; Hirai, M.Y. Drought Stress Responses in Context-Specific Genome-Scale Metabolic Models of Arabidopsis thaliana. Metabolites 2020, 10, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040159
Siriwach R, Matsuda F, Yano K, Hirai MY. Drought Stress Responses in Context-Specific Genome-Scale Metabolic Models of Arabidopsis thaliana. Metabolites. 2020; 10(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040159
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiriwach, Ratklao, Fumio Matsuda, Kentaro Yano, and Masami Yokota Hirai. 2020. "Drought Stress Responses in Context-Specific Genome-Scale Metabolic Models of Arabidopsis thaliana" Metabolites 10, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040159
APA StyleSiriwach, R., Matsuda, F., Yano, K., & Hirai, M. Y. (2020). Drought Stress Responses in Context-Specific Genome-Scale Metabolic Models of Arabidopsis thaliana. Metabolites, 10(4), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040159




