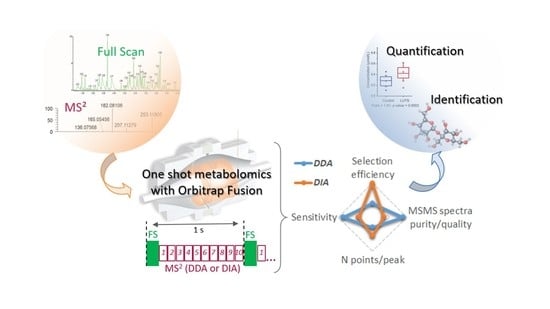
Comparative Evaluation of Data Dependent and Data Independent Acquisition Workflows Implemented on an Orbitrap Fusion for Untargeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Standard Samples and Plasma Extracts
2.3. LC/HRMS Analysis
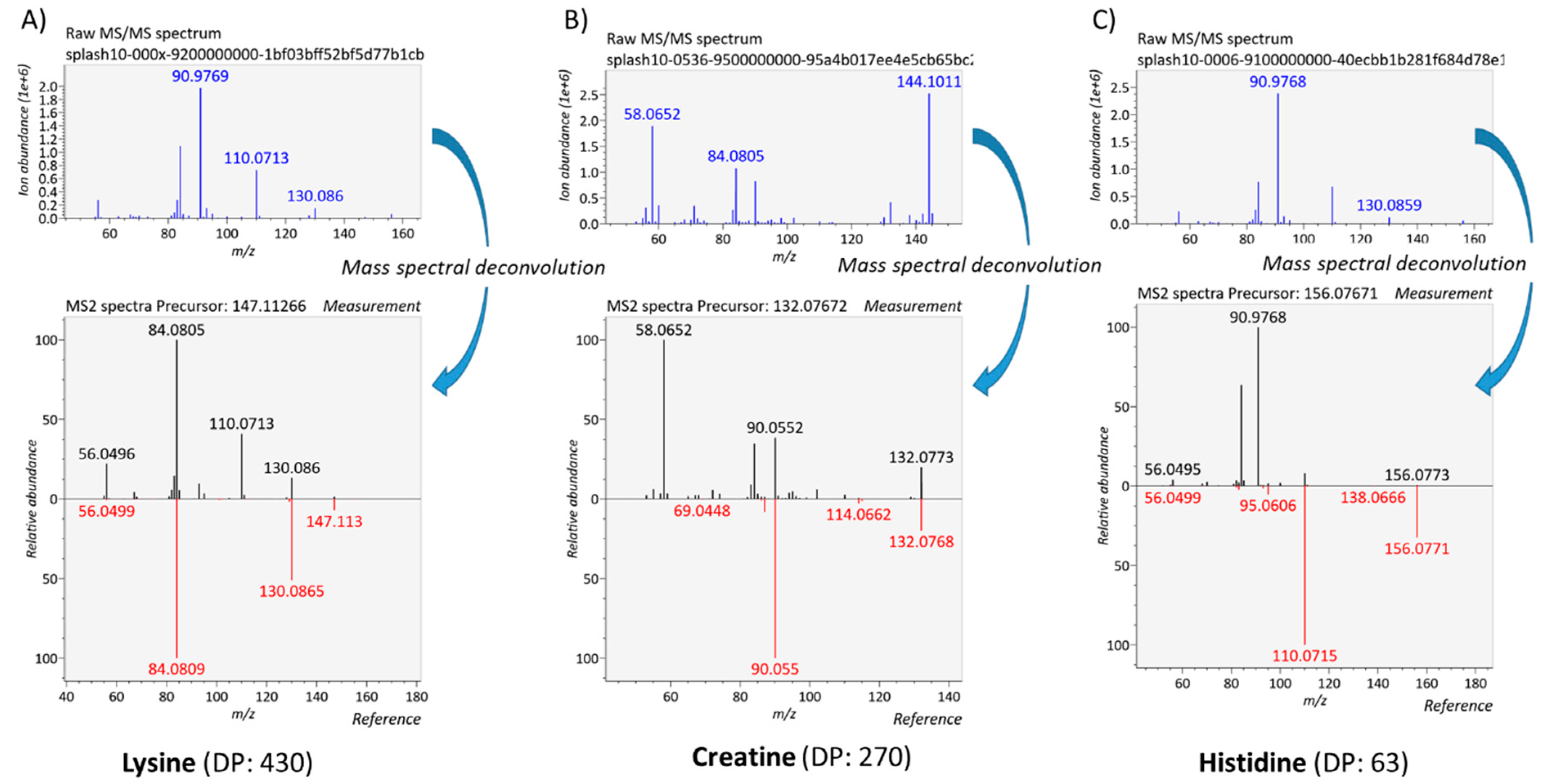
2.4. Data Processing and Evaluation of the Quality of MS/MS Spectra
3. Results and Discussion
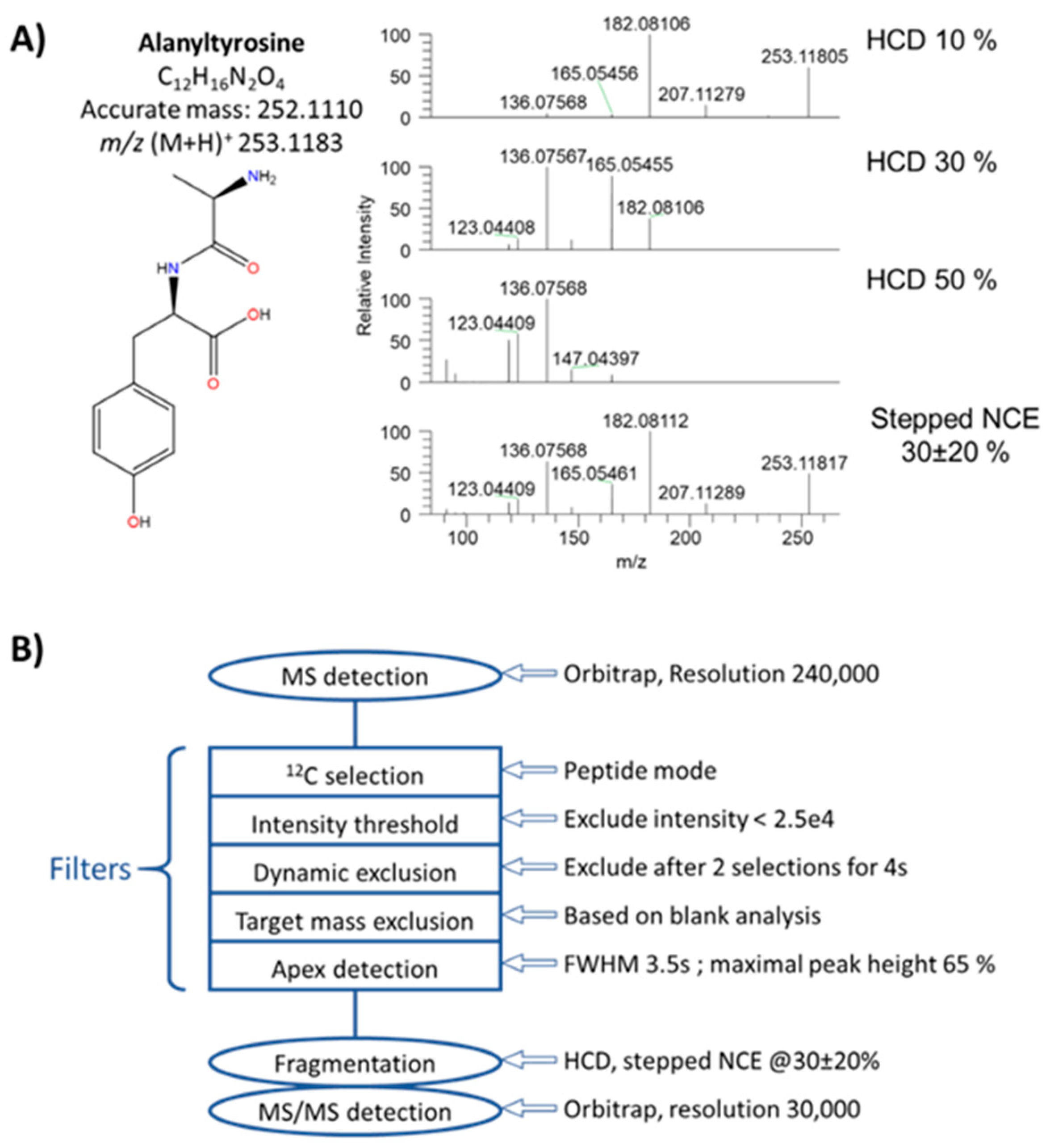
3.1. Implementation of a First “HCD-only” DDA Acquisition Protocol on Authentic Standards as a First Step toward the Collection of Meaningful MS/MS Data
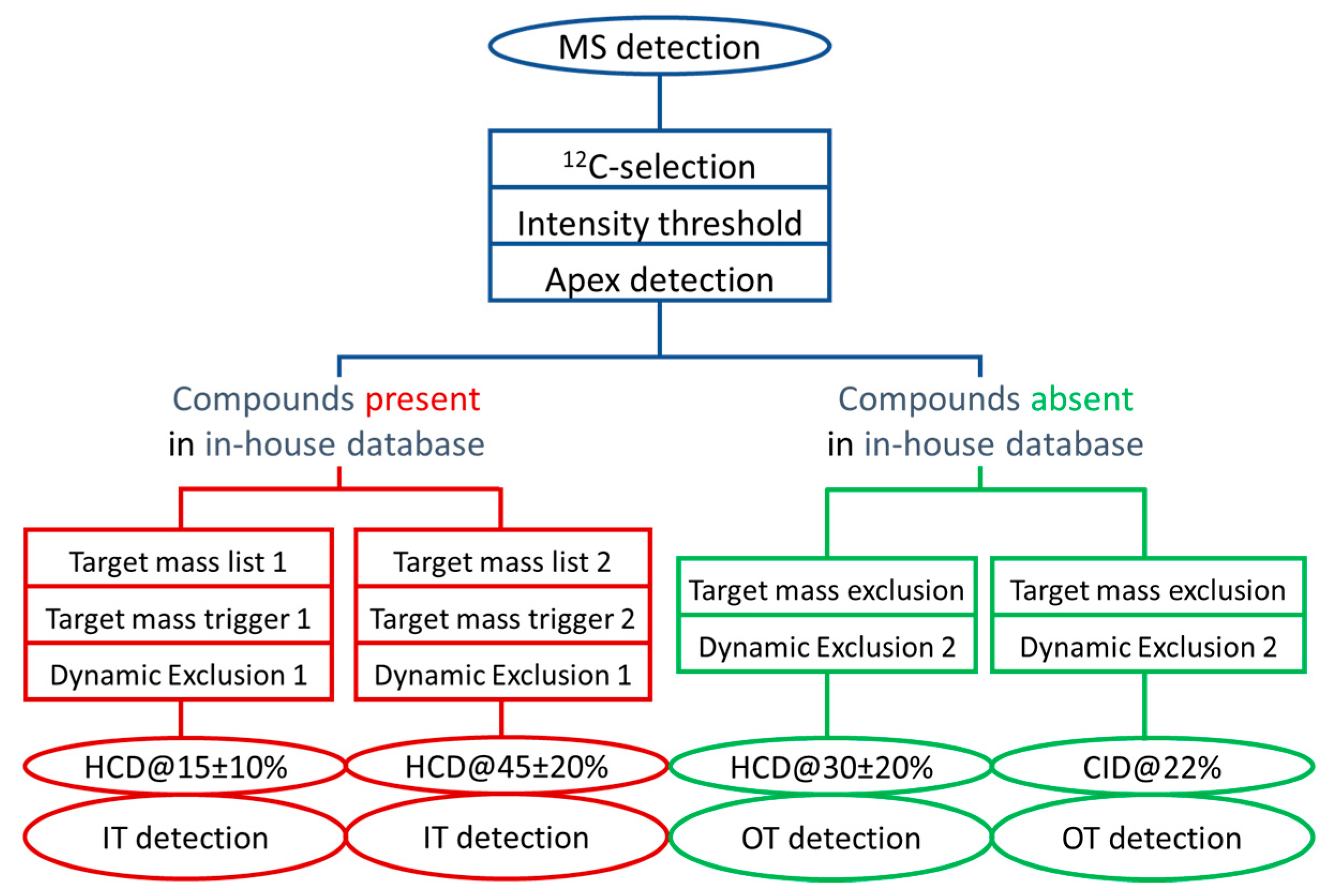
3.2. Collecting Meaningful MS/MS Data for Knowns and Unknowns using a DDA Workflow with Parallelized HCD and CID Fragmentations
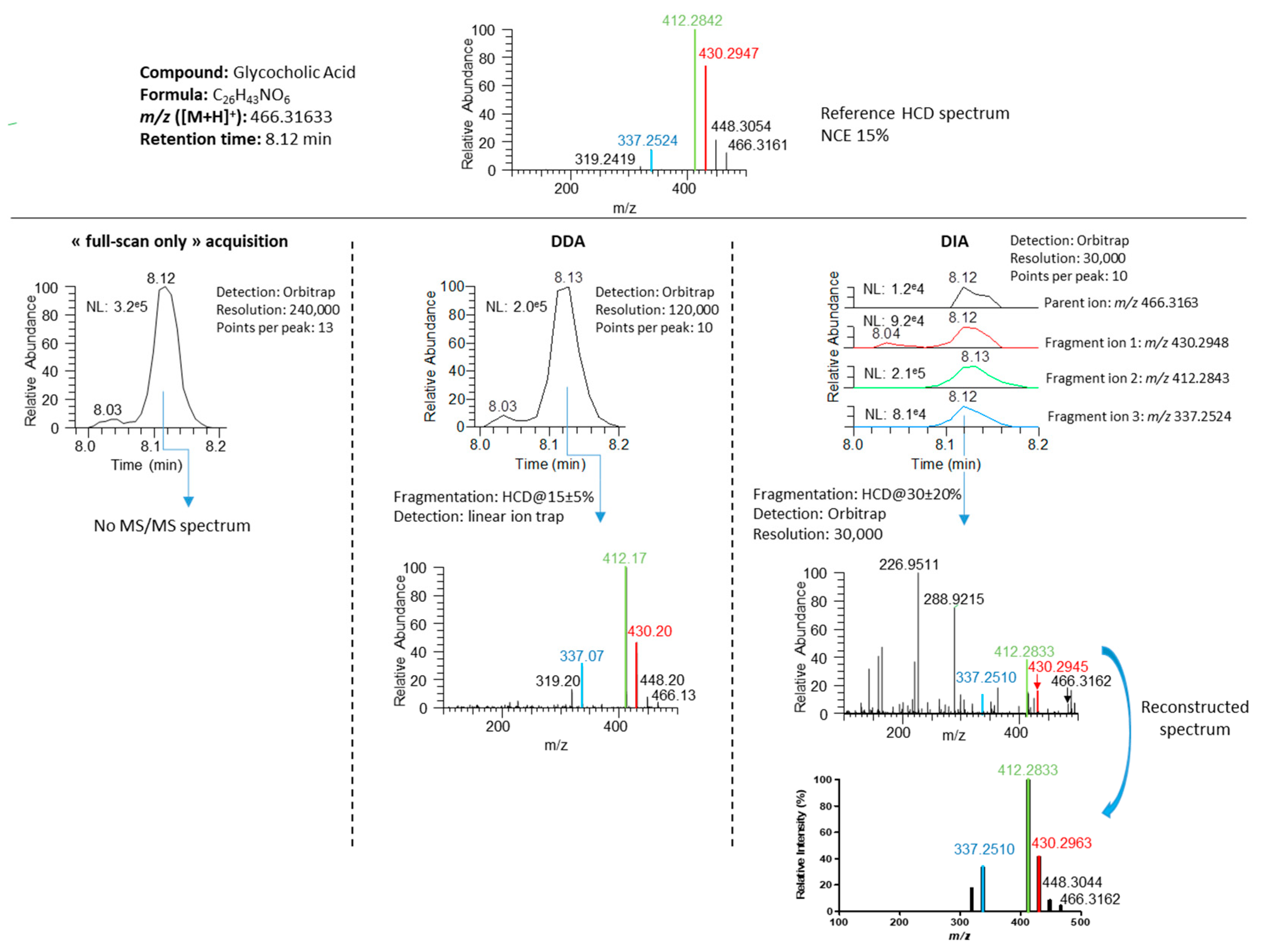
3.3. Development of a DIA Acquisition Workflow
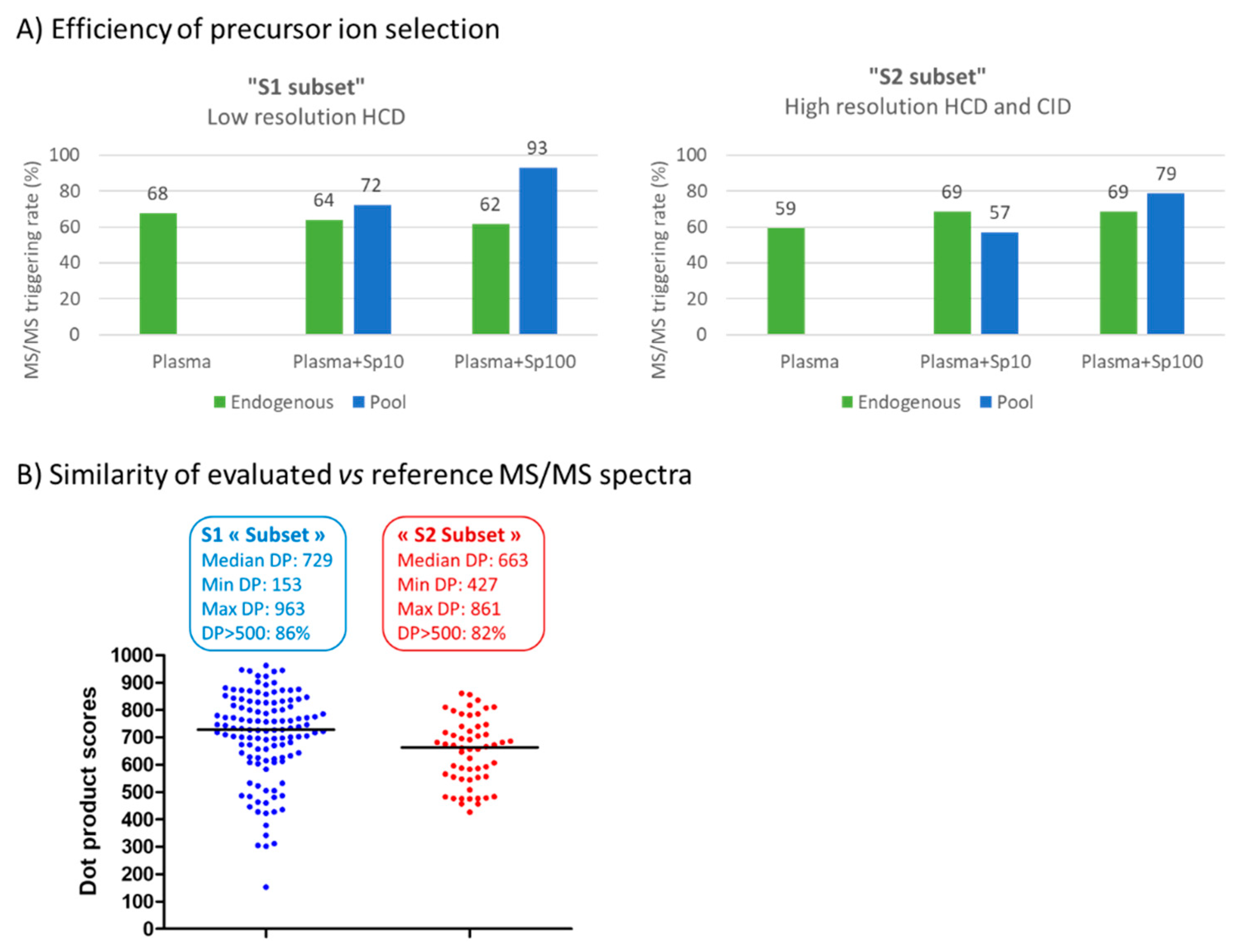
3.4. Performance Evaluation of DDA and DIA Strategies
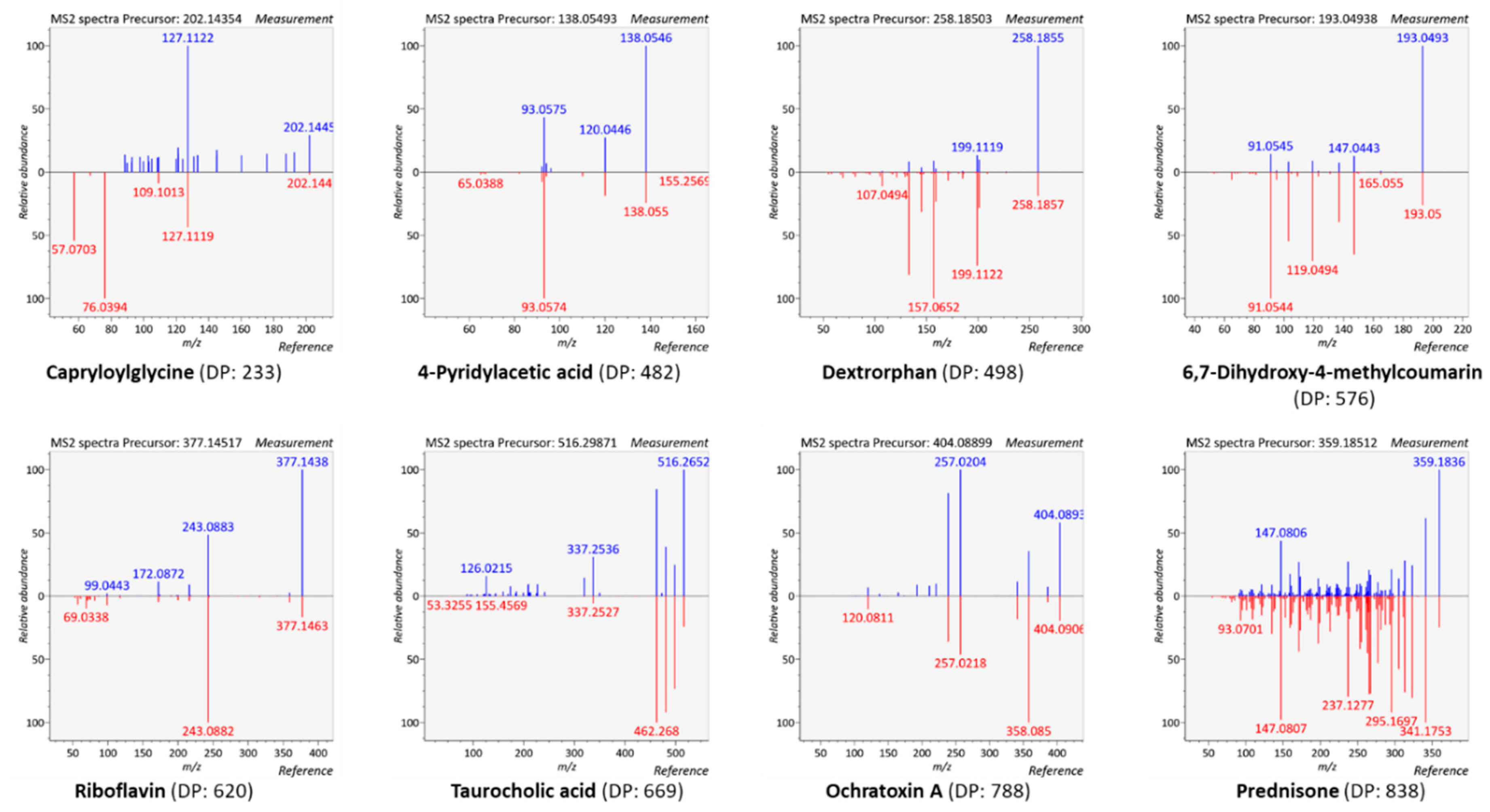
3.4.1. Generation of Meaningful MS/MS Spectra to Confirm the Annotation of Plasma Metabolites
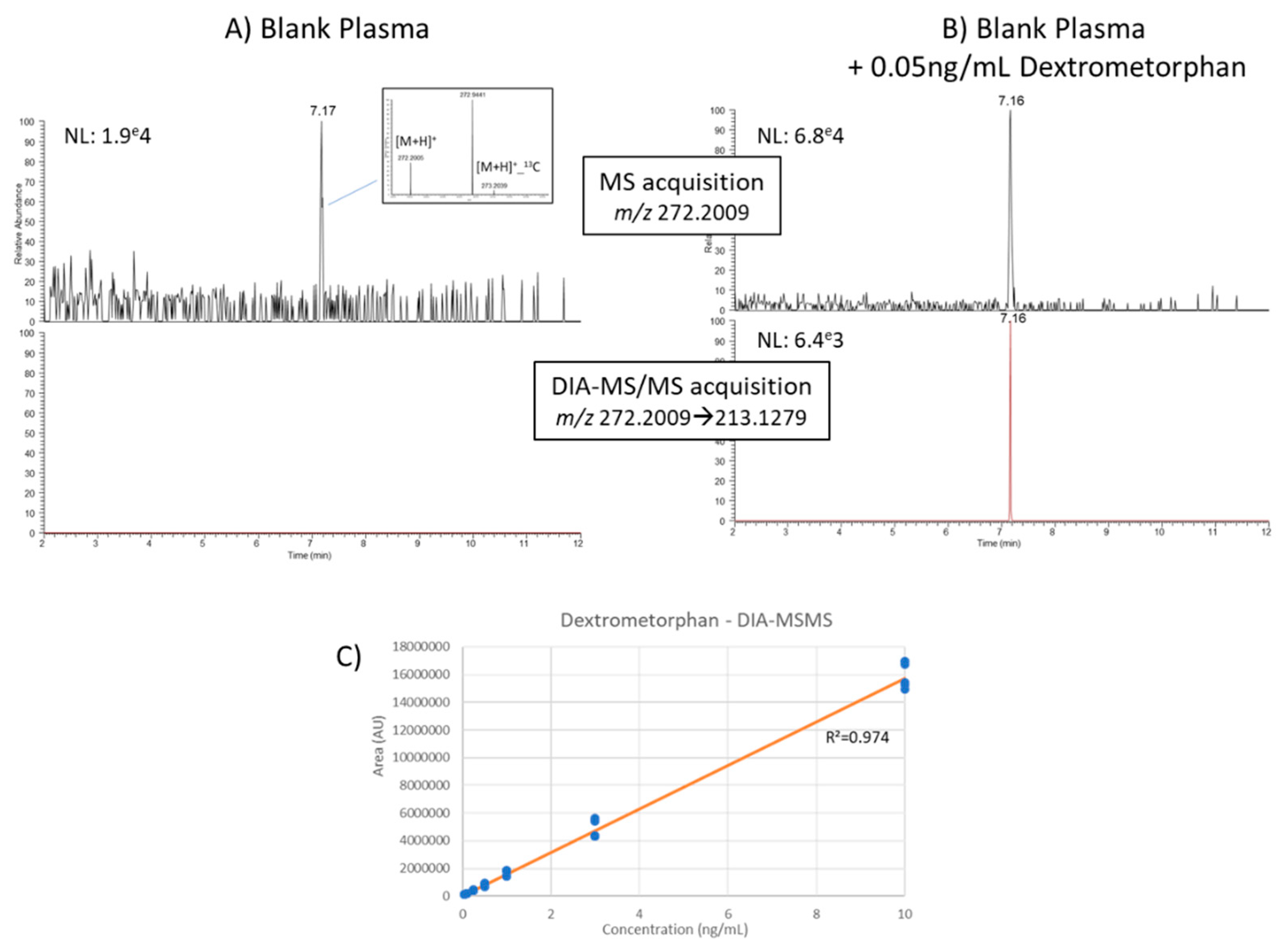
3.4.2. Quantification of Human Plasma Metabolites from DDA and DIA Modes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gika, H.; Virgiliou, C.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Wilson, I.D. Untargeted LC/MS-based metabolic phenotyping (metabonomics/metabolomics): The state of the art. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1117, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Julia, A. Analytical Methods in Untargeted Metabolomics: State of the Art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Quinn, R.A. Illuminating the dark matter in metabolomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12549–12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic database annotations via query of elemental compositions: Mass accuracy is insufficient even at less than 1 ppm. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier Saint Hilaire, P.; Hohenester, U.M.; Colsch, B.; Tabet, J.-C.; Junot, C.; Fenaille, F. Evaluation of the High-Field Orbitrap Fusion for Compound Annotation in Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3030–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, W.J.; Dunn, W.B. From mass to metabolite in human untargeted metabolomics: Recent advances in annotation of metabolites applying liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathahao-Paris, E.; Paris, A.; Bursztyka, J.; Jaeg, J.-P.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Debrauwer, L. Identification of xenobiotic metabolites from biological fluids using flow injection analysis high-resolution mass spectrometry and post-acquisition data filtering. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Ray, K.; Zhu, M. Mass defect filter technique and its applications to drug metabolite identification by high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 44, 999–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Chan, E.C.Y.; Neo, J.; Beuerman, R.W. Characterization of The Human Tear Metabolome by LC–MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, H.P.; Ivanisevic, J.; Mahieu, N.G.; Kurczy, M.E.; Johnson, C.H.; Franco, L.; Rinehart, D.; Valentine, E.; Gowda, H.; Ubhi, B.K.; et al. Autonomous metabolomics for rapid metabolite identification in global profiling. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.; Thum, A.; Böttcher, C. Nearline acquisition and processing of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry data. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Kroeger, N.M.; Gill, E.L.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Bowden, J.A.; Patterson, R.E.; Yost, R.A.; Garrett, T.J. Expanding Lipidome Coverage Using LC-MS/MS Data-Dependent Acquisition with Automated Exclusion List Generation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, T.N.; Weber, R.J.M.; Jones, M.R.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Rodrıguez-Blanco, G.; Di Guida, R.; Viant, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. msPurity: Automated Evaluation of Precursor Ion Purity for Mass Spectrometry-Based Fragmentation in Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2432–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junot, C.; Fenaille, F.; Colsch, B.; Bécher, F. High resolution mass spectrometry based techniques at the crossroads of metabolic pathways. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2014, 33, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, R.; Wang, R.; Yang, F.; Li, P.; Wan, J.-B. Enhanced MS/MS coverage for metabolite identification in LC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics by target-directed data dependent acquisition with time-staggered precursor ion list. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 992, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, G.; Allwood, J.W.; Weber, R.; Brown, M.; Begley, P.; Hollywood, K.A.; Jones, M.; Unwin, R.D.; Bishop, P.N.; Cooper, G.J.S.; et al. A new strategy for MS/MS data acquisition applying multiple data dependent experiments on Orbitrap mass spectrometers in non-targeted metabolomic applications. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenaille, F.; Barbier Saint-Hilaire, P.; Rousseau, K.; Junot, C. Data acquisition workflows in liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: Where do we stand? J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1526, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Tate, S.; Röst, H.; Selevsek, N.; Reiter, L.; Bonner, R.; Aebersold, R. Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent acquisition: A new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, O111.016717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Reinke, S.N.; Mathon, C.; Blankley, R.; Chaleckis, R.; Wheelock, C.E. Development of a Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Method with High Specificity for Metabolite Identification Using All Ion Fragmentation Acquisition. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7933–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, I.; Tsugawa, H.; Meister, I.; Zhang, P.; Shu, R.; Katsumi, R.; Wheelock, C.E.; Arita, M.; Chaleckis, R. Creating a Reliable Mass Spectral-Retention Time Library for All Ion Fragmentation-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart-Ayala, H.; Courant, F.; Severe, S.; Antignac, J.-P.; Morio, F.; Abadie, J.; Le Bizec, B. Versatile lipid profiling by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry using all ion fragmentation and polarity switching. Preliminary application for serum samples phenotyping related to canine mammary cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 796, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Walmsley, S.; Cheung, G.C.M.; Chen, L.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Beuerman, R.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Zhou, L.; Choi, H. Customized Consensus Spectral Library Building for Untargeted Quantitative Metabolomics Analysis with Data Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry and MetaboDIA Workflow. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4897–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, R.; Hopfgartner, G. SWATH data independent acquisition mass spectrometry for metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, L.; Yin, Y. Development of data-independent acquisition workflows for metabolomic analysis on a quadrupole-orbitrap platform. Talanta 2017, 164, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, F.; Fan, C.; Chang, J.; Chu, X. Multiplexing data independent untargeted workflows for mycotoxins screening on a quadrupole-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry platform. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudah, S.; Olivier, M.-F.; Aros-Calt, S.; Oliveira, L.; Fenaille, F.; Tabet, J.-C.; Junot, C. Annotation of the human serum metabolome by coupling three liquid chromatography methods to high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 966, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contrepois, K.; Jiang, L.; Snyder, M. Optimized Analytical Procedures for the Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling of Human Urine and Plasma by Combining Hydrophilic Interaction (HILIC) and Reverse-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPLC)-Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Clària, J.; Aguilar, F.; Fenaille, F.; Lozano, J.J.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B.; Caraceni, P.; Trebicka, J.; Pavesi, M.; et al. Blood metabolomics uncovers inflammation-associated mitochondrial dysfunction as a potential mechanism underlying ACLF. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, P.E.; Kulak, N.A.; Pichler, G.; Holdt, L.M.; Teupser, D.; Mann, M. Plasma Proteome Profiling to Assess Human Health and Disease. Cell Syst. 2016, 2, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruderer, R.; Muntel, J.; Müller, S.; Bernhardt, O.M.; Gandhi, T.; Cominetti, O.; Macron, C.; Carayol, J.; Rinner, O.; Astrup, A.; et al. Analysis of 1508 Plasma Samples by Capillary-Flow Data-Independent Acquisition Profiles Proteomics of Weight Loss and Maintenance. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Torbašinović, H.; Obrenović, S.; Mehta, S.S.; Tsugawa, H.; Wermuth, T.; Schauer, N.; Jahn, M.; Biedendieck, R.; et al. Comprehensive comparison of in silico MS/MS fragmentation tools of the CASMI contest: Database boosting is needed to achieve 93% accuracy. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Li, J.; Shen, S.; Sheng, Q.; Shyr, Y.; Qu, J. Performance Investigation of Proteomic Identification by HCD/CID Fragmentations in Combination with High/Low-Resolution Detectors on a Tribrid, High-Field Orbitrap Instrument. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Santiago, M.; Priego-Capote, F.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Enhanced detection and identification in metabolomics by use of LC-MS/MS untargeted analysis in combination with gas-phase fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7558–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bilbao, A.; Bruderer, T.; Luban, J.; Strambio-De-Castillia, C.; Lisacek, F.; Hopfgartner, G.; Varesio, E. The Use of Variable Q1 Isolation Windows Improves Selectivity in LC–SWATH–MS Acquisition. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 4359–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yin, Y. Development and Evaluation of a Parallel Reaction Monitoring Strategy for Large-Scale Targeted Metabolomics Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4478–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbier Saint Hilaire, P.; Rousseau, K.; Seyer, A.; Dechaumet, S.; Damont, A.; Junot, C.; Fenaille, F. Comparative Evaluation of Data Dependent and Data Independent Acquisition Workflows Implemented on an Orbitrap Fusion for Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040158
Barbier Saint Hilaire P, Rousseau K, Seyer A, Dechaumet S, Damont A, Junot C, Fenaille F. Comparative Evaluation of Data Dependent and Data Independent Acquisition Workflows Implemented on an Orbitrap Fusion for Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(4):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040158
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbier Saint Hilaire, Pierre, Kathleen Rousseau, Alexandre Seyer, Sylvain Dechaumet, Annelaure Damont, Christophe Junot, and François Fenaille. 2020. "Comparative Evaluation of Data Dependent and Data Independent Acquisition Workflows Implemented on an Orbitrap Fusion for Untargeted Metabolomics" Metabolites 10, no. 4: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040158
APA StyleBarbier Saint Hilaire, P., Rousseau, K., Seyer, A., Dechaumet, S., Damont, A., Junot, C., & Fenaille, F. (2020). Comparative Evaluation of Data Dependent and Data Independent Acquisition Workflows Implemented on an Orbitrap Fusion for Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(4), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040158