A Comparative Analysis between Standard and mm-Wave Optimized BEOL in a Nanoscale CMOS Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Testbench for the BEOL Comparison: Integrated Transformers and 77 GHz Down-Converter
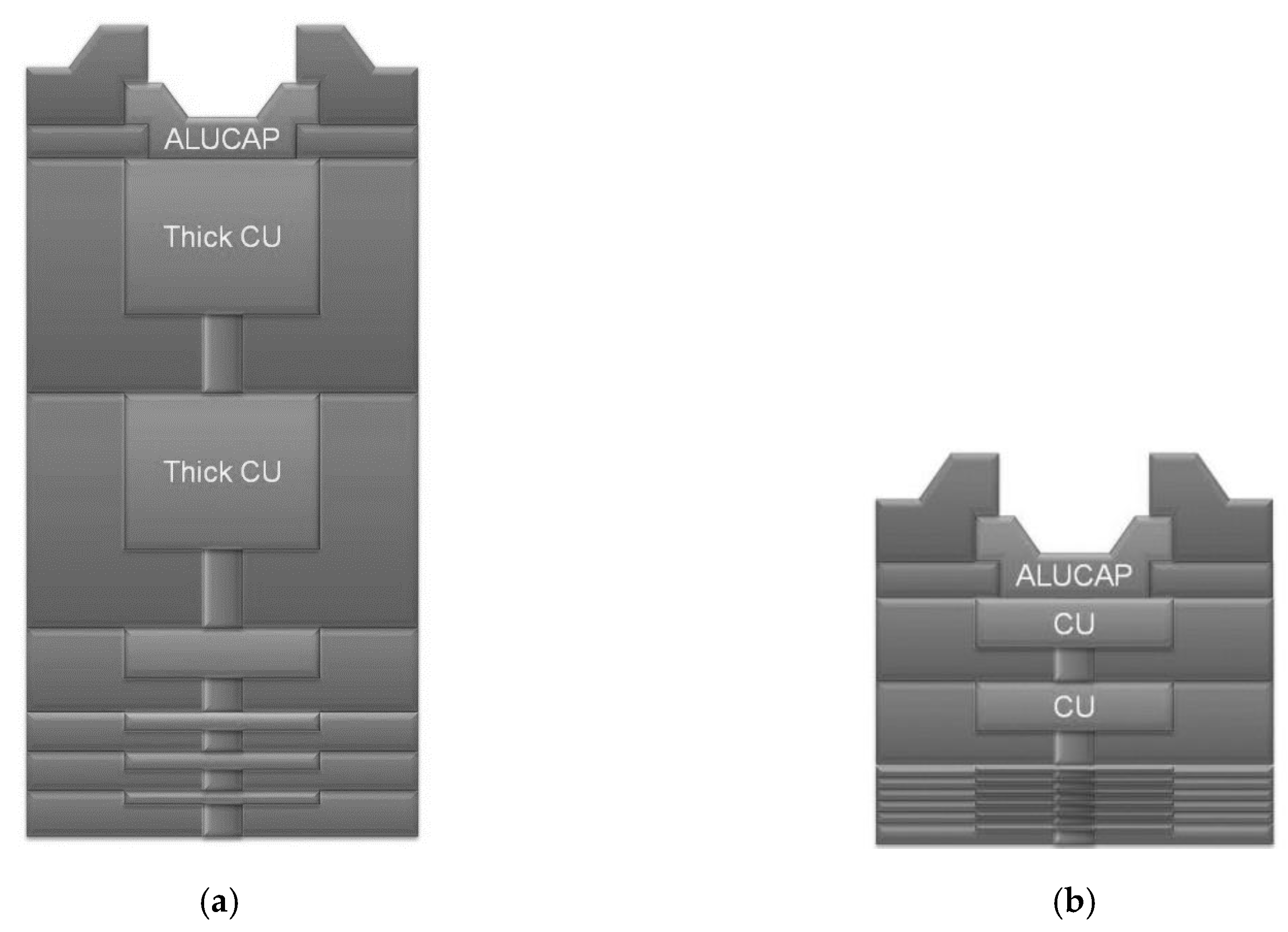
2.1. BEOLs and Integrated Transformers
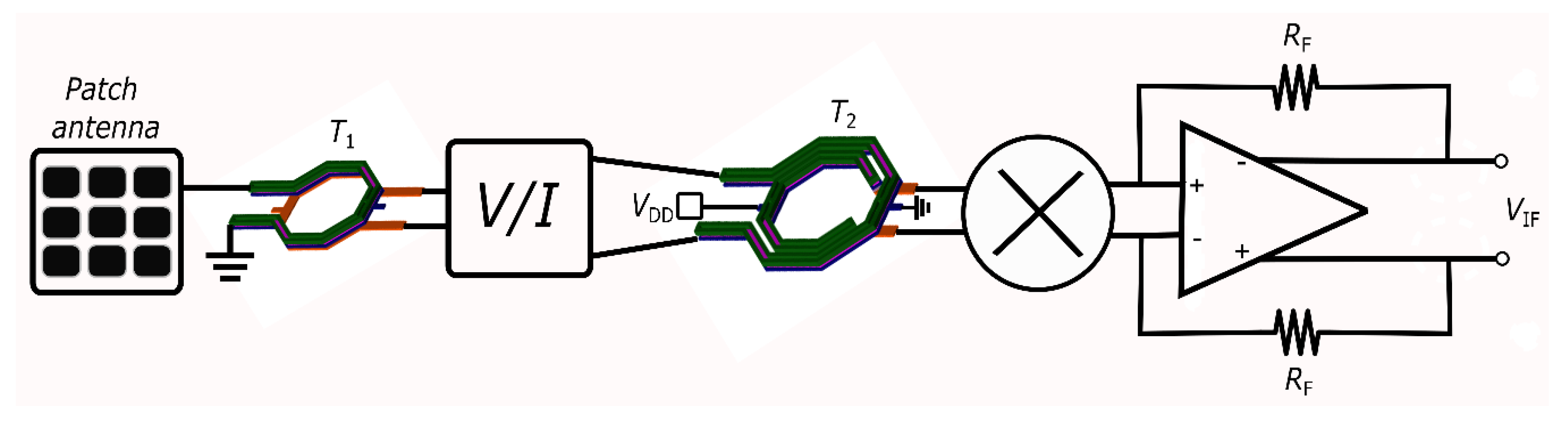
2.2. 77 GHz Down-Converter
2.3. Experimental Validation for the BEOL Analysis
3. BEOL Comparison
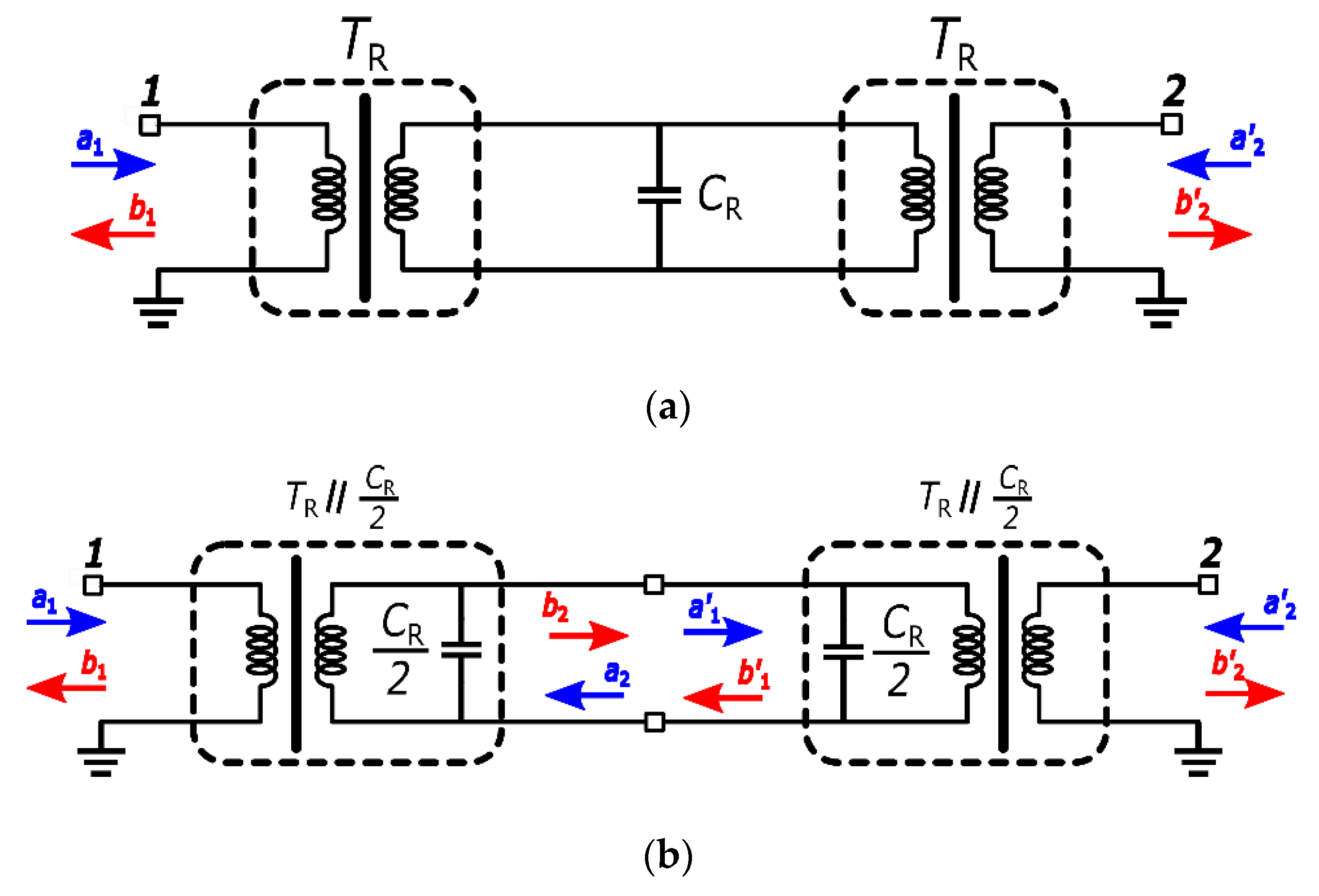
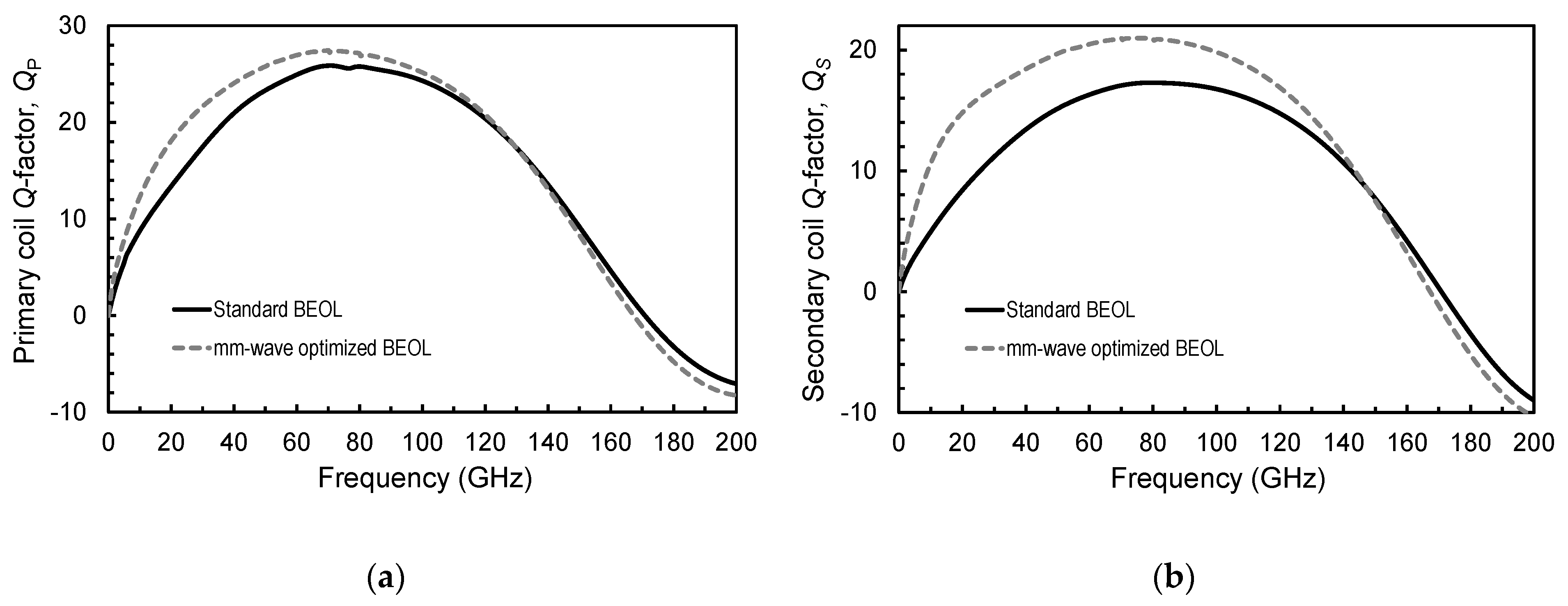
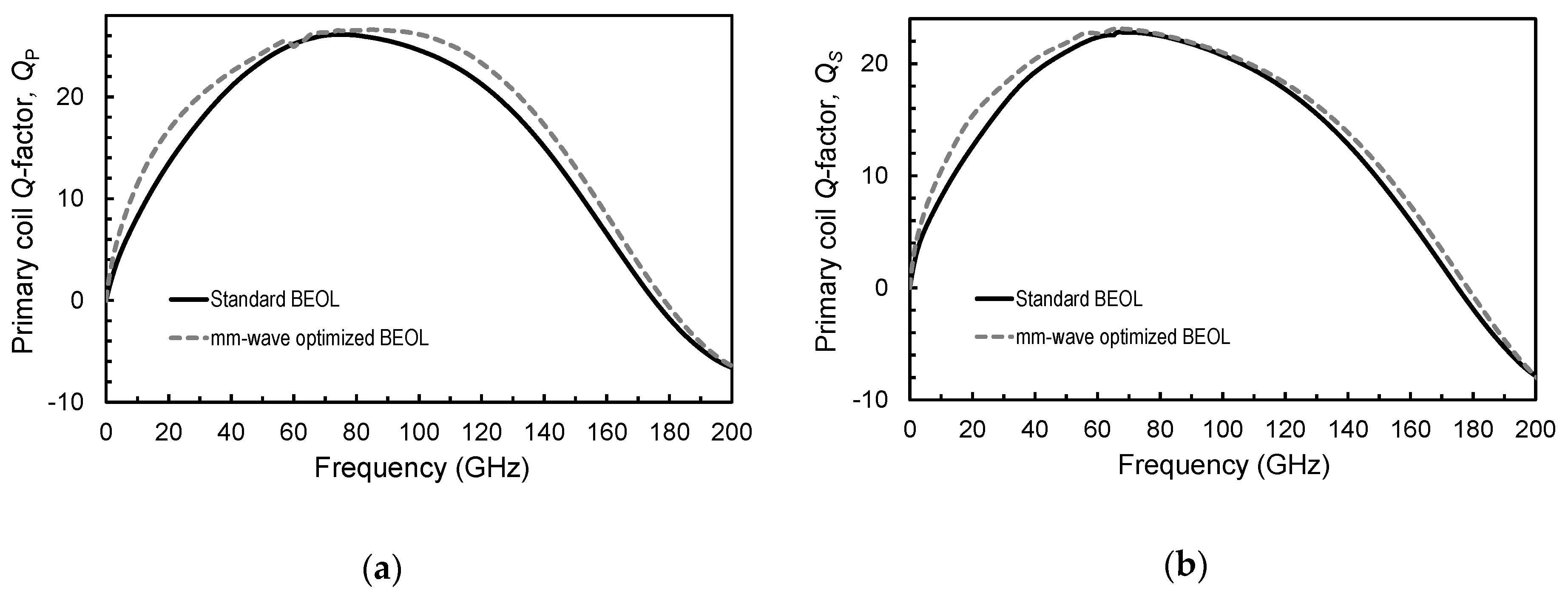
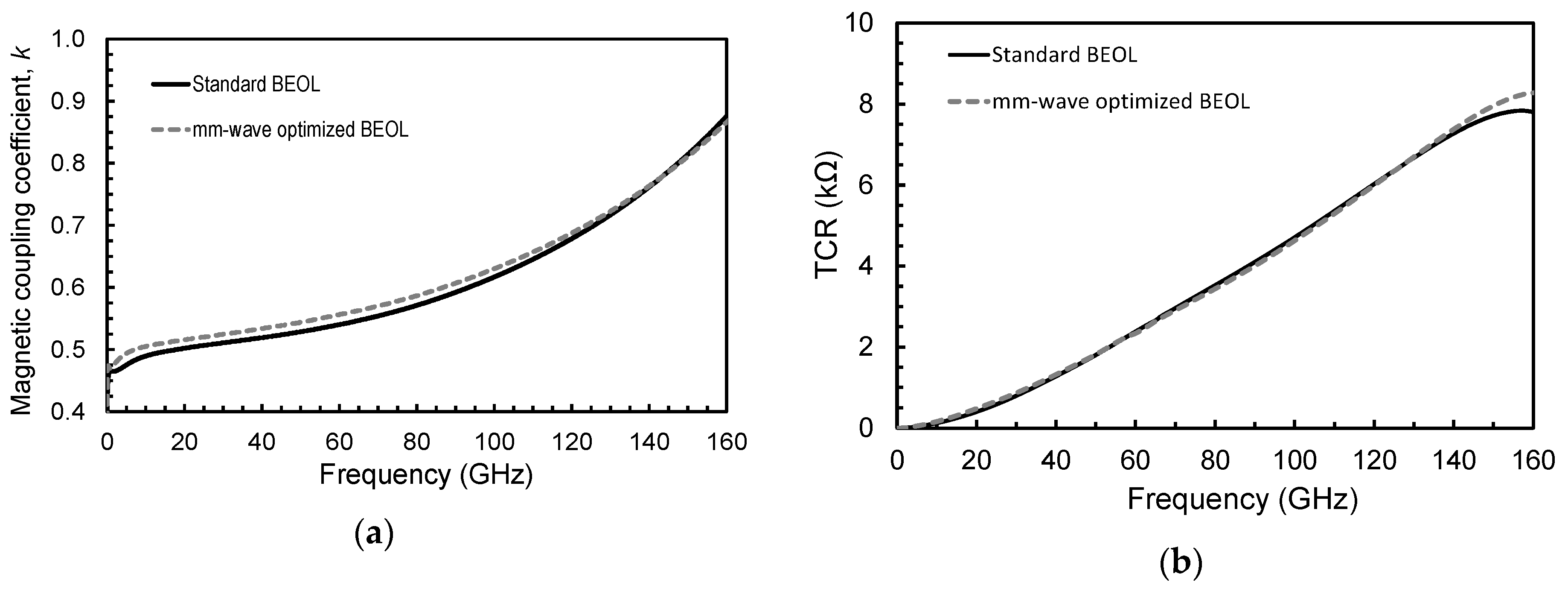
3.1. Stacked Transformer
3.2. Interleaved Transformer
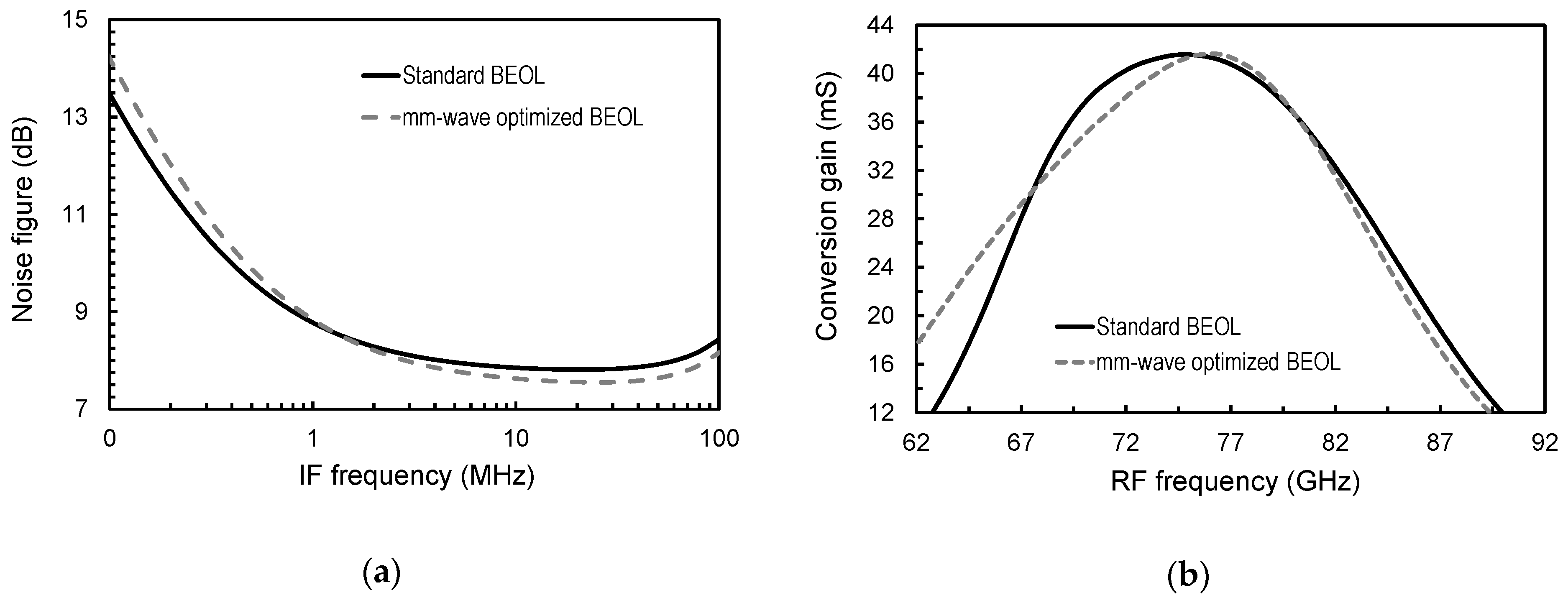
3.3. 77 GHz Down-Converter
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Serhan, A.; Lauga-Larroze, E.; Bourdel, S.; Fournier, J.-M.; Corrao, N. Comparison between MOS and bipolar mm-wave power amplifiers in advanced SiGe technologies. In Proceedings of the IEEE Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (BCTM), Coronado, CA, USA, 28 September–1 October 2014; pp. 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, P.; Liebl, W.; Rucker, H.; Gauthier, A.; Manger, D.; Heinemann, B.; Avenier, G.; Bock, J. SiGe BiCMOS Current Status and Future Trends in Europe. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE BiCMOS and Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuits and Technology Symposium (BCICTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 15–17 October 2018; pp. 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Spasaro, M.; Zito, D. Millimeter-Wave Integrated Silicon Devices: Active versus Passive—The Eternal Struggle Between Good and Evil: (Invited Paper). In Proceedings of the 2019 International Semiconductor Conference (CAS), Sinaia, Romania, 9–11 October 2019; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Avenier, G.; Diop, M.; Chevalier, P.; Troillard, G.; Loubet, N.; Bouvier, J.; Depoyan, L.; Derrier, N.; Buczko, M.; Leyris, C.; et al. 0.13 m SiGe BiCMOS Technology Fully Dedicated to mm-Wave Applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2009, 44, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.; Aufinger, K.; Boguth, S.; Dahl, C.; Knapp, H.; Liebl, W.; Manger, D.; Meister, T.F.; Pribil, A.; Wursthorn, J.; et al. SiGe HBT and BiCMOS process integration optimization within the DOTSEVEN project. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting—BCTM, Boston, MA, USA, 26–28 October 2015; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Pekarik, J.J.; Adkisson, J.; Gray, P.; Liu, Q.; Camillo-Castillo, R.; Khater, M.; Jain, V.; Zetterlund, B.; Divergilio, A.; Tian, X.; et al. A 90 nm SiGe BiCMOS technology for mm-wave and high-performance analog applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (BCTM), Coronado, CA, USA, 28 September–1 October 2014; pp. 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, P.; Avenier, G.; Ribes, G.; Montagné, A.; Canderle, E.; Céli, D.; Derrier, N.; Deglise, C.; Durand, C.; Buczko, M.; et al. A 55 nm triple gate oxide 9 metal layers SiGe BiCMOS technology featuring 320 GHz fT/370 GHz fMAX HBT and high-Q millimeter-wave passives. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2014; pp. 3.9.1–3.9.3. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, A.; Jain, V.; Ong, S.N.; Wolf, R.; Lim, S.F.; Singh, J. Technology positioning for mm-wave applications: 130/90nm SiGe BiCMOS vs. 28nm RFCMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE BiCMOS and Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuits and Technology Symposium (BCICTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 15–17 October 2018; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cathelin, A. Fully Depleted Silicon on Insulator Devices CMOS: The 28-nm Node Is the Perfect Technology for Analog, RF, mmW, and Mixed-Signal System-on-Chip Integration. IEEE Solid State Circuits Mag. 2017, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, C.; Cavarra, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G.; Papotto, G. Down-converter solutions for 77-GHz automotive radar sensors in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th Conference on Ph.D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), Prague, Czech Republic, 2–5 July 2018; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fujibayashi, T.; Takeda, Y.; Wang, W.; Yeh, Y.-S.; Stapelbroek, W.; Takeuchi, S.; Floyd, B. A 76- to 81-GHz Multi-Channel Radar Transceiver. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2017, 52, 2226–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, S.; Wintermantel, M.; Dixon, J.; Moeller, U.; Jammers, R.; Hauck, T.; Samulak, A.; Dehlink, B.; Shun-Meen, K.; Li, H.; et al. An RCP Packaged Transceiver Chipset for Automotive LRR and SRR Systems in SiGe BiCMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczkowski, J.; Thijs, S.; De Raedt, W.; Nauwelaers, B.; Wambacq, P. 50-to-67GHz ESD-protected power amplifiers in digital 45nm LP CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 382–383. [Google Scholar]
- Giammello, V.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. A 15-dBm SiGe BiCMOS PA for 77-GHz Automotive Radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, E.; Giammello, V.; Palmisano, G. A 24/77-GHz SiGe BiCMOS transmitter chipset for automotive radar. Wiley Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2013, 55, 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. 24-GHz ultra-wideband transmitter for vehicular short-range radar applications. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2009, 3, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, E.; Scuderi, A.; Giammello, V.; Palmisano, G. A SiGe BiCMOS 24-GHz receiver front-end for automotive short-range radar. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2010, 67, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammello, V.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. A Transformer-Coupling Current-Reuse SiGe HBT Power Amplifier for 77-GHz Automotive Radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammello, V.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Transformer-coupled cascode stage for mm-wave power amplifiers in sub-μm CMOS technology. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2010, 66, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, E.; Scuderi, A.; Biondi, T.; Palmisano, G. Scalable lumped modeling of single-ended and differential inductors for RF IC design. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2009, 19, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapone, G.; Ragonese, E.; Italia, A.; Palmisano, G. A 0.13-µm SiGe BiCMOS colpitts-based VCO for W-band radar transmitters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, M.H.; Tarkeshdouz, A.; Molavi, R.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Afshari, E.; Mirabbasi, S. On the Design of a High-Performance mm-Wave VCO With Switchable Triple-Coupled Transformer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 4450–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.H.; Lee, O.; Kim, H.; Lee, N.H.; Han, J.; Yang, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Chang, J.J.; Woo, W.; Lee, C.-H.; et al. Power-Combining Transformer Techniques for Fully-Integrated CMOS Power Amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2008, 43, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandstrom, D.; Martineau, B.; Varonen, M.; Karkkainen, M.; Cathelin, A.; Halonen, K.A.I. 94 GHz power-combining power amplifier with +13 dBm saturated output power in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–7 June 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi, A.; Ragonese, E.; Biondi, T.; Palmisano, G. Integrated Inductors and Transformers: Characterization, Design and Modeling for Rf and Mm-Wave Applications; CRC Press—Taylor Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Spataro, S.; Ragonese, E. Design and optimization of silicon-integrated inductive components for automotive radar applications in K- and W-bands. In Proceedings of the 2020 AEIT International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive (AEIT AUTOMOTIVE), Torino, Italy, 18–20 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ragonese, E.; Sapone, G.; Palmisano, G. High-performance interstacked transformers for mm-wave ICs. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2010, 52, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, F.; Italia, A.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Design methodology for the optimization of transformer-loaded RF circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2006, 53, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larie, A.; Kerhervé, E.; Martineau, B.; Vogt, L.; Belot, D. A 60 GHz 28 nm UTBB FD-SOI CMOS reconfigurable power amplifier with 21% PAE, 18.2 dBm P1 dB and 74 mW PDC. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Cavarra, A.; Nocera, C.; Papotto, G.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Transformer design for 77-GHz down-converter in 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS Technology. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Proceedings of the International Conference on Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society, Pisa, Italy, 26–27 September 2018; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Ragonese, E.; Sapone, G.; Giammello, V.; Palmisano, G. Analysis and modeling of interstacked transformers for mm-wave applications. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2011, 72, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataro, S.; Salerno, N.; Papotto, G.; Ragonese, E. The effect of a metal PGS on the Q -factor of spiral inductors for RF and mm-wave applications in a 28-nm CMOS technology. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2020, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponara, S.; Greco, M.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G.; Neri, B. Highly Integrated Low Power Radars; Artech House: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781608076659. [Google Scholar]
- Keysight Technologies. Momentum 3D Planar EM Simulator. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/en/pc-1887116/momentum-3d-planar-em-simulator?cc=US&lc=eng (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Design of a SiGe BiCMOS low-noise amplifier for 24-GHz UWB automotive radar. In Proceedings of the European Agilent Technologies ADS Users’ Group Meeting, Rome, Italy, 13 May 2009; Available online: http://www.home.agilent.com/upload/cmc_upload/All/RagoneseEuropeanADSMeetingweb.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Scuderi, A.; Biondi, T.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. Analysis and modeling of thick-metal spiral inductors on silicon. In Proceedings of the 2005 European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2005; pp. 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, H.; Nakamura, M. Capacitance of a strip capacitor. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1990, 13, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, S.Y.; Chew, W.C.; Kong, J.A. Approximate formulas for line capacitance and characteristic impedance of microstrip line. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1981, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, A. Microwave Transistor Amplifiers: Analysis and Design, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1984; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | Standard CMOS BEOL | mm-Wave-Optimized CMOS BEOL | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary/secondary coil width (w) | 5.5/5.5 | 5.5/5.5 | µm |
| Primary/secondary inner diameter (dIN) | 44/44 | 60/60 | µm |
| Primary/secondary coil inductance @ 77 GHz | 84/96 | 119/130 | pH |
| Primary/secondary coil Q-factor @ 77 GHz | 25/17 | 27/21 | - |
| Magnetic coupling factor (k) @ 77 GHz | 0.63 | 0.62 | - |
| Insertion loss (IL) @ 77 GHz (in resonance) | 1.3 | 1.1 | dB |
| Transformer characteristic resistance (TCR) @ 77 GHz | 2.3 | 3.6 | kΩ |
| Self-resonance frequency (SRF) | 170 | 170 | GHz |
| Parameters | Standard CMOS BEOL | mm-Wave-Optimized CMOS BEOL | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary/secondary coil width (w) | 5.5 | 5.5 | µm |
| Primary/secondary inner diameter (dIN) | 70/55 | 70/55 | µm |
| Primary/secondary coil inductance @ 77 GHz | 130/110 | 120/100 | pH |
| Primary/secondary coil Q-factor @ 77 GHz | 26/22.5 | 26.5/23 | - |
| Magnetic coupling factor (k) @ 77 GHz | 0.56 | 0.58 | - |
| Insertion loss (IL) @ 77 GHz (in resonance) | 1.4 | 1.2 | dB |
| Transformer characteristic resistance (TCR) @ 77 GHz | 3.4 | 3.3 | kΩ |
| Self-resonance frequency (SRF) | 175 | 175 | GHz |
| Parameters | Standard BEOL | mm-Wave-Optimized BEOL | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage supply | 1 | 1 | V |
| Current consumption | 15 | 15 | mA |
| Conversion gain at 77 GHz | 40.3 | 40.9 | mS |
| NF (IF = 1 MHz) | 9 | 9 | dB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragonese, E.; Nocera, C.; Cavarra, A.; Papotto, G.; Spataro, S.; Palmisano, G. A Comparative Analysis between Standard and mm-Wave Optimized BEOL in a Nanoscale CMOS Technology. Electronics 2020, 9, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9122124
Ragonese E, Nocera C, Cavarra A, Papotto G, Spataro S, Palmisano G. A Comparative Analysis between Standard and mm-Wave Optimized BEOL in a Nanoscale CMOS Technology. Electronics. 2020; 9(12):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9122124
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagonese, Egidio, Claudio Nocera, Andrea Cavarra, Giuseppe Papotto, Simone Spataro, and Giuseppe Palmisano. 2020. "A Comparative Analysis between Standard and mm-Wave Optimized BEOL in a Nanoscale CMOS Technology" Electronics 9, no. 12: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9122124
APA StyleRagonese, E., Nocera, C., Cavarra, A., Papotto, G., Spataro, S., & Palmisano, G. (2020). A Comparative Analysis between Standard and mm-Wave Optimized BEOL in a Nanoscale CMOS Technology. Electronics, 9(12), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9122124