Abstract
Removing a specific object from an image and replacing the hole left behind with visually plausible backgrounds is a very intriguing task. While recent deep learning based object removal methods have shown promising results on this task for some structured scenes, none of them have addressed the problem of object removal in facial images. The objective of this work is to remove microphone object in facial images and fill hole with correct facial semantics and fine details. To make our solution practically useful, we present an interactive method called MRGAN, where the user roughly provides the microphone region. For filling the hole, we employ a Generative Adversarial Network based image-to-image translation approach. We break the problem into two stages: inpainter and refiner. The inpainter estimates coarse prediction by roughly filling in the microphone region followed by the refiner which produces fine details under the microphone region. We unite perceptual loss, reconstruction loss and adversarial loss as joint loss function for generating a realistic face and similar structure to the ground truth. Because facial image pairs with or without microphone do not exist, we have trained our method on a synthetically generated microphone dataset from CelebA face images and evaluated on real world microphone images. Our extensive evaluation shows that MRGAN performs better than state-of-the-art image manipulation methods on real microphone images although we only train our method using the synthetic dataset created. Additionally, we provide ablation studies for the integrated loss function and for different network arrangements.
1. Introduction
Facial expressions are an important part of daily life communication. Smile can present our acceptance of a message while a scowl might indicate disagreement. However, when a person is speaking on a microphone in scenarios such as stage performance, press conference and speech, the microphone occludes the person’s face and makes it difficult to understand their facial expressions.
The goal of this research is to remove the microphone object in facial images. It involves detection of the microphone part, and then inpainting of the holes left behind with plausible correct contents. This problem is challenging because (1) the result heavily depends on the accuracy of detection of the microphone region, (2) it is not easy to recover complex semantics of the face under the microphone region detected, and (3) training data, i.e., facial image pairs with and without microphone are sparse or non-existent. Because we want our work to be deployed in the real world as a working application, we take an interactive approach that removes the microphone part in facial images by manually providing the microphone region in an image. After the user selects the microphone region although not exact, our algorithm successfully fills in the left behind hole with correct facial semantics with fine details. For the inpainting problem, we propose a novel image-to-image translation based method. To overcome the data scarcity problem, we have created a synthetic dataset by placing microphone object in facial images from CelebA database.
As shown in Figure 1, given an input image where some part of the face is covered by the microphone along with a rough outline of the microphone region provided by the user, we generate a plausible and natural face image with the microphone part removed. Because the rough microphone region is provided, a successful solution to the inpainting problem is critical. As previously mentioned, we formulate the inpainting problem into image-to-image translation. We employ “coarse-to-fine structure recovery approach” where the first inpainter network fills coarse information under the microphone part and an additional refiner network is employed to refine the inpainted area with perceptually plausible semantics.

Figure 1.
Microphone removal results of MRGAN on real world images.
We have trained the proposed network on the synthetically generated microphone dataset from the CelebA facial images and evaluated on real world facial images with microphone. We have compared the performance of MRGAN with state-of-art image inpainting methods. For fair comparison, we have made the information on the microphone region available to their methods. Experimental results show that MRGAN performs better than state-of-art image inpainting methods.
The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows.
- We propose a novel image-to-image translation based inpainting method for microphone removal in facial images.
- We unite reconstruction loss (, low level, loss and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM), high level, loss), feature level perceptual loss with adversarial loss to reconstruct plausible and natural face structure and texture.
- For training our network, we have created a synthetic dataset by inserting a synthetic microphone object in facial image. The performance on real world data is quite satisfactory although we only train our network using the synthetic dataset created.
- We experimentally show that MRGAN effectively removes the microphone object and generate plausible semantics in facial images than previous stat-of-the-art image manipulation methods.
2. Related Work
Object removal: Criminisi et al. [1] proposed an exemplar-based texture synthesis method, which is a unified scheme to fill in a target region with plausible texture. However, it is unable to produce reasonable results for the synthesis of areas for which similar patches do not exist in the image. Wang et al. [2] presented an improved exemplar-based inpainting technique for object removal. They used a combination of normalized cross correlation and a modified sum of squared differences to search for the best matching patch. Although it successfully removes the object in simple scenes, artifacts are produced at the boundaries of removed objects. Bau et al. [3] proposed a method to visualize and understand GANs at the unit-, object-, and scene-level which can remove objects like trees, curtains and windows. It struggles to remove objects such as tables and chairs from a conference room, however results are blurred. Since recovering facial semantics is hard due to its complex structure, aforementioned methods do not work well for microphone removal.
One recent work [4] automatically detects the object to be remove and fill hole with plausible outputs in general scene images. It heavily depends on the automatic detection of the object to remove. Often times their automatic mask generator is unable to detect microphone part due to diversity in shape, size, illumination and position of the microphone. For example, sometimes one holds a microphone in his/her hands, which hides the most part of the microphone. Moreover, they fill left behind holes by propagating image appearance information from surrounding pixels, which produces artifacts in facial images. Hence, these reasons make it practically less useful for the microphone removal problem in facial images.
Image inpainting: Image inpainting nowadays is one of the hot research topics in the field of computer vision. The goal of inpainting are countless, from the removing unwanted object, restoring damaged part to adding specific objects in an image. In this work, we focus on the removing microphone in facial images and complete the remaining hole with appropriate contents and fine details.
Traditional image inpainting methods propagate image information from neighboring pixels to fill-in the damaged part [5,6]. However, all those schemes can only inpaint small regions with stationary texture and may generate artifacts for the regions where texture and color variance is large. Patch-based methods copy-paste similar patches from source image into the target image [7,8]. These methods perform well for inpainting non-stationary texture. Since these methods work in iterative manner, which make them computationally expensive and inefficient for real-time systems.
Pathak et al. proposed the first CNN bsased based image inpainting network called Context Encoders (CE) [9]. CE can inpaint large damaged area conditioned on its surroundings information. They used both adversarial loss and pixel-wise reconstruction loss. However, CE is unable to recover high frequency details and produced artifacts. Structural inpainting [10], which is CE based method, used an additional loss term called perceptual reconstruction loss for image inpainting. It can generate better inpainting results to recover complex structures. Liu et al. proposed an approach to exploit multiple level supervision of objective functions for semantically consistent inpainting [11]. Similar to [9,10,11], we use low-level () and high-level (SSIM) as reconstruction loss to inpaint region under the microphone.
Song et al. [12] advocated an inpainting method which first inferences a coarser image and use the VGG network [13] to extract feature information. They match patches in feature space, which are finally translated to a high-resolution output image. Recently, a two-stage network to inpaint the mosaiced area in a face image was proposed in [14]. It removes the mosaic and generated face semantics in a coarse-to-fine manner. It can only inpaint square-shape damaged area. Iizuka et al. proposed Globally and Locally consistent Image completion (GLI) network, which can inpaint arbitrary damaged area [15]. It produced better inpainting results but output has some artifacts when the missing regions are at the margins of an image. Yu et al. introduced several changes to the method in [15] method. It is a two-stage network for generative inpainting with Contextual Attention (CA) layer [16]. CA learns structural information by explicitly considering relevant patches from nearby areas. Recently, Yang et al. proposed a joint CNN optimization framework to hallucinate the holes by exploiting both local texture information and global content information [17]. They used a multi-scale neural patch synthesis method, which was able to inpaint the image with high resolution. Similarly, our network is a two-stage approach to inpaint microphone region with fine details.
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN): GAN is used for image generation tasks and has shown powerful results [18]. It consists of two networks: a generator network and a discriminator network. Generator network learns data distribution, and discriminator network approximates the probability that a sample came from the generator or training data. Adversarial training is used to alternatively train the generator and the discriminator networks. GAN has shown promising ability to produce natural looking outputs [19]. Due to this ability, GAN’s have extensively been used for task such as texture synthesis [20,21], domain translation [22,23,24] and image inpainting [9,10,11,15,16,17,24,25].
EdgeConnect [26] used a two-stage GAN based model to inpaint damaged part by exploiting a hallucinated edge map of the damaged part. It heavily depends on the edge information generated by edge generator. EdgeConnect suffers when edge generator fails to generate correct edge information. SPG-Net [27] exploits a semantic segmentation mask for inpainting task to disentangle inter and intra class variations. It first inpaints the segmentation mask of damaged image then inpaints it with the help of segmentation mask. SPG-Net recovers clear boundaries between different regions but produce artifacts while recovering complex semantic structures such as eyes and nose.
Motivated by [26], we divide our problem into two sub tasks: (1) our inpainter network fills in the microphone part with a coarse prediction, (2) conditioned on the inpainter output, the refiner network generates facial images without the microphone with fine details. Our approach is a GAN based methodology, in which the generator architecture is similar to UNET [28], which has multiple skip-connections and discriminator is Patch-GAN [22] based, to capture details particularly under microphone area.
3. MRGAN
We propose our method called MRGAN: Microphone Removal using Generative Adversarial Network. MRGAN consists of two networks: (1) Inpainter Network (INP), and (2) Refiner Network (REF). Both inpainter and refiner networks follow a GAN approach, i.e., each network consists of a generator and a discriminator. The generator and discriminator for the face inpainter network are denoted by and , respectively. While, and denotes the generator and discriminator for the face refiner network, respectively. For simplicity, we used these notations in the following sections. The overall architecture of MRGAN is shown in Figure 2.
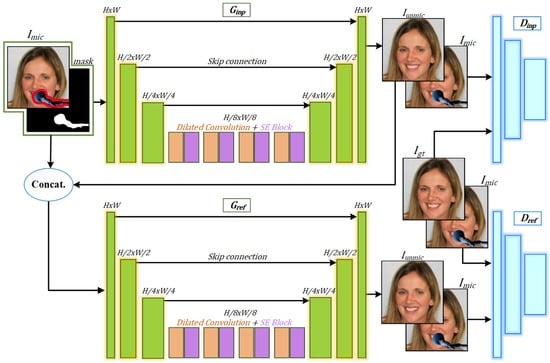
Figure 2.
The proposed architecture for microphone removal: The inpainter first estimates a coarse prediction for the microphone region, followed by the refiner which produces fine details there.
Inpainter network: Given a facial image with microphone as the input, the user roughly draws the outline of the microphone region, then a binary mask is produced internally for the microphone region. The inpainter network takes , which is the concatenation of the input image with the mask, to generate a coarse output image without microphone, . The inpainter network consists of two main blocks, Generator and Discriminator. Generator, , is a simple encoder-decoder (U-Net [28])-like architecture. Skip connections introduced by the U-Net architecture allows to retrieve the spatial information lost by the contracting and expanding the path of the network by combining local information with the global information while upsampling. Encoder feature maps are passed through skip connections to the decoder and concatenated with the corresponding decoder feature maps. Different from the UNET, we alternatively used four layers of dilated convolution (rate: 2, 4, 8, 16) [29] and squeeze and excitation (SE) blocks [30] in the middle of encoder and decoder in the generator model. The purpose of dilated convolution is to capture large field of view with less numbers of parameters, which makes the part under the microphone consistent with its surroundings. While SE block enhances the representational power of a network by learning the channel weights according to their importance and re-calibrates the feature maps.
The five layer encoder progressively down-samples the features. In Figure 2 we only show three layers in the encoder architecture for simplicity). Here, each layer is composed of relu, convolution and instant_norm, except the first and the last layer. The last layer of uses tanh as the activation function instead of relu. The decoder architecture progressively up-samples the features to image scale. We use transpose convolution instead of convolution in the decoder architecture. In contrast to conventional GAN discriminators, we exploit the Patch-GAN discriminator which penalizes dissimilar structure at the patch scale [22].
Refiner network: The refiner network architecture is similar to that of the inpainter network except that we exploit again at the refiner input along with the inpainter results, , as shown in Figure 2. The advantage of using at the refiner is that the refiner network captures details around edges of the microphone region. is the final output image without microphone with fine details in the removed region.
Furthermore, we use feature level reconstruction error from a pre-trained loss network and termed it as perceptual loss. As shown in Figure 3, feature maps of middle layer, i.e., convolution_3, convolution_4 and convolution_5 of the pre-trained VGG-19 [13] are used to measure perceptual loss. We have empirically found that middle layers have both low level and structural information which helps recover perceptually plausible face semantics.
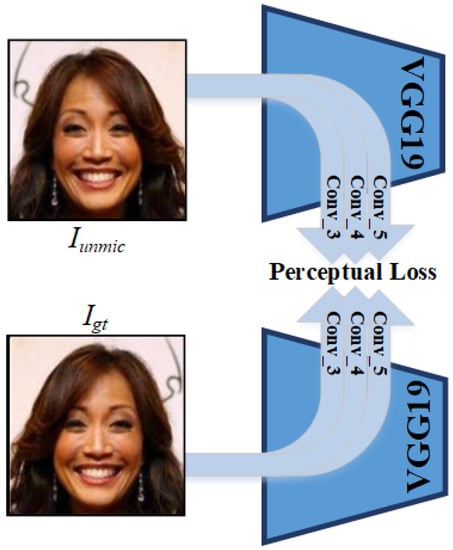
Figure 3.
Perceptual loss calculation from the pre-trained loss network [13].
Loss Function
Most of previous state-of-the-art image editing methods used reconstruction or similarity loss to recover the structure similar to the ground truth and naturalness loss (e.g., GAN loss [18] or Wasserstein GAN loss [31]) for generating realistic results. Our joint loss function is a combination of reconstruction loss, perceptual loss and adversarial loss. The overall joint loss function can be written as follows:
where and are constants to adjust the weights of reconstruction loss and perceptual loss. The reconstruction loss is a combination of low level loss and structural penalty, SSIM loss, which can be expressed as:
is pixel-wise difference between ground truth image, , and predicted unmic image, , can be expressed as:
where is the generator’s output image without microphone. SSIM loss, , is the second part of the our reconstruction loss, which is concerned with structural similarity between the ground truth image, , and the unmic image, ,32].
We include perceptual loss, , to penalize results that are not perceptually similar to the ground truth by comparing the distance measure between activation maps of the pre-trained network for generated image and the ground truth image. It is a feature level penalty from the pre-trained loss network.
where is the feature map of the layer of the pre-trained loss network. As shown in Figure 3, we have used convolution layer feature maps, specifically, convolution_3, convolution_4 and convolution_5 layers of the pre-trained VGG-19 network [13].
Total Variation (TV) regularization encourages spatial smoothness in the generated image. is constant to adjust the weight of Total Variation in perceptual loss. It removes spurious and excessive details whilst preserving important details [33].
where defines the neighborhoods of the current pixel that are horizontally and vertically adjacent. In addition to and , adversarial loss [18] is used at the inpainter and the refiner network as expressed in Equations (7) and (8), respectively.
The output of the inpainter gives us a coarse unmic predication, , with the correct semantics. To achieve this objective, and are set to 100 and 33 in inpainter training to capture better structure. The purpose of adversarial loss is to produce realistic results. Thus, and are set to 10 and 3.3 in the refiner network training to give more focus on for yielding of natural looking results.
4. Experiments
We train our model and state-of-the-art image manipulation methods such as Content-Aware Fill (Adobe Photoshop feature based on [34]), Iizuka et al. [15] and Yu et al. [16] using a synthetic dataset and evaluate on real world test images.
Synthetic dataset: To train our network, MRGAN, in a supervised setting, we have created a synthetic dataset of 20,000 images using the publicly available, CelebA Face dataset [35]. CelebA dataset contains face images of various celebrities with wild backgrounds. We first align the faces using OpenFace dlib [36] and then create a synthetic dataset by placing microphone object in the facial image using Adobe Photoshop CC 2018. Microphones of different size and scale are placed at different locations in the images of CelebA face dataset. However, we did not consider overhead and headset microphone in synthetic dataset because overhead microphone usually does not cover the face and headset microphone covers very small part of the face. We also create corresponding microphone masks. A couple of examples from the synthetic dataset created are shown in Figure 4.
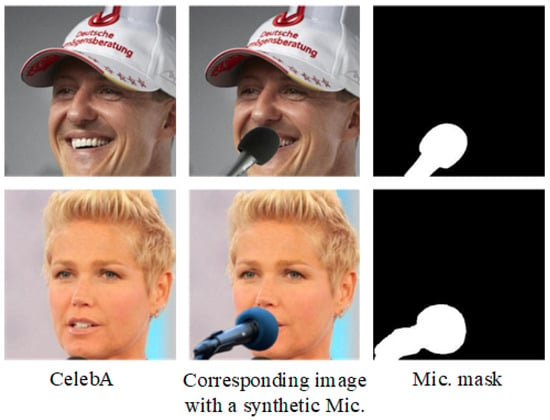

Figure 4.
Example images with their masks from the synthetic dataset.
Training: To train our network, a pair of and (ground truth image without microphone) are fed into the inpainter network. The integrated objective function, which is a combination of perceptual loss , reconstruction loss and adversarial loss is applied. The inpainter network produces the initial coarse image without microphone. Then, output of the inpainter, and the input image, , are fed into refiner, which produces a final unmic images using objectives in Equations (2), (5) and (8).
Adam optimizer [37] with momentum 0.5 and learning rate is used to alternatively train the inpainter and the refiner networks. We have used random flip and random crop augmentation methods with batch size 10. To avoid the problem of the generator being weak at the start of training, first, the generator is trained for 100 epochs and then both generator and discriminate are trained for 500 epochs. MRGAN is implemented using tensorflow library [38]. Training took 72 h on one NVIDIA GeForce 1080Ti GPU.
5. Comparison and Discussion
We now discuss the qualitative and quantitative performance of our method and its comparison with other previous state-of-the-art image manipulation methods on real world images with microphone.
5.1. Qualitative Evaluation
We present qualitative results of our method and comparison to Content-Aware Fill (Adobe Photoshop feature based on) [34], Iizuka et al. [15] and Yu et al. [16] on real world test images. We collect real face images with microphones of different sizes, shapes, locations and types from the Internet and interactively select microphone part.
As shown in Figure 5, MRGAN offers significantly improved results for real world data than the other previous state-of-the-art image manipulation methods. Content-Aware Fill inpaints the texture with right color and imminence, but is unable to generate correct structure. Iizuka et al. [15] generates better structure than Content-Aware Fill due to its global and local consistency penalties, but suffers some artifacts at the margins of inpainted area. Yu et al. [16] reduces the artifacts at margins but is unable to recover a complex face structure. The inpainter network of the proposed MRGAN generates a correct face semantic structure by carefully selecting loss function for each aspect of face reconstruction. On top of the inpainter, the refiner network is employed to produce high resolution face semantics without artifacts.

Figure 5.
Visual comparison of MRGAN with representative image completion methods on real world images. Note that our inpainter network alone performs better than the others but has some artifacts and color discrepancies which are removed by employing the refiner network on top of the inpainter.
To subjectively measure the perceptual assessment, we have performed a pilot user study. Given a real-world photo with microphone, a user was asked to choose the best photo without microphone based on the following criteria: (1) effective removal of microphone and (2) image quality and naturalness. The options are four randomly shuffled photos with microphone removed by four different methods, i.e., Content-Aware Fill [34], Iizuka et al. [15], Yu et al. [16] and MRGAN. The fifteen questions were asked form eighty-four users, who participated in the survey. 87% users selected results of MRGAN, 5% Yu et al., 4% Iizuka et al. and 4% Content-Aware Fill as their answer. These results confirm that MRGAN is superior to the other previous state-of-the-art image manipulation methods.
Although we have trained our network using the data that do not contain cases of overhead and headset microphones, we have also conducted experiments for some cases of overhead and headset microphones to see how our network works for very different types of microphones from those in the training images. Figure 6 shows the performance of MRGAN for real images with overhead and headset microphones. As expected, MRGAN does not produce as good results for overhead and headset cases as for the cases of commonly used microphones we have considered.

Figure 6.
The performance of MRGAN for real images with overhead and headset microphones. Our training dataset does not contain overhead and headset microphone images.
5.2. Quantitative Evaluation
We provide quantitative evaluations in term of Structural SIMilarity (SSIM), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Naturalness Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE) [39] and Blind/Referenceless Image Spatial Quality Evaluator (BRISQUE) [40]. NIQE and BRISQUE are non-reference image quality scores, which measure naturalness of image. For NIQE and BRISQUE, the smaller the better. Since real images with microphone do not have corresponding ground truth without microphone object, we have evaluated SSIM and PSNR on the synthetic test images. Table 1 provides a quantitative comparison with Content-Aware Fill (Adobe Photoshop feature based on [34]), Iizuka et al. [15] and Yu et al. [16]. It can be seen that for the microphone removal problem, MRGAN performs better than Content-Aware Fill, Iizuka et al. and Yu et al. Our method with careful selection of loss function and multistage approach allows to completely remove microphone and generate perceptually plausible UnMic images more closely to the original images.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of different methods in term of Structural SIMilarity (SSIM), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Naturalness Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE), and Blind/Referenceless Image Spatial Quality Evaluator (BRISQUE).
6. Ablation Study
In this section, we investigate the effect of using joint loss function, the role of giving the input image back at the refiner network input along with the inpainter network output and effect of dilated convolution.
6.1. Effect of Integrated Loss Function
We investigate the effectiveness of each component of our joint objective function. For this, we gradually add each loss term to our GAN based network and discuss the effect. The second column of Figure 7 shows that only using as reconstruction loss is unable to recover the structure of complex face semantics e.g., lips, teeth because is low level pixel to pixel penalty. To recover the correct semantic structure, we have added a structure level penalty to the reconstruction loss. As the third column of Figure 7 shows that SSIM helps recover most of the structure, but there are some artifacts which seem perceptually implausible. To cope with this issue, we have added the feature level perceptual loss from the pre-trained VGG-19 network [13]. The last row of Figure 7 shows a case where the mouth is completely covered with microphone. Although it is a challenging test image, our whole loss function almost recovers the missing face semantics. The last column of Figure 7 presents that the whole loss function successfully generates, (a) correct semantic structure, (b) perceptually plausible results and (c) recovers better resolution under the microphone. Table 2 reports the quantitative evaluation for the ablation study on loss function in term of SSIM, PSNR, NIQE, and BRISQUE. As we can see, in cases of PSNR, NIQE, and BRISQUE, our total loss () shows the best performance, but almost the same performance as the partial losses in SSIM. Note that these are the results of the inpainter network only, which are refined by the following stage.
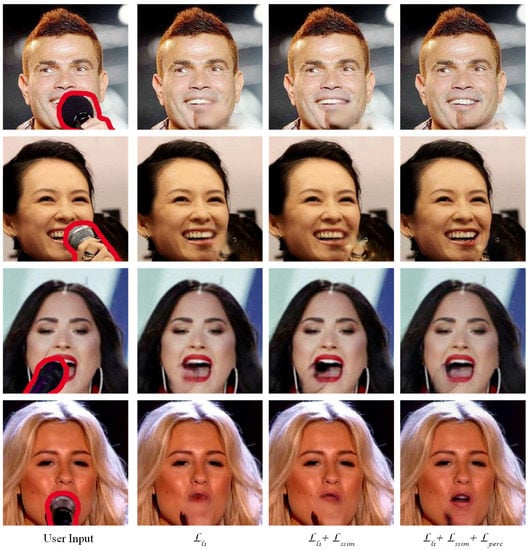

Figure 7.
Effects of different loss function for the inpainter network: From left to right, input image with microphone region provided by the user, results with reconstruction loss, , only, results with joint loss of and SSIM, , and the result with additional .

Table 2.
Quantitative evaluation for the ablation study on loss function in term of Structural SIMilarity (SSIM), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR), Naturalness Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE), and Blind/Referenceless Image Spatial Quality Evaluator (BRISQUE).
6.2. Role of Refiner Network Inputs
One may ask why we provide again as the input of refiner network. We investigate the effectiveness of providing again at the input of the refiner network. For this, we have conducted an ablation study. The second column of Figure 8 presents the result of the refiner network by providing the inpainter output only as the input. As one can see, there are some irregular structure at the boundaries of microphone region. It is because, without providing , the network is unable to locate the area to reconstruct, thus can not focus on the damaged part. The last column of Figure 8 shows the refiner results when both the microphone image and the inpainter output image are provided. Teeth and the area inside the mouth are more smooth and perceptually better. With the inpainter output concatenated with , the refiner learns about the damaged part and reconstructs more smooth image.
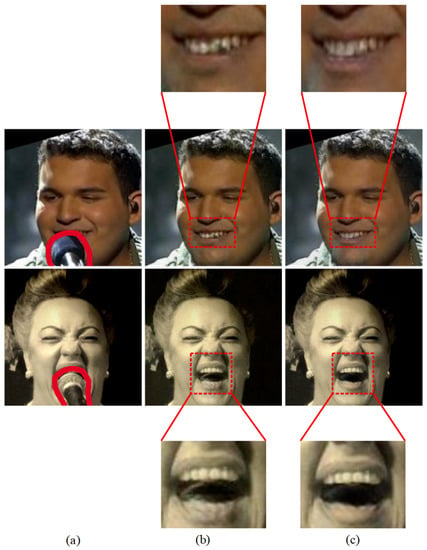

Figure 8.
The effect of providing Mic images again as the input of the refiner network. (a–c), input mic images , refiner output with the result of the inpainter network only, and refiner output with Mic images as well as the output of inpainter network.
6.3. Effect of Dilated Convolution
To investigate the effect of dilated convolution in the generator network, we have conducted an ablation study for dilated convolution. Figure 9 shows the results without dilated convolution and with dilated convolution. The results show that the recovered area on the chin is more consistent with its surrounding in case of using dilated convolution. This effect is more clearly seen in the first row of Figure 9. We can see that dilated convolution helps recover the part under the microphone consistent with its surroundings by capturing large field of view.
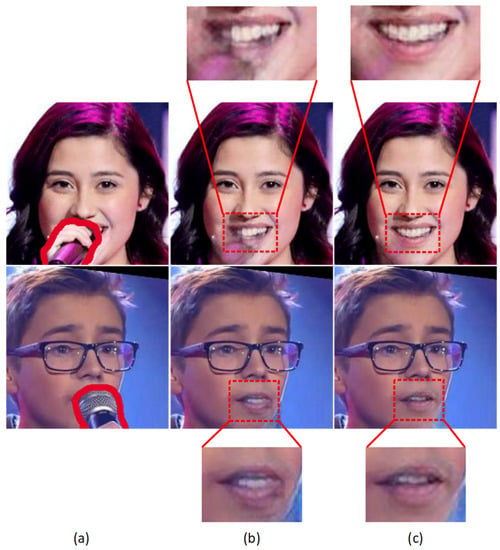

Figure 9.
The effect of dilated convolution. (a–c), input mic images , output of the network without dilated convolution and with dilated convolution.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented MRGAN that is a novel method for microphone removal using interactive inpainting in facial images. The interactive inpainter network removes the microphone region with coarse prediction under the damaged part followed by the refiner network, which produces perceptually plausible face semantics. Because of serious training data scarcity in our problem, we have created a synthetic dataset for training our network. We exploit joint loss for low level, structural and perceptual penalties to train our GAN network.
The performance on real world data is quite satisfactory although we train our network using the synthetic dataset only. MRGAN performs qualitatively and quantitatively better than other state-of-the-art image manipulation methods. To make it end-to-end trainable, one might need to automatically detect and generate mask of microphone object in facial images. In future work, we plan to expand our method to automatically detect and remove the microphone object in facial images by using object detection techniques. Furthermore, this work can be extended to microphone removal in recorded or live videos.
Author Contributions
M.K.J.K. developed the method; M.K.J.K., N.U.D. and S.B. performed the experiments and analysis; and J.Y. and M.K.J.K. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A1B03930428). We would like to offer our special thanks to Rahul Singh Maharjan and Donghwan Seo for their help in collection of real world images with microphone.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| CNN | Convolution Neural Network |
| MRGAN | Microphone Removal using Removal of Microphone |
| INP | Inpainter Network |
| REF | Refiner Network |
| SE | Squeeze and Excitation block |
References
- Criminisi, A.; Pérez, P.; Toyama, K. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, K.; Pan, D.; He, N.; Bao, B.K. Robust object removal with an exemplar-based image inpainting approach. Neurocomputing 2014, 123, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, D.; Zhu, J.Y.; Strobelt, H.; Zhou, B.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Freeman, W.T.; Torralba, A. GAN Dissection: Visualizing and Understanding Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv Preprint 2018, arXiv:1811.10597. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, R.R.; Fritz, M.; Schiele, B. Adversarial scene editing: Automatic object removal from weak supervision. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS: Denver, CO, USA, 2018; pp. 7717–7727. [Google Scholar]
- Bertalmio, M.; Sapiro, G.; Caselles, V.; Ballester, C. Image inpainting. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000; ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, C.; Bertalmio, M.; Caselles, V.; Sapiro, G.; Verdera, J. Filling-in by joint interpolation of vector fields and gray levels. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efros, A.A.; Freeman, W.T. Image quilting for texture synthesis and transfer. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 12–17 August 2001; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra, V.; Essa, I.; Bobick, A.; Kwatra, N. Texture optimization for example-based synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 2005, 24, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, H.V.; Duong, N.Q.; Pérez, P. Structural inpainting. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Multimedia Conference on Multimedia Conference, Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1948–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Qi, X.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I. Semantically Consistent Image Completion with Fine-grained Details. arXiv Preprint 2017, arXiv:1711.09345. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yang, C.; Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, H.; Jay Kuo, C.C. Contextual-based image inpainting: Infer, match, and translate. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the ICLR, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.K.J.; Din, N.U.; Seho, B.; Yi, J. Image unmosaicing without location information using Stacked Generative Adversarial Network. IET Comput. Vis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, S.; Simo-Serra, E.; Ishikawa, H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Generative image inpainting with contextual attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Lu, X.; Lin, Z.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O.; Li, H. High-Resolution Image Inpainting using Multi-Scale Neural Patch Synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; NIPS: Denver, CO, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv Preprint 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wand, M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with markovian generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–6 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 702–716. [Google Scholar]
- Jetchev, N.; Bergmann, U.; Vollgraf, R. Texture synthesis with spatial generative adversarial networks. arXiv Preprint 2016, arXiv:1611.08207. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8789–8797. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.; Din, N.U.; Javed, K.; Yi, J. Efficient Generation of Multiple Sketch Styles Using a Single Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 100666–100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, R.A.; Chen, C.; Yian Lim, T.; Schwing, A.G.; Hasegawa-Johnson, M.; Do, M.N. Semantic image inpainting with deep generative models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5485–5493. [Google Scholar]
- Nazeri, K.; Ng, E.; Joseph, T.; Qureshi, F.; Ebrahimi, M. EdgeConnect: Generative Image Inpainting with Adversarial Edge Learning. arXiv Preprint 2019, arXiv:1901.00212. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yang, C.; Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, Q.; Kuo, C.C.J. SPG-Net: Segmentation prediction and guidance network for image inpainting. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2018, (BMVC 2018), Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv Preprint 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A.C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS: Denver, CO, USA, 2017; pp. 5769–5779. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, L.I.; Osher, S.; Fatemi, E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 1992, 60, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.; Shechtman, E.; Finkelstein, A.; Goldman, D.B. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2009, 28, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3730–3738. [Google Scholar]
- Amos, B.; Ludwiczuk, B.; Satyanarayanan, M. OpenFace: A General-Purpose Face Recognition Library with Mobile Applications; Technical Report, CMU-CS-16-118; CMU School of Computer Science: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv Preprint 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. Tensorflow: A system for large-scale machine learning. OSDI 2016, 16, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. Blind/referenceless image spatial quality evaluator. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2011; pp. 723–727. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).