HF-EdgeFormer: A Hybrid High-Order Focus and Transformer-Based Model for Oral Ulcer Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- A new edge refinement module (PrecisionEdgeEnhance) used for mid encoders instead of the regular lesion-localization module present in the HF-UNet medical segmentation model.
- 2.
- Introduction of two low-level ResNet34 encoders trained on ImageNet; these two encoders are frozen for the first fifteen epochs in order to preserve generic low-level features, helping the model to stabilize better early on.
- 3.
- A much more modern vision transformer bottleneck inspired by the SegFormer UNet; this bottleneck consists of a SegFormer block, an efficient self-attention module, and a SegFormer MLP.
- 4.
- The dimension of the AutoOral dataset, even though it is much better than all the previous ones, is still pretty limited, so a new augmentation method was applied.
- 5.
- Introduction of test-time augmentation at inference in order to let the model see the test images from different angles, then aggregating the predictions by averaging them.
- 6.
- An upscaling method that can be applied on the resulting segmented images to increase the resolution, if needed.
- 7.
- The code will be made publicly available on GitHub https://github.com/DragosCornoiu/HF-EdgeFormer (accessed on 7 June 2025).
2. Related Work
2.1. Image Segmentation
2.2. Medical Image Segmentation
3. Methods
3.1. Used Dataset
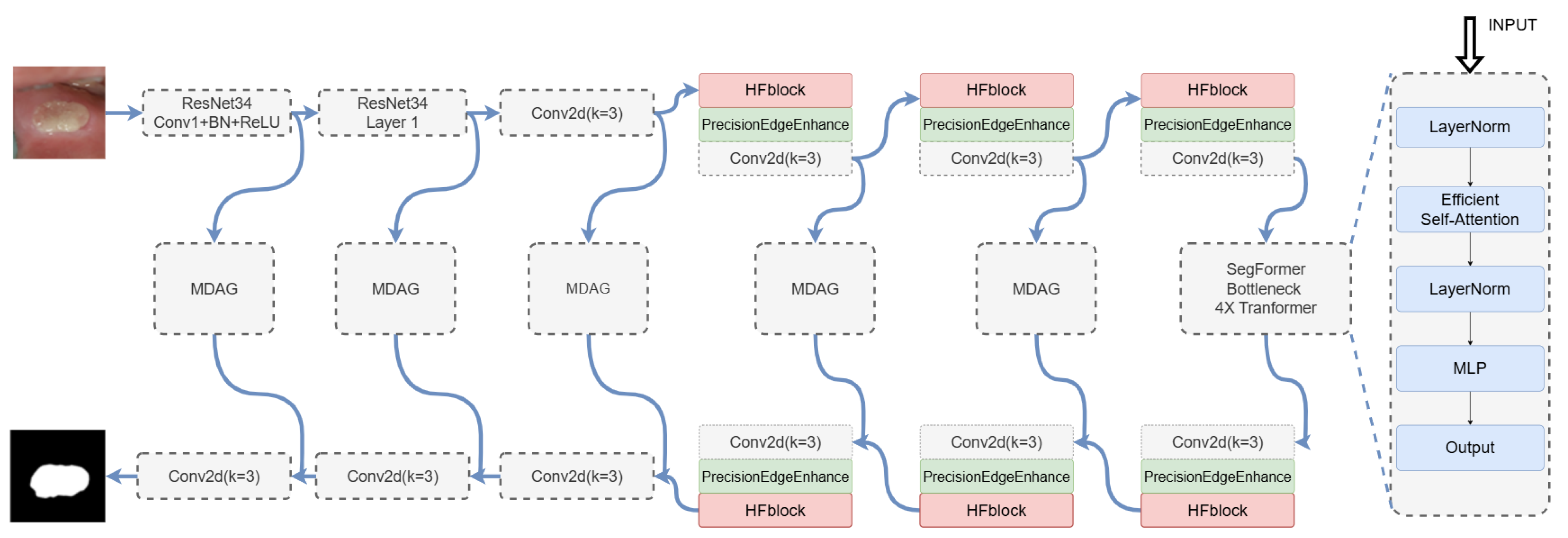
3.2. Overall Model Architecture
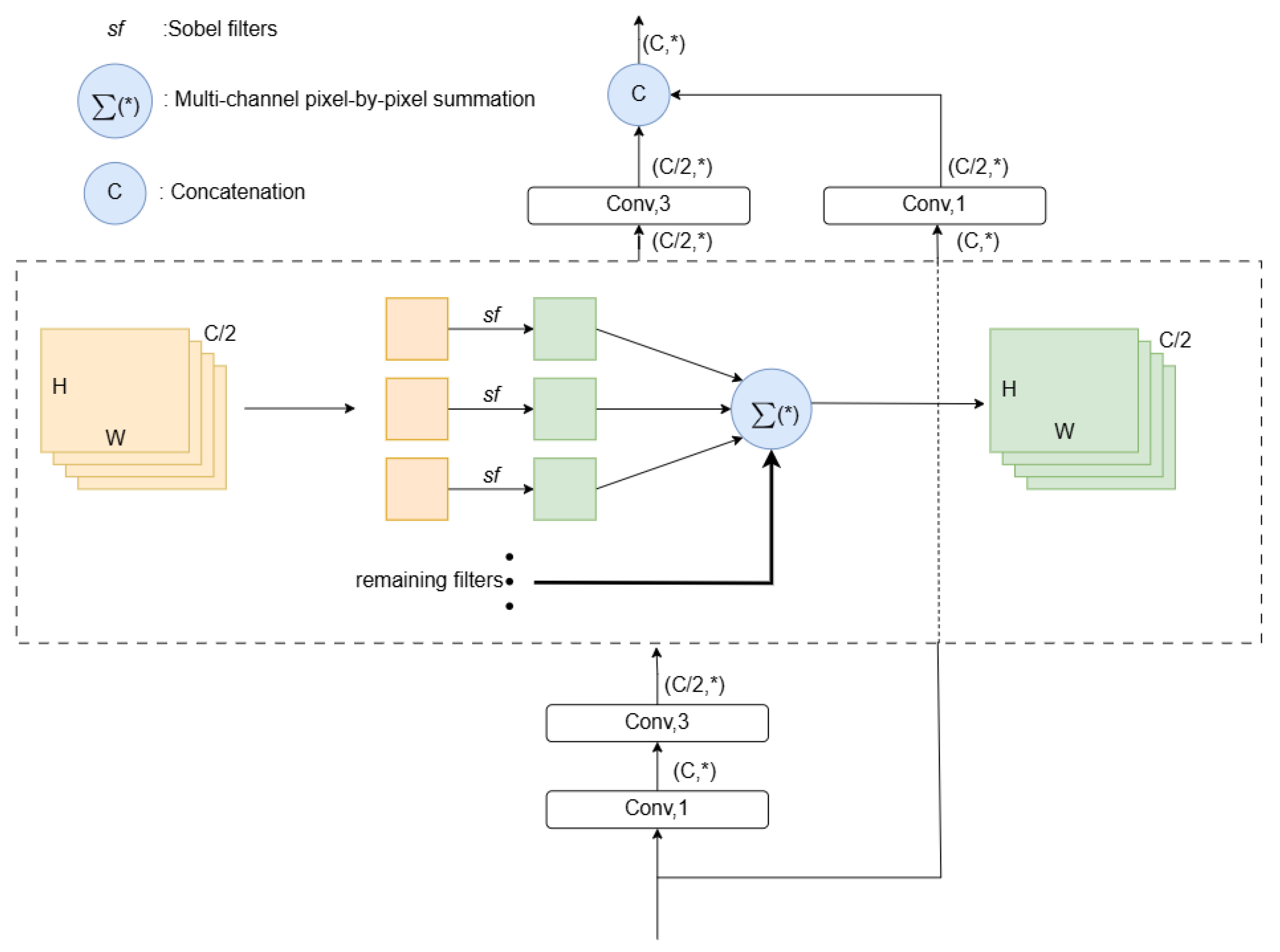
3.2.1. High-Order Focus Interaction Mechanism
3.2.2. First-Order Focus Interactions
3.2.3. High-Order Focus Interactions
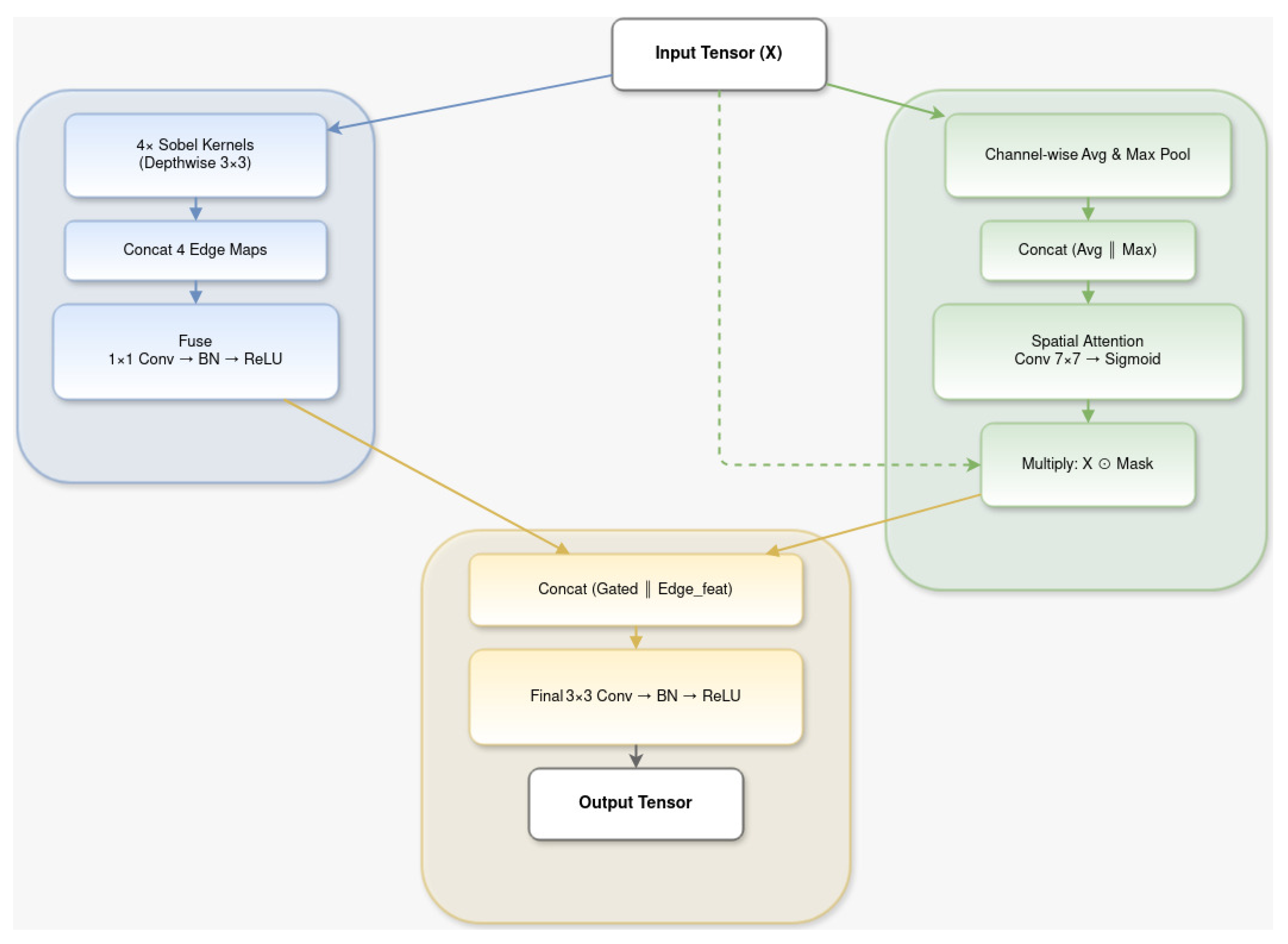
3.2.4. PrecisionEdgeEnhance Module
3.2.5. EdgeAware Module
3.2.6. ResNet Encoders
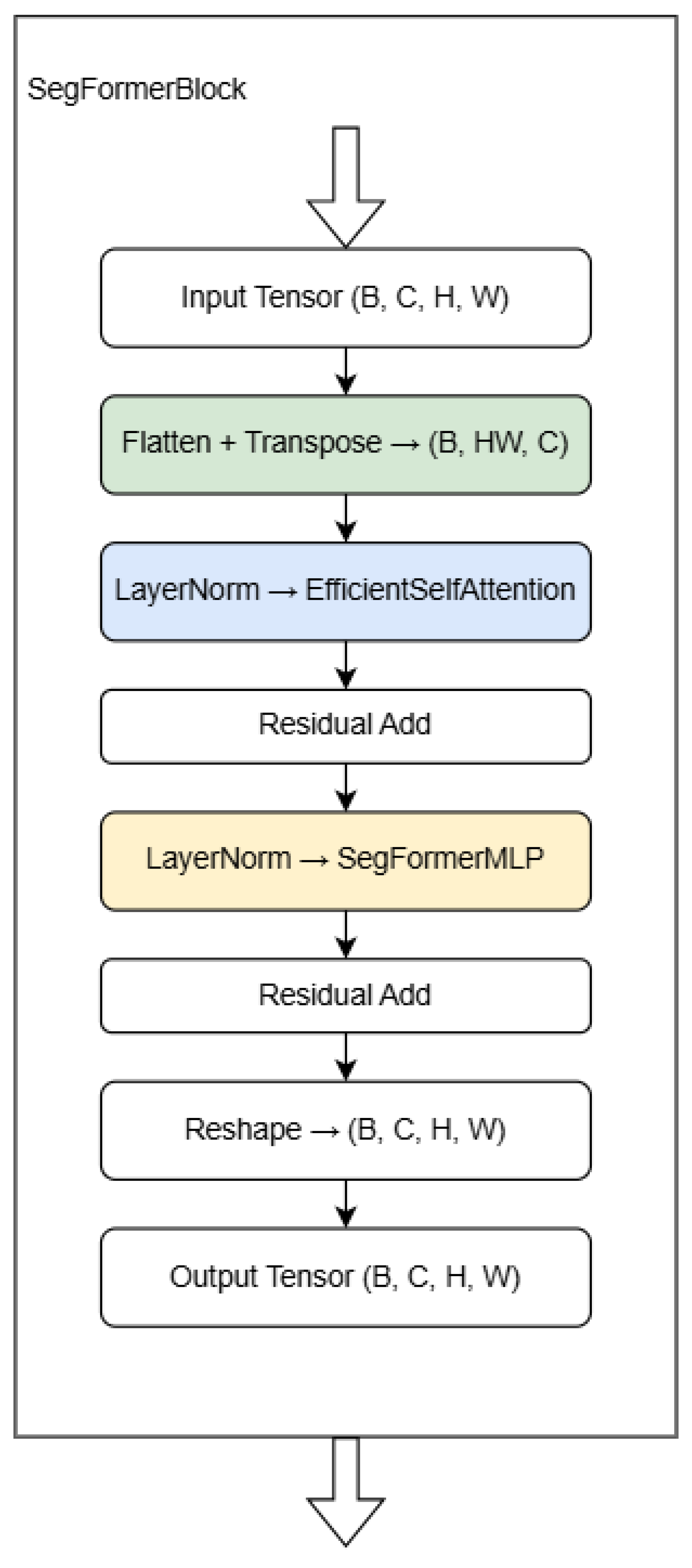
3.2.7. SegFormer Bottleneck
3.2.8. Multi-Dilation Gate Module (MDAG)
3.2.9. Test-Time Augmentation
3.2.10. Upscale Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Model Evaluation Criteria
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Techniques
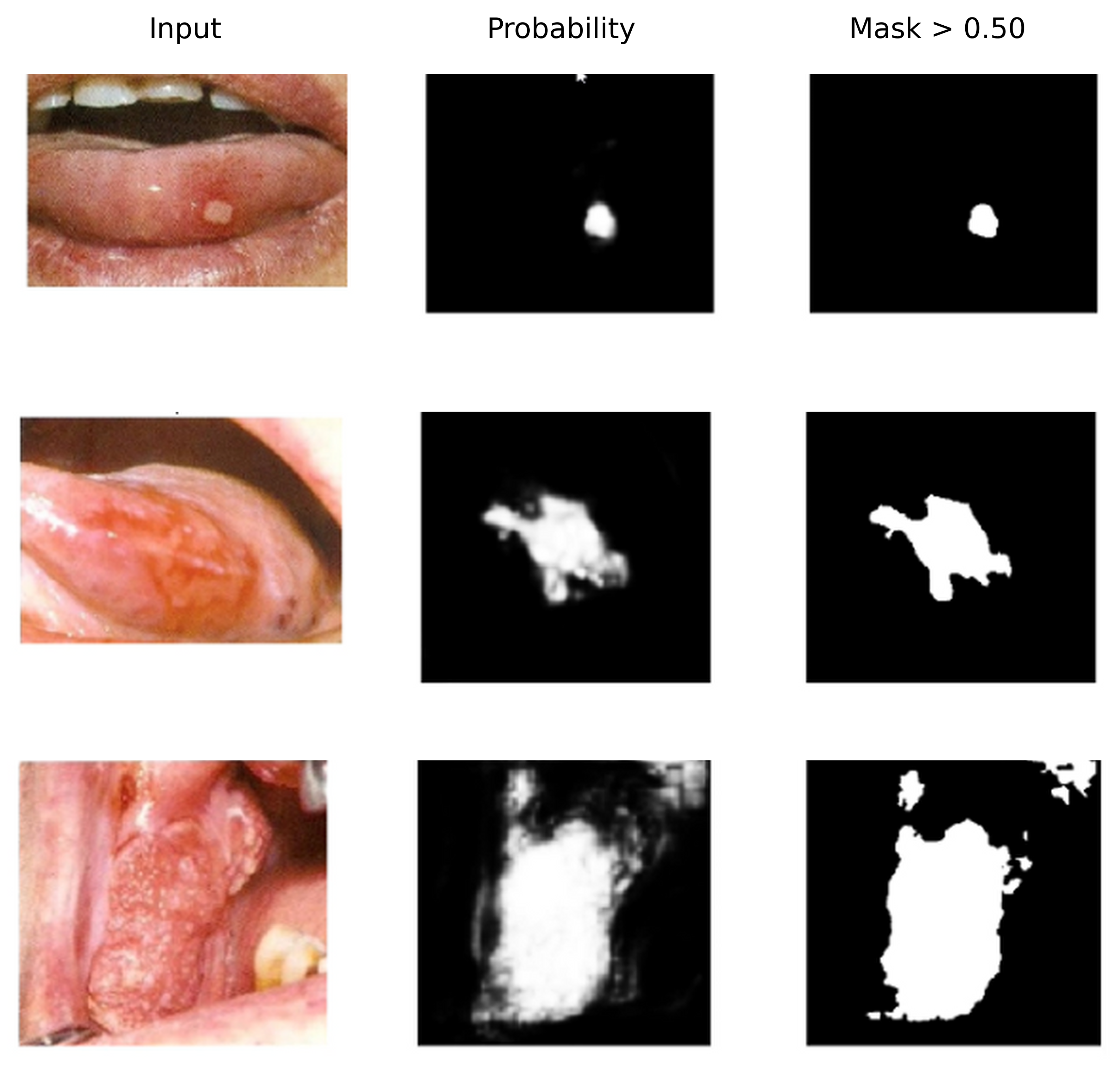
4.4. External Tests on New Samples
5. Discussion and Limitations
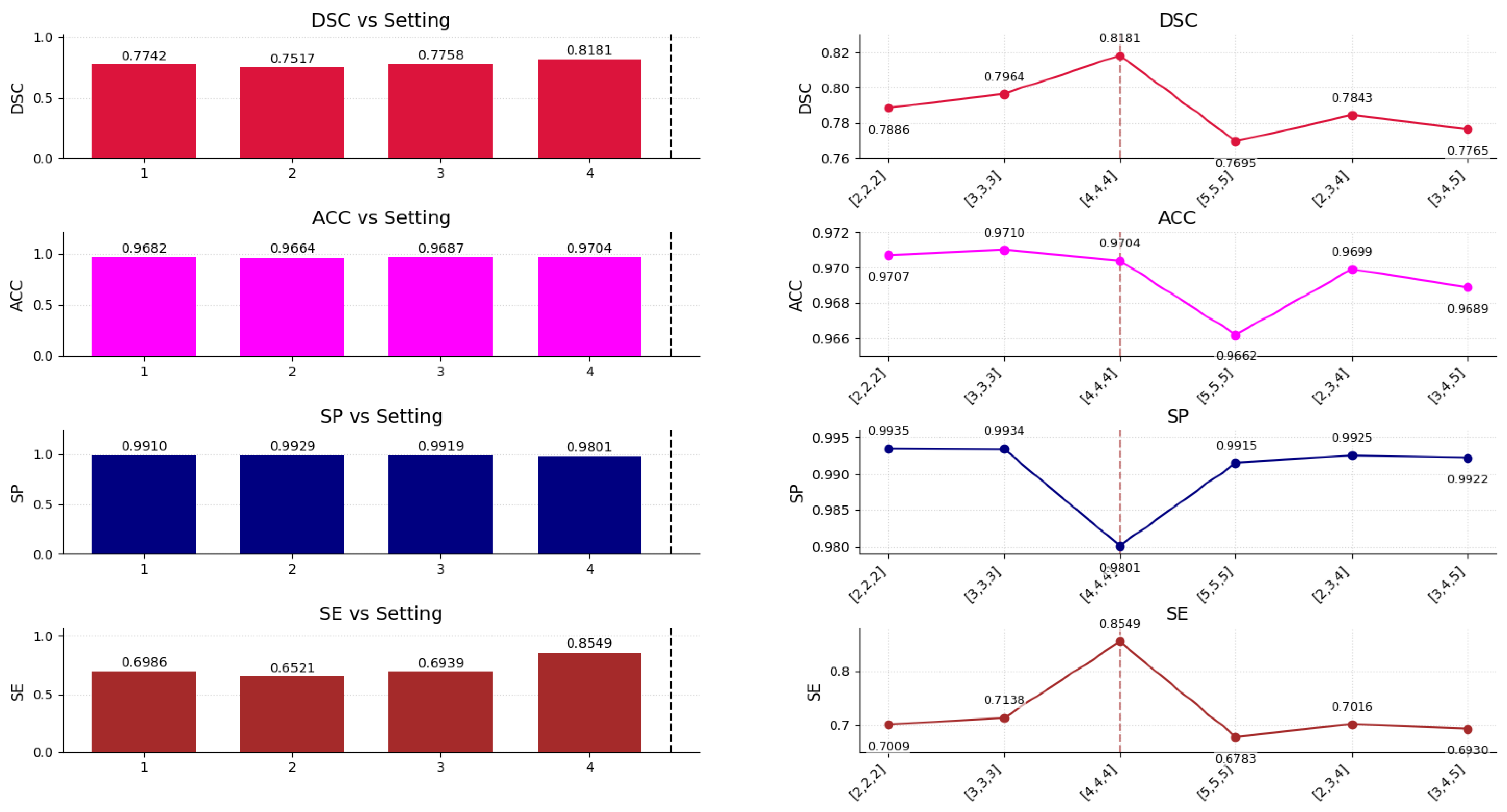
6. Ablation Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Zhong, L.; Dan, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Xie, D.; et al. Difficult and complicated oral ulceration: An expert consensus guideline for diagnosis. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, H.; Safi, Y.; Baharvand, M.J.; Rahmani, M.; Jafari, M.; Etemad-Moghadam, S.; Sadeghi, S.; Shahidi, S. Diagnostic features of common oral ulcerative lesions: An updated decision tree. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 7278925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ji, Z.; Zhuang, J.; et al. Deep learning models with multi-scale feature fusion for lesion segmentation in oral mucosal diseases. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested UNet Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.10165. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, Z.; Usman, M.; Jeon, M.; Gwak, J. Cascade multiscale residual attention CNNs with adaptive ROI for automatic brain tumor segmentation. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention UNet. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.; Xie, M.; Gao, J.; Liu, T.; Fu, Y. EGE-UNet: An Efficient Group Enhanced UNet for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougourzi, F.; Chefrour, M.; Djeraba, C. D-TrAttUnet: Dual-Decoder Transformer Attention UNet for COVID-19 Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.15576. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guan, Z.; Shen, X.; Shen, Z.; Xu, P. NTSM: A non-salient target segmentation model for oral mucosal diseases. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, P.; Fan, Y. A high-order focus interaction model and oral ulcer dataset for oral ulcer segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J. Focal self-attention for local-global interactions in vision transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.00641. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, M.; Givkashi, M.; Pri, F.; Karimi, N.; Samavi, S. Focal-UNet: UNet-like focal modulation for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.09263. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid Vision Transformer: A Versatile Backbone for Dense Prediction without Convolutions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, B.; Codella, N.; Liu, M.; Dai, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. TTA: Understanding Test-Time Augmentation; Ridge-i Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Xiong, L.; Zou, Y. Deep learning-based integrated circuit surface defect detection: Addressing information density imbalance for industrial application. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Usman, M.; Latif, S.; Gwak, J. Densely attention mechanism based network for COVID-19 detection in chest X-rays. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liao, Z.; Xia, Y. Devil is in channels: Contrastive single domain generalization for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.05254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cao, N.; Li, C.; Hu, C. IViT-CycleGAN: Synthetic CT generation based on CBCT using improved vision transformer CycleGAN. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Miao, S. M2SNet: Multi-scale in multi-scale subtraction network for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10894. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Ni, D. Medical SAM Adapter: Adapting Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment Anything. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ren, H.; Wei, X.; Xia, H.; Shen, C. Twins: Revisiting the Design of Spatial Attention in Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 7 December 2021; Volume 34, pp. 9355–9366. [Google Scholar]
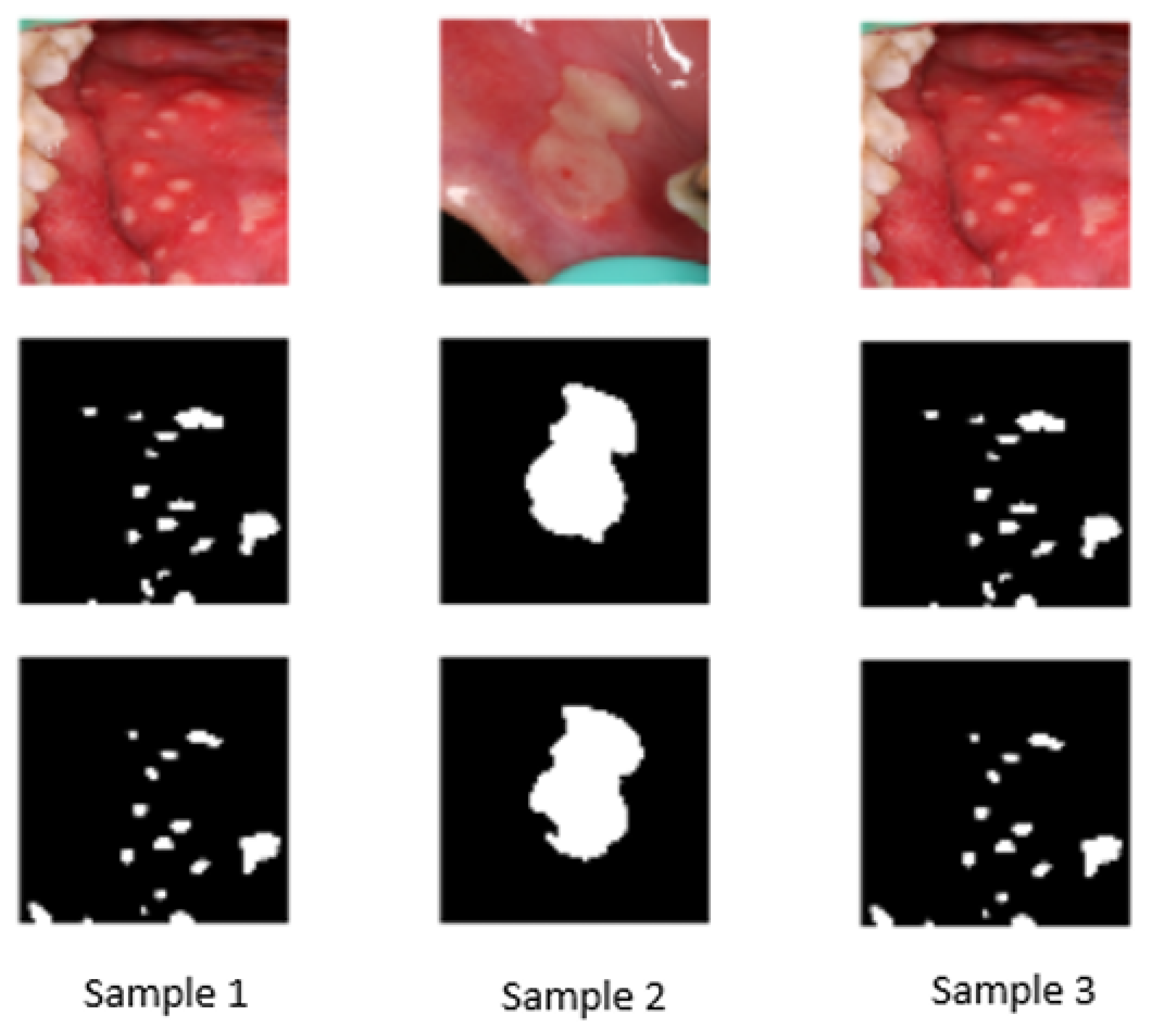
| Dataset | Age Range | Source | Number of Samples | Disease Category | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AutoOral | 7 to 84 | Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine | 420 | Cancerous ulcers | 12.33% |
| Traumatic ulcers and traumatic blood blister | 12.33% | ||||
| Herpes-like aphthous ulcers | 20.55% | ||||
| Mild aphthous ulcers | 24.66% | ||||
| Severe aphthous ulcers | 30.1% |
| Methods | Year | Memory (MB) ↓ | DSC ↑ | ACC ↑ | SP ↑ | SE ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet [4] | 2015 | 1567 | 0.7480 ± 0.005 | 0.9617 ± 0.002 | 0.9815 ± 0.002 | 0.7282 ± 0.006 |
| Att UNet [6] | 2018 | 1580 | 0.7404 ± 0.005 | 0.9632 ± 0.002 | 0.9879 ± 0.002 | 0.6716 ± 0.007 |
| SCR-Net [20] | 2021 | 1569 | 0.7069 ± 0.006 | 0.9602 ± 0.002 | 0.9896 ± 0.001 | 0.6148 ± 0.008 |
| TransNorm [21] | 2022 | 2113 | 0.5670 ± 0.005 | 0.9514 ± 0.002 | 0.9873 ± 0.002 | 0.4691 ± 0.007 |
| MALUNet [5] | 2022 | 1551 | 0.6318 ± 0.005 | 0.9409 ± 0.003 | 0.9655 ± 0.003 | 0.6500 ± 0.006 |
| C2SDG [22] | 2023 | 1723 | 0.7210 ± 0.004 | 0.9604 ± 0.002 | 0.9862 ± 0.002 | 0.6554 ± 0.006 |
| M2SNet [23] | 2023 | 1753 | 0.7482 ± 0.004 | 0.9669 ± 0.001 | 0.9953 ± 0.001 | 0.6300 ± 0.007 |
| MSA [24] | 2023 | 5173 | 0.7540 ± 0.004 | 0.9697 ± 0.001 | 0.9887 ± 0.002 | 0.7181 ± 0.005 |
| META-UNet [7] | 2023 | 1639 | 0.7535 ± 0.004 | 0.9695 ± 0.001 | 0.9842 ± 0.002 | 0.7227 ± 0.005 |
| MHorUNet [10] | 2024 | 1597 | 0.7618 ± 0.004 | 0.9657 ± 0.002 | 0.9867 ± 0.002 | 0.7143 ± 0.005 |
| VM-UNet [15] | 2024 | 1124 | 0.7639 ± 0.005 | 0.9636 ± 0.002 | 0.9812 ± 0.002 | 0.7555 ± 0.004 |
| H-VMUnet [16] | 2024 | 1060 | 0.7127 ± 0.004 | 0.9605 ± 0.002 | 0.9887 ± 0.001 | 0.6276 ± 0.006 |
| HF-UNet [12] | 2024 | 2029 | 0.7971 ± 0.004 | 0.9703 ± 0.001 | 0.9940 ± 0.001 | 0.7251 ± 0.005 |
| HF-EdgeFormer (Ours) | 2025 | 3062 | 0.8181 ± 0.003 | 0.9704 ± 0.001 | 0.9801 ± 0.002 | 0.8549 ± 0.004 |
| Model Variant | DSC ↑ | SE ↑ | Params (M) ↓ | FLOPs (G) ↓ | VRAM (MB) ↓ | FPS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o EdgeFormerBottleneck | 0.7750 | 0.7220 | 4.1 | 31.4 | 2032 | 24 |
| w/o PrecisionEdgeEnhance | 0.7820 | 0.8037 | 4.3 | 32.5 | 2890 | 24 |
| w/o TTA | 0.8030 | 0.8370 | 4.6 | 33.1 | 3062 | 24 |
| HF-EdgeFormer (Full) | 0.8181 | 0.8549 | 4.6 | 33.1 | 3062 | 24 |
| TTA Enabled | Year | DSC ↑ | SE ↑ | SP ↑ | ACC ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | 2025 | 0.8030 | 0.8370 | 0.9790 | 0.9690 |
| Yes | 2025 | 0.8181 | 0.8549 | 0.9781 | 0.9704 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Cornoiu, D.-C.; Popa, C.-A. HF-EdgeFormer: A Hybrid High-Order Focus and Transformer-Based Model for Oral Ulcer Segmentation. Electronics 2026, 15, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15030595
Cornoiu D-C, Popa C-A. HF-EdgeFormer: A Hybrid High-Order Focus and Transformer-Based Model for Oral Ulcer Segmentation. Electronics. 2026; 15(3):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15030595
Chicago/Turabian StyleCornoiu, Dragoș-Ciprian, and Călin-Adrian Popa. 2026. "HF-EdgeFormer: A Hybrid High-Order Focus and Transformer-Based Model for Oral Ulcer Segmentation" Electronics 15, no. 3: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15030595
APA StyleCornoiu, D.-C., & Popa, C.-A. (2026). HF-EdgeFormer: A Hybrid High-Order Focus and Transformer-Based Model for Oral Ulcer Segmentation. Electronics, 15(3), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15030595







