Abstract
In this paper, we present a millimeter-wave CMOS down-conversion mixer designed for 5G cellular communications. The proposed mixer integrates a local oscillator buffer, an RF transconductance (Gm) stage, and a switching stage. A transformer-based harmonic suppression technique and separate RF Gm stage and switching stage are employed to achieve a low noise figure (NF), high conversion gain (CG), and effective harmonic suppression. Intermodulation and gain characteristics are analyzed, demonstrating enhanced harmonic suppression, high gain, and low NF. Implemented in 65 nm CMOS technology, the proposed mixer occupies a core chip area of 0.51 mm2 and consumes a dc power of 7 mW. The implemented design achieves a CG of 6.4 dB, an NF of 6.1 dB, and an output third-order intercept point of 9.0 dBm at an RF frequency of 38.2 GHz. Additionally, harmonic suppression exceeds −26 dBc, highlighting the performance advantages of the proposed architecture.
1. Introduction
Recently, the standardization of fifth-generation (5G) New Radio (NR) has garnered significant attention for its ability to enable high-speed data transmission and massive connectivity, leveraging millimeter-wave (mm-wave) frequency bands. Frequency Range 2 (FR2), spanning 24.25–71 GHz, includes bands such as 24–30 GHz and 36–42 GHz, which have been allocated to various countries [1,2,3]. In these frequency bands, phased-array techniques have been proposed to extend communication distances and improve data rates [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
In mm-wave 5G transceivers, the mixer plays a critical role as it facilitates modulation, demodulation, and spectrum shifting. Key performance metrics for down-conversion mixers include high conversion gain (CG), low noise figure (NF), high linearity, effective harmonic suppression, and low power consumption. These parameters are essential to achieving optimal receiver performance in the mm-wave band.
Previous studies have made significant strides in developing wideband, multiband, and high-performance down-conversion mixers for mm-wave applications [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. CMOS technology is widely adopted for its low cost and seamless integration with digital baseband circuits. Many mm-wave CMOS mixers utilize double-balanced Gilbert-cell topologies [15,18,19,22] or separate RF transconductance (Gm) and switching stages [14,16,17,20,21]. For example, a Gilbert-cell mixer with an intermediate frequency (IF) buffer amplifier achieves a high CG of 4.8 dB but suffers from a high NF of 13.5 dB and requires a large local oscillator (LO) input power of 5 dBm [15]. Similarly, mixers with separate switching and Gm stages demonstrate broadband performance using band-switchable capacitors and transformers but exhibit limited CG (<3.1 dB) and high NF (>11 dB) [16,17]. Efforts to enhance performance have introduced mixers with body self-forward bias [18], large-resistance loads [21], or multi-gate transistors [22]. While these designs achieve specific performance gains, they often encounter trade-offs such as high NF, limited CG, or poor LO-RF isolation. For instance, a mixer employing multi-gate transistors (MGTR) achieves exceptional linearity with an IIP3 of 20.87 dBm but exhibits poor CG (−14.4 dB) and NF (16.75 dB) [22].
To address these challenges, this study presents a mm-wave CMOS down-conversion mixer optimized for 5G handheld devices, including smartphones, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and gaming consoles. The proposed mixer integrates an LO buffer amplifier, an RF Gm stage, and a switching stage while employing transformer-based harmonic suppression. This architecture achieves a CG of 6.4 dB, an NF of 6.1 dB, a LO-RF isolation exceeding 46 dB, and a 1 dB compression point (IP1dB) of −6 dBm. These results demonstrate that the proposed mixer is well-suited for low-power mm-wave 5G handheld applications.
2. Design Methodology
2.1. Design Considerations
Figure 1 illustrates the block diagram of the proposed down-conversion mixer designed for a super-heterodyne receiver. The mixer converts RF signals (37–41 GHz) to IF signals (10–12 GHz) using an LO frequency range of 27–29 GHz. The design includes a switching stage, an RF Gm stage, an LO buffer amplifier, and transformer-based harmonic suppression.
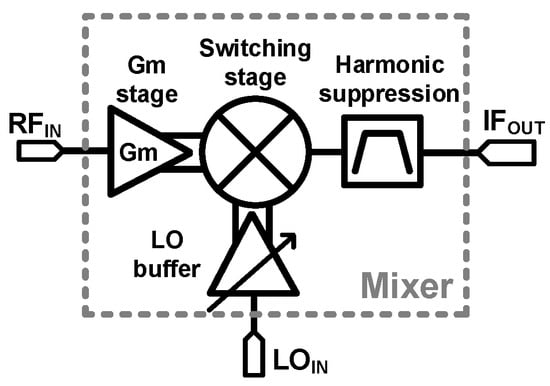
Figure 1.
Block diagram of down-conversion mixer.
In conventional Gilbert-cell mixers, large parasitic capacitance at the drain of the Gm stage leads to reduced CG and degraded NF. Additionally, using a single current source for both the Gm stage and switching stage results in performance trade-offs: insufficient current in the Gm stage degrades CG and NF, while excessive current in the switching stage slows down switching speed, further impairing CG and NF. To address these challenges, the proposed mixer separates the Gm stage and switching stage, optimizing gain, NF, and linearity [23].
The LO buffer amplifier is designed with a variable gain function to compensate for input power variations and deliver optimal LO power to the switching stage [24]. Furthermore, in a super-heterodyne receiver, suppressing unwanted harmonics is essential to ensure signal integrity.
Figure 2 presents the schematic of the proposed down-conversion mixer tailored for 5G handheld devices. The design incorporates an RF Gm stage, LO buffer amplifier, switching stage, and transformer-based harmonic suppression to perform RF-to-IF conversion from 39 GHz to 11 GHz. Separating the Gm stage and switching stage enhances NF, CG, and linearity. Additionally, a double-balanced mixer topology is employed to improve LO rejection compared to single-balanced mixers. Transformer-based harmonic suppression is utilized to effectively reject unwanted harmonics, ensuring robust performance in 5G applications.
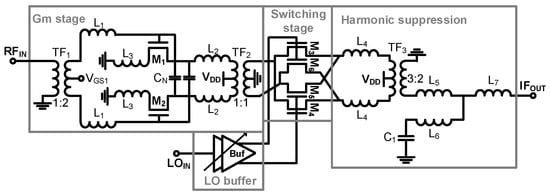
Figure 2.
Schematic of proposed down-conversion mixer.
2.2. Transconductance Stage
The Gm stage employs a differential common source configuration with a capacitance neutralization technique [25]. The gate-to-drain parasitic capacitance (Cgd) degrades stability, power gain, and reverse isolation due to unwanted feedback. To mitigate this, the capacitance neutralization technique enhances stability, power gain, and LO-to-RF isolation, while improving the mixer’s NF by boosting the Gm stage’s gain.
The differential RF signal is applied to the switching stage via a differential amplifier comprising transformers (TF1, TF2) and a neutralization capacitor (CN). Transformer, TF1, along with inductors, L1 and L3, achieves simultaneous gain and noise matching, while TF2 and inductor L2 provide conjugate matching between the Gm and switching stages.
To optimize the design, a custom metal–oxide–metal (MOM) capacitor [25] replaces the standard foundry-provided MOM capacitor for CN. This custom MOM capacitor utilizes a multi-stack metal plate design, reducing interconnections and chip area while improving the quality factor. Simulation results show minimal process variation (less than ±2%), ensuring consistent performance.
2.3. Switching Stage with Transformer-Based Harmonic Suppression
The switching stage consists of switching transistors (M3–M6) and transformer TF3 with harmonic suppression. Figure 3 illustrates the three- and two-dimensional layout of the switching stage, designed for symmetry to minimize LO leakage and improve LO-to-RF isolation.
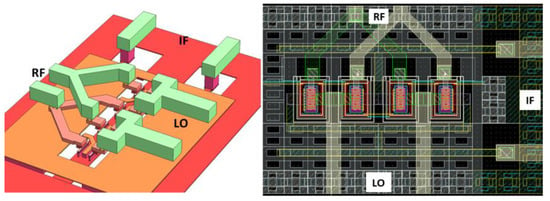
Figure 3.
Three- and two-dimensional layout of switching stage.
The layout ensures that the IF output is isolated from RF and LO signal lines using a grounded middle metal layer, while RF and LO signals are routed through the top two metal layers and top metal layer, respectively. This separation and symmetric layout prevent signal interference and enhance performance metrics such as LO leakage and RF-to-LO isolation.
Figure 4a illustrates a transformer model based on [26]. The transformer is represented as an ideal transformer with a turn ratio of 1:n/k, where the primary and secondary leakage inductances are modeled as series components with shunt inductors (1 − k2)LP and k2LP, respectively. Here, LP is the inductance of the primary winding; RP1 and RP2 are the parasitic resistances of the primary and secondary windings, respectively; CP1 and CP2 are the parasitic capacitances, including the winding capacitance; k is the magnetic coupling coefficient, and n is the turn ratio (, where LS is the inductance of the secondary winding.
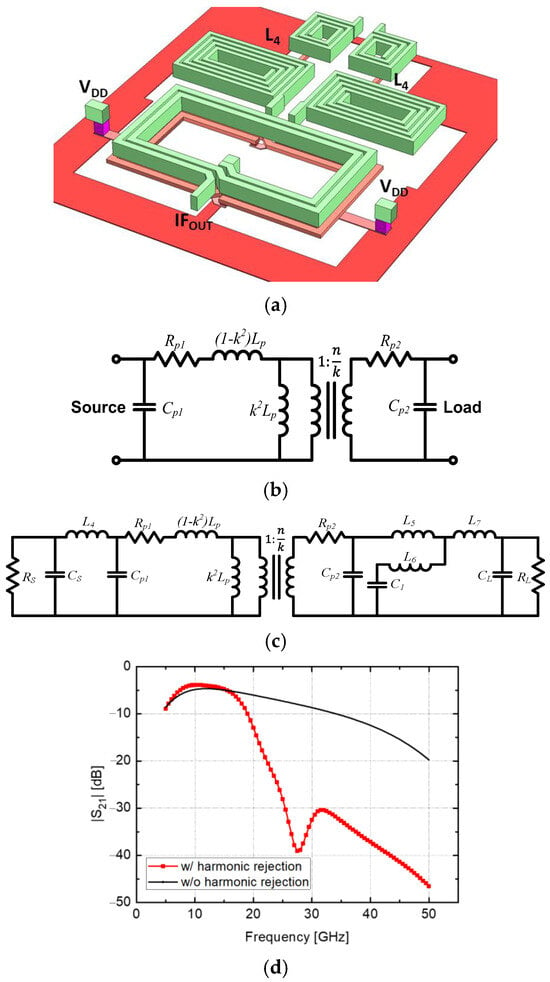
Figure 4.
(a) 3D layout of the transformer. (b) Transformer equivalent circuit model. (c) Matching network of the transformer with harmonic suppression. (d) Simulated insertion losses of transformers with and without harmonic suppression.
Figure 4a–c depict the 3D layout of the transformer, its equivalent circuit model, and the matching network with harmonic suppression at the switching stage output. The source resistance (RS) and (CS) represent the impedance looking into the switching transistors from the drain side, with a source impedance of 88.5-j438.4 Ω at 11 GHz. Similarly, the load resistance (RL) and capacitance (CL) represent the impedance looking into the linearization stage, with a load impedance of 26.5-j107.1 Ω at 11 GHz. Incorporating harmonic suppression and the matching network improves the simulated insertion loss by 3.6 dB within the 10–12 GHz range, and the transformer demonstrates effective high-frequency harmonic suppression. Specifically, the insertion loss is measured at 3.9 dB, 6.3 dB, and 38.9 dB at 11 GHz (IF), 17 GHz (2fLO-fRF), and 28 GHz (LO frequency), respectively.
The transformer TF3 is employed for differential-to-single conversion and is constructed using the top two metal layers for magnetic coupling. Its physical primary-to-secondary winding turn ratio is 3:2, with n = 0.71 and k = 0.85. The parasitic parameters include RS1 = 7.5 Ω, RS2 = 7 Ω, CS1 = 40 fF, and CS2 = 45 fF. To further optimize performance, inductors L4–L5 form a matching network that reduces insertion loss and rejects high-frequency components. Additionally, a shunt resonance circuit comprising L6 and C1 is employed for harmonic suppression and conjugate matching with L7.
Figure 4d compares the insertion losses of transformers with and without harmonic suppression, highlighting the effectiveness of the proposed design. The primary unwanted signals of the down-conversion mixer are 2fLO-fRF, 2fRF-2fLO, and fLO. The transformer with harmonic rejection improves suppression by 1 dB, 13 dB, and 31 dB at 17 GHz (2fLO-fRF), 22 GHz (2fRF-2fLO), and 28 GHz (fLO), respectively.
2.4. LO Buffer Amplifier
Figure 5 illustrates the schematic of the proposed LO buffer amplifier [24]. The design incorporates a cascode current-steering variable gain amplifier and a common-source amplifier with a capacitance neutralization technique. The LO buffer amplifier ensures a constant and sufficiently high voltage swing for the mixer core across varying input power levels. To achieve this, it included a gain control function that maintained constant output power across all gain control states.
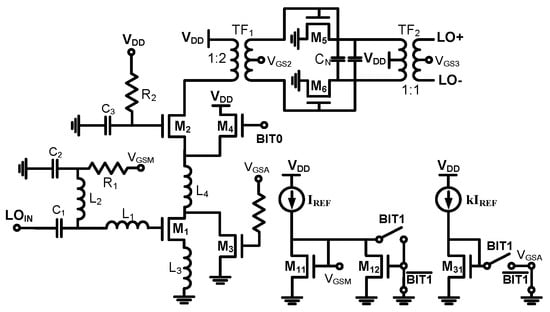
Figure 5.
Simplified schematic of proposed LO buffer amplifier.
A conventional current-steering variable gain amplifier [27] adjusts gain by steering the current of the common gate transistor (M2). However, it typically offers limited output power. To address this limitation and meet linearity requirements, the proposed design employs additional transistors (M3–M4) for 2 dB (BIT0) and 4 dB (BIT1) gain control, respectively, as shown in Figure 5. By steering the current through M1, the design achieves variable gain while maintaining constant output power, driven by the stable current of M2.
The differential common-source amplifier (M5–M6) with capacitance neutralization and transformers (TF1–TF2) enhances the LO buffer amplifier’s performance by providing high gain, improved linearity, and a well-balanced differential signal. This configuration minimizes gain and phase imbalances, reducing the linearity burden on the first stage.
The simulation results indicate that the proposed LO buffer amplifier achieves a power gain of 15–21 dB in 2 dB steps, with an output 1 dB compression point ranging from −1 dBm to 0.3 dBm. It delivers a 0.7-VP-P LO signal to the switching stage’s gate from an LO input power of −20 dBm. Compared to the conventional current-steering variable gain amplifier, the proposed design demonstrates a 4 dB higher output 1 dB compression point in simulations.
The two bottom metal layers are utilized as a ground plane with a mesh pattern. The inductors, transformers, neutralization capacitors, and interconnections are all modeled and analyzed using the HFSS 3-D EM simulator developed by Ansys, Canonsburg, US. All transistors feature a gate length of 60 nm.
With transformer-based harmonic suppression and the separation of the Gm stage and switching stage, the proposed down-conversion mixer, illustrated in Figure 2, achieves a simulated CG of 5.2–6.4 dB and a NF of less than 7.3 dB over an RF frequency range of 37–41 GHz and an LO frequency range of 27–29 GHz. The mixer demonstrates an input third-order intercept point (IIP3) of 3.1 dBm, an NF of 6.1 dB, a LO-to-RF isolation exceeding 46 dB, and an IP1 dB of −6 dBm.
3. Results
The proposed down-conversion mixer circuit was implemented in a standard 65 nm CMOS technology. Figure 6 shows a chip photograph of the proposed down-conversion mixer. The chip occupies an area of 0.57 × 0.9 mm2, excluding the pads. The mixer consumes 18 mW of DC power from a 1 V supply voltage, including the LO buffer amplifier’s power consumption of 11 mW. Figure 7 illustrates the measurement setups for S-parameters, CG, NF, and power-handling capability. The mixer’s performance was measured on-wafer using ground–signal–ground (GSG) and ground–signal–signal–ground (GSSG) probes. The S-parameters were measured using a Keysight E8361A vector network analyzer. The NF, CG, IP1dB, and IIP3 were measured with a noise figure analyzer, signal generators, and a spectrum analyzer. Losses from the probe tips, adapters, and coaxial cables were de-embedded from the raw measurement data.
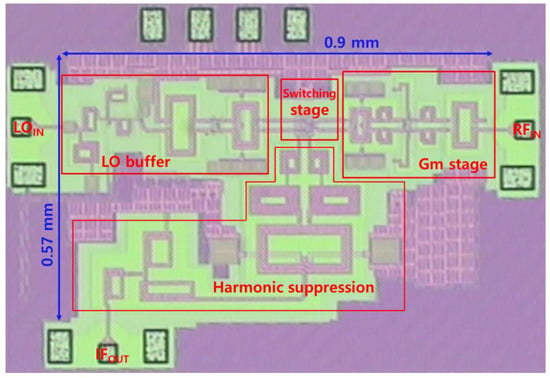
Figure 6.
Microphotograph of proposed mixer.
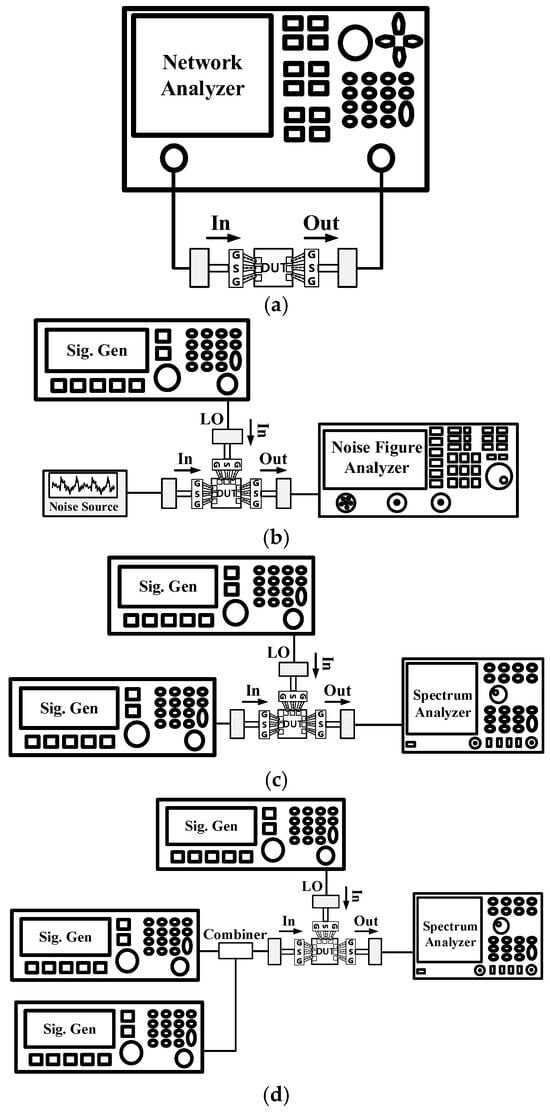
Figure 7.
Measurement setups for (a) S-parameter, (b) NF, (c) CG and IP1dB, and (d) IIP3.
Figure 8 shows the simulated and measured return losses of the proposed mixer. The measured return losses of the IF and LO ports exceed 10 dB over 8–14 GHz and 26–31 GHz, respectively. The measured return loss of the RF port is better than 8 dB over 36–41 GHz. For the 2-bit gain control in the LO buffer amplifier, the IF and RF ports show consistent return loss performance. Simulated data show good agreement with the measurement results. Figure 9 depicts the simulated and measured NFs of the mixer. The measured single-sideband NF is less than 7.3 dB over an RF frequency range of 37–41 GHz.
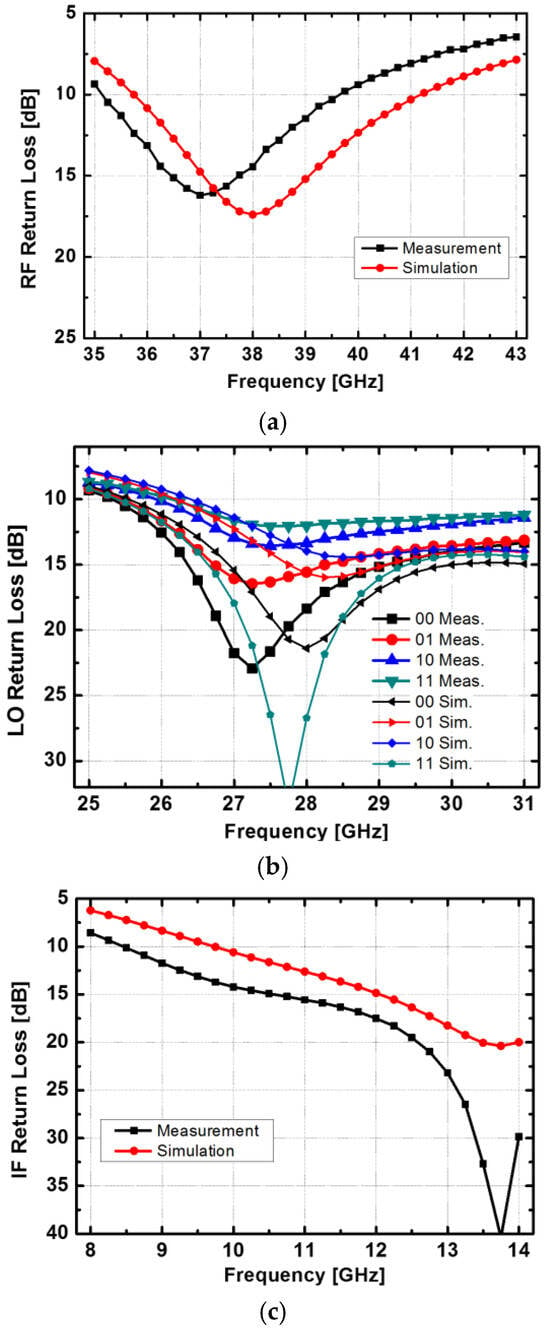
Figure 8.
Measured and simulated return losses of the proposed mixer: (a) RF port, (b) LO port, and (c) IF port. For the LO port, return losses of 2-bit gain control are shown.
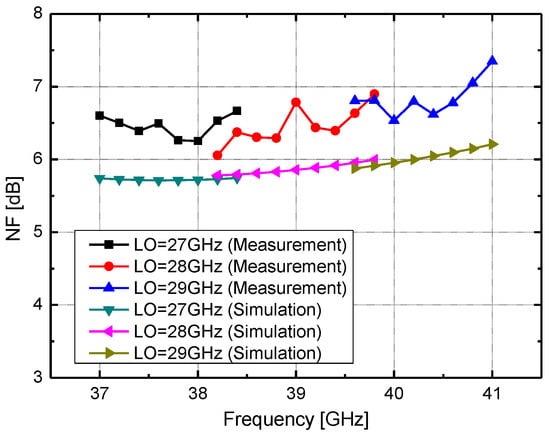
Figure 9.
Measured and simulated NF of the proposed mixer. LO power = −20 dBm.
Figure 10 illustrates the simulated and measured CG of the mixer. The LO frequencies are 27 GHz, 28 GHz, and 29 GHz, while the RF frequency ranges are 37–38.25 GHz, 38.25–39.75 GHz, and 39.75–41 GHz, respectively. The RF and LO input powers are −30 dBm and −20 dBm, respectively. The measured conversion gain is 5.2–6.4 dB over an RF frequency range of 37–41 GHz. The neutralization capacitors and the separation of the Gm and switching stages contribute to enhanced gain and NF performance. Figure 11 shows the CG of the mixer for varying RF input power, with an LO input power of −20 dBm. The measured IP1dB of the mixer is −6 dBm at an RF frequency of 39 GHz.
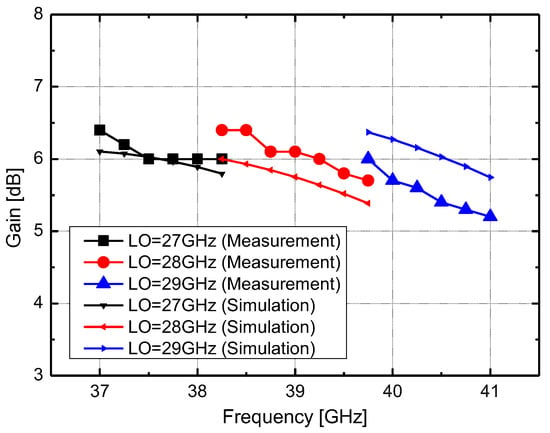
Figure 10.
Measured and simulated CG of proposed mixer. RF power = −30 dBm. LO power = −20 dBm.
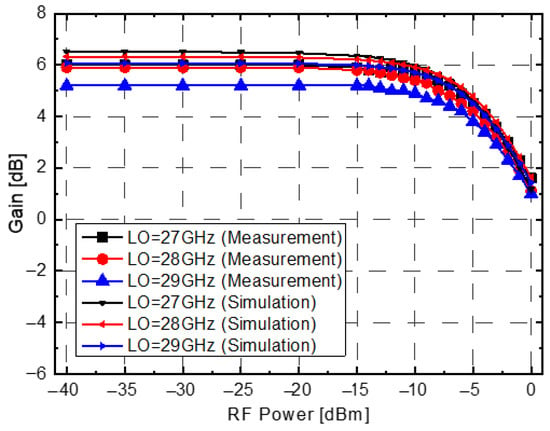
Figure 11.
Measured and simulated CG versus RF input power of proposed mixer. LO power = −20 dBm. RF frequencies are 37.75/39/40.25 GHz.
Figure 12 presents the simulated and measured output third-order intercept point (OIP3) of the mixer. The measured OIP3 exceeds 9.6 dBm at an RF frequency of 39 GHz and remains above 8.9 dBm across the RF frequency range of 37–41 GHz. The measured IIP3 is greater than 3.1 dBm across the same frequency range. Simulated data show good agreement with the measurement results. Figure 13 illustrates the measured LO-to-RF and LO-to-IF isolations. LO leakage generates unwanted spurious signals by mixing with other harmonics, leading to degraded linearity and reduced signal quality. Therefore, minimizing LO leakage is crucial to maintaining optimal performance. The LO-to-RF isolation is better than 25.3 dB, while the LO-to-IF isolation exceeds 45.7 dB. Figure 14 shows the measured output spectrum. The measured harmonic suppression for an RF input power of −30 dBm is better than −26 dBc across an RF frequency range of 37–41 GHz, with the output spectrum accounting for cable loss.
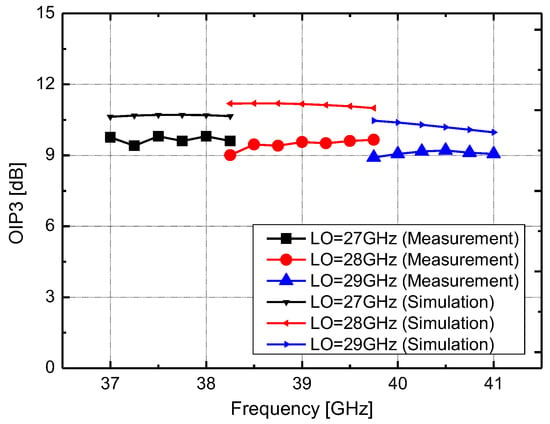
Figure 12.
Measured and simulated OIP3 versus RF frequency of proposed mixer. RF power = −30 dBm. LO power = −20 dBm.
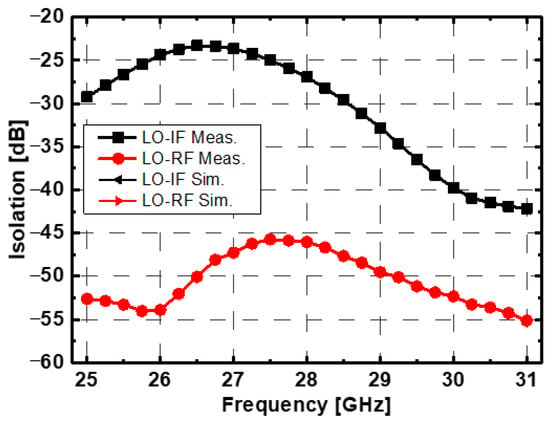
Figure 13.
Measured LO-IF and LO-RF isolations of proposed mixer.
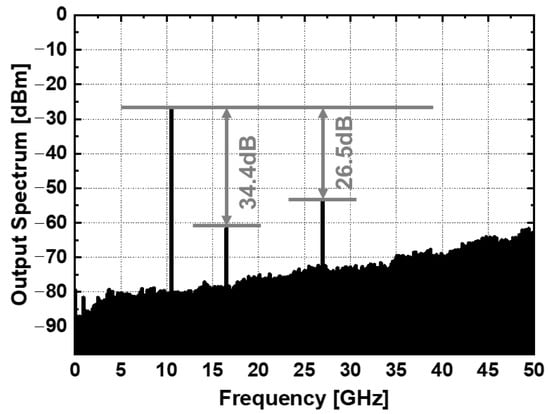
Figure 14.
Measured output spectrum for harmonic suppression: fLO = 27 GHz; fIF = 10.5 GHz; PLO = −20 dBm.
4. Discussion
Table 1 compares the performance of state-of-the-art 5G FR2 CMOS down-conversion mixers. A 5G FR2 down-conversion mixer should achieve low power consumption, high conversion gain, low noise figure, and high linearity. However, these performance parameters inherently involve trade-offs, and state-of-the-art down-conversion mixers typically prioritize two or three key aspects. The mixer utilizing MGTR at the Gm stage [22] demonstrates a high IIP3 of 20.87 dBm but suffers from a high NF of 16.75 dB and a low CG of −14.4 dB. Similarly, the mixer in [18] achieves a high CG of 12.6 dB; however, it employs a direct-conversion architecture and an IF buffer amplifier, resulting in an NF exceeding 10 dB. The proposed mixer, which incorporates neutralization capacitors, a separate Gm stage and switching stage, simultaneous gain and noise matching, and transformer-based harmonic suppression, achieves a significantly lower NF of less than 7.3 dB and a high CG of 5.2–6.4 dB, all without the need for an IF buffer amplifier. Additionally, the LO-RF isolation exceeds 46 dB, and the harmonic suppression is better than −26 dBc. The measurement results indicate that the proposed mixer is well-suited for 5G low-power mm-wave handheld devices, offering a balanced trade-off between performance and power efficiency.

Table 1.
Performance comparisons of state-of-the-art.
5. Conclusions
A 39 GHz down-conversion mixer circuit was successfully designed and implemented using standard 65 nm CMOS technology. By incorporating neutralization capacitors, a separate Gm stage and switching stage, simultaneous gain and noise matching, and transformer-based harmonic suppression, the proposed mixer achieves a low NF of less than 7.3 dB and a high CG of 5.2–6.4 dB, all without requiring an IF buffer amplifier. Moreover, the LO-RF isolation is better than 46 dB, and the harmonic suppression exceeds −26 dBc. The measurement results validate that the proposed mixer meets the performance requirements for 5G low-power mm-wave handheld devices. Its design demonstrates the feasibility of achieving high performance with low LO input power, making it a strong candidate for next-generation wireless communication systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; data curation, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; formal analysis, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; funding acquisition, C.-W.B.; investigation, C.-W.B.; methodology, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; project administration, C.-W.B.; resources, C.-W.B.; software I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; supervision, C.-W.B.; validation, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; visualization, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B.; writing—original draft, I.-C.Y.; writing—review and editing, I.-C.Y. and C.-W.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The EDA tool was supported by the IC Design Education Center (IDEC), Korea.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Song, J.-H.; Lee, E.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Son, J.-T.; Kim, J.-H.; Baek, M.-S.; Kim, C.-Y. A 37–40 GHz 6-Bits Switched-Filter Phase Shifter Using 150 nm GaN HEMT. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, S.H.; Altaf, A.; Anjum, M.R.; Afridi, S.; Arain, Z.A.; Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Lalbakhsh, A.; Khan, M.A.; et al. MIMO Antenna System for Modern 5G Handheld Devices with Healthcare and High Rate Delivery. Sensors 2021, 21, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.A.; Taher, F.; Alzaidi, M.S.; Hussain, I.; Ghoniem, R.M.; Sree, M.F.A.; Lalbakhsh, A.L. Wideband, High-Gain, and Compact Four-Port MIMO Antenna for Future 5G Devices Operating over Ka-Band Spectrum. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Ustundag, B.; Kibaroglu, K.; Sayginer, M.; Rebeiz, G.M. Wideband 23.5–29.5-GHz phased arrays for multistandard 5G applications and carrier aggregation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, I.C.; Cho, D.O.; Byeon, C.W. A Millimeter-wave CMOS Cross-Polarization Leakage Canceller for Dual-Polarized MIMO Systems. IDEC J. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 8, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu, B.; Paidimarri, A.; Lee, W.; Yeck, M.; Ozdag, C.; Tojo, Y. A 24-to-30GHz 256-element dual-polarized 5G phased array with fast beam-switching support for >30,000 beams. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–26 February 2022; Volume 65, pp. 436–438. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.; Oh, H.; Park, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.; et al. A 39 GHz 2 × 16-Channel Phased-Array Transceiver IC with Compact, High-Efficiency Doherty Power Amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–13 June 2023; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Pang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, P.; Chen, W.; Liao, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. A 39-GHz CMOS Bidirectional Doherty Phased-Array Beamformer Using Shared-LUT DPD with Inter-Element Mismatch Compensation Technique for 5G Base Station. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.; Chun, J.; Jeon, L.; Hong, S. A 28-GHz Four-Channel Beamforming Front-End IC with Dual-Vector Variable Gain Phase Shifters for 64-Element Phased Array Antenna Module. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2023, 58, 1142–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, T.; Alhamed, A.; Rebeiz, G.M. A 23–46-GHz Fully Planar 8 × 8 Multistandard 5G Phased Array With OFDM 400-MHz 64-QAM Waveforms at 40–44-dBm EIRP. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 72, 6739–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ozdag, C.; Plouchart, J.-O.; Valdes-Garcia, A.; Sadhu, B. A 24 to 30-GHz Phased Array Transceiver Front End With 2.8 to 3.1-dB RX NF and 22 to 24% TX Peak Efficiency. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 2788–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, B.; Paidimarri, A.; Watanabe, A.O.; Liu, D.; Gu, X.; Baks, C.W.; Tojo, Y.; Fujisaku, Y.; Sousa, I.D.; Yamaguichi, Y.; et al. A Heterogeneously Integrated 256-Element 5G Phased Array: Design, Assembly, Test. IEEE J. Microwaves 2025, 5, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, E.A. Predicting the Performance of a 26 GHz Transconductance Modulated Downconversion Mixer as a Function of LO Drive and DC Bias. Electronics 2022, 11, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, C.W.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, J.H. A high-linearity Ka-band CMOS down-conversion mixer. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.; Han, J. 24–40 GHz Gain-Boosted Wideband CMOS Down-Conversion Mixer Employing Body-Effect Control for 5G NR Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2022, 69, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, M.; Park, B.; Song, E.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Kwon, K. 24–40 GHz mmWave Down-Conversion Mixer With Broadband Capacitor-Tuned Coupled Resonators for 5G New Radio Cellular Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 16782–16792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Han, J. Dual-Band CMOS Down-Conversion Mixer Adopting Band-Switchable Transformer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2023, 70, 3902–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Lan, K.-S. Down-Conversion Mixer Using λ/4-TL-C-based Coupler and BSFB Technique for 28 GHz 5G NR. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–16 June 2023; pp. 1128–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Shi, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R. A High-Gain and Low-Noise Mixer with Hybrid Gm-Boosting for 5G FR2 Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, W.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, M.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, K.; Long, Z. A 19-32.8 GHz Low Power Down-Conversion Mixer with 8.2 dBm IP1dB for 5G Communication. In Proceedings of the 2024 54th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Paris, France, 24–26 September 2024; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dossanov, A.; Issakov, V. A 1.28mW K-Band Modified Gilbert-Cell Mixer Design in 22nm FDSOI CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems (SiRF), San Antonio, TX, USA, 21–24 January 2024; pp. 110–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Ma, K.; Ma, Z.; Wang, K. A Reusable Superheterodyne Dual-Band Down-Conversion Mixer With Hybrid Linearity-Enhanced Technique for 5G Non-Contiguous Multiband NR. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2024, 59, 3392–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. Design of millimeter-wave CMOS radios: A tutorial. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2009, 56, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, C.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Son, J.H. A Ka-band variable-gain amplifier with low OP1dB variation for 5G applications. IEEE Microw. Wireless Compon. Lett. 2019, 29, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Byeon, C.-W. A 60 GHz Power Amplifier with Neutralization Capacitors and Compensation Inductors. Electronics 2024, 13, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.R. Monolithic transformers for silicon RF IC design. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 1368–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Tsai, Z.; Tsai, J.; Wang, H. A 71–76 GHz CMOS variable gain amplifier using current steering technique. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 June 2008; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).