An Ultra-Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier with a New Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Technique for 28 nm CMOS Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
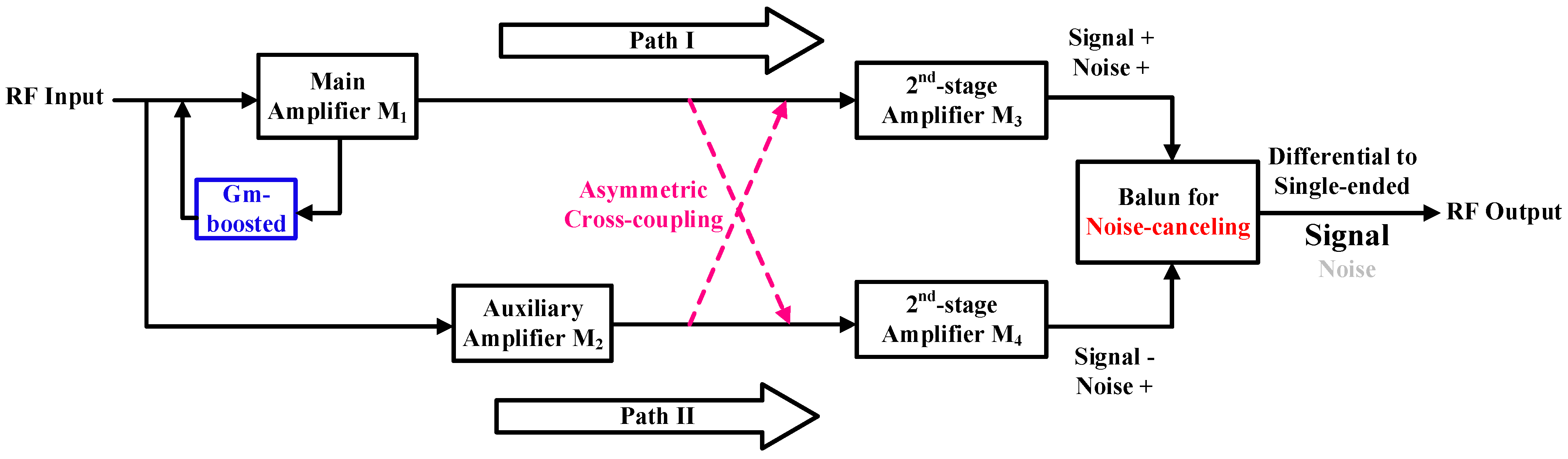
2. Principle of the Proposed LNA
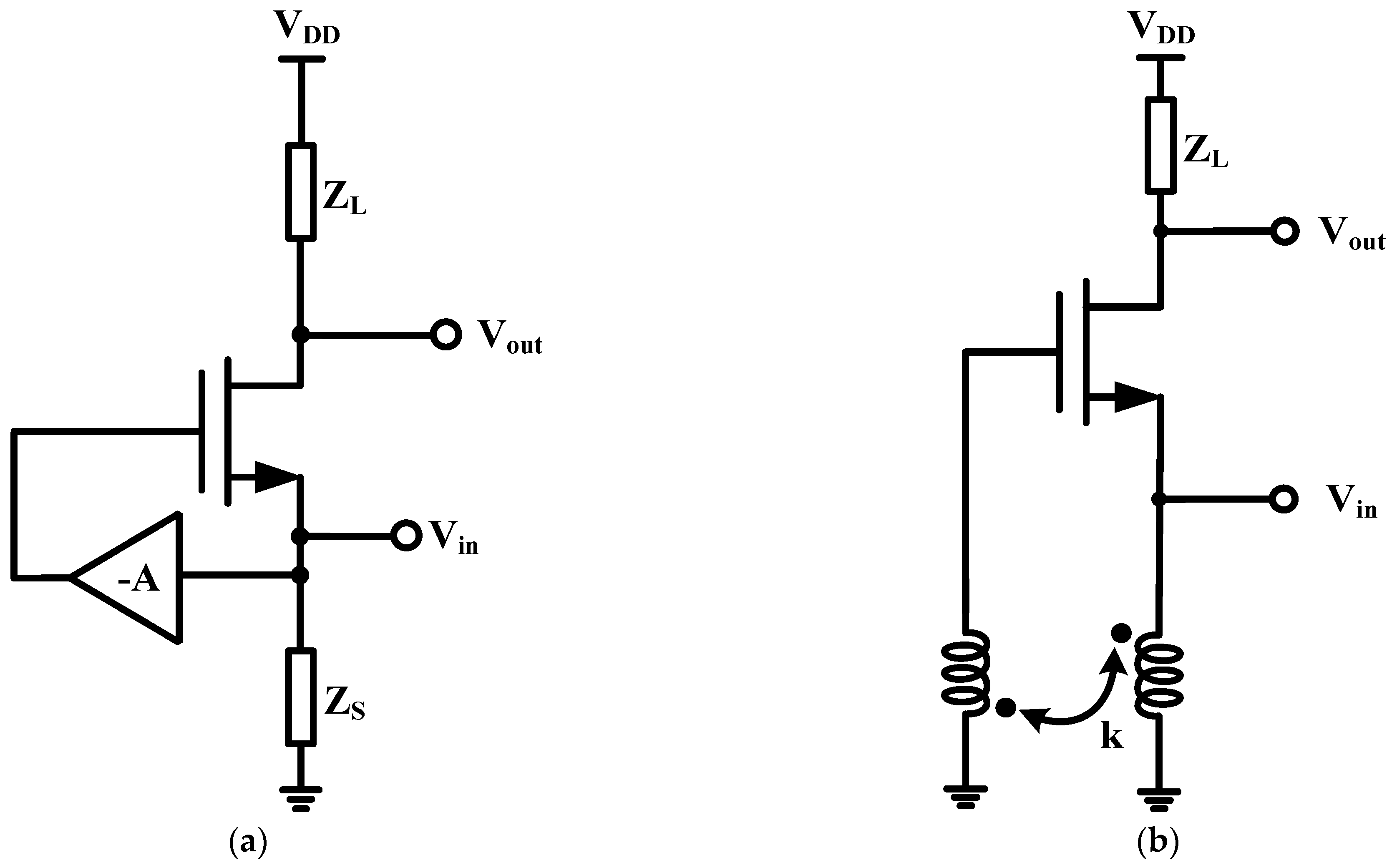
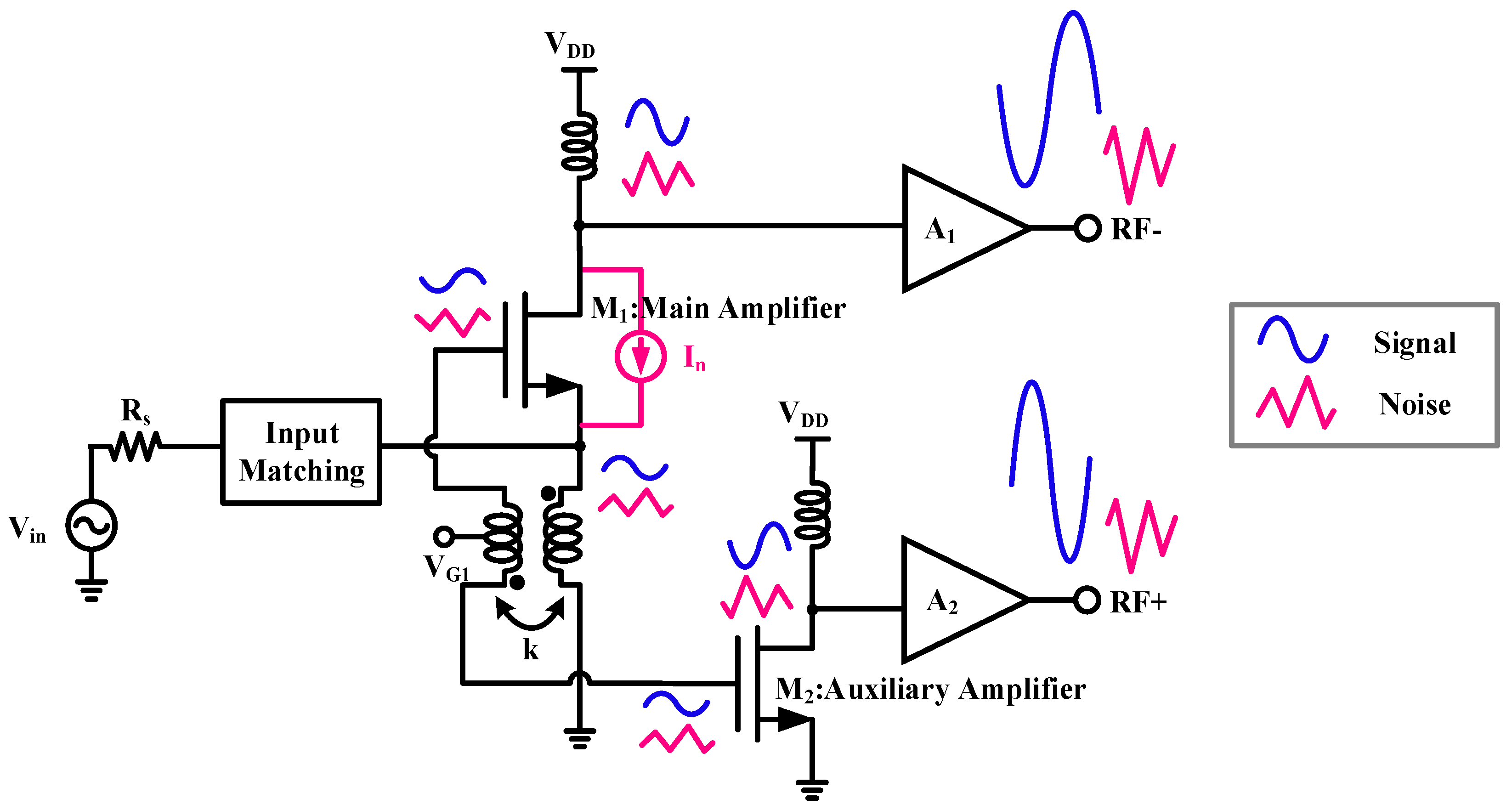
2.1. Transformer-Coupled Gm-Boosted Structure
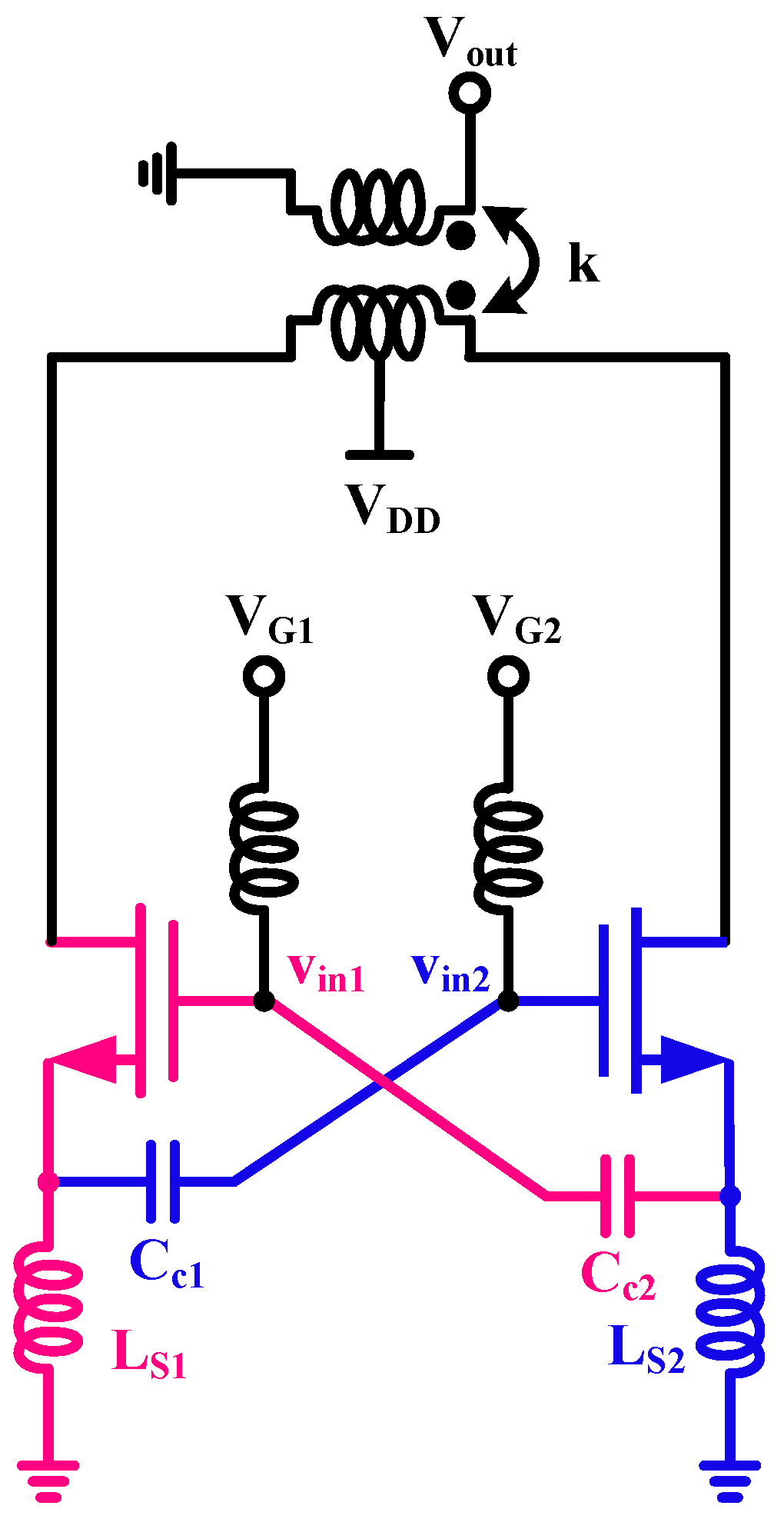
2.2. Asymmetric Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Structure
3. Circuit Design
3.1. First-Stage Amplifier Design
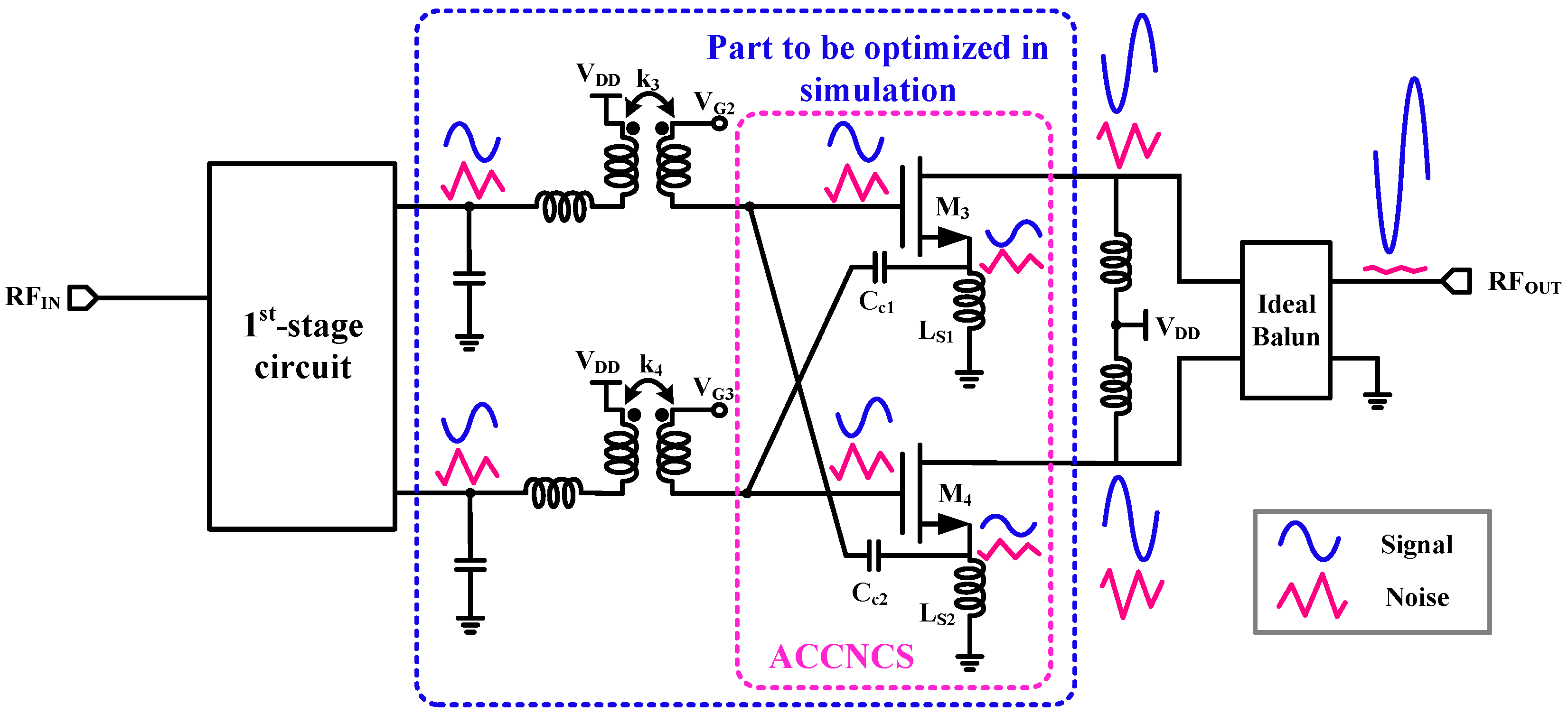
3.2. Second-Stage Amplifier Design
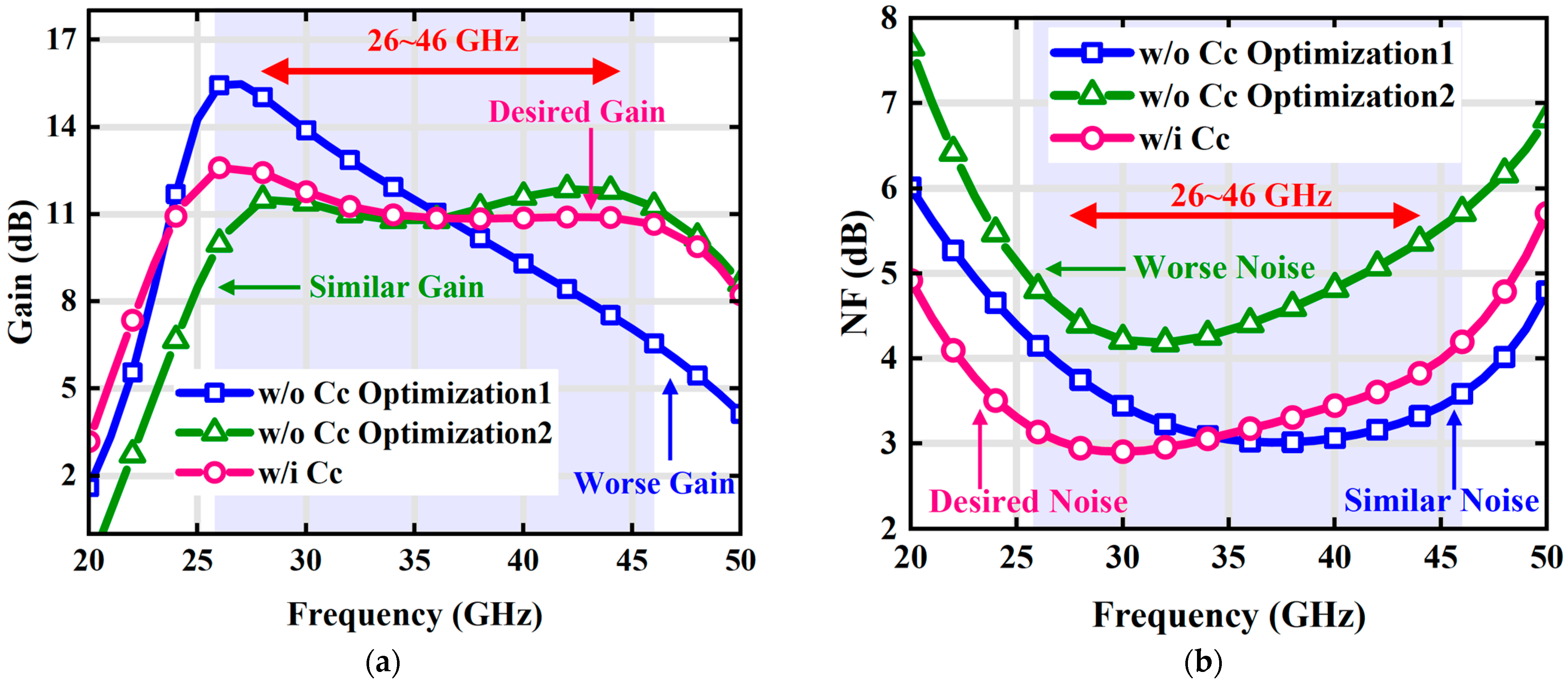
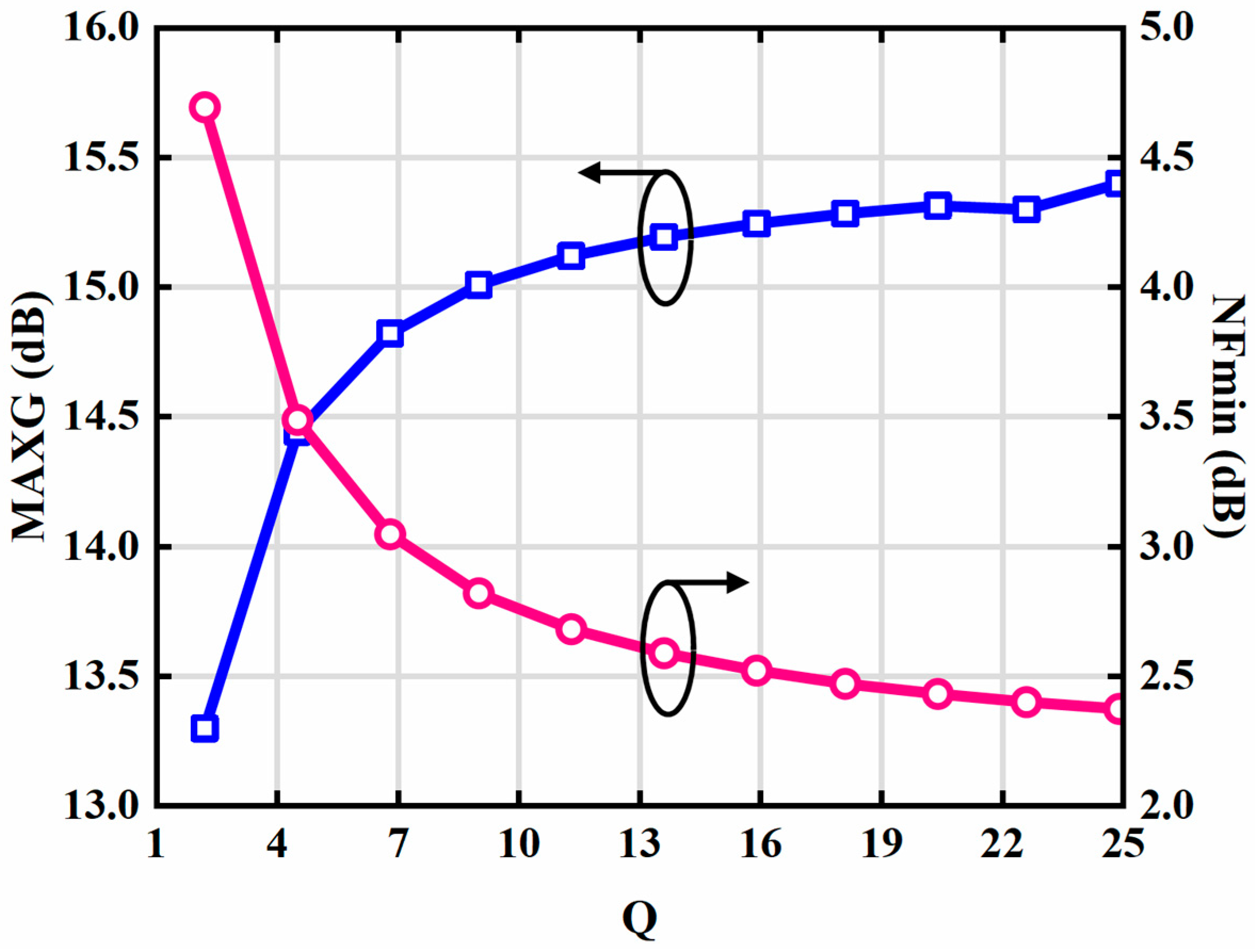
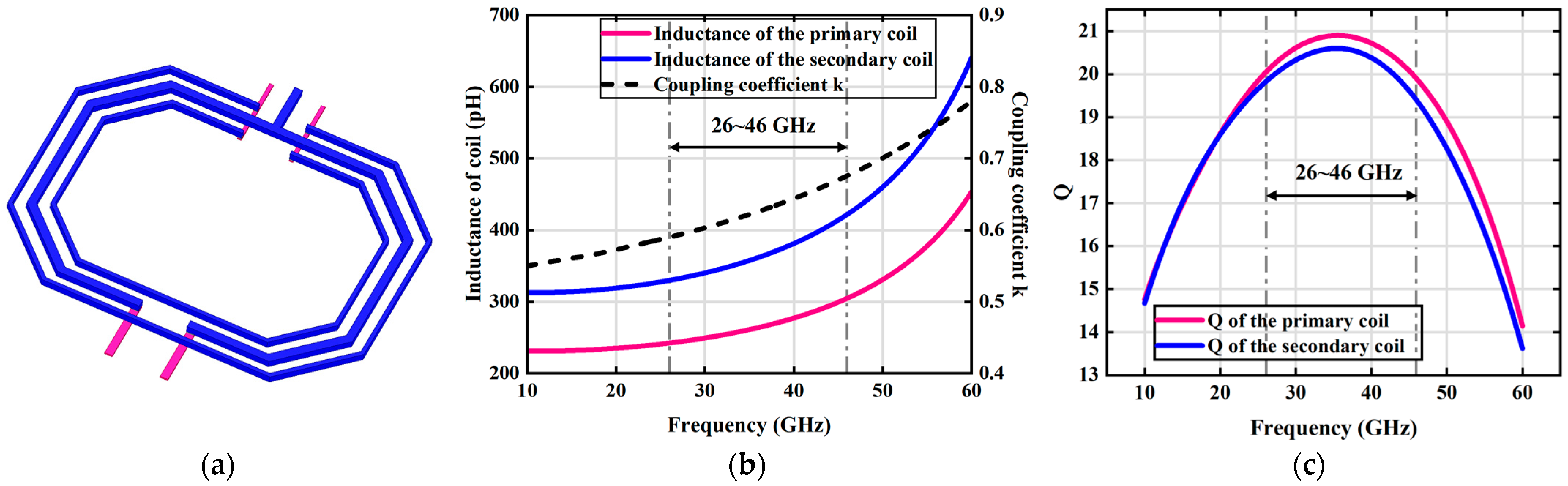
3.3. Transformer Design
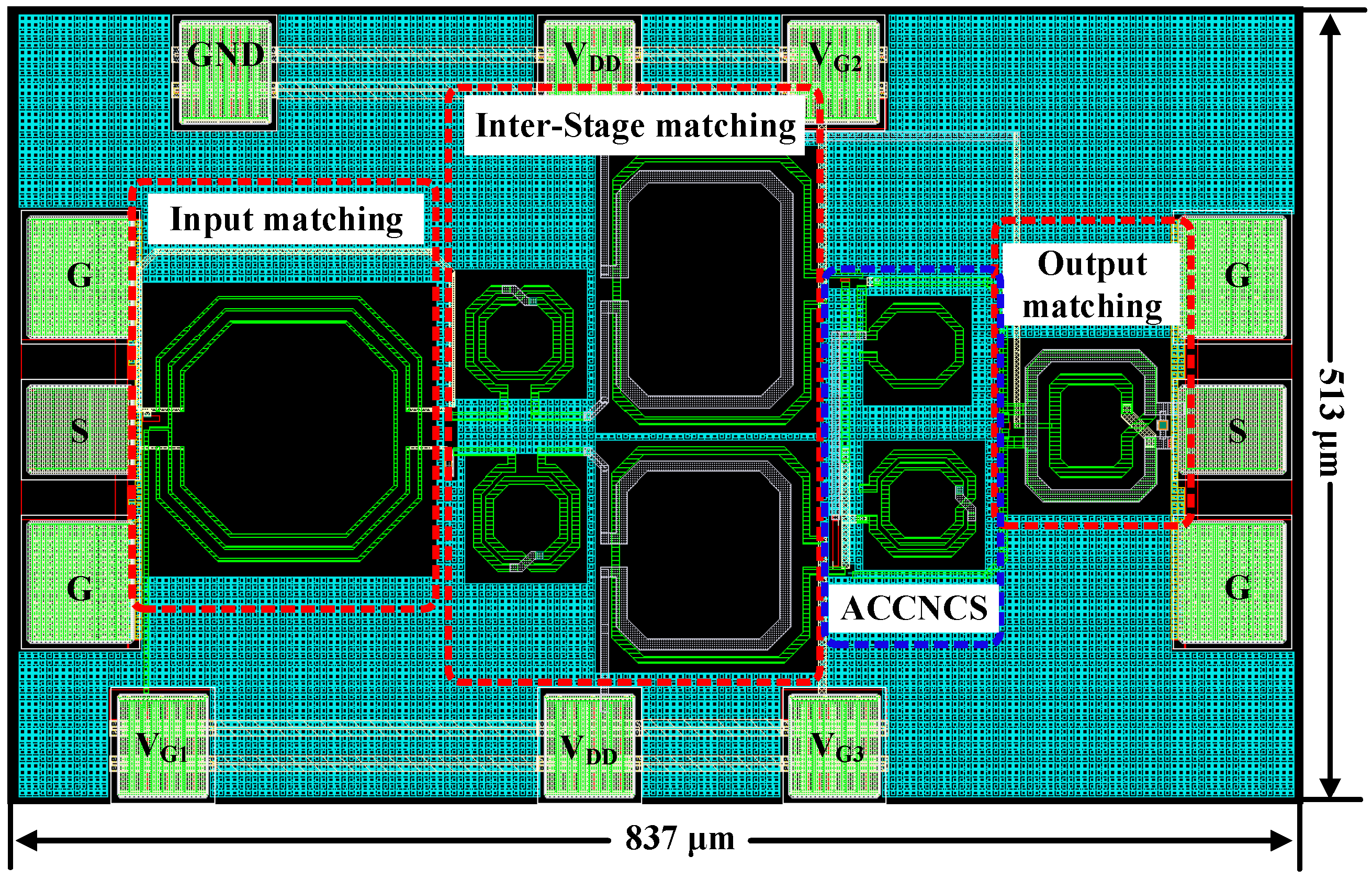
3.4. Complete LNA Circuit with Input and Output Matching Networks
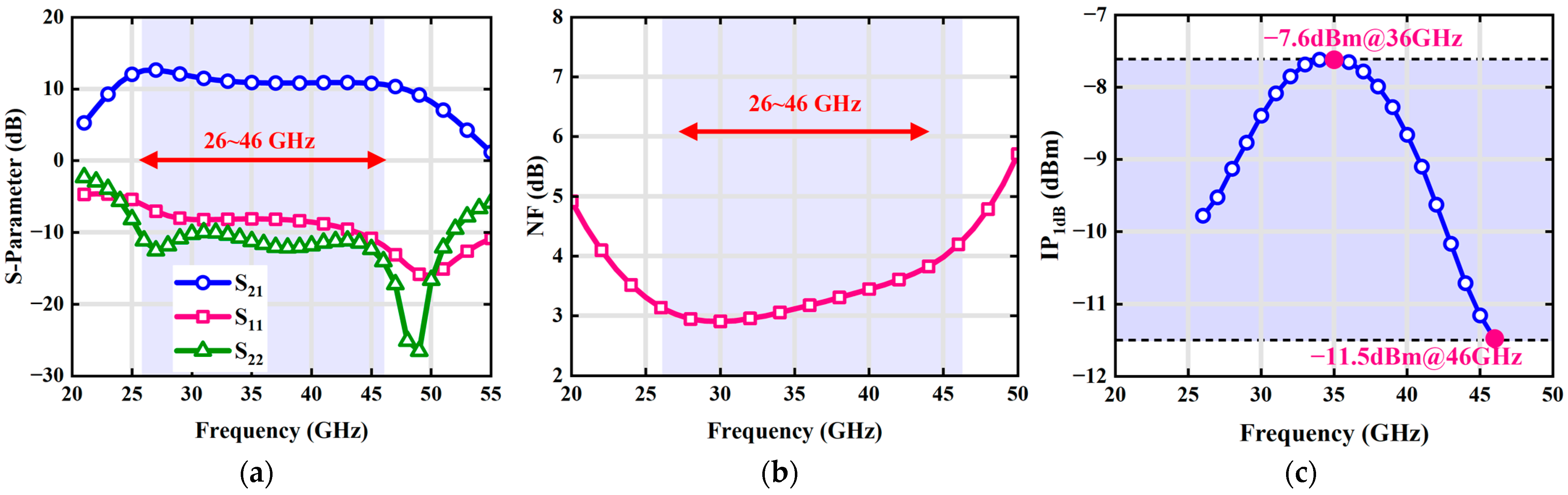
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaeffer, D.K. A 1.5-V, 1.5-GHz CMOS Low Noise Amplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1997, 32, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yeo, K.S.; Cabuk, A. A Novel CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier Design for 3.1 to 10.6-GHz Ultra-Wide-Band Wireless Receivers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2006, 53, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; You, X. A 20-GHz 1.9-mW LNA using gm-boost and current-reuse techniques in 65-nm CMOS for satellite communications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhao, C.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, K. A Ku-band CMOS LNA with transformer feedforward gm-boosting technique. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP), Chengdu, China, 20–22 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bozorg, A.; Staszewski, R.B. A 0.02–4.5-GHz LN(T)A in 28-nm CMOS for 5G Exploiting Noise Reduction and Current Reuse. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jang, S.; Lee, J.; Im, D. A Broadband PVT-Insensitive All-nMOS Noise-Canceling Balun-LNA for Subgigahertz Wireless Communication Applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2021, 31, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Choi, T.Y.; Jung, B. A 2.4-GHz Resistive Feedback LNA in 0.13-um CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 3019–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruccoleri, F.; Klumperink, E.; Nauta, B. Noise cancelling in wide-band CMOS LNAs. IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 1, 406–407. [Google Scholar]
- Blaakmeer, S.C.; Klumperink, E.A.M.; Leenaerts, D.M.W.; Nauta, B. Wideband balun-LNA with simultaneous output balancing, noise-canceling and distortion-canceling. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z. A Wideband Inductorless LNA with Local Feedback and Noise Cancelling for Low-Power Low-Voltage Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2010, 57, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Mukherjee, J. An Inductorless Noise Cancelling Wideband Balun LNA with Dual Shunt Feedback and Current Reuse. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 62nd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Dallas, TX, USA, 4–7 August 2019; pp. 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, S.; Lee, H.D.; Jang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, K.C. A 28-GHz CMOS LNA with stability-enhanced Gm-boosting technique using transformers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Boston, MA, USA, 4–6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Elkholy, M.; Shakib, S.; Dunworth, J.; Aparin, V.; Entesari, K. A Wideband Variable Gain LNA With High OIP3 for 5G Using 40-nm Bulk CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, V.; Floyd, B. A 24–44 GHz UWB LNA for 5G cellular frequency bands. In Proceedings of the 11th Global Symposium on Millimeter Waves (GSMM), Boulder, CO, USA, 22–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, B. Design of Analog CMOS Integrate Circuits, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 198–244. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shekhar, S.; Allstot, D.J. Gm-boosted common-gate LNA and differential colpitts VCO/QVCO in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.J.; Lin, K.Y.; Wang, H. Millimeter-wave low power and miniature CMOS multicascode low-noise amplifiers with noise reduction topology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.; Usman, M.; Atiq, H.; Ramzan, R. 28–32 GHz Wideband LNA for 5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Microwave, Antennas & Circuits (ICMAC), Islamabad, Pakistan, 21–22 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nozahi, M.; Sánchez-Sinencio, E.; Entesari, K. A millimeter-wave (23–32 GHz) wideband BiCMOS low-noise amplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobal, E.; Siriburanon, T.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, H.M.; Staszewski, R.B.; Zhu, A. A Gm-Boosting Technique for Millimeter-Wave Low-Noise Amplifiers in 28-nm Triple-Well Bulk CMOS Using Floating Resistor in Body Biasing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 5007–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Hong, W. A 24-40 GHz Wideband LNA with Gain Compensation in 40-nm CMOS for 5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 16th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT), Guangzhou, China, 31 August–3 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Du, J.; Li, Y. A 24-27GHz High Linearity LNA in 40nm CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Chengdu, China, 28–30 August 2024. [Google Scholar]


| Device | D/P | Device | D/P | Device | D/P | Device | D/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | (1.5 μm/30 nm) × 16 | L1 | 270 pH | L7 | 320 pH | k1 | 0.7 |
| M2 | (1 μm/30 nm) × 16 | L2 | 400 pH | L8 | 200 pH | k2 | 0.7 |
| M3 | (2 μm/30 nm) × 32 | L3 | 300 pH | L9 | 300 pH | k3 | 0.6 |
| M4 | (1 μm/30 nm) × 16 | L4 | 400 pH | L10 | 300 pH | k4 | 0.6 |
| Cc1 | 10 fF | L5 | 300 pH | Ls1 | 80 pH | VG1 | 0.55 V |
| Cc2 | 500 fF | L6 | 250 pH | Ls2 | 350 pH | VG2/VG3 | 0.5 V |
| Reference | This Work S | [12] M | [13] M | [18] S | [19] M | [20] M | [21] S | [22] S |
| Tech | 28 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 40 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 180 nm BiCMOS | 28 nm CMOS | 40 nm CMOS | 40 nm CMOS |
| Frequency (GHz) | 26–46 | 24.9–32.5 | 26–33 | 26–33.4 | 23–32 | 24.7–29.5 | 24–40 | 24–27 |
| GainMAX (dB) | 12.6 | 18.3 | 27 | 18.5 | 12 | 19.1 | 20 | 13.6 |
| NF (dB) | 2.9–4.2 | 3.25–4.2 | 3.3–4.3 | 3 | 4.5–6.3 | 3.3–3.5 | 3.7 | 5.8 |
| IP1dB (dBm) | −11.5 to −7.6 | −24 | −21.6 | −24.5 | −16.3 to −14.5 | −8.7 | −15.9 | −4.2 |
| PDC (mW) | 22 | 20.5 | 31.4 | 17 | 13 | 25.5 | 47.2 | 50.8 |
| Core Area (mm2) | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.34 |
| FBW * | 56% | 26% | 24% | 25% | 42% | 18% | 50% | 12% |
| FoM | 6.03 | 3.02 | 2.62 | 4.03 | 2.37 | 1.56 | 2.51 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Ma, K.; Hu, K. An Ultra-Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier with a New Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Technique for 28 nm CMOS Technology. Electronics 2025, 14, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101904
Cui Y, Ma K, Hu K. An Ultra-Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier with a New Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Technique for 28 nm CMOS Technology. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101904
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yuanping, Kaixue Ma, and Kejie Hu. 2025. "An Ultra-Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier with a New Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Technique for 28 nm CMOS Technology" Electronics 14, no. 10: 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101904
APA StyleCui, Y., Ma, K., & Hu, K. (2025). An Ultra-Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier with a New Cross-Coupling Noise-Canceling Technique for 28 nm CMOS Technology. Electronics, 14(10), 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14101904






