Fully Automatic Approach for Smoke Tracking Based on Deep Image Quality Enhancement and Adaptive Level Set Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
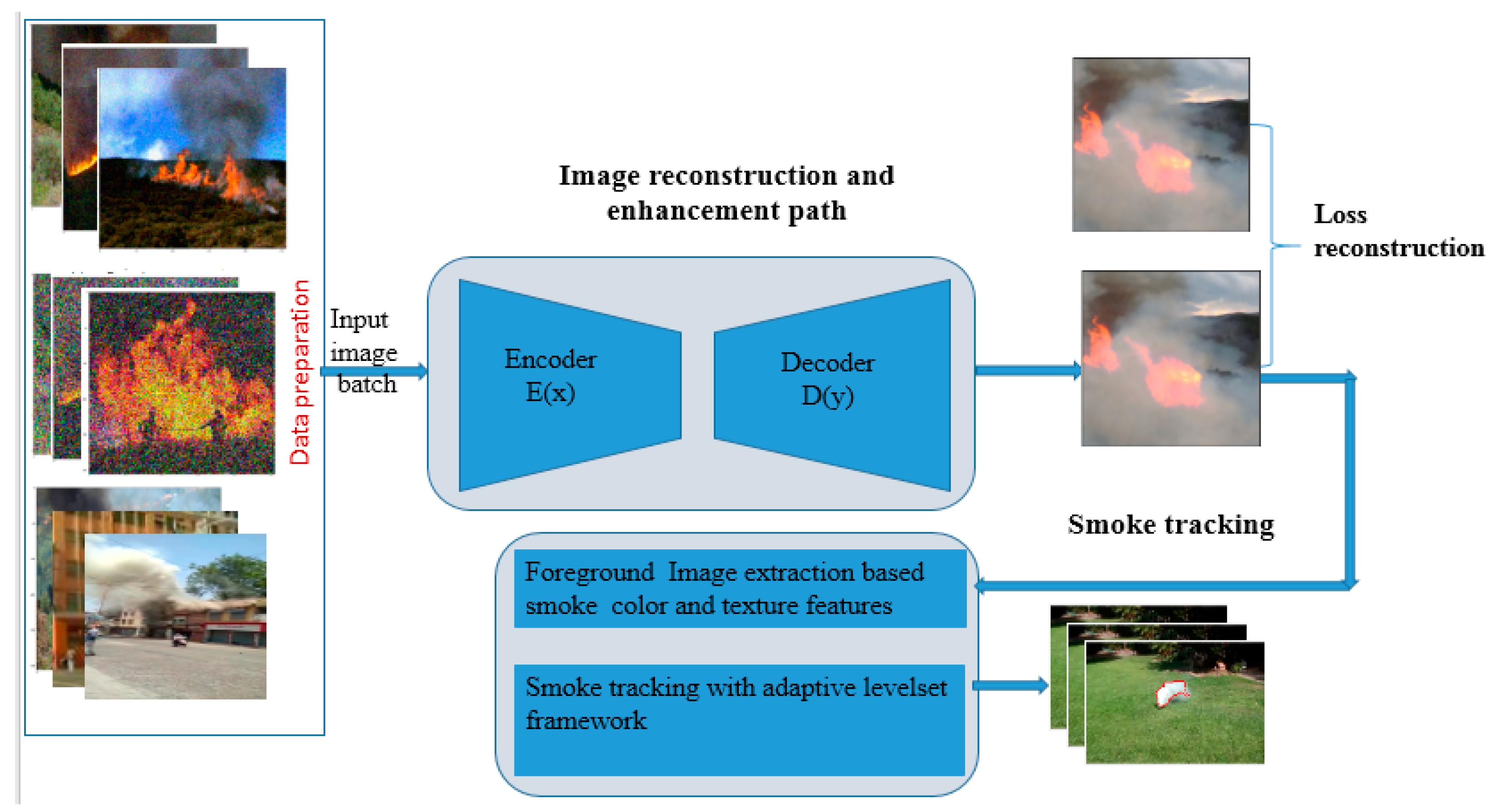
3. The Proposed Smoke Tracking Method
3.1. Image Enhancement Path
3.1.1. Dataset Preparation
3.1.2. The Proposed Lightweight CAE Network Architecture
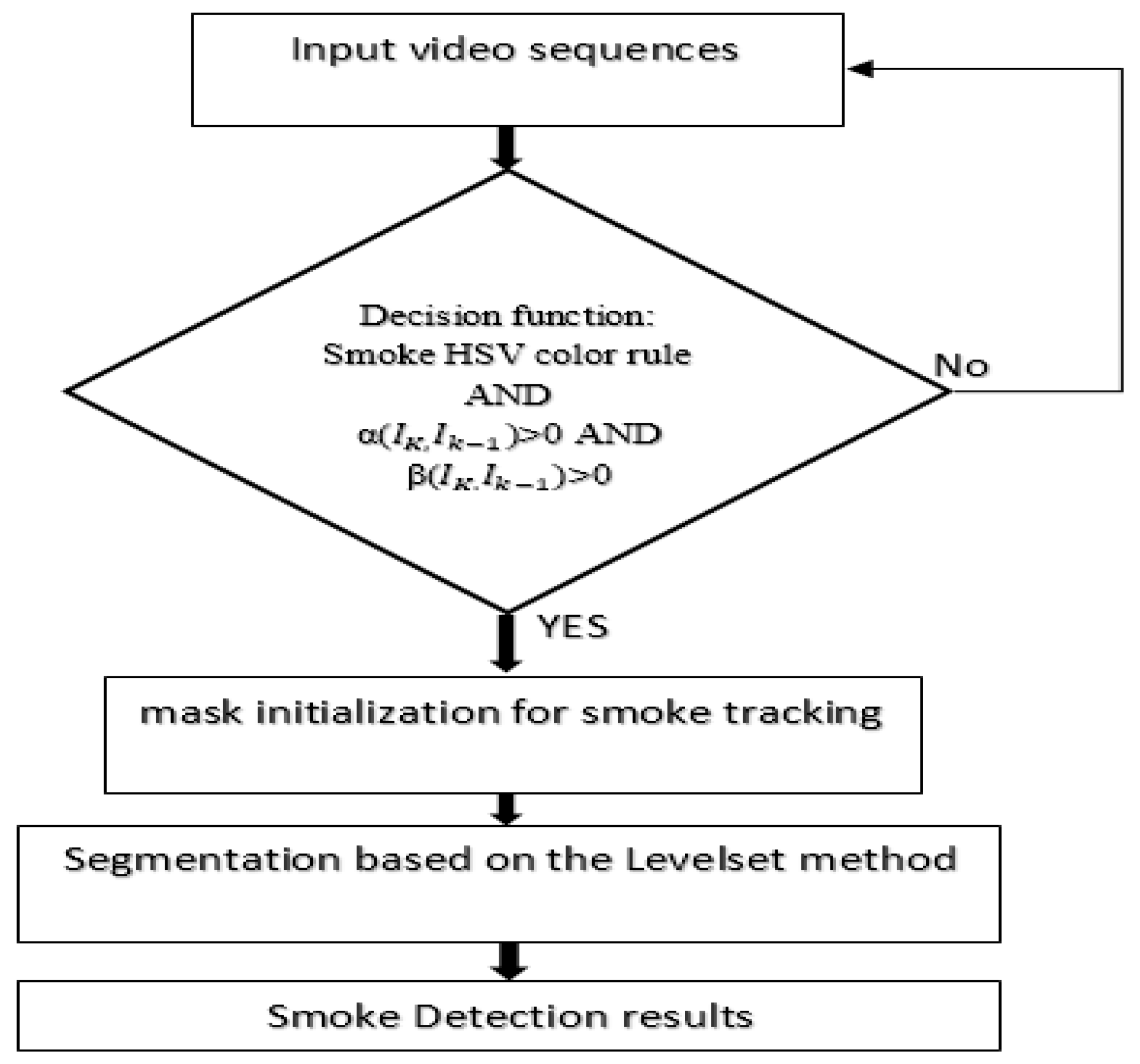
3.2. The Tracking Path
3.2.1. Color Modeling for Smoke Detection
3.2.2. Smoke Feature Extraction
3.2.3. Level Set Segmentation
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
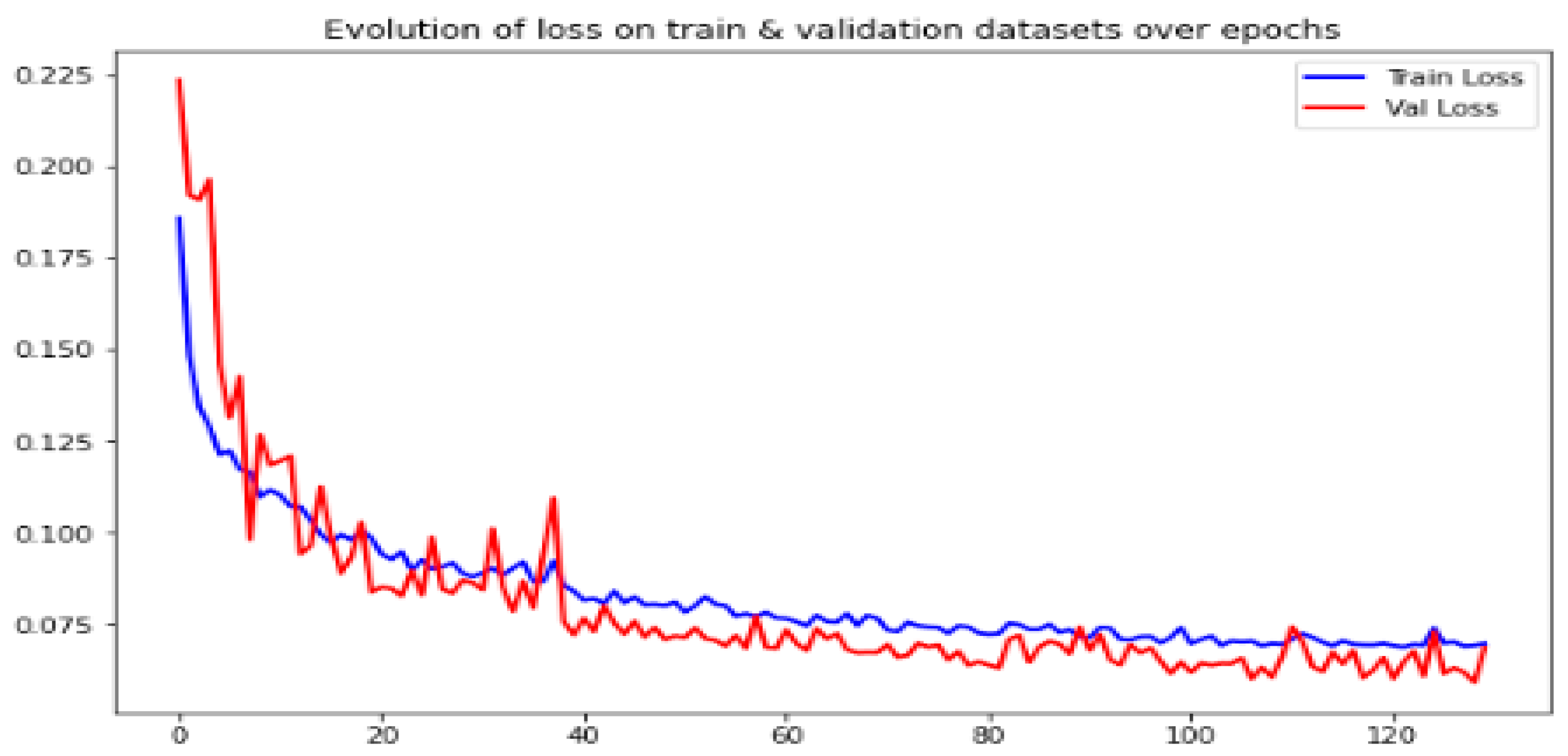
4.1. CAE Configuration and Image Quality Enhancement Results Evaluation
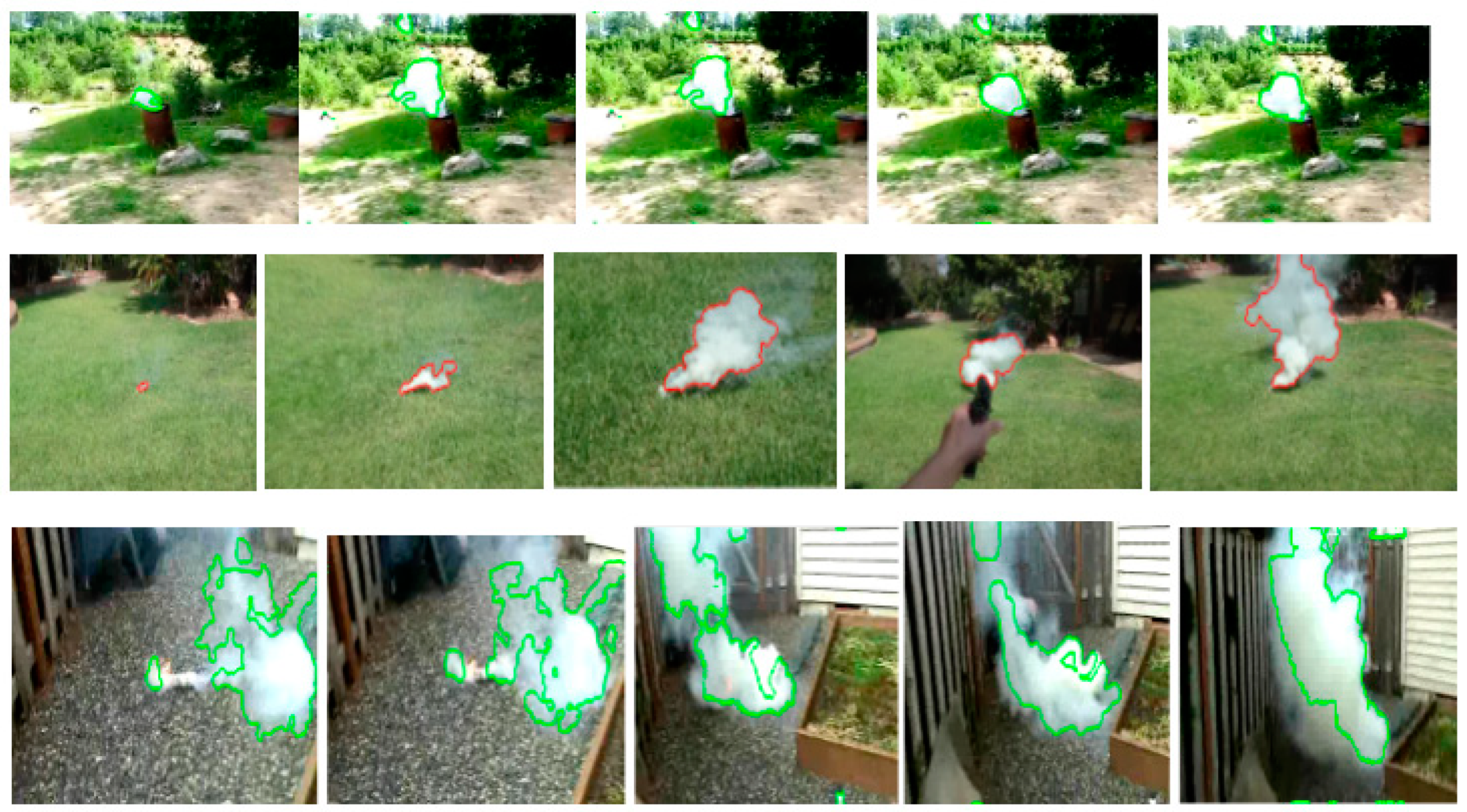
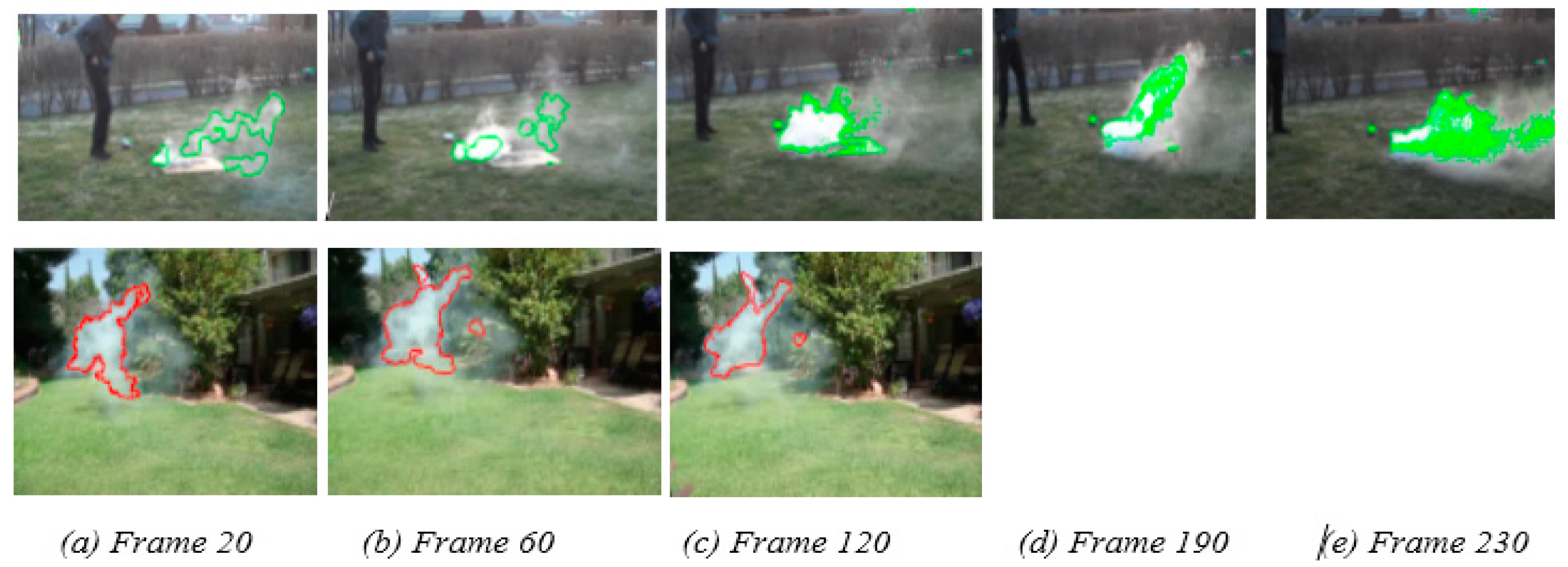
4.2. Video Smoke Tracking Path
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Jimenez, S.; Jurio, A.; Pagola, M.; De Miguel, L.; Barrenechea, E.; Bustince, H. Forest fire detection: A fuzzy system approach based on overlap indices. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 2, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Ogunbona, P. Smoke detection in video: An image separation approach. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2014, 106, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, J. Fire and smoke precise detection method based on the attention mechanism and anchor-free mechanism. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Gao, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Kou, L. Early smoke and flame detection based on transformer. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 2023, 4, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, V.E.; Cho, J.; Subramanian, M.; Sai Naren, O. Forest fire and smoke detection using deep learning-based learning without forgetting. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Chen, F.; Cheng, P.; Huang, Y. Smoke root detection from video sequences based on multi-feature fusion. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Zademehdi, A. Fire detection for video surveillance applications using ICA K-medoids-based color model and efficient spatio-temporal visual features. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 130, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Gao, W. A convolutional neural network-based flame detection method in video sequence. Signal Image Video Process. 2018, 12, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, A.; Mirghasemi, S.; Khosravi, A.; Lim, C.P.; Nahavandi, S. A new PSO-based approach to fire flame detection using K-medoids clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. Vol. 2017, 68, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.J.; Moutinho, A.; Almeida, M. Wildfire detection using transfer learning on augmented datasets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 142, 112975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tang, G.; Xu, M. Hierarchical detection of wildfire flame video from pixel level to semantic level. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 2, 4097–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonenko, A.; Hernández, D.C.; Jo, K. Fast smoke detection for video surveillance using CUDA. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. Smoke detection using spatio-temporal analysis, motion modeling and dynamic texture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference, EUSIPCO, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 1078–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Z. Smoke-detection framework for high-definition video using fused spatial- and frequency-domain features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 89687–89701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, W.; Dong, N. Fire smoke detection based on texture features and optical flow vector of contour. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, WCICA, Guilin, China, 12–15 June 2016; pp. 2879–2883. [Google Scholar]
- Appana, D.K.; Islam, R.; Khan, S.A.; Kim, J.-M. A video-based smoke detection using smoke flow pattern and spatial–temporal energy analyses for alarm systems. Inf. Sci. 2017, 418–419, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novac, I.; Geipel, K.R.; Gil, J.E.D.; Paula, L.G.D.; Hyttel, K.; Chrysostomou, D. A Framework for Wildfire Inspection Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 January 2020; pp. 867–872. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Gong, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F. Efficient attention based deep fusion CNN for smoke detection in fog environment. Neurocomputing 2021, 434, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguettaya, A.; Zarzour, H.; Taberkit, A.M.; Kechida, A. A Review on Early Wildfire Detection from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Using Deep Learning-Based Computer Vision Algorithms. Signal Process. 2022, 190, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; de Gioia, F.; Saponara, S. A real-time video smoke detection algorithm based on Kalman filter and CNN. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Xu, R.; Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y. A Vision-Based Detection and Spatial Localization Scheme for Forest Fire Inspection from UAV. Forests 2022, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabi, R.; Bouchouicha, M.; Mouelhi, A.; Sayadi, M.; Moreau, E. An Efficient Smoke Detection Algorithm Based on Deep Belief Network Classifier Using Energy and Intensity Features. Electronics 2020, 9, 1390–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J. Video smoke detection based on deep saliency network. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 105, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hua, C.; Ding, W.; Wu, R. Real-time detection of flame and smoke using an improved YOLOv4 network. SIViP 2022, 16, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Tang, Q.; Lu, X. An Attention Enhanced Bidirectional LSTM for Early Forest Fire Smoke Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 154732–154742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Hassan, B.; Khan, S.; Ahmed, R.; Abuassba, A. Deep Fire: A Novel Dataset and Deep Transfer Learning Benchmark for Forest Fire Detection. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 5358359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzi, S.; Bouchouicha, M.; Ginoux, J.; Moreau, E.; Sayadi, M. Convolutional neural network for smoke and fire semantic segmentation. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouelhi, A.; Bouchouicha, M.; Sayadi, M.; Moreau, E. A Neural Adaptive Level Set Method for Wildland Forest Fire Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. Indersci. 2021, 67, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zheng, A.; Wu, Z.; Tong, C. Real-Time Fire Smoke Detection Method Combining a Self-Attention Mechanism and Radial Multi-Scale Feature Connection. Sensors 2023, 6, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Mei, Z.; Zhang, X. A real-time video fire flame and smoke detection algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2013, 62, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigithan, D.; Behçet, T.; Gudukbay, U.; Cetin, A. Real-Time Fire and Flame Detection in Video, 1988 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. ICASSP-88 2005, 2, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Turgay, C. Fast and Efficient Method for Fire Detection Using Image Processing. ETRI J. 2010, 32, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, A.S.; Raman, B. Dual Deep Learning Model for Image Based Smoke Detection. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 2419–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wan, B.; Yuan, F.; Xia, X.; Shi, J. A Deep Normalization and Convolutional Neural Network for Image Smoke Detection. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18429–18438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreyin, B.U.; Dedeoglu, Y.; Cetin, A.E. Contour Based Smoke Detection in Video Using Wavelets. In Proceedings of the 14th European Signal Processing Conference, EUSIPCO 2006, Florence, Italy, 4–8 September 2006; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.-A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning, ACM, New York, NY, USA, 5 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Viren, J.; Seung, S. Natural image denoising with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, NY, USA, 8–10 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wu, P.; Chiou, Y. An Early Fire-Detection Method Based on Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Image Processing, 2004. ICIP’04, Singapore, 24–27 October 2004; pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.F.; Sandberg, B.Y.; Vese, L.A. Active contour without edges for vector-valued images. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2000, 11, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vese, L.A.; Chan, T.F. A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 53, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.; Yezze, A., Jr.; Willsky, A.S. Curve evolution implementation of the Mumford–Shah functional for image segmentation, denoising, interpretation, and magnification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousson, M.; Brox, T.; Deriche, R. Active unsupervised texture segmentation on a diffusion based feature space. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; pp. 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Gao, X.; Tao, D.; Li, X. A nonlinear adaptive level set for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Kong, J.; Kashyap, S.; Pastore, V.P.; Wang, F.; Wong, K.C.L.; Mukherjee, V. Convolutional autoencoder based model HistoCAE for segmentation of viable tumor regions in liver whole-slide images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondara, L. Medical image denoising using convolutional denoising autoencoders. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.04667v2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.N.; Chui, C.K.; Chang, S.; Ong, S.H. Integrating spatial fuzzy clustering with level set methods for automated medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2011, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
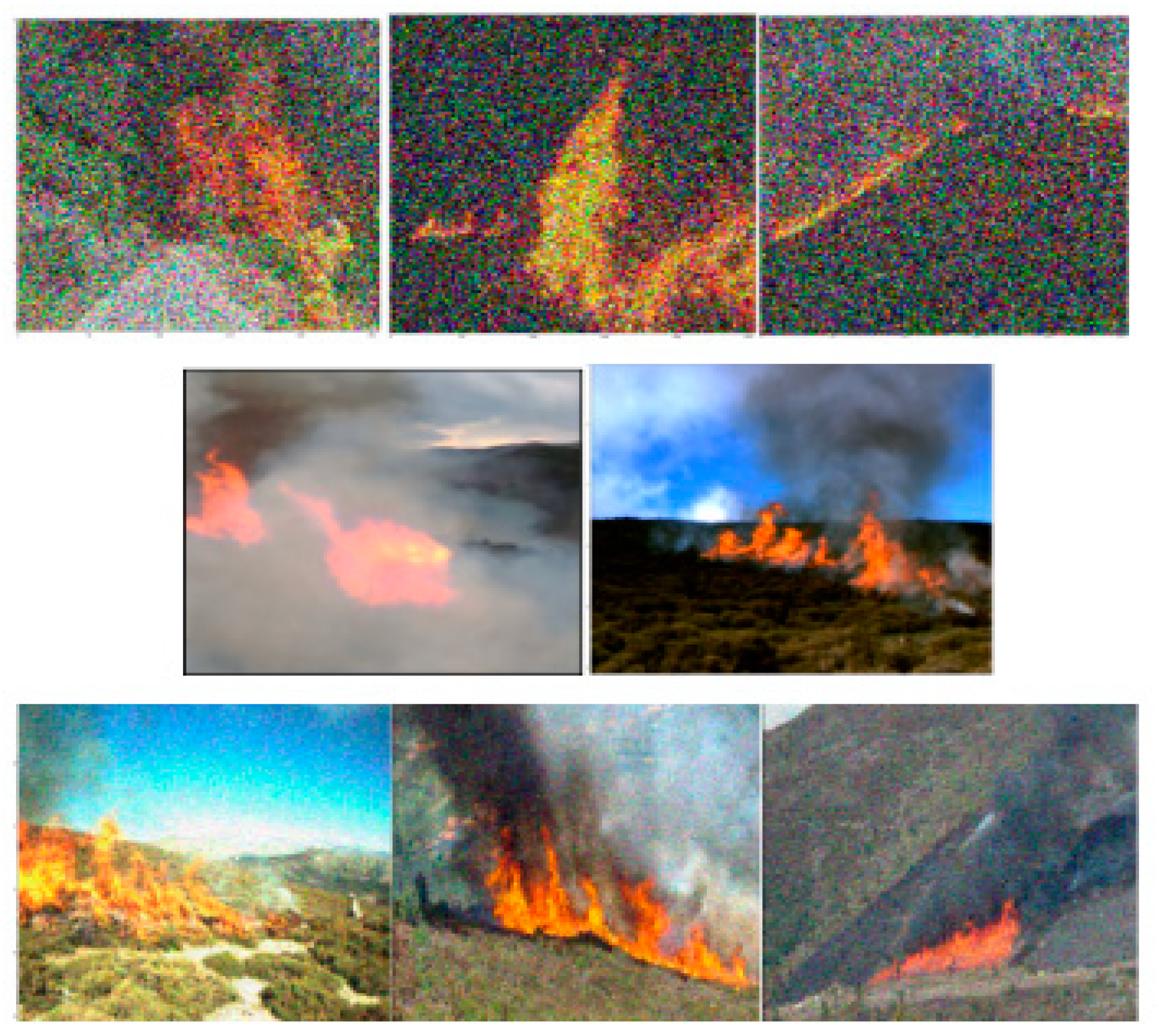
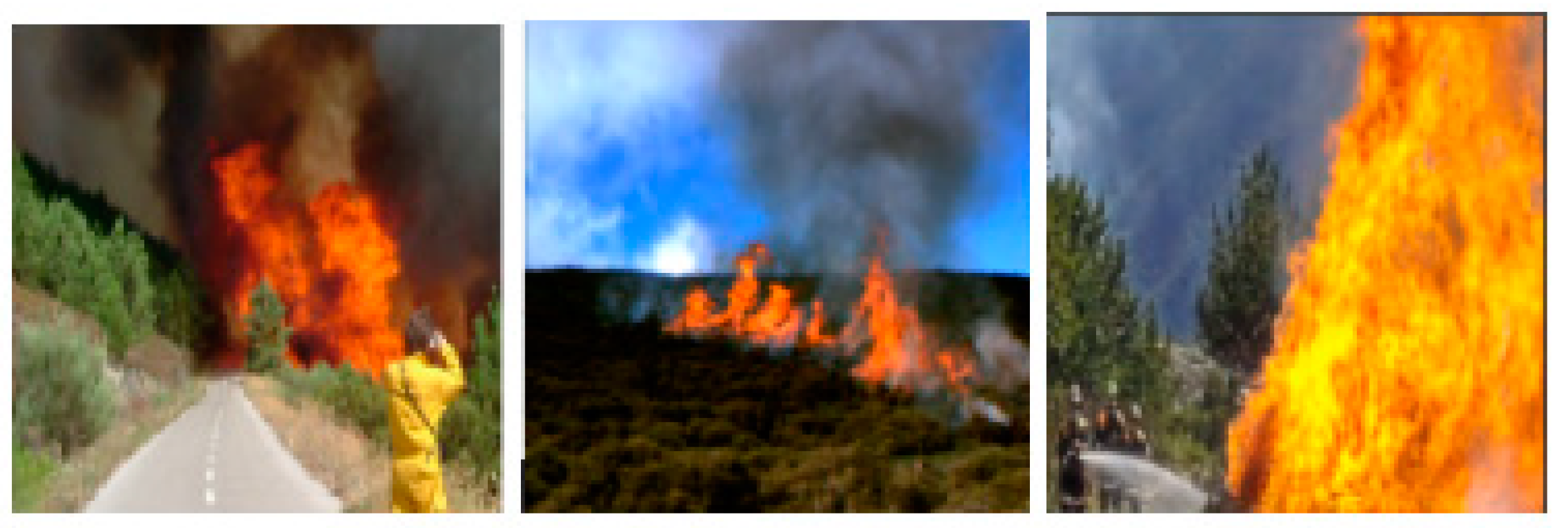





| Color Space | Features | Method | Accuracy (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashemzadeh [7] | RGB | Motion | CNN SVM | 97.6 |
| Pundir [33] | RGB | Motion Texture Color | Deep CNN | 97.4 |
| Yin [34] | RGB | Motion | CNN | 97.0 |
| Toreyin [35] | YUV | Motion Energy Disorder | Wavelet transform | - |
| Input Dimension | (256, 256, 3) |
| Epochs number | 130 |
| Loss | Formulation combines the SSIM, MSE, MAE |
| Weight decay | 1 × 10−5 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Trainable parameters | 299,139 |
| Image | PSNR | SSIM | MSE | Processing Time(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtered with the proposed CAE | 73.2 | 0.91 | 0.0030 | 0.6 |
| Filtered with a median filter | 72.3 | 0.79 | 0.0040 | 0.04 |
| Noisy image | 69.04 | 0.33 | 0.0081 | - |
| Filtering Type | SSIM |
|---|---|
| Noisy | 0.33 |
| Median filter | 0.79 |
| Gaussian filter | 0.90 |
| Gondara [46] | 0.89 |
| The proposed CAE | 0.91 |
| Original Image | Ground Truth | Our Method | FCM | Spatial FCM [47] | K-means |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(a)  |  |  |  |  |  |
(b)  |  |  |  |  |  |
(c)  |  |  |  |  |  |
(d)  |  |  |  |  |  |
(e)  |  |  |  |  |  |
(f)  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Max | Min | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaccard index (%) | 92.1 | 80.5 | 90.1 |
| Dice coefficient (%) | 90.0 | 79.6 | 89.5 |
| Processing time/frame (s) | 5.3 | 4.9 | 5.0 |
| Processing time/video (s) | 484.9 | 235.4 | 376.3 |
| Video Sequences | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video 1 | 675 | 674 | 670 | 99.20 |
| Video 2 | 407 | 403 | 403 | 99.02 |
| Video 3 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 100.00 |
| Video 4 | 310 | 308 | 308 | 99.35 |
| Video 5 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 100.00 |
| Jaccard Similarity Index (%) | Dice Coefficient (%) | Detection Time/ Image(s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| segmentation of raw images | 70.6 | 89.9 | 73.2 | 89.8 | 8.2 | 9 |
| segmentation of denoised images with a median filter | 64.7 | 87.3 | 65.5 | 86.9 | 4.6 | 5.1 |
| segmentation of denoised images with the proposed pipeline | 80.5 | 92.1 | 79.6 | 90.0 | 4.9 | 5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daoudi, R.; Mouelhi, A.; Bouchouicha, M.; Moreau, E.; Sayadi, M. Fully Automatic Approach for Smoke Tracking Based on Deep Image Quality Enhancement and Adaptive Level Set Model. Electronics 2023, 12, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183888
Daoudi R, Mouelhi A, Bouchouicha M, Moreau E, Sayadi M. Fully Automatic Approach for Smoke Tracking Based on Deep Image Quality Enhancement and Adaptive Level Set Model. Electronics. 2023; 12(18):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183888
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaoudi, Rimeh, Aymen Mouelhi, Moez Bouchouicha, Eric Moreau, and Mounir Sayadi. 2023. "Fully Automatic Approach for Smoke Tracking Based on Deep Image Quality Enhancement and Adaptive Level Set Model" Electronics 12, no. 18: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183888
APA StyleDaoudi, R., Mouelhi, A., Bouchouicha, M., Moreau, E., & Sayadi, M. (2023). Fully Automatic Approach for Smoke Tracking Based on Deep Image Quality Enhancement and Adaptive Level Set Model. Electronics, 12(18), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183888










