Broadband Millimeter-Wave 5G Power Amplifier Design in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI and 40 nm GaN HEMT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
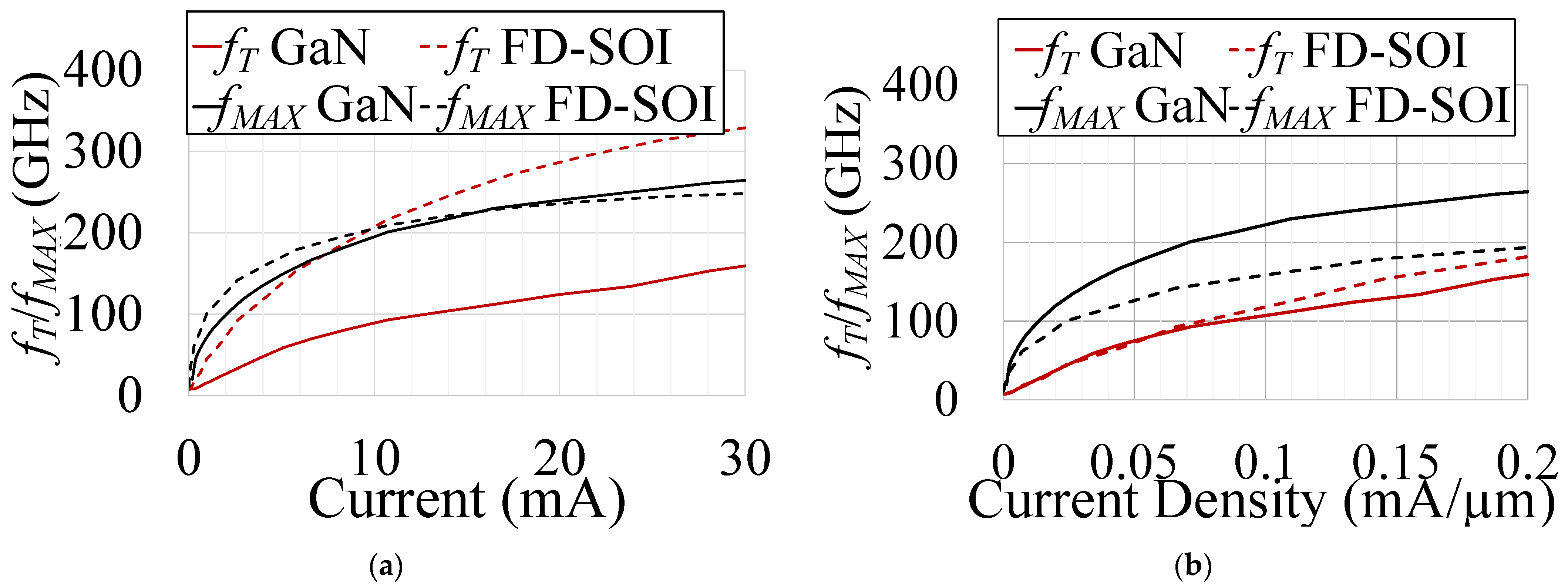
2. Design Methodology
3. Results
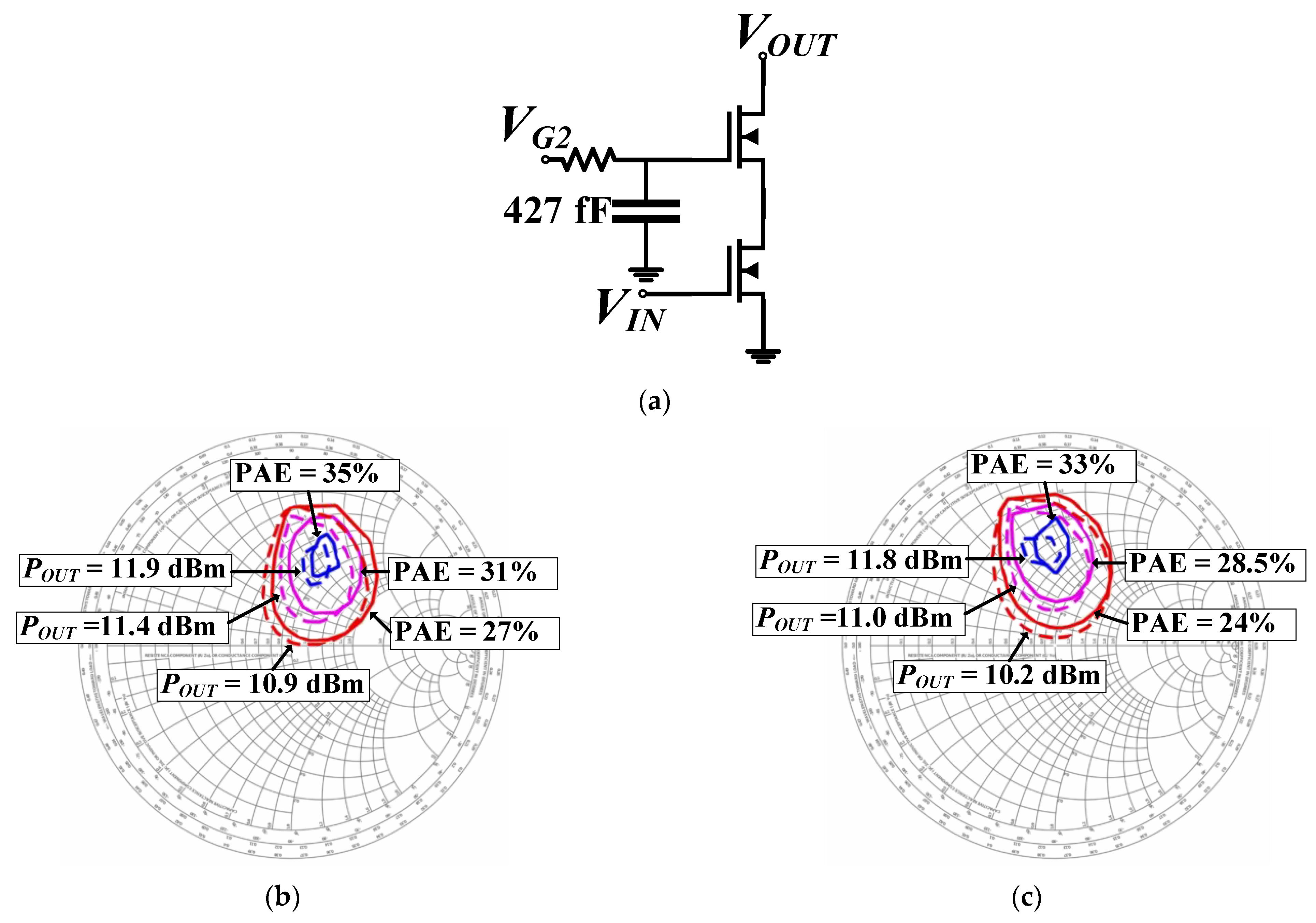
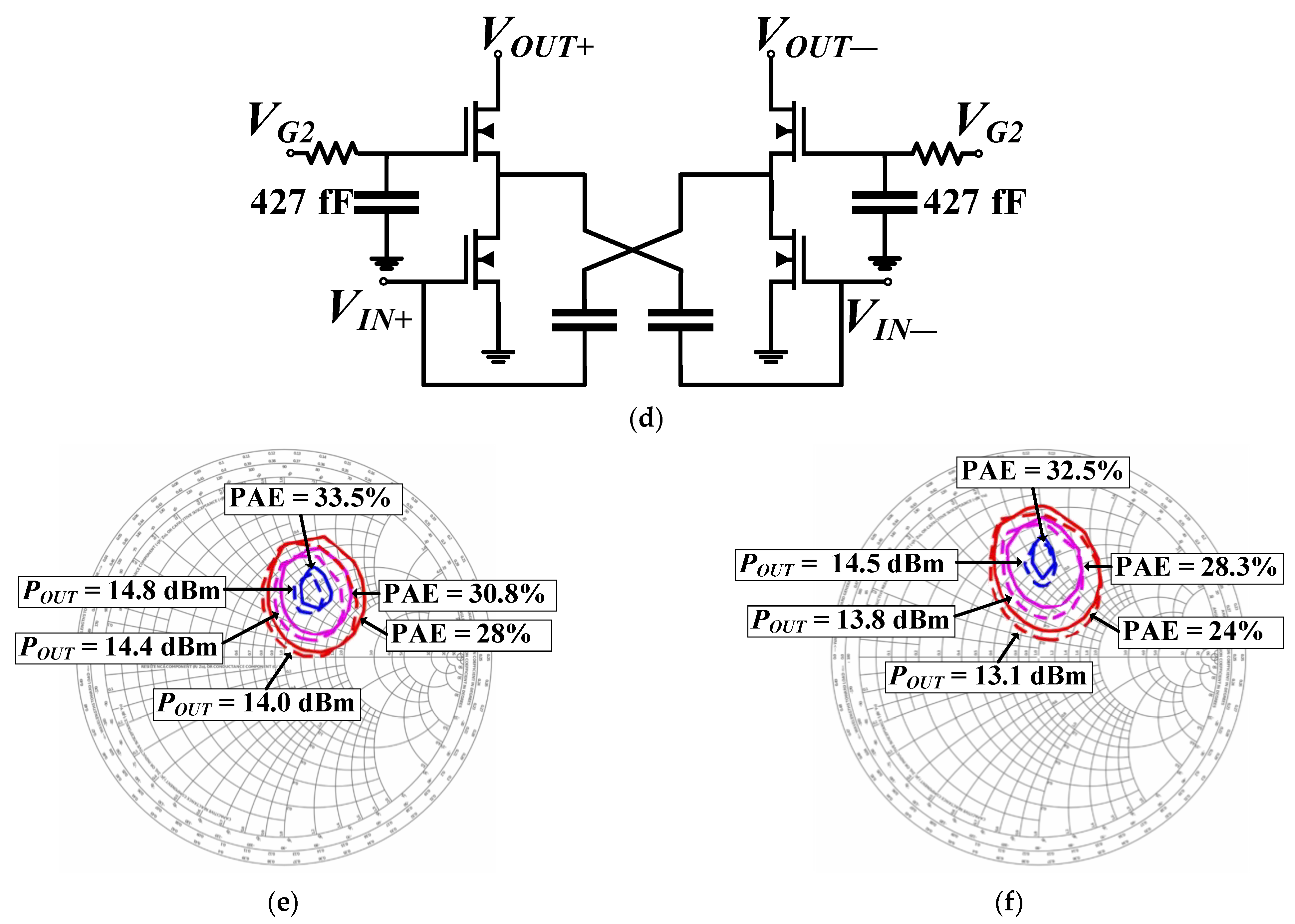
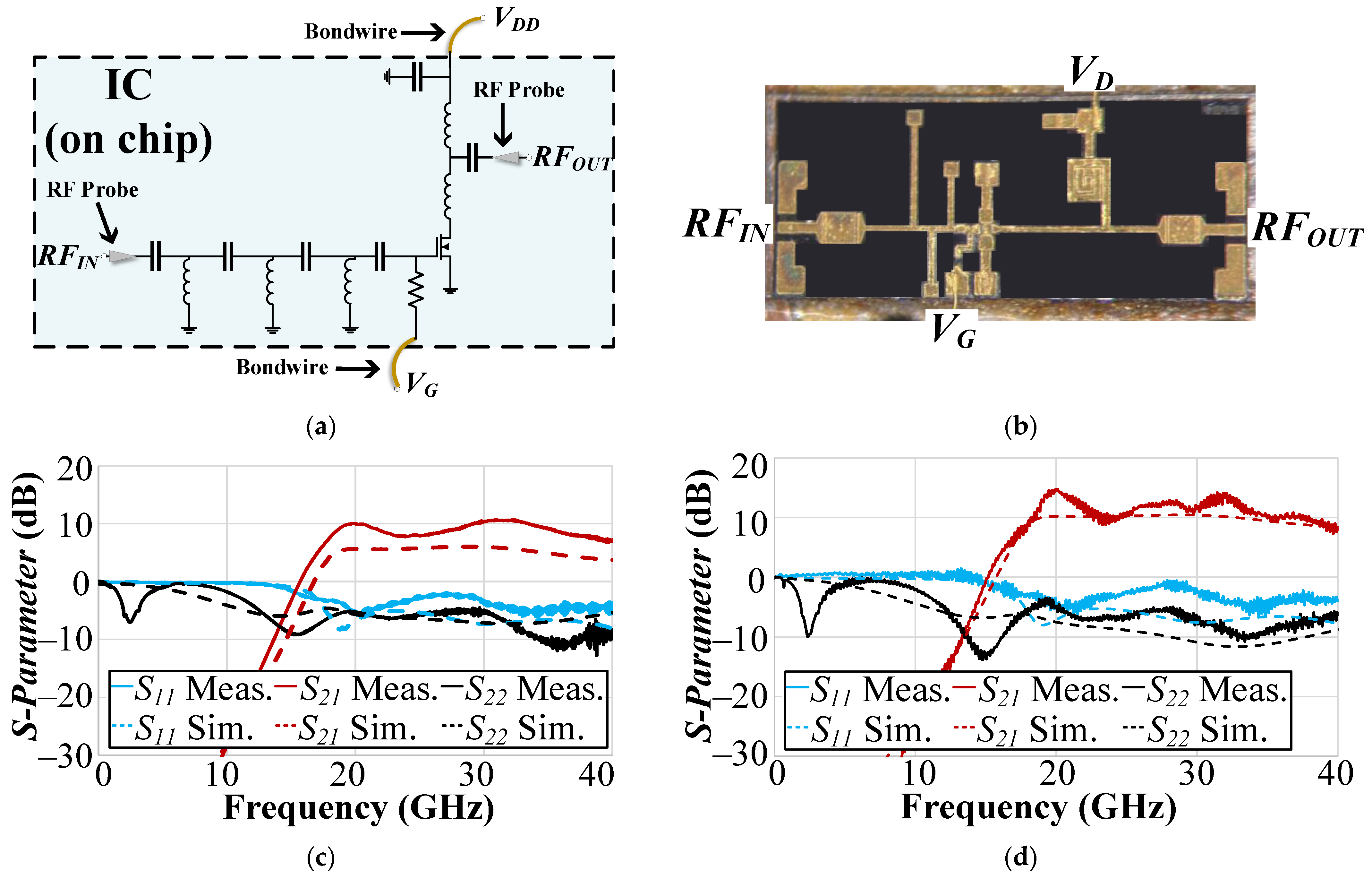
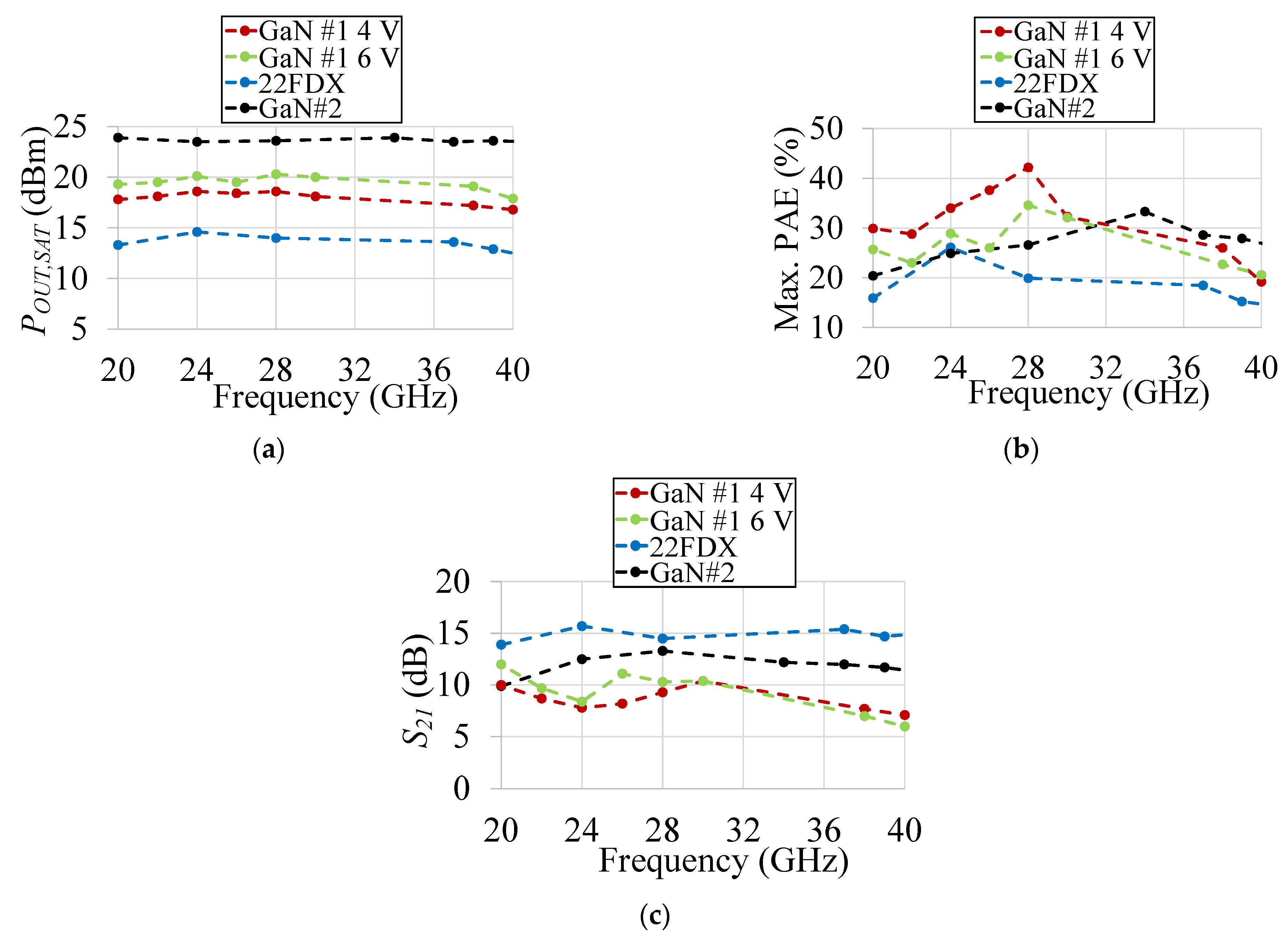
3.1. Single-Ended GaN (GaN #1) PA Measurement Results
3.2. Differential GaN (GaN #2) PA PEX EM Simulation Results
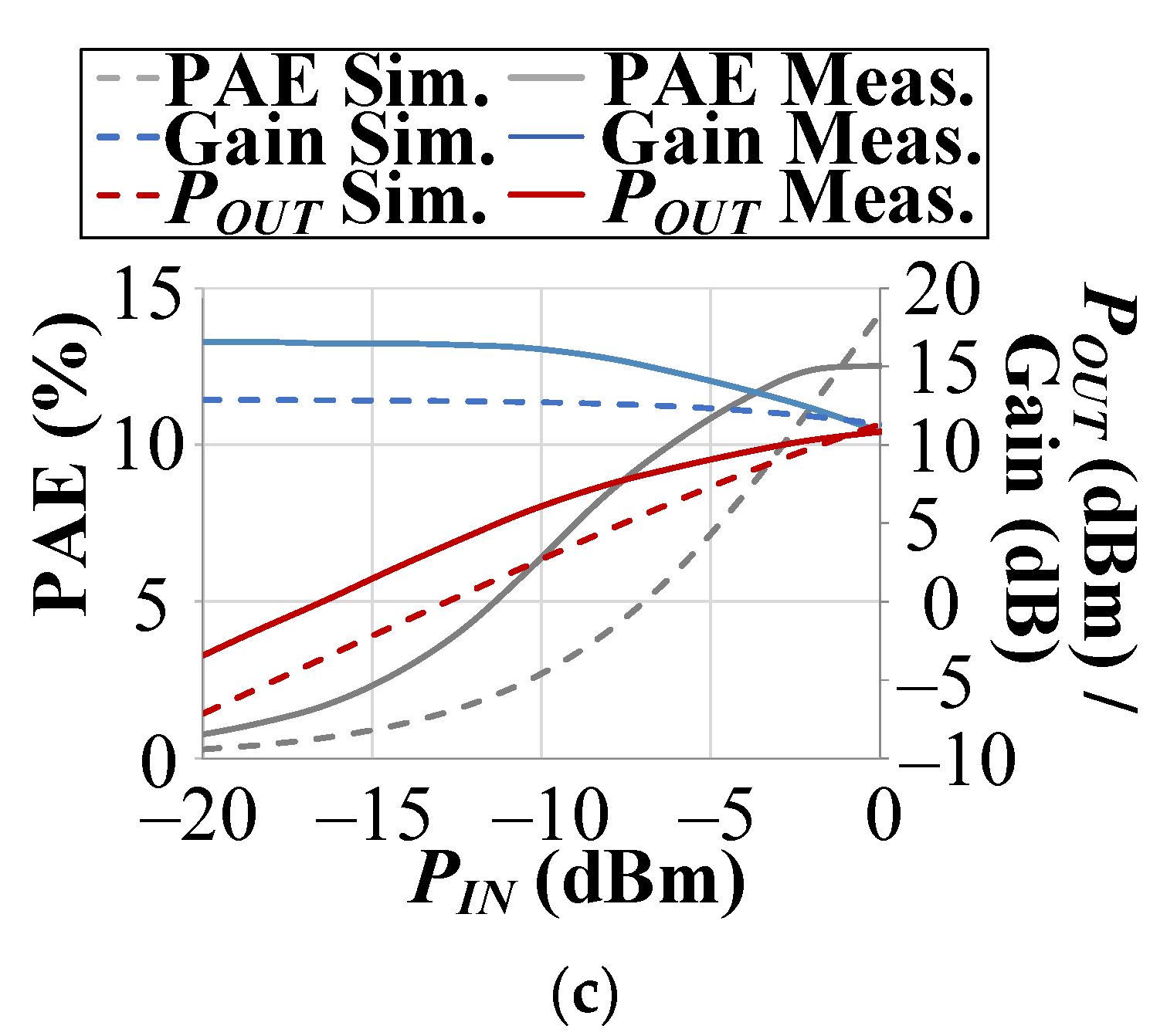
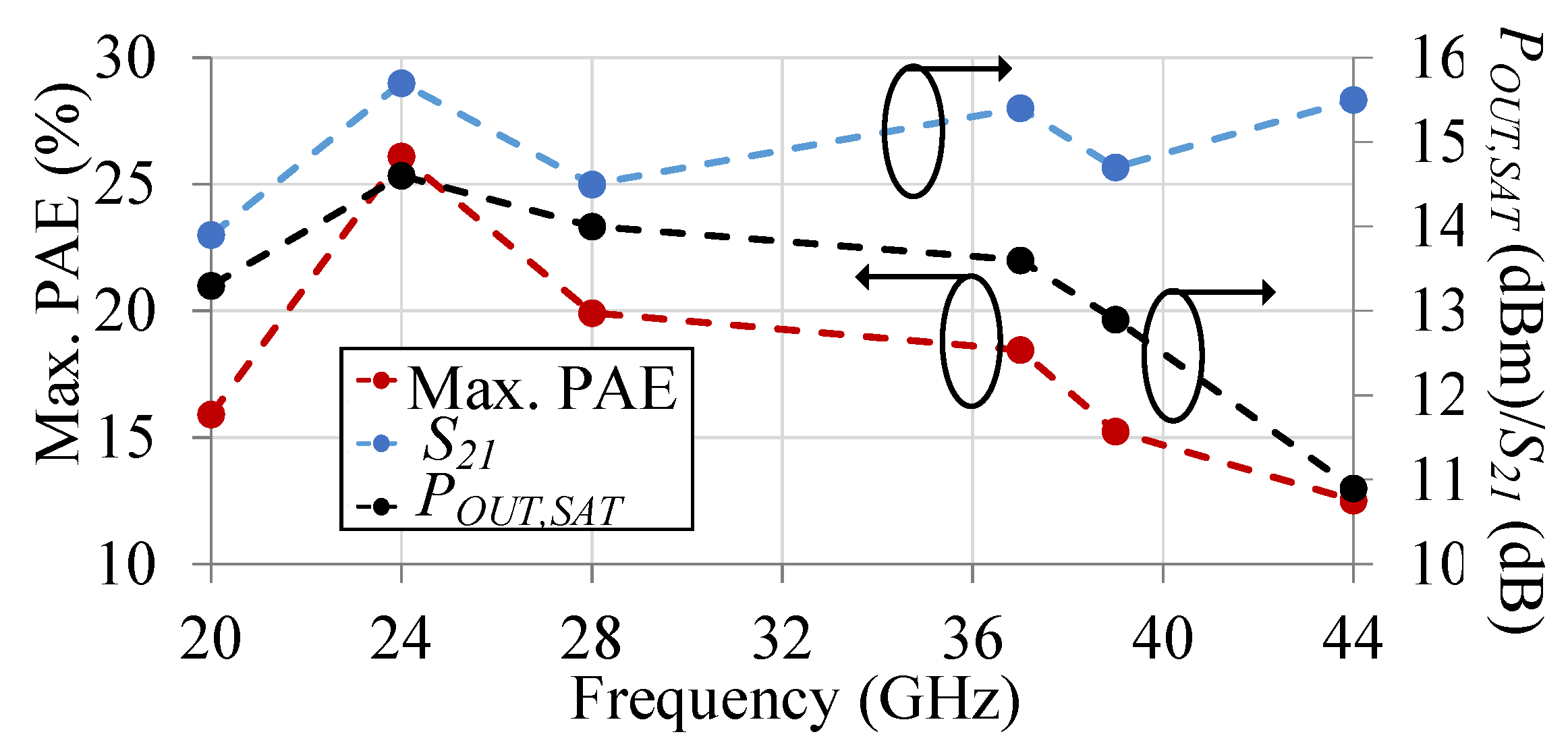
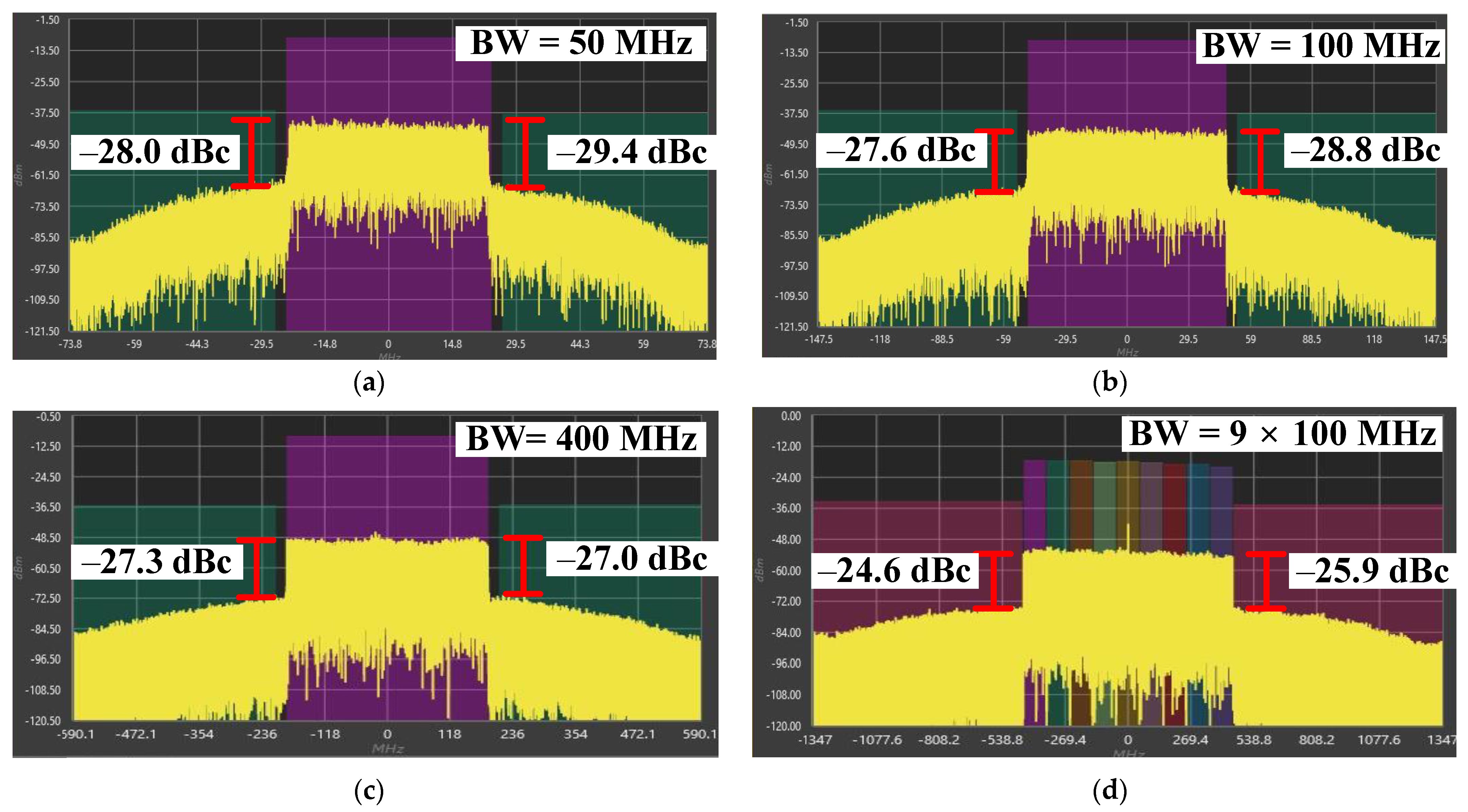
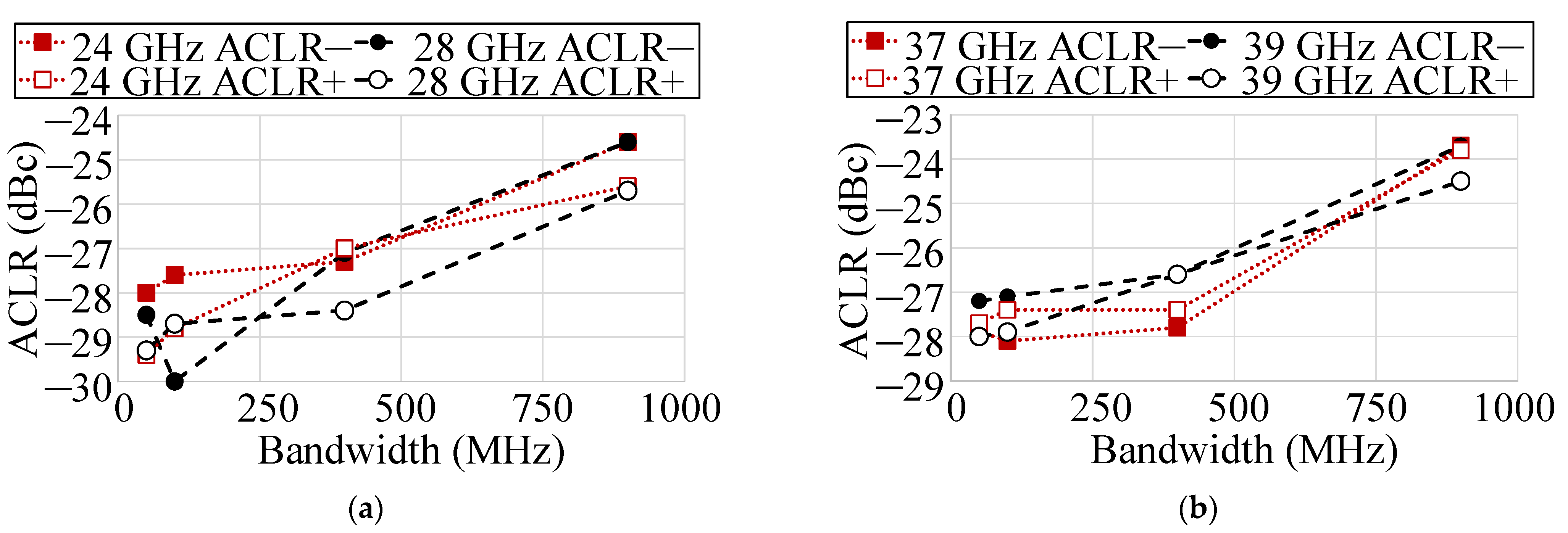
3.3. Differential Cascode CMOS PA Measurement Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: www.3gpp.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Lie, D.Y.C.; Mayeda, J.C.; Li, Y.; Lopez, J. A Review of 5G Power Amplifier Design at cm-Wave and mm-Wave Frequencies. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 6793814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voldman, S.H.; Botula, A.; Hui, D.T.; Juliano, P.A. Silicon Germanium heterojunction bipolar transistor ESD power clamps and the Johnson Limit. In Proceedings of the 2001 Electrical Overstress/Electrostatic Discharge Symposium, Portland, OR, USA, 11–13 September 2001; pp. 324–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, S.D.B.R.; Tai, J.; Brown, D.; Grabar, R.; Santos, D.; Magadia, J.; Khalaf, I.; Micovic, M. Reliability Characteristics and Mechanisms of HRL’s T3 GaN Technology. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2017, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: www.globalfoundries.com/technology-solutions/cmos/fdx/22fdx (accessed on 23 October 2021).
- Mayeda, J.C.; Tsay, J.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Lopez, J. Effective AM-PM Cancellation with Body Bias for 5G CMOS Power Amplifier Design in 22nm FD-SOI. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, K.; Relyea, C. Parasitic Extraction Technologies. Siemens Digital Industries Software. 2018. Available online: https://static.sw.cdn.siemens.com/siemens-disw-assets/public/81845/en-US/Siemens-SW-Parasitic-extraction-technologies-for-advanced-WP-81845-C2.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Asada, H.; Matsushita, K.; Bunsen, K.; Okada, K.; Matsuzawa, A. A 60GHz CMOS power amplifier using capacitive cross-coupling neutralization with 16 % PAE. In Proceedings of the 2011 41st European Microwave Conference, Manchester, UK, 10–13 October 2011; pp. 1115–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.L.; Long, J.R. 58–65 GHz Neutralized CMOS Power Amplifier with PAE Above 10% at 1-V Supply. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeda, J.C.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Sweeney, C.; Lopez, J. A 19.1–46.5 GHz Broadband Efficient Power Amplifier in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI for mm-Wave 5G. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- National Instruments “Instrument Innovations for mmWave Test”. Available online: https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/19/instrument-innovations-for-mmwave-test.html (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Stutzman, W.L.; Thiele, G.A. Broadband Antennas. In Antenna Theory and Design, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda, J.C.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Lopez, J. A Highly Efficient 18–40 GHz Linear Power Amplifier in 40-nm GaN for mm-Wave 5G. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2021, 31, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappidi, C.R.; Sengupta, K. A 26-42 GHz Broadband, Back-off Efficient and Vswr Tolerant CMOS Power Amplifier Architecture for 5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 9–14 June 2019; pp. C22–C23. [Google Scholar]
- Estella, N.; Camargo, E.; Schellenberg, J.; Bui, L. High-Efficiency, Ka-band GaN Power Amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Boston, MA, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Xu, R.; Xu, Y. Design of 18–40 GHz GaN reactive matching power amplifiers using one-order and two-order synthesised transformer networks. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2022, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qunaj, V.; Reynaert, P. A Compact Ka-Band Transformer-Coupled Power Amplifier for 5G in 0.15 um GaAs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE BiCMOS and Compound semiconductor Integrated Circuits and Technology Symposium (BCICTS), Nashville, TN, USA, 3–6 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, H. A 28GHz/37GHz/39GHz Multiband Linear Doherty Power Amplifier for 5G Massive MIMO Applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Huang, M.; Wang, H. Millimeter-Wave Continuous-Mode Power Amplifier for 5G MIMO Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H. An Instantaneously Broadband Ultra-Compact Highly Linear PA with Compensated Distributed-Balun Output Network Achieving >17.8 dBm P1dB and >36.6% PAEP1dB over 24 to 40 GHz and Continuously Supporting 64-/256-QAM 5G NR Signals over 24 to 42 GHz. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 372–374. [Google Scholar]



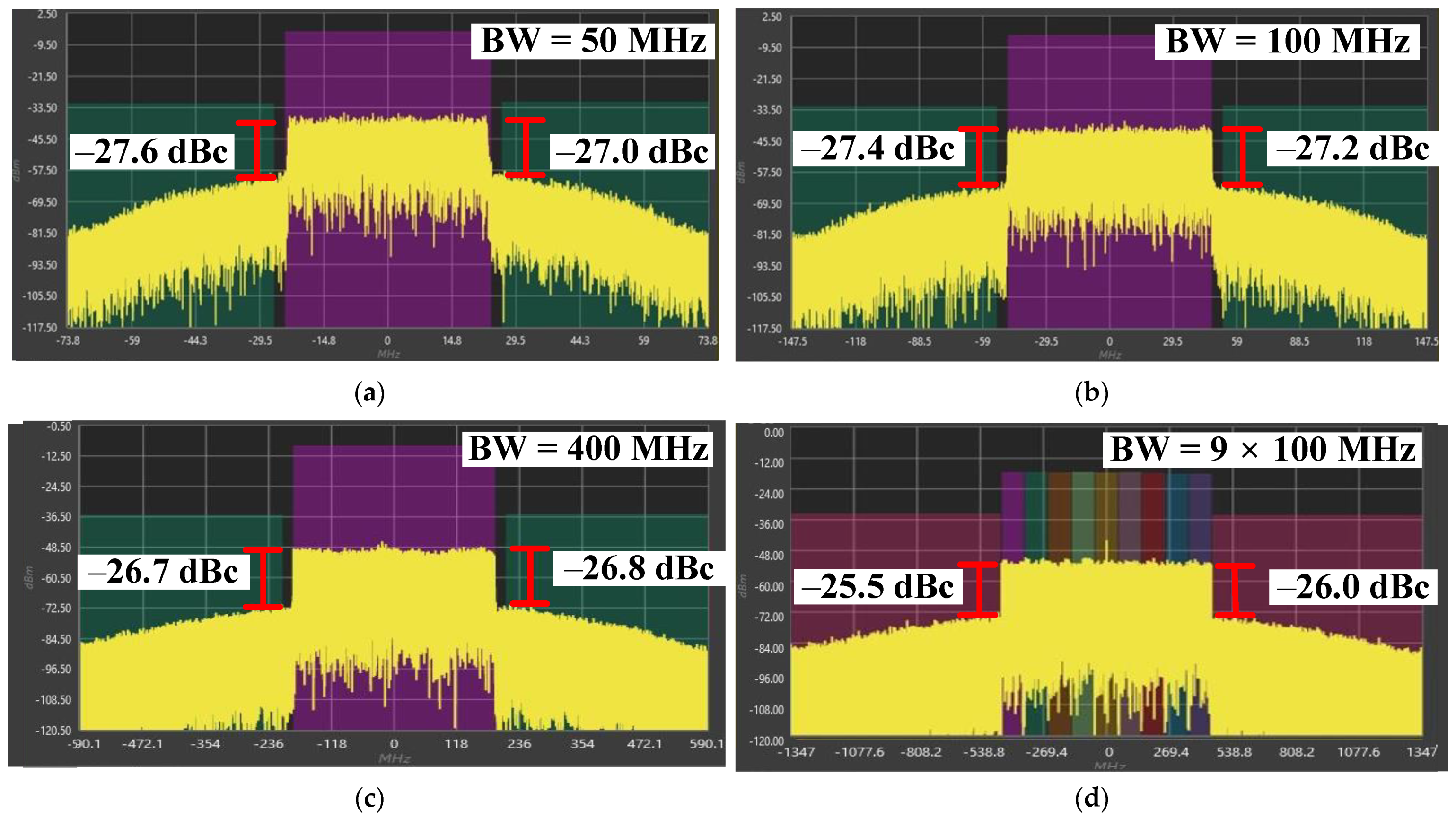


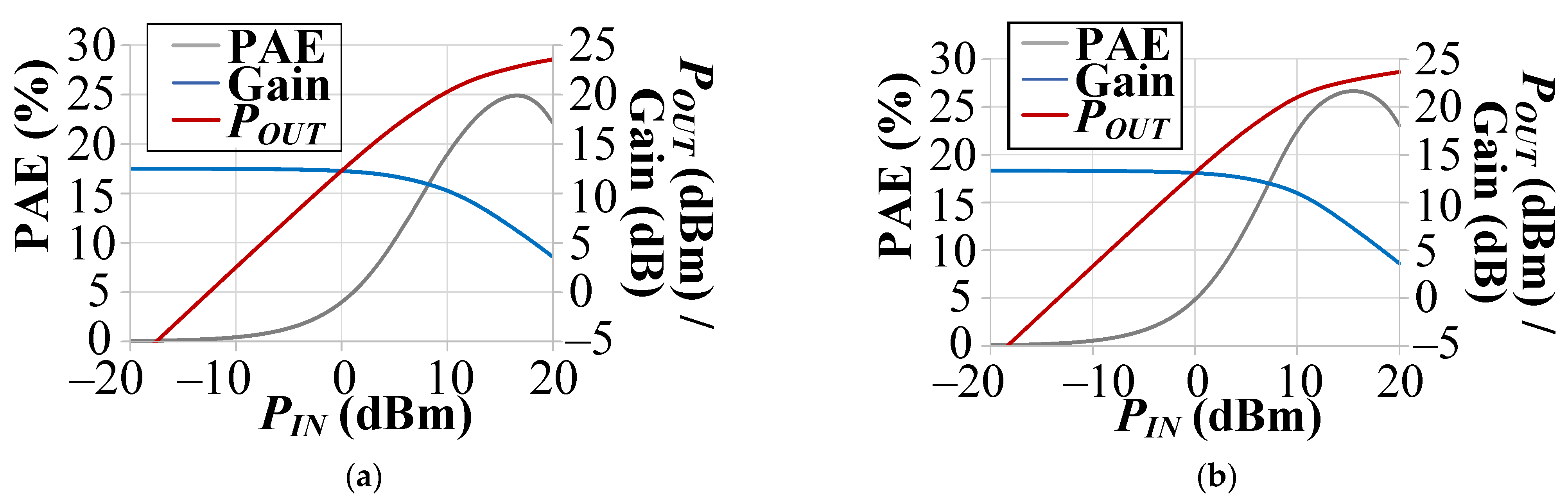

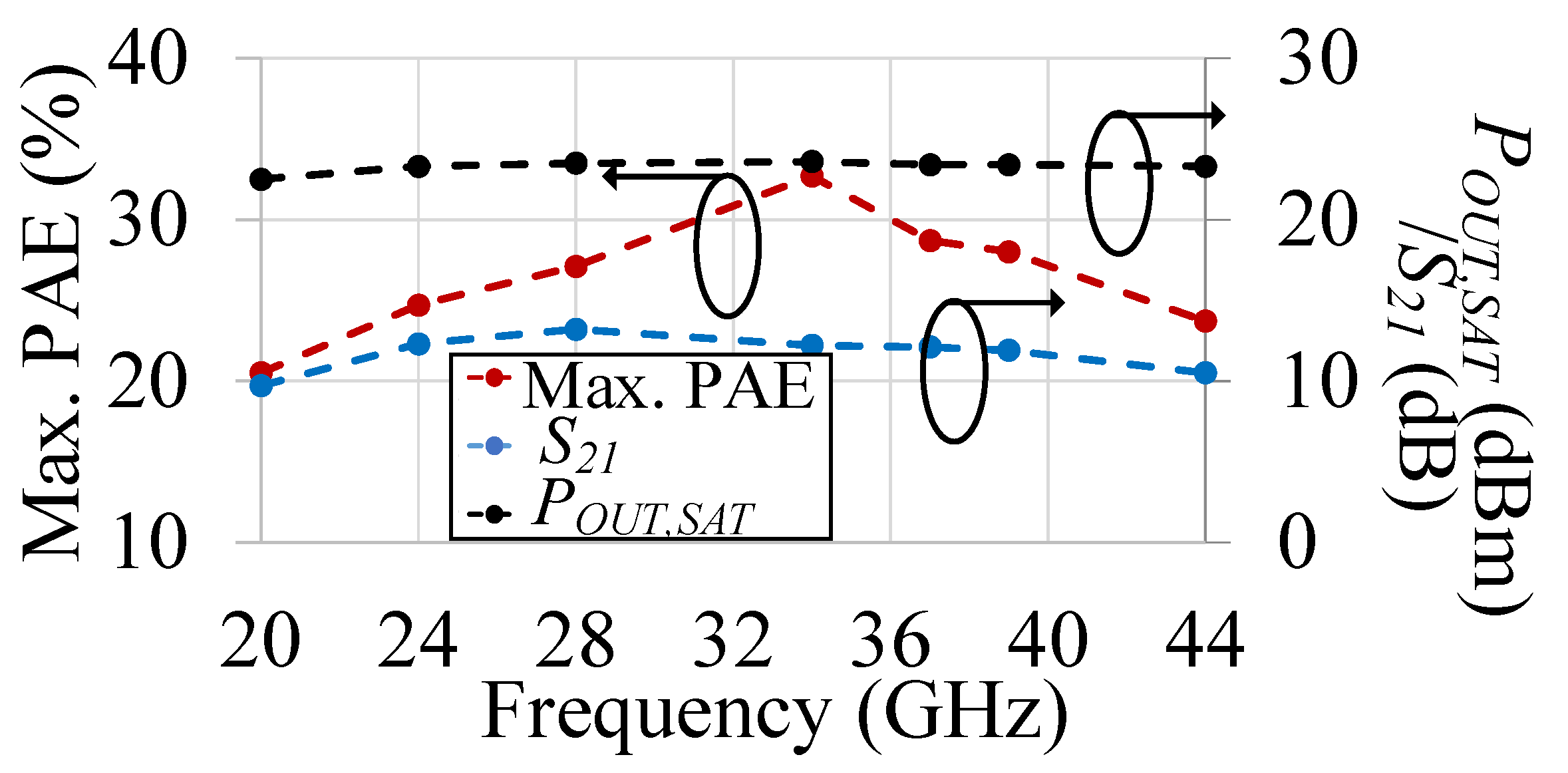
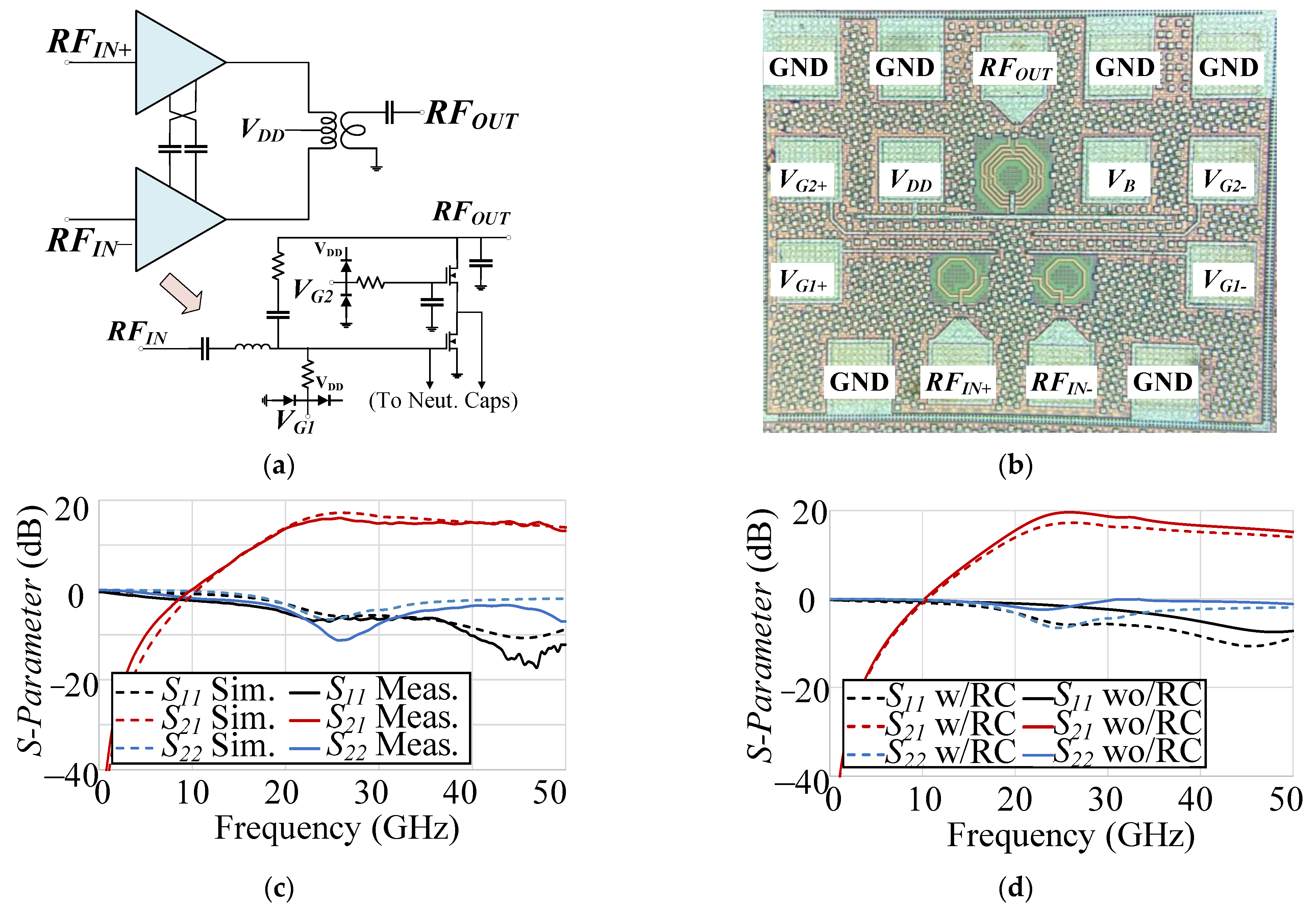

| Tech. | Design | VDD (V) | 3-dB BW (GHz) | Freq. (GHz) | POUT,sat (dBm) | P1dB (dBm) | Peak PAE (%) | Gain (dB) | Signal Type | ACLR (dBc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 nm CMOS FDSOI | Cascode with RC feedback; Differential | 1.8 | 19.1–46.5 (79.2%) | 24 | 14.6 | 11.5 | 26.1 | 15.7 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27@POUT = 7.1 dBm |
| PAE = 7.7% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −24.6@POUT = 7.3 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 8.1% | ||||||||||
| 28 | 14.0 | 9.2 | 19.9 | 14.5 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27.1@POUT = 7.1 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 5.3% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −23.7@POUT = 6.6 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 6.2% | ||||||||||
| 39 | 12.9 | 9.6 | 15.2 | 14.7 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −26.6@POUT = 6.4 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 5.8% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −24.2@POUT = 5.6 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 5.0% | ||||||||||
| 44 | 10.9 | 7.4 | 12.5 | 15.5 | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 40 nm GaN | 3rd-Order Input Matching; Single-ended | 4 | 18–40.3 (76.5%) | 24 | 18.6 | 13.6 | 34 | 7.8 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −25.4@POUT = 11.9 dBm |
| PAE = 15.4% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27.7@POUT = 9.7 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 8.1% | ||||||||||
| 28 | 18.6 | 13.2 | 42.1 | 9.2 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27.2@POUT = 11.2 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 13.1% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27@POUT = 11.3 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 13.9% | ||||||||||
| 39 | 17.2 | 13.4 | 26.0 | 8.7 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27@POUT = 11.1 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 11.1% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −25.6@POUT = 11.3 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 11.9% | ||||||||||
| 44 | 17.8 | 12.8 | 21.6 | 7.2 | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 6 | 18–38.7 (73.0%) | 24 | 20.1 | 14.9 | 28.9 | 9.6 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −26.5@POUT = 11.9 dBm | ||
| PAE = 10.2% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27@POUT = 11.9 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 10.2% | ||||||||||
| 28 | 20.3 | 14.4 | 34.6 | 11.9 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −26.3@POUT = 14.0 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 13.0% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −26.8@POUT = 14.2 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 14.0% | ||||||||||
| 39 | 18.1 | 12.3 | 22.8 | 9.3 | 400 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −28.7@POUT = 11.4 dBm | ||||
| PAE = 9.2% | ||||||||||
| 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −28@POUT = 11.8 dBm | |||||||||
| PAE = 9.7% | ||||||||||
| 44 | 19.3 | 13.9 | 19.1 | 8.1 | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 40 nm GaN * | 3rd-Order Input Matching; Differential | 6 | 20.1–44.3 (75.2%) | 24 | 23.5 | 17.5 | 24.9 | 12.5 | N/A | N/A |
| 28 | 23.6 | 18.3 | 26.6 | 13.3 | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 39 | 23.6 | 18.7 | 27.9 | 11.7 | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 44 | 23.3 | 17.4 | 23.3 | 10.4 | N/A | N/A |
| Ref. | Tech. | Design | Supply Voltage (V) | 3-dB BW (GHz) | Freq. (GHz) | POUT,sat (dBm) | P1dB (dBm) | Peak PAE (%) | Gain (dB) | Signal Type | ACLR (dBc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | 65-nm CMOS | Multi-port load-pulling | 1.1 | 26–42 (47.1%) | 28 | 19 | 19 | 21 | 15 | 1 GHz 64-QAM OFDM | POUT = 7.5 dBm |
| PAE = 5.1% | |||||||||||
| 37 | 19.6 | 16 | 21.9 | 16 | 2 GHz 64-QAM OFDM | −25@POUT = 9.8 dBm | |||||
| PAE = 10.2% | |||||||||||
| [15] | 0.2 µm GaN on SiC | 3-stage Harmonic Tuning | 28 | 29–34 (55.1%) | 33 | 39.5 | - | 36 | 25 | - | - |
| [16] | 0.1 µm GaN on SiC | One-order synthesized transformer network | 12 | 18–40 (75.9%) | 25 | 30 | 25 ** | 23.6 | 18 ** | - | - |
| [17] | 0.15 µm GaAs | Transformer-Coupled | 4 | 21.6–32.5 (40.3%) | 28 | 26.5 | 24.6 | 31 | 12.6 | 64QAM 6 Gb/s | −30@POUT = 21.6 dBm |
| PAE = 13.5% | |||||||||||
| 64QAM 9 Gb/s | −30@POUT = 19.9 dBm | ||||||||||
| PAE = 9.5% | |||||||||||
| [18] | 130-nm SiGe | 2-stage Doherty | 1.5 | 23.3–39.7 (52.1%) | 28 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 20.3 | 18.2 | 64-QAM 500 MSym/s | −28.4@POUT = 9.2 dBm |
| Coll. Eff. = 18.5% | |||||||||||
| 37 | 17.1 | 15.5 | 22.6 | 17.1 | −28.2@POUT = 9.5 dBm | ||||||
| Coll. Eff. = 19.2% | |||||||||||
| 39 | 17 | 15.4 | 21.4 | 16.6 | −29.8@POUT = 9.3 dBm | ||||||
| Coll. Eff. = 17.2% | |||||||||||
| [19] | 45-nm SOI CMOS | Continuous Hybrid Class F/F−1 | 2 | 23–40.5 (51.1%) | 28 | 18.9 | 16.9 | 43.2 | 18.7 | 64-QAM 500 MSym/s | −28@POUT = 10.3 dBm |
| PAE = 13.1% | |||||||||||
| 37 | 18.9 | 17 | 37 | 18 | −30.5@POUT = 11.7 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 11.9% | |||||||||||
| 39 | 18.9 | 17.4 | 36 | 15.6 | −28@POUT = 11 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 10.2% | |||||||||||
| [20] | 45-nm SOI CMOS | Compensated Distributed Balun | 2 | 25.8–43.4 (50.9%) | 24 | 20.0 | 19.6 | 38.9 | 20.1 * | 800 MHz 64-QAM 2-CC OFDM 5G NR | −25.2@POUT= 10.9dBm |
| PAE = 14.2% | |||||||||||
| 37 | 20.0 | 18.9 | 38.7 | 19.9 * | −27.9@POUT = 10.2 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 13.6% | |||||||||||
| 39 | 19.1 | 18.0 | 38.6 | 20.0 * | −26.1@POUT = 10.2 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 13.4% | |||||||||||
| This work | 22-nm CMOS FDSOI | RC feedback 1-stage diff. | 1.8 | 19.1–46.5 (83.5%) | 24 | 14.6 | 11.5 | 26.1 | 15.7 | 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −24.6@POUT = 7.3dBm |
| PAE = 8.1% | |||||||||||
| 28 | 14.0 | 9.2 | 19.9 | 14.5 | −23.7@POUT = 6.6 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 6.2% | |||||||||||
| 37 | 13.6 | 9.5 | 18.5 | 15.4 | −23.7@POUT = 6.0 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 5.4% | |||||||||||
| 39 | 12.9 | 9.6 | 15.2 | 14.7 | −24.2@POUT = 5.6 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 13.9% | |||||||||||
| This work | 40-nm GaN | 3rd-order input match 1-stage | 4 | 18–40.3 (76.5%) | 24 | 18.6 | 13.6 | 34 | 7.8 | 9 × 100 MHz 256-QAM 5G NR | −27.7@POUT = 9.7 dBm |
| PAE = 8.1% | |||||||||||
| 28 | 18.6 | 13.2 | 42.1 | 9.2 | −27@POUT = 11.3 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 13.9% | |||||||||||
| 39 | 17.2 | 13.4 | 26.0 | 8.7 | −27.9@POUT = 10.8 dBm | ||||||
| PAE = 12.6% | |||||||||||
| This work | 40-nm GaN * | 3rd-Order Input Matching; Differential | 6 | 20.1–44.3 (75.2%) | 24 | 23.5 | 17.5 | 24.9 | 12.5 | N/A | N/A |
| 28 | 23.6 | 18.3 | 26.6 | 13.3 | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 39 | 23.6 | 18.7 | 27.9 | 11.7 | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 44 | 23.3 | 17.4 | 23.3 | 10.4 | N/A | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayeda, J.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Lopez, J. Broadband Millimeter-Wave 5G Power Amplifier Design in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI and 40 nm GaN HEMT. Electronics 2022, 11, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11050683
Mayeda J, Lie DYC, Lopez J. Broadband Millimeter-Wave 5G Power Amplifier Design in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI and 40 nm GaN HEMT. Electronics. 2022; 11(5):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11050683
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayeda, Jill, Donald Y. C. Lie, and Jerry Lopez. 2022. "Broadband Millimeter-Wave 5G Power Amplifier Design in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI and 40 nm GaN HEMT" Electronics 11, no. 5: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11050683
APA StyleMayeda, J., Lie, D. Y. C., & Lopez, J. (2022). Broadband Millimeter-Wave 5G Power Amplifier Design in 22 nm CMOS FD-SOI and 40 nm GaN HEMT. Electronics, 11(5), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11050683








