Abstract
With the rising public awareness of environmental issues, consumers are increasingly demanding skin care products that create less environmental impact but still provide the same or even greater efficacy. In the skin care arena, microemulsions have been receiving increased attention as the promising delivery technology of skin care actives. Essential oils such as peppermint oil, lavender oil and eucalyptus oil are purported to have excellent antioxidant and antimicrobial properties that could be used as the eco-friendly alternatives for synthetic antioxidants and preservatives in the skin care formulations. This work therefore seeks to develop eco-friendly skin care formulations based on microemulsions of essential oil. Peppermint oil, lavender oil and eucalyptus oil were used as the oil phase to formulate naringin-loaded microemulsions, which demonstrated similar or better antioxidant and antimicrobial properties compared to the synthetic ones. When formulated into gel form, naringin-loaded microemulsion-gel formulations showed enhanced stability and release profile over their unformulated counterpart. Hence, microemulsions of essential oil developed in this work conferred a 4-fold benefits to the skin care formulations: (1) improved release (membrane permeation) of skin care active, (2) improved stability of skin care active, (3) as an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic antioxidant, and (4) a self-preserving system.
1. Introduction
In recent years, eco-friendly products are at the forefront in the skin care industry [1]. In line with the increased public awareness of environmental issues, many consumers are seeking eco-friendly skin care products in their purchases. Surveys reported that nowadays consumers are willing to pay more on eco-friendly products [2,3]. These heightened demands have driven various innovations along the skin care value chain, including formulation level to meet consumers’ expectations without compromising the quality and functionality of products. In order for the companies to stay ahead in the highly competitive skin care market, there is an urgent need for them to create eco-friendly products with greater product efficacy. Besides the traditional aesthetic effects, consumers nowadays are also expecting effective preventive and therapeutic effects with minimal side effects from the skin care products [4,5].
Delivery systems are used extensively in skin care products. They are incorporated in the skin care formulations to enable a controlled and targeted delivery of skin care actives, enhance penetration of skin care actives through the skin layers and provide protection to the skin care actives [5,6]. Microemulsions are among the advanced delivery technologies that have gained increasing attention from skin care formulators due to their good thermodynamic stability, superior solubilization power on lipophilic ingredients, appealing appearance (optically transparent) and ease of preparation [7,8]. These advantages have made microemulsions a promising alternative to overcome the major limitations of conventional emulsions. Microemulsions are clear isotropic mixtures of two immiscible liquids (such as oil and water) that are stabilized by surfactant or a mixture of surfactant with co-surfactant. Their droplet size is typically below 100 nm [8,9]. Whereas emulsions are coarse milky mixtures of two immiscible liquids that are stabilized by emulsifier, with droplet size in micron range [10]. Distinct from conventional emulsions that are typically opaque in nature and have a very limited shelf life due to their tendency to break down over a short time via various destabilizing processes such as sedimentation, coalescence, flocculation and the Ostwald ripening [11,12]), microemulsions are thermodynamically stable and readily provide a transparent and elegance appearance to enhance consumer appeal. Furthermore, microemulsions are easily scalable by low input of energy and without the requirement of any sophisticated equipment [8], making this technology platform simple and cost-effective from the manufacturing point of view.
Essential oils are volatile compounds extracted from different plant parts such as flowers, leaves, bark or roots through steam distillation or cold-pressing [13]. It has been estimated that nearly three thousand essential oils have been identified and about three hundreds of them are of commercial importance [14]. They are highly complex mixtures of chemical and bioactive constituents that not only provide pleasant aroma and flavour, but also offer various health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-mutagenic, anticancer, and antimicrobial [14,15,16]. These therapeutic properties have led to their long history of application in pharmaceutical, food and skin care. Essential oils have gained popularity as natural remedies in skin care products to treat various dermatological conditions and improve aesthetic benefits [17,18]. Moreover, they have also been explored as natural alternatives to artificial additives (e.g., preservatives and antioxidants) which are widely used in skin care formulations but found to be harmful to both consumers and environment [19,20].
Parabens are a family of esters derived from para-hydroxybenzoic acid that are used extensively as synthetic preservatives in skin care and cosmetic products such as shampoos, cleansers, moisturizers and makeup [21]. It has been reported that nearly 99% of leave-on skin care and cosmetic products contain some forms of paraben [22]. They are highly efficient in inhibiting microbial growth and hence are often used to prolong the shelf life of products and prevent the transfer of microorganism from the products onto the surface of the consumer’s skin (i.e., skin infections). Among the parabens, short chain parabens such as methylparaben and propylparaben are used most often in skin care and cosmetics products due to their lower toxicity. The shorter the alkyl chain, the lower the lipophilicity and toxicity of parabens [23]. Nevertheless, they remain one of the most controversial ingredients in skin care products because of their potential endocrine disruption and increased risk of breast cancer [24,25,26]. As parabens are structurally similar to estrogen, they may penetrate the skin and mimic the effects of physiological estrogen to promote the growth and proliferation of breast cancer cells [27]. Besides parabens, BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) is another synthetic ingredient that appears frequently in a wide range of skin care formulations (especially those are containing oils and fats) for stabilizing them against deterioration by free radicals [28]. It is used for its antioxidant properties in reducing the oxidation reaction and intrinsic odour of the formulations, thereby to improve the shelf life and quality of products. The use of BHT in skin care formulations has been criticised and associated with adverse effects such as DNA repair failure, oxidative stress, and pulmonary toxicities [29,30,31]. Although the safety risks of synthetic ingredients such as parabens and BHT remain controversial [32,33,34], the current consumers are increasingly mindful about the ingredients used in skin care products in order to safeguard their own health. Consumers’ perception of the safety of synthetic ingredients has triggered skin care manufacturers to search for safer alternatives to replace or reduce these synthetic ingredients in the skin care products. Multifunctional ingredients, which are added to the skin care formulations for a well-defined function while can concurrently contribute to other beneficial effects (e.g., antioxidant or antimicrobial activity), have emerged as the popular ingredients in formulating gentler and safer skin care products.
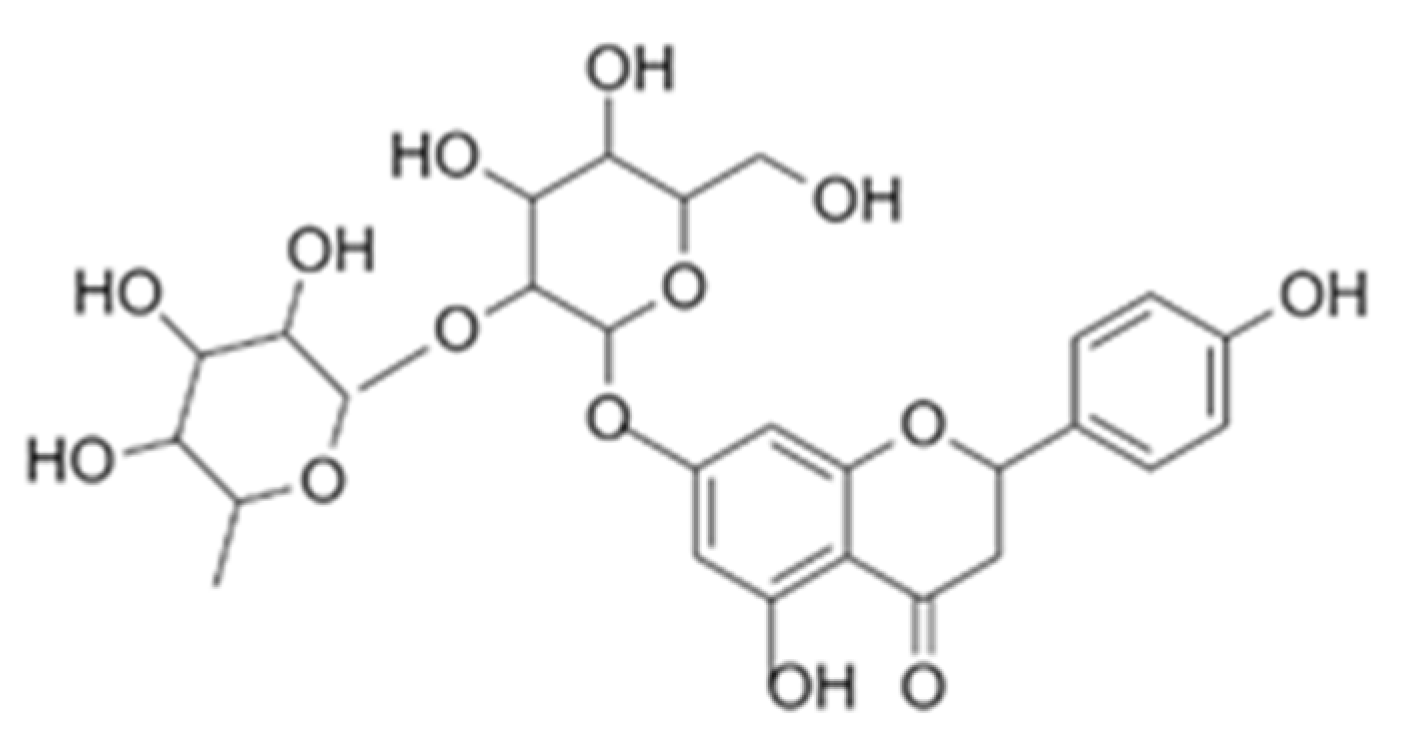
The aim of this work was to explore and investigate the feasibility of developing eco-friendly skin care formulations using microemulsions of essential oil. While microemulsions of essential oil act as the novel delivery systems in an attempt at improving the release (membrane permeation) and stability of the skin active, essential oils were innovatively used as the safer natural alternatives to synthetic antioxidants and preservatives in the skin care formulations. Naringin (chemical structure shown in Figure 1) was chosen as the skin care active in this work because of its excellent pharmacological actions such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antiviral characteristics that are highly favourable in skin care application [35,36,37]. However, formulating plant-based skin care active (e.g., naringin) could be challenging due to its stability issues [38]. Moreover, being a BSC class II drug, the skin care application of naringin is impeded by its poor water solubility [37]. Nagase’s newly developed Glucosyl Naringin (combination of glucose with naringin) presents one of the efforts to improve water solubility of naringin for skin care application [39]. In this work, microemulsions were exploited to enhance the release rate of poorly water-soluble naringin. To the best of our knowledge, no naringin-loaded microemulsion has been reported in the literature. The role of microemulsions of essential oil in the skin care formulations was envisioned to be 4-fold: (1) to improve the release (membrane permeation) of skin active, (2) to improve stability of skin active, (3) as a natural alternative to synthetic antioxidant, and (4) as a self-preserving system.
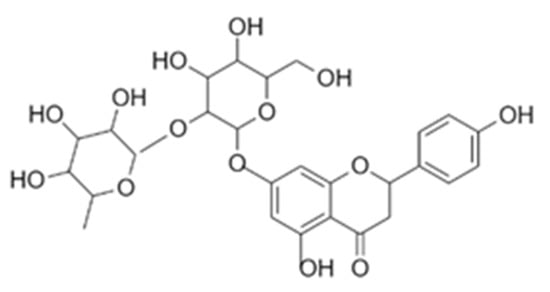
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of naringin.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Peppermint oil (PMO), lavender oil (LVO) and eucalyptus oil (EUO) were purchased from Euro Chem-Pharma Sdn. Bhd. (Johor Bahru, Malaysia). Naringin, Tween® 80 (polysorbate 80), diethylene glycol methyl ether (DGME), orthophosphoric acid, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPD), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), methylene blue and Sudan III were supplied from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). SimulgelTM NS (INCI name: hydroxyethyl acrylate/sodium acryloyldimethyl taurate copolymer and squalane and polysorbate 60) was a gift sample from Seppic (Courbevoie, France). HPLC grade acetonitrile (ACN) and absolute ethanol (EtOH) were obtained by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Ultra-pure water (Milli-Q® Gradient A10®, Millipore, Molsheim, France) was used in the experiments.
2.2. Construction of Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed using the water titration method to identify the microemulsion region of each oil-surfactant/co-surfactant-water system in this work. Firstly, the surfactant phase (surfactant/co-surfactant mixture, Smix) was prepared by mixing surfactant (Tween® 80) and co-surfactant (EtOH or DGME) at various weight ratio such as 1:1, 1:2 and 2:1. The accurately weighed oil phase (PMO, LVO or EUO) was then added into each surfactant phase at weight ratios of 1:9, 2:8, 3:7, 4:6, 5:5, 6:4, 7:3, 8:2, 9:1. Each mixture of oil and surfactant phase was homogenously mixed with a vortex mixer (Vortexer, Heathrow Scientific, Vernon Hills, IL, USA), followed by titration with multiple 10 µL aliquot of ultrapure water (water phase) until turbidity was visually observed. The amount of each component (oil, surfactant/co-surfactant, and water) to form clear microemulsions was calculated as weight percent and plotted on a triangular graph as the pseudo-ternary phase diagram.
2.3. Preparation of Naringin-Loaded Microemulsions and Microemulsion-Gel Formulations
Six microemulsions (MEs) at different component ratios were selected from the microemulsion regions in the pseudo-ternary phase diagrams and the naringin-loaded microemulsions (NMEs) were prepared (Table 1). To prepare naringin-loaded microemulsions, naringin was first dissolved in the oil phase. Next, the oil phase containing naringin was mixed with mixture of surfactant/co-surfactant until homogenous. The appropriate amount of ultra-pure water was then added dropwise into the mixture of oil-naringin-surfactant/co-surfactant under constant magnetic stirring.

Table 1.
Composition of naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations.
For the preparation of microemulsion-gel (MEG) formulations, SimulgelTM NS was used as the thickener as it is an environmentally friendly produced thickener with good stability and texturizing properties [40]. Between 2–3% (w/w) of the ultra-pure water in the microemulsions was replaced by SimulgelTM NS (Table 1). For the preparation of unformulated naringin plain gel (as reference gel), naringin was dissolved in ethanolic solution (ethanol: water, 10:90 v/v). 2% (w/w) of the ultra-pure water in naringin ethanolic solution was substituted with SimulgelTM NS. SimulgelTM NS was added slowly to the microemulsions (for preparing microemulsion-gel formulations) or ethanolic solution (for preparing naringin plain gel) while stirring with an overhead stirrer (Hei-TORQUE Core, Heidolph Instruments GmbH & CO. KG, Schwabach, Germany) at 150 rpm for 20 min. The final concentration of naringin in both microemulsion, microemulsion-gel formulations and plain gel was set to be 1% (w/w).
2.4. Characterization of Naringin-Loaded Microemulsions and Microemulsion-Gel Formulations
2.4.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
The particle size (z-average diameter) and polydispersity index (PdI) of the microemulsions were measured by dynamic light scattering technique (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK) at 25 °C.
2.4.2. pH Measurements
The pH of naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations were measured using a benchtop pH meter (SevenExcellence S470, Mettler-Toledo AG, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland) at 25 °C.
2.4.3. Viscosity Measurement
The viscosity of naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations were determined using a rotational viscometer (model DV2T, Brookfield, Stoughton, MA, USA) with spindle RV-03 at speed 150 rpm and spindle RV-05 at speed 20 rpm, respectively, at 25 °C.
2.4.4. Determination of Types of Microemulsion (via Dye Solubility and Conductivity Test)
The type of microemulsion (i.e., O/W or W/O microemulsion) was qualitatively evaluated via dye solubility test using methylene blue (water-soluble dye) and Sudan III (oil-soluble dye). An equal amount of each dye sample was separately added to microemulsions and the diffusion rate of each dye in the microemulsions was observed visually. The diffusion rate of methylene blue is observed faster than Sudan III in O/W microemulsions and slower than Sudan III in W/O microemulsions [41].
Electrical conductivity of microemulsions was measured using a benchtop conductivity meter (SevenExcellence S470, Mettler-Toledo AG, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland) fitted with an InLab® 741 conductivity probe with a cell constant of 0.105 cm−1 (Mettler-Toledo AG, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland) at 25 °C.
2.5. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Assay of Naringin
The assay of naringin was conducted by reversed phase HPLC (1100 series, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 column (4.6 mm × 150 mm, 3.5 μm) (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). A modified HPLC method [42] with a mobile phase consisting of a mixture of ACN (70:30 v/v) and 0.1% phosphoric acid was used. The flow rate, retention time and detection wavelength of quercetin were 1 mL/min, 2.5 min and 289 nm, respectively.
2.6. Stability
Naringin-loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-gel formulations were stored in 8-mL stoppered glass vials with PTFE/white silicone septa black solid cap (Newton 101 Pte. Ltd., Singapore) and equilibrated for one month at refrigerated conditions (4 °C/65% RH), ambient conditions (25 °C/60% RH) and accelerated conditions (40 °C/75% RH) (Binder KBF 115 RH Chamber, BINDER GmbH, Tuttlingen, Germany). After the storage period, the chemical stabilities of naringin in the microemulsion and microemulsion-gel formulations were analysed by HPLC and physical stabilities were assessed by visual inspection of samples for any signs of phase separation, precipitation or colour change. The stabilities of microemulsions were also accessed by measuring the particle size (z-average diameter) and polydispersity index (PdI) of microemulsion as described in Section 2.4.1.
2.7. In Vitro Release (Membrane Permeation) of Naringin
In vitro release (membrane permeation) of naringin from the microemulsion-gel formulations were conducted on static vertical Franz diffusion cells equipped with 20-mL receptor compartments, clamps, and stirrer bars on a six-cell drive system (V6B, PermeGear Inc., Hellertown, PA, USA). Each receptor compartment was filled with a receptor medium consisting of 80% (v/v) phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and 20% (v/v) methanol to maintain sink condition. The receptor medium was maintained at 32 ± 0.5 °C by a circulating water-bath (HAAKE S5P and SC100, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). When the system was equilibrated and stable, 200 ± 2 mg of microemulsion-gel formulation was evenly spread on the synthetic polyethersulfone membrane (Supor® 450, PALL Life Sciences, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) and sealed with a clamp over the membrane. 0.7 mL sample aliquots were withdrawn from the receptor compartment through the sampling port at regular time intervals (0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h) and analysed for their concentrations using the previously described HPLC method.
2.8. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
In vitro antioxidant activity of active-free microemulsions of essential oil (MEs) was determined using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay [43] with some modifications. Briefly, 1 mL of active-free microemulsion of essential oil was mixed with 1 mL of 0.15 mM DPPH solution in ethanol. The mixture was kept in a dark room for 20 min at room temperature before the absorbance of the mixture was measured using a UV–VIS spectrophotometer (Cary 60, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at 517 nm. The antioxidant activity (represented by percentage of inhibition) of sample was calculated as follows:
where Ao was the absorbance of control (mixture of equal volume of DPPH solution and EtOH) and As was the absorbance of sample (mixture of equal volume of DPPH solution and test sample). BHT was used as the standard reference.
% inhibition = [(Ao − As)/Ao] × 100%
2.9. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
In vitro antimicrobial activity of active-free microemulsions of essential oil (MEs) were evaluated using the disc diffusion method [44] against E. coli and S. epidermidis. The diluted bacterial inoculums (~106 CFU mL−1) were spread on trypticase soy agar (TSA) using sterile cotton swabs. Then, the sterile discs (6 mm diameter, Whatman No. 1, Whatman Ltd., Maidstobe, UK) were placed on surface of inoculated agar plates and impregnated with 20 µL of active-free microemulsions of essential oil and control. All the active-free microemulsions of essential oil and control were sterilized using 0.22 µm PTFE membrane (Sterlitech Corporation, Auburn, WA, USA) filtration method. Moreover, 0.25% (w/v) aqueous solution of methyl paraben was used as positive control. The agar plates were incubated in an incubator (LE-80D, Yihder Co., Ltd., Xinbei, Taiwan) at 37 °C for 24 h and the diameters zone of inhibitions were measured.
3. Results
3.1. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
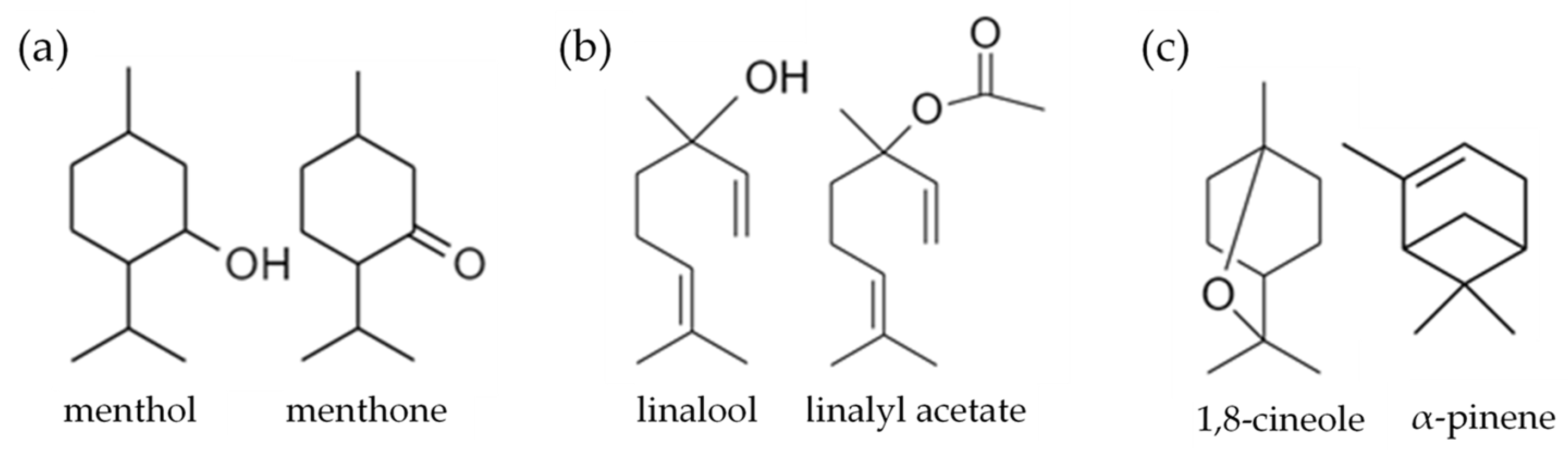
Peppermint oil (PMO), lavender oil (LVO) and eucalyptus oil (EUO) were selected as the essential oils for formulation of microemulsions as they have been reported to exhibit potent antioxidant and antimicrobial properties [45,46,47]. Although their main constituents (i.e., peppermint oil: menthol and menthone [48], lavender oil: linalool and linalyl acetate [49] and eucalyptus oil: 1,8-cineole and α-pinene [50] (chemical structures shown in Figure 2) are often associated with allergenic potential [51,52], their concentrations have been diluted with surfactant and water phase in microemulsion formulation. Hence, they are regarded as safer alternatives than direct application on the skin. Tween® 80 (polysorbate 80) was used as the surfactant for formulation of microemulsions due to its good emulsification, skin biocompatibility and low toxicity properties [53]. Ethanol (EtOH) and diethylene glycol monoethyl ether (DGME) are among the commonly used ingredients in various cosmetic and personal care products [54,55]. Both are well-recognized skin penetration enhancers for topical delivery [54,55,56] that can act as co-surfactant to promote the solubilization of immiscible liquid phases such as oil and water for formulation of microemulsions.
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of main constituents of (a) peppermint oil; (b) lavender oil and (c) eucalyptus oil.
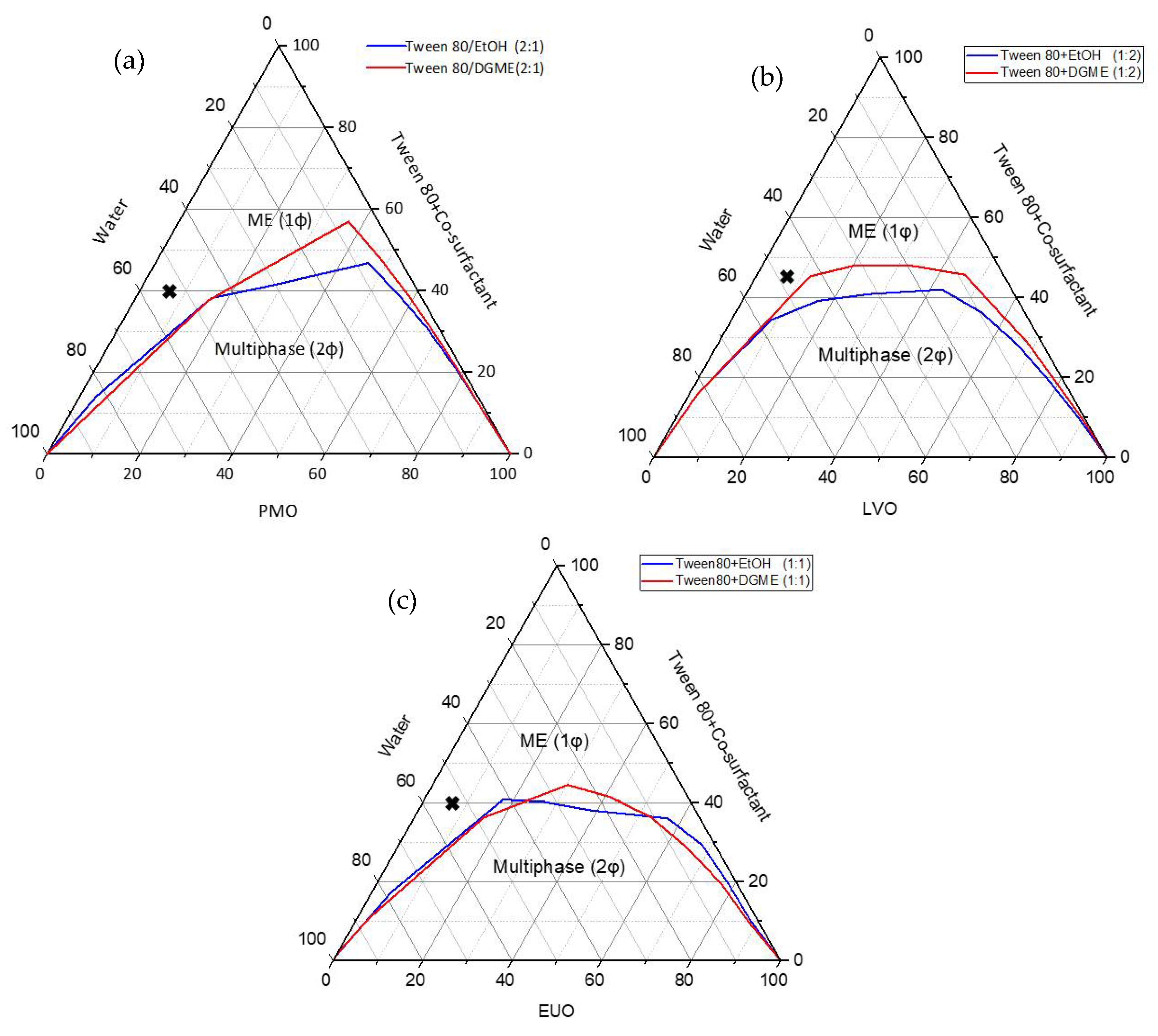
The pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed based on the selected oil (i.e., PMO, LVO or EUO) and a combination of surfactant Tween® 80 with co-surfactant EtOH or DGME (Smix) at designated weight ratios (i.e., Smix(PMO) 2:1, Smix(LVO) 1:2 and Smix(EUO) 1:1). Smix ratio of 2:1 was chosen for PMO as the largest and second largest microemulsion region (1φ) were obtained when EtOH and DGME were used as the co-surfactant, respectively, (1φ(EtOH) = 41.2% vs. 1φ(DGME) = 37.1%) (Table 2). For LVO and EUO, Smix ratios were fixed at 1:2 and 1:1, respectively, due to the formation of the largest microemulsion region whether EtOH (1φ(LVO) = 42.6% and 1φ(EUO) = 45.3%) or DGME (1φ(LVO) = 35.6% and 1φ(EUO) = 44.9%) was used as the co-surfactant (Table 2).

Table 2.
Percentages of microemulsion area in total phase diagram for each combination of co-surfactant and Smix weight ratios. Smix = weight ratio of surfactant to co-surfactant.
For microemulsions with PMO as the oil phase and Smix = 2:1, we observed larger microemulsion regions when EtOH was used as the co-surfactant as compared to when DGME was used as the co-surfactant (1φ(EtOH) = 41.2% vs. 1φ(DGME) = 37.1%) (Figure 3a). Similar observation was obtained when LVO was used as the oil phase in the microemulsion and Smix = 1:2 (1φ(EtOH) = 42.6% vs. 1φ(DGME) = 35.6%) (Figure 3b). This indicates that the type of co-surfactant had a marked effect on the phase behaviour of microemulsion and EtOH could be a more efficient co-surfactant than DGME in helping Tween® 80 to reduce the interfacial tension between the oil (i.e., PMO and LVO) and water in the microemulsion at the designated Smix weight ratios (i.e., Smix(PMO) = 2:1 and Smix(LVO) = 1:2). This effect was less significant when EUO was used as the oil phase and Smix weight ratio was fixed as 1:1 (1φ(EtOH) = 45.3% vs. 1φ(DGME) = 44.9%) (Figure 3c). Based on the microemulsion regions in the pseudo-ternary phase diagrams, six microemulsion formulations were selected from the water-rich region for the development of naringin-loaded O/W microemulsions (Table 1).
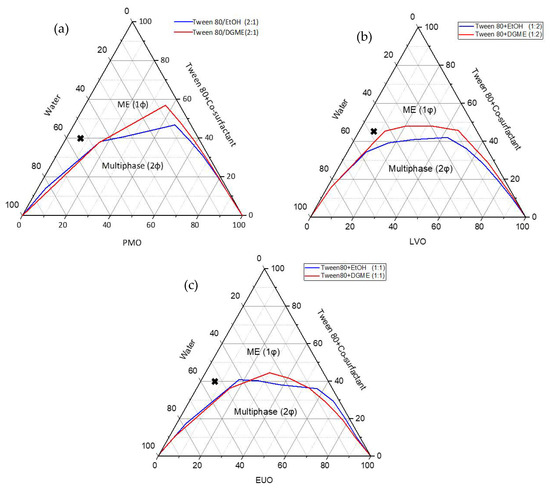
Figure 3.
The pseudo-ternary phase diagrams of (a) PMO/(Tween® 80 + co-surfactant (2:1))/water; (b) LVO/(Tween® 80 + co-surfactant (1:2))/water; (c) EUO/(Tween® 80 + co-surfactant (1:1))/water systems at room temperature. ME (1φ) represents single-phase ME region. The cross-marks shown in the pseudo-ternary phase diagrams represent the composition of selected microemulsions for preparing naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations.
3.2. Characterization of Naringin-Loaded Microemulsions and Microemulsion-Gel Formulations
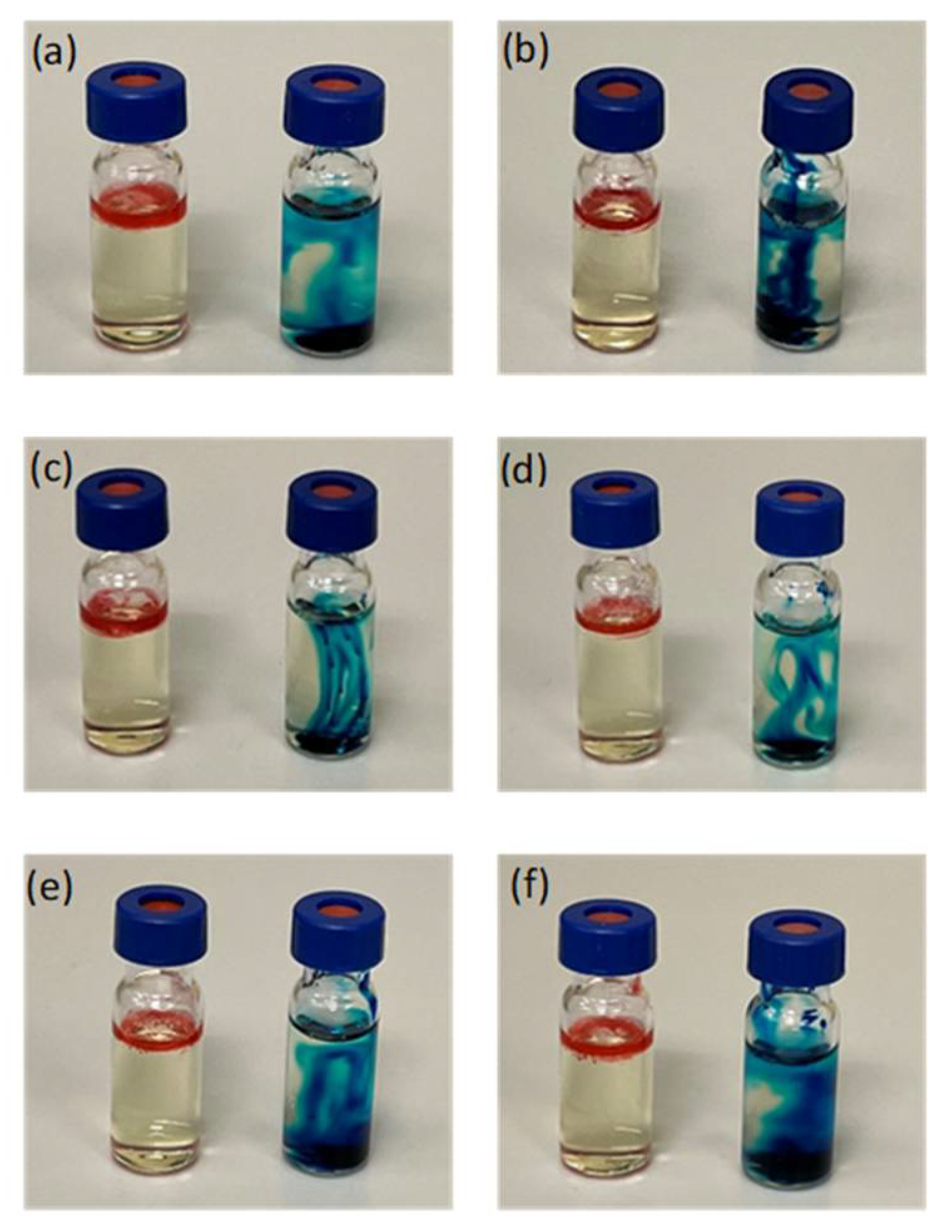
The physicochemical characteristics of naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. All of the naringin-loaded microemulsions were found to be clear and transparent with their conductivity values ranging from 58.27 ± 0.21 to 87.90 ± 0.40 µS/cm, similar to the published data for same type of microemulsions (i.e., O/W microemulsions) [57,58]. The O/W type of microemulsions was further evidenced by the dye solubility test. The faster spreads of water-soluble methylene blue throughout the microemulsion systems were observed as compared to oil-soluble Sudan III, thereby confirming the formation of O/W microemulsions (Figure 4).

Table 3.
Characterization of selected naringin-loaded microemsulsions. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).

Table 4.
Characterization of naringin-loaded microemulsion-gel formulations and naringin plain gel. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).
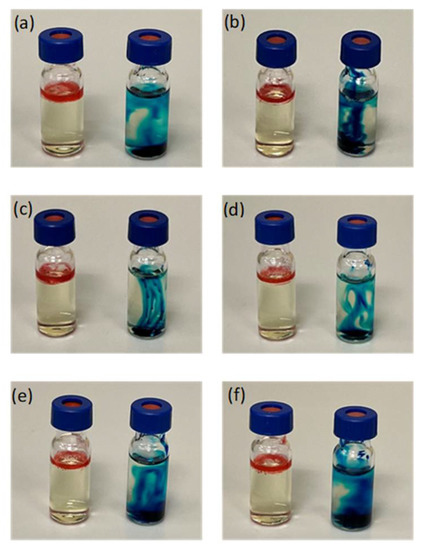
Figure 4.
Diffusion behaviour of Sudan III (left) and methylene blue (right) in (a) NME-1; (b) NME-2; (c) NME-3; (d) NME-4; (e) NME-5 and (f) NME-6 after 5 minutes.
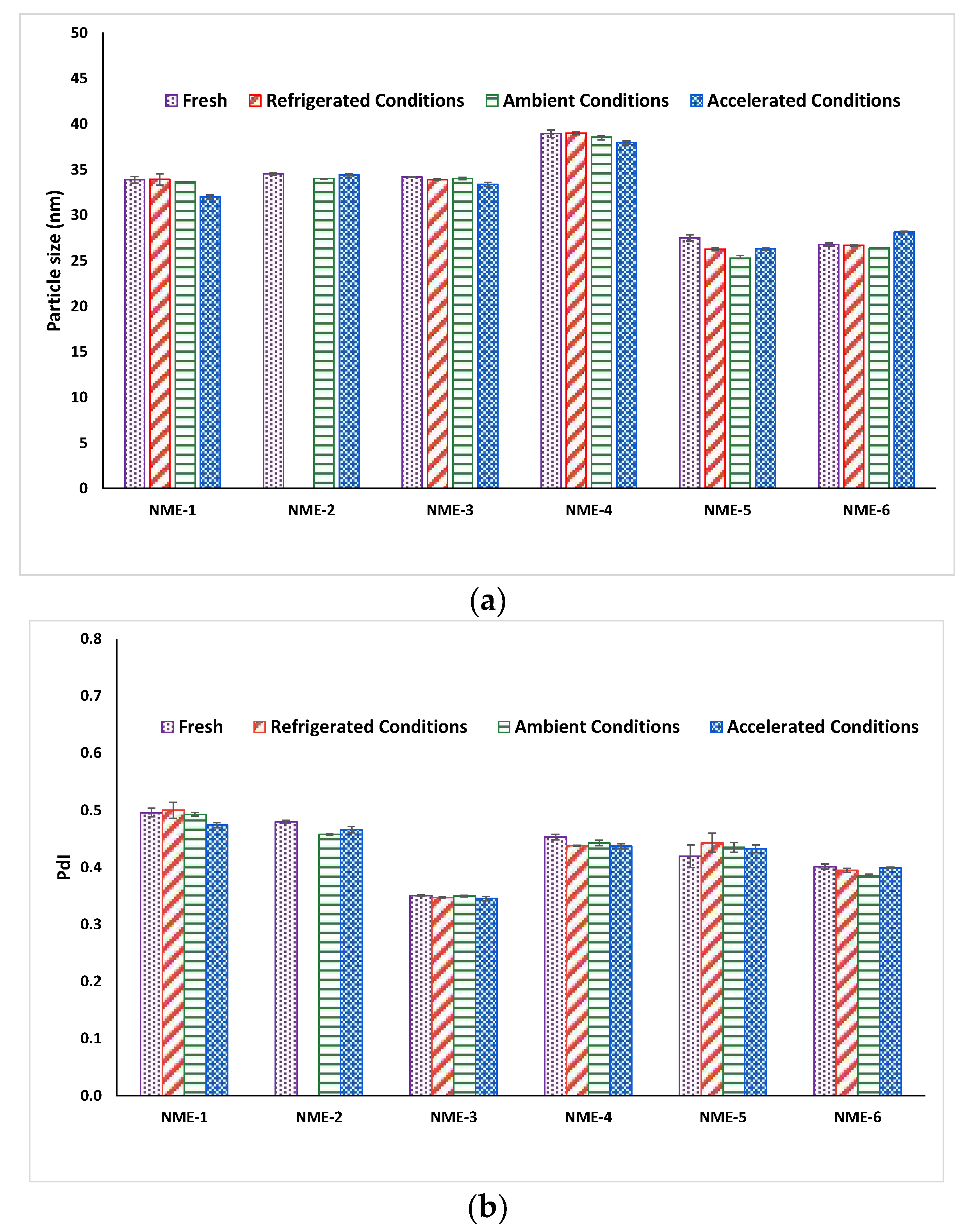
The particle size of naringin-loaded microemulsions varied between 26.75 ± 0.20 and 38.92 ± 0.40 µm (Table 3) with very low polydispersity index values (i.e., ≤0.5 ± 0.01), signalling the particle sizes of microemulsions were homogenous and had a narrow size distribution. The pH values of the naringin-loaded microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations were found to be mildly acidic in the range of pH 4.25 ± 0.02 to 5.62 ± 0.02 and pH 4.04 ± 0.01 to 5.38 ± 0.05, respectively (Table 3 and Table 4), which are highly compatible to human natural skin surface pH (i.e., pH 4.7) [59]. Formulating skin care systems at a slightly low pH (e.g., pH 4–6) is not only beneficial in fortifying the skin barrier and supporting the natural skin flora, but also helps to reduce the use of preservatives by preventing the colonization of pathogenic flora and promoting the persistence of normal microbial flora [60,61]. There was a small decrease in pH when the naringin-loaded microemulsions were formulated into their gel forms, but the decrease was not substantial.
The viscosity values of all of the naringin-loaded microemulsions were low (i.e., 36.43 ± 0.55 to 95.43 ± 0.70 cP), which were the typical observation for lowly viscous microemulsions. Higher viscosity values were observed for NME-1 and NME-2 (i.e., 90.30 ± 0.72 and 95.43 ± 0.70 cP) as compared to other naringin-loaded microemulsions. The amount of surfactant in the microemulsion likely affected the physical properties particularly the apparent viscosity of the formulation. Higher level of Tween® 80 surfactant (i.e., 23.3% w/w) in both NME-1 and NME-2 could have contributed to their increased viscosity values. It has been postulated that hydration and hydrogen bonding connection of the hydrophilic moieties of Tween® 80 in aqueous environment (i.e., continuous water phase) could promote the interaction between microemulsion droplets, thereby increasing the viscosity of microemulsions [62]. As NME-3 was found to have much lower viscosity value (i.e., 36.43 ± 0.55 cP) than other naringin-loaded microemulsions (ranging from 75.27 ± 0.64 to 95.43 ± 0.70 cP), the amount of thickener SimulgelTM NS was hence adjusted from 2% to 3% (w/w) when formulating NMEG-3 to ensure the viscosity values of all of the naringin-loaded microemulsion-gel formulations were within comparable range that is suitable for topical application (Table 4). An ideal gel preparation should be sufficiently mobile in order to facilitate delivery of the dosage form to the application site yet adequately viscous to remain at the application site at an effective concentration [63,64]. The gel preparations in this work exhibited adequate viscosity ranging from 3355.00 ± 13.22 to 4519.67 ± 40.10 cP (i.e., within the typical viscosity range of ~1000 cP to ~100,000 cP when the gelling agents are used in a concentration of less than 10% [65].
The drug contents of naringin in all of the microemulsions, microemulsion-gel formulations and plain gel were found to be very close to the theoretical naringin loading (i.e., 1% w/w) (Table 3), demonstrating the excellent drug entrapment in all microemulsions, microemulsion-gel formulations and plain gel.
3.3. Stability
Many skin care actives are sensitive to temperature variations, humidity, air and light [66]. They can be easily degraded by these environmental factors to become chemically unstable compounds, affecting the efficacy and safety of skin care products. The common practice to evaluate the functions of these actives is to observe any changes in physical properties (e.g., colour change, separation and precipitation) of the formulations, followed by the measurement of chemical properties (e.g., quantification of active content) upon various storage conditions and duration [67]. In this work, the stability of naringin-loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-gel formulations were monitored at refrigerated conditions (4 °C/65% RH), ambient conditions (25 °C/60% RH) and accelerated conditions (40 °C/75% RH) for one month.
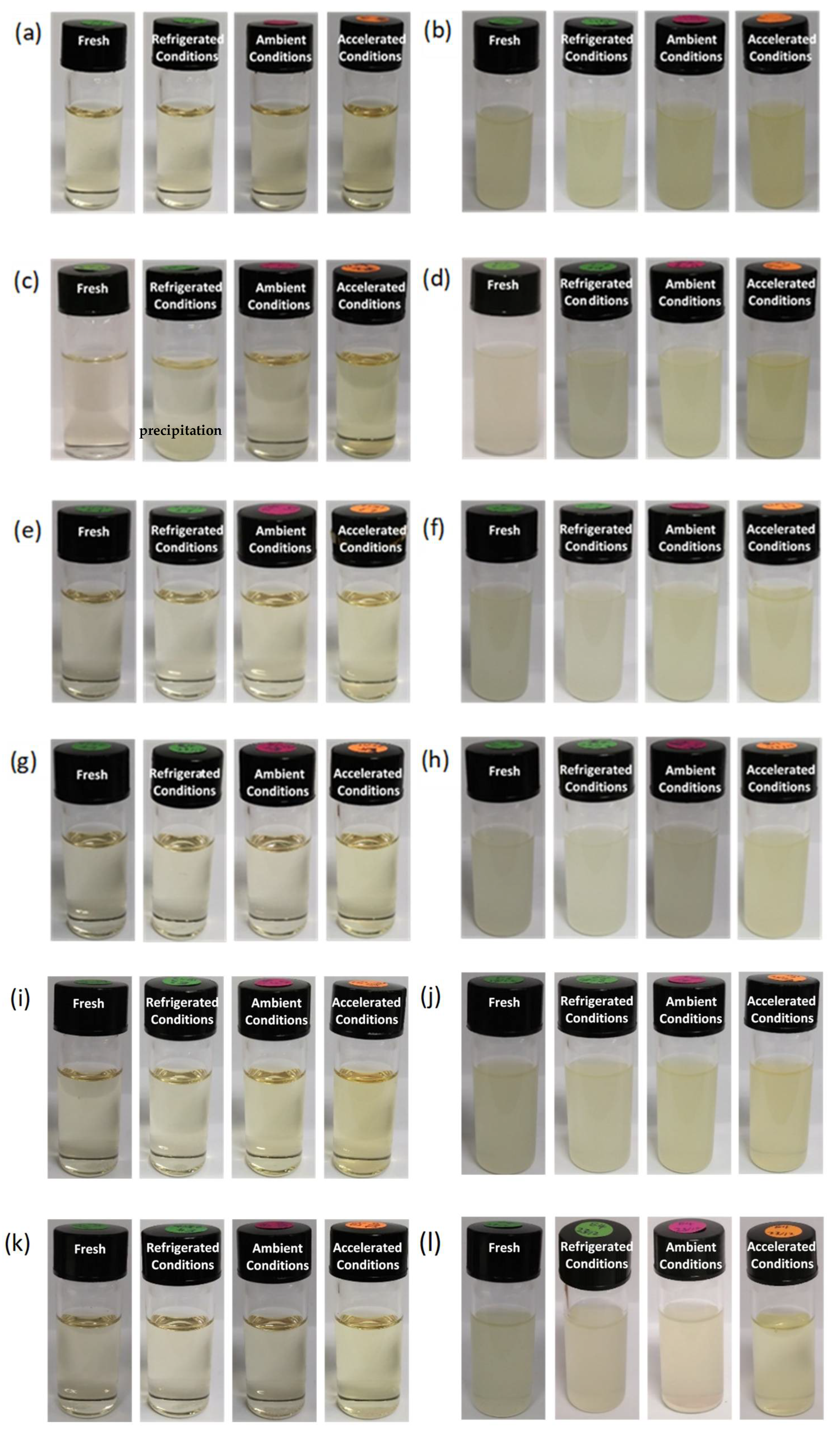
The particle size and particle size distribution of most microemulsions remained constant before and after one month storage at various conditions (Figure 5), reflecting the high inherent thermodynamic stability of microemulsions [68]. Furthermore, apart from NME-2 stored at refrigerated conditions, all of the microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations demonstrated good physical stability for up to one month at various storage conditions as there was no significant sign of colour change, phase separation or precipitation were observed (Figure 6). NME-2 turned cloudy after 1 month storage at refrigerated conditions (4 °C/65% RH) due to precipitation of naringin from the microemulsion because of decreased solubility at low temperature. Unformulated naringin plain gel (microemulsion-free gel) was found to be highly unstable and naringin precipitation was observed after only one day storage at various storage conditions.
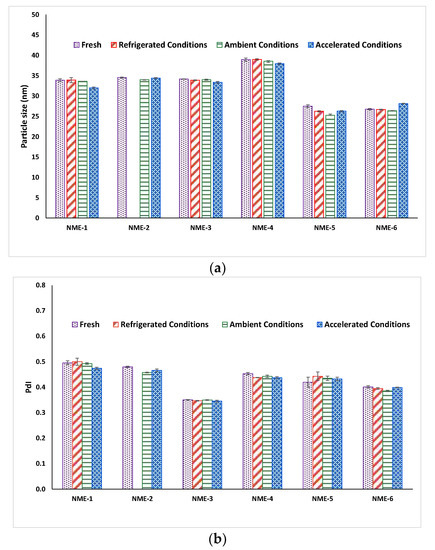
Figure 5.
(a) Particle size and (b) PdI of freshly prepared naringin-loaded microemulsions and after one month storage at refrigerated conditions, ambient conditions, and accelerated conditions, respectively. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Particle size and PdI of NME-2 at refrigerated conditions after one month were not measured because of naringin precipitation.

Figure 6.
Physical appearance of (a) NME-1; (b) NMEG-1; (c) NME-2; (d) NMEG-2; (e) NME-3; (f) NMEG-3; (g) NME-4; (h) NMEG-4; (i) NME-5; (j) NMEG-5; (k) NME-6 and (l) NMEG-6; (Left to Right) Fresh, refrigerated conditions (4 °C/65% RH), ambient conditions (25 °C/60% RH) and accelerated conditions (40 °C/75%).
The chemical stability of naringin was assessed based on the percentage of intact naringin remaining in the microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations. Table 5 shows that naringin was well retained (almost 100%) in the microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations (naringin content in refrigerated NME-2 was not analysed due to precipitation), indicating that naringin in the microemulsions and microemulsion-gel formulations was chemically stable for at least one month at various storage conditions.

Table 5.
Chemical stability data of naringin-loaded microemulsion and microemulsion gel formulations after 1 month storage at different storage conditions. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).
3.4. In Vitro Release (Membrane Permeation) Studies
Many skin care actives have low water solubilities. The ability of these poorly water-soluble actives to release from the formulations is an important prerequisite for successful penetration of skin care actives through the skin. This is to avoid active release from becoming the rate-limiting step for penetration of actives into skin [69]. In this context, in vitro release studies through polymeric synthetic membranes have been widely used to assess the active release profiles of semi-solid topical skin care formulations [70].
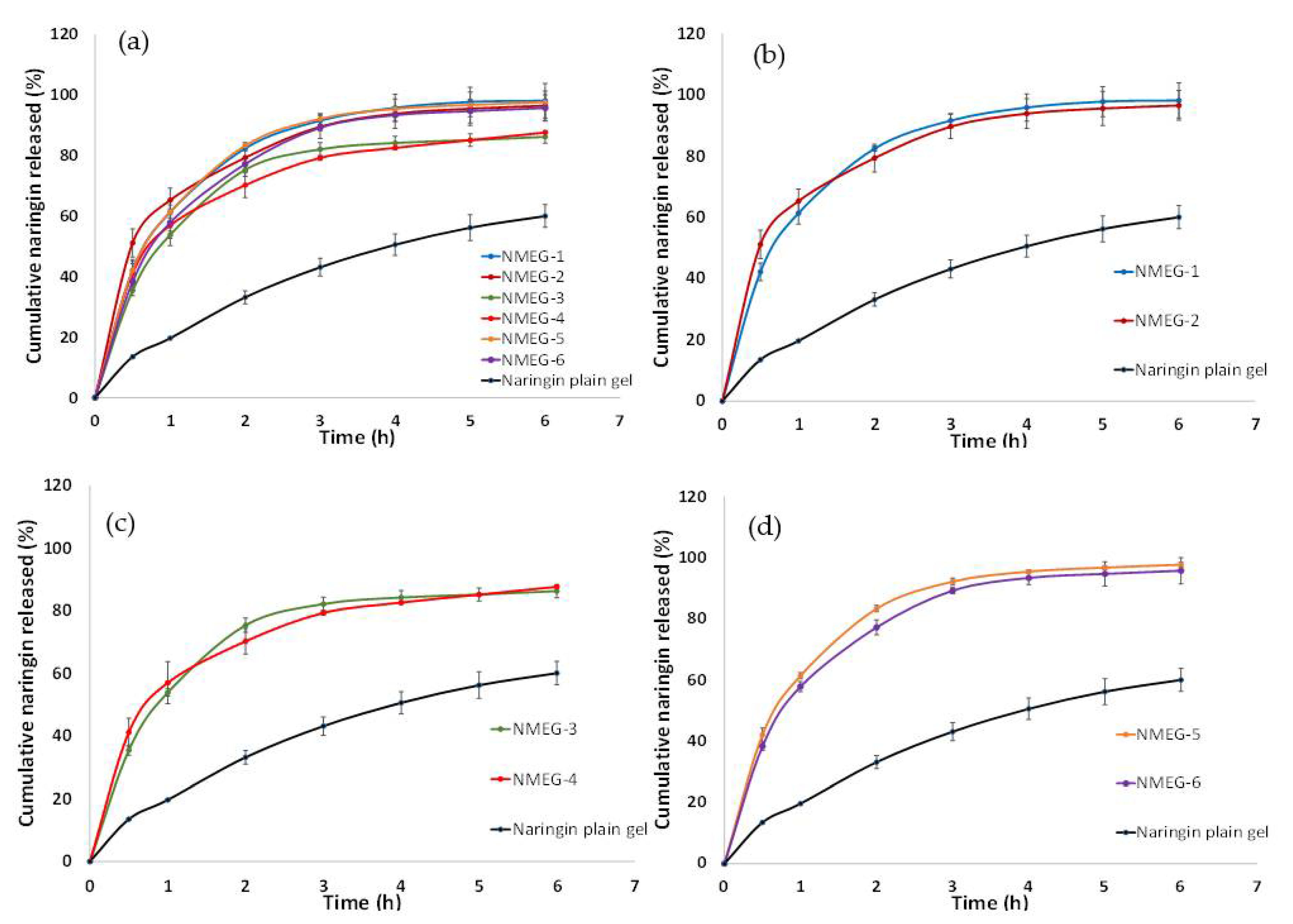
Figure 7 shows the release profiles of naringin from all of the 6 microemulsion-gel formulations (NMEG-1, NMEG-2, NMEG-3, NMEG-4, NMEG-5 and NMEG-6) and unformulated naringin plain gel (microemulsion-free gel), with all of them containing the same loading of naringin (i.e., 1% w/w). Overall, the cumulative release of naringin from microemulsion-gel formulations was more (i.e., ranging from 86.24 ± 2.12% to 98.15 ± 5.71%) than that observed from the unformulated naringin plain gel (i.e., 60.04 ± 2.12%) after 6 h (Figure 7a). Furthermore, almost 100% release of naringin was reached by 6 h for most of the microemulsion-gel formulations (i.e., NMEG-1, NMEG-2, NMEG-5 and NMEG-6).
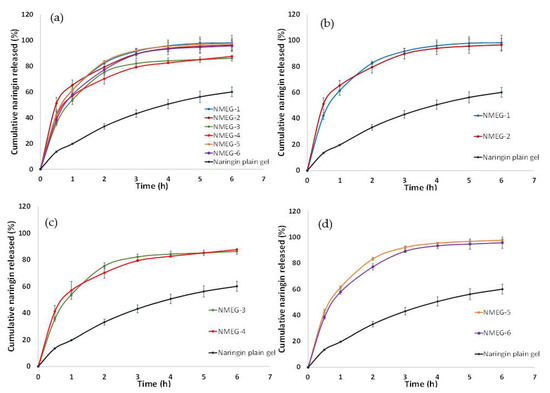
Figure 7.
Cumulative release of naringin from (a) microemulsion-gel formulations and naringin plain gel; (b) NMEG-1 and NMEG-2; (c) NMEG-3 and NMEG-4 and (d) NMEG-5 and NMEG-6. Each data point represents the mean ± SD (n = 3).
By incorporating naringin into microemulsions of essential oil, the release of naringin was remarkably improved over its counterpart from the unformulated naringin plain gel (microemulsion-free gel). During the first hour of the experiment, the cumulative release of naringin had increased at least 2.7-fold from 19.66 ± 0.16% (naringin plain gel) to 61.35 ± 3.61% (NMEG-1), 65.30 ± 3.90% (NMEG-2), 53.83 ± 1.16% (NMEG-3), 56.98 ± 6.72% (NMEG-4), 61.41 ± 0.98% (NMEG-5) and 57.84 ± 1.62% (NMEG-6) (Figure 7b–d). Among the microemulsion-gel formulations, it was observed that NMEG-1, NMEG-2, NMEG-5 and NMEG-6 released higher amount of naringin (ranging from 95.77 ± 4.32% to 98.16 ± 5.71%) than that of NMEG-3 and NMEG-4 (86.24 ± 2.13% and 87.66 ± 0.04%, respectively) after 6 h. The cumulative release of naringin from NMEG-3 and NMEG-4 after 6 h was about 10% less than that from MEG-1, MEG-2, MEG-5 and MEG-6. This could be attributed to the lower surfactant amount in the MEG-3 and MEG-4 (i.e., 15% w/w Tween® 80) compared to higher surfactant amount in NMEG-1, NMEG-2, NMEG-5 and NMEG-6 (i.e., 23.3% and 20% w/w Tween® 80). When the type of oil phase and Smix weight ratio were set to be the same, the release profile of naringin from microemulsion-gel formulations prepared using EtOH as the co-surfactant was quite similar to that of using DGME as the co-surfactant (i.e., NMEG-1 vs. NMEG-2, NMEG-3 vs. NMEG-4 and NMEG-5 vs. NMEG-6) (Figure 7b–d). This indicates that the type of co-surfactant (i.e., EtOH or DMGE) does not have a significant effect on the release profile of naringin from microemulsion-gel formulations.
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
The antioxidant activities of the essential oils (i.e., PMO, LVO and EUO) and active-free microemulsions (MEs) of essential oil were studied by evaluating their ability to scavenge the stable 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl free radical (DPPH•). During the DPPH antioxidant assay, the stable DPPH• will be scavenged by electron donation of antioxidant compound and transformed into its reduced form, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyne (DPPH-H) with discoloration from dark violet to light yellow [71]. The extent of discoloration indicates the scavenging activities of the antioxidants.
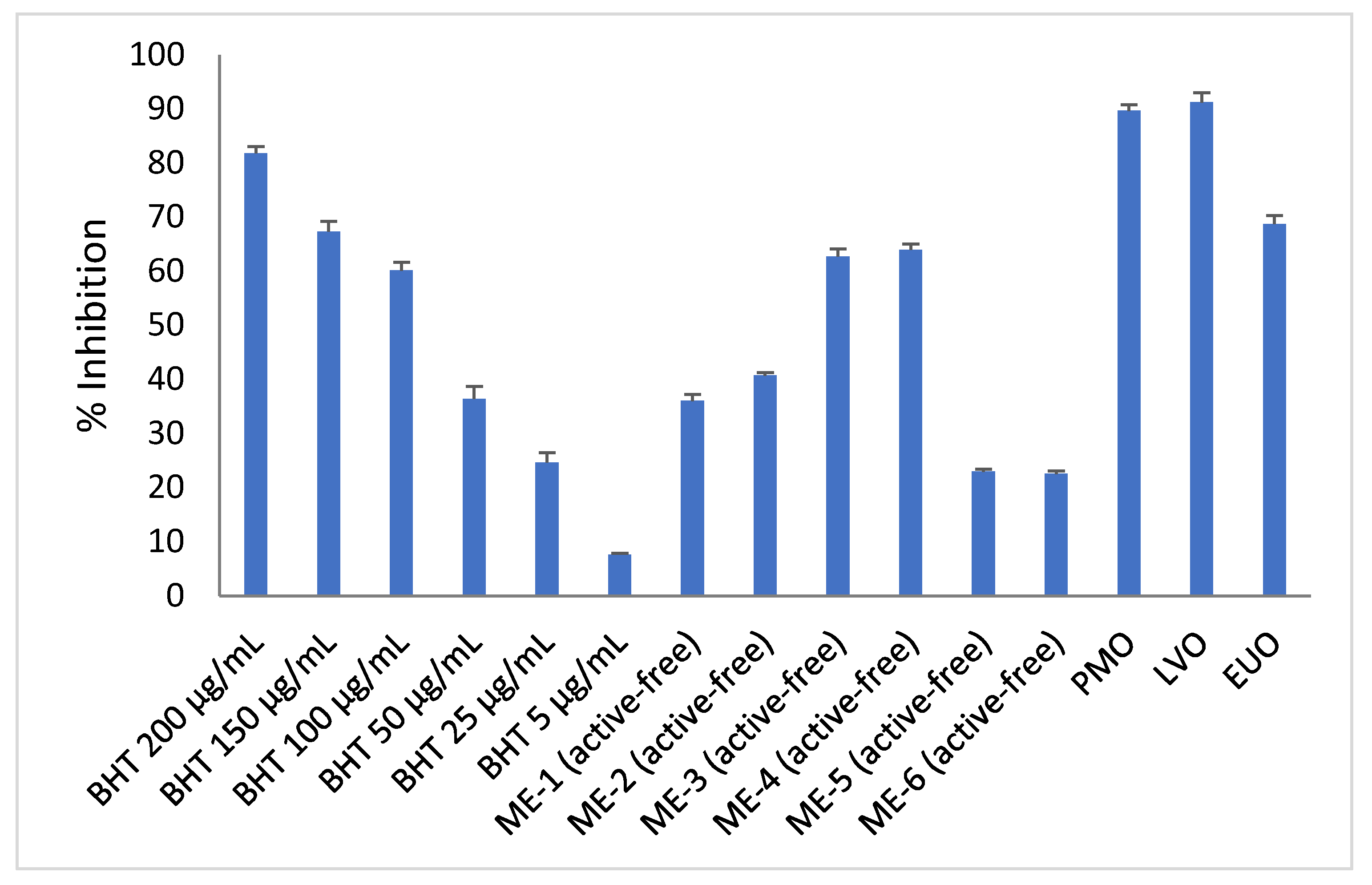
Figure 8 shows that active-free ME-3 and ME-4 exhibited the highest antioxidant activity (i.e., 62.73 ± 1.47% and 63.99 ± 1.06%), followed by active-free ME-1 and ME-2 (i.e., 36.06 ± 1.19% and 40.76 ± 0.54%). Active-free ME-5 and ME-6 exhibited the lowest antioxidant activity (i.e., 22.99 ± 0.45% and 22.58 ± 0.58%) among the active-free microemulsions of essential oil. It was apparent that the trend of DPPH inhibition level of active-free microemulsions of essential oil in this study was well correlated with the trend of DPPH inhibition level of pure essential oils (i.e., LVO > PMO > EUO) (Figure 8). Active-free microemulsions of PMO (i.e., ME-1 and ME-2) and LVO (i.e., ME-3 and ME-4) exhibited antioxidant activities that were comparable to 50 µg/mL BHT and 100 µg/mL BHT, respectively. Although the DPPH inhibition level of active-free microemulsions of EUO (ME-5 = 22.99 ± 0.45% and ME-6 = 22.58 ± 0.58%) was found to be lower than that of active-free microemulsions of LVO (i.e., ME-3 = 62.73 ± 1.47% and ME-4 = 63.99 ± 1.06%) and active-free microemulsions of PMO (i.e., ME-1 = 36.06 ± 1.18% and 40.76 ± 0.54%), active-free microemulsions of EUO still recorded an antioxidant activity close to 25 µg/mL of BHT (i.e., 24.68 ± 1.81%).
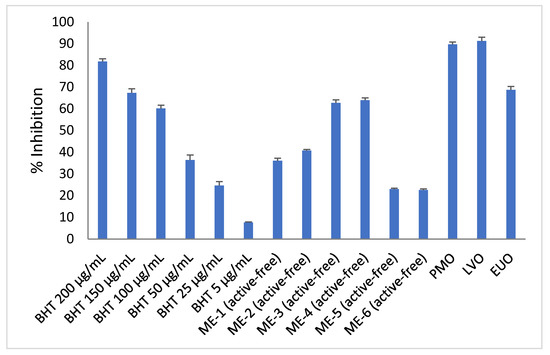
Figure 8.
DPPH scavenging activity of pure essential oils, active-free microemulsions of essential oil (MEs) and BHT of various concentrations. Each data point represents the mean ± SD (n = 3).
The amount of BHT used in skin care formulations can range from a concentration of 0.0002% to a concentration of 0.5% [34]. Hence, incorporation of synthetic antioxidant such as BHT in the skin care formulations could be eliminated or partially reduced with the presence of microemulsions of essential oil (e.g., ME-1, ME-2, ME-3, ME-4, ME-5 and ME-6). Furthermore, much higher antioxidant activity could potentially be exhibited by the microemulsions of essential oil when the content of essential oil is increased to more than 7% (w/w) (i.e., essential oil content in the microemulsions of this work).
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity
Although highly undesirable, microbial contamination in skin care products is very common. It may occur during manufacture through impurities and poor handling of raw materials or during consumer use [72]. Microbial contamination not only alters the organoleptic and rheological properties of skin care products such as colour, odour, and viscosity, but also affects the functional properties via deactivation of important constituents in the products [73]. Moreover, many microbial contaminants are opportunistic pathogens that could cause serious infection and hazard to human health [73]. To avoid microbial contamination of skin care products during manufacture, use, and storage, preservatives are typically added into skin care formulations by manufacturers. Due to the reported adverse effects of various synthetic preservatives, consumers generally prefer natural preservatives over synthetic preservatives [74]. The essential oils used as the oil phase to formulate microemulsions could serve as a natural multifunctional ingredient in the skin care formulations due to their intrinsic antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Therefore, microemulsions of essential oils could act as a self-preserving formulation by taking the advantages of essential oil in the formulations.
Table 6 shows the antimicrobial activity of active-free microemulsions (MEs) developed in this work and 0.25% (w/w) aqueous solution of methyl paraben against E. coli (gram-negative bacteria) and S. epidermidis (gram-positive bacteria) via disc diffusion method. The authorized use level of methyl paraben is up to 0.4% in single paraben or 0.8% in a mixture of parabens [32]. 0.25% (w/w) aqueous solution of methyl paraben (maximum aqueous solubility of methyl paraben) was used (instead of 0.4% w/w) as the reference sample in this work because of its limited aqueous solubility. Both E. coli and S. epidermidis strains were found to be susceptible to active-free microemulsions of essential oils (i.e., ME-1, ME-2, ME-3, ME-4, ME-5 and ME-6), with zone of inhibitions ranging from 12.00 ± 0.00 mm to 17.67 ± 2.31 mm and 12.00 ± 1.00 mm to 18.00 ± 1.00 mm, respectively. All of the active-free microemulsions of essential oil exhibited larger zone of inhibition than that of 0.25% (w/w) methyl paraben (9.20 ± 0.58 mm and 10.00 ± 0.70 mm for E. coli and S. epidermidis, respectively (Table 6)), demonstrating the great potential of microemulsions of essential oils as the self-preserving formulations for skin care application. Among all of the active-free microemulsions of essential oil, LVO containing microemulsions (i.e., ME-3 and ME-4) appeared to have slightly higher efficacy (i.e., zone of inhibition > 17 mm) against E. coli and S. epidermidis compared to the other microemulsions of essential oil. Although O/W microemulsions contain significant amount of water, which is often regarded as one of the culprits for antimicrobial contamination of skin care products, the water molecules in the microemulsions are tightly bound to surfactant and oil phase and hence relatively not as conducive as free water molecules for microbial growth [75].

Table 6.
Zone of inhibition (mm) of active-free microemulsions against E. coli and S. epidermidis. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).
4. Conclusions
This work demonstrated the feasibility of developing eco-friendly skin care formulations using microemulsions of essential oil. Six microemulsions of essential oil containing peppermint oil, lavender oil or eucalyptus oil, surfactant Tween® 80 and co-surfactant EtOH or DGME (i.e., ME-1, ME-2, ME-3, ME-4, ME-5 and ME-6) have been successfully developed and optimised via pseudo-ternary phase diagram. The essential oils used to formulate microemulsions were multifunctional ingredients that not only served as the oil phase of microemulsion but also exhibited antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. All of the six active-free microemulsions of essential oil showed an antioxidant activity equivalent to at least 25 µg/mL of synthetic antioxidant BHT, with the inhibition level of ME-3 and ME-4 as high as ~60% (approximately equivalent to antioxidant activity of 100 µg/mL BHT). Favourably, E. coli and S. epidermis strains were found to be more susceptible to all of the sixactive-free microemulsions of essential oil than 0.25% (w/w) synthetic preservative methyl paraben. These findings suggest the potential of microemulsions of essential oil as a safer alternative to synthetic antioxidant and as a self-preserving system. When loaded with 1% (w/w) of poorly water-soluble naringin and formulated into gel form, these naringin-loaded microemulsion-gel formulations (NMEG-1, NMEG-2, NMEG-3, NMEG-4, NMEG-5 and NMEG-6) demonstrated a significantly higher release of naringin and better stability than the unformulated naringin plain gel (microemulsion-free naringin gel). Therefore, a 4-fold benefit of microemulsion of essential of oil has been demonstrated in the developed naringin-loaded microemulsion-gel formulations: (1) improved release (membrane permeation) of naringin, (2) improved stability of naringin, (3) as a natural alternative to synthetic antioxidant such as BHT and (4) a self-preserving system. The application of microemulsions of essential oil in skin care and cosmetic formulations has indeed presented the opportunities for the formulators to develop eco-friendly skin care products while seeking more improvements in the product efficacy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.L., P.S.C. and C.K.Y.; Methodology, S.H.L.; Formal analysis, S.H.L.; Investigation, S.H.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, S.H.L.; Writing—review and editing, P.S.C. and C.K.Y.; Supervision, P.S.C. and C.K.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Engineering Research Council of A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), Singapore (Project Number: SC22/18-1A0320-0000).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data that support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Cher Wei Jing and Abdur Rahman for their kind assistance in the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bom, S.; Jorge, J.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. A step forward on sustainability in the cosmetics industry: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GreenPrint Survey Finds Consumers Want Eco-Friendly Products. Available online: https://www.convenience.org/Media/Daily/2021/Mar/23/6-GreenPrint-Survey-Finds-Consumers-Eco_Research (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Research Shows Consumers Willing to Pay Up to 5% More for Environmentally Friendly Products. Available online: https://www.environmentalleader.com/2019/11/research-shows-consumers-willing-to-pay-up-to-5-more-for-environmentally-friendly-products/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Das, S.; Lee, S.H.; Chow, P.S.; Macbeath, C. Microemulsion composed of combination of skin beneficial oils as vehicle: Development of resveratrol-loaded microemulsion based formulations for skin care applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.; Santos, L. Delivery systems for cosmetics—From manufacturing to the skin of natural antioxidants. Powder Technol. 2017, 322, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, H.A.E.; Grice, J.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Namjoshi, S.; Roberts, M.S. Topical and transdermal drug delivery: From simple potions to smart technologies. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.K.; Murthy, R.S. Microemulsions: A potential drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; García-Celma, M.J. Chapter 29—Microemulsions and Nano-emulsions for Cosmetic Applications. In Cosmetic Science and Technology; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Roohinejad, S.; Oey, I.; Wen, J.; Lee, S.J.; Everett, D.W.; Burritt, D.J. Formulation of oil-in-water β-carotene microemulsions: Effect of oil type and fatty acid chain length. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T.G.; Wilking, J.N.; Meleson, K.; Chang, C.B.; Graves, S.M. Nanoemulsions: Formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, R635–R666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Kamogawa, K.; Harusawa, F.; Momozawa, N.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M. Influence of oil droplet size on flocculation/coalescence in surfactant-free emulsion. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2001, 132, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Piorkowski, D.; McClements, D. Beverage emulsions: Recent developments in formulation, production, and applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 5–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmeen, J.B.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Zengin, G.; Maggi, F. Essential oils as natural sources of fragrance compounds for cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, H.A.E.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Shibamoto, T. Bioactivity of essential oils and their volatile aroma components: Review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of essential oils: A short review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Sureda, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Daglia, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Valussi, M.; Tundis, R.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; et al. Biological activities of essential oils: From plant chemoecology to traditional healing systems. Molecules 2017, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, C. Case history of infected eczema treated with essential oils. Grand Rounds Altern. Ther. 2001, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, R.; Lobl, M.; Higgins, S.; Clarey, D.; Wysong, A. The effects of lavender essential oil on wound healing: A review of the current evidence. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, M.; Wielgus, K. Application of essential oils as natural cosmetic preservatives. Herba Pol. J. 2013, 59, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Méndez, G.; Osorio-Fortich, M.; Ortega-Toro, R.; Pajaro-Castro, N.; Torrenegra-Alarcón, M.; Herrera-Barros, A. Design of an Emulgel-Type Cosmetic with Antioxidant Activity Using Active Essential Oil Microcapsules of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), Cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum J.), and Clove (Eugenia caryophyllata T.). Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 2874391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panico, A.; Serio, F.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Idolo, A.; De Giorgi, M.; Guido, M.; Congedo, M.; De Donno, A. Skin safety and health prevention: An overview of chemicals in cosmetic products. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2019, 60, E50–E57. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, S.C.; Schouten, A.; de Kruijf, N.; Weijland, J.W. Contents of methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, butyl- and benzylparaben in cosmetic products. Contact Dermat. 1995, 32, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, D.; Kovács, R.; Nagy, F.; Mező, M.; Poczok, N.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Pető, Á.; Fehér, P.; Fenyvesi, F.; Váradi, J.; et al. Interaction between Different Pharmaceutical Excipients in Liquid Dosage Forms-Assessment of Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbre, P.D.; Harvey, P.W. Paraben esters: Review of recent studies of endocrine toxicity, absorption, esterase and human exposure, and discussion of potential human health risks. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Yuan, C.; Tagmount, A.; Rudel, R.A.; Ackerman, J.M.; Yaswen, P.; Vulpe, C.D.; Leitman, D.C. Parabens and human epidermal growth factor receptor ligand cross-talk in breast cancer cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincho, J.; Martins, R.C.; Gomes, J. Paraben Compounds—Part I: An Overview of Their Characteristics, Detection, and Impacts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byford, J.R.; Shaw, L.E.; Drew, M.G.; Pope, G.S.; Sauer, M.J.; Darbre, P.D. Oestrogenic activity of parabens in MCF7 human breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 80, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehye, W.A.; Rahman, N.A.; Ariffin, A.; Abd Hamid, S.B.; Alhadi, A.A.; Kadir, F.A.; Yaeghoobi, M. Understanding the chemistry behind the antioxidant activities of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT): A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.K.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Keil, K.; Koski, K.; Malkinson, A.M. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) induction of pulmonary inflammation: A role in tumor promotion. Exp. Lung Res. 2001, 27, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, L.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Galhardi, C.M.; Ebaid, G.M.; Diniz, Y.S.; Fernandes, A.A.; Novelli, E.L. Butyl hydroxytoluene (BHT)-induced oxidative stress: Effects on serum lipids and cardiac energy metabolism in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 57, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, S.; Nishino, K.; Oikawa, S.; Inoue, S.; Mizutani, T.; Kawanishi, S. Oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis induced by metabolites of butylated hydroxytoluene. Biochem. Pharm. 1998, 56, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F.A. Final amended report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, isopropylparaben, butylparaben, isobutylparaben, and benzylparaben as used in cosmetic products. Int. J. Toxicol. 2008, 27, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, P.; Zhu, J.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Amended safety assessment of parabens as used in cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 5s–97s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanigan, R.S.; Yamarik, T.A. Final report on the safety assessment of BHT(1). Int. J. Toxicol. 2002, 21 (Suppl. 2), 19–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McHarek, N.; Hassen, I.; Hanchi, B.; Chevalier, Y. Contribution to the development of cosmetic products containing citrus flavonoids. Acta Hortic. 2013, 997, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.; Rani, N.; Krishnamurthy, B.; Arya, D.S. Preclinical evidence for the pharmacological actions of naringin: A review. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Bhardwaj, P.; Arya, S.K. Naringin: A potential natural product in the field of biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenzato, A.; Costantini, A.; Meloni, M.; Maramaldi, G.; Meneghin, M.; Baratto, G. Formulating O/W Emulsions with Plant-Based Actives: A Stability Challenge for an Effective Product. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glucosyl Naringin. Available online: https://www.nagase-personalcare.com/product/0000000045 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- SIMULGELTM NS. Available online: https://www.seppic.com/en/simulgel-ns (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Jian, C. Microemulsion-based anthocyanin systems: Effect of surfactants, cosurfactants, and its stability. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Sowmya, N.; Haraprasad, N.; Hema, B.P. Exploring the total flavonoid content of peels of Citrus auriantum, Citrus maxima and Citrus sinensis using different solvents and HPLC- analysis of flavonones—Naringin and Naringenin in peels of Citrus maxima. Pharma Innov. 2019, 8, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hangun-Balkir, Y.; McKenney, M.L. Determination of antioxidant activities of berries and resveratrol. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2012, 5, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Woo, P. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of peppermint oil products. J. Korea Soc. Plants People Environ. 2013, 16, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.; Truong, F.; Adal, A.M.; Sarker, L.S.; Mahmoud, S.S. Lavandula essential oils: A current review of applications in medicinal, food, and cosmetic industries of Lavender. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1934578X1801301038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Duarte, A.; Gominho, J.; Domingues, F.; Duarte, A.P. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-quorum sensing activities of Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus radiata essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Bail, S.; Buchbauer, G.; Stoilova, I.; Atanasova, T.; Stoyanova, A.; Krastanov, A.; Jirovetz, L. Chemical composition, olfactory evaluation and antioxidant effects of essential oil from Mentha x piperita. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokajewicz, K.; Białoń, M.; Svydenko, L.; Fedin, R.; Hudz, N. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of the New Cultivars of Lavandula angustifolia Mill. Bred in Ukraine. Molecules 2021, 26, 5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebei, K.; Sakouhi, F.; Herchi, W.; Khouja, M.L.; Boukhchina, S. Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of seven Eucalyptus species essential oils leaves. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindle, A.; Martin, K. Art of Prevention: Essential Oils—Natural Products Not Necessarily Safe. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2021, 7, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part IV: Contact Allergy. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.K.; Kaushal, R.; Junnarkar, A.Y.; Thomas, G.P.; Naidu, M.U.; Singh, P.P.; Tripathi, R.M.; Shridhar, D.R. Polysorbate 80: A pharmacological study. Arzneimittelforschung 1985, 35, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lachenmeier, D.W. Safety evaluation of topical applications of ethanol on the skin and inside the oral cavity. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2008, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.W. Diethylene glycol monoethyl ether: An emerging solvent in topical dermatology products. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2011, 10, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem-Quintanar, A.; Lafforgue, C.; Falson-Rieg, F.; Buri, P. Evaluation of the transepidermal permeation of diethylene glycol monoethyl ether and skin water loss. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 147, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juškaitė, V.; Ramanauskienė, K.; Briedis, V. Design and Formulation of Optimized Microemulsions for Dermal Delivery of Resveratrol. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 540916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo, E.; Gándola, Y.; González, L.; Bregni, C.; Carlucci, A.M. Development, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation of Tamoxifen Microemulsions. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 236713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, J.; Wohlfart, R.; Schürer, N.Y. Treatment of aged skin with a pH 4 skin care product normalizes increased skin surface pH and improves barrier function: Results of a pilot study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 1, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lukić, M.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S.D. Towards Optimal pH of the Skin and Topical Formulations: From the Current State of the Art to Tailored Products. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlogar, F.; Gasperlin, M.; Tomsic, M.; Jamnik, A.; Rogac, M.B. Structural characterisation of water-Tween 40/Imwitor 308-isopropyl myristate microemulsions using different experimental methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 276, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, L.; Mazál, J.; Petz, R.; Klang, V.; Valenta, C. The role of viscosity on skin penetration from cellulose ether-based hydrogels. Ski. Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batheja, P.; Sheihet, L.; Kohn, J.; Singer, A.J.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Topical drug delivery by a polymeric nanosphere gel: Formulation optimization and in vitro and in vivo skin distribution studies. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Comprehensive review on additives of topical dosage forms for drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryczyk-Poprawa, A.; Kwiecień, A.; Opoka, W. Photostability of Topical Agents Applied to the Skin: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsui, T. (Ed.) Stability of cosmetics. In New Cosmetic Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Warisnoicharoen, W.; Lansley, A.B.; Lawrence, M.J. Nonionic oil-in-water microemulsions: The effect of oil type on phase behaviour. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 198, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coneac, G.; Vlaia, V.; Olariu, I.; Muţ, A.M.; Anghel, D.F.; Ilie, C.; Popoiu, C.; Lupuleasa, D.; Vlaia, L. Development and evaluation of new microemulsion-based hydrogel formulations for topical delivery of fluconazole. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supe, S.; Takudage, P. Methods for evaluating penetration of drug into the skin: A review. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. The [DPPH●/DPPH-H]-HPLC-DAD Method on Tracking the Antioxidant Activity of Pure Antioxidants and Goutweed (Aegopodium podagraria L.) Hydroalcoholic Extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halla, N.; Fernandes, I.P.; Heleno, S.A.; Costa, P.; Boucherit-Otmani, Z.; Boucherit, K.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Ferreira, I.; Barreiro, M.F. Cosmetics Preservation: A Review on Present Strategies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundov, M.D.; Moesby, L.; Zachariae, C.; Johansen, J.D. Contamination versus preservation of cosmetics: A review on legislation, usage, infections, and contact allergy. Contact Dermat. 2009, 60, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Sati, N. Artificial preservatives and their harmful effects: Looking toward nature for safer alternatives. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Adham, I.; Khalil, E.; Al-Hmoud, N.D.; Kierans, M.; Collier, P. Microemulsions are membrane-active, antimicrobial, self-preserving systems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).