Bioglea as a Source of Bioactive Ingredients: Chemical and Biological Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis of the Microbial Assemblage Composition
2.3. Preparation of Samples
2.4. HPLC Analysis
2.5. UV Analysis
2.6. GC-MS Analysis
2.7. SPME Analysis
2.8. DPPH Assay
2.9. ORAC Assay
2.10. TEAC Analysis (ABTS assay)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition of the Thermal Photosynthetic Community
3.2. Extracts
3.3. HPLC and UV Analyses
3.4. GC-MS Analysis
3.5. SPME Analysis
3.6. Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazzulla, S.; De Stefano, S. Bioglee presenti nelle acque ipertermali sulfuree salso bromo iodiche delle Terme Lunigiane usate nelle terapie ionoforetiche. Med. Clin. Term. 1997, 39, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzulla, S.; De Stefano, S.; Martino, G. Bioglee presenti in acque ipertermali solfuree salso broiodiche: Loro uso in terapie ionoforetiche e valutazione di efficacia. Med. Clin. Term. 1998, 43, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzulla, S.; Chimenti, R.; Sesti, S.; De Stefano, S.; Morrone, M.; Martino, G. Effetto delle Bioglee solfuree su lesioni psoriasiche. Clin. Ter. 2004, 155, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tolomio, C.; Ceschi-Berrini, C.; Moschin, E.; Galzigna, L. Colonization by diatoms and antirheumatic activity of thermal mud. Cell Biochem. Funct. 1999, 17, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomio, C.; Ceschi-Berrini, C.; De Appolonia, F.; Galzigna, L.; Masiero, L.; Moro, L.; Moschin, E. Diatoms in the thermal mud of Abano Terme, Italy (Maturation period). Algol. Stud. 2002, 105, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomio, C.; De Apollonia, F.; Moro, I.; Ceschi-Berrini, C. Thermophilic microalgae growth on different substrates and at different temperature in experimental tanks in Abano Terme (Italy). Algol. Stud. 2004, 111, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, E.; Gul, H.; Macit, E.; Turan, M.; Yildz, O. Lipophilic Components of Different Therapeutic Mud Species. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2007, 10, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronkov, M.G.; Dolmaa, G.; Tserenpil, S.; Ugtahbayar, O.; Ganzaya, G.; Abzaeva, K.A. Chemical Composition of Peloids from Gurvan Nuur Middle Lake. Doklady Chem. 2009, 426, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserenpil, S.; Dolmaa, G.; Voronkov, M.G. Organic matters in healing muds from Mongolia. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, M.; Gonzalez, P.; Dominguez, R.; Bravo, A.; Malian, C.; Perez, M.; Herrera, I.; Blanco, D.; Hernandez, R.; Fagundo, J.R. Identification of Organic Compounds in San Diego de los Baños Peloid (Pinar del Río, Cuba). J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dychko, K.A.; Ryzhova, G.L.; Tyunina, M.A.; Khasanov, V.V.; Daneker, V.A. Aqueous Vibromagnetic Extraction of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Biologically Active Substances from Peloids of Varied Genesis. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara, S.; Carcangiu, G.; Padalino, G.; Palomba, M.; Tamanini, M. The bentonites in pelotherapy: Chemical, mineralogical and technological properties of materials from Sardinia deposits (Italy). Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 16, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrand, T.; Yvon, J. Thermal properties of clay pastes for pelotherapy. Appl. Clay Sci. 1991, 6, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Tateo, F. Geochemistry of two peats suitable for medical uses and their behavior during leaching. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 15, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viseras, C.; Lopez Galindo, A. Pharmaceutical applications of some Spanish clays (sepiolite, palygorskite, bentonite): Some preformulation studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I. Clay minerals and their beneficial effects upon human health. A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 21, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Scherer, S. UV protection in cyanobacteria. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.; Adhikary, S.P. Response of the estuarine cyanobacterium Lyngbya aestuarii to UV-B radiation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, J.M.; Al-Najjar, M.A.A.; Yilmaz, P.; Lavik, G.; de Beer, D.; Polerecky, L. Anoxygenic Photosynthesis Controls Oxygenic Phothosynthesis in a Cyanobacterium from a Sulfide Spring. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mar Fernandez-Arjona, M.; Banares-Espana, E.; Garcia-Sanchez, M.J.; Hernandez-Lopez, M.; Lopez-Rodas, V.; Costas, E.; Flores-Moya, A. Disentangling Mechanisms Involved in the Adaptation of Photosynthetic Microorganisms to the Extreme Sulphureous Water from Los Banos de Vito (Spain). Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 66, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, R.M.M.; Dobretsov, S.; Sudesh, K. Applications of cyanobacterial in biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subashchandrabosca, S.R.; Ramakrishnana, B.; Megheraja, M.; Venkateswarlua, K.; Naidua, R. Consortia of cyanobacteria/microalgae and bacteria: Biotechnogical potential. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerzak, L.; Lipok, J.; Strub, D.; Lochynski, S. Biotransformation of monoterpenes by photoautotrophic micro-organism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowitzka, M.A. Microalgae as sources of pharmaceuticals and other biologically active compounds. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulon, S.; Nomikos, T.; Oikonomou, A.; Kyriacon, A.; Andriotis, M.; Fragopoulon, E.; Pautazidou, A. Characterization of bioactive glicolipide from Scytonema julianum (Cyanobacteria). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2005, 140, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y. Microalgal metabolites. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.K.; Saleh, A.M. Spirulina an overview. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz, R.W.; Waterbury, J.B. Oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. Group I. Cyanobacteria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Staley, J.T., Bryant, M.P., Pfennig, N., Holt, J.G., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1989; Volume 3, pp. 1710–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Centini, M.; Tredici, M.R.; Biondi, N.; Buonocore, A.; Maffei Facino, R.; Anselmi, C. Thermal mud maturation: Organic matter and biological activity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi, C.; Centini, M.; Granata, P.; Sega, A.; Buonocore, A.; Bernini, A.; Maffei Facino, R. Antioxidant activity of ferulic acid alkyl esters in a heterophasic system: A mechanistic insight. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6425–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Sofic, E.; Prior, R.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant behaviour of flavonoids: Structure-activity relationships. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Pice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applaying an improbe ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzichelli, G.; Abdelahad, N.; Florenzano, G.; Tomaselli, L. Contributo alla conoscenza delle comunità fototrofiche delle Terme di Saturnia (Toscana). Ann. Bot. 1978, 37, 203–237. [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz, R.W.; Jorgensen, B.A.; D’Amelio, E.; Bauld, J. Photosynthetic and behavioral versatility of the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria boryana in a sulfide-rich microbial mat. FEMS Microbial. Ecol. 1991, 86, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenholz, R.W. The effect of sulphide on the blue-green algae of hot springs. II. Yellowstone National Park. Microb. Ecol. 1977, 3, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi, C.; Biondi, N.; Centini, M.; Andreassi, M.; Buonocore, A.; Fortunati, N.; Tredici, M. Evaluation of a biogenic agent: BiogleaTM from Saturnia SPA. In Proceeding of European Conference on Drug Delivery and Pharmaceutical Technology, Sevilla, Spain, 10–12 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pichel, F.; Castenholz, R.W. Characterization and biological implications of scytonemin a cyanobacterial sheath pigment. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pichel, F.; Castenholz, R.W. Occurence of UV-absorbing, mycosporine-like compounds among cyanobacterial isolates and an estimate of their screening capacity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Incharoensakdi, A. Sunscreening bioactive compounds mycosporine-like amino acids in naturally occurring cyanobacterial biofilms: Role in photoprotection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barre, S.; Roullier, C.; Boustic, J. Mycosporine-like Amino Acids [MAAs] in Biological Photosystems. In Marine Molecules: Chemistry, Biology, Analysis, 1st ed.; La Barre, S., Kornoprobst, J.M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KbaA: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 333–360. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sonami, R.R.; Madamwar, D. Cyanobacterial Sunscreen Scytonemin: Role in Photoprotection and Biomedical Research. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.D.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, V. Biotechnological applications of cyanobacterial phycobiliproteins. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2013, 2, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, S.S.; Maurya, J.N.; Pandey, V.D. Factors regulating phycobiliprotein production in cyanobacteria. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 764–771. [Google Scholar]
- Prasauda, R.; Sood, A.; Suresh, A.; Nayaic, S.; Kaushik, B.D. Potential and applications of algal pigments in biology and industry. Acta Biochim. Hung. 2007, 49, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raieshwari, K.R.; Rajashekhar, M. Biochemical composition of seven species of cyanobaterial isolated from different aquatic habitats of Western Ghats, Southern India. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnes, F.J.; Qureshi, A.A.; Semmler, E.J.; Porter, J.W. Prelycopersene pyrophosphate and lycopersene. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 218, 768–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, R.W.; Mier, W.; Giacosa, A. Phenolic compounds and squalene in olive oils: The concentration and antioxidant potential of total phenols, simple phenols, secoiridoids, ligands and squalene. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerenturk, E.J.; Sharpe, L.J.; Ikonen, E.; Brown, A.J. Desmosterol and DHCR24: Unexpected new directions for a terminal step in cholesterol synthesis. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colica, G.; De Philippis, R. Exopolysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible industrial applications. In Cyanobacteria: An Economic Perspetive, 1st ed.; Sharma, N.K., Rai, A.K., Stal, L.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Karautonis, H.C.; Nomikos, T.; Oikonomon, A.; Fragopoulou, E.; Pantazidou, A. Bioactive polar lipids from Chroococcidiopsis sp. (Cyanobacteria). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2005, 142, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, G.A.; Volkman, J.K.; Jeffrey, S.W.; Barret, S.M. Biochemical Composition of Microalgaceae and Prasinophyceae. 2. Lipid classes and fatty acids. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 161, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradossi, C.; Lotti, G.; Marchini, F.; Benelli, C. Ulteriori indagini sulla composizione delle alghe del Mediterraneo. Agrochimica 1993, 37, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, D.M.; Panke, S.; Kloppel, K.D.; Christ, P.; Fredrickson, H. Complex polar lipids of a hot spring cyanobacterial mat and its cultivated inhabitants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3358–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, R.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Shi, B.; Liang, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, L. Headspace solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber derivatization for the determination of aldehydes in algae by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, R.C.; Podell, S.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Pevzner, P.; Sherman, D.H.; Allen, E.E.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Characterization of cyanobacterial hydrocarbon composition and distribution of biosynthetic patways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuddus, M.L.; Singh, P.; Thomas, G.; Al-Hazimi, A. Recent Developments in Production and Biotechnological Applications of C-Phycocyanin. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 742859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, S.; Hasnain, S. Antioxidant potential of indigenous cyanobacterial strains in relation with their phenolic and flavonoid contents. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinero Estrada, J.E.; Bermejo Bescos, P.; Villar del Fresno, A.M. Antioxidant activity of different fractions of Spirulina platensis protean extract. Farmaco 2001, 56, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
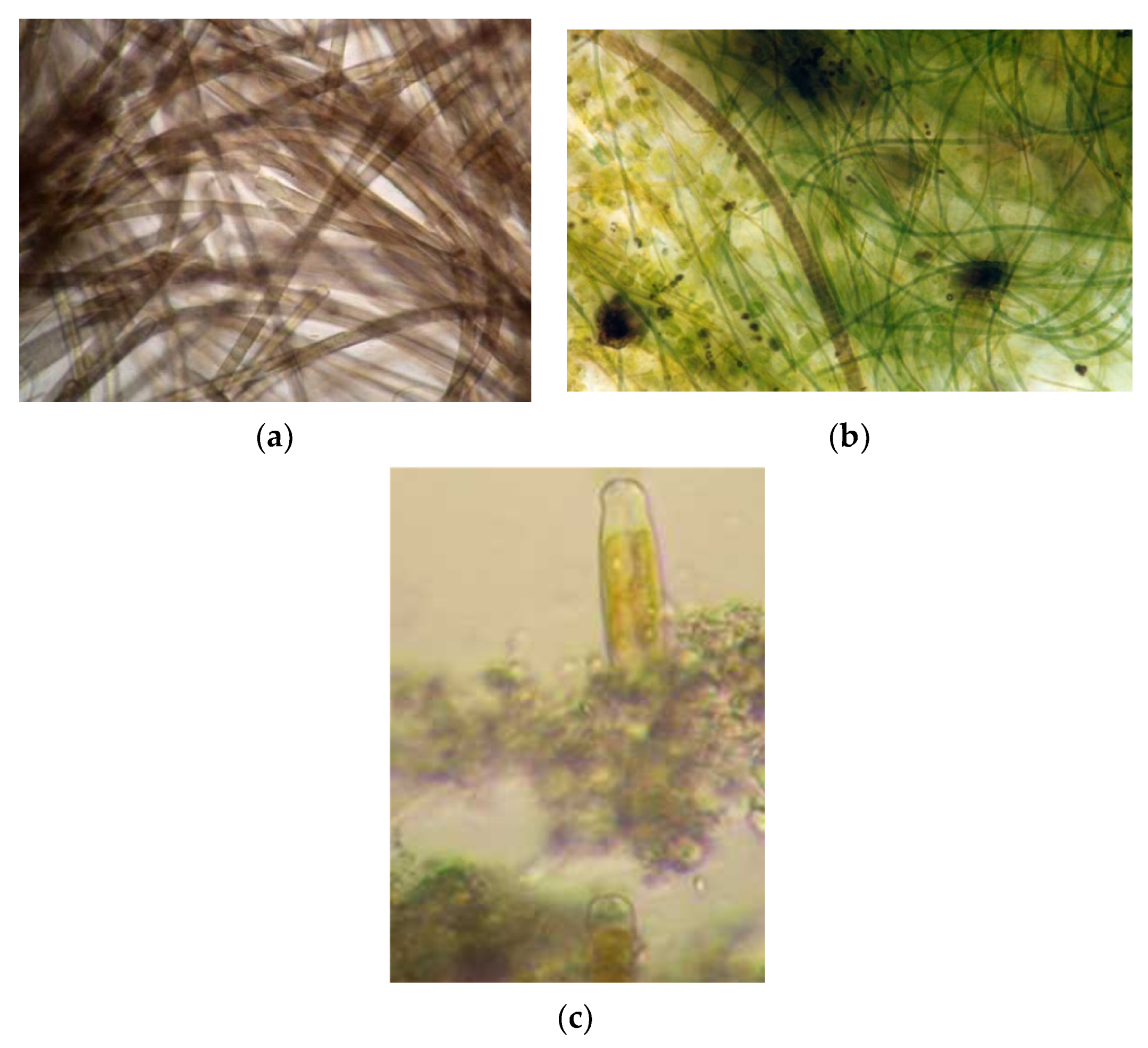
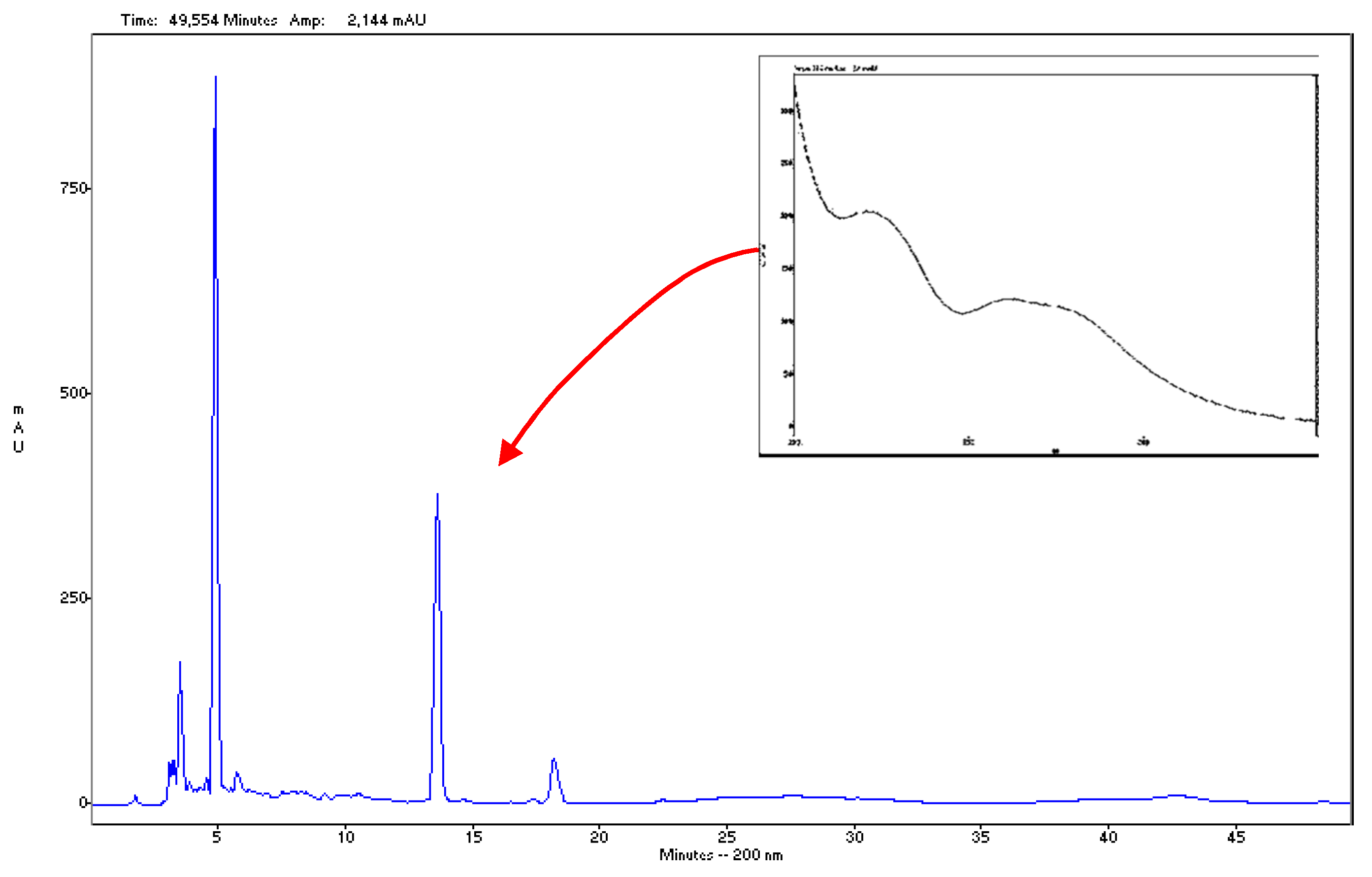
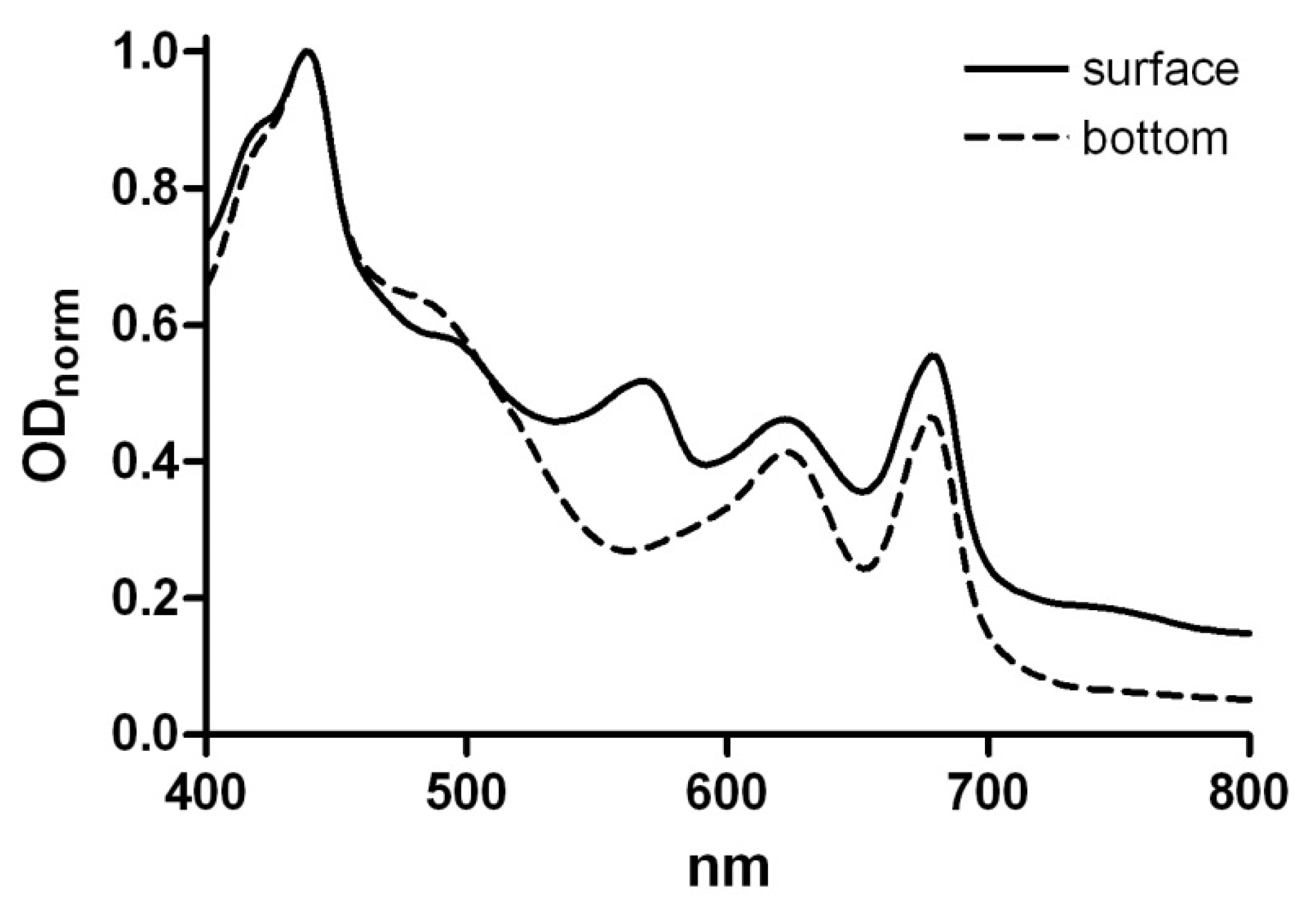
| Type of Extract | Type of Sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Bioglea | Bottom Bioglea | |||
| Hot extraction | mg/g bioglea | Colour | mg/g bioglea | Colour |
| PE | 19.25 ± 0.95 | Orange | 3.70 ± 0.66 | Orange |
| C | 17.19 ± 1.02 | Brown | 26.23 ± 0.61 | Brown |
| C/M (9:1) | 13.23 ± 1.04 | Reddish brown | 6.23 ± 0.59 | Reddish brown |
| M | 31.35 ± 1.00 | Green | 6.30 ± 0.63 | Brown |
| E/W (2:1) | 11.52 ± 0.97 | Light green | 4.30 ± 0.53 | Green |
| E/W (1:1) | 14.13 ± 0.84 | Light green | 2.89 ± 0.43 | Dark green |
| Cold extraction | mg/g bioglea | Colour | mg/g bioglea | Colour |
| C | 24.43 ± 1.02 | Reddish brown | 6.72 ± 0.65 | Brown |
| W/E (7:3) | 63.09 ± 0.83 | Dark green | 16.72 ± 0.69 | Green |
| Class of Compounds | Rt | C(c) Extract | W/E(c) (7:3) Extract | PE Extract | C(h) Extract | C/M (9:1) Extract | M Extract | E/W (2:1) Extract | E/W (1:1) Extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||||||
| (C9) Nonanoic acid | 5.920 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| (C10) Decanoic acid | 6.564 | − | − | 0.2 | 0.1 | − | 0.1 | − | − |
| (C12) Dodecanoic acid | 7.723 | 0.3 | − | − | 0.8 | − | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| (C14) Tetradecanoic acid | 8.783 | 3.8 | 0.8 | 12.5 | 6.5 | − | 2.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| (C15) Pentadecanoic acid | 9.273 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 16.3 | 9.7 | − | 4.2 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| (C16) Palmitic acid | 9.774 | 0.3 | − | 0.8 | 0.6 | 2.5 | − | − | − |
| (C17) Heptadecanoic | 10.235 | 2.5 | − | 9.2 | 7.5 | − | 3.5 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| (C18) Stearic acid | 10.650 | 0.5 | − | − | 0.9 | 1.7 | 0.1 | − | − |
| (C20) Eicosanoic acid | 11.692 | − | 0.5 | − | 0.3 | − | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| (C22) Docosanoic acid | 13.128 | − | − | − | 0.2 | − | 0.1 | − | − |
| Unsaturated fatty acids | |||||||||
| (C16) Palmitelaidic acid | 9.673 | 3.2 | 0.7 | 10.5 | 7.8 | − | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| (C18) Oleic acid | 10.599 | 2.4 | 0.5 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| (C18) Linoleic acid | 10.548 | − | − | 0.8 | 0.3 | − | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Sterols | |||||||||
| Cholesterol | 15.730 | − | − | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| β-sitosterol | 17.817 | − | − | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Lanost-8-en-3-beta-ol | 20.529 | − | − | − | 0.5 | − | − | − | − |
| Stigmasterol | 21.864 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 0.2 | − |
| Desmosterol | 22.797 | − | − | − | − | 0.3 | − | − | − |
| Class of Compounds | Rt | C(c) Extract | W/E(c) (7:3) Extract | PE Extract | C(h) Extract | C/M (9:1) Extract | M Extract | E/W (2:1) Extract | E/W (1:1) Extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-alanine | 4.914 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 5.8 | 5.1 |
| L-isoleucine | 5.487 | − | 0.5 | − | − | − | 0.5 | 4.2 | 4.1 |
| L-valine | 6.033 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 6.0 | 5.4 |
| L-leucine | 6.065 | − | − | − | − | 0.8 | − | 6.1 | 5.6 |
| Glycine | 6.545 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 4.3 | 3.9 |
| L-proline | 6.823 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2.7 | 2.2 |
| L-proline-5-oxo | 7.066 | − | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | − | − | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| N-(2-methyl-1-oxoprolyl) glycine | 7.325 | − | − | − | − | − | 0.1 | − | − |
| L-serine | 7.366 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2.5 | 2.3 |
| N-(2-methyl-1-oxobutyl) glycine | 7.446 | − | − | − | − | − | 0.1 | − | − |
| Glutamine | 7.556 | − | 0.5 | − | − | − | − | 2.8 | 3.1 |
| L-threonine | 7.615 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 3.3 | 3.0 |
| L-aspartic acid | 8.369 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 0.3 | 2.3 |
| L-methionine | 8.747 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| L-phenylalanine | 9.638 | − | − | − | − | − | 0.7 | 3.1 | 2.9 |
| L-tyrosine | 11.868 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2.9 | 3.0 |
| N-acetyl tyrosine | 13.977 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Class of Compounds | The Predominant Individual Compound | Rt | Class of Compounds | The Predominant Individual Compound | Rt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids | 2-butendioic acid | 5.580 | Carbohydrates | D-ribonic acid gamma lactone | 10.118 |
| Butanedioic acid | 5.600 | D-ribofuranose | 10.786 | ||
| 2-pentendioc acid | 6.715 | Methyl-α-D-mannofuranose | 10.900 | ||
| 4-methoxy benzoic acid | 8.753 | D-fruttose | 10.992 | ||
| 3-methoxy cinnamic acid | 9.294 | D-altrose | 11.228 | ||
| Abietic acid | 14.633 | Methyl-α-D-glucofuranose | 11.288 | ||
| Dehydroabietic acid | 14.655 | α-D-galactopyranose phosphate | 11.608 | ||
| Hydroxy acids | 2-hydroxypropanoic acid | 4.472 | 2-acetylamino-2-deoxy-α-D-mannopyranose | 12.914 | |
| 2-hydroxybutanoic acid | 5.151 | Alcohols | Dodecanol | 7.221 | |
| 3-hydroxybutanoic acid | 5.434 | Hexadecanol | 9.328 | ||
| 2-hydroxy-3-methyl butanoic acid | 5.500 | Phytol | 10.376 | ||
| 4-hydroxyvaleric acid | 5.837 | Octadecanol | 10.428 | ||
| 3-hydroxyvaleric acid | 6.172 | Hydrocarbons | Olean-13(18)-ene | 13.269 | |
| 4-hydroxybutanoic acid | 6.173 | Squalene | 16.953 | ||
| 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy cinnamic acid | 12.758 | Lycopersene | 16.960 | ||
| Esters | 2,3-dihydroxy benzoic acid methyl ester | 11.258 | Others | 2,4-bis-hydroxy pyrimidine | 7.145 |
| 5-methyl-2,4-bis-hydroxy pyrimidine | 7.725 |
| Compounds | Rt | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Dimethylsolfur | 6.65 | 9.50 |
| Limonene | 8.51 | 2.66 |
| p-cresole | 10.15 | 5.76 |
| Undecane | 11.13 | 0.87 |
| Decanal | 15.76 | 0.85 |
| Tridecane | 19.90 | 1.59 |
| Tetradecane | 24.33 | 4.64 |
| Branched Alcohol | 26.37 | 20.42 |
| Pentadecane | 28.61 | 3.81 |
| Hexadecane | 32.70 | 6.19 |
| Branched Alcohol | 34.45 | 4.91 |
| Heptadecene | 36.58 | 16.13 |
| Hepatadecane | 36.60 | 15.27 |
| Sample | DPPH | ORAC | TEAC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | Trolox Equivalent(µM) | mg TROLOX eq/mg extract | ||
| Surface | Bottom | |||
| Petroleum ether extract | 270.50 ± 0.58 | 3.15 ± 0.15 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 4.1 ± 0.2 |
| Chloroform extract | 203.84 ± 0.91 | 4.35 ± 0.12 | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.7 |
| Choloroform/methanol 9:1 extract | 498.29 ± 0.87 | 4.25 ± 0.15 | 9.1 ± 0.5 | 11.6 ± 0.6 |
| Methanol extract | 351.27 ± 0.72 | 4.20 ± 0.75 | 12.8 ± 0.6 | 15.2 ± 0.8 |
| Ethanol/water 2:1 extract | 379.10 ± 0.77 | 5.58 ± 1.20 | 11.1 ± 0.6 | 32.0 ± 1.6 |
| Ethanol/water 1:1 extract | 359.95 ± 0.65 | 6.75 ± 0.85 | 22.1 ± 1.1 | 20.8 ± 1.0 |
| Hydrophilic extract (RT) | 868.41 ± 0.85 | 2.80 ± 0.70 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Lipophilic extract room (RT) | 974.91 ± 0.47 | 1.90 ± 0.25 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Centini, M.; Roberto Tredici, M.; Biondi, N.; Buonocore, A.; Facino, R.M.; Anselmi, C. Bioglea as a Source of Bioactive Ingredients: Chemical and Biological Evaluation. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040081
Centini M, Roberto Tredici M, Biondi N, Buonocore A, Facino RM, Anselmi C. Bioglea as a Source of Bioactive Ingredients: Chemical and Biological Evaluation. Cosmetics. 2020; 7(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleCentini, Marisanna, Mario Roberto Tredici, Natascia Biondi, Anna Buonocore, Roberto Maffei Facino, and Cecilia Anselmi. 2020. "Bioglea as a Source of Bioactive Ingredients: Chemical and Biological Evaluation" Cosmetics 7, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040081
APA StyleCentini, M., Roberto Tredici, M., Biondi, N., Buonocore, A., Facino, R. M., & Anselmi, C. (2020). Bioglea as a Source of Bioactive Ingredients: Chemical and Biological Evaluation. Cosmetics, 7(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics7040081




