Abstract
Melanogenesis is a biosynthetic pathway that produces the pigment melanin in human skin. The catalyzation of the key enzyme tyrosinase is the first step in melanogenesis, and the downregulation of tyrosinase enzyme activity is the most reported method for inhibiting melanogenesis. Hyperpigmentation is an important issue in the cosmetic industry, and there is great demand for melanogenesis inhibitors. In the present study, we demonstrated the anti-melanogenic effect of Inonotus obliquus in alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)-induced B16F10 mouse melanoma cells and identified it as a new melanogenesis inhibitor. Comparing the B16F10 cells treated with the control and the Inonotus obliquus extract, we identified the melanin contents, mRNA and protein expression of tyrosinase, tyrosinase activity, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Mitf) activity using a constructed plasmid. Through these experiments, we confirmed that Inonotus obliquus extract inhibits melanin synthesis by downregulating the activity and expression of tyrosinase. Furthermore, we revealed that tyrosinase expression is regulated by Inonotus obliquus extract via the repression of Mitf transcriptional activity. Thus, in this study, we found that Inonotus obliquus extract has anti-melanogenic effects via the suppression of melanin synthesis. Taken together, we demonstrated that Inonotus obliquus extract is a good potential candidate for use as a natural source for the therapeutic treatment of hyperpigmentation and for applications in whitening cosmetic products.
1. Introduction
The skin has epidermal units, which are composed of a melanocyte surrounded by keratinocytes and regulated by a closed paracrine system [1]. Melanocytes are responsible for melanin production and distribution via a process called melanogenesis [2]. Melanin is the primary determinant of skin, hair, and eye color [3]. Melanogenesis is a complex process with different stages [2]. When melanin is deposited abnormally, it may cause various pigmentation disorders, which are classified as hypo- or hyperpigmentation [4]. Melanocytes are controlled by the enzyme tyrosinase [5]. Thus, tyrosinase activity has a significant effect on skin pigmentation. Because tyrosinase has such an important impact on skin color and the treatment of skin pigmentation defects, the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries are continuously seeking to identify new ingredients that are capable of regulating tyrosinase activity [6,7]. Therefore, new tyrosinase inhibitors are continually in demand to effectively treat melanogenesis-caused problems with as few side effects as possible. Therefore, the effects of various natural extracts on human skin whitening and melanogenesis inhibition have drawn considerable attention from researchers, and numerous studies have been conducted to verify the benefits of such natural extracts in cosmetic formulations [8,9].
In this study, we identified Inonotus obliquus extract as a potent melanogenesis inhibitor, because it decreases the activity of tyrosinase, a key enzyme in the synthetic pathway of melanin. Inonotus obliquus is commonly known as chaga mushroom, which is used as a natural medicine in many countries, such as Japan, China, Russia, and the Baltic countries [10]. Inonotus obliquus extract has been evaluated as a traditional and natural source of bioactive compounds for many centuries and has recently been used as a potential ingredient in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Inonotus obliquus extract has been reported to have numerous physiological functions, such as anticancer, homeostatic, antiviral, and antioxidant effects in both in vitro and in vivo models [11,12,13,14,15]. In this study, we explored a new physiological function of Inonotus obliquus extract—its ability to inhibit melanogenesis.
In the present study, we evaluated the anti-melanogenesis effect of Inonotus obliquus extract by monitoring the melanin contents, intracellular tyrosinase activity, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Mitf) expression in alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)-induced melanogenesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cell Culture
B16F10 mouse melanoma cells from neonatal tissue were obtained from the Korean cell line bank (Seoul, Korea) and grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Springfield Township, NJ, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Sigma-Aldrich, ST. Louis, MO, USA), 10% penicillin (Gibco, 100 units/mL), and 10% streptomycin (Gibco, 100 μg/mL) at 37 °C in 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
2.2. Preparation of Inonotus Obliquus Extract
Inonotus obliquus was washed and dried entirely at 60 °C in a dryer (ON-50; Daihan Science, Wonju, Korea). The dried Inonotus obliquus were powdered by a grinder (SMX-5800LM; Shinil, Korea) and extracted in 70% ethanol at 60 °C over 30 min. To increase efficiency, we used ultrasonic waves over 20 kHz (Ultrasonic cleaner 8891; Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA). After the extraction process, the residue was separated from the extract by filter paper (Whatman No.2; GE Healthcare Life Science, USA). The ethanolic extract was evaporated using a rotary evaporator (EYELA N-3010; Tokyo Rikakikai, Japan) and a freeze dryer (LP 10-30; Ilshin, Korea). The lyophilized extracts were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to yield a stock solution concentration of 100 μg/mL.
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
To determine cell viability, we performed a 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The B16F10 mouse melanoma cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 3 × 103 cells per well to 80% confluence. The B16F10 cells were treated with Inonotus obliquus extracts with concentrations of 0–200 μg/mL. After 48 h of incubation, the cells were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and treated with 0.5 mg/mL of MTT (Sigma-Aldrich) and incubated for an additional 1 h. The MTT formazan was placed in DMSO and measured by a microplate reader (SpectraMax® i3x; Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) at an absorbance of 595 nm.
2.4. Measurement of Melanin Content
The B16F10 cells were harvested 48 h after the cotreatment with α-MSH and the Inonotus obliquus extract, washed with PBS, and lysed in 1 N of sodium hydroxide (NaOH; Sigma-Aldrich) at 95 °C for 15 min. The melanin content was determined using a microplate reader (SpectraMax® i3x; Molecular Deviced, USA) at an absorbance of 450 nm. The amount of melanin was calculated using a melanin standard curve, which was obtained using synthetic melanin (Sigma-Aldrich). The protein concentration of each lysate was determined using a Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cellular melanin content was normalized to a total protein concentration.
2.5. Tyrosinase Activity Assay
The B16F10 cells were washed with PBS and lysed with lysis buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 (Biopure), 150 mM of NaCl (Biopure), 50 mM of HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid; pH 7.5; Biopure), and 5 mM of EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Biopure). The supernatant was separated from the cell lysate by centrifugation and mixed with 2 mM of L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine; Sigma-Aldrich) in 0.1 M of sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) solution. The mushroom tyrosinase activity assay used 100 units of mushroom tyrosinase (Sigma-Aldrich) instead of the cell lysate, and the other reagents were same. After 30 min of incubation at 37 °C, the absorbance at 450 nm was read using a microplate reader (SpectraMax® i3x; Molecular Deviced, USA). The protein concentration of each lysate was determined by a Bradford protein assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The activity of the intracellular tyrosinase was normalized to a total protein concentration.
2.6. Expression of Tyrosinase mRNA
The total RNA was isolated using TRIzolTM (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The purity and concentration of the RNA was evaluated based on a MaestroNano®, a micro volume spectrophotometer (Maestrogen Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan). The cDNAs were synthesized from total RNAs by using a miScript Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using a StepOnePlusTM Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Tyrosinase mRNA expression was performed using the following tyrosinase-specific primers: Tyrosinase forward 5’-CAAGTACAGGGATCGGCCAAC-3’; Tyrosinase reverse 5’-GGTGCATTGGCTTCTGGGTAA-3’. PCR was performed using the HOT FIREPol EvaGreen® qPCR Mix Plus (ROX). The expression of mRNA was analyzed by 2−ΔΔCT calculate method and normalized with β-actin.
2.7. Determination of Tyrosinase Protein
The cells were washed with cold PBS and lysed at 1% SDS lysis buffer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) at 95 °C for 20 min in a rotator, and then, 5X sample buffer [10% SDS, 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 50% glycerol, 25% β-mercaptoethanol, 1% bromophenol blue] (Sigma-Aldrich) was added. The total proteins were normalized by using a Bradford Protein Assay Kit. The same amounts of protein extraction were loaded on 12 % Tris-polyacrylamide gels (SDS-PAGE). Anti-tyrosinase and anti-β-actin primary antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA). The detection system used was a ClarityTM Western ECL Substrate (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The chemiluminescence signals were visualized under a Fusion FX7 Imaging System (Vilber Lourmat, Collégien, France).
2.8. Mitf Transcriptional Activity
To determine the transcriptional activity of Mitf when the B16F10 cells were treated with Inonotus obliquus extract, B16F10 melanoma cells were transfected with the pGL3 (Invitrogen) and pGL3- Mitf plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) and co-transfected with the pCMV-β-galactosidase plasmid to normalize the transfection efficiency. After incubation for 24 h, the transfected cells were treated with the Inonotus obliquus extracts. After treatment, the cells were lysed with Passive Lysis Buffer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The luciferase activity was determined by VeritasTM Microplate Luminometer (Veritas, Madison, WI, USA). The results are the averages of three independent experiments.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All the data were presented as a means ± standard deviation of the different measurements obtained by at least three independent experiments. The significance of the data was estimated by student’s t-test. A p value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant (p values: * < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability of Inonotus obliquus Extract in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells
We first examined whether Inonotus obliquus is cytotoxic to B16F10 melanoma cells using MTT assay. The B16F10 cells were treated with Inonotus obliquus extract at the indicated concentrations, respectively, and measured 48 h later. Treatment with the Inonotus obliquus extract caused no significant change in the cell viability at the concentrations of up to 100 μg/mL but markedly reduced it at 200 μg/mL as revealed by a short-term (48 h) cell viability assay (Figure 1). Therefore, the following experiments regarding the Inonotus obliquus extract were performed with the concentrations that had no cytotoxicity.
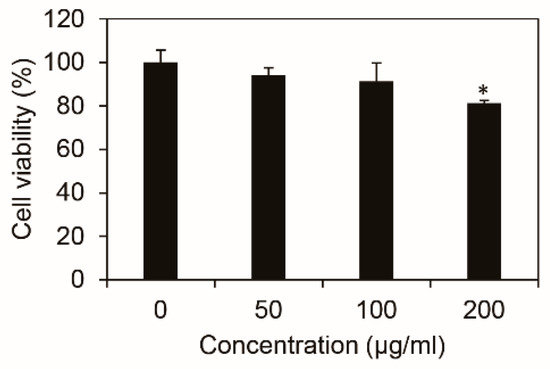
Figure 1.
Effects of Inonotus obliquus extract on the cell cytotoxicity of B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. There is no significant difference between the control and the Inonotus obliquus extract-treated cells. The cell viability is shown as a percentage of the control at the stated concentration. *: cytotoxicity at the stated concentration. The data values were obtained from the average of three independent experiments ±SD (standard deviation).
3.2. Inonotus obliquus Extract Decreases Melanin Contents in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells
To measure the melanin contents, after the cotreatment with the α-MSH (200 ng/mL) and Inonotus obliquus extract for 48 h, the cells were compared with α-MSH as a control (Figure 2). The Inonotus obliquus extract dose-dependently reduced the melanin contents of the B16F10 cells at the concentrations that did not influence the cell viability (at or below 100 μg/mL). The Inonotus obliquus extract (100 μg/mL) was found to have a greater inhibitory effect on melanin contents in the cells.
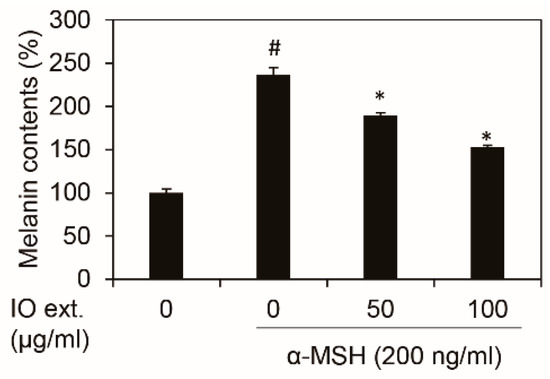
Figure 2.
Effects of the Inonotus obliquus extract on the melanin contents in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. The Inonotus obliquus extract decreased the melanin contents in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. The number of cells was counted, and the amount of melanin in the cells was measured. The melanin contents were shown as a percentage of the control at the stated concentrations. The data values were obtained from the average of three independent experiments ±SD (standard deviation). #: p < 0.05 compared to the non-treated B16F10 cells; *: p < 0.05 compared with the α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells; IO ext.: Inonotus obliquus extracts; and α-MSH: alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
3.3. Inonotus obliquus Extract Directly Inhibits Tyrosinase Activity
Tyrosinase is a rate-limiting enzyme for controlling melanin synthesis. Many melanin synthesis inhibitors reduce melanogenesis by directly inhibiting tyrosinase activity. We examined the effect of Inonotus obliquus extract on tyrosinase activity by using intracellular tyrosinase activity and mushroom tyrosinase activity. The inhibitory effect of the Inonotus obliquus extract on melanin synthesis was remarkable. Figure 3A shows the change in the intracellular tyrosinase activity when the Inonotus obliquus extracts with concentrations in the range of 0–100 μg/mL were exposed to the α-MSH treated B16F10 mouse melanoma cells 48 h. The tyrosinase activity was dose-dependently decreased when the Inonotus obliquus extract was added to the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells as compared with the control. The mushroom tyrosinase also decreased when Inonotus obliquus extract with a concentration of 100 μg/mL was added. These results indicate that the inhibitory effect of the Inonotus obliquus extract on melanin synthesis was related to the tyrosinase activity.
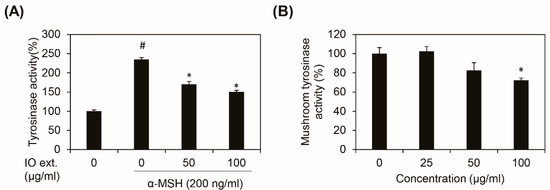
Figure 3.
Effects of Inonotus obliquus extract on tyrosinase activity. The Inonotus obliquus extract decreased the tyrosinase activity in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. (A) Intracellular tyrosinase activity; (B) mushroom tyrosinase activity. After adding L-DOPA as a substrate, the mixture was incubated. The amount of generated dopachrome was determined by evaluating the absorbance at 450 nm. The tyrosinase and mushroom tyrosinase activity are shown as a percentage of the control value. All the data values were obtained from the average of three independent experiments ±SD (standard deviation). #: p < 0.05 compared with the non-treated B16F10 cells; *: p < 0.05 compared with the α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells; IO ext.: Inonotus obliquus extracts; and α-MSH: alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
3.4. Inonotus obliquus Extract Downregulates α-MSH-induced Tyrosinase Expression
To evaluate the effect of Inonotus obliquus extract on tyrosinase expression, the B16F10 cells were pre-treated with the Inonotus obliquus extract before stimulation with α-MSH, and the tyrosinase protein levels were examined using western blot analysis. Treatment with Inonotus obliquus extract at concentrations of 50 and 100 μg/mL for 48 h inhibited the α-MSH-induced accumulation of tyrosinase proteins in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 4A). RT-PCR analysis shows similar results in the 50 and 100 μg/mL concentrations (Figure 4B). These data demonstrated that Inonotus obliquus extract significantly decreases α-MSH-induced tyrosinase expression at the mRNA level without eliciting cytotoxic effect in B16F10 melanoma cells.
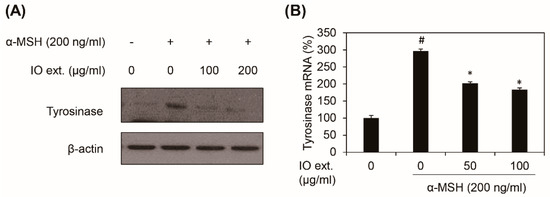
Figure 4.
Effects of Inonotus obliquus extract on tyrosinase expression. The Inonotus obliquus extract decreased the tyrosinase expression in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. (A) The protein level of tyrosinase was identified by western blotting. β-Actin was used as the loading control; (B) The mRNA expression of tyrosinase was identified by qRT-PCR. The mRNA levels of tyrosinase were shown as a percentage of the control at the stated concentrations. All the data values were obtained from the average of three independent experiments ±SD (standard deviation). #: p < 0.05 compared with the non-treated B16F10 cells; *: p < 0.05 compared with the α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells; IO ext.: Inonotus obliquus extract extracts; and α-MSH: alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
3.5. Inonotus obliquus Extract Downregulates Mitf Transcriptional Activity Stimulated by α-MSH
To determine whether Inonotus obliquus extract affects the Mitf transcriptional activity and if so, which regulatory region is required for Inonotus obliquus extract-mediated suppression of the Mitf activity, we constructed a reporter plasmid containing a Mitf binding promoter. The luciferase reporter activities of the constructed Mitf binding promoter were increased by α-MSH stimulation, which was respectably reduced by the treatment with the Inonotus obliquus extract (Figure 5). These data suggest that Inonotus obliquus extract downregulates Mitf promoter activity and that the Inonotus obliquus extract is responsible for the suppression of the Mitf transcriptional activity.
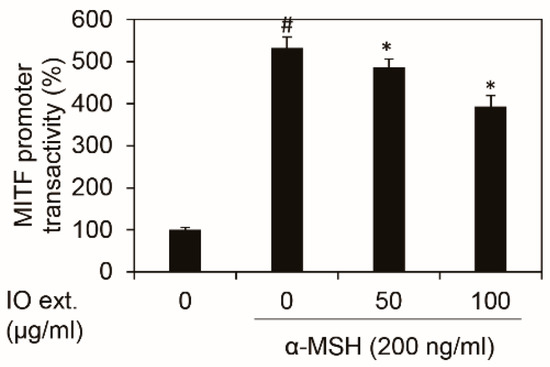
Figure 5.
Effects of Inonotus obliquus extract on Mitf transcriptional activity. The Inonotus obliquus extract decreased the Mitf transcriptional activity in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. The transcriptional activity of Mitf was shown as a percentage of the control at the stated concentrations. The data values were obtained from the average of three independent experiments M ± SD (mean±standard deviation). #: p < 0.05 compared with the non-treated B16F10 cells; *: p < 0.05 compared with the α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells; Mitf: microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; IO ext.: Inonotus obliquus extract; and α-MSH: alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
4. Discussion
Melanogenesis is a biosynthetic pathway that produces the pigment melanin for human eye, hair, and skin color [2]. Melanogenesis is a complex process with different steps. The catalyzation of the key enzyme tyrosinase is the first step of melanogenesis, and the downregulation of tyrosinase activity is the most investigated method for the inhibition of melanogenesis [3]. Because hyperpigmentation is an important issue in the cosmetic industry, there is a great demand for melanogenesis inhibitors [16,17,18].
There are many requirements for cosmetic products, but the most important is that they should be safe, having no negative side effects but having positive effects on the skin. Recently, natural products have attracted extensive attention in the cosmetic industry. There are numerous products from natural sources, such as foods, fruits, and plants, which are being exploited in pharmaceuticals or cosmetics, and many potential products have yet to be investigated or used [8,9,19]. Inonotus obliquus is a medicinal mushroom and is use in traditional oriental therapy and several nutritious foods [10]. Inonotus obliquus extract has been reported to have physiological functions, such as anticancer, homeostatic, antiviral, and antioxidant effects [11,12,13,14,15]. In this study, we explored a new physiological function of Inonotus obliquus extract—its anti-melanogenesis effect. Over the last few years, the improved understanding of melanocyte biology and melanin synthesis processes and increased consumer interest in skin whitening and hyperpigmentation treatments have encouraged the discovery of new melanogenesis inhibitors [6,20]. Many other approaches to the inhibition of melanogenesis include accelerating tyrosinase degradation and inhibiting tyrosinase mRNA transcription through the reduction of Mitf activity, in addition to the direct inhibition of tyrosinase activity.
We investigated the effects of Inonotus obliquus extract on melanogenesis by using mushroom tyrosinase in a cell-free system and intracellular tyrosinase in cultured B16F10 melanoma cells with α-MSH as a control. In advance of the following experiments, we measured the melanin contents. The melanin contents in the Inonotus obliquus extract-treated cells were significantly reduced. Then, we examined the effect of Inonotus obliquus extract at the intracellular tyrosinase level. B16F10 cells treated with Inonotus obliquus extract showed significantly decreased intracellular tyrosinase activity as well. When measuring the mushroom tyrosinase activity, the inhibition effect of the Inonotus obliquus extract was evident, but the inhibition effect of the intracellular tyrosinase activity was more significant. These results of several experiments indicate that Inonotus obliquus extract significantly inhibits not only melanin production, but also intracellular tyrosinase activity in α-MSH-induced B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. The results of the western blot and the real-time RT-PCR analysis also show that the tyrosinase protein and mRNA levels were decreased by the Inonotus obliquus extracts. We suggest that Inonotus obliquus extract inhibits melanogenesis at the transcriptional level and also directly inhibits tyrosinase activity. Tyrosinase gene expression is regulated by Mitf [5]. Mitf is a melanocyte-specific transcription factor that can regulate biological process in melanoma and melanocyte cells, including pigmentation, proliferation, and survival [5]. Mitf binds and activates the melanogenic gene, a tyrosinase promoter, thereby increasing their expression, which results in stimulated melanin synthesis. To determine whether Inonotus obliquus affects Mitf activity, we constructed a plasmid that has an Mitf promoter region and performed a Luciferase assay using the plasmid. In this experiment, the Inonotus obliquus extract also decreased the Mitf transcriptional activity in a concentration-dependent manner. Thus, we expect that the anti-melanogenesis effect of Inonotus obliquus extract is contributed by a mechanism related to Mitf transcriptional activity.
Taking all this together, we suggest that the Inonotus obliquus extract was a melanogenesis inhibitor in the B16F10 mouse melanoma cells, which stimulated α-MSH, and that the mechanism might include the decreasing of intracellular tyrosinase at the mRNA level by inhibiting Mitf transcriptional activity.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we determined the anti-melanogenic capability of Inonotus obliquus extracts in B16F10 melanoma cells in vitro. The experiments proved that Inonotus obliquus extracts can play a key role in whitening skin by regulating melanogenesis. These data led us to believe that Inonotus obliquus is a promising candidate for use as an anti-melanogenesis ingredient in whitening cosmetic products.
Author Contributions
Data curation, E.J.L.; Formal analysis, E.J.L.; Project administration, H.J.C.; and Original draft preparation, H.J.C.
Funding
This research was supported by Osan University in 2018 and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1D1A1B03028380).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Osan University in 2018 and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1D1A1B03028380).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Seiberg, M. Keratinocyte-melanocyte interactions during melanosome transfer. Pigment. Cell Res. 2001, 14, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin Pigmentation in Mammalian Skin and Its Hormonal Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovanský, J.; Wiley, I. Melanins and Melanosomes Biosynthesis, Biogenesis, Physiological, and Pathological Functions; John Wiley Distributor c2011: Weinheim/Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.Y.; Fisher, D.E. Melanocyte biology and skin pigmentation. Nature 2007, 445, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, P.; Healy, E.; Jackson, I.; Rees, J.L.; Thody, A.J. Variants of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor gene are associated with red hair and fair skin in humans. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. Natural Melanogenesis Inhibitors Acting Through the Down-Regulation of Tyrosinase Activity. Materials 2012, 5, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Park, J.U.; Su, X.D.; Kim, K.T.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y. Identification of Anti-Melanogenesis Constituents from Morus alba L. Leaves. Molecules 2018, 23, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ji, J.; Park, S.H. Antiwrinkle and antimelanogenesis activity of the ethanol extracts of Lespedeza cuneata G. Don for development of the cosmeceutical ingredients. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Ko, J.-H.; Kang, H.-K.; Kim, S.; Kang, C.I.; Lee, J.N.; Park, S.-M.; Hyun, C.-G. Antimelanogenic Effects of Polygonum tinctorium Flower Extract from Traditional Jeju Fermentation via Upregulation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and Protein Kinase B Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkina, M.Y.; Shashkin, P.N.; Sergeev, A.V. Chemical and medicobiological properties of chaga (review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2006, 40, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, T.; Watanabe, O.; Maruyama, S. Inhibition of HIV-1 protease by water-soluble lignin-like substance from an edible mushroom, Fuscoporia obliqua. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arata, S.; Watanabe, J.; Maeda, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsuhashi, H.; Mochizuki, M.; Kagami, N.; Honda, K.; Inagaki, M. Continuous intake of the Chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) aqueous extract suppresses cancer progression and maintains body temperature in mice. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Géry, A.; Dubreule, C.; André, V.; Rioult, J.P.; Bouchart, V.; Heutte, N.; Eldin de Pécoulas, P.; Krivomaz, T.; Garon, D. Chaga (Inonotus obliquus), a Future Potential Medicinal Fungus in Oncology? A Chemical Study and a Comparison of the Cytotoxicity Against Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells (A549) and Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B). Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieszek, M.K.; Langner, E.; Kaczor, J.; Kandefer-Szerszen, M.; Sanecka, B.; Mazurkiewicz, W.; Rzesky, W. Anticancer effects of fraction isolated from fruiting bodies of Chaga medicinal mushroom, Inonotus obliquus (Pers.:Fr.) Pilát (Aphyllophoromycetideae): In vitro studies. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2011, 13, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sugiura, N. Comparative studies of antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect of hot water and ethanol extracts from the mush- room Inonotus obliquus. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 107, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, I.F.; Moura, D.F.; Magina, S. Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia 2013, 88, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The regulation of skin pigmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27557–27561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.D.; Bahkali, A.H.; Moslem, M.A. Fungi—An unusual source for cosmetics. Fungal Divers. 2010, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Moellmann, G.; Kuklinska, E. L-Tyrosine, L-DOPA, and tyrosinase as positive regulators of the subcellular apparatus of melanogenesis in bomirski Ab amelanotic melanoma cells. Pigment. Cell Res. 1989, 2, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).